












中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 198-207.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0640
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
丛文成1,2( ), 袁立敏2,3(
), 袁立敏2,3( ), 蒙仲举1,2, 杨宇3,4
), 蒙仲举1,2, 杨宇3,4
收稿日期:2022-08-06
接受日期:2022-09-01
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-02-04
通讯作者:
袁立敏
作者简介:丛文成 E-mail:cwc0429@163.com;
基金资助:
Wencheng CONG1,2( ), Limin YUAN2,3(
), Limin YUAN2,3( ), Zhongju MENG1,2, Yu YANG3,4
), Zhongju MENG1,2, Yu YANG3,4
Received:2022-08-06
Accepted:2022-09-01
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-02-04
Contact:
Limin YUAN
摘要:
为探索玉米芯在干旱地区的有效利用方式、提高其利用率,通过土柱模拟的方法,将1.5~6.0 mm玉米芯颗粒与风沙土混合开展吸水与蒸发试验。以未添加玉米芯的土柱为对照,设置10种添加玉米芯处理,对不同处理土柱的吸水量、湿润锋、蒸发量、蒸发强度等进行测定,分析玉米芯及其用量对风沙土吸水、保水效果的影响。结果表明,混合土壤毛管水上升高度比对照低0.0%~76.3%,毛管水平均上升速率比对照低7.3%~78.7%,蒸发强度比对照低10.7%~64.2%。玉米芯添加量≤40%时,吸水量比对照高8.6%~16.2%;玉米芯添加量>40%时,吸水量比对照低1.1%~46.0%。毛管水上升高度与时间之间呈幂函数关系,水分补给量与时间之间呈幂函数关系,水分补给量与毛管水上升高度之间呈线性相关。吸水条件下的Green-Ampt模型调整后可用于模拟混合土壤的毛管水上升过程。Rose蒸发模型能很好地表达混合土壤累计蒸发量随时间的变化特征。研究结果为沙化土地治理、秸秆还田改良耕地等研究与实践提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
丛文成, 袁立敏, 蒙仲举, 杨宇. 玉米芯颗粒对风沙土毛管水运移和蒸发特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 198-207.
Wencheng CONG, Limin YUAN, Zhongju MENG, Yu YANG. Effects of Corncob on Capillary Water Transport and Evaporation Characteristics of Sandy Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 198-207.
| 指标Index | 砂粒Grit | 粉粒Powder | 黏粒Cosmid |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粒径Grain size/mm | 2.000~0.020 | 0.020~0.002 | <0.002 |
| 占比Proportion/% | 25.8 | 61.2 | 13.0 |
表1 试供土壤粒级组成
Table 1 Grain size composition of the test soil
| 指标Index | 砂粒Grit | 粉粒Powder | 黏粒Cosmid |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粒径Grain size/mm | 2.000~0.020 | 0.020~0.002 | <0.002 |
| 占比Proportion/% | 25.8 | 61.2 | 13.0 |
玉米芯添加量 Corn cob added amount | 毛管水上升高度与时间的关系 Relationship between rising height of capillary water and time | R2 | 样本数 Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | H=7.868 80T0.206 88 | 0.94* | 3 |
| 10% | H=7.053 93T0.225 91 | 0.91* | 3 |
| 20% | H=7.919 02T0.205 57 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 30% | H=6.890 74T0.209 60 | 0.91* | 3 |
| 40% | H=7.028 60T0.194 38 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 50% | H=5.690 05T0.210 42 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 60% | H=6.364 99T0.171 10 | 0.87* | 3 |
| 70% | H=6.097 55T0.171 61 | 0.87* | 3 |
| 80% | H=5.513 96T0.161 13 | 0.88* | 3 |
| 90% | H=3.887 75T0.168 56 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 100% | H=1.823 35T0.213 24 | 0.91* | 3 |
表2 毛管水上升高度与时间的拟合结果
Table 2 Fitting result of capillary water rise height and time
玉米芯添加量 Corn cob added amount | 毛管水上升高度与时间的关系 Relationship between rising height of capillary water and time | R2 | 样本数 Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | H=7.868 80T0.206 88 | 0.94* | 3 |
| 10% | H=7.053 93T0.225 91 | 0.91* | 3 |
| 20% | H=7.919 02T0.205 57 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 30% | H=6.890 74T0.209 60 | 0.91* | 3 |
| 40% | H=7.028 60T0.194 38 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 50% | H=5.690 05T0.210 42 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 60% | H=6.364 99T0.171 10 | 0.87* | 3 |
| 70% | H=6.097 55T0.171 61 | 0.87* | 3 |
| 80% | H=5.513 96T0.161 13 | 0.88* | 3 |
| 90% | H=3.887 75T0.168 56 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 100% | H=1.823 35T0.213 24 | 0.91* | 3 |
玉米芯添加量 Corb cob added amount | 吸水量与时间的关系(Kostiakov模型) Water absorption versus time (Kostiakov model) | R2 | 样本数 Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | IK=60.572 74T0.206 92 | 0.95* | 3 |
| 10% | IK=53.465 94T0.256 14 | 0.92* | 3 |
| 20% | IK=72.829 45T0.205 63 | 0.94* | 3 |
| 30% | IK=66.128 84T0.209 65 | 0.91* | 3 |
| 40% | IK=72.371 95T0.194 43 | 0.93* | 3 |
| 50% | IK=60.295 21T0.210 47 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 60% | IK=75.088 38T0.171 15 | 0.93* | 3 |
| 70% | IK=73.151 39T0.171 66 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 80% | IK=74.421 43T0.161 17 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 90% | IK=58.302 75T0.168 60 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 100% | IK=31.898 56T0.213 30 | 0.91* | 3 |
表3 吸水量与时间的拟合结果
Table 3 Fitting results of water absorption and time
玉米芯添加量 Corb cob added amount | 吸水量与时间的关系(Kostiakov模型) Water absorption versus time (Kostiakov model) | R2 | 样本数 Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | IK=60.572 74T0.206 92 | 0.95* | 3 |
| 10% | IK=53.465 94T0.256 14 | 0.92* | 3 |
| 20% | IK=72.829 45T0.205 63 | 0.94* | 3 |
| 30% | IK=66.128 84T0.209 65 | 0.91* | 3 |
| 40% | IK=72.371 95T0.194 43 | 0.93* | 3 |
| 50% | IK=60.295 21T0.210 47 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 60% | IK=75.088 38T0.171 15 | 0.93* | 3 |
| 70% | IK=73.151 39T0.171 66 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 80% | IK=74.421 43T0.161 17 | 0.90* | 3 |
| 90% | IK=58.302 75T0.168 60 | 0.89* | 3 |
| 100% | IK=31.898 56T0.213 30 | 0.91* | 3 |
玉米芯添加量 Corn cob added amount | 毛管水上升高度/给水量 Capillary water rise/water feed | 吸水量与毛管水上升高度的关系 Relationship between water absorption and capillary water rise | 样本数 Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | I=7.698 2H | 3 | |
| 10% | I=8.695 7H | 3 | |
| 20% | I=9.199 6H | 3 | |
| 30% | I=9.596 9H | 3 | |
| 40% | I=10.298 7H | 3 | |
| 50% | I=10.593 2H | 3 | |
| 60% | I=11.792 5H | 3 | |
| 70% | I=11.961 7H | 3 | |
| 80% | I=13.495 3H | 3 | |
| 90% | I=14.992 5H | 3 | |
| 100% | I=17.482 5H | 3 |
表4 水补给量与毛管水上升高度的关系
Table 4 Relationship between water replenishment and capillary water rise
玉米芯添加量 Corn cob added amount | 毛管水上升高度/给水量 Capillary water rise/water feed | 吸水量与毛管水上升高度的关系 Relationship between water absorption and capillary water rise | 样本数 Number of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | I=7.698 2H | 3 | |
| 10% | I=8.695 7H | 3 | |
| 20% | I=9.199 6H | 3 | |
| 30% | I=9.596 9H | 3 | |
| 40% | I=10.298 7H | 3 | |
| 50% | I=10.593 2H | 3 | |
| 60% | I=11.792 5H | 3 | |
| 70% | I=11.961 7H | 3 | |
| 80% | I=13.495 3H | 3 | |
| 90% | I=14.992 5H | 3 | |
| 100% | I=17.482 5H | 3 |
| 指标Index | 玉米芯添加量 Corn cob added amount | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | 60% | 70% | 80% | 90% | 100% | |
| a | 57.89 | 96.52 | 88.39 | 88.65 | 59.17 | 51.58 | 45.34 | 47.67 | 28.65 | 51.86 | 34.84 |
| b | 24.42 | 9.53 | 7.48 | 1.93 | 3.00 | 3.93 | 2.75 | 3.75 | 6.12 | 1.95 | 8.42 |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
表5 Rose蒸发模型拟合参数
Table 5 Fitting parameters of Rose evaporation model
| 指标Index | 玉米芯添加量 Corn cob added amount | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | 60% | 70% | 80% | 90% | 100% | |
| a | 57.89 | 96.52 | 88.39 | 88.65 | 59.17 | 51.58 | 45.34 | 47.67 | 28.65 | 51.86 | 34.84 |
| b | 24.42 | 9.53 | 7.48 | 1.93 | 3.00 | 3.93 | 2.75 | 3.75 | 6.12 | 1.95 | 8.42 |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
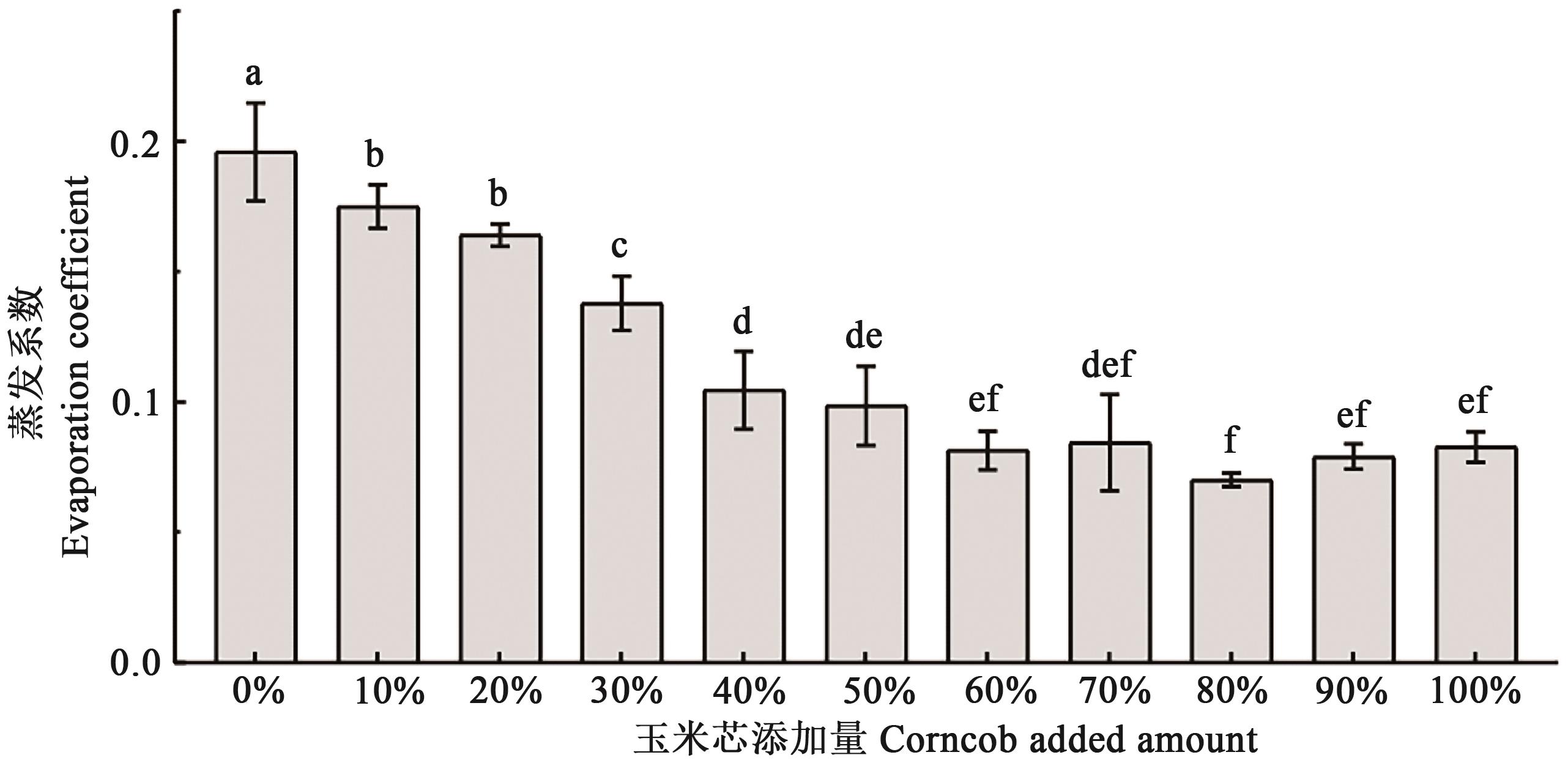
图7 不同玉米芯添加量下的蒸发系数注:不同字母表示组间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 7 Evaporation coefficient of different corn cob additionNote: Different letters indicate significant differences between groups at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 孙东宝. 北方旱作区作物产量和水肥利用特征与提升途径[D].北京:中国农业大学,2017. |
| SUN D B. Yield, water and nutrient use efficiency of dryland crops in northern China [D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 2 | 李新荣,赵洋,回嵘,等.中国干旱区恢复生态学研究进展及趋势评述[J].地理科学进展,2014,33(11):1435-1443. |
| LI X R, ZHAO Y, HUI R, et al.. Progress and trend of development of restoration ecology research in the arid regions of China [J]. Prog. Geogr., 2014,33(11):1435-1443. | |
| 3 | 杨彬如.生态文明视角下西北干旱区农业可持续发展研究[C]//2017中国环境科学学会科学与技术年会论文集(第三卷). 北京:中国环境科学学会,2017:780-786. |
| 4 | 陈盛,黄达,张力,等.秸秆还田对土壤理化性质及水肥状况影响的研究进展[J].灌溉排水学报,2022,41(6):1-11. |
| CHEN S, HUANG D, ZHANG L, et al.. The effects of straw incorporation on physicochemical properties of soil: a review [J]. J. Irr. Drain., 2022,41(6):1-11. | |
| 5 | 张奇,陈粲,陈效民,等.不同秸秆还田深度对黄棕壤土壤物理性质及其剖面变化的影响[J].土壤通报,2020,51(2):308-314. |
| ZHANG Q, CHEN C, CHEN X M, et al.. Effects of different depths of straw returning to field on soil physical properties and profile changes of yellow brown soil [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci.,2020,51(2):308-314. | |
| 6 | 高飞,贾志宽,路文涛,等. 秸秆不同还田量对宁南旱区土壤水分玉米生长及光合特性的影响[J].生态学报,2011,31(3):777-783. |
| GAO F, JIA Z K, LU W T, et al.. Effects of different straw returning treatments on soil water,maize growth and photosynthetic characteristics in the semi-arid area of Southern Ningxia [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2011,31(3):777-783. | |
| 7 | ZHANG P, WEI T, JIA Z K, et al.. Soil aggregate and crop yield changes with different rates of straw incorporation in semiarid areas of northwest China [J]. Geoderma, 2014,11(230~231):41-49. |
| 8 | 徐莹莹,王俊河,刘玉涛,等.秸秆不同还田方式对土壤物理性状、玉米产量的影响[J].玉米科学,2018,26(5):78-84. |
| XU Y Y, WANG J H, LIU Y T, et al.. Effects of different returning methods of straw on soil physical property, yield of corn [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2018,26(5):78-84. | |
| 9 | 杜璇.粉碎秸秆还田用量对土壤主要物理化学性状和作物生长的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2011. |
| DU X. The effect of crushed straw dosage on the main physical and chemical properties of soil and crop growth [D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2011. | |
| 10 | 李波,陈天助,姚名泽,等.东北半湿润地区深埋秸秆周围土壤水分的动态变化[J].灌溉排水学报,2016,35(9):51-55. |
| LI B, CHEN T Z, YAO M Z, et al.. Dynamic change of soil moisture around buried straw in the northeast semi-humid region [J]. J. Irr. Drain., 2016,35(9):51-55. | |
| 11 | 王婧,张莉,逄焕成,等.秸秆颗粒化还田加速腐解速率提高培肥效果[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(6):177-183. |
| WANG J, ZHANG L, PANG H C, et al.. Returning granulated straw for accelerating decomposition rate and improving soil fertility [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2017,33(6):177-183. | |
| 12 | 马南,陈智文,张清.不同类型秸秆还田对土壤有机碳及酶活性的影响综述[J].江苏农业科学,2021,49(3):53-57. |
| 13 | WU L, MA H, ZHAO Q, et al.. Changes in soil bacterial community and enzyme activity under five years straw returning in paddy soil [J/OL]. Eur. J. Soil Biol., 2020, 100: 103215 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 14 | 张淑梅.浅谈玉米秸秆粉碎还田技术[J].现代农业,2016(12):14-15. |
| 15 | 张银平,迟岩杰,王振伟,等.秸秆混土还田对两熟区玉米秸秆腐解速度的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(19):245-249. |
| 16 | 王红彦,张轩铭,王道龙,等.中国玉米芯资源量估算及其开发利用[J].中国农业资源与区划, 2016,37(1):1-8. |
| WANG H Y, ZHANG X M, WANG D L, et al.. Estimation and utilization of corncob resources in China [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Res. Region. Plan., 2016,37(1):1-8. | |
| 17 | QU Y, FENG B L. Straw mulching improved yield of field buckwheat (Fagopyrum) by increasing water-temperature use and soil carbon in rain-fed farmland [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2022,42(1):11-16. |
| 18 | MISAGH P, SHABANPOUR M, LUCAS-BORJA M E, et al.. Effects of length and application rate of rice straw mulch on surface runoff and soil loss under laboratory simulated rainfall [J]. Int. J. Sediment Res., 2021,36(4):468-478. |
| 19 | 申胜龙.不同覆盖方式与覆盖量对土壤水热氮利用及夏玉米生长发育的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2018. |
| SHEN S L. Effects of mulching method and amount on soil moisture, temperature, nitrate nitrogen and summer maize growth [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2018. | |
| 20 | CAO J S, LIU C M, ZHANG W J, et al.. Effect of integrating straw into agricultural soils on soil infiltration and evaporation [J]. Water Sci. Technol., 2012,65(12): 2213-2218. |
| 21 | 李鹏,潘英华,何福红,等.黄河三角洲湿地土壤毛管水运动特性研究[J].中国农业气象,2017,38(6):378-387. |
| LI P, PAN Y H, HE F H, et al.. Research on capillary water absorption characteristics of Yellow River delta wetland soil [J]. Chin. J. Agrometeorol., 2017,38(6):378-387. | |
| 22 | 尹娟,费良军,程东娟.均质土壤毛管水上升特性室内试验研究[J].农业工程学报,2007,23(6):91-94. |
| YIN J, FEI L J, CHENG D J. Laboratory experiment on characteristics of capillary water upward movement from homoge-neous soil [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng.,2007,23(6):91-94. | |
| 23 | 贾浩,李文昊,王振华,等.可降解膜覆盖对土壤水分蒸发特性的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2020,38(2):1-9. |
| JIA H, LI W H, WANG Z H, et al.. Effects of biodegradable mulching film on soil water evaporation characteristics [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas,2020,38(2):1-9. | |
| 24 | 汪言在,苏正安,周明华.北方农牧交错带表层土壤孔隙度特征及其影响因素[J].草业科学,2020,37(7):1249-1258. |
| WANG Y Z, SU Z A, ZHOU M H. Characteristics and influence of topsoil porosity in the northern agro-pastoral ecotone [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2020,37(7):1249-1258. | |
| 25 | HILLEL D. Environmental Soil Physics [M]. New York: Aca-demic Press, 1998:1-771. |
| 26 | 董荣泽.水质对沙土毛管水上升特性及滴灌土壤水盐运移的影响[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2018. |
| DONG R Z. An-investigation on capillary water upward movement in sand soil and the salt-water transport in drip irrigation under the influence of water quality [D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 27 | ZHANG P, HAO W U, YIN H J, et al.. Effect of constitution of soil on upward movement of capillary water [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2011, 18: 265-267. |
| 28 | 汪晓鹏.简介农业废弃物玉米芯的资源化和应用[J].西部皮革,2021,43(3):20-21. |
| 29 | 张金星,宋晓东,王荣耕,等.改性玉米芯作为吸水材料的探索研究[J].化工新型材料,2016,44(5):230-231. |
| ZHANG J X, SONG X D, WANG R G, et al.. Study on modified corncob used as an absorbent material [J]. New Chem. Materials, 2016,44(5):230-231. | |
| 30 | 詹舒婷,宋明丹,李正鹏,等.不同秸秆生物炭对土壤水分入渗和蒸发的影响[J].水土保持学报,2021,35(1):294-300. |
| ZHAN S T, SONG M D, LI Z P, et al.. Effects of different straw biochars on soil water infiltration and evaporation [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv.,2021,35(1):294-300. | |
| 31 | 肖茜,张洪培,沈玉芳,等.生物炭对黄土区土壤水分入渗、蒸发及硝态氮淋溶的影响[J].农业工程学报,2015,31(16):128-134. |
| XIAO Q, ZHANG H P, SHEN Y F, et al.. Effects of biochar on water infiltration, evaporation and nitrate leaching in semi-arid loess area [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2015,31(16):128-134. | |
| 32 | WANG T T, STEWART C E, SUN C C, et al.. Effects of biochar addition on evaporation in the five typical Loess Plateau soils [J]. Catena,2018,162:29-39. |
| 33 | ZHANG Y P, GU K, LI J W, et al.. Effect of biochar on desiccation cracking characteristics of clayey soils [J/OL]. Geoderma,2020,364:114182 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 34 | 许健,牛文全,张明智,等.生物炭对土壤水分蒸发的影响[J].应用生态学报,2016,27(11):3505-3513. |
| XU J, NIU W Q, ZHANG M Z, et al.. Effect of biochar addition on soil evaporation [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol.,2016,27(11):3505-3513. | |
| 35 | 王志强.秸秆混掺对土壤水盐运移的试验研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2021. |
| WANG Z Q. Experimental research on the effect of straw mixture on soil water and salt transport [D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang University, 2021. | |
| 36 | 周宏.基于多入渗模型的荒漠砂质土壤积水入渗模拟对比[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(1):123-134. |
| ZHOU H. A comparative study of ponded infiltration in a desert sandy soil based on multi-hydrological models [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2022,39(1):123-134. | |
| 37 | SIHAG P, TIWARI N K, RANJAN S. Modelling of infiltration of sandy soil using gaussian process regression [J]. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ.,2017, 3(3): 1091-1100. |
| 38 | ZOLFAGHARI A A, MIRZAEEL S, GORJI M. Comparison of different models for estimating cumulative infiltration [J]. Int. J. Soil Sci., 2012, 7(3): 108-115. |
| [1] | 何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [2] | 辛崇博,孜力汗,刘晨光,白凤武*. 响应面法优化玉米芯同步糖化发酵预处理条件[J]. , 2013, 15(5): 173-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 29
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 178
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号