




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 223-233.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0475
• 海洋农业 淡水渔业 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-06-06
接受日期:2022-08-20
出版日期:2023-01-15
发布日期:2023-04-17
通讯作者:
黄和,周雪巍
作者简介:方昕 E-mail:m18545655699@163.com
基金资助:
Xin FANG1( ), He HUANG1(
), He HUANG1( ), Xuewei ZHOU2(
), Xuewei ZHOU2( )
)
Received:2022-06-06
Accepted:2022-08-20
Online:2023-01-15
Published:2023-04-17
Contact:
He HUANG,Xuewei ZHOU
摘要:
为阐明湛江市养殖墨西哥湾扇贝中14种微量元素的含量及分布特征,并进行膳食暴露风险评估,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, ICP-MS)测定了6个养殖区域扇贝全部软体部分、性腺、外套膜、消化腺、闭壳肌、鳃和海水中14种微量元素的含量,通过目标危害系数(target hazard quotient,THQ)评估有害微量元素潜在的膳食暴露风险。结果表明,全部样品中14种微量元素均有检出,含量由高到低依次为Mn>Fe>Zn>Sr>As>Cd>V>Cu>Co>Ba>Pb>Cr>Ni>Ga,并且表现出区域差异性。微量元素主要分布在扇贝的性腺、消化腺和鳃中,养殖区域海水中与扇贝中Cd的含量变化趋势相同,扇贝体内的微量元素含量存在季节性差异。扇贝中As与Cd含量间呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),可能对人体有害微量元素的复合目标危害系数(total target hazard quotient, TTHQ)值为0.208(<1)。综上,扇贝体内微量元素分布具有组织特异性,其中As与Cd可能具有相同的污染源,并且Cd的蓄积受养殖环境的影响,食用墨西哥湾扇贝不存在有害微量元素暴露风险,不会引起健康风险。研究结果为扇贝中有害元素膳食暴露风险评估提供科学数据。
中图分类号:
方昕, 黄和, 周雪巍. 湛江市养殖墨西哥湾扇贝中14种微量元素的分布特征及其膳食暴露评估[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 223-233.
Xin FANG, He HUANG, Xuewei ZHOU. Distribution of 14 Trace Elements in Argopecten irradians concentricus from Zhanjiang City and Their Dietary Exposure Assessment[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 223-233.
图1 广东省湛江市养殖海域墨西哥湾扇贝采样点位置
Fig. 1 Sampling sites of the Argopecten irradians concentricus in different marine aquaculture areas in Zhanjiang, Guangdong province
元素 Element | 养殖区Aquaculture area | 总计 Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | |||
必需微量元素 Essential trace element | Cu | 5.67±0.09 c | 7.18±0.83 ab | 7.40±0.97 ab | 5.63±0.24 c | 6.35±0.15 bc | 7.75±0.55 a | 6.66±0.91 |
| Ni | 1.01±0.07 c | 2.63±0.81 ab | 3.05±0.59 a | 1.62±0.03 bc | 2.48±0.48 ab | 2.44±0.16 ab | 2.21±0.75 | |
| V | 4.19±0.24 c | 9.58±1.88 b | 16.65±1.36 a | 8.60±0.51 b | 11.48±2.71 b | 9.06±0.75 b | 9.93±4.08 | |
| Co | 3.93±0.30 c | 4.85±0.38 b | 7.52±0.58 a | 4.08±0.08 bc | 4.50±0.26 bc | 7.22±0.30 a | 5.35±1.60 | |
| Zn | 143.84±7.18 d | 147.68±10.84 d | 207.87±17.48 c | 191.92±5.91 c | 246.11±5.95 b | 401.91±15.86 a | 223.22±95.58 | |
| Fe | 411.77±25.13 d | 963.80±233.94 bc | 1 535.89±213.04 a | 720.91±20.38 cd | 1 251.03±382.91 ab | 727.08±87.26 cd | 935.08±406.11 | |
| Mn | 1 411.32±146.42 c | 2 192.43±232.41 b | 2 011.70±110.74 b | 1 897.80±8.34 b | 1 429.68±35.99 c | 3 620.82±99.12 a | 2 093.96±811.60 | |
| 可能对人体有害微量元素Potentially toxic element | As | 9.94 ± 0.25 c | 8.77±0.62 c | 11.57±0.80 b | 9.30±0.29 c | 12.20±0.21 b | 19.28±0.34 a | 11.84±3.87 |
| Cd | 5.89±0.44 d | 7.63±0.91 cd | 8.44±1.30 c | 6.22±0.22 d | 13.55±0.65 b | 19.71±0.38 a | 10.24±5.40 | |
| Pb | 3.11±0.20 c | 4.74±0.21 a | 3.53±0.66 c | 3.71±0.08 bc | 4.52±0.72 ab | 5.29±0.25 a | 4.15±0.83 | |
| Cr | 0.74±0.05 c | 3.49±0.37 a | 3.24±0.53 a | 1.90±0.09 b | 3.01±0.80 a | 3.73±.022 a | 2.69±1.14 | |
| 其他微量元素 Other trace element | Ba | 1.90±0.16 d | 4.89±1.33 bc | 8.58±1.50 a | 4.31±0.15 cd | 7.28±2.17 ab | 4.90±0.50 bc | 5.31±2.35 |
| Ga | 0.30±0.02 d | 0.72±0.16 c | 1.34±0.18 a | 0.67±0.03 cd | 1.15±0.36 ab | 0.84±0.11 bc | 0.84±0.37 | |
| Sr | 35.48±3.59 c | 56.36±10.47 b | 51.63±5.23 b | 36.30±1.56 c | 47.44±5.02 bc | 68.81±2.57 a | 49.34±12.64 | |
表1 墨西哥湾扇贝全部软体部分中14种微量元素含量 (mg·kg-1)
Table 1 Contents of 14 trace elements in whole soft parts of the Argopecten irradians concentricus
元素 Element | 养殖区Aquaculture area | 总计 Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | |||
必需微量元素 Essential trace element | Cu | 5.67±0.09 c | 7.18±0.83 ab | 7.40±0.97 ab | 5.63±0.24 c | 6.35±0.15 bc | 7.75±0.55 a | 6.66±0.91 |
| Ni | 1.01±0.07 c | 2.63±0.81 ab | 3.05±0.59 a | 1.62±0.03 bc | 2.48±0.48 ab | 2.44±0.16 ab | 2.21±0.75 | |
| V | 4.19±0.24 c | 9.58±1.88 b | 16.65±1.36 a | 8.60±0.51 b | 11.48±2.71 b | 9.06±0.75 b | 9.93±4.08 | |
| Co | 3.93±0.30 c | 4.85±0.38 b | 7.52±0.58 a | 4.08±0.08 bc | 4.50±0.26 bc | 7.22±0.30 a | 5.35±1.60 | |
| Zn | 143.84±7.18 d | 147.68±10.84 d | 207.87±17.48 c | 191.92±5.91 c | 246.11±5.95 b | 401.91±15.86 a | 223.22±95.58 | |
| Fe | 411.77±25.13 d | 963.80±233.94 bc | 1 535.89±213.04 a | 720.91±20.38 cd | 1 251.03±382.91 ab | 727.08±87.26 cd | 935.08±406.11 | |
| Mn | 1 411.32±146.42 c | 2 192.43±232.41 b | 2 011.70±110.74 b | 1 897.80±8.34 b | 1 429.68±35.99 c | 3 620.82±99.12 a | 2 093.96±811.60 | |
| 可能对人体有害微量元素Potentially toxic element | As | 9.94 ± 0.25 c | 8.77±0.62 c | 11.57±0.80 b | 9.30±0.29 c | 12.20±0.21 b | 19.28±0.34 a | 11.84±3.87 |
| Cd | 5.89±0.44 d | 7.63±0.91 cd | 8.44±1.30 c | 6.22±0.22 d | 13.55±0.65 b | 19.71±0.38 a | 10.24±5.40 | |
| Pb | 3.11±0.20 c | 4.74±0.21 a | 3.53±0.66 c | 3.71±0.08 bc | 4.52±0.72 ab | 5.29±0.25 a | 4.15±0.83 | |
| Cr | 0.74±0.05 c | 3.49±0.37 a | 3.24±0.53 a | 1.90±0.09 b | 3.01±0.80 a | 3.73±.022 a | 2.69±1.14 | |
| 其他微量元素 Other trace element | Ba | 1.90±0.16 d | 4.89±1.33 bc | 8.58±1.50 a | 4.31±0.15 cd | 7.28±2.17 ab | 4.90±0.50 bc | 5.31±2.35 |
| Ga | 0.30±0.02 d | 0.72±0.16 c | 1.34±0.18 a | 0.67±0.03 cd | 1.15±0.36 ab | 0.84±0.11 bc | 0.84±0.37 | |
| Sr | 35.48±3.59 c | 56.36±10.47 b | 51.63±5.23 b | 36.30±1.56 c | 47.44±5.02 bc | 68.81±2.57 a | 49.34±12.64 | |
元素 Element | 养殖区Aquaculture area | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | ||
| As | 2.16 | 2.28 | 2.43 | 2.20 | 2.11 | 2.13 | 2.22±0.12 |
| Cd | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06±0.01 |
| Pb* | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04±0.00 |
| Cr | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.17±0.03 |
| Zn | 4.53 | 4.56 | 8.05 | 13.67 | 4.59 | 3.94 | 6.56±3.79 |
| Cu* | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.32±0.11 |
| Ni | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 1.05 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.79±0.14 |
| V | 3.36 | 2.51 | 2.87 | 2.71 | 2.97 | 3.24 | 2.94±0.32 |
| Co | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13±0.02 |
| Fe | 2.16 | 1.62 | 1.82 | 3.55 | 2.07 | 1.80 | 2.17±0.70 |
| Mn | 0.94 | 0.49 | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.84±0.18 |
| Ba | 7.42 | 6.09 | 6.60 | 6.45 | 6.53 | 9.24 | 7.06±1.16 |
表2 不同养殖区域海水中微量元素含量 (μg·L-1)
Table 2 Trace elements content of seawater in different aquaculture areas
元素 Element | 养殖区Aquaculture area | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | ||
| As | 2.16 | 2.28 | 2.43 | 2.20 | 2.11 | 2.13 | 2.22±0.12 |
| Cd | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06±0.01 |
| Pb* | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04±0.00 |
| Cr | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.17±0.03 |
| Zn | 4.53 | 4.56 | 8.05 | 13.67 | 4.59 | 3.94 | 6.56±3.79 |
| Cu* | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.32±0.11 |
| Ni | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 1.05 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.79±0.14 |
| V | 3.36 | 2.51 | 2.87 | 2.71 | 2.97 | 3.24 | 2.94±0.32 |
| Co | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13±0.02 |
| Fe | 2.16 | 1.62 | 1.82 | 3.55 | 2.07 | 1.80 | 2.17±0.70 |
| Mn | 0.94 | 0.49 | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.84±0.18 |
| Ba | 7.42 | 6.09 | 6.60 | 6.45 | 6.53 | 9.24 | 7.06±1.16 |
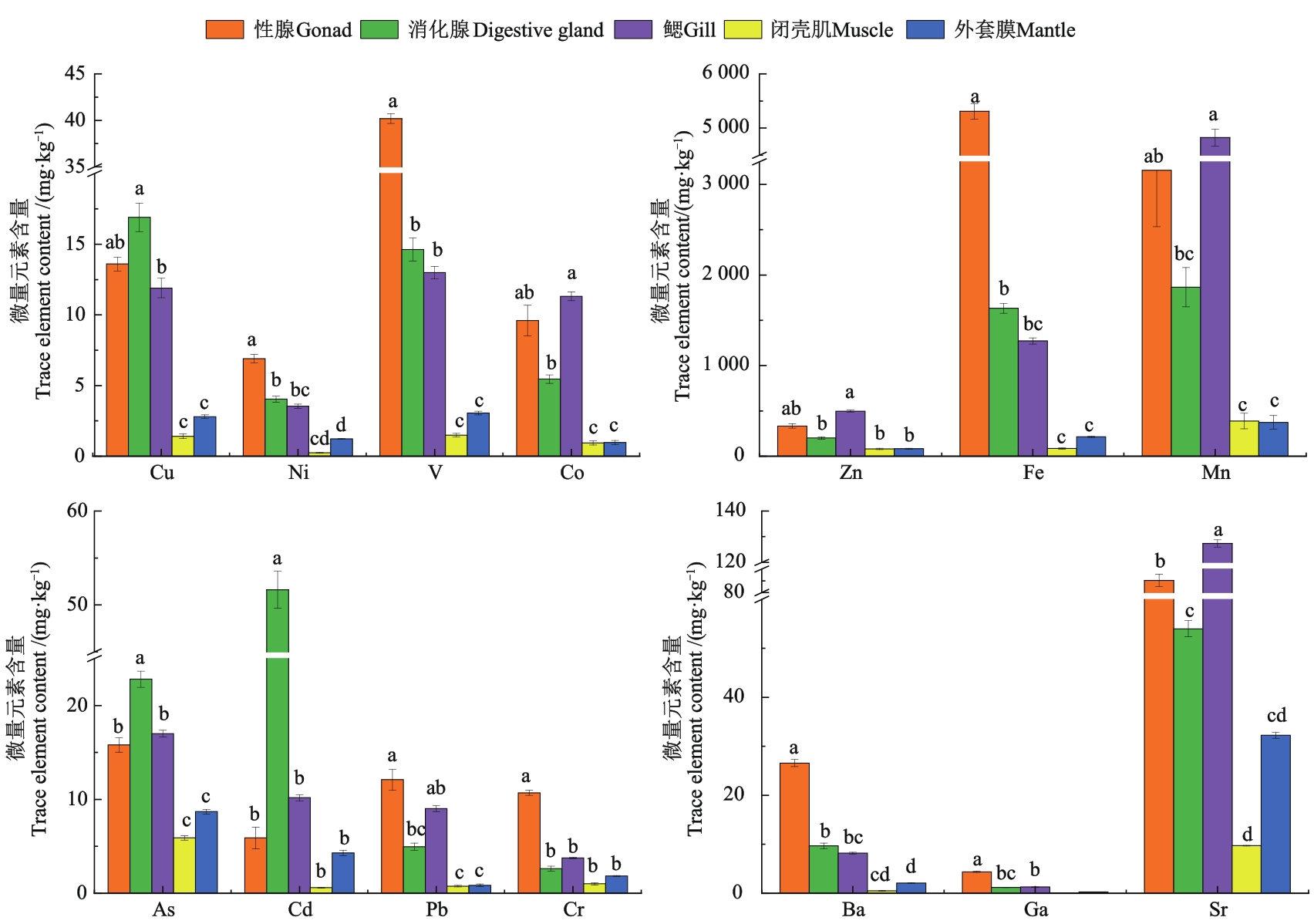
图 2 墨西哥湾扇贝不同微量元素在不同组织中的含量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同组织间的差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Contents of trace elements in different tissues of Argopecten irradians concentricusNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences between different tissues at P<0.05 level.
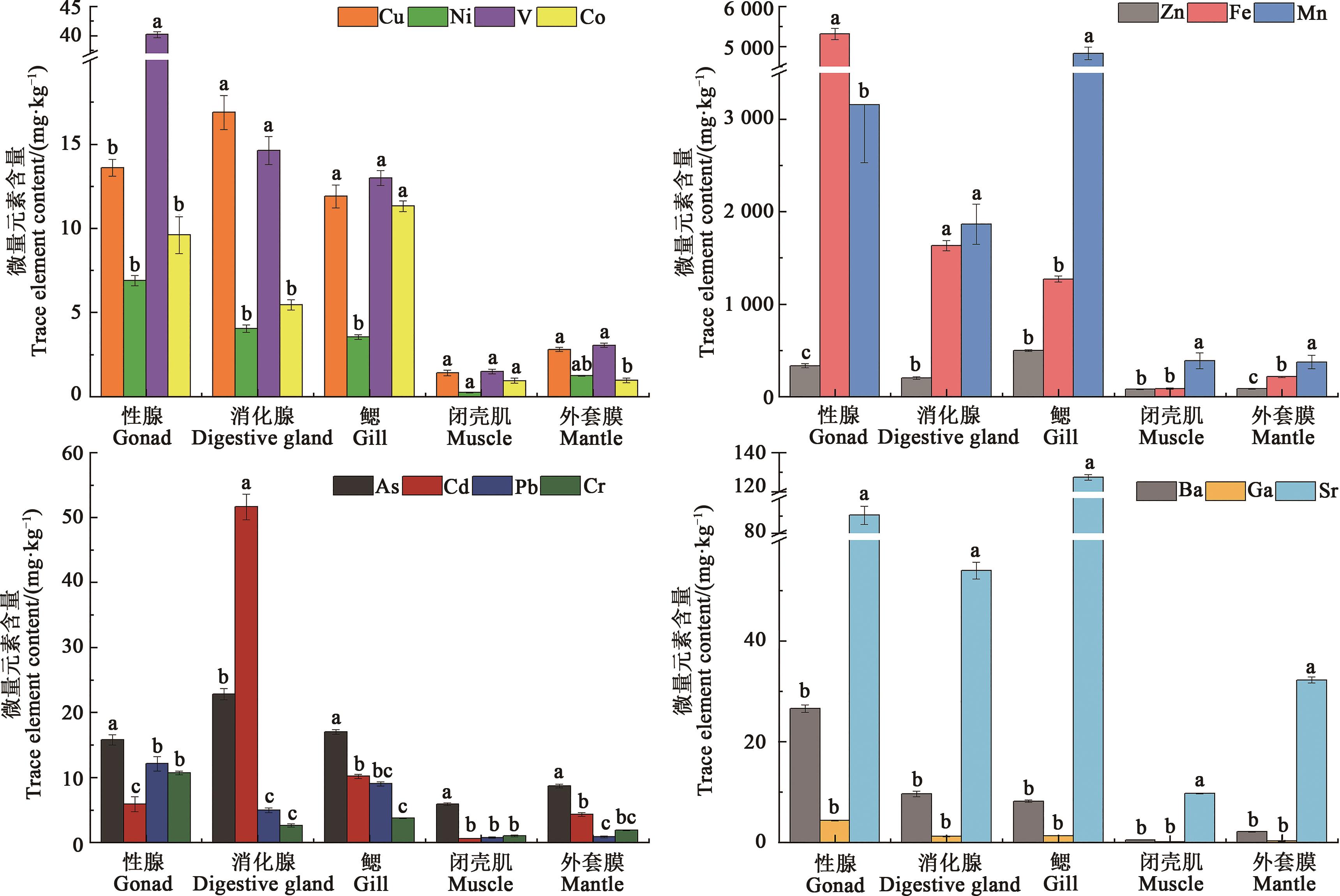
图3 墨西哥湾扇贝性腺、消化腺、鳃、闭壳肌、外套膜中微量元素的含量注:同一组织中不同小写字母表示不同元素间差异在P < 0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Contents of trace elements in different tissues of Argopecten irradians concentricusNote: Different lowercase letters in same tissue indicate significant differences between different elements at P < 0.05 level.
| 元素Element | As | Cd | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.943* | ||
| Pb | 0.626 | 0.798 | |
| Cr | 0.494 | 0.631 | 0.802 |
表3 墨西哥湾扇贝可能对人体有害微量元素之间的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between potentially toxic elements in Argopecten irradians concentricus
| 元素Element | As | Cd | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.943* | ||
| Pb | 0.626 | 0.798 | |
| Cr | 0.494 | 0.631 | 0.802 |
元素 Element | 养殖时期 Aquaculture season | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | ||
必需微量元素 Essential trace element | Cu | 5.63±0.24 b | 7.18±0.21 a | 7.30±0.36 a |
| Ni | 1.62±0.03 a | 1.27±0.06 b | 1.59±0.12 a | |
| V | 8.60±0.51 a | 2.93±0.07 b | 3.38±0.12 b | |
| Co | 4.08±0.08 a | 1.04±0.06 b | 4.03±0.18 a | |
| Zn | 191.92±5.90 b | 240.77±47.92 b | 392.38±30.85 a | |
| Fe | 720.91±20.38 a | 1 364.83±397.33 a | 1 288.62±309.59 a | |
| Mn | 1 897.80±8.34 a | 1 328.26±190.70 b | 1 464.43±42.01 ab | |
| 可能有害微量元素 Potentially toxic element | As | 9.3±0.29 ab | 8.39±0.28 b | 11.17±0.41 a |
| Cd | 6.22±0.22 a | 5.82±0.08 a | 6.71±0.24 a | |
| Pb | 3.71±0.08 a | 1.76±0.03 b | 1.81±0.05 b | |
| Cr | 1.90±0.09 a | 1.46±0.04 b | 1.38±0.06 b | |
其他微量元素 Other trace element | Ba | 4.31±0.15 a | 2.44±0.05 b | 1.88±0.08 c |
| Ga | 0.67±0.03 a | 0.22±0.02 b | 0.15±0.04 c | |
| Sr | 36.30±1.56 a | 31.58±1.30 ab | 34.24±0.80 b | |
表4 不同养殖季节墨西哥湾扇贝体内的微量元素比较
Table 4 Comparison of trace elements in Argopecten irradians concentricus in different aquaculture season
元素 Element | 养殖时期 Aquaculture season | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | ||
必需微量元素 Essential trace element | Cu | 5.63±0.24 b | 7.18±0.21 a | 7.30±0.36 a |
| Ni | 1.62±0.03 a | 1.27±0.06 b | 1.59±0.12 a | |
| V | 8.60±0.51 a | 2.93±0.07 b | 3.38±0.12 b | |
| Co | 4.08±0.08 a | 1.04±0.06 b | 4.03±0.18 a | |
| Zn | 191.92±5.90 b | 240.77±47.92 b | 392.38±30.85 a | |
| Fe | 720.91±20.38 a | 1 364.83±397.33 a | 1 288.62±309.59 a | |
| Mn | 1 897.80±8.34 a | 1 328.26±190.70 b | 1 464.43±42.01 ab | |
| 可能有害微量元素 Potentially toxic element | As | 9.3±0.29 ab | 8.39±0.28 b | 11.17±0.41 a |
| Cd | 6.22±0.22 a | 5.82±0.08 a | 6.71±0.24 a | |
| Pb | 3.71±0.08 a | 1.76±0.03 b | 1.81±0.05 b | |
| Cr | 1.90±0.09 a | 1.46±0.04 b | 1.38±0.06 b | |
其他微量元素 Other trace element | Ba | 4.31±0.15 a | 2.44±0.05 b | 1.88±0.08 c |
| Ga | 0.67±0.03 a | 0.22±0.02 b | 0.15±0.04 c | |
| Sr | 36.30±1.56 a | 31.58±1.30 ab | 34.24±0.80 b | |
| 1 | FERNÁNDEZ A, GRIENKE U, SOLER-VILA A, et al.. Seasonal and geographical variations in the biochemical composition of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) from Ireland [J]. Food Chem., 2015, 177: 43-52. |
| 2 | 李乐,郑兴,宋仲辉,等. 海上吊养和循环水养殖的马氏珠母贝软体部矿物元素含量比较[J].热带生物学报, 2016, 7(4): 417-421. |
| LI L, ZHENG X, SONG Z H, et al.. Analysis of mineral elements in the soft tissue of Pinctada martensii from sea cage aquaculture and re-circulating aquaculture [J]. J. Trop. Biol., 2016, 7(4): 417-421. | |
| 3 | ZHAO Y F, KANG X M, DING H Y, et al.. Bioaccumulation and biotransformation of inorganic arsenic in zhikong scallop (Chlamys farreri) after waterborne exposure [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2021, 277(3):130270 [2022-05-06] .. |
| 4 | ZHANG L L, YAN W, XIE Z Y, et al.. Bioaccumulation and changes of trace metals over the last two decades in marine organisms from Guangdong coastal regions, South China [J]. J. Environ. Sci., 2020, 98: 103-108. |
| 5 | NASER H A. Assessment and management of heavy metal pollution in the marine environment of the Arabian Gulf: a review [J]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2013, 72(1): 6-13. |
| 6 | LIU S, LIU Y L, YANG D F, et al.. Trace elements in shellfish from Shenzhen, China: implication of coastal water pollution and human exposure [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020, 263: 114582 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 7 | BARBOSA I D S, BRITO G B, SANTOS G L D, et al.. Multivariate data analysis of trace elements in bivalve molluscs: characterization and food safety evaluation [J]. Food Chem., 2019, 273: 64-70. |
| 8 | KATO L L S, FERRARI R G, LEITE J V M, et al.. Arsenic in shellfish: a systematic review of its dynamics and potential health risks [J/OL]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2020, 161: 111693 [2022-05-06].. |
| 9 | WEN J, ZENG L, CHEN Z, et al.. Species identification of dried scallop adductor muscle (yao zhu) products sold on the market [J]. Food Control, 2017, 71: 83-87. |
| 10 | 黄亚楠,王文杰,魏钰恒,等. 墨西哥湾扇贝(Argopecten irradians concentricus)选育系F7在广西北部湾海域的生长比较研究[J].海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(5): 1222-1231. |
| HUANG Y N, WANG W J, WEI Y H, et al.. Comparison in growth of F7 generation of Argopecten irradians concentricus in Beibu Gulf, Guangxi, China [J]. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 2020, 51(5): 1222-1231. | |
| 11 | 谭杰,姚高友,陶雅晋,等. 不同大小规格墨西哥湾扇贝(Argopecten irradians concentricus)转录组分析及生长相关基因筛选[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2019, 38(1): 40-50. |
| TAN J, YAO G Y, TAO Y J, et al.. Transcriptome analysis and growth-related genes screening of Argopecten irradians concentricus of different sizes [J]. Genomics Appl. Biol., 2019, 38(1): 40-50. | |
| 12 | 彭张明. 墨西哥湾扇贝新品系的选择育种及养殖[D]. 湛江:广东海洋大学, 2015. |
| PENG Z M. Selective breeding and culture of new Argopecten irradians concentricus line [D].Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2015. | |
| 13 | 姚高友. 墨西哥湾扇贝杂交育种及杂交子代高温耐受性与遗传特征分析[D]. 湛江:广东海洋大学, 2019. |
| YAO G Y. Genetic and stress resistance analysis of diallel cross between Argopecten irradians concentricus and "Bohai Red" [D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2019. | |
| 14 | XIE Q, LI H X, LIN L, et al.. Characteristics of expanded polystyrene microplastics on island beaches in the Pearl River estuary: abundance, size, surface texture and their metals-carrying capacity [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2021, 30: 1632-1643. |
| 15 | 李鹏. 福建部分沿海地区贝类重金属污染及镉形态的分析研究[D]. 厦门:集美大学, 2020. |
| LI P. Studies of heavy metal pollution and cadmium species in shellfish collected from some coastal areas of Fujian [D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2020. | |
| 16 | LIN Y, LU J, WU J. Heavy metals pollution and health risk assessment in farmed scallops: low level of Cd in coastal water could lead to high risk of seafood [J/OL]. Ecotox. Environ. Safe, 2021, 208: 111768 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 17 | 张建江,王佳,舒为群. 饮水中锶的健康效应和安全水平[J].卫生研究, 2021, 50(4): 686-690, 697. |
| ZHANG J J, WANG J, SHU W Q. Health effects and safe levels of strontium in drinking water [J]. J. Hyg. Res., 2021, 50(4): 686-690, 697. | |
| 18 | QIN L Y, ZHANG R C, LIANG Y D, et al.. Concentrations and health risks of heavy metals in five major marketed marine bivalves from three coastal cities in Guangxi, China [J/OL]. Ecotox. Environ. Safe., 2021, 223(3): 112562 [2022-05-06].. |
| 19 | LI P M, GAO X L. Trace elements in major marketed marine bivalves from six northern coastal cities of China: concentrations and risk assessment for human health [J]. Ecotox. Environ. Safe., 2014, 109: 1-9. |
| 20 | 林丽华,魏虎进,黄华梅. 大亚湾表层沉积物和底栖生物中重金属的污染特征与生物积累[J].生态科学, 2017, 36(6): 173-181. |
| LIN L H, WEI H J, HUANG H M. Contamination status and bioaccumulation of the heavy metals in the surface sediments and benthos in Daya Bay [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2017, 36(6): 173-181. | |
| 21 | RAHMAN M A, HASEGAWA H, LIM R P. Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and trophic transfer of arsenic in the aquatic food chain [J]. Environ. Res., 2012, 116: 118-135. |
| 22 | NEMR A E, EL-SAID G F, RAGAB S, et al.. The distribution, contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and shellfish from the Red Sea coast, Egypt [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 165: 369-380. |
| 23 | YUAN Y, SUN T, WANG H, et al.. Bioaccumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metals to bivalve species in Daya Bay (South China Sea): consumption advisory [J/OL]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2020, 150: 110717 [2022-05-06]. . |
| 24 | JEBALI J, CHOUBA L, BANNI M, et al.. Comparative study of the bioaccumulation and elimination of trace metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Mn and Fe) in the digestive gland, gills and muscle of bivalve Pinna nobilis during a field transplant experiment [J]. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol., 2014, 28(2): 212-217. |
| 25 | SCHNEIDER L, MAHER W A, POTTS J, et al.. Trophic transfer of metals in a seagrass food web: bioaccumulation of essential and non-essential metals [J]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2018, 131: 468-480. |
| 26 | PAN K, WANG W X. Biodynamics to explain the difference of copper body concentrations in five marine bivalve species [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43(6):2137-2143. |
| 27 | LIU Q, LIAO Y, SHOU L. Concentration and potential health risk of heavy metals in seafoods collected from Sanmen bay and its adjacent areas, China [J]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2018, 131: 356-364. |
| 28 | BUSTAMANTE P, MIRAMAND P. Subcellular and body distributions of 17 trace elements in the variegated scallop Chlamys varia from the French coast of the Bay of Biscay [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2005, 337(1-3): 59-73. |
| 29 | NORUM U, LAI V W M, CULLEN W R. Trace element distribution during the reproductive cycle of female and male spiny and Pacific scallops, with implications for biomonitoring [J]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2005, 50(2): 175-184. |
| 30 | METIAN M, BUSTAMANTE P, HEDOUIN L, et al.. Accumulation of nine metals and one metalloid in the tropical scallop Comptopallium radula from coral reefs in New Caledonia [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2008, 152(3): 543-552. |
| 31 | LIU J H, CAO L, DOU S Z. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and health risk assessment in three benthic bivalves along the coast of Laizhou Bay, China [J]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2017, 117(1-2): 98-110. |
| 32 | 王增焕,林钦,王许诺,等. 华南沿海牡蛎重金属含量特征及其风险评估[J]. 水产学报, 2011, 35(2): 291-297. |
| WANG Z H, LIN Q, WANG X N, et al.. The variation features of heavy metal contents in oyster samples from the coast of South China Sea and their safety assessment [J]. J. Fish. China, 2011, 35(2): 291-297. | |
| 33 | BEZUIDENHOUT J, DAMES N, BOTHA A, et al.. Trace elements in mediterranean mussels mytilus galloprovincialis from the south African west coast [J]. Ecol. Chem. Eng., 2016, 22(4): 489-498. |
| 34 | LU J, LI A, DONG J, et al.. The effect of Typhoon Talim on the distribution of heavy metals on the inner shelf of the East China sea [J/OL]. Cont. Shelf Res., 2021, 229: 104547 [2022-05-06]. . |
| [1] | 杨小虎, 张曼玉, 杨海昌, 张凤华, 江宜霖, 易小兰. 基于组合模型的玛纳斯河流域农田土壤盐分反演[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 134-141. |
| [2] | 孙永文, 张胜茂, 唐峰华, 王书献, 樊伟, 范秀梅, 杨胜龙. 基于卫星船位数据的北太平洋作业渔船分布及类型研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 207-217. |
| [3] | 张繁, 谷悦, 曹琛, 刘保华. 油菜秸秆纤维对水泥胶砂孔隙特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 189-195. |
| [4] | 齐天明, 李志坚, 秦培友, 任贵兴, 周帮伟. 藜麦栽培技术研究与应用展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 157-165. |
| [5] | 杨亮彦, 黎雅楠, 范鸿建, 王雅婷. 毛乌素沙地蒸散发时空分布及影响因素分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 169-178. |
| [6] | 张雪可, 张虹, 章鹏飞, 秦委, 刘守金, 彭代银, 李雷. 湖北黄精潜在分布区预测及生态适宜性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 185-192. |
| [7] | 周治. 我国农业秸秆高值化利用现状与困境分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 9-16. |
| [8] | 刘星宏, 张青青, 张广鹏, 李宏. 塔里木河下游植物群落空间分布及影响因素分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 131-144. |
| [9] | 高素红1,2,武海燕2,温晓蕾2,路常宽2,赵春明2,张琪2,丁元元2. 绿盲蝽越冬卵在葡萄园中的空间分布型和抽样技术研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 116-122. |
| [10] | 罗燕,李武强,万芳新,黄晓鹏*. 基于Weibull分布函数的桔梗切片热风干燥特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 132-140. |
| [11] | 王冰洁1,潘波1,姜蕾1,林勇1*,赵帅2,莫宇星2. 植保无人机作业参数对雾滴在火龙果树冠层沉积分布的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(10): 101-109. |
| [12] | 冯雷1,2,李雪3,徐万里1*,唐光木1,孙宁川1,顾美英4. 不同盐渍化土壤栽培的黑果枸杞品质评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(10): 167-174. |
| [13] | 李晓1,何振嘉2*. 灌水器流量对涌泉根灌湿润体肥液入渗影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 87-97. |
| [14] | 吴祖立1,2,章守宇1*. 台风对浙江枸杞岛大型底栖海藻分布的影响分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(9): 159-168. |
| [15] | 石祖梁1,2,王飞1,2,王久臣1,2,李想1*,孙仁华1,宋成军1. 我国农作物秸秆资源利用特征、技术模式及发展建议[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(5): 8-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号