




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 172-181.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0955
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
张然1( ), 高永1(
), 高永1( ), 梁钰镁1, 党晓宏2, 高苗苗1, 刘宏义3, 高雪琴3
), 梁钰镁1, 党晓宏2, 高苗苗1, 刘宏义3, 高雪琴3
收稿日期:2023-12-26
接受日期:2024-04-17
出版日期:2025-07-15
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
高永
作者简介:张然 E-mail:1327466705@qq.com;
基金资助:
Ran ZHANG1( ), Yong GAO1(
), Yong GAO1( ), Yumei LIANG1, Xiaohong DANG2, Miaomiao GAO1, Hongyi LIU3, Xueqin GAO3
), Yumei LIANG1, Xiaohong DANG2, Miaomiao GAO1, Hongyi LIU3, Xueqin GAO3
Received:2023-12-26
Accepted:2024-04-17
Online:2025-07-15
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Yong GAO
摘要:
为探究飞播30年后花棒、沙拐枣2种植物对结皮土壤颗粒组成和有机质的影响及其差异,明确植物生长过程中结皮土壤颗粒组成和有机质之间的关系,以腾格里沙漠东北缘飞播造林区为研究区,花棒、沙拐枣植株下结皮为研究对象,以无植物结皮为对照(CK),分析不同植株大小对不同位置结皮土壤颗粒组成和有机质含量的影响。结果表明,花棒、沙拐枣下结皮相较于CK细砂含量高、粗砂含量低;植株大小相同时,沙拐枣下结皮对细砂累积效应更明显。随着植株变大、距根部越近,结皮对细砂的保持效果越强。花棒、沙拐枣下结皮有机质含量均高于CK,且与植株大小呈正相关,花棒的结皮有机质含量整体高于沙拐枣。植株大小相同时,距根部0.5 m处的结皮有机质含量高于1.0 m处。2种植株的结皮有机质含量与细颗粒含量呈显著正相关,与粗颗粒含量呈极显著负相关。极细砂和极粗砂是二者结皮有机质积累与否的关键粒级。综上,在腾格里沙漠地区飞播30年后花棒对当地结皮有机质的积累效果更好,沙拐枣对结皮中细砂的保持效果更好。以上研究结果为干旱飞播区荒漠风蚀防治和恢复以及飞播选种配比提供理论基础和科学依据。
中图分类号:
张然, 高永, 梁钰镁, 党晓宏, 高苗苗, 刘宏义, 高雪琴. 两种飞播植物对结皮土壤颗粒组成和有机质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 172-181.
Ran ZHANG, Yong GAO, Yumei LIANG, Xiaohong DANG, Miaomiao GAO, Hongyi LIU, Xueqin GAO. Effects of Two Aerial Plants on Soil Particle Composition and Organic Matter in Crust Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 172-181.
植物 Plant | 植株大小 Plant size | 距离 Distance/m | 粒配组成Grain composition/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏粒 Clay | 粉粒 Silt | 极细砂 Very fine sand | 细砂 Fine sand | 中砂 Medium sand | 粗砂 Coarse sand | 极粗砂 Very coarse sand | |||
花棒 Hedysarum scoparium | 大株 Large plant | 0.5 | 0.72±0.32 | 9.73±4.53 | 7.07±4.32 | 29.23±3.44 | 19.21±5.97 | 25.34±4.48 | 8.68±4.13 |
| 1.0 | 0.83±0.13 | 11.16±1.89 | 6.80±2.07 | 29.85±7.50 | 18.62±4.48 | 24.48±5.90 | 8.23±4.01 | ||
中株 Medium plant | 0.5 | 0.68±0.16 | 9.83±2.07 | 6.33±2.82 | 32.18±11.29 | 17.86±5.99 | 24.94±7.83 | 8.15±5.89 | |
| 1.0 | 11.04±14.07 | 24.02±18.46 | 8.52±6.65 | 23.57±15.28 | 11.99±11.67 | 15.98±16.89 | 4.85±3.40 | ||
小株 Small plant | 0.5 | 0.66±0.32 | 10.42±4.82 | 7.52±5.13 | 35.94±9.75 | 17.20±8.34 | 20.00±8.48 | 8.23±5.76 | |
| 1.0 | 0.96±0.47 | 10.51±4.29 | 5.63±2.13 | 30.73±9.69 | 17.99±8.05 | 23.59±11.40 | 10.55±6.19 | ||
沙拐枣 Calligonum mongolicum | 大株 Large plant | 0.5 | 6.58±13.62 | 13.06±12.29 | 8.55±6.88 | 30.34±9.64 | 17.28±10.87 | 18.39±10.60 | 5.75±3.50 |
| 1.0 | 0.96±0.70 | 11.32±6.64 | 5.84±2.24 | 26.17±6.02 | 19.45±4.53 | 28.69±8.85 | 7.54±1.56 | ||
中株 Medium plant | 0.5 | 0.82±0.45 | 8.74±4.53 | 4.74±2.44 | 22.54±7.01 | 15.50±2.19 | 35.82±10.75 | 11.81±4.85 | |
| 1.0 | 1.29±0.90 | 10.54±3.39 | 6.61±3.33 | 31.83±12.47 | 13.22±5.64 | 22.92±8.35 | 13.55±9.46 | ||
小株 Small plant | 0.5 | 0.87±0.63 | 10.58±5.01 | 7.08±2.05 | 32.58±9.75 | 19.64±6.80 | 22.70±6.65 | 6.52±3.11 | |
| 1.0 | 1.99±3.42 | 9.15±6.24 | 6.20±4.09 | 28.87±17.39 | 16.76±13.21 | 13.38±9.95 | 3.72±3.52 | ||
| CK | 0.86±0.25 | 10.08±2.71 | 6.67±3.01 | 28.70±2.75 | 17.12±5.33 | 25.15±2.68 | 11.39±6.79 | ||
表1 2种飞播植物下结皮机械组成
Table 1 Mechanical composition of crusts under 2 different fly-seeded plants
植物 Plant | 植株大小 Plant size | 距离 Distance/m | 粒配组成Grain composition/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏粒 Clay | 粉粒 Silt | 极细砂 Very fine sand | 细砂 Fine sand | 中砂 Medium sand | 粗砂 Coarse sand | 极粗砂 Very coarse sand | |||
花棒 Hedysarum scoparium | 大株 Large plant | 0.5 | 0.72±0.32 | 9.73±4.53 | 7.07±4.32 | 29.23±3.44 | 19.21±5.97 | 25.34±4.48 | 8.68±4.13 |
| 1.0 | 0.83±0.13 | 11.16±1.89 | 6.80±2.07 | 29.85±7.50 | 18.62±4.48 | 24.48±5.90 | 8.23±4.01 | ||
中株 Medium plant | 0.5 | 0.68±0.16 | 9.83±2.07 | 6.33±2.82 | 32.18±11.29 | 17.86±5.99 | 24.94±7.83 | 8.15±5.89 | |
| 1.0 | 11.04±14.07 | 24.02±18.46 | 8.52±6.65 | 23.57±15.28 | 11.99±11.67 | 15.98±16.89 | 4.85±3.40 | ||
小株 Small plant | 0.5 | 0.66±0.32 | 10.42±4.82 | 7.52±5.13 | 35.94±9.75 | 17.20±8.34 | 20.00±8.48 | 8.23±5.76 | |
| 1.0 | 0.96±0.47 | 10.51±4.29 | 5.63±2.13 | 30.73±9.69 | 17.99±8.05 | 23.59±11.40 | 10.55±6.19 | ||
沙拐枣 Calligonum mongolicum | 大株 Large plant | 0.5 | 6.58±13.62 | 13.06±12.29 | 8.55±6.88 | 30.34±9.64 | 17.28±10.87 | 18.39±10.60 | 5.75±3.50 |
| 1.0 | 0.96±0.70 | 11.32±6.64 | 5.84±2.24 | 26.17±6.02 | 19.45±4.53 | 28.69±8.85 | 7.54±1.56 | ||
中株 Medium plant | 0.5 | 0.82±0.45 | 8.74±4.53 | 4.74±2.44 | 22.54±7.01 | 15.50±2.19 | 35.82±10.75 | 11.81±4.85 | |
| 1.0 | 1.29±0.90 | 10.54±3.39 | 6.61±3.33 | 31.83±12.47 | 13.22±5.64 | 22.92±8.35 | 13.55±9.46 | ||
小株 Small plant | 0.5 | 0.87±0.63 | 10.58±5.01 | 7.08±2.05 | 32.58±9.75 | 19.64±6.80 | 22.70±6.65 | 6.52±3.11 | |
| 1.0 | 1.99±3.42 | 9.15±6.24 | 6.20±4.09 | 28.87±17.39 | 16.76±13.21 | 13.38±9.95 | 3.72±3.52 | ||
| CK | 0.86±0.25 | 10.08±2.71 | 6.67±3.01 | 28.70±2.75 | 17.12±5.33 | 25.15±2.68 | 11.39±6.79 | ||
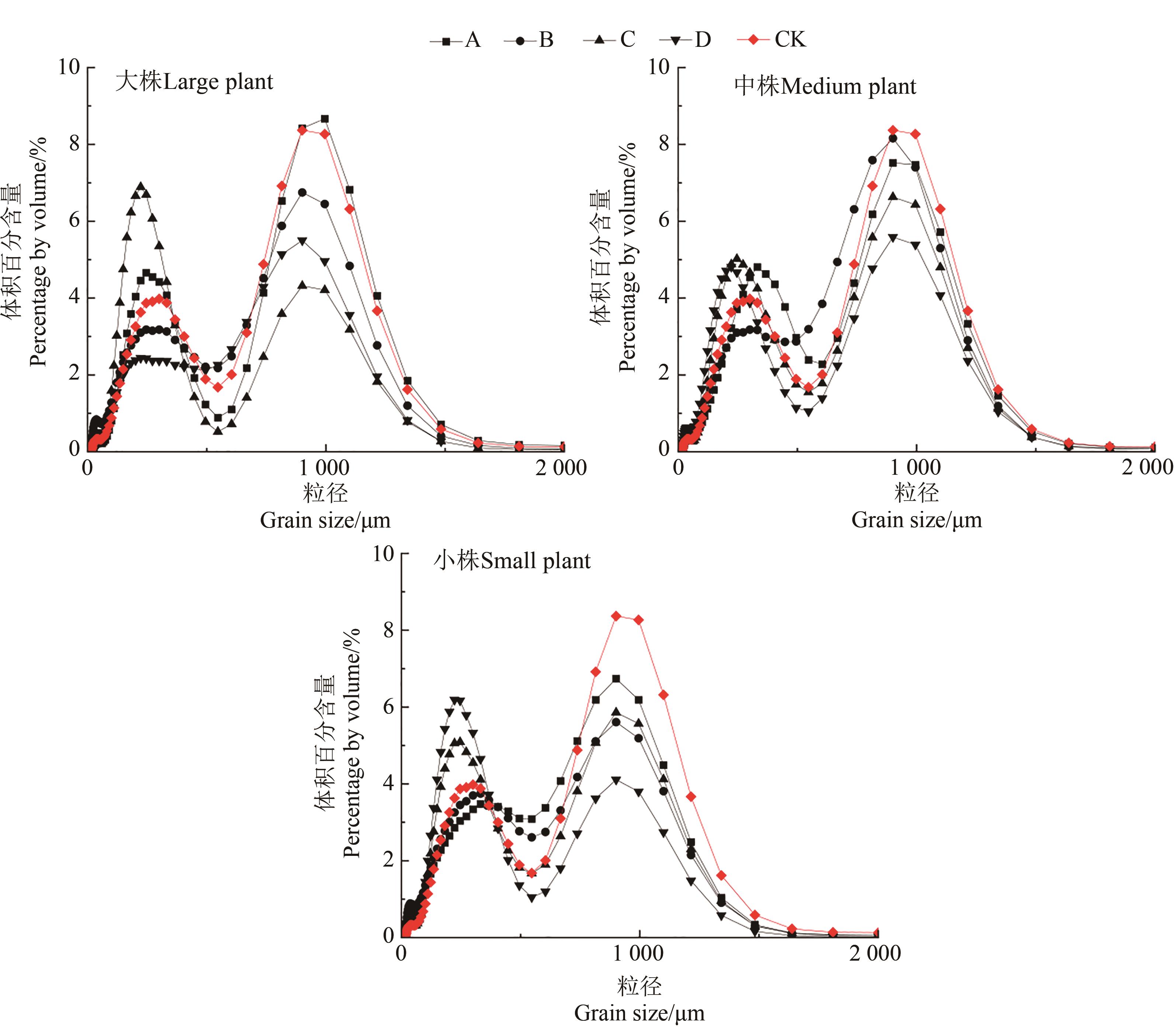
图2 不同大小飞播植物下结皮土壤颗粒频率分布曲线注:A—花棒下0.5 m处结皮;B—花棒下1.0 m处结皮;C—沙拐枣下0.5 m处结皮;D—沙拐枣下1.0 m处结皮。
Fig. 2 Frequency distribution curves of crusted particles under fly-seeded plants of different sizesNote:A—The crust 0.5 m below the Hedysarum scoparium; B—The crust 1.0 m below the Hedysarum scoparium; C —The crust 0.5 m below the Calligonum mongolicum;D—The crust 1.0 m below the Calligonum mongolicum.
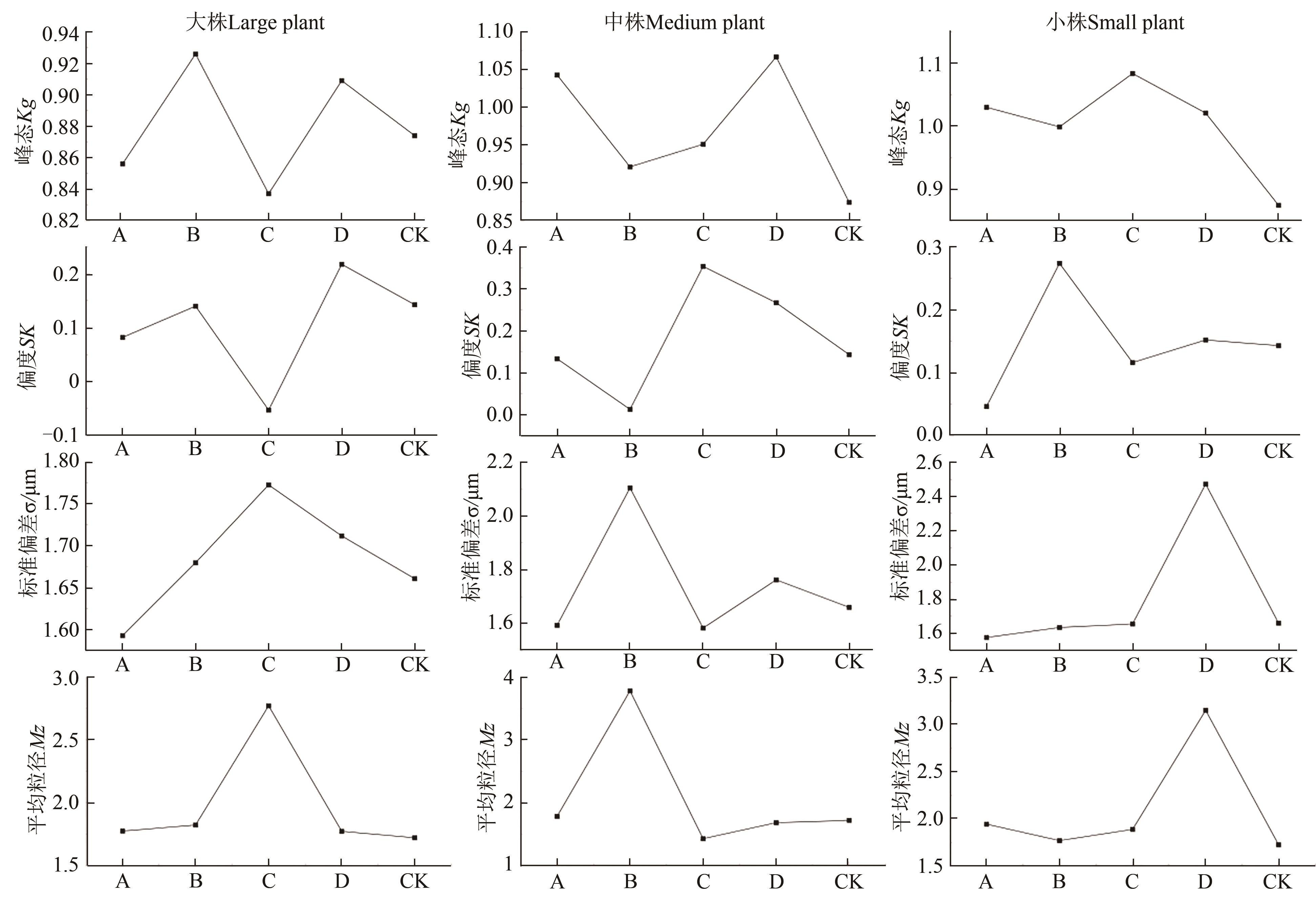
图3 两种飞播植物下结皮土壤粒度参数注:A—花棒下0.5 m处结皮;B—花棒下1.0 m处结皮;C—沙拐枣下0.5 m处结皮;D—沙拐枣下1.0 m处结皮。
Fig. 3 Crusting soil particle size parameters under different fly-seeded plantsNote:A—The crust 0.5 m below the Hedysarum scoparium; B—The crust 1.0 m below the Hedysarum scoparium; C —The crust 0.5 m below the Calligonum mongolicum;D—The crust 1.0 m below the Calligonum mongolicum.
距植株根部距离 Distance from plant root/m | 植株大小 Plant size | 有机质含量 Organic content/(g·kg-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
花棒 Hedysarum scoparium | 沙拐枣 Calligonum mongolicum | CK | ||
| 0.5 | 大株 Large plant | 15.38±1.99 αa | 12.95±2.79 αa | 8.30±1.23 β |
中株 Medium plant | 12.52±2.86 αab | 11.51±1.51 αa | 8.30±1.23 β | |
小株 Small plant | 10.71±1.65 αβb | 11.61±2.28 αa | 8.30±1.23 β | |
| 1.0 | 大株 Large plant | 12.37±1.49 αa | 11.96±1.02 αa | 8.30±1.23 β |
中株 Medium plant | 11.11±2.18 αab | 10.31±1.12 αβa | 8.30±1.23 β | |
小株 Small plant | 9.54±1.17 αb | 9.89±1.52 αa | 8.30±1.23 α | |
表2 2种飞播植物下结皮有机质含量
Table 2 Crusting organic matter content under different fly-seeded plants
距植株根部距离 Distance from plant root/m | 植株大小 Plant size | 有机质含量 Organic content/(g·kg-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
花棒 Hedysarum scoparium | 沙拐枣 Calligonum mongolicum | CK | ||
| 0.5 | 大株 Large plant | 15.38±1.99 αa | 12.95±2.79 αa | 8.30±1.23 β |
中株 Medium plant | 12.52±2.86 αab | 11.51±1.51 αa | 8.30±1.23 β | |
小株 Small plant | 10.71±1.65 αβb | 11.61±2.28 αa | 8.30±1.23 β | |
| 1.0 | 大株 Large plant | 12.37±1.49 αa | 11.96±1.02 αa | 8.30±1.23 β |
中株 Medium plant | 11.11±2.18 αab | 10.31±1.12 αβa | 8.30±1.23 β | |
小株 Small plant | 9.54±1.17 αb | 9.89±1.52 αa | 8.30±1.23 α | |
颗粒径级 Particle diameter grade | 花棒 Hedysarum scoparium | 沙拐枣 Calligonum mongolicum | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
大株 Large plant | 中株 Medium plant | 小株 Small plant | 大株 Large plant | 中株 Medium plant | 小株 Small plant | |
黏粒 Clay | 0.217 | 0.16 | 0.204 | 0.736* | 0.018 | -0.355 |
粉粒 Silt | 0.268 | 0.246 | 0.724* | 0.608 | -0.390 | 0.184 |
极细砂 Very fine sand | 0.454 | 0.584 | 0.852** | 0.753* | -0.373 | 0.293 |
| 细砂Fine sand | -0.137 | 0.063 | -0.103 | -0.379 | -0.294 | 0.047 |
中砂 Medium sand | -0.229 | -0.395 | -0.533 | -0.686* | 0.281 | 0.581 |
粗砂 Coarse sand | 0.026 | -0.378 | -0.045 | -0.547 | 0.441 | 0.289 |
极粗砂 Very coarse sand | -0.166 | -0.071 | -0.161 | -0.826** | -0.061 | -0.209 |
表3 2种飞播植物下结皮土壤颗粒组成与有机质相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of crustal particle size and organic matter under different fly-seeded plants
颗粒径级 Particle diameter grade | 花棒 Hedysarum scoparium | 沙拐枣 Calligonum mongolicum | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
大株 Large plant | 中株 Medium plant | 小株 Small plant | 大株 Large plant | 中株 Medium plant | 小株 Small plant | |
黏粒 Clay | 0.217 | 0.16 | 0.204 | 0.736* | 0.018 | -0.355 |
粉粒 Silt | 0.268 | 0.246 | 0.724* | 0.608 | -0.390 | 0.184 |
极细砂 Very fine sand | 0.454 | 0.584 | 0.852** | 0.753* | -0.373 | 0.293 |
| 细砂Fine sand | -0.137 | 0.063 | -0.103 | -0.379 | -0.294 | 0.047 |
中砂 Medium sand | -0.229 | -0.395 | -0.533 | -0.686* | 0.281 | 0.581 |
粗砂 Coarse sand | 0.026 | -0.378 | -0.045 | -0.547 | 0.441 | 0.289 |
极粗砂 Very coarse sand | -0.166 | -0.071 | -0.161 | -0.826** | -0.061 | -0.209 |
| [1] | 李新荣,谭会娟,回嵘,等.中国荒漠与沙地生物土壤结皮研究[J].科学通报,2018,63(23):2320-2334. |
| LI X R, TAN H J, HUI R, et al.. Researches in biological soil crust of China: a review [J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2018,63(23):2320-2334. | |
| [2] | 周虹,吴波,高莹,等.毛乌素沙地臭柏(Sabina vulgaris)群落生物土壤结皮细菌群落组成及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(5):130-141. |
| ZHOU H, WU B, GAO Y, et al.. Composition and influencing factors of the biological soil crust bacterial communities in the Sabina vulgaris community in Mu Us sandy land [J]. J. Desert Res., 2020,40(5):130-141. | |
| [3] | 姚宏佳,王宝荣,安韶山,等.黄土高原生物结皮形成过程中土壤胞外酶活性及其化学计量变化特征[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(2):456-468. |
| YAO H J, WANG B R, AN S S, et al.. Variation in soil extracellular enzyme activities stoichiometry during biological soil crust formation in the Loess Plateau [J].Arid Zone Res.,2022,39(2): 456-468. | |
| [4] | 李新荣,张志山,刘玉冰,等.长期生态学研究引领中国沙区的生态重建与恢复[J].中国科学院院刊,2017,32(7):790-797. |
| LI X R, ZHANG Z S, LIU Y B, et al.. Long-term ecological research leads the ecological reconstruction and restoration of sandy areas in China [J]. J. Chin. Acad. Sci., 2017,32(7):790-797. | |
| [5] | 郭琦,卜崇峰,李宜坪,等.区域尺度生物结皮下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征:以毛乌素沙地为例[J].土壤学报,2022,59(3):699-707. |
| GUO Q, BU C F, LI Y P, et al.. The spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrients underlying biological crusts at regional scale:a case study of mu us sandy land [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2022,59(3):699-707. | |
| [6] | 吴丽,张高科,陈晓国,等.生物结皮的发育演替与微生物生物量变化[J].环境科学,2014,35(4):1479-1485. |
| WU L, ZHANG G K, CHEN X G, et al.. Development and succession of biological soil crusts and the changes of microbial biomasses [J]. Environ. Sci., 2014,35(4):1479-1485. | |
| [7] | WEST N E. Structure and function of microphytic soil crusts in wildland ecosystems of arid to semi-arid regions [J]. Adv. Ecol.Res., 1990,20:179-223. |
| [8] | 杨军刚,张玲卫,郭星,等.古尔班通古特沙漠生物土壤结皮下土壤有机碳垂直分布特征及影响因素[J].生态学报,2024,44(7):2946-2954. |
| YANG J G, ZHANG L Y, GUO X, et al.. Vertical distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon under biological soil crusts in Gurbantunggut desert [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2024, 44(7):2946-2954. | |
| [9] | 凌裕泉,屈建军,胡玟. 沙面结皮形成与微环境变化[J].应用生态学报, 1993,4(4):393-398. |
| LING Y Q, QU J J, HU W. Crust formation on sand surface and micro-environment change [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 1993,4(4):393-398. | |
| [10] | 苏延桂,李新荣,张景光,等.生物土壤结皮对土壤种子库的影响[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(6):997-1001. |
| SU Y G, LI X R, ZHANG J G, et al.. Effects of biological soil crusts on seed bank [J]. J. Desert Res., 2006,26(6):997-1001. | |
| [11] | LI X R, ZHANG J G, WANG X P, et al.. Study on soil microbiotic crust andIts influences on sandfixing vegetationin arid desert region [J]. Acta Bot. Sin., 2000, 42(9): 965-970. |
| [12] | 李宜坪.毛乌素沙地生物结皮及其下伏土壤的养分特征与碳储量研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2018. |
| LI Y P. Study on nutrient characteristics and carbon storage of biological crust and its underlying soil in Mu Us sandy land [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2018. | |
| [13] | 邓佑.岷江上游干旱河谷坡地不同利用模式下土壤理化性质的比较研究[D].成都:成都理工大学,2010. |
| DENG Y. Comparative study on soil physical and chemical properties under different land use patterns in arid valley slope of the upper reaches of Minjiang river [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010. | |
| [14] | RODRÍGUEZ -CABALLERO E, CASTRO A J, CHAMIZO S, et al.. Ecosystem services provided by biocrusts: from ecosystem functions to social values [J]. J. Arid Environ., 2017,159(12):45-53. |
| [15] | THOMAS A D, DOUGILL A J. Distribution and characteristics of cyanobacterial soil crusts in the Molopo Basin, South Africa [J]. J. Arid Environ., 2006,64(2):270-283. |
| [16] | PRASSE R, BORNKAMM R. Effect ofmicrobiotic soil surface crusts on emergence ofvascular plants [J]. Plant Ecol., 2000, 150: 65-75. |
| [17] | 赵哈林,郭轶瑞,周瑞莲,等.人工林建设对沙地土壤结皮发育及其表土理化特性的影响[J].水土保持学报,2010,24(1):202-207. |
| ZHAO H L, GUO Y R, ZHOU R L, et al.. Effects of plantation establishment on soil crust development and physico-chemical properties of topsoil under crust [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv.,2010, 24(1):202-207. | |
| [18] | 杨巧云,赵允格,包天莉,等.黄土丘陵区不同类型生物结皮下的土壤生态化学计量特征[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(8):2699-2706. |
| YANG Q Y, ZHAO Y G, BAO T L, et al.. Soil ecological stoichiometry characteristics under different types of biological soil crusts in the hilly Loess Plateau Region, China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019,30(8):2699-2706. | |
| [19] | 齐雁冰,常庆瑞,惠泱河.高寒地区人工植被恢复过程中沙表生物结皮特性研究[J].干旱地区农业研究,2006,24(6):98-102. |
| QI Y B, CHANG Q R, HUI Y H. Effect of vegetation recovery on desertification sand-fixing in high frigid region [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2006,24(6):98-102. | |
| [20] | 闫德仁,薛英英,刘果厚.库布齐沙漠生物结皮层土壤理化特性的研究[J].土壤,2008,40(1):145-148. |
| YAN D R, XUE Y Y, LIU G H. Soil physical and chemical properties of bio-crust in kubuqi desert [J]. Soils, 2008,40(1):145-148. | |
| [21] | 陈萍,夏江宝,王善龙,等.黄河三角洲滨海滩涂不同密度柽柳林的土壤盐碱与养分特征[J].生态学报,2022,42(24):10180-10190. |
| CHEN P, XIA J B, WANG S L, et al.. Variations in soil salinity and nutrient contents of Tamarix chinensis with different densities on the beach of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2022,42(24):10180-10190. | |
| [22] | 高苗苗,蒙仲举,高永,等.腾格里沙漠东北缘飞播造林对植被多样性的影响[J].农业与技术,2022,42(19):69-73. |
| [23] | 高广磊,丁国栋,赵媛媛,等.生物结皮发育对毛乌素沙地土壤粒度特征的影响[J].农业机械学报,2014,45(1):115-120. |
| GAO G L, DING G D, ZHAO Y Y, et al.. Effects of biological soil crusts on soil particle size characteristics in Mu Us sandland [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2014,45(1):115-120. | |
| [24] | FOLK R L, WARD W C. Brazos River bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters [J]. J. Sed. Res., 1957,27(1):3-26. |
| [25] | 吴恙,陈江.重铬酸钾容量法测定土壤有机质——加热法研究[J].中国高新技术企业(中旬刊),2016(9):11-12. |
| [26] | 左小安,赵学勇,赵哈林,等.科尔沁沙质草地群落物种多样性、生产力与土壤特性的关系[J].环境科学,2007,28(5):945-951. |
| ZUO X A, ZHAO X Y, ZHAO H L, et al.. Changes of species diversity and productivity in relation to soil properties in sandy grassland in Horqin sand land [J]. Environ. Sci., 2007,28(5):945-951. | |
| [27] | 李玉强,赵哈林,移小勇,等.沙漠化过程中科尔沁沙地植物-土壤系统碳氮储量动态[J].环境科学,2006,27(4):635-640. |
| LI Y Q, ZHAO H L, YI X Y, et al.. Dynamics of carbon and nitrogen storages in plant-soil system during desertification process in Horqin sandy land [J]. Environ. Sci., 2006,27(4):635-640. | |
| [28] | 苏永中,赵哈林.持续放牧和围封对科尔沁退化沙地草地碳截存的影响[J]. 环境科学,2003,24(4):23-28. |
| SU Y Z, ZHAO H L. Influences of grazing and exclosure on carbon sequestration in degraded sandy grassland Inner Mongolia North, China [J]. Environ. Sci., 2003,24(4):23-28. | |
| [29] | 段争虎,刘新民,屈建军.沙坡头地区土壤结皮形成机理的研究[J].干旱区研究,1996,13(2):31-36. |
| DUAN Z H, LIU X M, QU J J. Study on formation mechanism of soil crust in the Shapotou area [J]. Arid Zone Res., 1996,13(2):31-36. | |
| [30] | 崔燕,吕贻忠,李保国.鄂尔多斯沙地土壤生物结皮的理化性质[J].土壤,2004,36(2):197-202. |
| CUI Y, LYU Y Z, LI B G. Physico-chemical properties of soil microbiotic crusts on Erdos plateau [J]. Soils, 2004,36(2):197-202. | |
| [31] | 闫德仁,季蒙,薛英英.沙漠生物结皮土壤发育特征的研究[J].土壤通报,2006,37(5):990-993. |
| YAN D R, JI M, XUE Y Y. Development characteristics of desert biological crust [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2006,37(5):990-993. | |
| [32] | 李卫红,任天瑞,周智彬,等.新疆古尔班通古特沙漠生物结皮的土壤理化性质分析[J].冰川冻土,2005,27(4):619-626. |
| LI W H, REN T R, ZHOU Z B, et al.. Study on the soil physicochemical characteristics of biological crusts on sand-dune surface in Gurbantünggtüt desert, Xinjiang region [J]. J. Glaciol. Geocryol., 2005,27(4):619-626. | |
| [33] | 张军红,徐义萍,王文鑫,等.毛马素沙地油蒿植冠下表层土壤粒径特征分析[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2018,38(6):36-40, 55. |
| ZHANG J H, XU Y P, WANG W X, et al.. Analysis of particle size characteristics of surface soil under Artemisia ordosica canopy in Mu Us sandy and [J]. J. Central South Univ. For. Technol., 2018,38(6):36-40, 55. | |
| [34] | 闫德仁.库布齐沙漠生物结皮层的肥岛特征研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2008. |
| YAN D R. Study on the characteristics of fertile island of biological crust in Kubuqi Desert [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2008. | |
| [35] | 卜崇峰,蔡强国,张兴昌,等.黄土结皮的发育机理与侵蚀效应研究[J].土壤学报,2009,46(1):16-23. |
| BU C F, CAI Q G, ZHANG X C, et al.. Mechanism and erosion effect of development of soil crust of loess [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin.,2009,46(1):16-23. | |
| [36] | 张桂华,刘洪妍,介冬梅,等.科尔沁沙地不同类型沙丘表土有机质与粒度特征差异分析[J].生态环境学报,2020,29(11):2223-2230. |
| ZHANG G H, LIU H Y, JIE D M, et al.. Difference analysis of organic matter and grain size characteristics of topsoil in different types of dunes in Horqin sandy land [J]. J. Ecol. Environ., 2020,29(11):2223-2230. |
| [1] | 王兴松, 王娜, 杜宇, 周鹏, 王戈, 贾孟, 徐照丽, 白羽祥. 有机肥对玉溪植烟土壤有机质组分和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 201-212. |
| [2] | 王世芳, 宋海燕. 土壤有机质可见-近红外反射光谱特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 183-188. |
| [3] | 张伟健, 冯景翊, 李悦, 何婉莹, 车延静, 王紫颖, 白雪燕, 谷思玉. 内-外源有机质对黑土磷素吸附及有效性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 180-190. |
| [4] | 蒯雁, 苏欣悦, 王晋峰, 范志勇, 李建华, 孙楠, 张久权, 徐明岗. 大理典型烟区土壤有机质与全氮时空演变特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 177-185. |
| [5] | 郭晗1,2,张序1*,陆洲2,田婷3,徐飞飞2,罗明2,吴正贵4,孙振军5. 基于机载高光谱影像的南方水稻土有机质含量估算[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 60-71. |
| [6] | 程介虹1,陈争光1*,张庆华2. 不同波长选择方法在土壤有机质含量检测中对比研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 162-170. |
| [7] | 朱茜1,林杰2*. 基于137Cs的苏南丘陵区的土壤侵蚀和土壤养分研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(8): 134-141. |
| [8] | 林李华,支胡钰. 蚕沙土壤调理剂对酸性土壤改良及豆角生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(4): 108-114. |
| [9] | 唐杰,王昌全*,李冰,曾建,李启权,徐强,李一丁,李珊. 川中丘陵区土壤有机质和碱解氮空间变异特征研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(6): 124-130. |
| [10] | 孙书斌1,于庆涛2,姚雪梅2,杨虹琦1*,刘光辉2,张保全3. 隆回植烟土壤有机质含量分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(6): 94-101. |
| [11] | 田稼1,孙超1,杨明琰2,张晓琦1*. 黄土高原不同苹果园土壤酶、有机质、微生物及树体产量品质的调查研究[J]. , 2012, 14(5): 115-122. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号