




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 147-157.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.1052
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
周宇1( ), 李佳玉1, 王乐1, 贾晓爽1, 高思琦1, 王潇2, 焦健1(
), 李佳玉1, 王乐1, 贾晓爽1, 高思琦1, 王潇2, 焦健1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-02
接受日期:2023-02-01
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-13
通讯作者:
焦健
作者简介:周宇 E-mail:18201538379@163.com;
基金资助:
Yu ZHOU1( ), Jiayu LI1, Le WANG1, Xiaoshuang JIA1, Siqi GAO1, Xiao WANG2, Jian JIAO1(
), Jiayu LI1, Le WANG1, Xiaoshuang JIA1, Siqi GAO1, Xiao WANG2, Jian JIAO1( )
)
Received:2022-12-02
Accepted:2023-02-01
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Jian JIAO
摘要:
稳定型金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)小菌落突变体(small colony variants, SCVs)的获得,为抗SCVs药物的研究提供了重要的生物学材料。以S. aureus ATCC43300为出发菌株,利用低质量浓度(1.25~5.00 μg·mL-1)庆大霉素二次诱导技术获得稳定型SCVs,并对其特性进行分析。结果表明,1/2×最小抑菌浓度(minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC)及2×MIC庆大霉素分别诱导6 和12 h,可获得稳定型SCVs。SCVs生长缓慢,培养24 h可见较小菌落,培养7 h至生长对数期;对庆大霉素敏感性及产生物膜能力分别提高3和1倍;传代20次后恢复突变率为0%,抗逆性、药物敏感性、抗凝血性均增强,SigB调控系统及生物膜相关基因呈上调趋势,Agr调控系统及毒力因子下调。该方法的成功建立为SCVs的获得提出新的筛选策略,并为开展SCVs致病机理研究及新型抗SCVs药物研发提供稳定型受试菌株。
中图分类号:
周宇, 李佳玉, 王乐, 贾晓爽, 高思琦, 王潇, 焦健. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变体诱导筛选及特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 147-157.
Yu ZHOU, Jiayu LI, Le WANG, Xiaoshuang JIA, Siqi GAO, Xiao WANG, Jian JIAO. Induction Screening and Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 147-157.
基因 Gene | 引物序列(5’-3’) Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 类别 Category |
|---|---|---|
| agrA-F | AAGCATGACCCAGTTGGTAACA | Agr调控系统相关基因 Agr regulatory system genes |
| agrA-R | ATCCATCGCTGCAACTTTGTAGA | |
| agrB-F | CCCATTCCTGTGCGACTTAT | |
| agrB-R | TTGAATGAATTGGGCAAATG | |
| agrC-F | TAGTGACCATGATCATAATGTATTTGAG | |
| agrC-R | CTTCTTGATTTCGTTTGTATTTCATCTC | |
| agrD-F | AACATVGCAGCTTATAG | |
| agrD-R | TTCGTGTAATTGTGTTA | |
| RNAIII-F | GCATGTAAGCTATCGTAAACAACA | |
| RNAIII-R | AGGGGCTCACGACCATATAC | |
| sigB-F | GGTGCCATAAATAGATTCGATATGTCCTT | SigB调控系统相关基因 SigB regulatory system genes |
| sigB-R | CTTTTGATTTCACCGATTACAGTAGGTACT | |
| rsbV-F | ACGAAGTTAAAGTCGGTGGAGA | |
| rsbV-R | ATTCGACCTCCGTTCCTTCA | |
| rsbU-F | CGCGTGAAGATGTGTTCAAGAC | |
| rsbU-R | CTATCTCTTTATCGTGAACTTGAAG | |
| rsbW-F | GCGAAGGTGGCCTAGGTTTA | |
| rsbW-R | GCCATTATTTCGCACCTGCT | |
| relQ-F | AGAAAGTGGTTACCGCTCGT | 生物膜相关基因 Biofilm related genes |
| relQ-R | TCATCCGGATAAGCACCATCA | |
| relP-F | TTGCCGGAATTCGCGTAGTA | |
| relP-R | CGCGTTCTGCTAAAAAGACTGG | |
| rsh-F | TACATCGCACTGATTGCCCA | |
| rsh-R | TTAAATTGCCGGCTGTCGAG |
表1 Agr及SigB调控系统中相关基因的扩增引物[32-37]
Table 1 Amplification primers of Agr and SigB regulatory system genes[32-37]
基因 Gene | 引物序列(5’-3’) Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 类别 Category |
|---|---|---|
| agrA-F | AAGCATGACCCAGTTGGTAACA | Agr调控系统相关基因 Agr regulatory system genes |
| agrA-R | ATCCATCGCTGCAACTTTGTAGA | |
| agrB-F | CCCATTCCTGTGCGACTTAT | |
| agrB-R | TTGAATGAATTGGGCAAATG | |
| agrC-F | TAGTGACCATGATCATAATGTATTTGAG | |
| agrC-R | CTTCTTGATTTCGTTTGTATTTCATCTC | |
| agrD-F | AACATVGCAGCTTATAG | |
| agrD-R | TTCGTGTAATTGTGTTA | |
| RNAIII-F | GCATGTAAGCTATCGTAAACAACA | |
| RNAIII-R | AGGGGCTCACGACCATATAC | |
| sigB-F | GGTGCCATAAATAGATTCGATATGTCCTT | SigB调控系统相关基因 SigB regulatory system genes |
| sigB-R | CTTTTGATTTCACCGATTACAGTAGGTACT | |
| rsbV-F | ACGAAGTTAAAGTCGGTGGAGA | |
| rsbV-R | ATTCGACCTCCGTTCCTTCA | |
| rsbU-F | CGCGTGAAGATGTGTTCAAGAC | |
| rsbU-R | CTATCTCTTTATCGTGAACTTGAAG | |
| rsbW-F | GCGAAGGTGGCCTAGGTTTA | |
| rsbW-R | GCCATTATTTCGCACCTGCT | |
| relQ-F | AGAAAGTGGTTACCGCTCGT | 生物膜相关基因 Biofilm related genes |
| relQ-R | TCATCCGGATAAGCACCATCA | |
| relP-F | TTGCCGGAATTCGCGTAGTA | |
| relP-R | CGCGTTCTGCTAAAAAGACTGG | |
| rsh-F | TACATCGCACTGATTGCCCA | |
| rsh-R | TTAAATTGCCGGCTGTCGAG |
基因 Gene | 引物序列(5’-3’) Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 类别 Category |
|---|---|---|
| icaD-F | ATGGTCAAGCCCAGACAGAG | 生物膜相关基因 Biofilm related genes |
| icaD-R | AGTATTTTCAATGTTTAAAGCAA | |
| ccp-F | ATGATGTAGCAAGAGAAGCGCG | |
| ccp-R | TAACTGATGCTATATGTGCATCC | |
| luxS-F | GTCATTCACAAATACGACATTCG | |
| luxS-R | CCTGTACCGAAAACATCATGCC | |
| eno-F | ACGTGCAGCAGCTGACT | |
| eno-R | CAACAGCATCTTCAGTACCTTC | |
| clfA-F | ATTGGCGTGGCTTCAGTGCT | |
| clfA-R | CGTTTCTTCCGTAGTTGCATTTG | |
| sarA-F | ATGGCAATTACAAAAATCAATGATTGC | |
| sarA-R | TTATAGTTCAATTTCGTTGTTTGC | |
| pvl-F | TCTCATGAAAAAGGCTCAGGA | 毒力基因 Virulence genes |
| pvl-R | TTGCCATAGTGTGTTGTTCTTCT | |
| hla-F | ACCCGGTATATGGCAATCAA | |
| hla-R | AGCGAAGTCTGGTGAAAACC | |
| spa-F | GCGCAACACGATGAAGCTCAACAA | |
| spa-R | ACGTTAGCACTTTGGCTTGGATCA |
表1 Agr及SigB调控系统中相关基因的扩增引物[32-37] (续表Continued)
Table 1 Amplification primers of Agr and SigB regulatory system genes[32-37]
基因 Gene | 引物序列(5’-3’) Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 类别 Category |
|---|---|---|
| icaD-F | ATGGTCAAGCCCAGACAGAG | 生物膜相关基因 Biofilm related genes |
| icaD-R | AGTATTTTCAATGTTTAAAGCAA | |
| ccp-F | ATGATGTAGCAAGAGAAGCGCG | |
| ccp-R | TAACTGATGCTATATGTGCATCC | |
| luxS-F | GTCATTCACAAATACGACATTCG | |
| luxS-R | CCTGTACCGAAAACATCATGCC | |
| eno-F | ACGTGCAGCAGCTGACT | |
| eno-R | CAACAGCATCTTCAGTACCTTC | |
| clfA-F | ATTGGCGTGGCTTCAGTGCT | |
| clfA-R | CGTTTCTTCCGTAGTTGCATTTG | |
| sarA-F | ATGGCAATTACAAAAATCAATGATTGC | |
| sarA-R | TTATAGTTCAATTTCGTTGTTTGC | |
| pvl-F | TCTCATGAAAAAGGCTCAGGA | 毒力基因 Virulence genes |
| pvl-R | TTGCCATAGTGTGTTGTTCTTCT | |
| hla-F | ACCCGGTATATGGCAATCAA | |
| hla-R | AGCGAAGTCTGGTGAAAACC | |
| spa-F | GCGCAACACGATGAAGCTCAACAA | |
| spa-R | ACGTTAGCACTTTGGCTTGGATCA |
| 菌株Strain | 最小抑菌浓度 MIC/(μg·mL-1) | 最小杀菌浓度 MBC/(μg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC43300 | 2.5 | 5 |
| 小菌落突变体SCVs | 12.5 | 25 |
表2 MIC和MBC的测定
Table 2 Determination of MIC and MBC
| 菌株Strain | 最小抑菌浓度 MIC/(μg·mL-1) | 最小杀菌浓度 MBC/(μg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC43300 | 2.5 | 5 |
| 小菌落突变体SCVs | 12.5 | 25 |
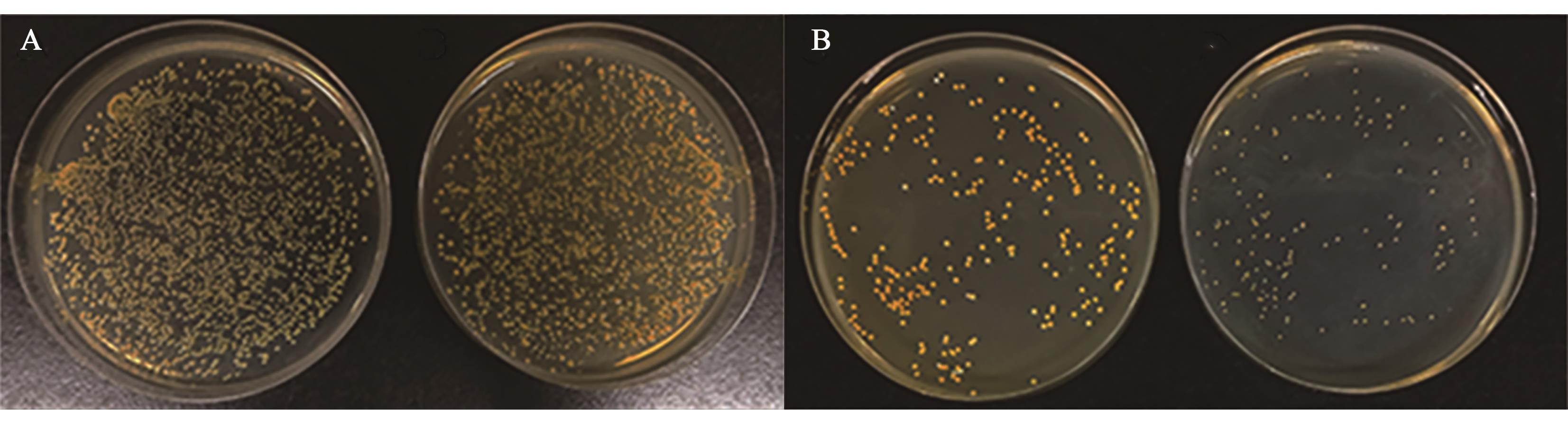
图1 低质量浓度庆大霉素对SCVs的筛选A:经1/2×MIC庆大霉素诱导的S. aureus ATCC43300,小菌落为SCVs(右),未诱导的S. aureus ATCC43300(左);B:经2×MIC庆大霉素二次诱导的小菌落突变体,小菌落为SCVs(右),图A中未诱导的S. aureus ATCC43300为对照菌株(左)
Fig. 1 Screening of SCVs with gentamicin at low mass concentrationA: Induced S. aureus ATCC43300 with 1/2×MIC gentamicin, the small colony variants are SCVs (right), uninduced S. aureus ATCC43300 (left); B: Secondary induced S. aureus ATCC43300 with 2×MIC gentamicin, the small colony variants are SCVs (right), the uninduced S. aureus ATCC43300 colonies of figure A are cultured as the control(left)
时间 Time | 对照CK | S. aureus ATCC43300 | 小菌落突变体SCVs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 0.120±0.018 | 1.270±0.266 | 2.940±0.106 |
表3 结晶紫法鉴定形成生物膜能力
Table 3 Identification of biofilm forming ability of crystal violet staining
时间 Time | 对照CK | S. aureus ATCC43300 | 小菌落突变体SCVs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 0.120±0.018 | 1.270±0.266 | 2.940±0.106 |
药品名称 Drug | S. aureus ATCC43300 | 小菌落突变体SCVs |
|---|---|---|
青霉素/(10 μg·片-1) Penicillin/(10 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
氨苄西林/(10 μg·片-1) Ampicillin/(10 μg·tablet-1) | R | R |
头孢曲松/(30 μg·片-1) Ceftriaxone/(30 μg·tablet-1) | S | I |
四环素/(30 μg·片-1) Tetracycline/(30 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
红霉素/(15 μg·片-1) Erythromycin/(15 μg·tablet-1) | I | R |
林可霉素/(2 μg·片-1) Lincomycin/(2 μg·tablet-1) | R | R |
复方新诺明/(25 μg·片-1) Sulfamethoxazole/(25 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
氯霉素/(30 μg·片-1) Chloramphenicol/(30 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
表4 小菌落突变体与野生型S. aureus ATCC43300药敏试验
Table 4 SCVs and S. aureus ATCC43300 drug susceptibility test
药品名称 Drug | S. aureus ATCC43300 | 小菌落突变体SCVs |
|---|---|---|
青霉素/(10 μg·片-1) Penicillin/(10 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
氨苄西林/(10 μg·片-1) Ampicillin/(10 μg·tablet-1) | R | R |
头孢曲松/(30 μg·片-1) Ceftriaxone/(30 μg·tablet-1) | S | I |
四环素/(30 μg·片-1) Tetracycline/(30 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
红霉素/(15 μg·片-1) Erythromycin/(15 μg·tablet-1) | I | R |
林可霉素/(2 μg·片-1) Lincomycin/(2 μg·tablet-1) | R | R |
复方新诺明/(25 μg·片-1) Sulfamethoxazole/(25 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
氯霉素/(30 μg·片-1) Chloramphenicol/(30 μg·tablet-1) | S | S |
菌株 Strain | 存活率Survival rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 25% NaCl | 30% NaCl | 35% NaCl | |
| S. aureus ATCC43300 | 58 | 11 | 10 |
| 小菌落突变体SCVs | 57 | 38 | 31 |
表5 高渗透压下野生型S. aureus ATCC43300与SCVs的存活率 (%)
Table 5 Survival rate of S. aureus ATCC43300 and SCVs under high osmotic pressure
菌株 Strain | 存活率Survival rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 25% NaCl | 30% NaCl | 35% NaCl | |
| S. aureus ATCC43300 | 58 | 11 | 10 |
| 小菌落突变体SCVs | 57 | 38 | 31 |
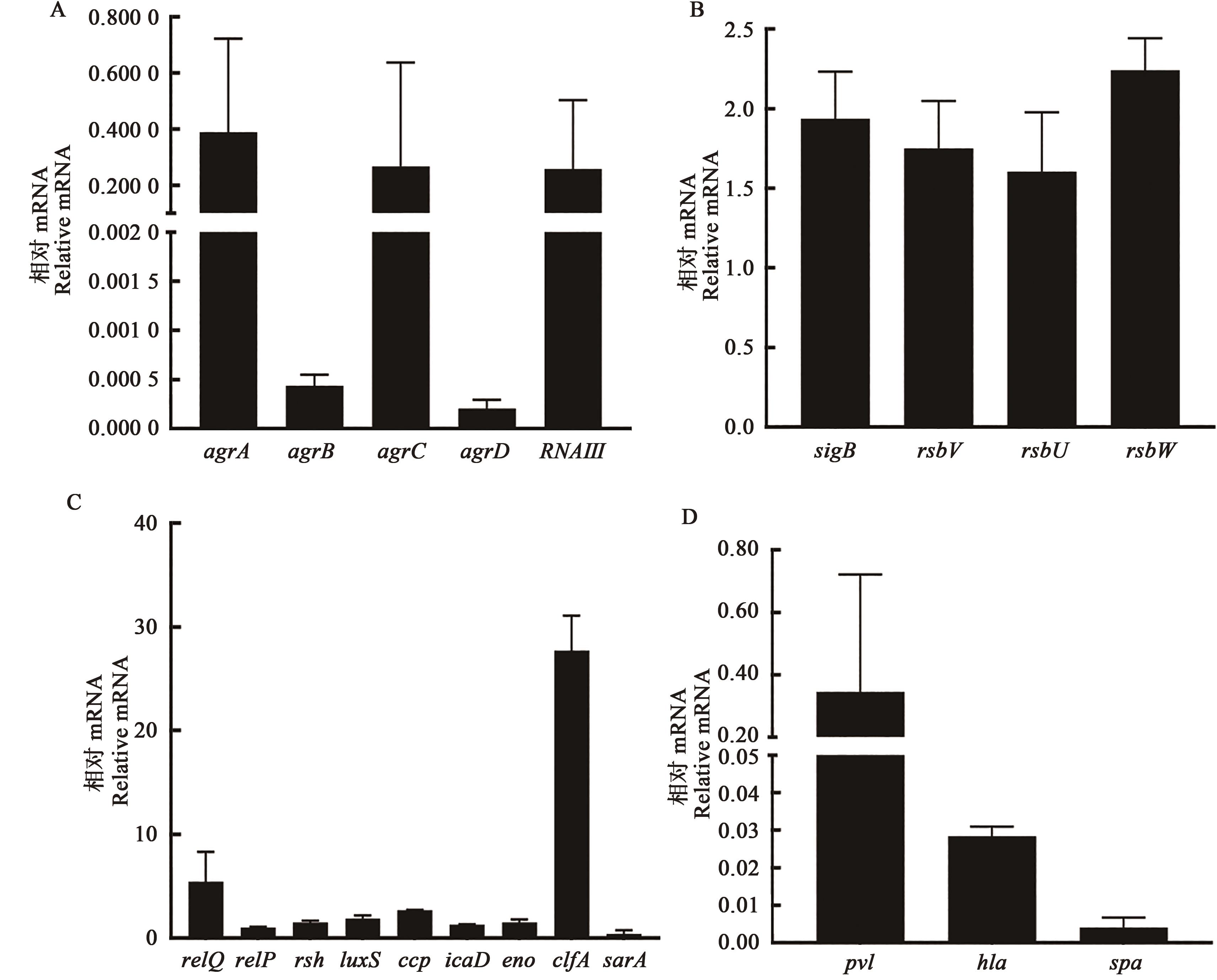
图4 SCVs特性基因相对表达A: Agr调控系统相关基因; B: SigB调控系统相关基因; C: 生物膜相关基因; D: 毒力基因
Fig. 4 Relative expression of characteristic genes in SCVsA: Agr regulatory system genes; B: SigB regulatory system genes; C: Biofilm related genes; D:Virulence genes
| 1 | KAHL B C, BECKER K, LÖFFLER B. Clinical significance and pathogenesis of Staphylococcal small colony variants in persistent infections [J]. Clinical Microbiol. Rev., 2016, 29(2):401-427. |
| 2 | NOTEBAERT S, MEYER E. Mouse models to study the pathogenesis and control of bovine mastitis. A review [J]. Vet Q., 2006, 28(1):2-13. |
| 3 | MARTIN V, WILHELM P, LENG BNIELSEN J B, et al.. Novel pathways for ameliorating the fitness cost of gentamicin resistant small colony variants [J]. Front. Microbiol., 2016, 22(7):1866-1878. |
| 4 | PROCTOR R, EIFF C V, KAHL B, et al.. Small colony variants: a pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections [J]. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.,2006, 4(4):295-305. |
| 5 | GLÄSER R, BECKER K, EIFF C V, et al.. Decreased susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants toward human antimicrobial peptides [J]. J. Invest. Dermatol.,2014, 134(9):2347-2350. |
| 6 | ATALLA H, GYLES C, MALLARD B. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants (SCVs) and their role in disease [J]. Anim. Health Res. Rev., 2011, 12(1):33-45. |
| 7 | LOSS G, SIMES P M, VALOUR F, et al.. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants (SCVs): news from a chronic prosthetic joint infection [J/OL]. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 2019, 9:363 [2023-01-06]. . |
| 8 | 时永强, 祝宇, 龚蕾, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变株体外感染奶牛乳腺上皮细胞的研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2017(17):182-184. |
| SHI Y Q, ZHU Y, GONG L, et al.. The observation of bovine mammary epithelial cells infected with Staphylococcus aureus small colony mutant in vitro [J]. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Veterinary Med., 2017(17):182-184. | |
| 9 | 宋娟. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变株所致相关感染的研究进展[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2018, 18(4):440-444. |
| SONG J. Research update on the infections caused by small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Chin. J. Infect. Chemotherapy, 2018, 18(4):440-444. | |
| 10 | LONG M, HOFFMANN P, TURNIDGE J D, et al.. Prolonged growth of a clinical Staphylococcus aureus strain selects for a stable small-colony-variant cell type [J]. Infect. Immun., 2015, 83(2):470-481. |
| 11 | MELTER O, RADOJEVIČ B. Small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus review [J]. Folia Microbiol., 2010, 55(6):548-558. |
| 12 | EDWARDS A M. Phenotype switching is a natural consequence of Staphylococcus aureus replication [J]. J. Bacteriol., 2012, 194(19): 5404-5412. |
| 13 | KAHL B C. Small colony variants (SCVs) of Staphylococcus aureus-a bacterial survival strategy [J]. Infect. Genet. Evol., 2014, 21:515-522. |
| 14 | DAMIR B, CHRISTOF V E, TSUJI B T. Daptomycin pharmacodynamics against Staphylococcus aureus hemB mutants displaying the small colony variant phenotype [J]. J.Antimicrob. Chemothe., 2009, 63(5):977-981. |
| 15 | SEAMAN P F, DIETMAR O, DAY M J. Small-colony variants: a novel mechanism for triclosan resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [J]. J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 2007, 59(1):43-50. |
| 16 | TUCHSCHERR L, KREIS C A, HOERR V, et al.. Staphylococcus aureus develops increased resistance to antibiotics by forming dynamic small colony variants during chronic osteomyelitis [J]. J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 2016, 71(2):438-448. |
| 17 | PROCTOR R A, KRIEGESKORTE A, KAHL B C, et al.. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants (SCVs): a road map for the metabolic pathways involved in persistent infections [J]. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol., 2014, 4:99-107. |
| 18 | MITCHELL G, BROUILLETTE E, SÉGUIN D, et al.. A role for sigma factor B in the emergence of Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants and elevated biofilm production resulting from an exposure to aminoglycosides [J]. Microb. Pathog., 2010, 48(1):18-27. |
| 19 | GABRIEL M, ALEXANDRE F, KARINE P G, et al.. SigB is a dominant regulator of virulence in Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants [J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 21;8(5):e65018 [2023-01-06]. . |
| 20 | TUCHSCHERR L, BISCHOFF M, LATTAR S M, et al.. Sigma factor sigB is crucial to mediate Staphylococcus aureus adaptation during chronic infections [J/OL]. PLoS Pathog., 2015, 29;11(4):e1004870 [2023-01-06]. . |
| 21 | TUCHSCHERR L, GERACI J, LÖFFLER B. Staphylococcus aureus regulator sigma B is important to develop chronic infections in hematogenous murine osteomyelitis model [J]. Pathogens, 2017, 6(3):31-37. |
| 22 | HÄFFNER N, BÄR J, HAUNREITER V D, et al.. Intracellular environment and agr system affect colony size heterogeneity of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Front. Microbiol., 2020, 11:1415-1426. |
| 23 | WATANABE Y, OIKAWA N, HARIU M, et al.. Evaluation of agar culture plates to efficiently identify small colony variants of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Infect. Drug. Resist., 2019, 12:1743-1748. |
| 24 | VULIN C, LEIMER N, HUEMER M, et al.. Prolonged bacterial lag time results in small colony variants that represent a sub-population of persisters [J]. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1):4074-4082. |
| 25 | TUCHSCHERR L, LFFLER B, PROCTOR R A. Persistence of Staphylococcus aureus: multiple metabolic pathways impact the expression of virulence factors in small-colony variants (SCVs) [J]. Front. Microbiol., 2020, 11:1028-1038. |
| 26 | WIEGAND I, KAI H, HANCOCK R. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances [J]. Nat. Protoc., 2008, 3(2):163-175. |
| 27 | JIAO J, WANG S, LIANG M L, et al.. Basal transcription profiles of the rhamnose-inducible promoter P LRA3 and the development of efficient P LRA3 -based systems for markerless gene deletion and a mutant library in Pichia pastoris [J]. Curr. Genet., 2019, 65(3):785-798. |
| 28 | TREMBLAY Y, LAMARCHE D, CHEVER P, et al.. Characterization of the ability of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from the milk of canadian farms to form biofilm [J]. J. Dairy Sci., 2013, 96(1):234-246. |
| 29 | 贾梓渤, 彭健康, 朱燕, 等. 奶牛乳房炎金黄色葡萄球菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2022, 43(1): 124-128. |
| JIA Z B, PENG J K, ZHU Y, et al.. Isolation, identification and antimicrobial sensitivity test of Staphylococcus aureus from dairy cow mastitis [J]. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci., 2022, 43(1): 124-128. | |
| 30 | 刘兴中, 沈雪, 陈琦, 等. 社区获得性肺炎患者感染病原菌特点及凝血、纤溶相关指标水平分析[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2019, 14(12): 1452-1455. |
| LIU X Z, SHEN X, CHEN Q, et al.. Serum levels of indices related to coagulation and fibrinolysis in patients with more less severe CAP and analysis of characteristics of pathogens related to CAP [J]. J. Pathogen Biol., 2019, 14 (12): 1452-1455. | |
| 31 | 朱梦娇. 冷诱导金黄色葡萄球菌性质变化及生物被膜形成控制[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHU M J. Properties and biofilm control of cold induced staphylococcus aureus [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 32 | RICHARD P N, EDWARD G. Quorum sensing in Staphylococci [J]. Annu. Rev. Genet., 2008, 42(1):541-564. |
| 33 | LONG B, STEPHEN P K. A full genomic characterization of the development of a stable small colony variant cell-type by a clinical Staphylococcus aureus strain [J]. Infect. Genet. Evol.,2015, 36: 345-355. |
| 34 | ZHOU J L, JIAO J, TAN X Y, et al.. Design of a novel antimicrobial peptide 1018M targeted ppGpp to inhibit MRSA biofilm formation [J/OL]. AMB Express.,2021, 11(1):49 [2023-01-06]. . |
| 35 | BARBARA C K, BELLING G B, PETRA B, et al.. Thymidine-dependent Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants are associated with extensive alterations in regulator and virulence gene expression profiles [J]. Infect. Immun., 2005, 73(7):4119-4126. |
| 36 | BUM A K, EUN B J, CHEOL H Y, et al.. Lipoteichoic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation [J]. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9:327-340. |
| 37 | COSTA F N, BELO N O, COSTA E A, et al.. Frequency of enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin-1, and biofilm formation genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cows with mastitis in the northeast of Brazil [J]. Trop. Anim. Health Prod., 2018, 50(5):1089-1097. |
| 38 | PROCTOR R A, VAN L P, KRISTJANSSON M, et al.. Persistent and relapsing infections associated with small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Clin. Infect. Dis., 1995, 20(1):95-102. |
| 39 | SEIDL K, LEEMANN M, MARQUES M P, et al.. High level methicillin resistance correlates with reduced Staphylococcus aureus endothelial cell damage [J]. Int. J. Med. Microbiol., 2017, 307(1):11-20. |
| 40 | CTÉ-GRAVEL J, BROUILLETTE E, MALOUIN F. Vaccination with a live-attenuated small-colony variant improves the humoral and cell-mediated responses against Staphylococcus aureus [J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2019, 27;14(12):e0227109 [2023-01-06]. . |
| 41 | CHAIEB K, MAHDOUANI K, BAKHROUF A. Detection of icaA and icaD loci by polymerase chain reaction and biofilm formation by Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from dialysate and needles in a dialysis unit [J]. J. Hosp. Infect., 2005, 61(3): 225-230. |
| 42 | KUSSMANN M, KARER M, OBERMUELLER M, et al.. Emergence of a dalbavancin induced glycopeptide/lipoglycopeptide non-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus during treatment of a cardiac device-related endocarditis [J]. Emerg. Microbes Infect., 2018, 7(1):202-212. |
| 43 | SCHWERDT M, NEUMANN C, SCHWARTBECK B, et al.. Staphylococcus aureus in the airways of cystic fibrosis patients—a retrospective long-term study [J]. Int. J. Med. Microbiol., 2018, 308(6):631-639. |
| 44 | NINA S, URSULA K, MIKE D, et al.. The energy-coupling factor transporter module EcfAA'T, a novel candidate for the genetic basis of fatty acid-auxotrophic small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9:1863-1877. |
| 45 | SCHLEIMER N, KASPAR U, BALLHAUSEN B, et al.. Adaption of an episomal antisense silencing approach for investigation of the phenotype switch of Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants [J]. Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10:2044-2052. |
| 46 | 熊甘爽, Alkasir Rashad, 仲亮,等. 奶牛乳房炎金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变株的表型鉴定及其遗传基础分析[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2020, 52(5): 64-72. |
| XIONG G S, ALKASIR R, ZHONG L, et al.. Phenotypic identification and genetic basis of staphylococcus SCV associated with persistent bovine mastitis [J]. Anim. Husb. Veterinary Med., 2020, 52(5): 64-72. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号