




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 201-208.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0782
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-10-25
接受日期:2023-11-25
出版日期:2025-04-15
发布日期:2025-04-15
通讯作者:
俞志敏
作者简介:侯晓晴 E-mail:hxq17866507885@163.com;
基金资助:
Xiaoqing HOU( ), Zihao JIANG, Yang FU, Zhongzhen SONG, Zhimin YU(
), Zihao JIANG, Yang FU, Zhongzhen SONG, Zhimin YU( )
)
Received:2023-10-25
Accepted:2023-11-25
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Zhimin YU
摘要:
微生物所产的胞外多糖(extracellular polysaccharides,EPS)作为一种对环境友好的绿色制剂,在促生植物方面具有广阔的应用前景。以鞘氨醇单胞菌(Sphingomonas sp.)CX7发酵所产的EPS为研究对象,分析其一级结构,并探究其对大麦幼苗的促生和抗逆性作用。结果显示,CX7所产EPS是一种由葡萄糖、甘露糖、鼠李糖、岩藻糖、核糖、葡萄糖醛酸、半乳糖、半乳糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖、木糖组成的杂多糖,质量比为5.68∶3.25∶1.99∶1.62∶1.00∶0.81∶0.27∶0.06∶0.02∶0.01。配制不同剂量的EPS喷施大麦叶片,结果表明,大麦生长最适的EPS剂量为2 g·L-1,在此剂量下大麦的根长、株高、鲜重和干重分别增加47.45%、19.28%、18.15%和37.88%;叶片的叶绿素、可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白和脯氨酸含量及过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶活性分别增加52.47%、25.55%、27.36%、94.44%、82.81%、97.91%。综上所述,鞘氨醇单胞菌所产EPS对植物生长具有一定的促生作用,提高植物抗逆性,为绿色生物制剂替代传统农用叶面肥提供一定的参考依据。
中图分类号:
侯晓晴, 姜子豪, 富洋, 宋忠振, 俞志敏. 鞘氨醇单胞菌胞外多糖的组成结构及其对大麦幼苗的促生作用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 201-208.
Xiaoqing HOU, Zihao JIANG, Yang FU, Zhongzhen SONG, Zhimin YU. Composition and Structure of Extracellular Polysaccharides from Sphingomonas sp. and Their Promoting Effects on Barley Seedlings[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 201-208.
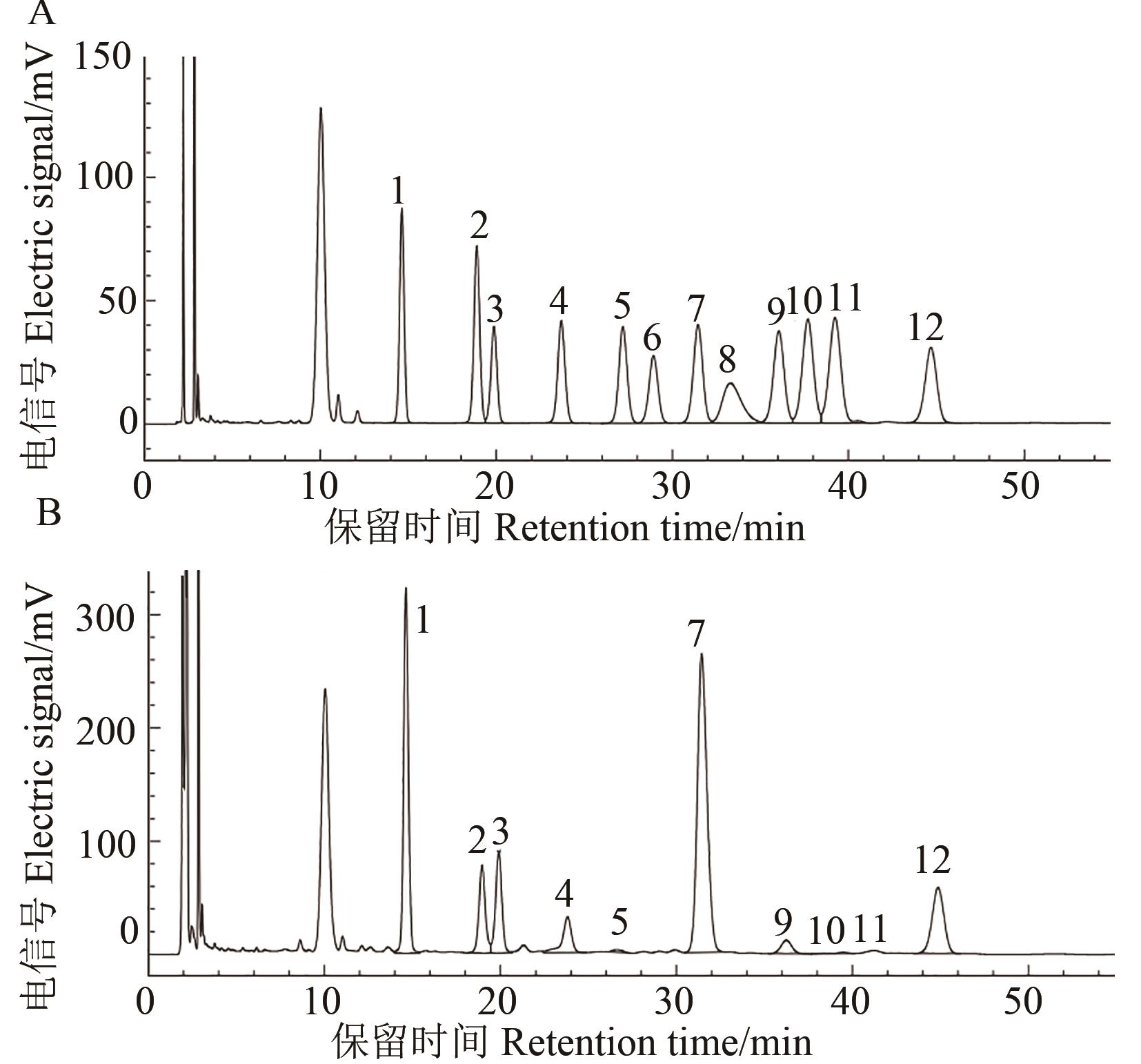
图1 鞘氨醇单胞菌EPS的单糖组成A:单糖标准品;B:EPS;1—甘露糖;2—核糖;3—鼠李糖;4—葡萄糖醛酸;5—半乳糖醛酸;6—N-乙酰-氨基葡萄糖;7—葡萄糖;8—N-乙酰-氨基半乳糖;9—半乳糖;10—木糖;11—阿拉伯糖;12—岩藻糖
Fig. 1 Monosaccharide composition of EPSfrom Sphingomonas sp.A: Standard sugarmonosaccharide; B: EPS; 1—Mannose; 2—Ribose; 3—Rhamnose; 4—Glucuronic acid; 5—Galacturonic acid; 6—N-Acetylglucosamine; 7—Glucose; 8—N-Acetylaminogalactose; 9—Galactose; 10—Xylose; 11—Arabinose; 12—Fucose
| 指标Index | EPS含量EPS content/(g·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 根长Root length/cm | 6.09±0.40 b | 7.23±0.35 b | 8.98±0.67 a | 7.03±0.19 b |
| 根长效应值Root length effect value/% | - | 18.72 | 47.45 | 15.44 |
| 株高Plant height/cm | 19.87±2.21 b | 21.26±2.14 b | 23.70±2.16 a | 21.00±1.93 b |
| 株高效应值Plant height effect value/% | - | 7.00 | 19.28 | 5.69 |
| 鲜重Fresh weight/g | 3.14±0.22 b | 3.66±0.08 a | 3.71±0.17 a | 3.62±0.20 a |
| 鲜重效应值Fresh weight effect value/% | - | 16.56 | 18.15 | 15.29 |
| 干重Dry weight/g | 0.66±0.02 b | 0.84±0.05 a | 0.91±0.03 a | 0.71±0.09 b |
| 干重效应值Dry weight effect value/% | - | 27.27 | 37.88 | 7.58 |
表1 不同EPS处理下大麦幼苗的株高、根长和干重、鲜重
Table 1 Plant height, root length, dry weight, and fresh weight of barley seedlings under different EPS treatments
| 指标Index | EPS含量EPS content/(g·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 根长Root length/cm | 6.09±0.40 b | 7.23±0.35 b | 8.98±0.67 a | 7.03±0.19 b |
| 根长效应值Root length effect value/% | - | 18.72 | 47.45 | 15.44 |
| 株高Plant height/cm | 19.87±2.21 b | 21.26±2.14 b | 23.70±2.16 a | 21.00±1.93 b |
| 株高效应值Plant height effect value/% | - | 7.00 | 19.28 | 5.69 |
| 鲜重Fresh weight/g | 3.14±0.22 b | 3.66±0.08 a | 3.71±0.17 a | 3.62±0.20 a |
| 鲜重效应值Fresh weight effect value/% | - | 16.56 | 18.15 | 15.29 |
| 干重Dry weight/g | 0.66±0.02 b | 0.84±0.05 a | 0.91±0.03 a | 0.71±0.09 b |
| 干重效应值Dry weight effect value/% | - | 27.27 | 37.88 | 7.58 |
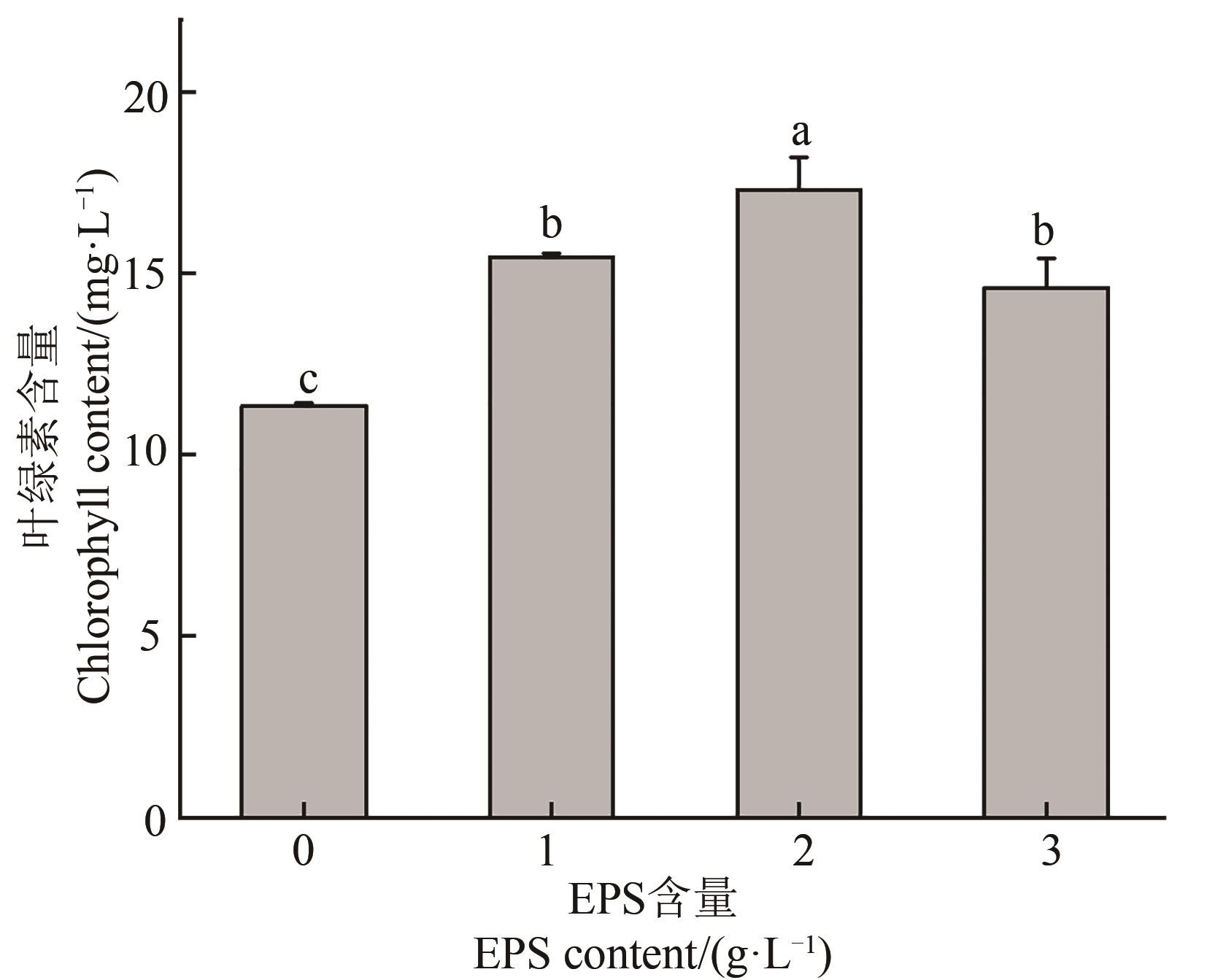
图4 不同EPS处理下大麦幼苗的叶绿素含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Chlorophyll content in barley seedlings under different EPS treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
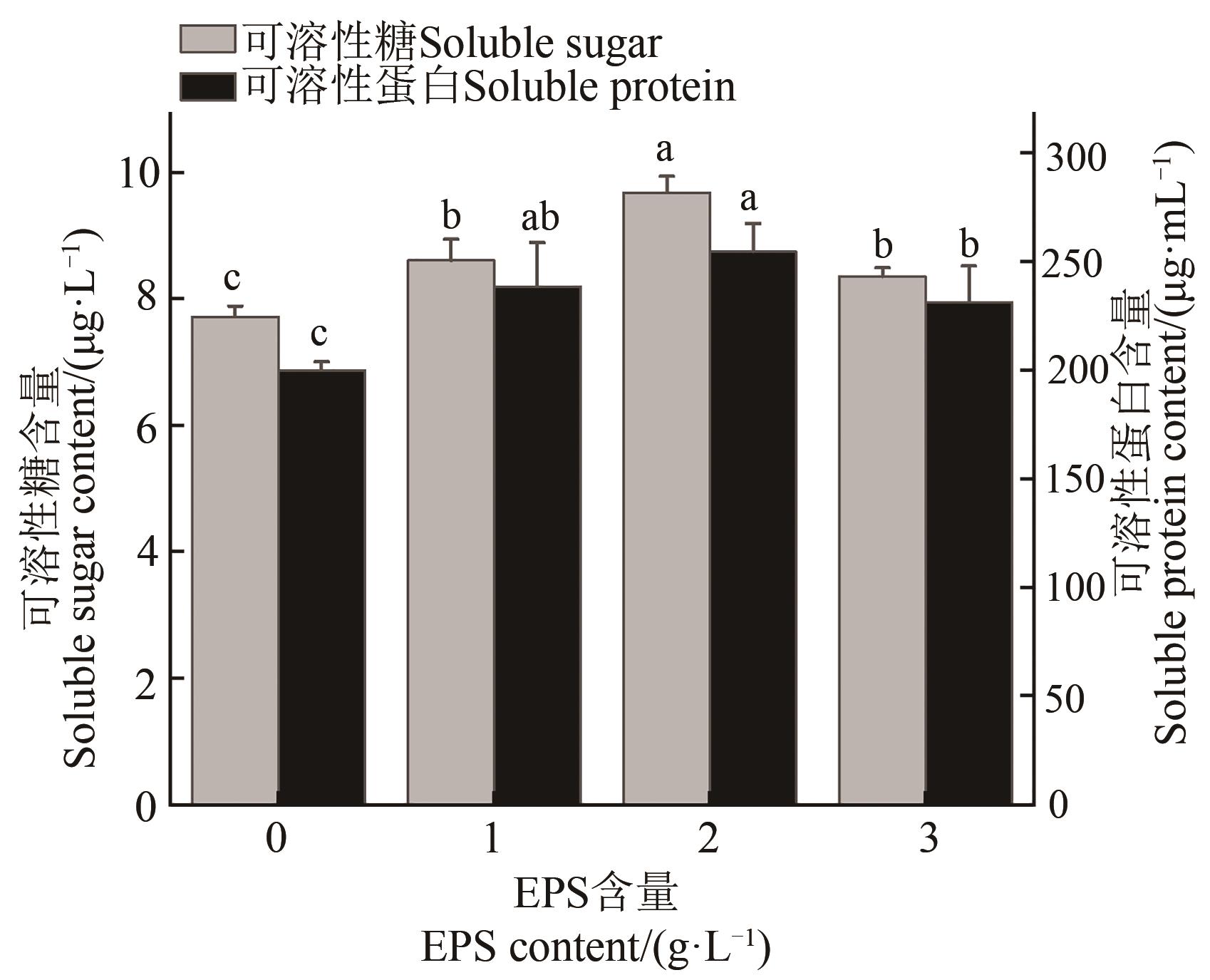
图5 不同EPS处理下大麦幼苗的可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Contents of soluble sugar and soluble protein in barley seedlings under different EPS treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
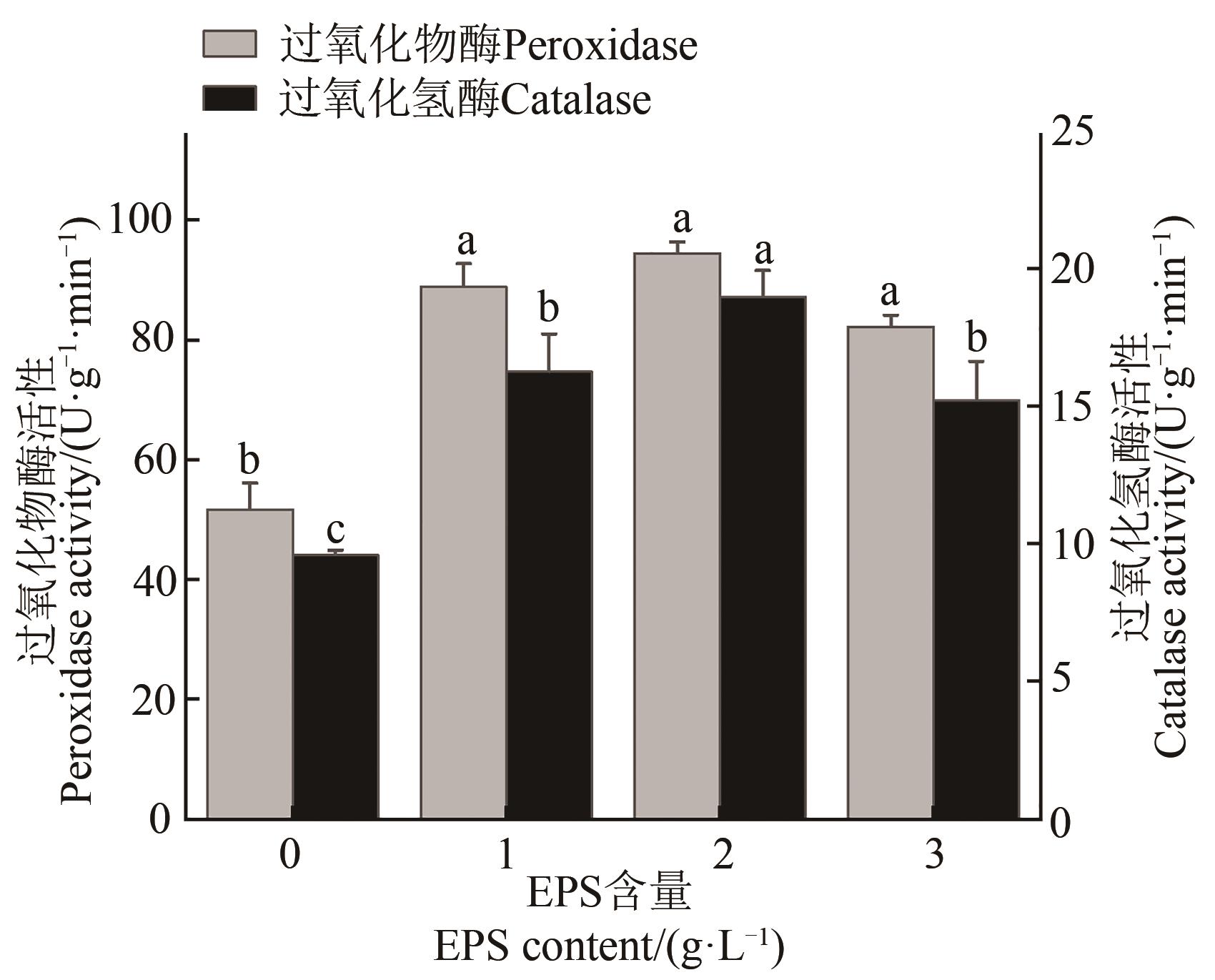
图6 不同EPS处理下大麦幼苗的过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶酶活注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Activities of peroxidase and catalase in barley seedlings under different EPS treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05level.
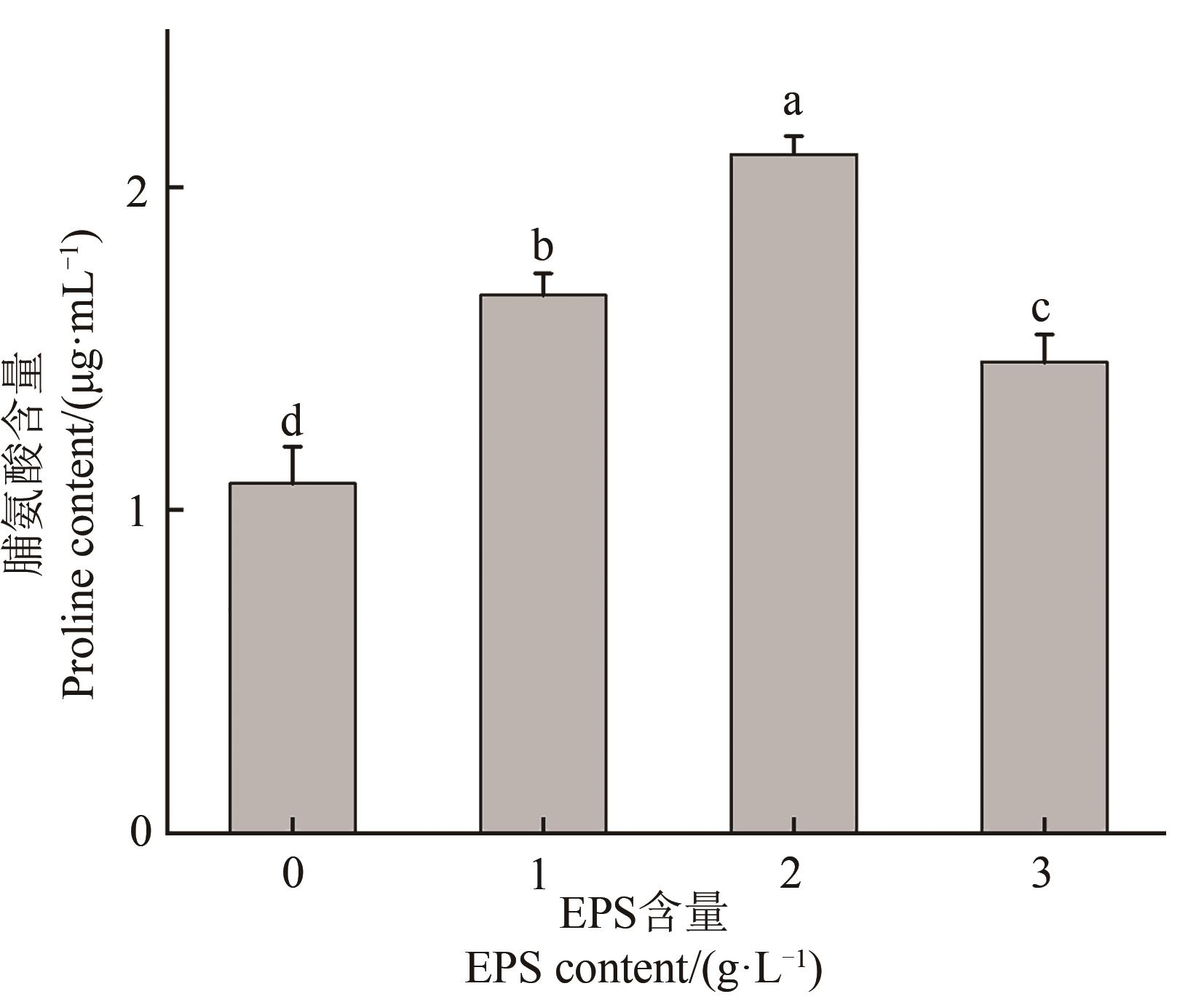
图7 不同EPS处理下大麦幼苗的脯氨酸含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 7 Proline content in barley seedlings under different EPS treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | TATSU S, MATSUO Y, NAKAHARA K, et al.. Key odorants in Japanese roasted barley tea (Mugi Cha) differences between roasted barley tea prepared from naked barley and roasted barley tea prepared from hulled barley [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2020, 68(9):2728-2737. |
| 2 | WIEGMANN M T, WILLIAM T B, BULL H J, et al.. Wild barley serves as a source for biofortification of barley grains [J]. Plant Sci., 2019, 283:83-94. |
| 3 | 聂攀,丁信文,吴艳,等.植物乳杆菌发酵对全谷物黑大麦多酚富集的影响[J].中国食品学报,2023,23(8):186-196. |
| NIE P, DING X W, WU Y, et al.. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on enrichment of polyphenols in whole grain black barley [J]. J. Chin. Institute Food Sci. Technol., 2023, 23(8):186-196. | |
| 4 | 卢伟,耿楠,陆宁.大麦苗粉营养成分及其制品研究进展[J].包装与食品机械,2018,36(1):63-67. |
| LU W, GENG N, LU N. Research progress of nutritional components and products of barley leaf powde [J]. Package Food Mach., 2018, 36(1): 63-67. | |
| 5 | SAJID R, MARIAM A, HOUDA H, et al.. Traits discovery in Hordeum vulgare sbsp. Spontaneum accessions and in lines derived from interspecific crosses with wild Hordeum species for enhancing barley breeding efforts [J]. Crop Sci., 2021, 61(1):219-233. |
| 6 | GUNASEKARAN Y, THIYAGESHWARI S, ARIYAN M, etal .. Alleviation of sodic stress in rice by exploring the exopolysaccharide-producing sodic-tolerant bacteria [J/OL]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(9):1451 [2023-09-25]. . |
| 7 | 任新宇.植物乳杆菌胞外多糖对酸—镉复合胁迫下大麦幼苗生长及土壤环境的影响[D].南昌:江西农业大学,2023. |
| REN X Y. Effects of exopolysaccharides of Lactobacillus plantarum on the growth of rice seedling and soil environment under acid-cadmium compound stress [D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| 8 | BARCELOS C S M, VESPERMANN K A C, PELISSARI F M, et al.. Current status of biotechnological production and applications of microbial exopolysaccharides [J]. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci., 2020, 60(9):1475-1495. |
| 9 | HILAL Y, NEVA K. Microbial exopolysaccharides: resources and bioactive properties [J]. Process Biochem., 2018, 72:41-46. |
| 10 | BHATIA S K, GYRAV R, CHOI Y K, et al.. Bioprospecting of exopolysaccharide from marine Sphingobium yanoikuyae BBL01: production, characterization, and metal chelation activity [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2021, 324:124674 [2023-09-25]. . |
| 11 | SOROURIL B, RODRIGUEZ C I, GAUT B S, et al.. Variation in Sphingomonas traits across habitats and phylogenetic clades [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol, 2023, 114:6165 [2023-09-25]. . |
| 12 | YABUCHI E, YANO I, OYAZIU H, et al.. Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis Gen. Nov. and Comb. Nov [J]. Microbiol. Immunol., 1990, 34:99-119. |
| 13 | MENEGHINE A K, MORETTO C, CASTELLANE T C L, et al.. Production, characterization and bioemulsifying activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Sphingomonas sp. isolated from freshwater [J]. J. Polym. Environ., 2017, 25(4):1080-1086. |
| 14 | ABUBAKAR D, ZAHAIR A Z, MUHAMMAD I, et al.. Efficacy of rhizobacterial exopolysaccharides in improving plant growth, physiology, and soil properties [J/OL]. Environ. Monit. Assess., 2021, 193(8): 09286-6 [2023-09-25]. . |
| 15 | CANBOLAT M Y, BILEN S, ÇAKMAKCI R, et al.. Effect of plant growth-promoting bacteria and soil compaction on barley seedling growth, nutrient uptake, soil properties and rhizosphere microflora [J]. Biol Fert. Soils., 2006, 42(4):350-357. |
| 16 | HUSSAIN A, KAMRAN M A, JAVED M T, et al.. Individual and combinatorial application of Kocuria rhizophila and citric acid on phytoextraction of multi-metal contaminated soils by Glycine max L. [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2019, 159:23-33. |
| 17 | YUE F F, ZHANG J R, XU J X, et al.. Effects of monosaccharide composition on quantitative analysis of total sugar content by phenol-sulfuric acid method [J/OL]. Front. Nutr., 2022, 9:963318 [2023-09-25]. . |
| 18 | BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quanitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding [J]. Anal. Biochem., 1976, 72(1-2):248-254. |
| 19 | MAEHLY A C, CHANCE B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases [J]. Methods Biochem. Anal., 1954, 110:357-424. |
| 20 | GOTH L A. Simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range [J]. Clin. Chim. Acta, 1991, 196(2-3):143-151. |
| 21 | BATES L, WALDREN R, TEARE L. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies [J]. Plant Soil, 1973, 39:205-207. |
| 22 | WEI D I, ZHANG Y C, YI H X, et al.. Research methods for structural analysis of lactic acid bacteria induced exopolysaccharides [J]. Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 2018, 46(6):875-882. |
| 23 | JABBROVA D, DAVRANOV K, JABBAROV Z, et al.. Dual inoculation of plant growth-promoting Bacillus endophyticus and Funneliformis mosseae improves plant growth and soil properties in ginger [J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 39:34779-34788. |
| 24 | 孙姗姗.水分胁迫下糖类浸种对玉米萌发及根际微生物的影响[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2017. |
| SUN S S. Under water stress carbohydrate soaking on germination of maize and rhizosphere microorganisms [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 25 | 张金菊,田青,郭有燕,等.黑果枸杞根系对干旱胁迫响应的生理机制[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2023,58(4):1-13. |
| ZHANG J J, TIAN Q, GUO Y Y, et al.. Physiological mechanism of root response to drought stress in Lycium ruthenicum [J]. J. Gansu Agric. Univ., 2023, 58(4):1-13. | |
| 26 | GARGALLO G A, PREECE C, SARDANS J, et al.. Root exudate metabolomes change under drought and show limited capacity for recovery [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2018, 8:12696 [2023-09-25]. . |
| 27 | 李慧芬,方安然,冯海霞,等.胞外多糖产生菌的筛选鉴定及其促生改土作用[J].微生物学通报,2023,50(5):1941-1957. |
| LI H F, FANG A R, FENG H X, et al.. Screening and identification of extracellular polysaccharide-producing strain and the influence on soil quality and crop growth [J]. Microbiol. China, 2023, 50(5):1941-1957. | |
| 28 | PANKAJ U, SINGH N D, MISHRA P, et al.. Autochthonous halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria promote bacoside A yield of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Nash and phytoextraction of salt-affected soil [J]. Pedosphere, 2020, 30(5):671-683. |
| 29 | 张迪,侯扬威,张岩岩,等.不同复配叶面肥对箭叶淫羊藿黄酮类成分的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(6):1461-1465. |
| ZHANG D, HOU Y W, ZHANG Y Y, et al.. Effects of different compound foliar fertilizers on the composition of Epimedium sagittatum [J]. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res., 2023, 34(6):1461-1465. | |
| 30 | 张文平,王清,黄诗宸,等.乳酸菌胞外多糖对水稻生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J].浙江农业学报,2019,31(1):130-138. |
| ZHANG W P, WANG Q, HUANG S C, et al.. Effects of exopolysaccharides of lactic acid bacteria on rice growth and soil physicochemical properties [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(1):130-138. | |
| 31 | 贾朋,罗树凯,王方.3种木兰科植物叶片SPAD值的分布特征及其与叶绿素含量的关系[J].广东园林,2022,44(2):85-89. |
| JIA P, LUO S K, WANG F. Distribution characteristics of leaf SPAD value and its relationship with chlorophyll content in lesves of three Magnoliaceae species [J]. Guangdong Land. Architecture, 2022, 44(2):85-89. | |
| 32 | WHITE J A, TODD J, NEWAN T, et al.. A new set of Arabidopsis expressed sequence tags from developing seeds. The metabolic pathway from carbohydrates to seed oil [J]. Plant Physiol., 2001, 124(4):1582-1594. |
| 33 | ARNDT S K, CLIFFORD S C, WANEK W, et al.. Physiological and morphological adaptations of the fruit tree Ziziphus rotundifolia in response to progressive drought stress [J]. Tree Physiol., 2001, 21(11):705-715. |
| 34 | 杜小凤,顾大路,仲秀娟,等.氨基多糖水溶肥对小麦生理特性、产量及籽粒品质的影响[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(6):16-23. |
| DU X F, GU D L, ZHONG X J, et al.. Aminopolysaccharide water-soluble fertilizer: effects on physiological characteristics, yield and grain quality of wheat [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021, 37(6):16-23. | |
| 35 | XU X Y, SUN L, LI S, et al.. Welan gum promoted the growth of rice seedlings by enhancing carbon and nitrogen assimilation [J]. Carbohyd. Res., 2020, 498(8):108-181. |
| 36 | 王艳成,张纪月,冯帅奇,等.外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J].中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8):196-202. |
| WANG Y C, ZHANG J Y, MENG S Q, et al.. Effects of exogenous PGPR combined with organic fertilizers on soil properties and stress resistance of ginseng under drought stress [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023, 25(8):196-202. | |
| 37 | CANBOLATA M Y, BILEN S, RAMAZAN A, et al.. Effect of plant growth-promoting bacteria and soil compaction on barley seedling growth, nutrient uptake, soil properties and rhizosphere microflora [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2006, 42(4):350-357. |
| 38 | DE F, PAULO A F, DE C H H, et al.. Salt acclimation in sorghum plants by exogenous proline: physiological and biochemical changes and regulation of proline metabolism [J]. Plant Cell Rep., 2019, 38(1):403-416. |
| [1] | 杨智敏, 张慧豪, 张园园, 杜红岩, 刘晓东, 侯亚光, 王毅, 徐道龙, 黄金贵, 程晓宁, 随洋, 王瑞利, 于超, 赵玲玲, 陈春梅, 雅茹, 贾丽, 张明月, 王宏伟, 姚淞耀, 赵莹, 邵科. 娄彻氏链霉菌HM85的鉴定及其对甜菜的防病促生作用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 148-155. |
| [2] | 常峻嘉, 盖佳鑫, 陶刚, 莫转龙海. 哈茨木霉菌对烟草的促生及其黑胫病的诱导抗性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 168-176. |
| [3] | 田振祥, 丁伟, 程茁, 戴航宇. 大豆内生细菌的分离及其作用效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 47-57. |
| [4] | 孟玉, 陶刚, 黄德棋, 姚遐俊. 溶磷真菌的多样性及其在农业与生态中的应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 208-217. |
| [5] | 周茂超1,2,黄艳娜2,段赛菲1,2,束仕元1,2,唐雪明2*. 微生物种衣剂的研制及其对玉米苗期生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 110-118. |
| [6] | 李婷,何来,梁泉峰*. 非豆科植物的根瘤菌促生机制的研究进展[J]. , 2013, 15(2): 97-102. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号