




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 48-56.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0599
秦宁1( ), 李俊茹1, 田蕊1, 邵振启1, 李喜焕1(
), 李俊茹1, 田蕊1, 邵振启1, 李喜焕1( ), 张彩英2(
), 张彩英2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-21
接受日期:2021-09-22
出版日期:2022-03-15
发布日期:2022-03-14
通讯作者:
李喜焕,张彩英
作者简介:秦宁 E-mail: 1362822834@qq.com
基金资助:
Ning QIN1( ), Junru LI1, Rui TIAN1, Zhenqi SHAO1, Xihuan LI1(
), Junru LI1, Rui TIAN1, Zhenqi SHAO1, Xihuan LI1( ), Caiying ZHANG2(
), Caiying ZHANG2( )
)
Received:2021-07-21
Accepted:2021-09-22
Online:2022-03-15
Published:2022-03-14
Contact:
Xihuan LI,Caiying ZHANG
摘要:
生育酚具有抗氧化、防止人体动脉硬化和心血管疾病等多种功效,在大豆籽粒中含量丰富,但有关其遗传位点与基因发掘工作开展甚少。鉴于此,利用大豆重组自交系群体,通过高效液相色谱鉴定其籽粒生育酚,结合群体SNP连锁图谱与转录组数据,发掘其遗传位点并筛选候选基因。结果表明,供试群体籽粒生育酚存在较大遗传变异,α-、γ-、δ-生育酚及总生育酚含量变异系数分布在9.24%~36.62%之间,各组分占比的变异系数分布在5.05%~35.59%之间;发掘到7个控制生育酚及其组分一因多效QTLs,表型贡献率范围3.08%~21.92%,其中8号染色体qTOC?A2可同时控制α-、δ-和总生育酚含量以及α-生育酚占比和γ-生育酚占比,表型贡献率范围3.85%~6.77%;5号染色体qTOC?A1可同时控制α-生育酚及其占比、γ-生育酚及其占比以及总生育酚含量,表型贡献率范围6.34%~21.92%;筛选到Glyma.12G014200、Glyma.12G014300和Glyma.18G141100等参与大豆生育酚合成代谢候选基因,为进一步开展生育酚分子遗传改良与遗传机制解析提供了选择标记及基因。
中图分类号:
秦宁, 李俊茹, 田蕊, 邵振启, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆籽粒生育酚遗传位点发掘及候选基因筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 48-56.
Ning QIN, Junru LI, Rui TIAN, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Mining of Genetic Loci and Screening of Candidate Genes for Seed Tocopherol Content in Soybean[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 48-56.
项目 Item | 均值 Mean | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV/% | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 偏度 Skew | 峰度 Kurt | 显著性(P值) Sig. (P value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
α-生育酚 α-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 7.10 | 2.60 | 36.62 | 15.48 | 0.91 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 2.54×10‒10 |
γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 127.86 | 12.19 | 9.53 | 165.23 | 97.34 | 0.33 | -0.17 | 2.50×10‒10 |
δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 65.65 | 9.21 | 14.03 | 90.58 | 39.13 | -0.06 | -0.16 | 2.34×10‒10 |
总生育酚 Total-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 200.61 | 18.53 | 9.24 | 253.90 | 149.13 | 0.04 | -0.12 | 1.67×10‒10 |
α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion/% | 3.54 | 1.26 | 35.59 | 7.62 | 0.56 | 0.34 | -0.04 | 3.23×10‒10 |
γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion/% | 63.80 | 3.22 | 5.05 | 74.47 | 54.54 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 2.78×10‒10 |
δ-生育酚占比 δ-tocopherol proportion/% | 32.66 | 2.84 | 8.70 | 40.55 | 24.32 | -0.07 | 0.09 | 2.52×10‒10 |
表1 供试大豆RIL群体籽粒生育酚及其组分遗传变异
Table 1 Genetic variations of seed tocopherol and its components in RIL population
项目 Item | 均值 Mean | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV/% | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 偏度 Skew | 峰度 Kurt | 显著性(P值) Sig. (P value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
α-生育酚 α-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 7.10 | 2.60 | 36.62 | 15.48 | 0.91 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 2.54×10‒10 |
γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 127.86 | 12.19 | 9.53 | 165.23 | 97.34 | 0.33 | -0.17 | 2.50×10‒10 |
δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 65.65 | 9.21 | 14.03 | 90.58 | 39.13 | -0.06 | -0.16 | 2.34×10‒10 |
总生育酚 Total-tocopherol/(μg·g‒1) | 200.61 | 18.53 | 9.24 | 253.90 | 149.13 | 0.04 | -0.12 | 1.67×10‒10 |
α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion/% | 3.54 | 1.26 | 35.59 | 7.62 | 0.56 | 0.34 | -0.04 | 3.23×10‒10 |
γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion/% | 63.80 | 3.22 | 5.05 | 74.47 | 54.54 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 2.78×10‒10 |
δ-生育酚占比 δ-tocopherol proportion/% | 32.66 | 2.84 | 8.70 | 40.55 | 24.32 | -0.07 | 0.09 | 2.52×10‒10 |
项目 Item | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 总生育酚 Total-tocopherol | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | ‒0.018 | |||||
δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 0.256** | 0.410** | ||||
总生育酚 Total-tocopherol | 0.256** | 0.859** | 0.803** | |||
α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 0.966** | ‒0.237** | 0.064 | 0.011 | ||
γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | ‒0.515** | 0.298** | ‒0.713** | ‒0.231** | ‒0.479** | |
δ-生育酚占比 δ-tocopherol proportion | 0.154** | ‒0.233** | 0.780** | 0.256** | 0.098 | ‒0.921** |
表2 供试大豆RIL群体籽粒生育酚及各组分相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients of tocopherol and its components in RIL population
项目 Item | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 总生育酚 Total-tocopherol | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | ‒0.018 | |||||
δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 0.256** | 0.410** | ||||
总生育酚 Total-tocopherol | 0.256** | 0.859** | 0.803** | |||
α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 0.966** | ‒0.237** | 0.064 | 0.011 | ||
γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | ‒0.515** | 0.298** | ‒0.713** | ‒0.231** | ‒0.479** | |
δ-生育酚占比 δ-tocopherol proportion | 0.154** | ‒0.233** | 0.780** | 0.256** | 0.098 | ‒0.921** |
| QTL | 单个QTL Individual QTL | 性状 Trait | 染色体Chromo-some | 左标记 Left marker | 物理位置 Physical position | 右标记 Right marker | 物理位置 Physical position | 遗传位置Genetic position | LOD | 贡献率 PVE/% | 加性效应 Additive | 区间 Confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 左Left | 右Right | ||||||||||||
| qTOC‑A2 | qα‑TOC‑A2 | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 8 | ss715602131 | 43 896 715 | ss715602331 | 45 913 059 | 268.4 | 5.2 | 6.26 | 0.691 | 256.4 | 269.4 |
| qδ‑TOC‑A2 | δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 258.2 | 3.6 | 6.77 | 2.726 | 244.6 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qTotal‑TOC‑A2 | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | 266.3 | 3.4 | 4.98 | 3.981 | 252.9 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑A2 | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 267.5 | 3.3 | 4.08 | 0.269 | 253.6 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qγ‑/Total‑TOC‑A2 | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | 255.1 | 2.5 | 3.85 | -0.748 | 239.3 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qTOC‑A1 | qα‑TOC‑A1 | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 5 | ss715591799 | 40 916 521 | ss715591790 | 40 974 254 | 98.2 | 7.5 | 8.52 | 0.801 | 97.3 | 98.7 |
| qγ‑/Total‑TOC‑A1 | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | 98.2 | 6.0 | 6.34 | -0.956 | 97.4 | 98.7 | ||||||
| qγ‑TOC‑A1 | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | ss715591790 | 40 974 254 | ss715591780 | 41 007 475 | 98.7 | 18.1 | 21.92 | -5.564 | 98.2 | 98.7 | ||
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑A1 | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 98.3 | 11.9 | 13.72 | 0.491 | 98.2 | 98.7 | ||||||
| qTotal‑TOC‑A1 | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | ss715591954 | 39 886 822 | ss715591831 | 40 684 517 | 94.3 | 9.1 | 12.32 | -6.226 | 90.4 | 96.4 | ||
| qTOC‑H | qα‑TOC‑H | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 12 | ss715611499 | 1 379 873 | ss715613700 | 980 800 | 153.7 | 5.5 | 6.22 | -0.685 | 147.8 | 153.7 |
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑H | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 152.9 | 5.1 | 5.83 | -0.320 | 147.5 | 157.9 | ||||||
| qγ‑/Total‑TOC‑H | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | 153.8 | 3.9 | 4.10 | 0.769 | 150.0 | 156.7 | ||||||
| qTOC‑F | qγ‑TOC‑F | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | 13 | ss715616114 | 39 590 255 | ss715616142 | 39 911 642 | 116.6 | 6.6 | 7.53 | -3.272 | 115.7 | 119.2 |
| qTotal‑TOC‑F | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | 116.5 | 5.0 | 6.26 | -4.454 | 115.7 | 119.4 | ||||||
| qTOC‑G | qδ‑TOC‑G | δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 18 | ss715629792 | 20 419 500 | ss715629811 | 20 502 705 | 104.5 | 3.8 | 4.50 | 2.222 | 104.4 | 104.8 |
| qTotal‑TOC‑G | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | ss715629923 | 21 629 092 | ss715629930 | 21 908 634 | 106.4 | 2.7 | 3.21 | 3.191 | 105.5 | 106.8 | ||
| qδ‑/Total‑TOC‑G | δ-生育酚占比 δ-tocopherol proportion | ss715629675 | 19 772 410 | ss715629709 | 19 955 096 | 103.6 | 3.4 | 6.19 | 0.643 | 103.3 | 103.6 | ||
| qTOC‑L | qα‑TOC‑L | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 19 | ss715633071 | 514 053 | ss715636028 | 580 135 | 116.0 | 4.9 | 5.43 | 0.639 | 115.8 | 116.8 |
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑L | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | ss715636293 | 809 326 | ss715636173 | 674 202 | 110.1 | 5.2 | 5.77 | 0.318 | 104.0 | 113.4 | ||
| qTOC‑M | qγ‑TOC‑M | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | 7 | ss715598313 | 5 265 136 | ss715598195 | 4 429 189 | 99.2 | 3.5 | 4.43 | 2.503 | 92.2 | 107.6 |
| qTotal‑TOC‑M | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | ss715597765 | 3 872 947 | ss715597135 | 3 167 571 | 110.1 | 2.6 | 3.08 | 3.112 | 109.2 | 115.8 | ||
表3 供试大豆RIL群体籽粒生育酚及其各组分一因多效QTLs
Table 3 Pleiotropic QTLs of seed tocopherol and its components in soybean RIL population
| QTL | 单个QTL Individual QTL | 性状 Trait | 染色体Chromo-some | 左标记 Left marker | 物理位置 Physical position | 右标记 Right marker | 物理位置 Physical position | 遗传位置Genetic position | LOD | 贡献率 PVE/% | 加性效应 Additive | 区间 Confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 左Left | 右Right | ||||||||||||
| qTOC‑A2 | qα‑TOC‑A2 | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 8 | ss715602131 | 43 896 715 | ss715602331 | 45 913 059 | 268.4 | 5.2 | 6.26 | 0.691 | 256.4 | 269.4 |
| qδ‑TOC‑A2 | δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 258.2 | 3.6 | 6.77 | 2.726 | 244.6 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qTotal‑TOC‑A2 | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | 266.3 | 3.4 | 4.98 | 3.981 | 252.9 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑A2 | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 267.5 | 3.3 | 4.08 | 0.269 | 253.6 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qγ‑/Total‑TOC‑A2 | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | 255.1 | 2.5 | 3.85 | -0.748 | 239.3 | 269.4 | ||||||
| qTOC‑A1 | qα‑TOC‑A1 | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 5 | ss715591799 | 40 916 521 | ss715591790 | 40 974 254 | 98.2 | 7.5 | 8.52 | 0.801 | 97.3 | 98.7 |
| qγ‑/Total‑TOC‑A1 | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | 98.2 | 6.0 | 6.34 | -0.956 | 97.4 | 98.7 | ||||||
| qγ‑TOC‑A1 | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | ss715591790 | 40 974 254 | ss715591780 | 41 007 475 | 98.7 | 18.1 | 21.92 | -5.564 | 98.2 | 98.7 | ||
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑A1 | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 98.3 | 11.9 | 13.72 | 0.491 | 98.2 | 98.7 | ||||||
| qTotal‑TOC‑A1 | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | ss715591954 | 39 886 822 | ss715591831 | 40 684 517 | 94.3 | 9.1 | 12.32 | -6.226 | 90.4 | 96.4 | ||
| qTOC‑H | qα‑TOC‑H | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 12 | ss715611499 | 1 379 873 | ss715613700 | 980 800 | 153.7 | 5.5 | 6.22 | -0.685 | 147.8 | 153.7 |
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑H | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | 152.9 | 5.1 | 5.83 | -0.320 | 147.5 | 157.9 | ||||||
| qγ‑/Total‑TOC‑H | γ-生育酚占比 γ-tocopherol proportion | 153.8 | 3.9 | 4.10 | 0.769 | 150.0 | 156.7 | ||||||
| qTOC‑F | qγ‑TOC‑F | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | 13 | ss715616114 | 39 590 255 | ss715616142 | 39 911 642 | 116.6 | 6.6 | 7.53 | -3.272 | 115.7 | 119.2 |
| qTotal‑TOC‑F | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | 116.5 | 5.0 | 6.26 | -4.454 | 115.7 | 119.4 | ||||||
| qTOC‑G | qδ‑TOC‑G | δ-生育酚 δ-tocopherol | 18 | ss715629792 | 20 419 500 | ss715629811 | 20 502 705 | 104.5 | 3.8 | 4.50 | 2.222 | 104.4 | 104.8 |
| qTotal‑TOC‑G | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | ss715629923 | 21 629 092 | ss715629930 | 21 908 634 | 106.4 | 2.7 | 3.21 | 3.191 | 105.5 | 106.8 | ||
| qδ‑/Total‑TOC‑G | δ-生育酚占比 δ-tocopherol proportion | ss715629675 | 19 772 410 | ss715629709 | 19 955 096 | 103.6 | 3.4 | 6.19 | 0.643 | 103.3 | 103.6 | ||
| qTOC‑L | qα‑TOC‑L | α-生育酚 α-tocopherol | 19 | ss715633071 | 514 053 | ss715636028 | 580 135 | 116.0 | 4.9 | 5.43 | 0.639 | 115.8 | 116.8 |
| qα‑/Total‑TOC‑L | α-生育酚占比 α-tocopherol proportion | ss715636293 | 809 326 | ss715636173 | 674 202 | 110.1 | 5.2 | 5.77 | 0.318 | 104.0 | 113.4 | ||
| qTOC‑M | qγ‑TOC‑M | γ-生育酚 γ-tocopherol | 7 | ss715598313 | 5 265 136 | ss715598195 | 4 429 189 | 99.2 | 3.5 | 4.43 | 2.503 | 92.2 | 107.6 |
| qTotal‑TOC‑M | 总生育酚Total-tocopherol | ss715597765 | 3 872 947 | ss715597135 | 3 167 571 | 110.1 | 2.6 | 3.08 | 3.112 | 109.2 | 115.8 | ||
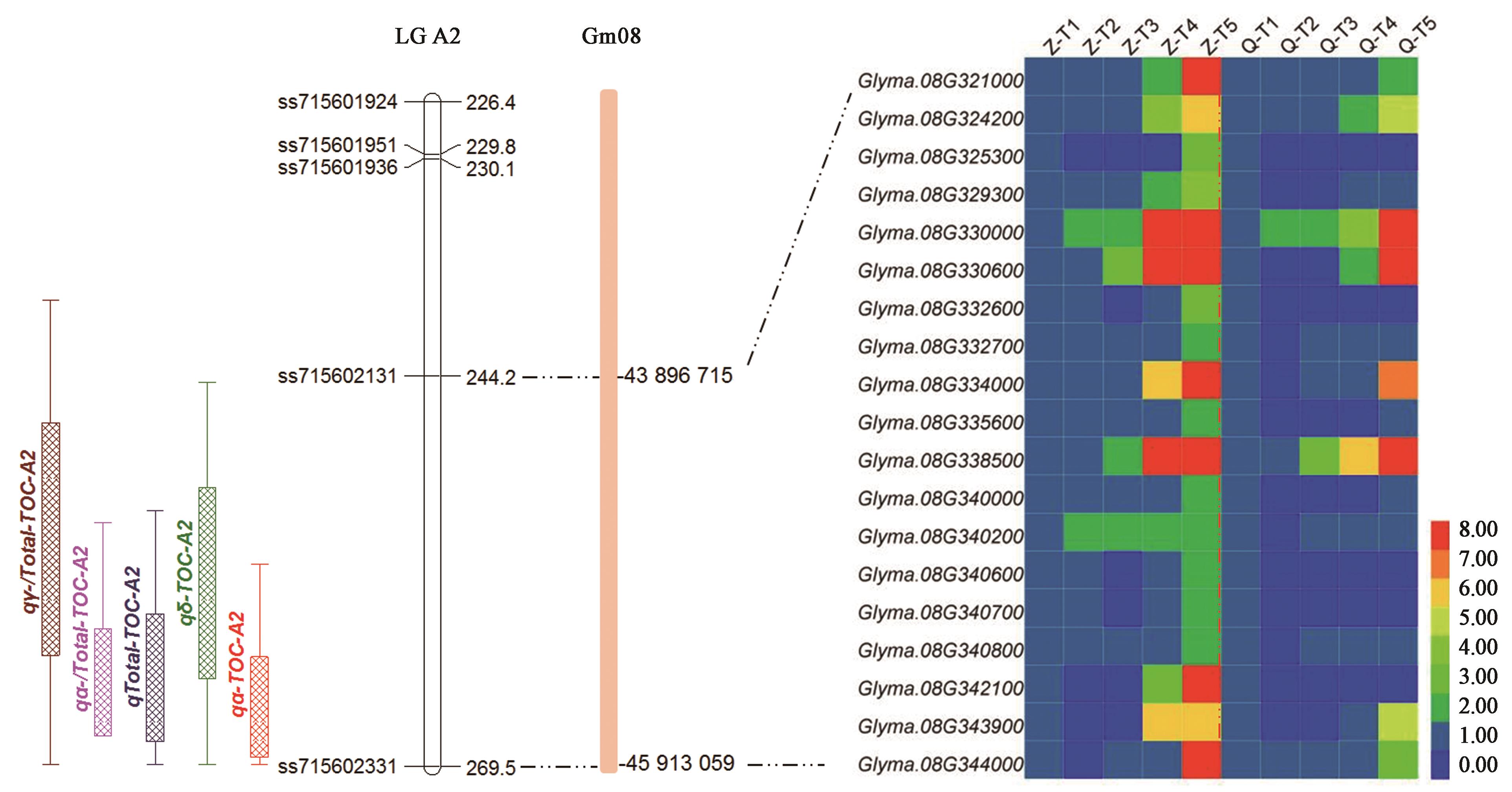
图2 大豆8号染色体籽粒生育酚一因多效QTL及其候选基因注:Z—郑92116; Q—齐黄30。
Fig. 2 Pleiotropic QTL and candidate gene for soybean seed tocopherol and its components on chromosome 8Note: Z— Zheng 92116; Q—Qihuang 30.
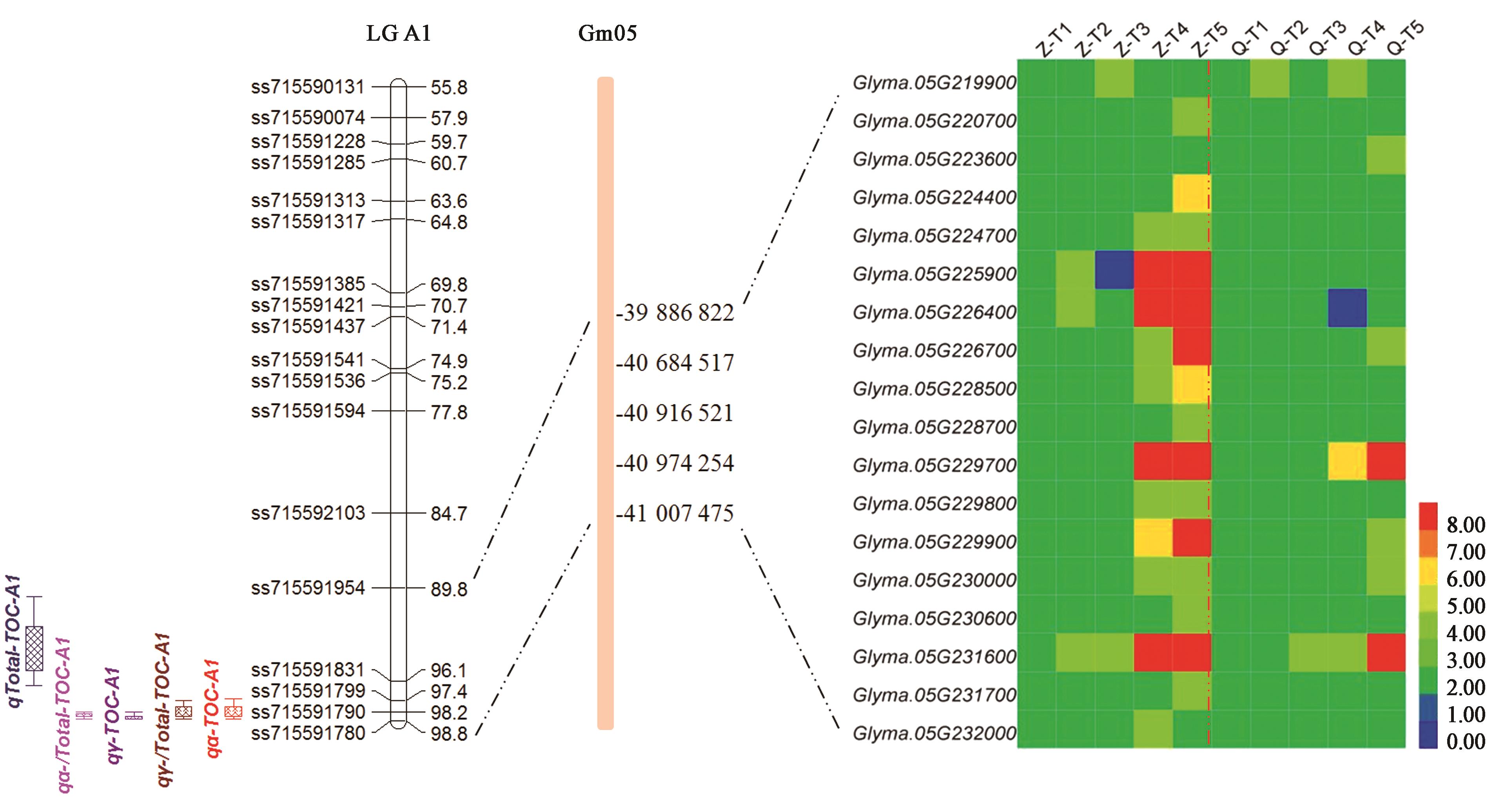
图3 大豆5号染色体籽粒生育酚一因多效QTL及其候选基因注:Z—郑92116; Q—齐黄30。
Fig. 3 Pleiotropic QTL and candidate gene for soybean seed tocopherol and its components on chromosome 5Note: Z— Zheng 92116; Q—Qihuang 30.
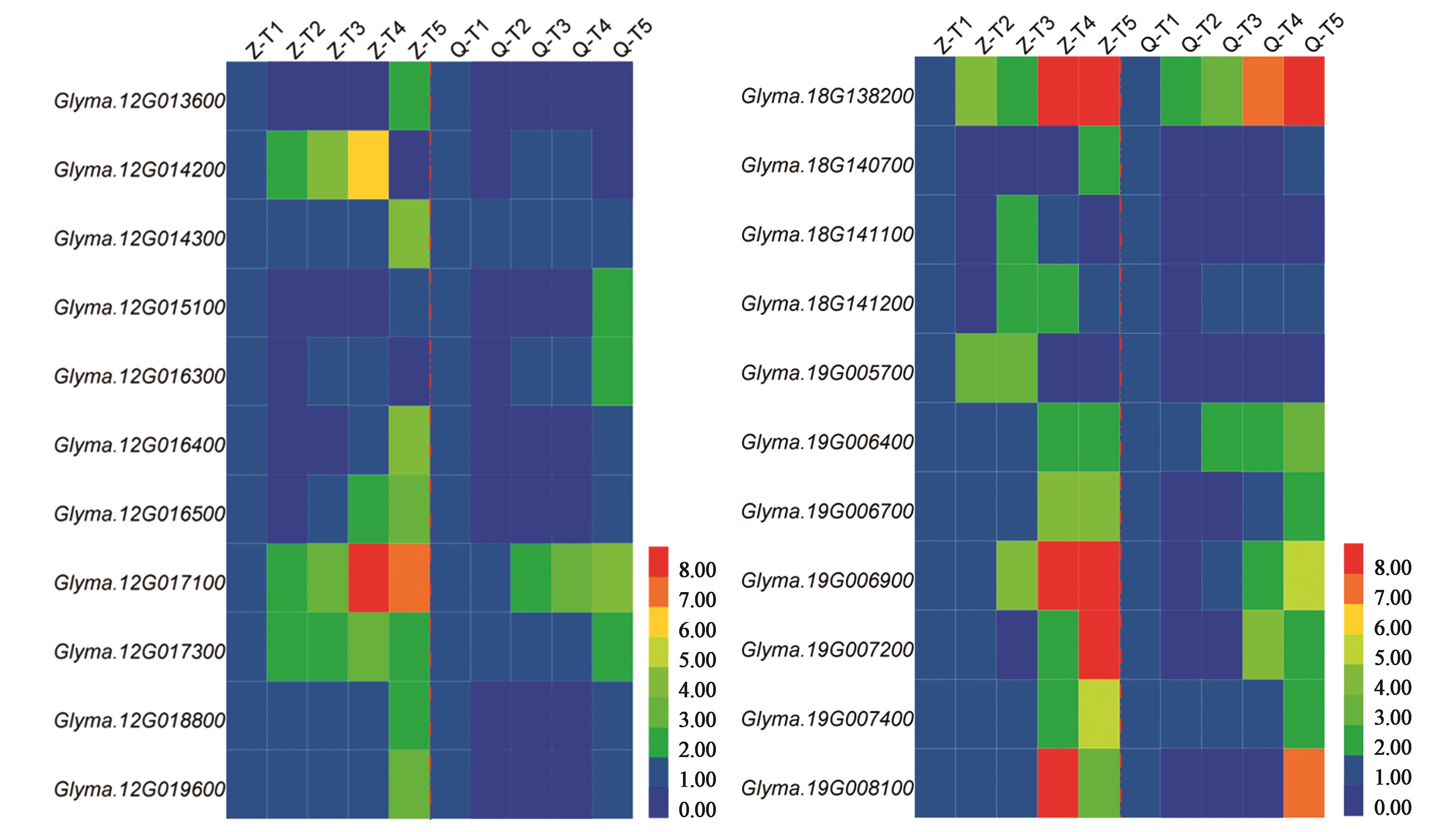
图4 大豆12号、18号和19号染色体生育酚候选基因注:Z—郑92116; Q—齐黄30。
Fig. 4 Candidate gene for soybean tocopherol on chromosomes 12, 18 and 19Note: Z— Zheng 92116; Q—Qihuang 30.
| 1 | 赵亚民,张丽静,傅华.维生素E在饲草及畜产品中的应用研究[J].草业科学, 2011, 28(6): 1167-1172. |
| ZHAO Y M, ZHANG L J, FU H. Application study of vitamin E in forage grass and livestock products [J]. Pratacul. Sci., 2011, 28(6): 1167-1172. | |
| 2 | 赵贵兴.高维生素E含量大豆胚芽油的制备及其微胶囊化研究[J].农业工程, 2012, 2(4): 34-41. |
| ZHAO G X. Preparation of soybean embryo oil with high content of vitamin E and research of its microencapsulation [J]. Agric. Eng., 2012, 2(4): 34-41. | |
| 3 | 张红梅,李海朝,文自翔,等.大豆籽粒维生素E含量的QTL分析[J].作物学报, 2015, 41(2): 187-196. |
| ZHANG H M, LI H C, WEN Z Y, et al.. Identification of QTL associated with vitamin E content in soybean seeds [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2015, 41(2): 187-196. | |
| 4 | MUNNE B S. The role of α-tocophherol in plant stress tolerance [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2005, 162: 743-748. |
| 5 | BURTON G W. Vitamin E: molecular and biological function [J]. P. Nutr. Soc., 1994, 53(2): 251-262. |
| 6 | BRAMLEY P, ELMADFA I, KAFATOS A, et al.. Vitamin E [J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2000, 80(7): 913-938. |
| 7 | BURING J E, HENNEKENS C H. Antioxidant vitamins and cardiovascular disease [J]. Nutr. Rev., 1997, 55: S53-S60. |
| 8 | RAEDERSTORFF D, WYSS A, CALDER P C, et al.. Vitamin E function and requirements in relation to PUFA [J]. Brit. J. Nutr., 2015, 114: 1113-1122. |
| 9 | SATO K, GOSHO M, YAMAMOTO T, et al.. Vitamin E has a beneficial effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Nutrition, 2015, 31: 923-930. |
| 10 | CAO Y C, LI S G, WANG Z L, et al.. Identification of major quantitative trait loci for seed oil content in soybeans by combining linkage and genome-wide association mapping [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8: 1222 [2021-11-15]. . |
| 11 | 李禄慧,徐妙云,张兰,等.不同作物中维生素E含量的测定和比较[J].中国农学通报, 2011, 27(26): 124-128. |
| LI L H, XU M Y, ZHANG L, et al.. Determinate and analysis the content of vitamin E in different species [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2011, 27(26): 124-128. | |
| 12 | 刘焕成,韩英鹏,腾卫丽,等.东北大豆与北美大豆维生素E含量的分析[J].大豆科学, 2008, 27(6): 925-928. |
| LIU H C, HAN Y P, TENG W L, et al.. Analysis of vitamin E content in soybeans derived from northeast China and north America [J]. Soybean Sci., 2008, 27(6): 925-928. | |
| 13 | 李海燕.大豆维生素E含量的遗传分析及QTL定位[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学, 2010. |
| LI H Y. Genetic and QTL analysis of the content of vitamin E in soybean [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2010. | |
| 14 | 梁慧珍,许兰杰,董薇,等.大豆γ-生育酚的混合遗传分析与QTL定位[J].中国农业科学, 2020, 53(11): 2149-2160. |
| LIANG H Z, XU L J, DONG W, et al.. Mixed inheritance analysis and QTL mapping for γ-tocopherol content in soybean [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2020, 53(11): 2149-2160. | |
| 15 | 刘焕成.大豆维生素E遗传变异、QTL及环境互作效应分析[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2017. |
| LIU H C. Genetic variation, QTL and QTL-by-environment interactions for seed vitamin E in soybean [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 16 | ZHAN Y H, LI H Y, SUI M N, et al.. Genome wide association mapping for tocopherol concentration in soybean seeds across multiple environments [J]. Industrial Crops Products, 2020, 154: 112674. |
| 17 | SUI M N, JING Y, LI H Y, et al.. Identification of loci and candidate genes analyses for tocopherol concentration of soybean seed [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11: 539460 [2021-11-15]. . |
| 18 | LI X H, KAMALA S, TIAN R, et al.. Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci controlling seed isoflavone content across multiple environments and backgrounds in soybean [J/OL]. Mol. Breeding, 2018, 38(1): 8 [2021-11-15]. . |
| 19 | 秦宁,李俊茹,李文龙,等.大豆籽粒生育酚及其组分含量鉴定与优异种质筛选[J].作物杂志, 2021, 3: 34-39. |
| QIN N, LI J R, LI W L, et al.. Screening of elite germplasms and identification of seed tocopherol and its component contents in soybean [J]. Crops, 2021, 3: 34-39. | |
| 20 | LI X H, SHAO Z Q, TIAN R, et al.. Mining QTLs and candidate genes for seed protein and oil contents across multiple environments and backgrounds in soybean [J/OL]. Mol. Breeding, 2019, 39: 139 [2021-11-15]. . |
| 21 | LI H Y, LIU H C, HAN Y P, et al.. Identification of QTL underlying vitamin E contents in soybean seed among multiple environments [J]. Theor. Appl. Genet., 2010, 120: 1405-1413. |
| 22 | LI H Y, WANG Y, HAN Y P, et al.. Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) underlying seed vitamin E content in soybean with main, epistatic and QTL × environment effects [J]. Plant Breeding, 2016, 135: 208-214. |
| 23 | LIU H C, CAO G L, HAN Y P, et al.. Identification of the QTL underlying the vitamin E content of soybean seeds [J]. Plant Breeding, 2017, 136(2): 147-154. |
| 24 | SHAW E J, RAJCAN I. Molecular mapping of soybean seed tocopherols in the cross ‘OAC Bayfield’ × ‘OAC Shire’ [J]. Plant Breeding, 2017, 136(1): 83-93. |
| 25 | MACDUFF M. Validation of QTL associated with tocopherol levels in three half-sib populations derived from Keszthelyi Aproszemu Sarga Soybean [D]. Guelph: University of Guelph, 2011. |
| [1] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 罗彦忠, 刘源, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因抗虫、耐除草剂及品质改良复合性状玉米BBHTL8-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 77-85. |
| [2] | 邢馨竹, 杨占武, 孔佑宾, 李文龙, 杜汇, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶GmCCD8固氮功能解析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 46-53. |
| [3] | 范文华, 戴建军, 张树山, 孙玲伟, 吴彩凤, 张德福. 大豆卵磷脂稀释液中添加原花青素对山羊冻精效果的影响#br#[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 78-86. |
| [4] | 陈士亮, 孙亚倩, 邵振启, 李文龙, 孔佑宾, 杜汇, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆鲜荚籽粒上位性QTL及其互作效应分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 25-36. |
| [5] | 张永芳,高志慧,史鹏清,韩志平*. 基于不同大豆品种农艺性状及品质性状的适应性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 25-32. |
| [6] | 李智,王宏富*,王钰云,杨净,鱼冰星,黄珊珊. 谷子大豆间作对作物光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 168-175. |
| [7] | 金林雪1,唐红艳1*,武荣盛1,王惠贞1,刘林春2. 内蒙古大豆干旱灾害风险分析与区划[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 106-115. |
| [8] | 白玉哲1,马钰聪1,孟一泽1,廉瑞娇1,王莹1,李喜焕1*,张彩英2*. 大豆籽粒蛋白与脂肪含量上位性QTLs分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(6): 36-42. |
| [9] | 张丽梅,马欣,韩宝吉,石磊*. 大豆-油菜轮作中不同硼肥及后效对作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 133-139. |
| [10] | 曹慧方,李新新,张玥琦,石鹏君,柏映国*,姚斌*. 来源于脂环酸芽孢杆菌的GH1家族β-葡萄糖苷酶的葡萄糖耐受性分子改造[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(5): 26-33. |
| [11] | 耿金剑,王春艳*,程婉莹,杨雪玲,李茂松. 极早熟区大豆冠层受光量及其对产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(5): 111-123. |
| [12] | 孟强1§,姜奇彦2§,牛风娟2,孙现军2,胡正2,张辉2*. 盐胁迫下不同抗性野生大豆(Glycine soja) 生理生化性状比较分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(8): 25-32. |
| [13] | 刘渊1,李文龙1,李喜焕1,王瑞霞2,常文锁1,张彩英1,3*. 施肥水平和种植密度对河北山区夏播大豆产量及品质影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(8): 115-123. |
| [14] | 孔佑宾1,王冰1,张华1,刘渊1,李喜焕1*,张彩英2*. 植物蛋白融合HA标签通用载体构建与应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(6): 131-137. |
| [15] | 刘渊1,李文龙1,李喜焕1,王瑞霞2,常文锁1,张彩英1,3*. 河北省北部山区大豆丰产高效栽培技术探索[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(4): 101-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号