




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 145-155.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0303
• ANIMAL AND PLANT HEALTH • Previous Articles
Li YANG1( ), Li YU1, Zhuo SUN1, Tongyu ZHANG1, Yang ZHANG2(
), Li YU1, Zhuo SUN1, Tongyu ZHANG1, Yang ZHANG2( ), Limin YANG1(
), Limin YANG1( )
)
Received:2021-04-12
Accepted:2021-07-26
Online:2022-06-15
Published:2022-06-21
Contact:
Yang ZHANG,Limin YANG
杨莉1( ), 于俐1, 孙卓1, 张桐毓1, 张阳2(
), 于俐1, 孙卓1, 张桐毓1, 张阳2( ), 杨利民1(
), 杨利民1( )
)
通讯作者:
张阳,杨利民
作者简介:杨莉 E-mail: yangliff@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Li YANG, Li YU, Zhuo SUN, Tongyu ZHANG, Yang ZHANG, Limin YANG. Allelopathic Effects of Organic Acids and Saponins in Ginseng Root Exudates on Pathogenic and Biocontrol Bacteria[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 145-155.
杨莉, 于俐, 孙卓, 张桐毓, 张阳, 杨利民. 人参根系分泌物中有机酸及皂苷对人参病原菌与生防菌的化感差异研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 145-155.
病原菌 Pathogenic bacteria | 处理 Treatment/ (mg·L-1) | 抑制率±RSD Inhibiting ratio±RSD/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苯甲酸 Benzoic acid | 丁二酸 Succinic acid | 己二酸 Adipic acid | 邻苯二甲酸 Phthalic acid | ||
强壮土赤壳菌 Ilyonectria robusta | 0.001 | 16.52±4.88* | -2.36±5.33 | 5.31±2.29* | 30.09±3.15* |
| 0.010 | 1.06±6.51 | 10.62±0.72* | 4.87±2.23* | 14.38±1.96* | |
| 0.100 | 1.55±6.67 | 9.73±2.66* | 1.42±1.14 | 11.50±4.85* | |
| 1.000 | -6.42±6.19 | 7.96±0.04* | 9.38±4.54** | 13.05±2.33* | |
| 5.000 | 20.53±4.65* | -3.10±4.59 | 29.87±4.05* | 1.55±9.12 | |
| CK | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | |
人参核盘菌 Sclerotinia ginseng | 0.001 | -5.52±4.07 | -9.99±3.25* | -17.25±1.60* | -0.27±6.67 |
| 0.010 | -7.80±4.24* | -19.70±2.27* | -17.34±1.79* | -6.05±2.78 | |
| 0.100 | -13.05±6.75* | -21.80±2.27* | 5.85±8.49 | -8.15±2.27 | |
| 1.000 | -14.80±1.21* | -15.50±1.05* | 2.00±0.61 | -10.77±0.61* | |
| 5.000 | -0.27±3.88 | 3.14±2.33 | -19.49±3.69* | -2.20±2.19 | |
| CK | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | |
腐皮镰孢菌 Fusarum solani | 0.001 | -5.60±2.68 | -4.33±2.45 | -9.41±3.85* | -3.82±7.78 |
| 0.010 | -8.65±2.89* | -4.58±0.76 | -5.85±1.17* | 7.06±2.89 | |
| 0.100 | -4.58±3.33 | -3.31±3.61 | -1.02±6.17 | 7.12±1.17 | |
| 1.000 | -0.25±4.84 | -2.29±0.02 | -3.56±1.59 | 5.85±5.36 | |
| 5.000 | -1.02±3.09 | -2.29±11.90 | 0.76±0.77 | 2.80±4.96 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | |
人参链格孢菌 Alternaria panax | 0.001 | -5.42±5.87 | -4.58±2.64 | 9.44±5.96* | 1.04±1.79 |
| 0.010 | -2.48±3.68 | -3.11±6.75 | 5.08±0.61 | 0.95±0.61 | |
| 0.100 | -8.15±1.82* | -2.69±0.11 | 4.19±3.98 | -1.50±2.97 | |
| 1.000 | 5.87±1.21* | 0.88±3.20 | 0.46±4.48 | -2.55±0.74 | |
| 5.000 | 10.54±6.19* | 0.88±3.53 | -1.64±4.29 | -1.59±1.01 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | |
Table 1 Influence of organic acids on the growth of pathogenic bacteria
病原菌 Pathogenic bacteria | 处理 Treatment/ (mg·L-1) | 抑制率±RSD Inhibiting ratio±RSD/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
苯甲酸 Benzoic acid | 丁二酸 Succinic acid | 己二酸 Adipic acid | 邻苯二甲酸 Phthalic acid | ||
强壮土赤壳菌 Ilyonectria robusta | 0.001 | 16.52±4.88* | -2.36±5.33 | 5.31±2.29* | 30.09±3.15* |
| 0.010 | 1.06±6.51 | 10.62±0.72* | 4.87±2.23* | 14.38±1.96* | |
| 0.100 | 1.55±6.67 | 9.73±2.66* | 1.42±1.14 | 11.50±4.85* | |
| 1.000 | -6.42±6.19 | 7.96±0.04* | 9.38±4.54** | 13.05±2.33* | |
| 5.000 | 20.53±4.65* | -3.10±4.59 | 29.87±4.05* | 1.55±9.12 | |
| CK | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | |
人参核盘菌 Sclerotinia ginseng | 0.001 | -5.52±4.07 | -9.99±3.25* | -17.25±1.60* | -0.27±6.67 |
| 0.010 | -7.80±4.24* | -19.70±2.27* | -17.34±1.79* | -6.05±2.78 | |
| 0.100 | -13.05±6.75* | -21.80±2.27* | 5.85±8.49 | -8.15±2.27 | |
| 1.000 | -14.80±1.21* | -15.50±1.05* | 2.00±0.61 | -10.77±0.61* | |
| 5.000 | -0.27±3.88 | 3.14±2.33 | -19.49±3.69* | -2.20±2.19 | |
| CK | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | |
腐皮镰孢菌 Fusarum solani | 0.001 | -5.60±2.68 | -4.33±2.45 | -9.41±3.85* | -3.82±7.78 |
| 0.010 | -8.65±2.89* | -4.58±0.76 | -5.85±1.17* | 7.06±2.89 | |
| 0.100 | -4.58±3.33 | -3.31±3.61 | -1.02±6.17 | 7.12±1.17 | |
| 1.000 | -0.25±4.84 | -2.29±0.02 | -3.56±1.59 | 5.85±5.36 | |
| 5.000 | -1.02±3.09 | -2.29±11.90 | 0.76±0.77 | 2.80±4.96 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | |
人参链格孢菌 Alternaria panax | 0.001 | -5.42±5.87 | -4.58±2.64 | 9.44±5.96* | 1.04±1.79 |
| 0.010 | -2.48±3.68 | -3.11±6.75 | 5.08±0.61 | 0.95±0.61 | |
| 0.100 | -8.15±1.82* | -2.69±0.11 | 4.19±3.98 | -1.50±2.97 | |
| 1.000 | 5.87±1.21* | 0.88±3.20 | 0.46±4.48 | -2.55±0.74 | |
| 5.000 | 10.54±6.19* | 0.88±3.53 | -1.64±4.29 | -1.59±1.01 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | |
病原菌 Pathogenic bacteria | 处理 Treatment/(mg·L-1) | 抑制率±RSD Inhibiting ratio±RSD/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rb2 | Rc | Rd | Re | Rg1 | ||
强壮土赤壳菌 Ilyonectria robusta | 0.001 | 0.00±4.45 | 19.12±4.83* | 14.82±6.15* | 44.07±3.03* | 6.64±2.34 |
| 0.010 | 12.39±5.87* | 30.09±5.04* | 19.47±1.53* | 18.23±3.52* | -2.95±56.06 | |
| 0.100 | 27.08±2.91* | 7.30±3.91* | 30.80±3.42* | 15.75±0.85* | 8.85±4.40* | |
| 1.000 | 24.78±4.68* | 7.96±4.57* | 0.00±3.38 | 14.16±1.77* | 31.33±8.46* | |
| 5.000 | 13.86±4.09* | -1.77±5.45 | -16.81±2.17* | 23.89±5.06* | 17.70±3.15* | |
| CK | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | |
人参核盘菌 Sclerotinia ginseng | 0.001 | -1.32±6.09 | -5.26±6.61 | -7.07±2.92 | -2.90±3.74 | -22.85±2.78* |
| 0.010 | -6.05±1.58* | -3.73±8.55 | -8.50±7.60 | -12.09±1.99* | 13.64±0.53* | |
| 0.100 | -9.55±0.61* | -17.60±4.77* | -8.67±6.09 | -18.91±4.95* | -15.85±0.61* | |
| 1.000 | -3.95±3.09 | -11.82±5.18* | -16.20±1.21* | -2.71±2.41 | -20.75±1.21* | |
| 5.000 | 7.86±1.60* | -22.59±1.32* | -14.80±7.60* | -3.42±6.67 | -6.31±1.01 | |
| CK | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | |
腐皮镰孢菌 Fusarum solani | 0.001 | 1.78±6.49 | -1.08±3.08 | 8.14±7.53 | -7.12±4.91 | -4.35±1.92 |
| 0.010 | -5.85±5.78 | -8.65±2.89 | 4.83±3.92 | -0.51±2.2 | -7.38±1.92* | |
| 0.100 | -4.83±5.36 | -3.82±2.02 | -3.56±1.17 | 0.25±0.88 | 3.56±3.08 | |
| 1.000 | -8.91±1.17* | -1.02±1.17 | 1.02±4.20 | -1.27±3.18 | 6.62±7.33 | |
| 5.000 | -5.85±0.88 | -3.82±2.75 | 2.54±5.83 | 5.09±7.72 | 0.95±1.59 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | |
人参链格孢菌 Alternaria panax | 0.001 | -2.06±2.72 | -2.55±3.38 | -9.83±3.61* | -0.54±4.06 | -8.41±2.33* |
| 0.010 | -7.73±2.05* | -3.11±3.67 | -2.48±0.33 | -1.85±6.47 | -1.64±1.73 | |
| 0.100 | -3.32±7.57 | 2.14±1.05 | -2.27±2.42 | -1.59±1.60 | -3.74±4.37 | |
| 1.000 | -1.75±2.72 | -6.47±1.60* | 5.50±3.38 | 1.30±3.98 | 0.04±2.78 | |
| 5.000 | -3.32±6.87 | -3.95±3.71* | 2.00±3.21 | 2.00±5.78 | 2.00±4.24 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | |
Table 2 Influence of saponins on the growth of pathogenic bacteria
病原菌 Pathogenic bacteria | 处理 Treatment/(mg·L-1) | 抑制率±RSD Inhibiting ratio±RSD/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rb2 | Rc | Rd | Re | Rg1 | ||
强壮土赤壳菌 Ilyonectria robusta | 0.001 | 0.00±4.45 | 19.12±4.83* | 14.82±6.15* | 44.07±3.03* | 6.64±2.34 |
| 0.010 | 12.39±5.87* | 30.09±5.04* | 19.47±1.53* | 18.23±3.52* | -2.95±56.06 | |
| 0.100 | 27.08±2.91* | 7.30±3.91* | 30.80±3.42* | 15.75±0.85* | 8.85±4.40* | |
| 1.000 | 24.78±4.68* | 7.96±4.57* | 0.00±3.38 | 14.16±1.77* | 31.33±8.46* | |
| 5.000 | 13.86±4.09* | -1.77±5.45 | -16.81±2.17* | 23.89±5.06* | 17.70±3.15* | |
| CK | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | 0.00±2.34 | |
人参核盘菌 Sclerotinia ginseng | 0.001 | -1.32±6.09 | -5.26±6.61 | -7.07±2.92 | -2.90±3.74 | -22.85±2.78* |
| 0.010 | -6.05±1.58* | -3.73±8.55 | -8.50±7.60 | -12.09±1.99* | 13.64±0.53* | |
| 0.100 | -9.55±0.61* | -17.60±4.77* | -8.67±6.09 | -18.91±4.95* | -15.85±0.61* | |
| 1.000 | -3.95±3.09 | -11.82±5.18* | -16.20±1.21* | -2.71±2.41 | -20.75±1.21* | |
| 5.000 | 7.86±1.60* | -22.59±1.32* | -14.80±7.60* | -3.42±6.67 | -6.31±1.01 | |
| CK | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | 0.00±2.16 | |
腐皮镰孢菌 Fusarum solani | 0.001 | 1.78±6.49 | -1.08±3.08 | 8.14±7.53 | -7.12±4.91 | -4.35±1.92 |
| 0.010 | -5.85±5.78 | -8.65±2.89 | 4.83±3.92 | -0.51±2.2 | -7.38±1.92* | |
| 0.100 | -4.83±5.36 | -3.82±2.02 | -3.56±1.17 | 0.25±0.88 | 3.56±3.08 | |
| 1.000 | -8.91±1.17* | -1.02±1.17 | 1.02±4.20 | -1.27±3.18 | 6.62±7.33 | |
| 5.000 | -5.85±0.88 | -3.82±2.75 | 2.54±5.83 | 5.09±7.72 | 0.95±1.59 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | 0.00±1.53 | |
人参链格孢菌 Alternaria panax | 0.001 | -2.06±2.72 | -2.55±3.38 | -9.83±3.61* | -0.54±4.06 | -8.41±2.33* |
| 0.010 | -7.73±2.05* | -3.11±3.67 | -2.48±0.33 | -1.85±6.47 | -1.64±1.73 | |
| 0.100 | -3.32±7.57 | 2.14±1.05 | -2.27±2.42 | -1.59±1.60 | -3.74±4.37 | |
| 1.000 | -1.75±2.72 | -6.47±1.60* | 5.50±3.38 | 1.30±3.98 | 0.04±2.78 | |
| 5.000 | -3.32±6.87 | -3.95±3.71* | 2.00±3.21 | 2.00±5.78 | 2.00±4.24 | |
| CK | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | 0.00±1.99 | |
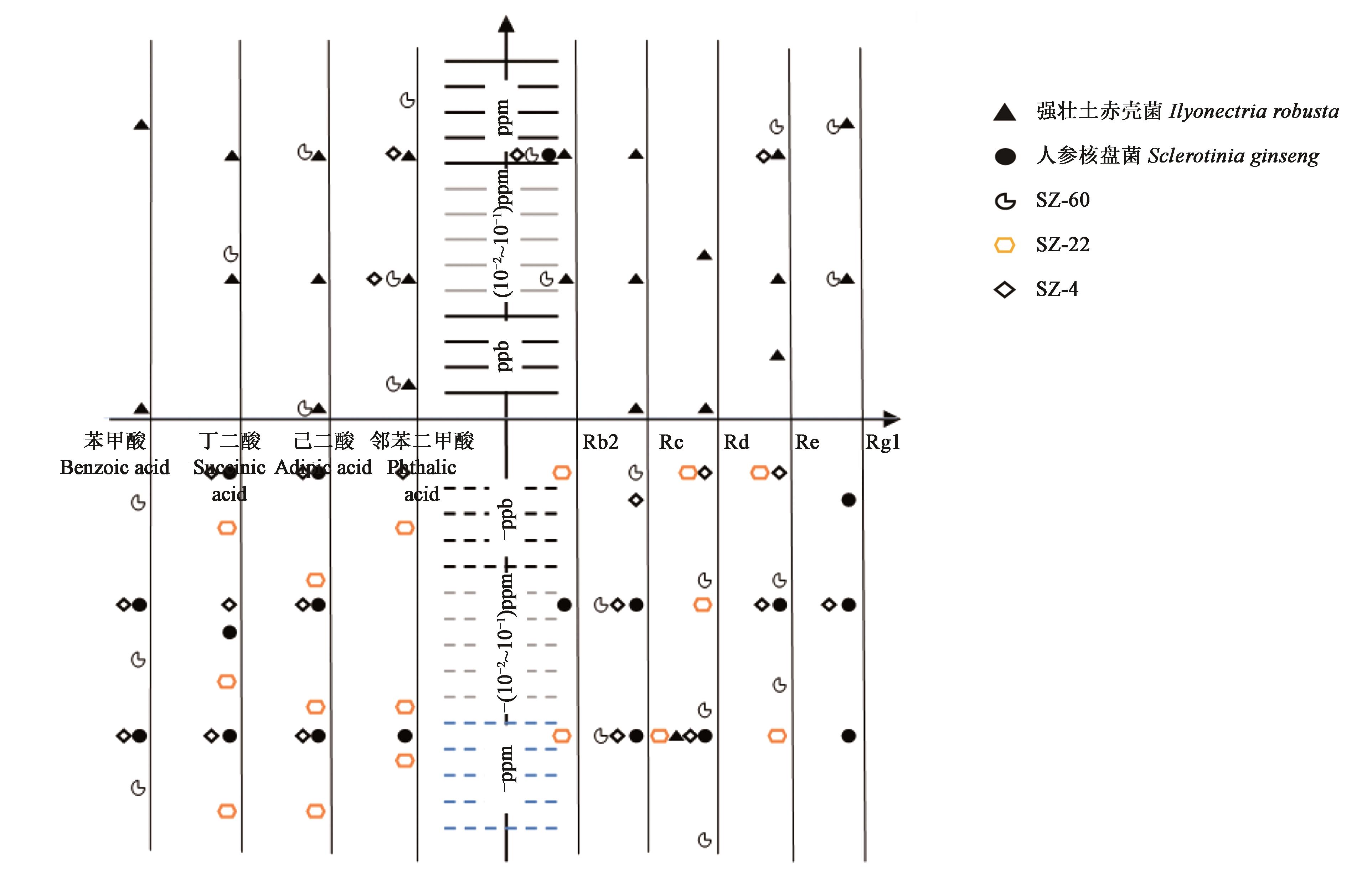
Fig. 3 Comparative analysis of the effects of organic acids and saponins on microorganismsNote:Positive value of ppb, (10-2~10-1) ppm, ppm represents inhibition, negative value represents promotion, ppb represents gradient 0.001 mg·L-1, (10-2~10-1)ppm represents gradient 0.010-0.100 mg·L-1, ppm represents gradient 1.000~5.000 mg·L-1, each large scale is divided into 5 small scales, each represents the action intensity 0~20%, 21%~40%, 41%~60%, 61%~80%, 81%~100%.

Fig. 4 Pairwise comparison results of Kruskal?Wallis testNote: Solid line indicates the difference is not significant, broken line indicates the difference is significant (P<0.05).
| 1 | 吴林坤, 林向民, 林文雄. 根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物互作关系研究进展与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. |
| WU L K, LIN X M, LIN W X. Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2014,38(3): 298-310. | |
| 2 | 艾超, 孙静文, 王秀斌, 等. 植物根际沉积与土壤微生物关系研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015,21(5): 1343-1351. |
| AI C, SUN J W, WANG X B, et al.. Advances in the study of the relationship between plant rhizodeposition and soil microorganism [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci.,2015, 21(5): 1343-1351. | |
| 3 | 张重义, 陈慧, 杨艳会, 等. 连作对地黄根际土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(11): 2843-2848. |
| ZHANG C Y, CHEN H, YANG Y H, et al.. Effects of continuous cropping on bacterial community diversity in rhizosphere soil of Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2010, 21(11): 2843-2848. | |
| 4 | BULGARELLI D, SCHLAEPPI K, SPAEPEN S,et al.. Structure and function of the bacterial microbiota of plants [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2013, 64 (1): 807-838. |
| 5 | 陈宏宇, 李晓鸣, 王敬国. 抗病性不同大豆品种根面及根际微生物区系的变化Ⅰ.非连作大豆(正茬)根面及根际微生物区系的变化[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005(6): 98-103. |
| CHEN H Y, LI X M, WANG J G. Change of microflora in the rhizoplane and rhizosphere of different disease resistance soybean cultivars Ⅰ. change of microflora in the rhizoplane and rhizosphere of soybean under normal rotation cropping condition [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2005(6): 98-103. | |
| 6 | FONS F, AMELLAL N, LEYVAL C, et al.. Effects of gypsophila saponins on bacterial growth kinetics and selection of subterranean clover rhizosphere bacteria [J]. Can. J. Microbiol., 2003, 49(6): 367-373. |
| 7 | 吴林坤, 黄伟民, 王娟英, 等. 不同连作年限野生地黄根际土壤微生物群落多样性分析[J]. 作物学报, 2015, 41(2): 308-317. |
| WU L K, HUANG W M, WANG J Y, et al.. Diversity analysis of rhizosphere microflora of Wild R. glutinosa grown in monocropping for different years [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2015, 41(2): 308-317. | |
| 8 | 孔垂华, 娄永根. 化学生态学前沿[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社,2010:1-63. |
| 9 | 孙浩, 黄璐明, 黄璐琦, 等. 基于生态位理论的药用植物化感作用与连作障碍的探讨[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2008, 33(17):2197-2200. |
| SUN H, HUANG L M, HUANG L Q, et al..Study on medicinal plant allelopathy and soil sickness based on ecological niche [J]. China J. Chin. Materia Medica, 2008, 33(17): 2197-2200. | |
| 10 | HÄTTENSCHWILER S, VITOUSEK P M. The role of polyphenols in terrestrial ecosystem nutrient cycling [J]. Trends Ecol. Evol., 2000, 15(6): 238-243. |
| 11 | INDERJIT, DAVID A W, RICHARD K, et al.. The ecosystem and evolutionary contexts of allelopathy [J]. Trends Ecol. Evol., 2011, 26(12): 655-662. |
| 12 | 陈爱国, 李明杰, 张宝, 等. 连作介导的药用植物及其根际微生态灾变机制研究展望[J]. 中国现代中药, 2016, 18(2): 239-245. |
| CHEN A G, LI M J, ZHANG B, et al.. Review on catastrophe mechanism of medicinal plant and its rhizosphere microecosystem mediated by consecutive monoculture [J]. Mod. Chin. Med., 2016, 18(2): 239-245. | |
| 13 | 杨利民. 中药材生态种植理论与技术前沿[J].吉林农业大学学报, 2020, 42(4): 355-363. |
| YANG L M. Theory and technology frontiers of ecological planting of chinese medicinal materials [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2020, 42(4): 355-363. | |
| 14 | 雷锋杰, 张爱华, 张秋菊, 等. 人参、西洋参化感作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志, 2010, 35(17): 2221-2226. |
| LEI F J, ZHANG A H, ZHANG Q J, et al.. Advances in allelopathy of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium [J]. China J. Chin. Materia Medica, 2010,35(17): 2221-2226. | |
| 15 | 孙卓. 人参病害生防细菌的筛选及其防病作用研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2014. |
| SUN Z. Screening of biocontrol bacteria against ginseng diseases [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 16 | 杨莉, 任晶, 韩梅, 等. 人参根系分泌物中酸性物质的化感活性与互作效应[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2017, 39(5): 570-574 . |
| YANG L, REN J, HAN M, et al.. Allelopathy and interaction of acidic materials in ginseng root exudates [J]. J. Jilin Agric.Univ., 2017, 39(5): 570-574. | |
| 17 | 任晶. 人参根际有机酸的化感活性及环境行为研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学, 2016. |
| REN J. Allelopathic activity and environmental behavior of organic acids in ginseng rhizosphere [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 18 | LATIF S, GENEVIÈVE C, WESTON L A. Allelopathy and the role of allelochemicals in plant defence [J]. Adv. Botanical Res., 2017, 82:19-54. |
| 19 | LIU J, LI X, JIA Z, et al.. Effect of benzoic acid on soil microbial communities associated with soilborne peanut diseases [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2016, 110 (Complete):34-42. |
| 20 | 周柳婷, 罗扬, 李建鹃, 等. 酚酸介导下连栽木麻黄根际微生物变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(4): 1021-1028. |
| ZHOU L T, LUO Y, LI J J, et al.. The variation of rhizosphere microorganisms of replanted Casuarina equisetifolia plantations mediated by phenolic acids [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2021,40(4): 1021-1028. | |
| 21 | 孙香荣, 李娟, 钮颜宇, 等. 基于膜技术的地黄根区土壤化感物质分离效果研究[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2021,55(1): 35-43. |
| SUN X R, LI J, NIU Y Y, et al.. Study on the separation effect of soil allelochemicals in Rehmannia glutinosa root zone based on membrane technology [J]. J. Henan Agric.Univ., 2021, 55(1): 35-43. | |
| 22 | 刘芳君. 无土栽培人参根系分泌物的化感作用研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2014. |
| LIU F J. Allelopathy of root exudates from soilless cultivated Ginseng [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 23 | 吴红淼, 林文雄. 药用植物连作障碍研究评述和发展透视[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(6): 775-793. |
| WU H M, LIN W X.A commentary and development perspective on the consecutive monoculture problems of medicinal plants [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2020, 28(6): 775-793. | |
| 24 | 李浩成, 左应梅, 杨绍兵, 等. 三七根系分泌物在连作障碍中的生态效应及缓解方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 159-167. |
| LI H C, ZUO Y M, YANG S B, et al.. Ecological effect of root exudates of panax notoginseng on continuous cropping obstacles and its alleviating methods [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020, 22(8): 159-167. | |
| 25 | 付佳, 王洋, 阎秀峰. 萜类化合物的生理生态功能及经济价值[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2003, 31(6):59-62. |
| FU J, WANG Y, YAN X F. The eco-physiological function and economic value of terpenoids [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2003, 31(6): 59-62. | |
| 26 | 王朋, 王莹, 孔垂华. 植物挥发性单萜经土壤载体的化感作用——以三裂叶豚草(Ambrosia trifida L.)为例[J]. 生态学报, 2008(1): 62-68. |
| WANG P, WANG Y, KONG C H. Allelopathy of plant volatile monoterpenes mediated by soil: a case study of Ambrosia trifida L. [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2008(1): 62-68. | |
| 27 | 张一鸣. 人参根际土壤提取物对人参病原菌和拮抗菌的影响研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2014. |
| ZHANG Y M. Effect of ginseng rhizosphere soil extracts on pathogenic fungi and their antagonistic microorganisms [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 28 | 张爱华, 匙坤, 许永华, 等. 立枯丝核菌和菌核菌对人参总皂苷化学趋向性的响应[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(5): 200-204. |
| ZHANG A H, CHI K, XU Y H, et al.. Chemotaxis response of Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotinia schinsengto total ginsenosides [J]. J. Northwest Sci-Tech Univ. Agric. For.(Nat. Sci.), 2016, 44(5): 200-204. | |
| 29 | ZANARDO D, LIMA R B, FERRARESE M, et al.. Soybean root growth inhibition and lignification induced by p-coumaric acid [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2009, 66(1): 25-30. |
| 30 | 向维. 三七根系分泌物的自毒作用及自毒物质研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2016. |
| XIANG W. Autotoxicity in Panax Notoginseng of root exudates [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2016. | |
| 31 | 李培栋,王兴祥,李奕林,等.连作花生土壤中酚酸类物质的检测及其对花生的化感作用[J].生态学报,2010,30(8):2128-2134. |
| LI P D, WANG X X, LI Y L, et al.. The contents of phenolic acids in continuous cropping peanut and their allelopathy [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010,30(8):2128-2134. | |
| 32 | 阎凤鸣. 化学生态学[M].北京: 科学出版社, 2003:1-438. |
| 33 | 杨靖春, 李治平, 酒井斐子. 人参根系分泌物及其对人参根际微生物作用的研究[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版),1982(1): 71-77. |
| YANG J C, LI Z P, FEIZI S K. Studies on Ginseng root exudates and their effects on microorganisms in Ginseng rhizosphere [J]. J. Northeast Normal Univ.(Nat. Sci.), 1982(1): 71-77. | |
| 34 | 赵雪淞, 刘民, 马丹丹, 等. 皂苷与植物病原真菌相互关系研究进展[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2011, 27(3): 404-409. |
| ZHAO X S, LIU M, MA D D, et al.. Research advances in interactions between Saponins and Phytopathogenic Fungi [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Control,2011, 27(3): 404-409. |
| [1] | Jiahuan HUO, Xiaolei WEN, Shuangmin LI, Lina FENG, Shuhui LAN, Lixin DONG, Sirou GUO, Jianing LI, Jianhua WANG, Huixia QI. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Root Rot of Atractylodes chinensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 137-144. |
| [2] | ZHANG Nana§, LI Shuangmin§, WEN Xiaolei, FENG Lina, WANG Junfeng, YANG Wenjie, HUO Jiahuan, LAN Shuhui, SUN Weiming, QI Huixia. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Pink Disease of Chestnut [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 145-152. |
| [3] | ZHANG Zhuoran§, YANG Liu§, WANG Dongqi, JING Yuling, WANG Wei, GUO Rongjun, XIAO Nengwu, XIANG Shibiao, LI Shidong. Symptom Types and Casual Pathogens of Amorphaphallus konjac Rot Disease in Several Fields Located in Shiyan City [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(12): 116-124. |
| [4] | LI Haocheng1,2, ZUO Yingmei2, YANG Shaobing2, YANG Tianmei2, LI Jichao2, YANG Weize2, ZHANG Jinyu2*. Ecological Effect of Root Exudates of Panax notoginseng on Continuous Cropping Obstacles and its Alleviating Methods [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(8): 159-167. |
| [5] | LIU Mengli1, LI Jin2, ZHANG Jungao2, ZHOU Xiaoyun2, DU Pengcheng1, GUO Qingyuan1*, LEI Bin2*. Differences of Toxin Activities Among Different Pathogenic Strains of Fusarium verticillioides [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 99-105. |
| [6] | CHENG Liang1,2. Identification and Characterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and P. atrosepticum of Potato Pathogenic Bacteria in Northwest China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 106-116. |
| [7] | WEN Xiaolei1,2, QI Huixia1*, SUN Weiming1, LIU Yijian1, FENG Lina1, MENG Tongyao2, HAN Zhiling1, CAO Jia1, WANG Junfeng1. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen (Fusarium equiseti) Causing Shoot Blight of Atractylodes chinensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(5): 115-121. |
| [8] | LI Qingkai1,2,3, LIU Ping2,3*, ZHAO Haijun3, SONG Xiaozong2, LIN Haitao2, SHEN Yuwen2, LI Lin1, WAN Shubo1,3*. Effects of Maize Root Exudates on Allelopathy of Phenolic Acids in Soil of Continuous Cropping Peanut [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(3): 119-130. |
| [9] | WANG Nan1, LI Gangqiang1, LI Yunlong2, LI Yongbin2, ZHANG Haowei2, WANG Minyang2, WANG Liying2, LIU Dehu1, CHEN Sanfeng2*. Isolation and Identification of Nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus spp. and Determination of Their Plant-growth Oromoting and Plant Pathogen-inhibiting Activities [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(5): 95-103. |
| [10] | HONG Gengde1, JIANG Zhenjie2, CHEN Sixu1, ZHAN Liqiang2, CAI Zhicheng2, LIN Ziqi3, CAI Mingsheng4*, LI Meili4*. Effect of D-limonene Nanoemulsion Against Foodborne Pathogens in Raw Beef [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(5): 121-128. |
| [11] | LIU Huiying1,2, QIAO Yu1, SHI Bo1, PENG Qing1*. Study on the Bacteriostasis of ZnO Micro/Nano-particles with Different Morphologies on Foodborne Pathogens [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(5): 140-147. |
| [12] | WANG Yongjie, CHEN Honglian, CHENG Yunsheng, WANG Fen. Isolation, Identification and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of Gold Carp Visceral Sarcoidosis of Pathogen [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(12): 104-109. |
| [13] | HUANG Ze-ying, WANG Ji-min*. Economic Impact of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza on Broiler Industry in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(1): 189-199. |
| [14] | LI Yang, LI Qiang*, ZHANG Xian\|yu. Research Progress on Vibrio harveyi and its Main Pathogenic Factors [J]. , 2014, 16(4): 159-166. |
| [15] | CHENG Liang1,2, GUO Qing\|yun1,2*. Potential Research of Fusarium avenaceum Isolate GD\|2 as a Bioherbicide Agent for Wild Oats(Avena fatua L.) [J]. , 2014, 16(3): 70-80. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号