




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 224-233.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0821
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
岳伶俐1( ), 陈永忠2, 夏雄1, 刘栋1, 王湘南2, 吴友杰1(
), 陈永忠2, 夏雄1, 刘栋1, 王湘南2, 吴友杰1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-19
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-13
通讯作者:
吴友杰
作者简介:岳伶俐 E-mail: YueLingli0609@163.com;
基金资助:
Lingli YUE1( ), Yongzhong CHEN2, Xiong XIA1, Dong LIU1, Xiangnan WANG2, Youjie WU1(
), Yongzhong CHEN2, Xiong XIA1, Dong LIU1, Xiangnan WANG2, Youjie WU1( )
)
Received:2021-09-19
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Youjie WU
摘要:
为深入探究南方丘陵区油茶林地降雨同位素变化规律,揭示该森林系统水循环对水汽来源和气候的响应机理,利用向后轨迹模型(hybrid single particle lagrangian intergrated trajectory,HYSPLIT)对油茶林地不同水汽轨迹进行聚类分析,采用偏相关分析综合评估降雨同位素组成的主要影响因素。结果表明,林地降雨季风期(5—9月)水汽来源主要是印度洋(14%)和西太平洋(37%)输送的暖湿气团,非季风期水汽来源中75%以上来自局部蒸发水汽和南下冷空气;同位素组成表现出季风期贫乏,非季风期富集,呈现出“V”形的季节性变化规律。2019年林地降水线δD=8.3δ18O+13.5(R2=0.99),反映了林地的较低蒸发水平和湿润气候条件,林地降雨同位素存在显著的降雨量效应、风速效应和湿度效应,降雨量效应远远大于温度效应,湿度效应对于温度的变化十分敏感。以上结果为长沙油茶林地的水循环机理研究提供了理论参考,有利于指导地区水资源科学调控,促进林业生态发展。
中图分类号:
岳伶俐, 陈永忠, 夏雄, 刘栋, 王湘南, 吴友杰. 南方丘陵区降雨同位素组成及影响因素的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 224-233.
Lingli YUE, Yongzhong CHEN, Xiong XIA, Dong LIU, Xiangnan WANG, Youjie WU. Study on Isotopic Composition and Influencing Factors of Rainfall in Southern Hilly Region[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 224-233.
| 月份Month | δD/‰ | δ18O/‰ | d-excess/‰ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 最大值Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | |
| 4 | -0.52 | -119.07 | -42.60±25.55 b | -1.76 | -16.65 | -7.06±5.72 b | 14.26 | 13.40 | 13.85±0.36 b |
| 5 | -74.20 | -150.12 | -110.49±23.66 a | -10.42 | -19.97 | -14.85±2.96 a | 9.60 | 6.01 | 8.28±1.15 a |
| 6 | -114.90 | -121.20 | -118.05±3.15 a | -15.42 | -15.90 | -15.66±0.24 a | 8.50 | 6.03 | 7.27±1.23 a |
| 7 | -56.86 | -136.83 | -102.31±26.23 a | -8.21 | -17.96 | -13.86±3.27 a | 9.90 | 6.86 | 8.53±1.00 a |
| 8 | 98.30 | -110.28 | -102.41±5.57 a | -13.10 | -14.93 | -13.76±0.83 a | 9.19 | 6.49 | 7.69±1.12 a |
| 10 | 12.55 | -51.05 | -16.33±23.18 b | 0.03 | -8.04 | -3.66±2.93 b | 14.37 | 12.00 | 12.93±0.83 b |
表1 各月降雨同位素的分布情况
Table 1 Distribution of precipitation isotopes in each month
| 月份Month | δD/‰ | δ18O/‰ | d-excess/‰ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 最大值Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | |
| 4 | -0.52 | -119.07 | -42.60±25.55 b | -1.76 | -16.65 | -7.06±5.72 b | 14.26 | 13.40 | 13.85±0.36 b |
| 5 | -74.20 | -150.12 | -110.49±23.66 a | -10.42 | -19.97 | -14.85±2.96 a | 9.60 | 6.01 | 8.28±1.15 a |
| 6 | -114.90 | -121.20 | -118.05±3.15 a | -15.42 | -15.90 | -15.66±0.24 a | 8.50 | 6.03 | 7.27±1.23 a |
| 7 | -56.86 | -136.83 | -102.31±26.23 a | -8.21 | -17.96 | -13.86±3.27 a | 9.90 | 6.86 | 8.53±1.00 a |
| 8 | 98.30 | -110.28 | -102.41±5.57 a | -13.10 | -14.93 | -13.76±0.83 a | 9.19 | 6.49 | 7.69±1.12 a |
| 10 | 12.55 | -51.05 | -16.33±23.18 b | 0.03 | -8.04 | -3.66±2.93 b | 14.37 | 12.00 | 12.93±0.83 b |
| 气象因子Meteorological factor | 与δD的相关关系 Correlation with δD | 与δD的偏相关关系(控制温度) Partial correlation with δD (Temperature control) | 与δD的偏相关关系(控制降雨量)Partial correlation with δD (Precipitation control) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | P | R | P | R | P | |
| 温度Temperature | -0.306 | 0.11 | -0.520 | 0.01 | ||
| 降雨量Precipitation | -0.622 | 0.00 | -0.711 | 0.00 | ||
| 平均风速Average wind velocity | -0.691 | 0.00 | -0.745 | 0.00 | -0.570 | 0.00 |
| 相对湿度Relative humidity | -0.496 | 0.01 | -0.546 | 0.00 | -0.312 | 0.11 |
表2 气候因子与δD相关性和偏相关性分析
Table 2 Analysis of correlation and partial correlation between climatic factors and δD
| 气象因子Meteorological factor | 与δD的相关关系 Correlation with δD | 与δD的偏相关关系(控制温度) Partial correlation with δD (Temperature control) | 与δD的偏相关关系(控制降雨量)Partial correlation with δD (Precipitation control) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | P | R | P | R | P | |
| 温度Temperature | -0.306 | 0.11 | -0.520 | 0.01 | ||
| 降雨量Precipitation | -0.622 | 0.00 | -0.711 | 0.00 | ||
| 平均风速Average wind velocity | -0.691 | 0.00 | -0.745 | 0.00 | -0.570 | 0.00 |
| 相对湿度Relative humidity | -0.496 | 0.01 | -0.546 | 0.00 | -0.312 | 0.11 |
日期 Date(m-d) | 高度 Height/m | 时间 Time | 历时 Last time/h | 水汽来源Moisture source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 高度 Height/m | 相对湿度 Relative humidity/% | 地理位置 Location | ||||
| 4-15 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 39°83′N | 86°78′E | 3 779 | 40.6 | 若羌县Ruoqiang county |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 26°47′N | 109°22′E | 517 | 34.1 | 锦屏县Jinping county | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 29°85′N | 72°26′E | 4 207 | 69.4 | Vehari, Punjab, Pakistan | |
| 5-13 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 26°84′N | 113°42′E | 0 | 72.7 | 茶陵县Chaling county |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 26°65′N | 81°33′E | 2 664 | 27.2 | Barabanki, Uttar Pradesh, India | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 19°11′N | 79°20′E | 6 268 | 6.5 | Adilabad, Telangana, India | |
| 6-22 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 32°15′N | 120°92′E | 3 403 | 39.5 | 南通市通州区 Tongzhou district, Nantong city |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°64′N | 118°50′E | 1 666 | 65.4 | 泾县Jing county | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°38′N | 86°18′E | 2 835 | 37.0 | 昂仁县Ngamring county | |
| 7-5 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 29°89′N | 119°72′E | 1 216 | 55.1 | 杭州市富阳区 Fuyang district, Hangzhou city |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°71′N | 114°48′E | 221 | 47.6 | 武汉市黄陂区 Huangpi district, Wuhan city | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 19°15′N | 113°23′E | 2 429 | 80.8 | 武汉市黄陂区 Huangpi district, Wuhan city | |
| 7-8 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 18°13′N | 97°21′E | 440 | 95.2 | Papun, Kayin, Myanmar |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 20°33′N | 96°72′E | 881 | 88.4 | Papun, Kayin, Myanmar | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 21°41′N | 97°92′E | 1 385 | 91.7 | Lai Hka, Shan, Myanmar | |
| 8-15 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 40°29′N | 113°98′E | 2 473 | 75.9 | 天镇县Tianzhen county |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 40°88′N | 113°47′E | 1 815 | 76.4 | 察哈尔右翼前旗Chahar right front banner | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 36°47′N | 110°86′E | 5 113 | 14.5 | 蒲县Pu county | |
| 9-8 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°50′N | 106°87′E | 2 836 | 95.8 | 广安市前锋区 Qianfeng district, Guang’an city |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 34°88′N | 103°49′E | 3 318 | 47.4 | 卓尼县Zhuoni county | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 36°19′N | 63°27′E | 6 908 | 4.2 | Mary, Turkmenistan | |
| 10-16 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 36°16′N | 129°13′E | 1 778 | 24.6 | Pohang, North Gyeongsang, South Korea |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 23°04′N | 97°51′E | 2 537 | 61.7 | Namtu, Shan, Myanmar | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 25°29′N | 82°92′E | 5 275 | 3.2 | Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India | |
表3 不同时期的水汽来源
Table 3 Water vapor sources in different periods
日期 Date(m-d) | 高度 Height/m | 时间 Time | 历时 Last time/h | 水汽来源Moisture source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 高度 Height/m | 相对湿度 Relative humidity/% | 地理位置 Location | ||||
| 4-15 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 39°83′N | 86°78′E | 3 779 | 40.6 | 若羌县Ruoqiang county |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 26°47′N | 109°22′E | 517 | 34.1 | 锦屏县Jinping county | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 29°85′N | 72°26′E | 4 207 | 69.4 | Vehari, Punjab, Pakistan | |
| 5-13 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 26°84′N | 113°42′E | 0 | 72.7 | 茶陵县Chaling county |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 26°65′N | 81°33′E | 2 664 | 27.2 | Barabanki, Uttar Pradesh, India | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 19°11′N | 79°20′E | 6 268 | 6.5 | Adilabad, Telangana, India | |
| 6-22 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 32°15′N | 120°92′E | 3 403 | 39.5 | 南通市通州区 Tongzhou district, Nantong city |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°64′N | 118°50′E | 1 666 | 65.4 | 泾县Jing county | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°38′N | 86°18′E | 2 835 | 37.0 | 昂仁县Ngamring county | |
| 7-5 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 29°89′N | 119°72′E | 1 216 | 55.1 | 杭州市富阳区 Fuyang district, Hangzhou city |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°71′N | 114°48′E | 221 | 47.6 | 武汉市黄陂区 Huangpi district, Wuhan city | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 19°15′N | 113°23′E | 2 429 | 80.8 | 武汉市黄陂区 Huangpi district, Wuhan city | |
| 7-8 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 18°13′N | 97°21′E | 440 | 95.2 | Papun, Kayin, Myanmar |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 20°33′N | 96°72′E | 881 | 88.4 | Papun, Kayin, Myanmar | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 21°41′N | 97°92′E | 1 385 | 91.7 | Lai Hka, Shan, Myanmar | |
| 8-15 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 40°29′N | 113°98′E | 2 473 | 75.9 | 天镇县Tianzhen county |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 40°88′N | 113°47′E | 1 815 | 76.4 | 察哈尔右翼前旗Chahar right front banner | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 36°47′N | 110°86′E | 5 113 | 14.5 | 蒲县Pu county | |
| 9-8 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 30°50′N | 106°87′E | 2 836 | 95.8 | 广安市前锋区 Qianfeng district, Guang’an city |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 34°88′N | 103°49′E | 3 318 | 47.4 | 卓尼县Zhuoni county | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 36°19′N | 63°27′E | 6 908 | 4.2 | Mary, Turkmenistan | |
| 10-16 | 1 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 36°16′N | 129°13′E | 1 778 | 24.6 | Pohang, North Gyeongsang, South Korea |
| 3 000 | 0:00 | 72 | 23°04′N | 97°51′E | 2 537 | 61.7 | Namtu, Shan, Myanmar | |
| 5 500 | 0:00 | 72 | 25°29′N | 82°92′E | 5 275 | 3.2 | Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India | |
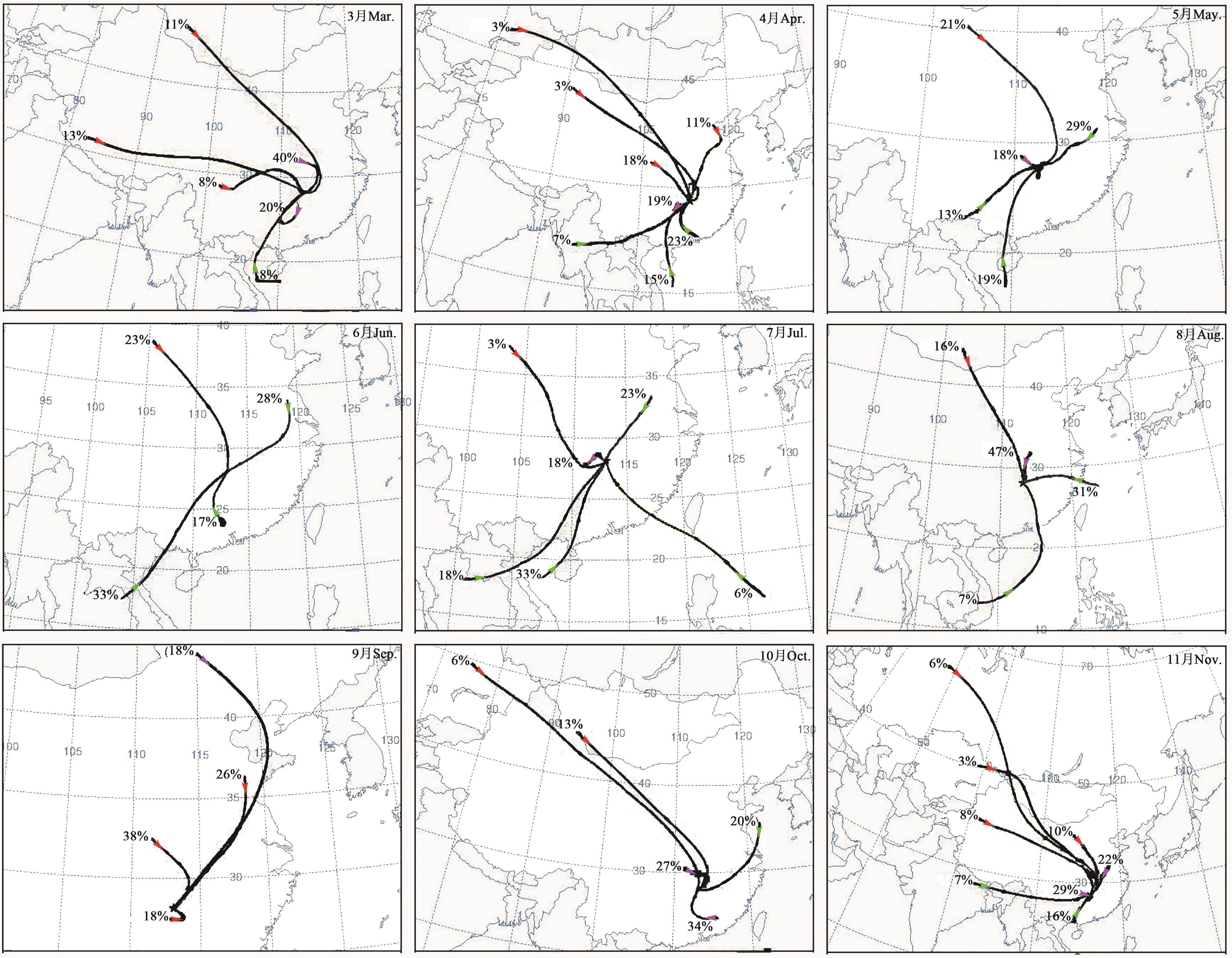
图4 不同时期水汽输送过程的追踪注:红色箭头为大陆性气团;紫色箭头为局部水汽;绿色箭头为海洋性气团。
Fig. 4 Tracking of water vapor transport process in different periodsNote: Red arrow indicates continental air; purple arrow indicates local water vapor; green arrow indicates maritime air.
| 1 | SUN C J, CHEN W, CHEN Y N, et al.. Stable isotopes of atmospheric precipitation and its environmental drivers in the Eastern Chinese Loess Plateau, China [J]. J. Hydrol., 2020, 581(C):1-40. |
| 2 | DANSGAARD W. Stable isotopes in precipitation [J]. Tellus, 1964, 16(4):436-468. |
| 3 | YU W S, YAO T D, TIAN L D, et al.. Relationships between δ18O in precipitation and air temperature and moisture origin on a south-north transect of the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Atmos. Res., 2008, 87(2):158-169. |
| 4 | 李维杰,王建力,王家录.西南地区不同地形降水稳定同位素特征及其水汽来源[J].长江流域资源与环境,2018,27(5):1132-1142. |
| LI W J, WANG J L, WANG J L. Characteristics of the stable isotopes in precipitation and the source of water vapor in different terrain in the southwest region [J]. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin., 2018, 27(5):1132-1142. | |
| 5 | 刘洁遥,张福平,冯起,等.西北地区降水稳定同位素的云下二次蒸发效应[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(5):1479-1488. |
| LIU J Y, ZHANG F P, FENG Q, et al.. Influence of below-cloud secondary evaporation on stable isotope composition in precipitation in northwest China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2018, 29(5):1479-1488. | |
| 6 | 李小飞,张明军,马潜,等.我国东北地区大气降水稳定同位素特征及其水汽来源[J].环境科学,2012,33(9):2924-2931. |
| LI X F, ZHANG M J, MA Q, et al.. Characteristics of stable isotopes in precipitation over northeast China and its water vapor sources [J]. Environ. Sci., 2012, 33(9):2924-2931. | |
| 7 | 柳鉴容,宋献方,袁国富,等.中国东部季风区大气降水δ18O的特征及水汽来源[J].科学通报,2009,54(22):3521-3531. |
| LIU J R, SONG X F, YUAN G F, et al.. Characteristics of δ18O in precipitation over eastern monsoon China and the water vapor sources [J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2009, 54(22):3521-3531. | |
| 8 | YANG N A, WANG G C. Moisture sources and climate evolution during the last 30 kyr in northeastern Tibetan Plateau:insights from groundwater isotopes (2H, 18O, 3H and 14C) and water vapour trajectories modeling [J]. Quat. Sci. Rev., 2020, 242:1-11. |
| 9 | ZHANG M J, WANG S J. A review of precipitation isotope studies in China: basic pattern and hydrological process [J]. J. Geogr. Sci., 2016, 26(7):921-938. |
| 10 | 张君,陈洪松,黄荣.桂西北喀斯特小流域降雨稳定氢氧同位素组成及影响因素[J].生态学报,2022,42(1):236-245. |
| ZHANG J, CHEN H S, HUANG R. Composition of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopic of precipitation and its influencing factors in karst area northwest Guangxi of China [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2022,42(1):236-245. | |
| 11 | 孔蒙.2016-2018年金华地区大气降水的水汽输送特征[D].金华:浙江师范大学,2019. |
| KONG M. Water vapor transport characteristics of atmospheric precipitation in Jinhua area form 2016 to 2018 [D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2019. | |
| 12 | 柳鉴容,宋献方,袁国富,等.我国南部夏季季风降水水汽来源的稳定同位素证据[J].自然资源学报,2007,22(6):1004-1012. |
| LIU J R, SONG X F, YUAN G F, et al.. Stable isotope evidence of vapor sources in summer monsoonal precipitation over southern China [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2007, 22(6):1004-1012. | |
| 13 | 邓三龙,陈永忠.中国油茶[M].长沙:湖南科学技术出版社,2019:1-372. |
| 14 | GUAN H D, ZHANG X P, SKRZYPEK G, et al.. Deuterium excess variations of rainfall events in a coastal area of South Australia and its relationship with synoptic weather systems and atmospheric moisture sources [J]. J. Geophysi. Res. Atmos., 2013, 118(2):1123-1138. |
| 15 | DRAXLER R R, HESS G D. An overview of the HYSPLIT-4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition [J]. Aust. Meteorol. Mag., 1998, 47(4):295-308. |
| 16 | 吴华武,章新平,关华德,等.不同水汽来源对湖南长沙地区降水中δD、δ18O的影响[J].自然资源学报,2012,27(8):1404-1414. |
| WU H W, ZHANG X P, GUAN H D, et al.. Influences of different moisture sources on δD and δ18O in precipitation in Changsha,Hunan province [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2012, 27(8):1404-1414. | |
| 17 | 吴华武,章新平,孙广禄,等.湖南长沙地区大气降水中稳定同位素特征变化[J].长江流域资源与环境,2012,21(5):540-546. |
| WU H W, ZHANG X P, SUN G L, et al.. Variations of stable isotopes characteristics of atmospheric precipitation from Changsha, Hunan [J]. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin, 2012, 21(5):540-546. | |
| 18 | 王涛.中国东部季风区域降水稳定同位素的时空分布特征及其气候意义[D].南京:南京信息工程大学,2012. |
| WANG T. The stable isotopes temporal-spatial distribution of modern prec ipitation over east monsoon China and its implication for climate [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2012. | |
| 19 | 陶泽,司炳成,靳静静.矮化枣树冠层改变降雨截留历时过程同位素和化学特征[J].水土保持学报,2017, 31(5):189-195. |
| TAO Z, SI B C, JIN J J. Canopy interception modified intra-rainfall isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of dwarfed jujube tree [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 31(5):189-195. | |
| 20 | HASEGAWA H, AKATA N, KAWABATA H, et al.. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope ratios in precipitation collected in a snowfall region, Aomori prefecture, Japan [J]. Geochem. J., 2014, 48(1):9-18. |
| 21 | WU X, ZHU X Y, PAN M C, et al.. Seasonal variability of oxygen and hydrogen stable isotopes in precipitation and cave drip water at Guilin, southwest China [J]. Environ. Earth Sci., 2014, 72(8):3183-3191. |
| 22 | WU H W, LI X Y, ZHANG J M, et al.. Stable isotopes of atmospheric water vapour and precipitation in the northeast Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau [J]. Hydrol. Processes, 2019, 33(23):2997-3009. |
| 23 | THOMAS E K, HOLLISTER K V, CLUETT A A, et al.. Reconstructing arctic precipitation seasonality using aquatic leaf wax δ2H in lakes with contrasting residence times [J/OL]. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol., 2020, 35(7):3886 [2021-07-20]. . |
| 24 | 马菁,宋维峰,吴锦奎,等.元阳梯田水源区林地降水与土壤水同位素特征[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(2):243-248, 254. |
| MA J, SONG W F, WU J K, et al.. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of precipitation and soil water in woodland in water source area of Yuanyang terrace [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2016, 30(2):243-248, 254. | |
| 25 | 常昕,章新平,戴军杰,等.不同时间尺度氢氧稳定同位素效应的比较——以长沙降水为例[J].第四纪研究,2021,41(1):99-110. |
| CHANG X, ZHANG X P, DAI J J, et al..Comparison of stable isotope effects under different time scales: taking Changsha as an example [J]. Quat. Sci., 2021, 41(1):99-110. | |
| 26 | 柳鉴容,宋献方,袁国富,等.西北地区大气降水δ18O的特征及水汽来源[J].地理学报,2008,63(1):12-22. |
| LIU J R, SONG X F, YUAN G F, et al.. Character istics of δ18O in precipitation over northwest China and its water vapor sources [J]. Acta Geogr. Sin., 2008, 63(1):12-22. | |
| 27 | 王婷,高德强,徐庆,等.三峡库区秭归段大气降水δD和δ18O特征及水汽来源[J].林业科学研究,2020,33(6):88-95. |
| WANG T, GAO D Q, XU Q, et al.. Characteristics of δD and δ18O in precipitation and water vapor sources in Zigui section of the Three Gorges Reservoir [J]. For. Res., 2020, 33(6):88-95. | |
| 28 | 郑淑蕙,侯发高,倪葆龄.我国大气降水的氢氧稳定同位素研究[J].科学通报,1983(13):801-806. |
| ZHENG S H, HOU F G, NI B L. Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes of precipitation in China [J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 1983(13):801-806. | |
| 29 | 陈婕,高德强,徐庆,等.西鄂尔多斯荒漠夏季大气降水氢氧同位素特征与水汽来源[J].林业科学研究,2016(6):118-125. |
| CHEN J, GAO D Q, XU Q, et al.. Characteristics of δD and δ18O in summer precipitation in the west Ordos desert and its water vapor sources [J]. For. Res., 2016(6):118-125. | |
| 30 | TIAN L D, YU W S, SCHUSTER F P, et al.. Control of seasonal water vapor isotope variations at Lhasa, southern Tibetan Plateau [J]. J. Hydro., 2020, 580(8):124-237. |
| 31 | WU Y J, DU T S, DING R S, et al.. An isotope method to quantify soil evaporation and evaluate water vapor movement under plastic film mulch [J]. Agric. Water Manag., 2017, 184:59-66. |
| [1] | 王洪博, 赵栗, 高阳, 王兴鹏, 曹辉, . 南疆无膜滴灌棉田灌溉模式及耗水规律研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 153-160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号