













中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 126-133.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0228
收稿日期:2021-03-18
接受日期:2021-04-14
出版日期:2022-04-15
发布日期:2022-04-19
通讯作者:
吴景贵
作者简介:谷月 E-mail:18643540991@163.com;
基金资助:Received:2021-03-18
Accepted:2021-04-14
Online:2022-04-15
Published:2022-04-19
Contact:
Jinggui WU
摘要:
为探究长期覆膜滴灌条件下不同来源有机物料还田对土壤有机碳、全氮、微生物量碳和氮及微生物熵的影响,在玉米生育期,设置空白(CK)及施加秸秆(MS)、牧草(FG)和羊粪(SM)共4个处理,分析比较不同处理土壤中碳、氮含量的变化。结果表明,在玉米生育期内,物料的施用使土壤有机碳(soil organic carbon,SOC)、全氮(total nitrogen,TN)含量提高了2.78%~19.83%,土壤生物量碳(microbial biomass carbon,MBC)和土壤生物量氮(microbial biomass nitrogen,MBN)含量分别提高了6.64%~39.91%和4.05%~112.00%;有机物料的施用导致微生物碳熵(quotient of microbial biomass carbon,qMBC)、微生物氮熵(quotient of microbial biomass nitrogen,qMBN)高于CK,表明物料的添加能提高微生物量在土壤碳氮中的占比;土壤代谢熵随生育期呈现波动性变化。在3种有机物料中,MS处理有利于提高土壤qMBC和qMBN,较好地增加MBC和MBN含量;SM处理qMBC、qMBN值较低,但SOC、TN含量较高。综上所述,物料还田有利于土壤中碳、氮贮存,为当地有机物料还田提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
谷月, 吴景贵. 有机物料还田土壤碳、氮及微生物量动态影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 126-133.
Yue GU, Jinggui WU. Study on Dynamic Effects of Organic Materials on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Microbial Biomass[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 126-133.
| pH | 有机碳 OC/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/ (g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 Nitrate-N/(mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate-N/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾Available K/(mg·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N/(mg·kg-1) | 微生物量碳MBC/ (mg·kg-1) | 微生物量氮 MBN/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.77 | 16.36 | 1.18 | 37.07 | 19.57 | 23.55 | 68.25 | 85.83 | 54.21 | 11.35 |
表1 试验地基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of the test
| pH | 有机碳 OC/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/ (g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 Nitrate-N/(mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate-N/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾Available K/(mg·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N/(mg·kg-1) | 微生物量碳MBC/ (mg·kg-1) | 微生物量氮 MBN/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.77 | 16.36 | 1.18 | 37.07 | 19.57 | 23.55 | 68.25 | 85.83 | 54.21 | 11.35 |
| 性状Trait | MS | SM | FG |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳 OC/(g·kg-1) | 468.18±53.50 | 200.67±6.53 | 379.52±12.26 |
| 全氮TN/(g·kg-1) | 6.70±0.77 | 7.08±0.24 | 18.32±0.62 |
| 碳/氮C/N | 69.92±0.02 | 28.34±0.06 | 20.72±0.04 |
| 木质素Lignin/% | 5.79±0.66 | 1.87±0.06 | 9.29±0.30 |
| 纤维素Cellulose/% | 41.28±4.72 | 28.07±0.91 | 14.79±0.48 |
表2 不同来源有机废弃物的基本性质
Table 2 Basic properties of agricultural waste materials from different sources
| 性状Trait | MS | SM | FG |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳 OC/(g·kg-1) | 468.18±53.50 | 200.67±6.53 | 379.52±12.26 |
| 全氮TN/(g·kg-1) | 6.70±0.77 | 7.08±0.24 | 18.32±0.62 |
| 碳/氮C/N | 69.92±0.02 | 28.34±0.06 | 20.72±0.04 |
| 木质素Lignin/% | 5.79±0.66 | 1.87±0.06 | 9.29±0.30 |
| 纤维素Cellulose/% | 41.28±4.72 | 28.07±0.91 | 14.79±0.48 |
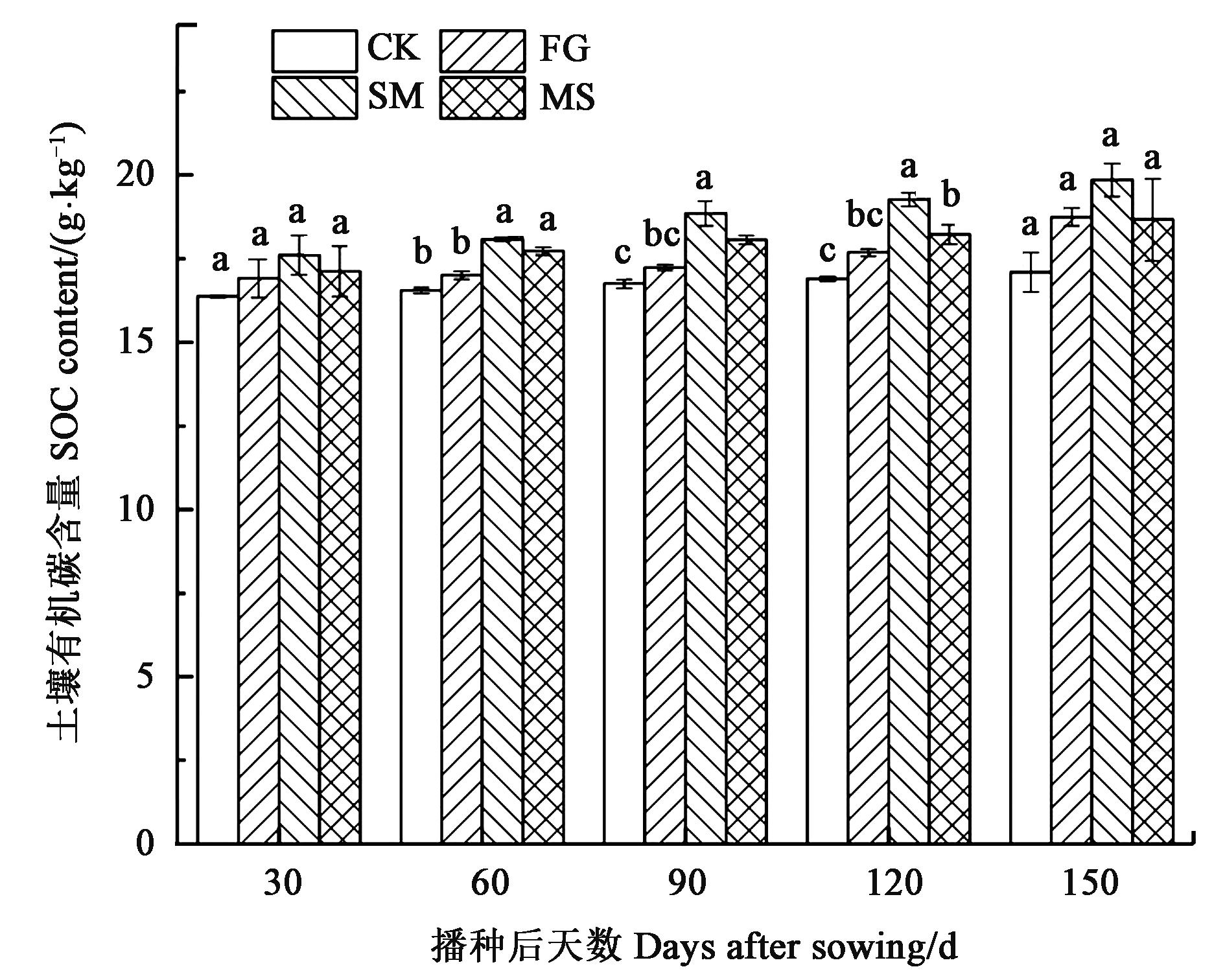
图1 不同处理土壤有机碳含量注:不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 SOC contents of different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.

图2 不同处理的土壤全氮含量注:不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 TN contents of different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.
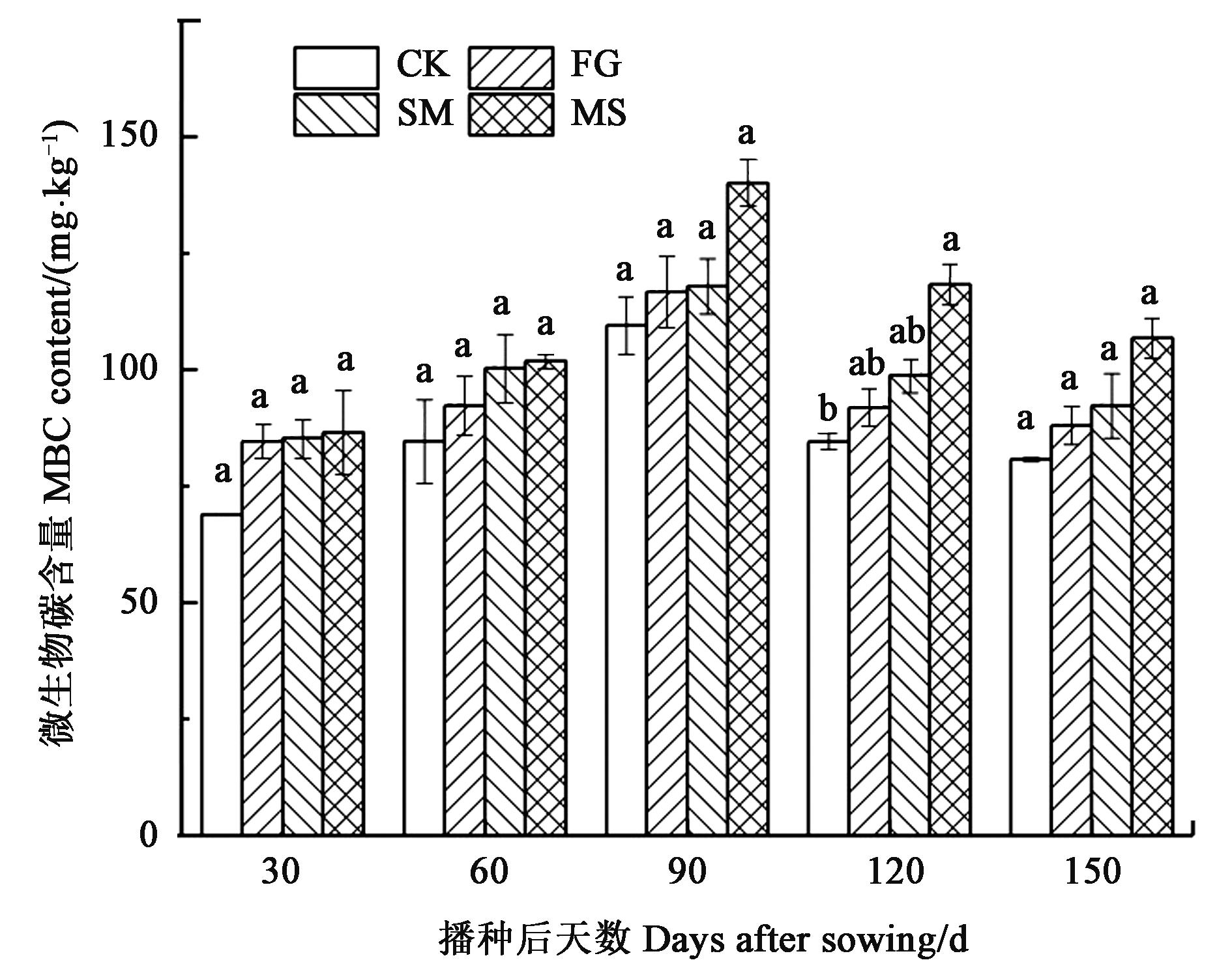
图3 不同处理的土壤微生物量碳含量注:不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 MBC contents of different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.
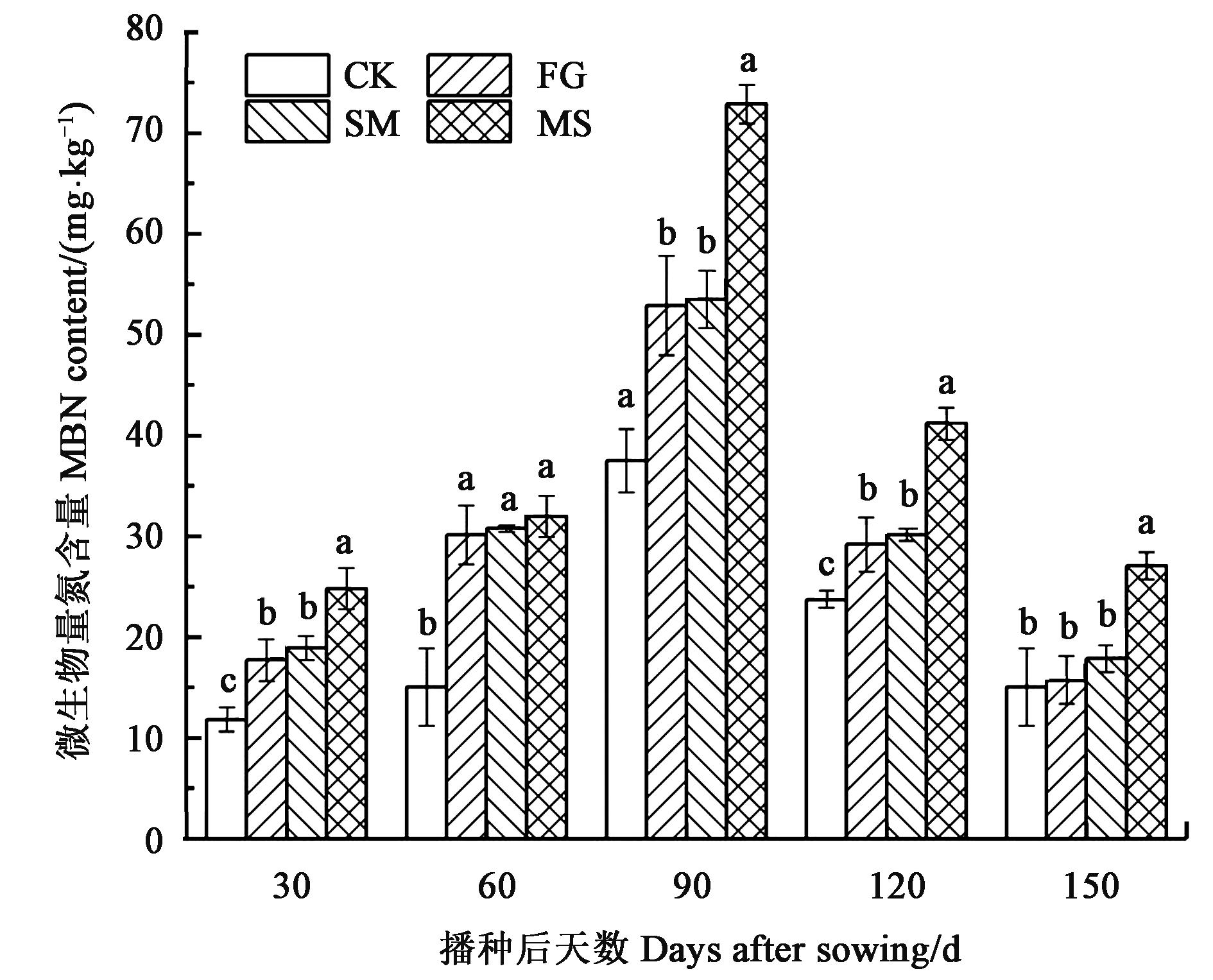
图4 不同来源有机物料下土壤的微生物量氮含量注:不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.4 MBN content of organic materials from different sourcesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.
| 播种后天数 Days after sowing/d | 处理 Treatment | 微生物量碳氮比 MBC/MBN | 微生物碳熵 qMBC | 微生物氮熵 qMBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | FG | 4.95±0.79 ab | 0.50±0.02 a | 1.36±0.14 b |
| SM | 4.53±0.79 ab | 0.48±0.07 a | 1.39±0.07 b | |
| MS | 3.53±0.45 b | 0.51±0.07 a | 1.87±0.15 a | |
| CK | 5.94±0.54 a | 0.42±0.001 a | 0.98±0.13 b | |
| 60 | FG | 3.15±0.50 a | 0.54±0.04 a | 2.45±0.27 a |
| SM | 3.26±0.26 a | 0.55±0.04 a | 2.34±0.00 a | |
| MS | 3.20±0.17 a | 0.57±0.07 a | 2.48±0.20 a | |
| CK | 7.22±3.16 a | 0.51±0.01 a | 1.56±0.33 b | |
| 90 | FG | 2.22±0.11 b | 0.68±0.05 a | 4.28±0.39 b |
| SM | 2.19±0.23 b | 0.62±0.07 a | 4.22±0.25 b | |
| MS | 1.93±0.12 b | 0.78±0.03 a | 5.99±0.88 a | |
| CK | 2.94±0.20 a | 0.65±0.03 a | 3.30±0.17 b | |
| 120 | FG | 3.22±0.45 a | 0.52±0.02 a | 2.46±0.31 ab |
| SM | 3.27±0.06 a | 0.51±0.02 a | 2.17±0.04 b | |
| MS | 2.86±0.20 a | 0.65±0.06 a | 3.08±0.25 a | |
| CK | 3.49±0.63 a | 0.48±0.07 a | 2.05±0.01 b | |
| 150 | FG | 6.01±1.37 a | 0.47±0.03a | 1.30±0.22 a |
| SM | 5.20±0.37 a | 0.46±0.03 a | 1.28±0.14 a | |
| MS | 3.98±0.52 a | 0.57±0.05 a | 2.00±0.08 a | |
| CK | 6.48±2.20 a | 0.47±0.02 a | 1.30±0.60 a |
表3 不同有机物料还田下土壤微生物量碳氮比、qMBC及qMBN
Table 3 Soil microbial biomass carbon to nitrogen ratio, qMBC and qMBN under different organic materials returned to the field
| 播种后天数 Days after sowing/d | 处理 Treatment | 微生物量碳氮比 MBC/MBN | 微生物碳熵 qMBC | 微生物氮熵 qMBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | FG | 4.95±0.79 ab | 0.50±0.02 a | 1.36±0.14 b |
| SM | 4.53±0.79 ab | 0.48±0.07 a | 1.39±0.07 b | |
| MS | 3.53±0.45 b | 0.51±0.07 a | 1.87±0.15 a | |
| CK | 5.94±0.54 a | 0.42±0.001 a | 0.98±0.13 b | |
| 60 | FG | 3.15±0.50 a | 0.54±0.04 a | 2.45±0.27 a |
| SM | 3.26±0.26 a | 0.55±0.04 a | 2.34±0.00 a | |
| MS | 3.20±0.17 a | 0.57±0.07 a | 2.48±0.20 a | |
| CK | 7.22±3.16 a | 0.51±0.01 a | 1.56±0.33 b | |
| 90 | FG | 2.22±0.11 b | 0.68±0.05 a | 4.28±0.39 b |
| SM | 2.19±0.23 b | 0.62±0.07 a | 4.22±0.25 b | |
| MS | 1.93±0.12 b | 0.78±0.03 a | 5.99±0.88 a | |
| CK | 2.94±0.20 a | 0.65±0.03 a | 3.30±0.17 b | |
| 120 | FG | 3.22±0.45 a | 0.52±0.02 a | 2.46±0.31 ab |
| SM | 3.27±0.06 a | 0.51±0.02 a | 2.17±0.04 b | |
| MS | 2.86±0.20 a | 0.65±0.06 a | 3.08±0.25 a | |
| CK | 3.49±0.63 a | 0.48±0.07 a | 2.05±0.01 b | |
| 150 | FG | 6.01±1.37 a | 0.47±0.03a | 1.30±0.22 a |
| SM | 5.20±0.37 a | 0.46±0.03 a | 1.28±0.14 a | |
| MS | 3.98±0.52 a | 0.57±0.05 a | 2.00±0.08 a | |
| CK | 6.48±2.20 a | 0.47±0.02 a | 1.30±0.60 a |
| 播种后天数Day after sowing/d | 处理 Treatment | 代谢熵qCO2 |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | MS | 1.63±0.63 |
| FG | 1.24±0.08 | |
| SM | 1.50±0.41 | |
| CK | 1.49±0.03 | |
| 60 | MS | 1.52±0.04 |
| FG | 1.53±0.44 | |
| SM | 1.42±0.15 | |
| CK | 1.61±0.22 | |
| 90 | MS | 1.36±0.05 |
| FG | 1.50±0.10 | |
| SM | 1.55±0.19 | |
| CK | 1.55±0.09 | |
| 120 | MS | 1.34±0.24 |
| FG | 1.53±0.11 | |
| SM | 1.45±0.25 | |
| CK | 1.73±0.31 | |
| 150 | MS | 1.80±0.17 |
| FG | 1.78±0.09 | |
| SM | 1.55±0.13 | |
| CK | 1.62±0.06 |
表4 不同处理的土壤代谢熵
Table 4 Soil qCO2 of different treatments
| 播种后天数Day after sowing/d | 处理 Treatment | 代谢熵qCO2 |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | MS | 1.63±0.63 |
| FG | 1.24±0.08 | |
| SM | 1.50±0.41 | |
| CK | 1.49±0.03 | |
| 60 | MS | 1.52±0.04 |
| FG | 1.53±0.44 | |
| SM | 1.42±0.15 | |
| CK | 1.61±0.22 | |
| 90 | MS | 1.36±0.05 |
| FG | 1.50±0.10 | |
| SM | 1.55±0.19 | |
| CK | 1.55±0.09 | |
| 120 | MS | 1.34±0.24 |
| FG | 1.53±0.11 | |
| SM | 1.45±0.25 | |
| CK | 1.73±0.31 | |
| 150 | MS | 1.80±0.17 |
| FG | 1.78±0.09 | |
| SM | 1.55±0.13 | |
| CK | 1.62±0.06 |
指标 Index | 全氮TN | 微生物量碳MBC | 微生物量氮MBN | 微生物量碳氮比 MBC/MBN | 微生物碳熵qMBC | 微生物氮熵qMBN | 土壤代谢熵qCO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳SOC | 0.675** | 0.373 | 0.202 | -0.217 | 0.093 | 0.119 | 0.077 |
| 全氮TN | 0.159 | 0.027 | -0.167 | -0.023 | -0.087 | -0.281 | |
| 微生物量碳MBC | 0.947** | -0.759** | 0.956** | 0.927** | -0.232 | ||
| 微生物量氮MBN | -0.828** | 0.942** | 0.992** | -0.337 | |||
| 微生物量碳氮比MBC/MBN | -0.736** | -0.788** | 0.298 | ||||
| 微生物碳熵qMBC | 0.946** | -0.330 | |||||
| 微生物氮熵qMBN | -0.306 |
表5 土壤微生物量碳氮与土壤有机碳、全氮的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen with soil organic carbon and total nitrogen
指标 Index | 全氮TN | 微生物量碳MBC | 微生物量氮MBN | 微生物量碳氮比 MBC/MBN | 微生物碳熵qMBC | 微生物氮熵qMBN | 土壤代谢熵qCO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳SOC | 0.675** | 0.373 | 0.202 | -0.217 | 0.093 | 0.119 | 0.077 |
| 全氮TN | 0.159 | 0.027 | -0.167 | -0.023 | -0.087 | -0.281 | |
| 微生物量碳MBC | 0.947** | -0.759** | 0.956** | 0.927** | -0.232 | ||
| 微生物量氮MBN | -0.828** | 0.942** | 0.992** | -0.337 | |||
| 微生物量碳氮比MBC/MBN | -0.736** | -0.788** | 0.298 | ||||
| 微生物碳熵qMBC | 0.946** | -0.330 | |||||
| 微生物氮熵qMBN | -0.306 |
| 1 | 刘婕雅,岳文婷,朱玲,等.农业废弃物资源化利用的生态价值评估——以地膜回收利用为例[J].现代农业科技,2019(13):164-166, 170. |
| LIU J Y, YUE W T, ZHU L, et al.. Ecological value assessment of agricultural waste resource utilization: taking plastic film recycling as an example [J]. Modern Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019(13):164-166, 170. | |
| 2 | 刘俊杰.玉米覆膜滴灌种植技术[J].农家参谋,2021(4):43-44. |
| 3 | GUO Z, ZHANG J, FAN J,et al.. Does animal manure application improve soil aggregation? Insights from nine long-term fertilization experiments [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 660:1029-1037. |
| 4 | RASOOL R, KUKAL S, HIRA G. Soil organic carbon and physical properties as affected by long-term application of FYM and inorganic fertilizers in maize-wheat system [J]. Soil Till. Res., 2008, 101(1-2):31-36. |
| 5 | SINGH G, JALOTA S K, SINGH Y. Manuring and residue management effects on physical properties of a soil under the rice–wheat system in Punjab,India [J]. Soil Till. Res., 2007, 94(1):229-238. |
| 6 | 赵红,袁培民,吕贻忠,等.施用有机肥对土壤团聚体稳定性的影响[J].土壤,2011,43(2):306-311. |
| ZHAO H, YUAN P M, LYU Y Z, et al.. Effects of organic manure application on stability of soil aggregates [J]. Soils, 2011, 43(2):306-311. | |
| 7 | NAIR A, NGOUAJIO M. Soil microbial biomass, functional microbial diversity, and nematode community structure as affected by cover crops and compost in an organic vegetable production system [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2012, 58:45-55. |
| 8 | ZAVALLONI C, ALBERTI G, BIASIOL S, et al.. Microbial mineralization of biochar and wheat straw mixture in soil: a short-term study [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2011, 50(1):45-51. |
| 9 | HEMWONG S, CADISCH G, TOOMSAN B, et al.. Dynamics of residue decomposition and N2 fixation of grain legumes upon sugarcane residue retention as an alternative to burning [J]. Soil Till. Res., 2008, 99(1):84-97. |
| 10 | 吴荣美,王永鹏,李凤民,等.秸秆还田与全膜双垄集雨沟播耦合对半干旱黄土高原玉米产量和土壤有机碳库的影[J].生态学报,2012,32(9):2855-2862. |
| WU R M, WANG Y P, LI F M, et al.. Effects of coupling film-mulched furrow-ridge cropping with maize straw soil incorporation on maize yields and soil organic carbon pool at a semiarid loess site of China [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2012, 32(9):2855-2862. | |
| 11 | 贾会娟.西南丘陵区保护性耕作下旱作农田土壤有机碳、氮相关组分的研究[D].重庆:西南大学, 2015. |
| JIA H J. Research on related components of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in dry farmland under conservation tillage in Southwest hilly region [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2015. | |
| 12 | 薛菁芳,高艳梅,汪景宽.长期施肥与地膜覆盖对土壤微生物量碳氮的影响[J].中国土壤与料,2007(3):55-58. |
| XUE J F, GAO Y M, WANG J K. Effects of long-term fertilization and plastic film mulching on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2007(3):55-58. | |
| 13 | 于树,汪景宽,高艳梅.地膜覆盖及不同施肥处理对土壤微生物量碳和氮的影响[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2006,37(4):602-606. |
| YU S, WANG J K, GAO Y M. The effect of plastic film mulching and different fertilization treatments on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen [J]. J. Shenyang Agric.Univ., 2006, 37(4):602-606. | |
| 14 | 梁尧,韩晓增,宋春,等.不同有机物料还田对东北黑土活性有机碳的影响[J].中国农业科学,2011,44(17):3565-3574. |
| LIANG Y, HAN X Z, SONG C, et al.. Impacts of returning organic materials on soil labile organic carbon fractions redistribution of mollisol in northeast China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2011, 44(17):3565-3574. | |
| 15 | 刘耀宏,戴鸣钧,余存祖.施加有机物料对土壤有机质影响的研究[J]. 中国科学院水利部西北水土保持研究所集刊, 1989(1):117-123. |
| 16 | 鲍士旦.土壤农业化学分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| BAO S D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000:1-495. | |
| 17 | VAN-SOEST P J. Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feed seedstion, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry olignin [J]. J. Am. Leather Chem. AS, 1963, 46:829-835. |
| 18 | 魏亮,盛浩,潘博,等.湘东丘陵区不同母质发育底土的土壤微生物商[J].土壤与作物,2016,5(4):255-260. |
| WEI L, SHENG H, PAN B, et al.. Subsoil microbial quotient derived from different parent materials in East Hunan Province [J]. Soil Crop, 2016, 5(4):255-260. | |
| 19 | 王清奎,汪思龙,冯宗炜,等.土壤活性有机质及其与土壤质量的关系[J].生态学报,2005(3):513-519. |
| WANG Q K, WANG S L, FENG Z W, et al.. Active soil organic matter and its relationship with soil quality [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2005(3):513-519. | |
| 20 | 宗雅婕.生物质炭施用对土壤呼吸、土壤有机碳及微生物量碳影响的整合分析[D].南京:南京农业大学,2015. |
| ZONG Y J. Response of soil respiration, soil organic and microbial biomsaa carbon to biochar amendment: a meta-analysis [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 21 | 李利利,王朝辉,王西娜,等.不同地表覆盖栽培对旱地土壤有机碳、无机碳和轻质有机碳的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2009,15(2):478-483. |
| LI L L, WANG C H, WANG X N, et al.. Effects of different surface mulch cultivation on dryland soil organic carbon, inorganic carbon and light organic carbon [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2009, 15(2):478-483. | |
| 22 | 代红翠,陈源泉,赵影星,等.不同有机物料还田对华北农田土壤固碳的影响及原因分析[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(S2):103-110. |
| DAI H C, CHEN Y Q, ZHAO Y X, et al.. Effects and causes of different organic materials amendment on soil carbon in North China Plain [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016, 32(S2):103-110. | |
| 23 | 卜玉山,邵海林,王建程,等.秸秆与地膜覆盖春玉米和春小麦耕层土壤碳氮动态[J].中国生态农业学报,2010,18(2):322-326. |
| BU Y S, SHAO H L, WANG J C, et al.. Dynamics of soil carbon and nitrogen in plowed layer of spring corn and spring wheat fields mulched with straw and plastic film [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2010, 18(2):322-326. | |
| 24 | 刘慧镯.夏玉米施肥技术[J].河南农业,2011,27(1):23. |
| 25 | 董林林,王海侯,陆长婴,等.秸秆还田量和类型对土壤氮及氮组分构成的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(4):68-75. |
| DONG L L, WANG H H, LU C Y, et al.. Effects of straw returning amount and type on soil nitrogen and its composition [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(4):68-75. | |
| 26 | 周元,陈远学,蒋帆,等.玉米地土壤微生物量碳、氮及微生物熵对不同物料还田的响应[J].水土保持学报,2020,34(2):173-180. |
| ZHOU Y, CHEN Y X, JIANG F, et al.. Responses of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and microbial entropy to different materials returning to corn field [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2020, 34(2):173-180. | |
| 27 | LI C X, MA S C, YUN S, et al.. Effects of long-term organic fertilization on soil microbiologic characteristics, yield and sustainable production of winter wheat [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2018, 17(1):210-219. |
| 28 | AZEEZ J O, AVERBEKE W V. Nitrogen mineralization potential of three animal manures applied on a sandy clay loam soil [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2010, 101(14):5645-5651. |
| 29 | 张志丹,姜海超,李桥,等.覆膜滴灌黑钙土微生物生物量碳及溶解性有机碳特性研究[J].水土保持学报,2013,27(6):226-230, 248. |
| ZHANG Z D, JIANG H C, LI Q, et al.. Research on characteristics of microbial biomass carbon and dissolved organic carbon of chernozem in drip irrigation under film mulched [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2013, 27(6):226-230, 248. | |
| 30 | Wardle D A. Controls of temporal variability of the soil microbial biomass: a global-scale synthesis [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 1998, 30(13):1630-1637. |
| 31 | 王传杰,王齐齐,徐虎,等.长期施肥下农田土壤-有机质-微生物的碳氮磷化学计量学特征[J].生态学报,2018,38(11):3848-3858. |
| WANG C J, WANG Q Q, XU H, et al.. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry characteristics of bulk soil, organic matter, and soil microbial biomass under long-term fertilization in cropland [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2018, 38(11):3848-3858. | |
| 32 | SPARLING G P. Ratio of microbial biomass carbon to soil organic carbon as a sensitive indicator of changes in soil organic matter [J]. Soil Res., 1992, 30(2):195-207. |
| 33 | 张帆,王晨冰,赵秀梅,等.果园垄膜覆盖对土壤微生物量碳氮及土壤呼吸的影响[J].核农学报,2018,32(7):1448-1455. |
| ZHANG F, WANG C B, ZHAO X M, et al.. Effect of the ridge film mulching on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and soil basal respiration in dryland apple orchard [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2018, 32(7):1448-1455. | |
| 34 | 刘志鹏,徐杰男,佘冬立,等.添加生物质炭对土壤热性质影响机理研究[J].土壤学报,2018,55(4):933-944. |
| LIU Z P, XU J N, SHE D L, et al.. Effects of biochar addition on thermal properties of loamy soil [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2018, 55(4):933-944. | |
| 35 | LEHMANN J, RILLIG M C, THIES J, et al.. Biochar effects on soil biota: A review [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2011, 43(9):1812-1836. |
| 36 | CHEN J, SUN X, LI L, et al.. Change in active microbial community structure, abundance and carbon cycling in an acid rice paddy soil with the addition of biochar [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci., 2016, 67(6):857-867. |
| 37 | JIANG X, DENEF K, STEWART C E, et al.. Controls and dynamics of biochar decomposition and soil microbial abundance, composition, and carbon use efficiency during long-term biochar-amended soil incubations [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2016, 52(1):1-14. |
| 38 | 朱孟涛,刘秀霞,王佳盟,等.生物质炭对水稻土团聚体微生物多样性的影响[J].生态学报, 2020,40(5):1-12. |
| ZHU M T, LIU X X, WANG J M, et al.. Effects of biochar application on soil microbial diversity in soil aggregates from paddy soil [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2020, 40(5):1-12. |
| [1] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 陈如冰, 李俐俐. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 83
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 416
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号 