




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 179-188.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0831
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
徐海蓉1( ), 王林1, 吴聪敏1, 俞元春1(
), 王林1, 吴聪敏1, 俞元春1( ), 戴成2
), 戴成2
收稿日期:2021-09-24
接受日期:2022-03-27
出版日期:2022-10-15
发布日期:2022-10-25
通讯作者:
俞元春
作者简介:徐海蓉 E-mail:xu17372596205@163.com;
基金资助:
Hairong XU1( ), Lin WANG1, Congmin WU1, Yuanchun YU1(
), Lin WANG1, Congmin WU1, Yuanchun YU1( ), Cheng DAI2
), Cheng DAI2
Received:2021-09-24
Accepted:2022-03-27
Online:2022-10-15
Published:2022-10-25
Contact:
Yuanchun YU
摘要:
为探讨张家港地区适合青椒种植的沼液施用水平和方式,分别设置浇施或喷施54(T1)、84(T2)、114(T3)、144(T4)、204 m3·hm-2(T5) 5个沼液施用量,分析青椒产量和品质、土壤pH、有机质和氮磷钾含量等以确定最佳的沼液施用方式和施用量。结果表明,沼液的适量施用可以有效提高青椒的产量和品质,且浇施效果明显好于喷施。浇施114 m3·hm-2可以充分发挥沼液肥效,相比未施沼液的CK1,青椒产量增加97.74%,Vc和蛋白质含量分别增加32.77%和83.82%,且硝酸盐含量符合我国蔬菜硝酸盐污染程度一级标准。施用沼液显著提高0—20 cm土层的有机质、全氮、有效磷和速效钾含量,但有可能加深土壤盐碱化程度。综上所述,沼肥可以代替传统化肥用于青椒的种植生产,采用114 m3·hm-2的施肥量对青椒种植地进行浇施最利于青椒的生长。研究结果为促进当地沼液利用,解决沼液排放带来的环境污染问题提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
徐海蓉, 王林, 吴聪敏, 俞元春, 戴成. 沼液施用对青椒生长和土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 179-188.
Hairong XU, Lin WANG, Congmin WU, Yuanchun YU, Cheng DAI. Effects of Biogas Slurry Application on Green Pepper Growth and Soil Properties[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(10): 179-188.
处理 Treatment | 基肥施用量 Amount of base fertilizer/ (m3·hm-2) | 追肥施用量 Amount of top-dressing fertilizer/(m3·hm-2) | 施肥总量 Total fertilization/(m3·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CK2 | 24 | 0 | 24 |
| T1 | 24 | 10 | 54 |
| T2 | 24 | 20 | 84 |
| T3 | 24 | 30 | 114 |
| T4 | 24 | 40 | 144 |
| T5 | 24 | 60 | 204 |
表1 沼液施用量
Table 1 Application amount of biogas slurry
处理 Treatment | 基肥施用量 Amount of base fertilizer/ (m3·hm-2) | 追肥施用量 Amount of top-dressing fertilizer/(m3·hm-2) | 施肥总量 Total fertilization/(m3·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CK2 | 24 | 0 | 24 |
| T1 | 24 | 10 | 54 |
| T2 | 24 | 20 | 84 |
| T3 | 24 | 30 | 114 |
| T4 | 24 | 40 | 144 |
| T5 | 24 | 60 | 204 |
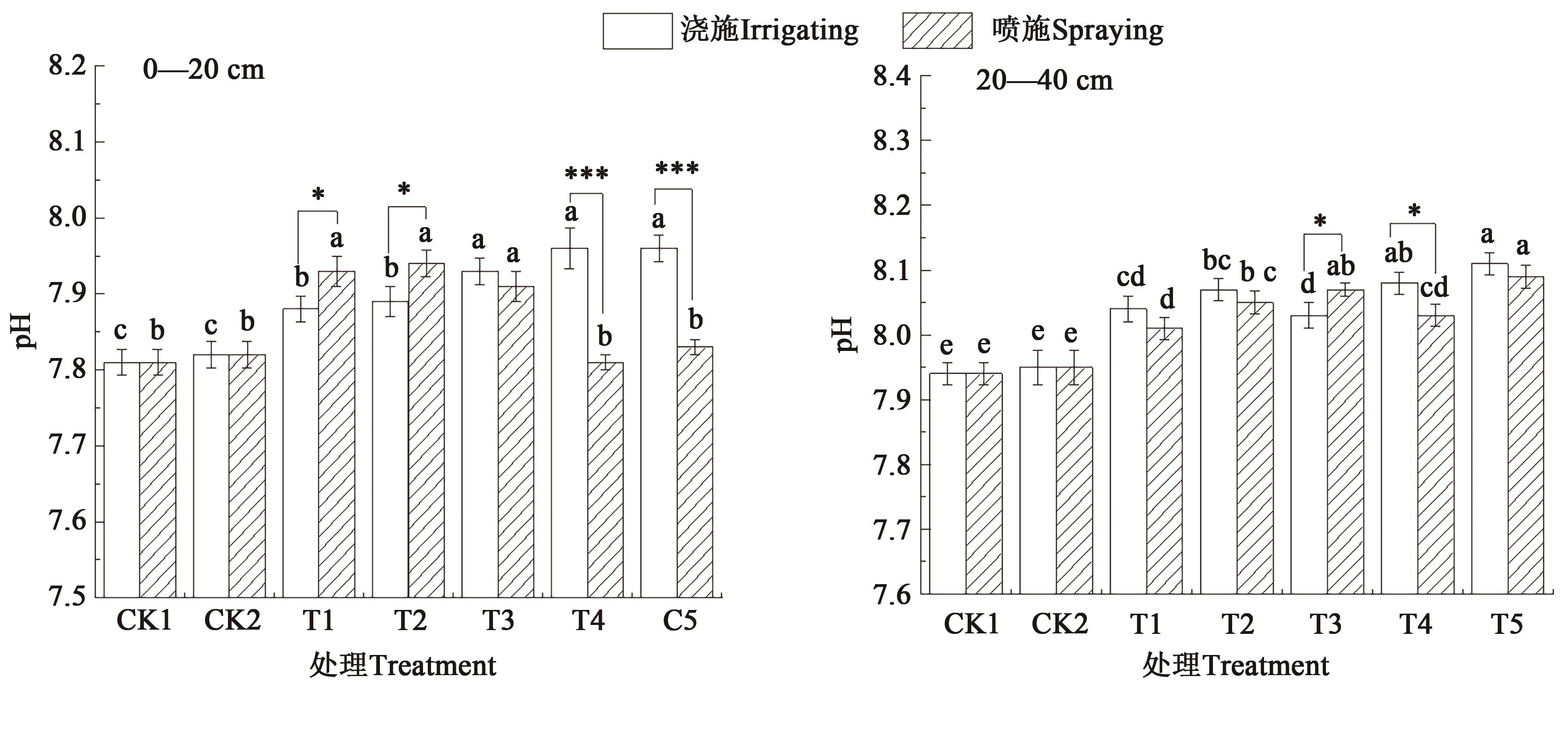
图1 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒种植土壤的pH注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;*和***分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式间差异在P<0.05和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 1 pH of the soil for planting green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; * and *** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.05 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
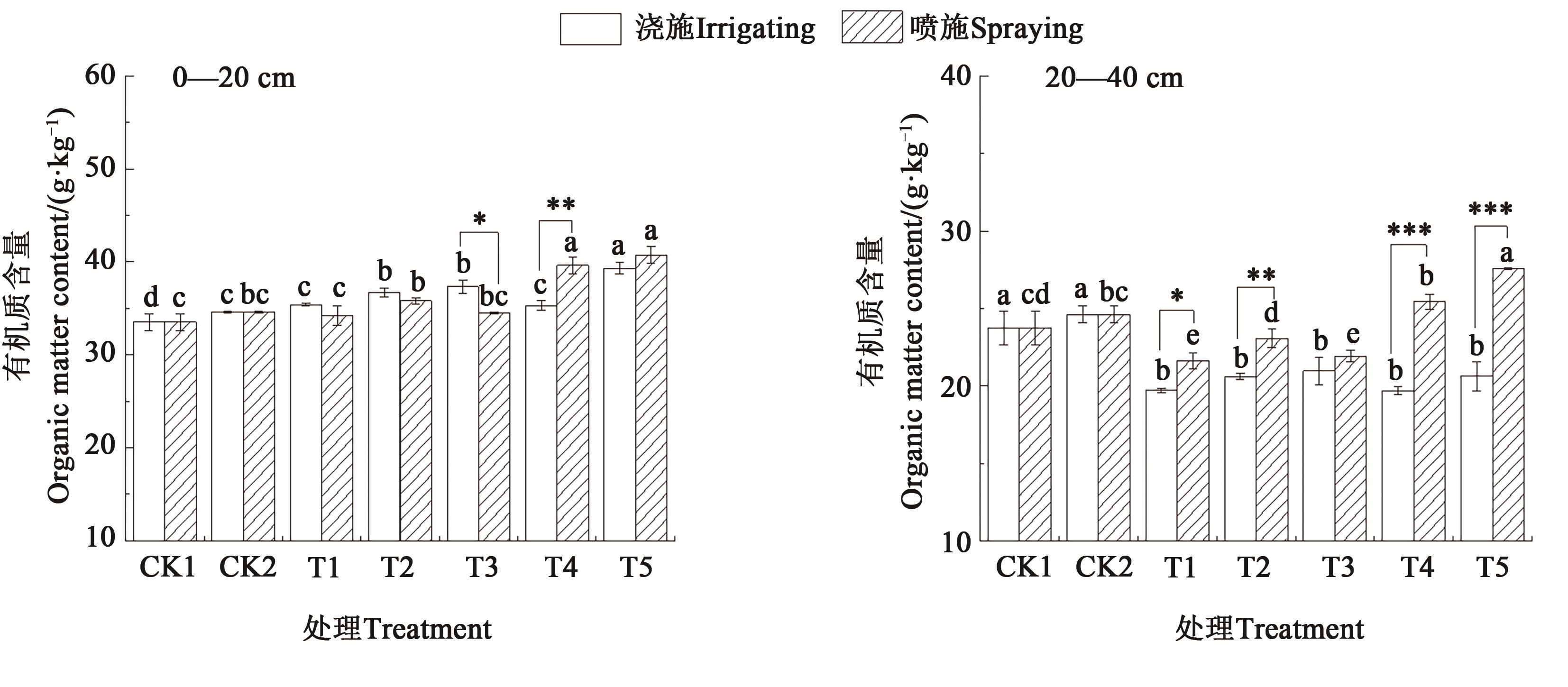
图2 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒种植土壤的有机质含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;*、**和***分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式间差异在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 2 Organic matter content of the soil for planting green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; *,** and *** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
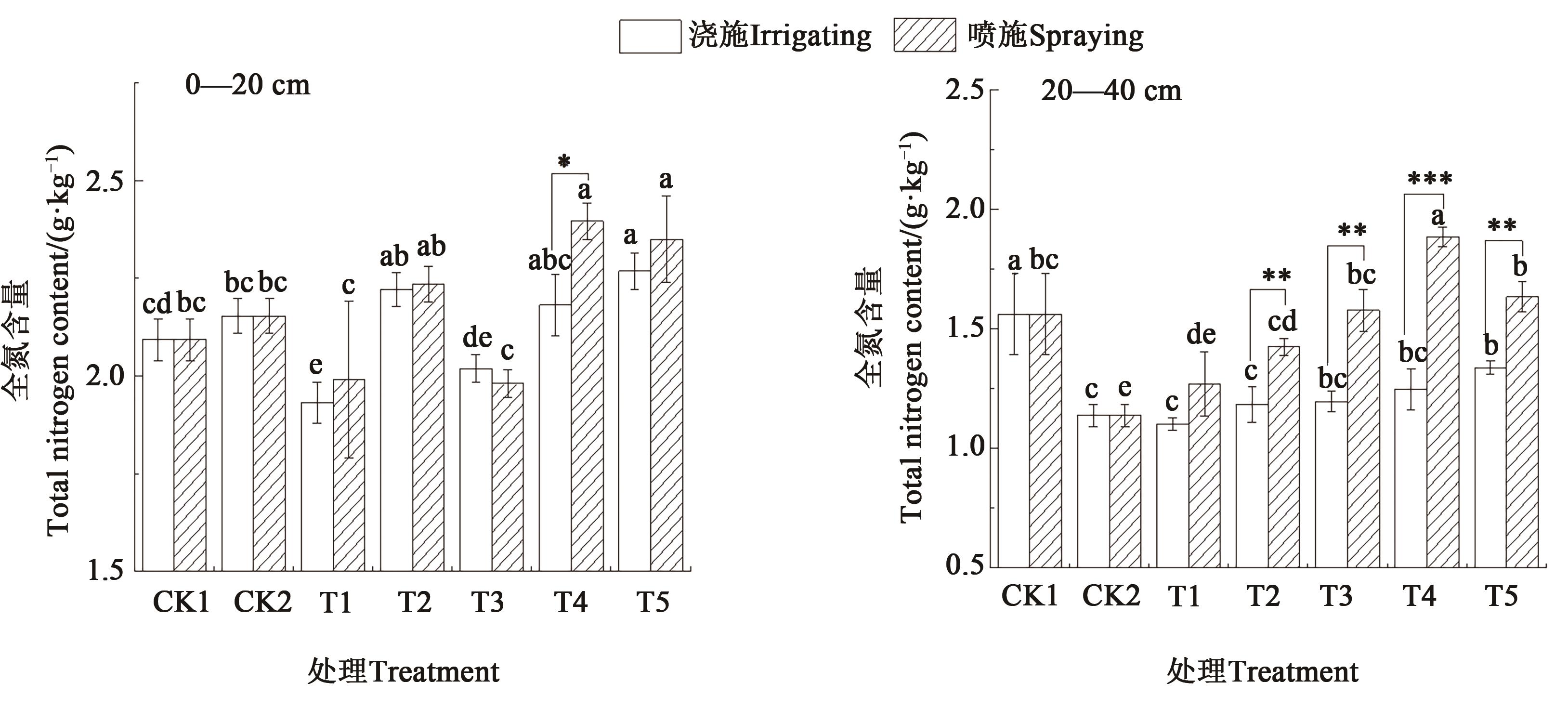
图3 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒种植土壤的全氮含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;*、**和***分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式间差异在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 3 Total nitrogen content of the soil for planting green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; *,** and *** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
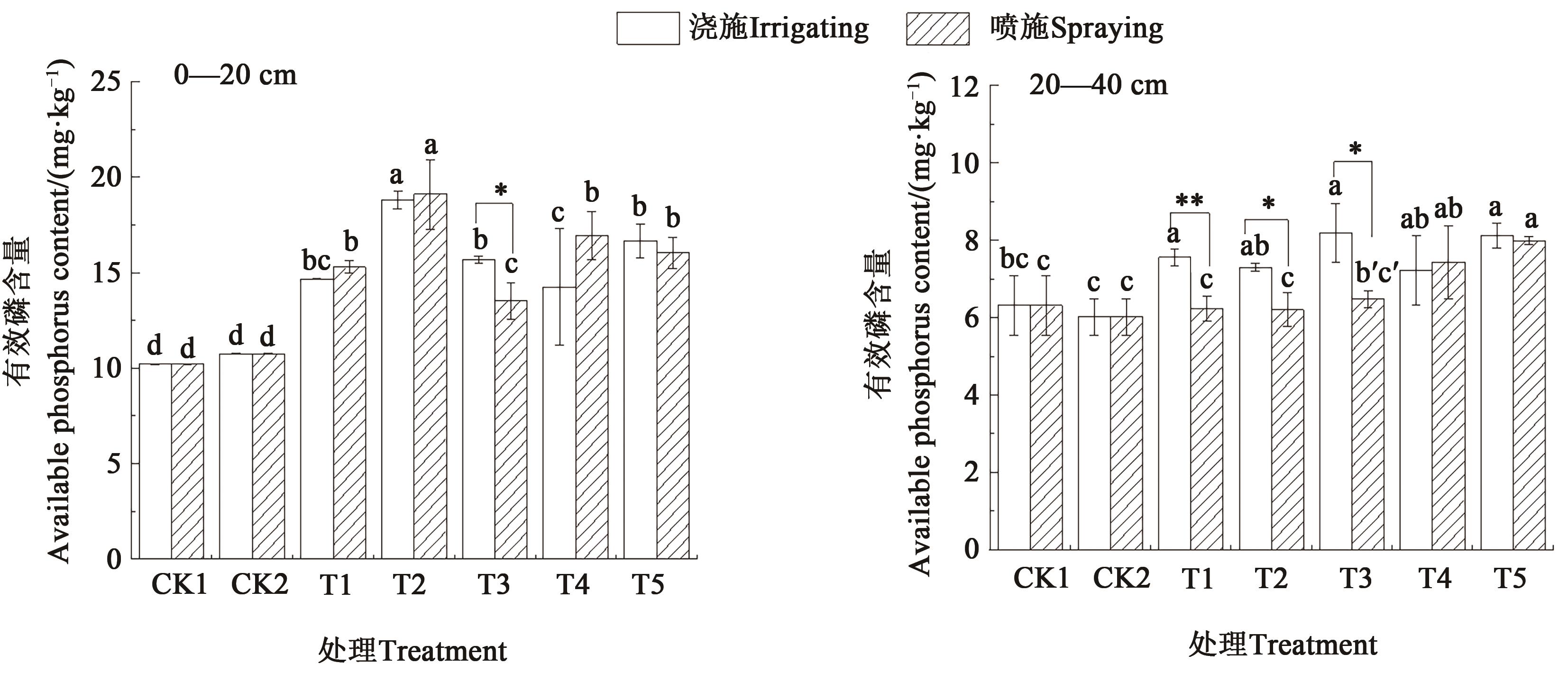
图4 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒种植土壤的有效磷含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;*和**分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式间差异在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 4 Aavailable phosphorus content of the soil for planting green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; * and ** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
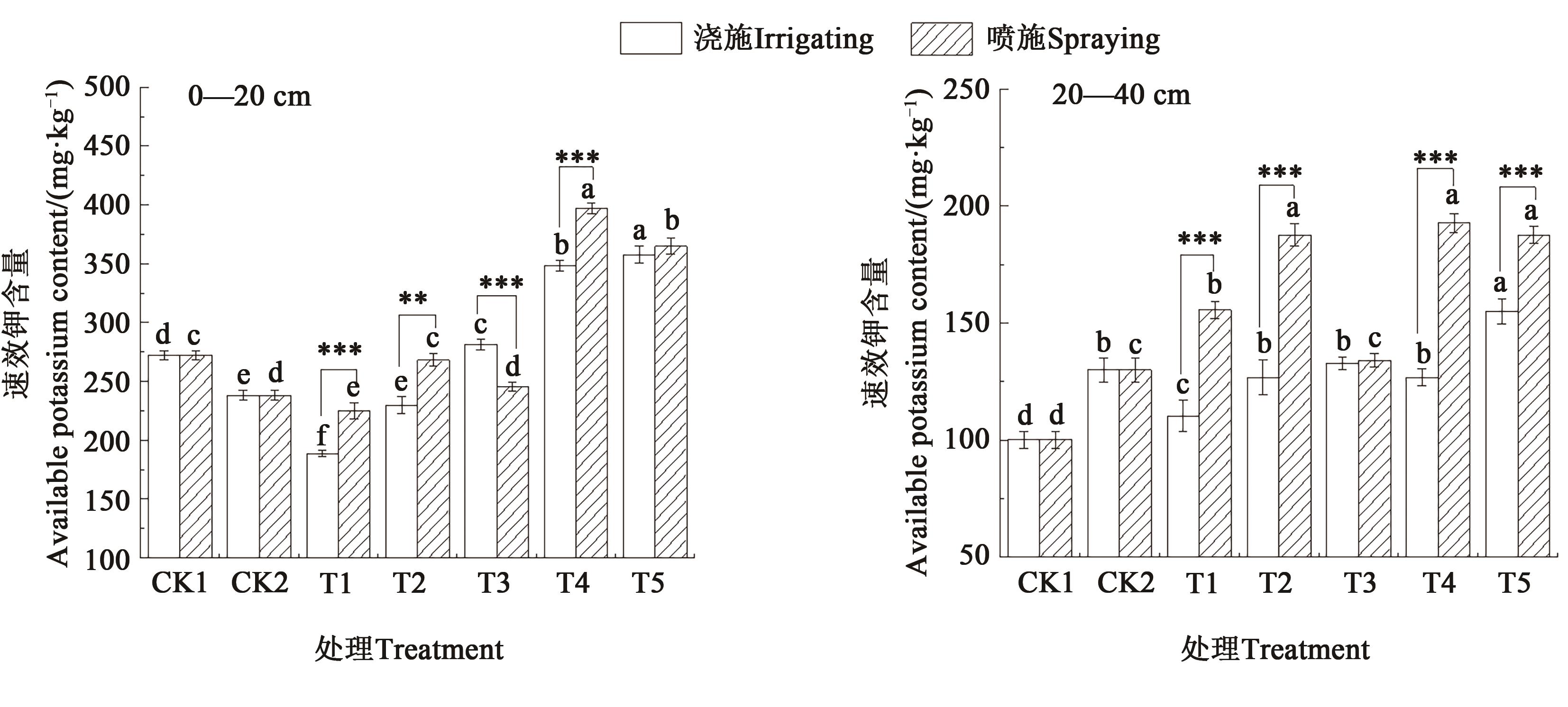
图5 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒种植土壤的速效钾含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;**和***分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式间差异在P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 5 Available potassium content of the soil for planting green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; ** and *** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
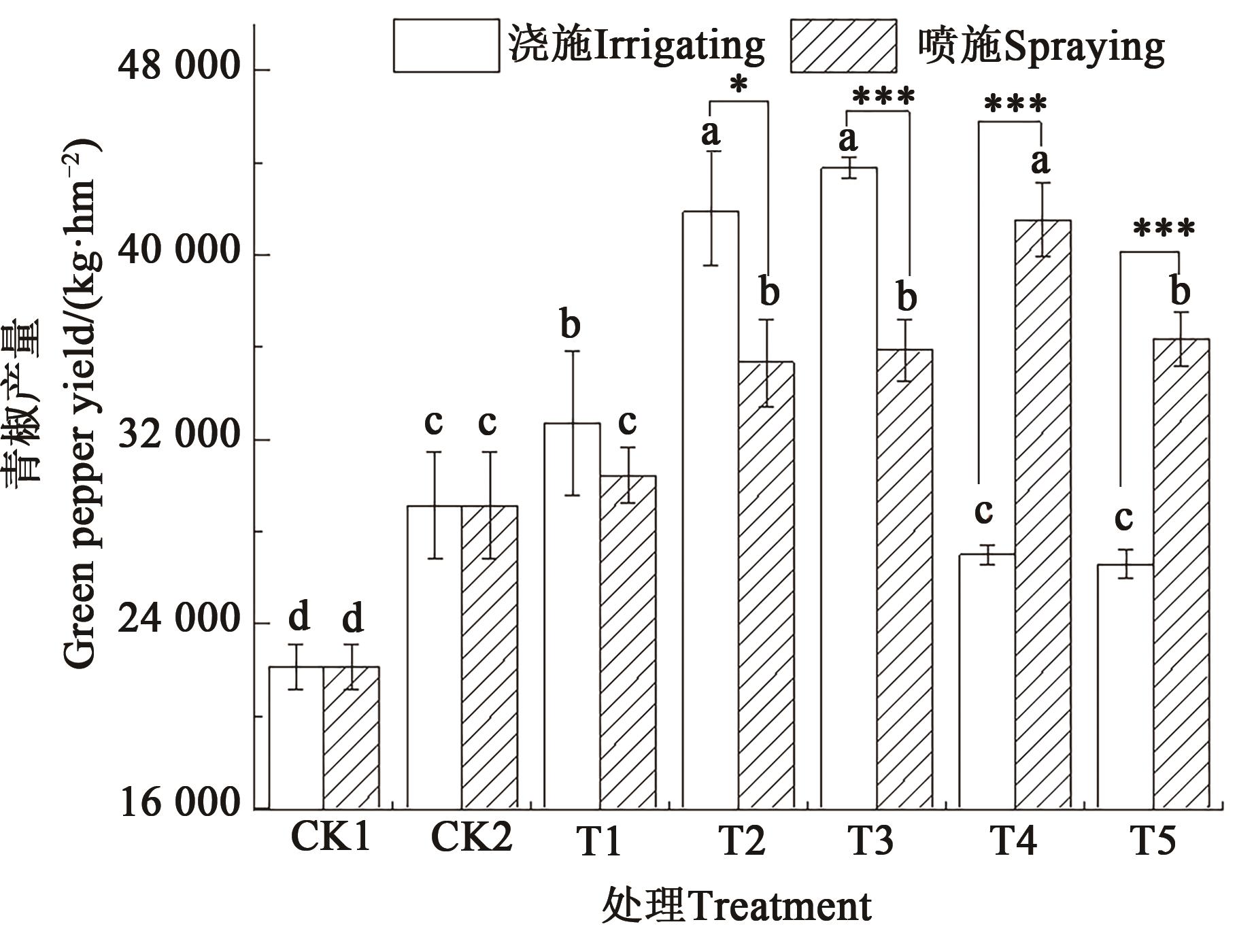
图6 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒的产量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;*和***分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式差异在P<0.05和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 6 Yield of green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; * and *** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.05 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
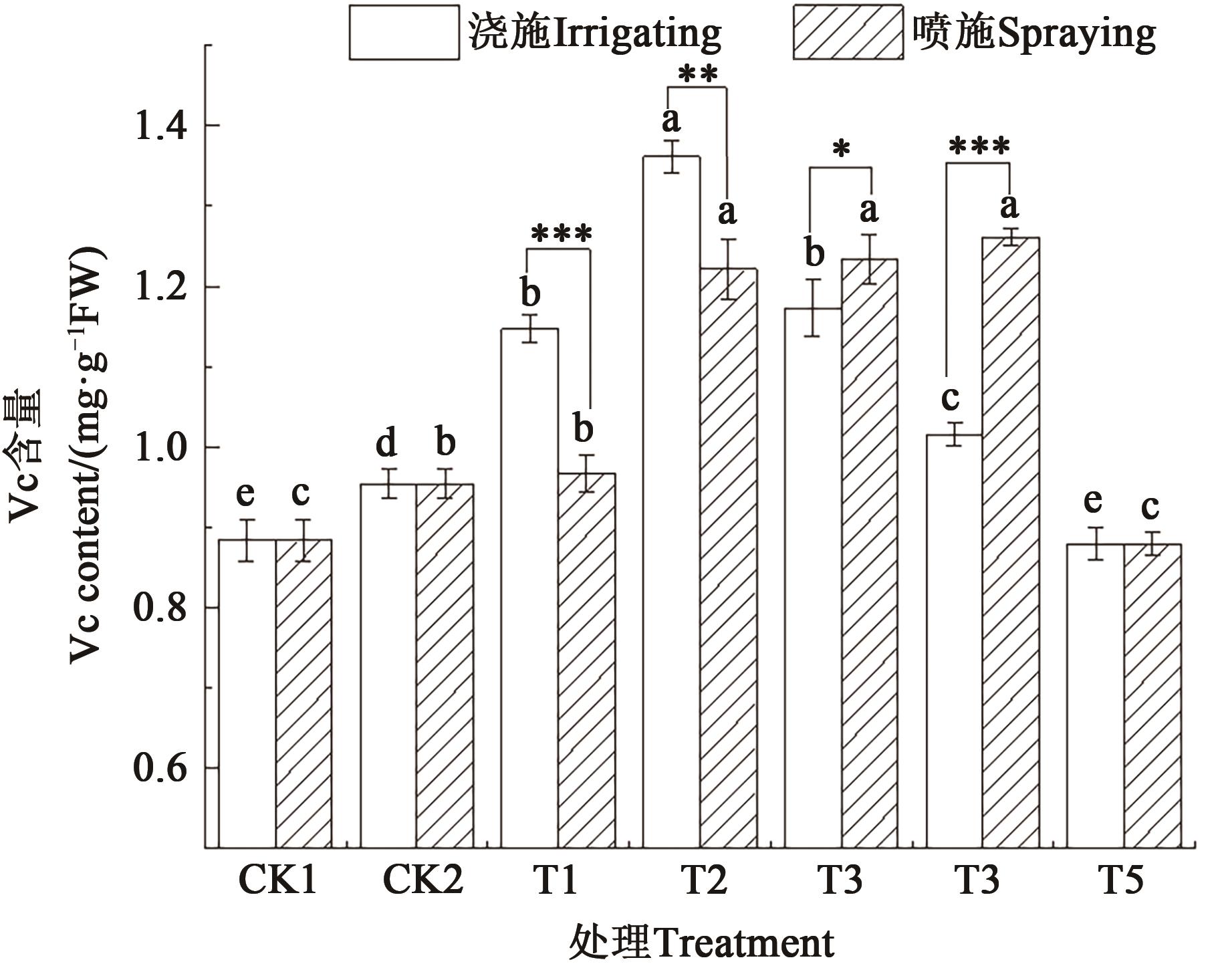
图7 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒的Vc含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著;*、**和***分别表示同一施肥量下不同施肥方式差异在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 7 Vc content of green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level; *,** and *** indicate significant differences between different fertilization methods in same fertilization amount at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
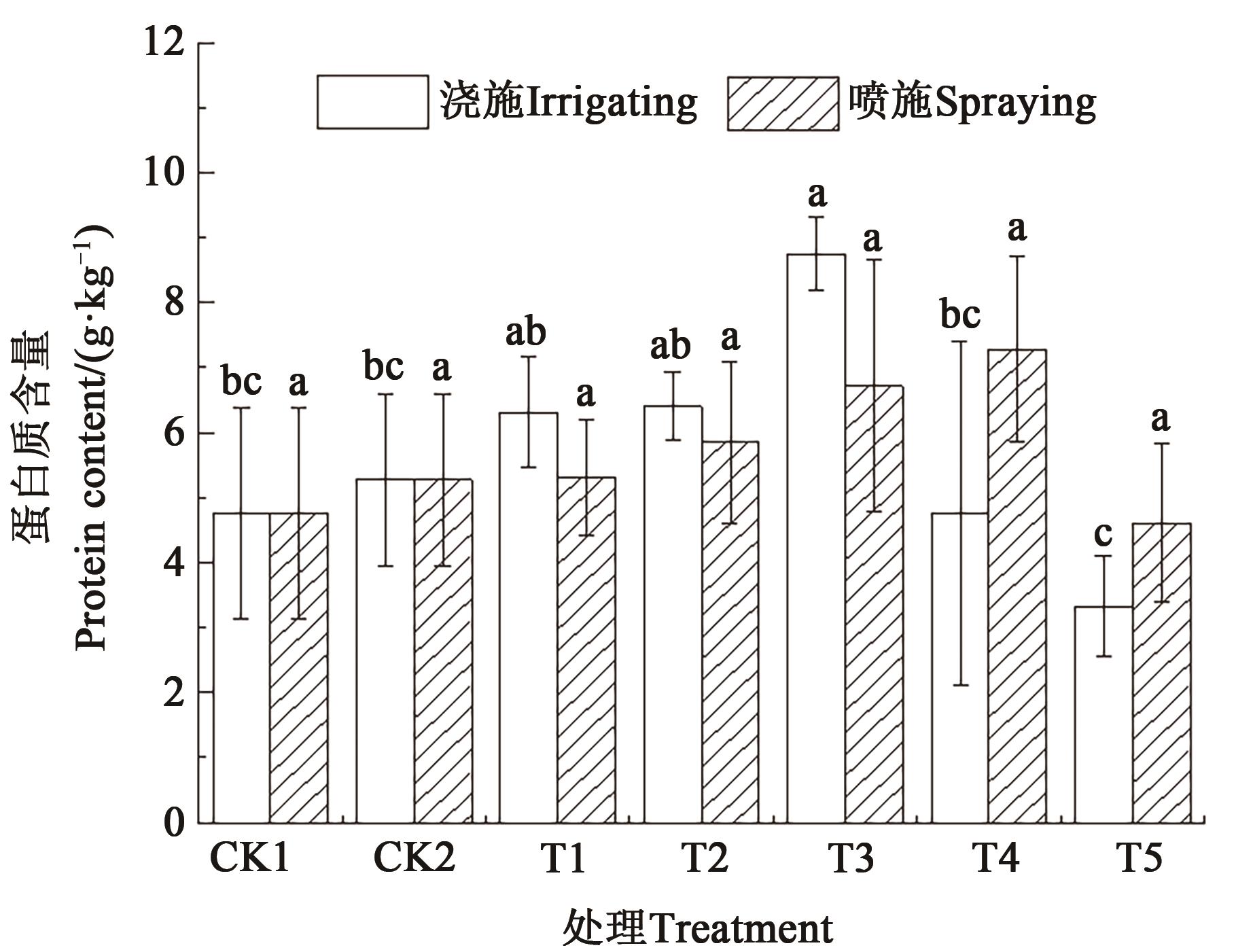
图8 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒的蛋白质含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 8 Protein content of green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level.
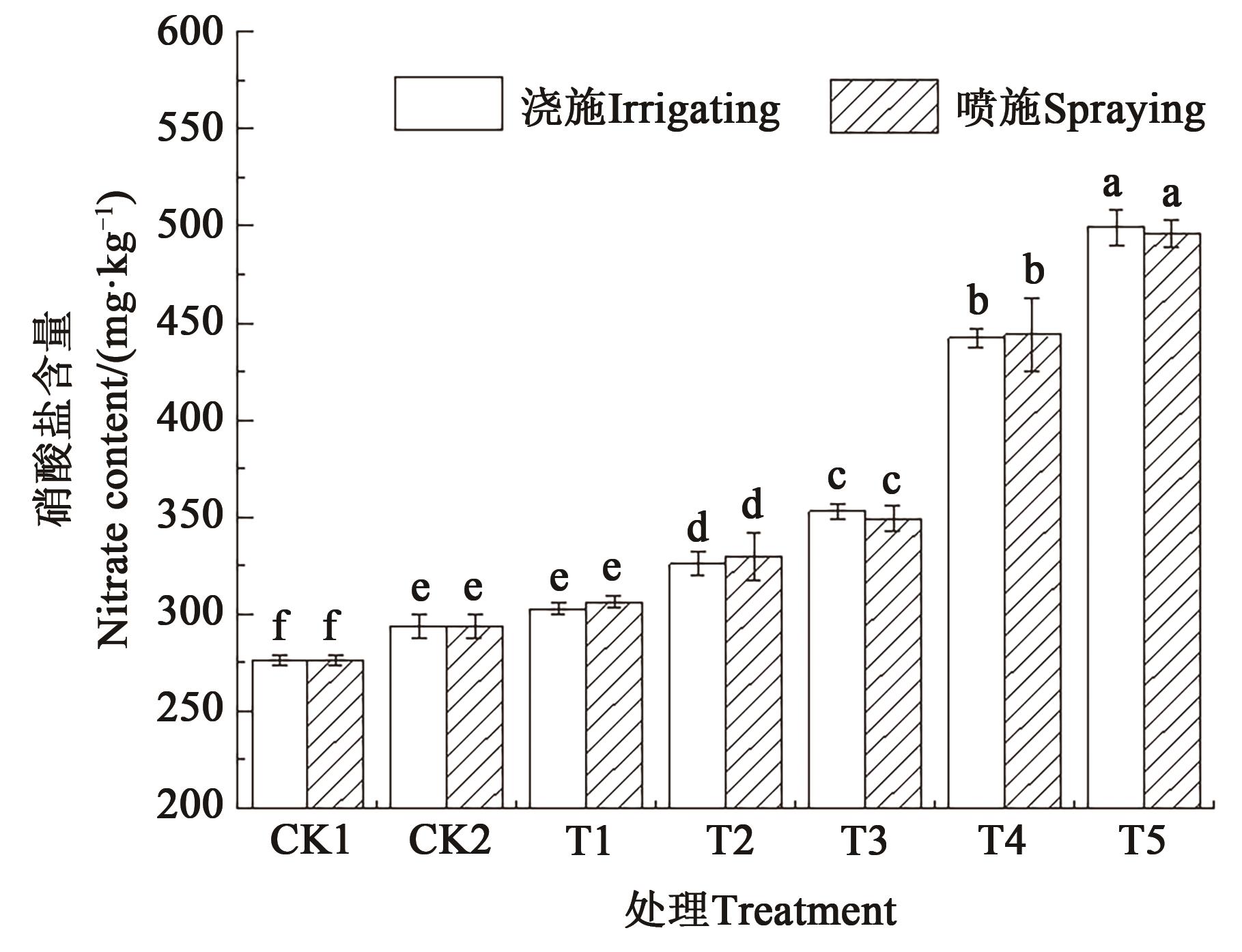
图9 不同施肥方式和施肥量下青椒的硝酸盐含量注:不同小写字母表示同一施肥方式不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 9 Nitrate content of green pepper under different fertilization methods and amountsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same fertilization method at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 罗尔呷.政策对沼气生产与利用的影响研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2020. |
| LUO E G. Research on the influence of policy on biogas production and utilization [D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. | |
| 2 | 张浩.生猪规模养殖企业环境行为演化分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019. |
| ZHANG H. Environmental behavior evolution analysis of pig scale breeding enterprises [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University,2019. | |
| 3 | 尹鹏,张辉文,刘宏达,等.4省市沼渣沼液养分含量和重金属分析[J].中国沼气,2021,39(5):43-50. |
| YIN P, ZHANG H W, LIU H D, et al.. Analysis of nutrients and heavy metals of biogas residue and biogas slurry in four provinces and cities [J]. China Biogas,2021,39(5):43-50. | |
| 4 | 石吕,刘建,魏亚凤,等.沼液在农业领域的资源化利用现状[J].中国农学通报,2019,35(35):109-117. |
| SHI L, LIU J, WEI Y F, et al.. Current status of resource utilization of biogas slurry in agriculture [J]. Chin.Agric. Sci. Bull.,2019,35(35):109-117. | |
| 5 | 武立叶,郑佩佩,赵吉祥,等.沼液灌溉对大白菜产量、品质及土壤养分含量的影响[J].中国沼气,2014,32(3):90-93. |
| WU L Y, ZHENG P P, ZHAO J X, et al.. The effect of biogas slurry irrigation on Chinese cabbage Beassica pekinensis L. and the soil quality [J]. China Biogas,2014,32(3):90-93. | |
| 6 | 张彦宁.不同沼液配比和灌溉量对番茄生长及根区土壤环境的影响[D].兰州:兰州理工大学,2018. |
| ZHANG Y N. Effects of biogas slurry ratio and irrigation amount on tomato growth and soil environment in root zone [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology,2018. | |
| 7 | 吴晓梅,叶美锋,吴飞龙,等.沼液灌溉对芥菜产量及养分吸收的影响研究[J].中国沼气,2017,35(5):66-70. |
| WU X M, YE M F, WU F L,et al.. Effect of biogas slurry irrigation on the yield and nutrient content of mustard [J]. China Biogas,2017,35(5):66-70. | |
| 8 | BACHMANN S, GROPP M. Phosphorus availability and soil microbial activity in a 3 year field experiment amended with digested dairy slurry [J]. Biomass Bioenergy,2014,70:429-439. |
| 9 | GRIGATTI M, GIROLAMO G D, CHINCARINI R,et al.. Potential nitrogen mineralization, plant utilization efficiency and soil CO2 emissions following the addition of anaerobic digested slurries [J]. Biomass Bioenergy,2011,35(11):4619-4629. |
| 10 | CORDOVIL C M D S, VARENNES A D, PINTO R,et al.. Changes in mineral nitrogen, soil organic matter fractions and microbial community level physiological profiles after application of digested pig slurry and compost from municipal organic wastes to burned soils [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem.,2011,43(4):845-852. |
| 11 | GARG R N, PATHAK H, DAS D K,et al.. Use of flyash and biogas slurry for improving wheat yield and physical properties of soil [J]. Environ. Monitor. Assessment,2005,107(1-3):1-9. |
| 12 | 贾政浩.纤维素乙醇厌氧沼液对小麦生长及土壤改良作用研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2016. |
| JIA Z H. Effect of cellulosic ethanol anaerobic wastewater on the growth of wheat and soil improvement [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University,2019. | |
| 13 | 刘占伟.养殖粪污循环利用对土壤改良和青贮玉米产量品质的影响[D].泰安:山东农业大学, 2018. |
| LIU Z W. Effect of livestock waste recycling on soil improvement and silage maize yield and quality [D].Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University,2019. | |
| 14 | 国家环境保护总局. 土壤环境监测技术规范: [S].北京:中国环境科学出版社,2005. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration. Technical specification for soil environmental monitoring: [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press,2005. | |
| 15 | 王孝平,邢树礼.考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白含量的研究[J].天津化工,2009,23(3):40-42. |
| WANG X P, XING S L. Determination of protein quantitation using the method of coomassie brilliant blue [J]. Tianjin Chem. Ind.,2009,23(3):40-42. | |
| 16 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:147-271. |
| 17 | 沈明珠,翟宝杰,东惠茹,等.蔬菜硝酸盐累积的研究—Ⅰ.不同蔬菜硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐含量评价[J].园艺学报,1982,9(4):41-48. |
| SHEN M Z, ZHAI B J, DONG H R, et al.. Studies on nitrate accumulation in vegetable crops—Ⅰ. evalution of nitrate and nitrite in different vegetables [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 1982, 9(4): 41-48. | |
| 18 | 魏彬萌,韩霁昌,王欢元,等.灌施沼液比例对石灰性土壤性质和辣椒生长的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2017(2):42-47. |
| WEI B M, HAN J C, WANG H Y,et al.. Effect of biogas slurry irrigation concentration on the calcareous soil properties and pepper growth [J]. Soil Fert. Sci.,2017(2):42-47. | |
| 19 | 黄海丽,庄海峰,张春荣,等.沼液替代化肥对土壤肥力与胡柚品质的影响[J].浙江农业科学,2021,62(2):324-329. |
| HUANG H L, ZHUANG H F, ZHANG C R,et al.. Effects of biogas slurry substituting chemical fertilizers on soil fertility and Huyou quality [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci.,2021,62(2):324-329. | |
| 20 | 胡振民,万青,李欢,等.喷灌沼液对茶园土壤性质及茶叶产量和品质的影响[J].南方农业学报,2020,51(11):2757-2763. |
| HU Z M, WAN Q, LI H,et al.. Effects of sprinkler irrigation with biogas slurry on tea garden soil and tea yield [J]. J. Southern Agric.,2020,51(11):2757-2763. | |
| 21 | 林少华,凌玮,孙芹菊,等.滨海盐碱地施用沼液对紫甘蓝生长及土壤性状的影响[J].中国沼气,2019,37(1):85-92. |
| LIN S H, LING W, SUN Q J,et al.. Effects of biogas slurry application on purple cabbage growth and the soil properties in coast saline-alkali land [J]. China Biogas,2019,37(1):85-92. | |
| 22 | DOU Z, TOTH J D, GALLIGAN D T,et al.. Laboratory procedures for characterizing manure phosphorus [J]. J. Environ. Quality,2000,29(2):508-514. |
| 23 | SHARPLEY A, MOYER B. Phosphorus forms in manure and compost and their release during simulated rainfall [J]. J. Environ. Quality,2000,29(5):1462-1469. |
| 24 | MAGUIRE R O, SIMS J T, SAYLOR W W,et al.. Influence of phytase addition to poultry diets on phosphorus forms and solubility in litters and amended soils [J]. J. Environ. Quality,2004,33(6):2306-2316. |
| 25 | TOOR G S, PEAK J D, SIMS J T. Phosphorus speciation in broiler litter and turkey manure produced from modified diets [J]. J. Environ. Quality,2005,34(2):687-697. |
| 26 | LEHMANN J, LAN Z, HYLAND C,et al.. Long-term dynamics of phosphorus forms and retention in manure-amended soils [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol.,2005,39(17):6672-6680. |
| 27 | 孙芹菊,凌玮,韩建刚,等.沼液施肥对滨海盐碱地土壤性状的影响[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,42(5):95-102. |
| SUN Q J, LING W, HAN J G,et al.. Effects of biogas slurry application on the coastal saline-alkali soil properties [J]. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.),2018,42(5):95-102. | |
| 28 | 袁祖华,石洪艳. 沼液在黄瓜上的应用效果研究[J].现代农业科技,2010(14):97-99. |
| YUAN Z H, SHI H Y. Study on the application effect of biogas slurry on cucumber [J]. Mod. Agric.Sci. Technol.,2010(14):97-99. | |
| 29 | 张利,李立军,冯志国,等.不同沼肥用量对番茄产量和品质的影响[J].中国农学通报,2012,28(16):266-271. |
| ZHANG L, LI L J, FENG Z G,et al.. Influence of biogas fertilizer on quality and yield of tomato [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull.,2012,28(16):266-271. | |
| 30 | 徐卫红,王正银,王旗,等. 不同沼液及用量对莴笋硝酸盐及营养品质的影响[J].中国沼气,2003,21(2):11-13. |
| XU W H, WANG Z Y, WANG Q,et al.. Effects of different biogas slurry and amount on nitrate and nutritional quality of lettuce [J]. China Biogas,2003,21(2):11-13. |
| [1] | 孟艳, 汪微, 葸全财, 李屹, 陈来生, 杜中平, 韩睿. 沼液预处理对蔬菜秸秆厌氧消化性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 188-196. |
| [2] | 郑杰, 陈红, 孟令剑, 李善军, 马露畅. 不同类型灌水器滴头对沼液抗堵塞性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 108-116. |
| [3] | 陈腾,董红敏*,张万钦,尹福斌. 猪场沼液热处理对病原微生物杀灭的关键因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 91-99. |
| [4] | 刘结友1,2,曲亮1,3*. 基于全混合厌氧反应器厌氧发酵猪粪产生沼液的环境影响分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(11): 127-134. |
| [5] | 马艳茹1,2,孟海波2,沈玉君2,丁京涛2,王黎明1*. 改性生物炭对沼液氨氮的吸附效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(11): 135-144. |
| [6] | 丁京涛,沈玉君,孟海波*,刘越,程红胜. 沼渣沼液养分含量及稳定性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(4): 139-146. |
| [7] | 陈永杏,尚斌,董红敏,陶秀萍,朱志平. 猪粪发酵沼液对油菜(Brassica chinensis L.)品质的影响[J]. , 2011, 13(3): 117-121. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号