




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 148-156.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0679
收稿日期:2020-08-03
接受日期:2020-09-14
出版日期:2022-01-15
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
吴娜
作者简介:王志丹 E-mail:2513235089@qq.com;
基金资助:
Zhidan WANG( ), Jili LIU, Na WU(
), Jili LIU, Na WU( )
)
Received:2020-08-03
Accepted:2020-09-14
Online:2022-01-15
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Na WU
摘要:
为研究粉垄耕作对甜高粱光合生理特性及产量的影响,在宁夏银川市贺兰山农牧场,以BJ0603为供试品种,设置传统耕作(CK)、粉垄30 cm(FL30)、粉垄50 cm(FL50)和深翻40 cm(DT40)4种耕作方式,测定甜高粱农艺性状、产量及叶片光合生理指标。结果表明,相比CK和DT40处理,粉垄耕作(FL30和FL50)能显著提高甜高粱的茎节数、干物质量、糖含量和籽粒产量;相关分析表明,生物产量和籽粒产量均与株高、茎节数、干物质量、糖含量呈极显著正相关。粉垄耕作(FL30、FL50)下,甜高粱整个生育期各项光合生理指标都优于CK;在开花期和成熟期优于DT40处理。主成分分析显示,FL50、FL30、DT40、CK处理的综合值分别为0.20、0.11、-0.03、-0.14。由此表明,粉垄耕作有助于提高甜高粱的光合生理特性,为干旱、半干旱地区粉垄耕作技术的推广提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
王志丹, 刘吉利, 吴娜. 粉垄耕作对甜高粱光合生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 148-156.
Zhidan WANG, Jili LIU, Na WU. Effects of Fenlong Tillage on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics and Yield of Sweet Sorghum[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 148-156.
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/m | 茎粗 Stem stick/cm | 茎节数 Node number | 干物质量 Dry matter content/(t·hm-2) | 糖含量 Sugar content/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.25±0.04 b | 2.32±0.48.b | 12.5±1.2 c | 16.02±0.23 c | 5.07±0.09 c |
| FL30 | 3.28±0.07 a | 2.15±0.37 c | 14.8±1.6 a | 18.32±0.71 b | 7.52±0.11 a |
| FL50 | 3.37±0.05 a | 2.39±0.29 a | 15.6±1.9 a | 21.63±0.15 a | 7.92±0.21 a |
| DT40 | 3.33±0.06 a | 2.17±0.41 c | 13.9±1.4 b | 19.35±0.31 b | 6.47±0.19 b |
表1 不同耕作方式下甜高粱的农艺性状
Table 1 Agronomic traits of sweet sorghum under different tillage modes
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/m | 茎粗 Stem stick/cm | 茎节数 Node number | 干物质量 Dry matter content/(t·hm-2) | 糖含量 Sugar content/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.25±0.04 b | 2.32±0.48.b | 12.5±1.2 c | 16.02±0.23 c | 5.07±0.09 c |
| FL30 | 3.28±0.07 a | 2.15±0.37 c | 14.8±1.6 a | 18.32±0.71 b | 7.52±0.11 a |
| FL50 | 3.37±0.05 a | 2.39±0.29 a | 15.6±1.9 a | 21.63±0.15 a | 7.92±0.21 a |
| DT40 | 3.33±0.06 a | 2.17±0.41 c | 13.9±1.4 b | 19.35±0.31 b | 6.47±0.19 b |
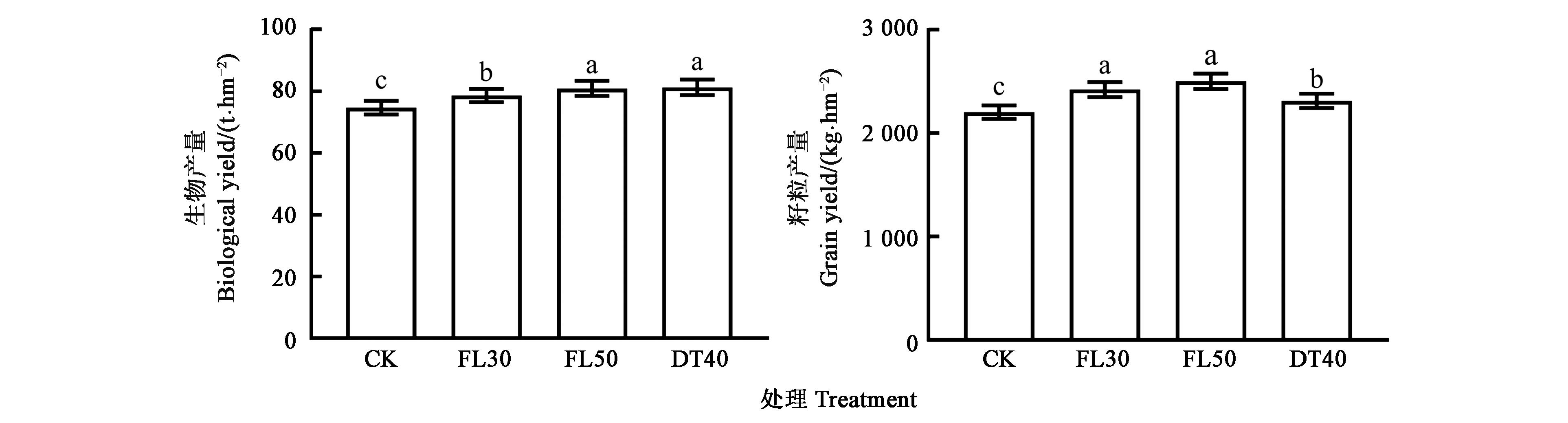
图1 不同耕作方式下甜高粱的产量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性。
Fig.1 Yield of sweet sorghum under different tillage modesNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 株高 Plant height | 茎粗 Stem stick | 茎节数 Node number | 干物质含量 Dry matter content | 糖含量 Sugar content | 籽粒产量 Grain yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎粗Stem stick | -0.357 | |||||
| 茎节数Node number | 0.866** | -0.002 | ||||
| 干物质含量Dry matter content | 0.848** | 0.182 | 0.884** | |||
| 糖含量Sugar content | 0.498** | 0.000 | 0.939** | 0.830** | ||
| 籽粒产量Grain yield | 0.812** | 0.063 | 0.992** | 0.862** | 0.942** | |
| 生物产量Biological yield | 0.946** | -0.212 | 0.755** | 0.839** | 0.691** | 0.691** |
表2 甜高粱农艺性状及产量的相关分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of agronomic characters and yield of sweet sorghum
| 株高 Plant height | 茎粗 Stem stick | 茎节数 Node number | 干物质含量 Dry matter content | 糖含量 Sugar content | 籽粒产量 Grain yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎粗Stem stick | -0.357 | |||||
| 茎节数Node number | 0.866** | -0.002 | ||||
| 干物质含量Dry matter content | 0.848** | 0.182 | 0.884** | |||
| 糖含量Sugar content | 0.498** | 0.000 | 0.939** | 0.830** | ||
| 籽粒产量Grain yield | 0.812** | 0.063 | 0.992** | 0.862** | 0.942** | |
| 生物产量Biological yield | 0.946** | -0.212 | 0.755** | 0.839** | 0.691** | 0.691** |
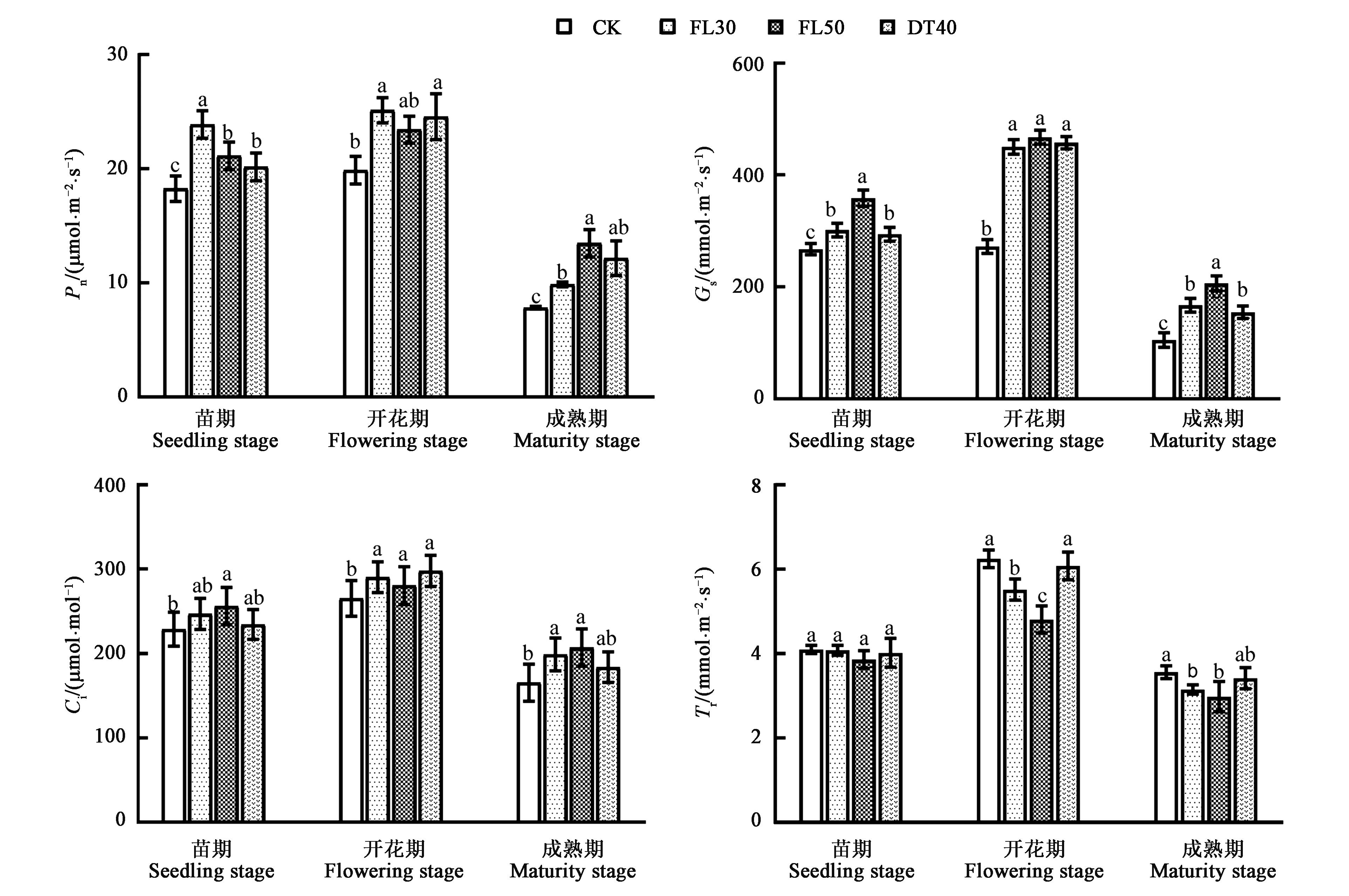
图2 不同耕作方式下甜高粱叶片的光合参数注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性。
Fig.2 Photosynthetic parameters of sweet sorghum under different tillage modesNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
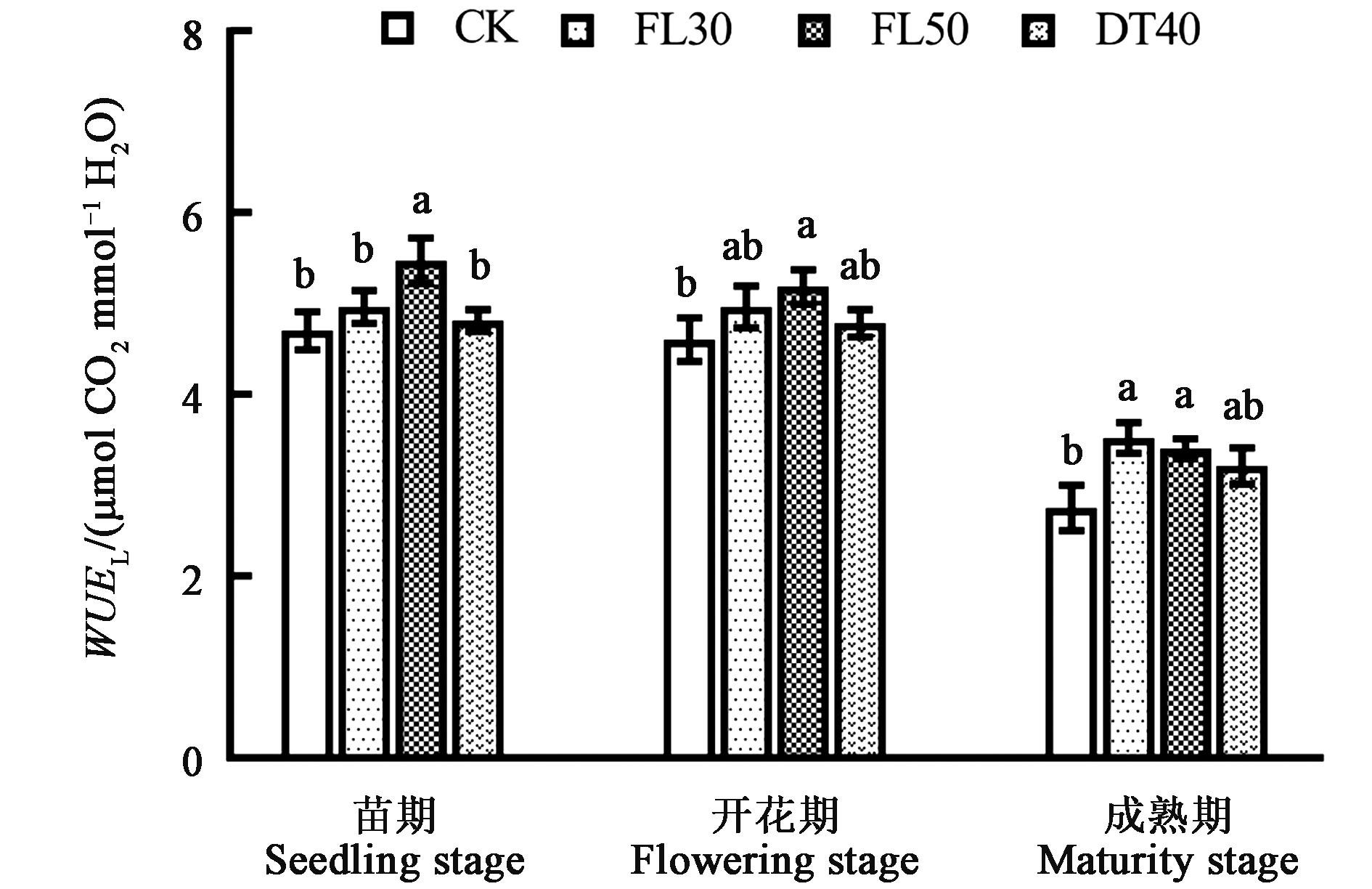
图3 不同耕作方式下甜高粱的叶片水平水分利用效率注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性。
Fig.3 Leaf water use efficiency (WUEL) of sweet sorghum under different tillage modesNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
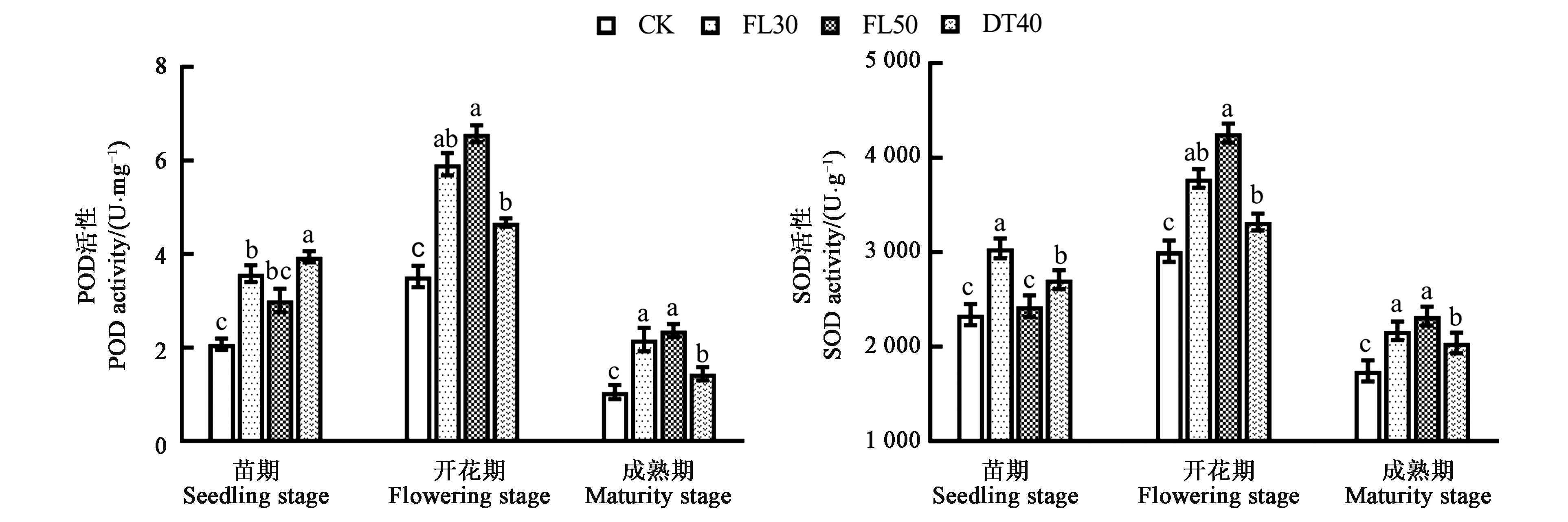
图4 不同耕作方式下甜高粱叶片的POD和SOD活性注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig.4 Activity of POD and SOD in leaf of sweet sorghum under different tillage modesNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
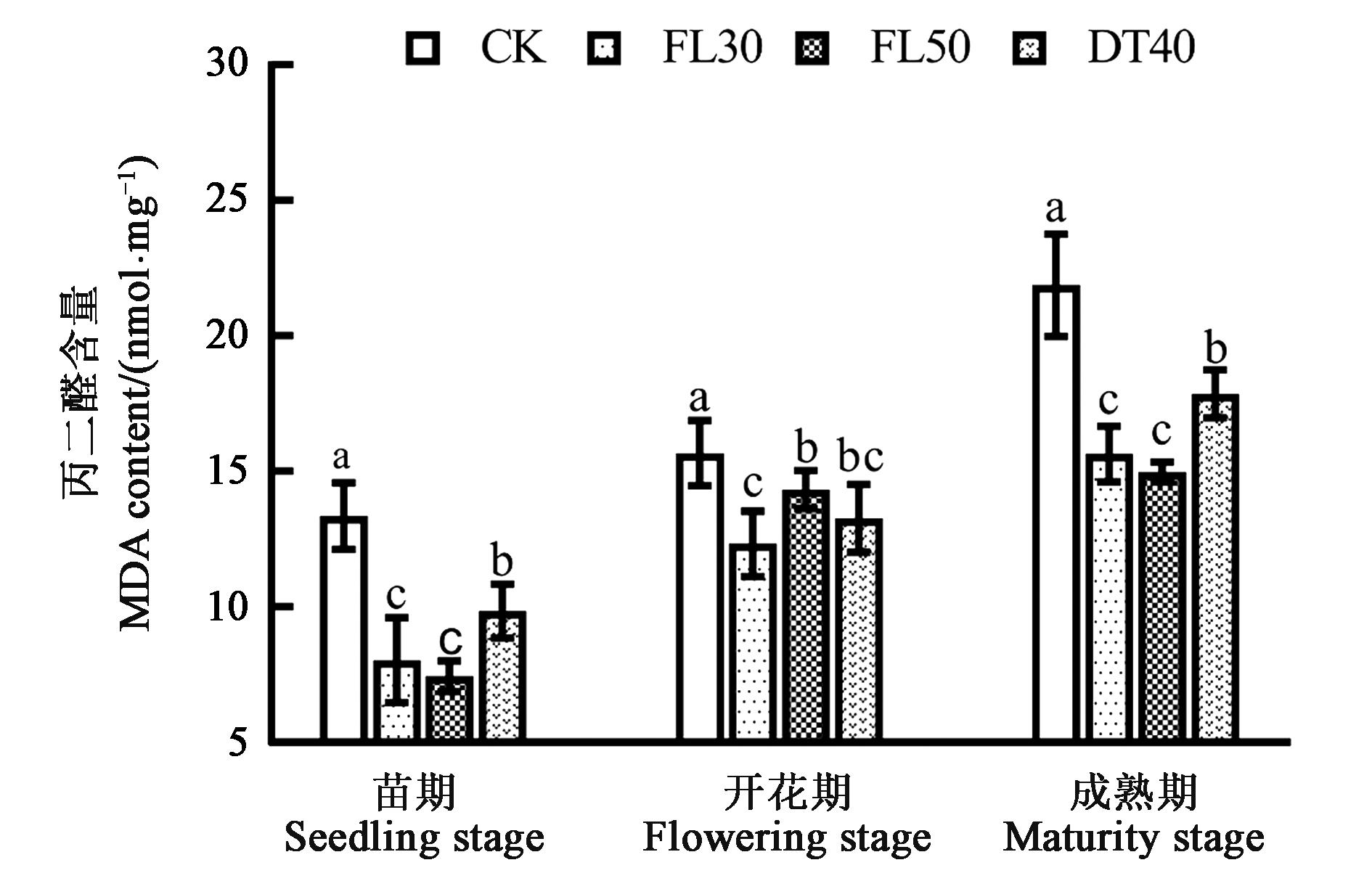
图5 不同耕作方式下甜高粱的丙二醛含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig.5 MDA content in sweet sorghum under different tillage modesNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
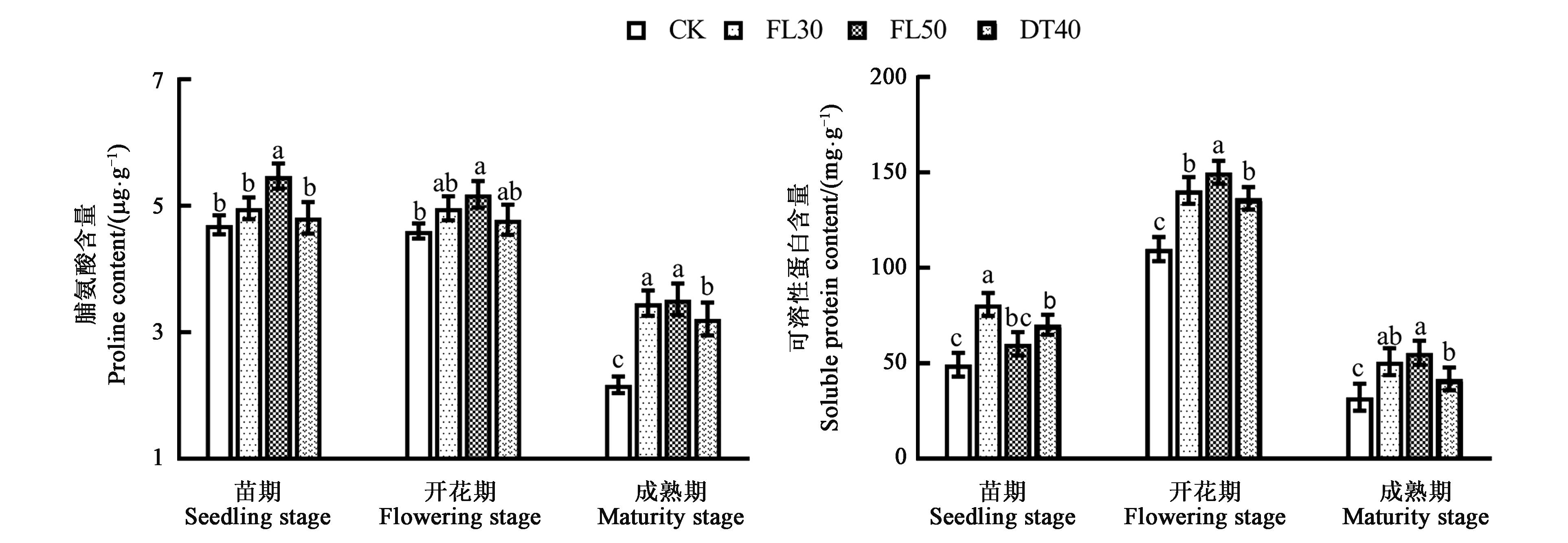
图6 不同耕作方式下甜高粱叶片的脯氨酸和可溶性蛋白含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig.6 Content of proline and soluble protein in leaf of sweet sorghum under different tillage modesNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigen value | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.30 | 83.02 | 83.02 |
| 2 | 1.26 | 12.61 | 95.64 |
表3 甜高粱光合生理指标主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis of photosynthetic physiological index of sweet sorghum
| 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigen value | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.30 | 83.02 | 83.02 |
| 2 | 1.26 | 12.61 | 95.64 |
| 处理Treatment | PC1 | PC2 | 综合值Comprehensive value | 排名Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.06 | -1.09 | -0.14 | 4 |
| FL30 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.11 | 2 |
| FL50 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.20 | 1 |
| DT40 | -1.43 | 0.35 | -0.03 | 3 |
表4 各处理下甜高粱各主成分值与综合排名
Table 4 Principal component value and comprehensive ranking of sweet sorghum under each treatment
| 处理Treatment | PC1 | PC2 | 综合值Comprehensive value | 排名Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.06 | -1.09 | -0.14 | 4 |
| FL30 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.11 | 2 |
| FL50 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.20 | 1 |
| DT40 | -1.43 | 0.35 | -0.03 | 3 |
| 1 | WORLEY J W, CUNDIFF J S, VAUGHAN, D H, et al.. Influence of sweet sorghum spacing on stalk pith yield [J]. Biores. Technol., 1991, 36(21):133-139. |
| 2 | 闫鸿雁,付立中,胡国宏,等.国内外甜高梁研究现状及应用前景分析[J].吉林农业科学,2006,31(5):63-65. |
| 3 | NAKATSU S, HIGASHIDA S, SAWAZAKI A. Easy estimation method for plow pan and effect of improved pan-breaking [J]. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2004, 75(2):265-268. |
| 4 | ZHANG X Y, SHAO L W, SUN H Y, et al.. Incorporation of soil bulk density in simulating root distribution of winter wheat and maize in two contrasting soils [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2012, 76(2):638-647. |
| 5 | 聂胜委,张玉亭,汤丰收,等.粉垄耕作对潮土冬小麦生长及产量的影响初探[J].河南农业科学,2015,44(2):19-21. |
| NIE S W, ZHANG Y T, TANG F S, et al.. Effects of smashing ridge tillage on growth and yield of winter wheat in fluvo-aquic soil region [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2015, 44(2):19-21. | |
| 6 | 韦本辉,甘秀芹,申章佑,等.粉垄栽培甘蔗试验增产效果[J].中国农业科学,2011,44(21):4544-4550. |
| WEI B H, GAN X Q, SHEN Z R, et al.. Yield increase of smash-ridging cultivation of sugarcane [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2011, 44(21):4544-4550. | |
| 7 | 韦本辉,甘秀芹,陈耀福,等.稻田粉垄冬种马铃薯试验[J].中国马铃薯,2011,25(6):342-344. |
| WEI B H, GAN X Q, CHEN Y F, et al.. Planting winter potato in rice field by using smash-ridging technique [J]. Chin. Potato J., 2011, 25(6):342-344. | |
| 8 | 靳晓敏,杜军,沈润泽,等.宁夏引黄灌区粉垄栽培对玉米生长和产量的影响[J].农业科学研究,2013,34(1):50-53. |
| JIN X M, DU J, SHEN R Z, et al.. The effection of sumash-ridging cultivation technology on the growth and yield of corn in yellow river irrigation district of Ningxia [J]. J. Agric. Sci., 2013, 34(1):50-53. | |
| 9 | 甘秀芹,韦本辉,申章佑,等.桑树粉垄栽培的根系、植株及产量性状表现[J].浙江农业科学,2011(3):705-707. |
| GAN X Q, WEI B H, SHEN Z R, et al.. Roots, plants and yield of mulberry by smash-ridging cultivation [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2011(3):705-707. | |
| 10 | 甘秀芹,韦本辉,刘斌,等.粉垄后第6季稻田土壤变化与水稻产量品质分析[J].南方农业学报,2014,45(9):1603-1607. |
| GAN X Q, WEI B H, LIU B, et al.. Effects of smash-ridging cultivation on soil properties, yield and quality of the sixth season of rice [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2014, 45(9):1603-1607. | |
| 11 | 刘波,吴礼树,鲁剑巍,等.不同耕作方式对土壤理化性质影响研究进展[J].耕作与栽培,2010(2):55-58,65. |
| 12 | 吕婧娴,陈占飞,田帅,等.榆林市风沙草滩区粉垄耕作对玉米根系及产量的影响[J].现代农业科技,2017,(2):5-7. |
| 13 | 唐茂艳,王强,陈雷,等.水稻粉垄耕作生长及生理特性研究[J].湖北农业科学,2015,54(16):3854-3856. |
| TANG M Y, WANG Q, CHEN L, et al.. On the growth and physiological characteristics of rice under smashing ridge tillage [J]. Hubei Agric. Sci., 2015, 54(16):3854-3856. | |
| 14 | 聂胜委,张玉亭,汤宁,等.粉垄耕作后效对夏玉米生长及产量的影响[J].山西农业科学,2015,43(7):837-839,873. |
| NIE S W, ZHANG Y T, TANG N, et al.. Effects of effect of tillage on growth and yield of summer corn [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2015,43(7):837-839,873. | |
| 15 | 韦本辉,申章佑,甘秀芹,等.粉垄栽培对旱地作物产量品质的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2012,14(4):101-105. |
| WEI B H, SHEN Z Y, GAN X Q, et al.. Effects of powder ridge cultivation on yield quality of dry land crops [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2012, 14(4):101-105. | |
| 16 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:184-261. |
| 17 | 韦本辉.旱地作物粉垄栽培技术研究简报[J].中国农业科学, 2010, 43(20):4330. |
| 18 | 赖洪敏,林北森,罗刚.粉垄耕作对烤烟生长发育的影响[J].浙江农业科学,2017,58(5):736-738. |
| 19 | 王奇,陈培赛,周佳,等.粉垄耕作对甘蔗农艺性状及产量的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2019,47(4):65-68. |
| 20 | 韦本辉,甘秀芹,陈保善,等.粉垄整地与传统整地方式种植玉米和花生效果比较[J].安徽农业科学,2011,39(6):3216-3219. |
| WEI B H, GAN X Q, CHEN B S, et al.. Comparison of the cultivation of maize and peanuts by smash-riding and traditional land preparation methods [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2011, 39(6):3216-3219. | |
| 21 | 邹剑秋,宋仁本,卢庆善,等.新型绿色可再生能源作物——甜高粱及其育种策略[J].杂粮作物,2003,23(3):134-135. |
| ZOU J Q, SONG E B, LU Q S, et al.. A new green renewable energy crop—sweet sorghum and its breeding tactics [J]. Rain Fed Crops, 2003, 23(3):134-135. | |
| 22 | 陈仕林,胡钧铭,黄忠华,等.粉垄耕作对平地和坡耕地蔗田土壤有机碳矿化和结构的影响[J].中国农业气象,2020,41(5):299-307. |
| CHEN S L, HU J M, HUANG Z H, et al.. Effects of smash ridging on soil organic carbon mineralization and structure of sugarcane field in flat and slope farmland [J].Chin. J. Agrometeorol., 2020, 41(5):299-307. | |
| 23 | 韦本辉.中国粉垄活土增粮生态[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2013:86-87. |
| 24 | 李华,逄焕成,任天志,等.深旋松耕作法对东北棕壤物理性状及春玉米生长的影响[J].中国农业科学,2013,46(3):647-656. |
| LI H, FENG H C, REN T Z, et al.. Effects of deep rotary-subsoiling tillage method on brown physical properties and maize growth in northeast of China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2013, 46(3):647-656. |
| [1] | 王健, 许爱玲, 卫晓东, 席吉龙, 杨娜, 王珂, 席天元, 张建诚. 运城盆地不同播期小麦春季冻害风险评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 137-147. |
| [2] | 苏煜, 黄劭理. 增施生物有机肥对烤烟光合特性及根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 164-171. |
| [3] | 黄渝岚§, 龙盛风§, 叶兴枝, 李艳英, 申章佑, 周佳, 周灵芝, 劳承英, 韦本辉. 木薯在湖北恩施的农艺性状及产量品质研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 46-55. |
| [4] | 孙梦遥, 徐岚俊, 李小龙, 李传友, 陈华, 张传帅, 刘婞韬. 不同节水方式对油菜水分利用、分配及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 138-143. |
| [5] | 李生梅, 张大伟, 迪丽拜尔·迪力买买提, 魏鑫, 芮存, 杨涛, 耿世伟, 高文伟. 减量灌溉对转ScALDH21基因棉花农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 152-159. |
| [6] | 李成晨, 索海翠, 罗焕明, 安康, 刘计涛, 王丽, 单建伟, 杨少海, 李小波. 化肥减施和施肥方式对马铃薯产量和块茎氮素积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 173-182. |
| [7] | 蒲全明, 杨鹏, 雍磊, 邓榆川, 何自涵, 林邦民, 施松梅, 向承勇, 方芳. 萝卜紫红叶色突变体的色素含量及光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 45-54. |
| [8] | 吴子帅, 李虎, 黄秋要, 陈传华, 罗群昌, 周新明, 吴佳桔, 刘广林. 施氮量和栽插密度对桂育11号产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 154-162. |
| [9] | 翁文安, 程爽, 李绍平, 田晋钰, 陶钰, 胡群, 胡雅杰, 郭保卫, 魏海燕, 邢志鹏, 张洪程. 氮肥一次性基施对不同成穗方式下直播常规粳稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 163-172. |
| [10] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 陈如冰, 李俐俐. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| [11] | 坚天才, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 刘根红, 高娣, 马雪莹, 李鑫. 氮素缓解春小麦花后高温早衰的抗氧化特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 33-44. |
| [12] | 张胜珍, 马艳芝. 氯化钙对盐胁迫下荆芥种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 65-71. |
| [13] | 周旋, 康兴蓉, 彭建伟, 杨相东, 钟雪梅, 胡文峰, 龙俊佑. 聚氨酯包膜氮肥减施对双季早稻生长、产量及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 153-161. |
| [14] | 罗友谊, 王慰亲, 郑华斌, 刘功义, 巢英, 徐彩, 郑志刚, 李雪倩, 韦银兰, 唐启源. 不同机械有序种植方式对水稻生长特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 162-171. |
| [15] | 于显枫, 张绪成, 缪平贵, 方彦杰, 马一凡, 王红丽, 侯慧芝. 深施肥对立式深旋耕马铃薯水分利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 182-190. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号