




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 239-249.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0917
• 方法与技术创新 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-12-13
接受日期:2024-03-08
出版日期:2025-05-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
通讯作者:
刘冰
作者简介:王宏利 E-mail:1075933838@qq.com;
基金资助:
Hongli WANG( ), Lin NIU, Xiaodan ZHAO, Lei CHEN, Bing LIU(
), Lin NIU, Xiaodan ZHAO, Lei CHEN, Bing LIU( )
)
Received:2023-12-13
Accepted:2024-03-08
Online:2025-05-15
Published:2025-05-20
Contact:
Bing LIU
摘要:
采用新型绿色的复合活化剂酒石酸钾与氯化锌一步碳化法制备山竹壳多孔炭材料,优化制备条件并探究其吸附性能。以碘吸附值为评价指标,测定山竹壳多孔炭在不同条件下的吸附能力,结果表明, 在山竹壳粉与复合活化剂浸渍比1∶1.5、酒石酸钾∶氯化锌质量比为1.5∶1、活化温度700 ℃、活化时间1 h条件下,山竹壳多孔炭材料 (SSZAC3-700) 吸附量最大,为1 068 mg·g-1。通过场发射扫描电子显微镜、比表面积及孔隙分析仪、红外光谱对材料进行形貌特征、孔隙结构以及表面官能团进行表征发现,SSZAC3-700材料比表面积为1 294.69 m2·g-1,总孔容为0.651 0 cm3·g-1,材料孔隙结构以微孔为主,存在大量的含氧官能团。对刚果红的吸附试验表明,SSZAC3-700的吸附动力学符合准二级动力学模型,以化学吸附为主。等温吸附过程符合Langmuir吸附等温吸附模型,为单分子层吸附。热力学结果?H>0,吸附过程为吸热过程。SSZAC3-700材料对刚果红吸附再生次数为3次,去除率远高于市售活性炭。该制备方法实现了对农业废弃物山竹壳的重复再利用,为山竹壳的综合循环再利用提供了一种新思路,为环境中去除染料残留提供了一种简单快速的方法。
中图分类号:
王宏利, 牛琳, 赵晓丹, 陈雷, 刘冰. 双活化法制备山竹壳多孔炭材料及其对刚果红的吸附性能研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 239-249.
Hongli WANG, Lin NIU, Xiaodan ZHAO, Lei CHEN, Bing LIU. Preparation of Porous Carbon Material from Mangosteen Shell by Double Activation Method and Its Adsorption Properties for Congo Red[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 239-249.
样品 Sample | 元素 Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
碳 Carbon | 氮 Nitrogen | 氧 Oxygen | 硫 Sulfur | |
| SZK | 74.26 | 1.58 | 22.89 | 1.18 |
| SZAC | 86.32 | 1.13 | 12.15 | 0.74 |
| SZAC2-700 | 93.48 | 1.05 | 8.36 | 1.23 |
| SSZAC3-700 | 94.62 | 1.12 | 7.05 | 0.68 |
表1 山竹壳及炭材料的元素组成 (%)
Table 1 Elemental composition of mangosteen shell and its carbon materials
样品 Sample | 元素 Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
碳 Carbon | 氮 Nitrogen | 氧 Oxygen | 硫 Sulfur | |
| SZK | 74.26 | 1.58 | 22.89 | 1.18 |
| SZAC | 86.32 | 1.13 | 12.15 | 0.74 |
| SZAC2-700 | 93.48 | 1.05 | 8.36 | 1.23 |
| SSZAC3-700 | 94.62 | 1.12 | 7.05 | 0.68 |
样品 Sample | 比表面积 Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | 总孔容 Total pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | 微孔孔容 Microporous pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | 介孔孔容 Mesoporous pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径 Mean aperture/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZT | 530.63 | 0.252 0 | 0.242 8 | 0.009 2 | 15.899 5 |
| SZAC2-700 | 1 016.61 | 0.573 3 | 0.333 6 | 0.239 7 | 2.255 9 |
| SSZAC3-700 | 1 294.69 | 0.651 0 | 0.498 5 | 0.152 5 | 2.011 2 |
表2 山竹壳及其炭材料孔结构参数
Table 2 Pore structure parameters of mangosteen shell and its carbon materials
样品 Sample | 比表面积 Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | 总孔容 Total pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | 微孔孔容 Microporous pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | 介孔孔容 Mesoporous pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径 Mean aperture/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZT | 530.63 | 0.252 0 | 0.242 8 | 0.009 2 | 15.899 5 |
| SZAC2-700 | 1 016.61 | 0.573 3 | 0.333 6 | 0.239 7 | 2.255 9 |
| SSZAC3-700 | 1 294.69 | 0.651 0 | 0.498 5 | 0.152 5 | 2.011 2 |
模型 Sample | 参数 Argument | 温度 Temperature/℃ | 刚果红质量浓度 Congo red mass concentration/(mg·L-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 45 | 150 | 200 | 250 | ||
准一级动力学模型 Quasi-first-order kinetic model | 平衡吸附量qe/(mg·g-1) | 95.357 9 | 101.762 7 | 105.728 8 | 86.627 8 | 95.357 9 | 102.093 8 |
| 准一级动力学常数K1/(·min-1) | 0.237 6 | 0.224 2 | 0.228 9 | 0.174 6 | 0.237 6 | 0.254 2 | |
| 相关系数R2 | 0.993 6 | 0.980 0 | 0.990 7 | 0.944 1 | 0.993 6 | 0.966 2 | |
准二级动力学模型 Quasi-second-order kinetic model | 平衡吸附量qe/(mg·g-1) | 97.519 2 | 104.627 4 | 108.383 7 | 90.234 4 | 97.519 2 | 106.868 5 |
| 准二级动力学常数K2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 0.004 5 | 0.003 5 | 0.003 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.004 5 | 0.004 0 | |
| 相关系数R2 | 0.998 7 | 0.995 2 | 0.999 4 | 0.980 9 | 0.998 7 | 0.987 8 | |
颗粒内扩散模型 Intra particle diffusion model | 平衡吸附量qe/(mg·g-1) | 50.866 7 | 50.992 1 | 54.765 3 | 40.195 5 | 50.866 6 | 52.010 8 |
| 颗粒内扩散常数Kpi/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 2.977 0 | 3.454 5 | 3.435 4 | 3.164 1 | 2.977 0 | 3.428 4 | |
| 相关系数R2 | 0.423 6 | 0.508 7 | 0.463 8 | 0.563 3 | 0.423 6 | 0.498 0 | |
表 3 山竹壳多孔炭材料对溶液中刚果红的吸附动力学模型参数
Table 3 Adsorption kinetic model parameters of mangosteen shell porous carbon material for Congo red adsorption in solution
模型 Sample | 参数 Argument | 温度 Temperature/℃ | 刚果红质量浓度 Congo red mass concentration/(mg·L-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 45 | 150 | 200 | 250 | ||
准一级动力学模型 Quasi-first-order kinetic model | 平衡吸附量qe/(mg·g-1) | 95.357 9 | 101.762 7 | 105.728 8 | 86.627 8 | 95.357 9 | 102.093 8 |
| 准一级动力学常数K1/(·min-1) | 0.237 6 | 0.224 2 | 0.228 9 | 0.174 6 | 0.237 6 | 0.254 2 | |
| 相关系数R2 | 0.993 6 | 0.980 0 | 0.990 7 | 0.944 1 | 0.993 6 | 0.966 2 | |
准二级动力学模型 Quasi-second-order kinetic model | 平衡吸附量qe/(mg·g-1) | 97.519 2 | 104.627 4 | 108.383 7 | 90.234 4 | 97.519 2 | 106.868 5 |
| 准二级动力学常数K2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 0.004 5 | 0.003 5 | 0.003 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.004 5 | 0.004 0 | |
| 相关系数R2 | 0.998 7 | 0.995 2 | 0.999 4 | 0.980 9 | 0.998 7 | 0.987 8 | |
颗粒内扩散模型 Intra particle diffusion model | 平衡吸附量qe/(mg·g-1) | 50.866 7 | 50.992 1 | 54.765 3 | 40.195 5 | 50.866 6 | 52.010 8 |
| 颗粒内扩散常数Kpi/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 2.977 0 | 3.454 5 | 3.435 4 | 3.164 1 | 2.977 0 | 3.428 4 | |
| 相关系数R2 | 0.423 6 | 0.508 7 | 0.463 8 | 0.563 3 | 0.423 6 | 0.498 0 | |
模型 Model | 参数 Parameter | 温度 Temperature/℃ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 45 | ||
Langmuir模型 Langmuir model | 吸附常数KL/(L·mg-1) | 0.268 3 | 0.274 9 | 0.286 3 |
| 最大饱和吸附量qm/(mg·g-1) | 167.870 3 | 171.313 2 | 174.432 3 | |
| 决定系数R2 | 0.997 6 | 0.994 4 | 0.996 1 | |
Freundlich模型 Freundlich model | 吸附常数KF/(mg·g-1·(1/mg)1/n) | 84.673 8 | 87.751 8 | 91.178 2 |
| 常数n | 7.370 4 | 7.547 6 | 7.780 3 | |
| 决定系数R2 | 0.904 7 | 0.885 6 | 0.877 6 | |
Temkin模型 Temkin model | 模型常数A/(L·mg-1) | 44.238 2 | 51.309 5 | 63.979 4 |
| 吸收热常数B | 14.821 8 | 16.785 3 | 17.791 1 | |
| 决定系数R2 | 0.941 8 | 0.925 8 | 0.918 1 | |
表4 山竹壳多孔炭材料吸附刚果红的吸附等温线模型参数
Table 4 Adsorption isotherm model parameters of the porous carbon material of the mangosteen for Congo red
模型 Model | 参数 Parameter | 温度 Temperature/℃ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 45 | ||
Langmuir模型 Langmuir model | 吸附常数KL/(L·mg-1) | 0.268 3 | 0.274 9 | 0.286 3 |
| 最大饱和吸附量qm/(mg·g-1) | 167.870 3 | 171.313 2 | 174.432 3 | |
| 决定系数R2 | 0.997 6 | 0.994 4 | 0.996 1 | |
Freundlich模型 Freundlich model | 吸附常数KF/(mg·g-1·(1/mg)1/n) | 84.673 8 | 87.751 8 | 91.178 2 |
| 常数n | 7.370 4 | 7.547 6 | 7.780 3 | |
| 决定系数R2 | 0.904 7 | 0.885 6 | 0.877 6 | |
Temkin模型 Temkin model | 模型常数A/(L·mg-1) | 44.238 2 | 51.309 5 | 63.979 4 |
| 吸收热常数B | 14.821 8 | 16.785 3 | 17.791 1 | |
| 决定系数R2 | 0.941 8 | 0.925 8 | 0.918 1 | |
质量浓度 Mass concentration/(mg·L-1) | 温度 Temperature/℃ | 吉布斯自由能 ΔG(kJ·mol-1) | 自由焓变 ΔH(kJ·mol-1) | 吸附期间焓变 ΔS(J·mol-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 25 | -3.940 6 | 1.177 5 | 119.222 4 |
| 35 | -5.289 2 | |||
| 45 | -6.319 7 | |||
| 300 | 25 | -2.402 7 | 1.201 3 | 116.188 7 |
| 35 | -3.707 6 | |||
| 45 | -4.721 8 |
表5 山竹壳多孔炭材料吸附刚果红的吸附热模型参数
Table 5 Adsorption heat model parameters of Congo red adsorbed by porous carbon material of mangosteen shell
质量浓度 Mass concentration/(mg·L-1) | 温度 Temperature/℃ | 吉布斯自由能 ΔG(kJ·mol-1) | 自由焓变 ΔH(kJ·mol-1) | 吸附期间焓变 ΔS(J·mol-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 25 | -3.940 6 | 1.177 5 | 119.222 4 |
| 35 | -5.289 2 | |||
| 45 | -6.319 7 | |||
| 300 | 25 | -2.402 7 | 1.201 3 | 116.188 7 |
| 35 | -3.707 6 | |||
| 45 | -4.721 8 |
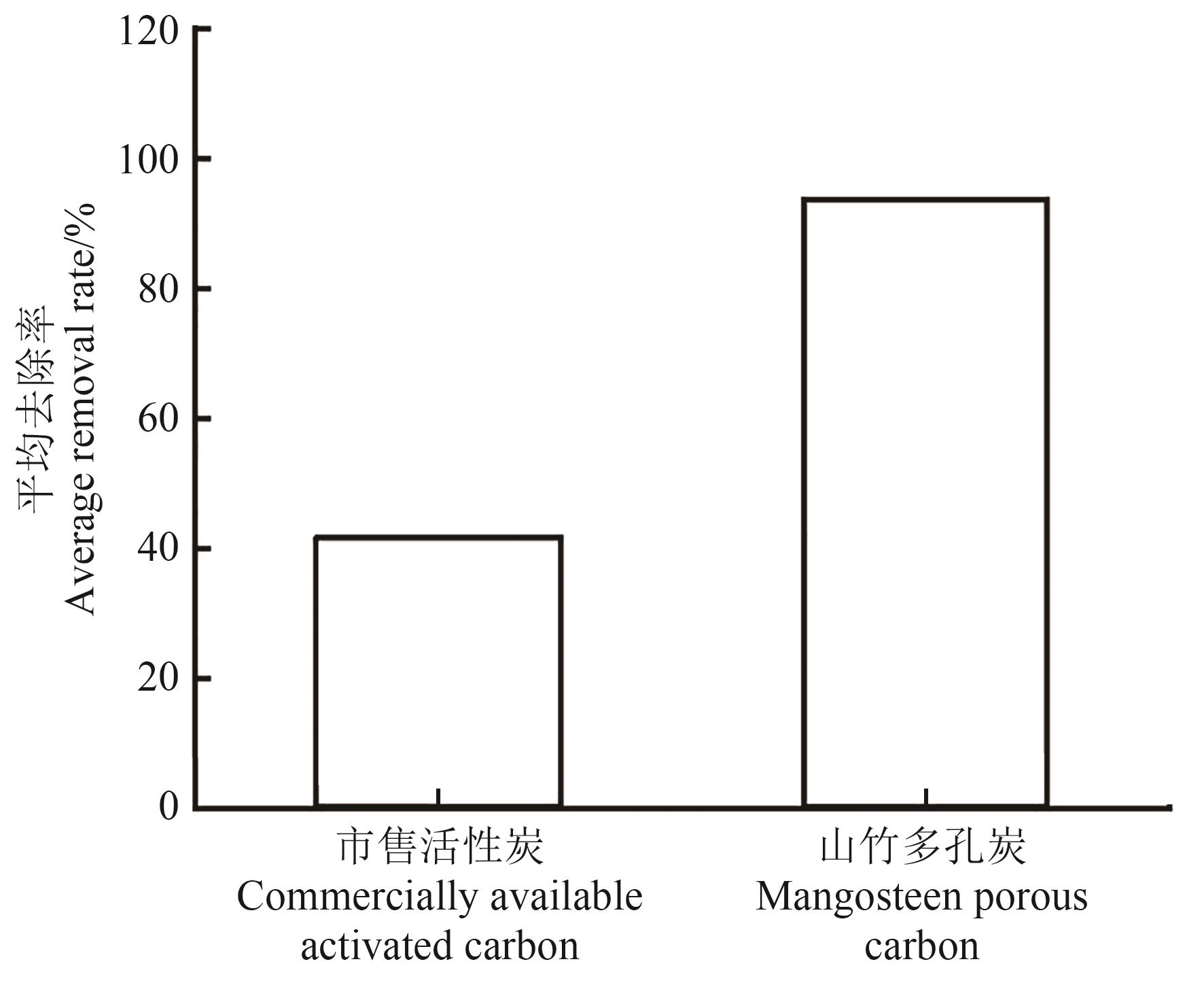
图5 山竹壳多孔炭材料与市售木质活性炭的吸附性能对比
Fig. 5 Comparison of adsorption properties between mangosteen shell porous carbon material and commercially available wood activated carbon
| 1 | 包维维. 吸附材料的制备及其对重金属离子和染料吸附性能研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2013. |
| BAO W W. Preparation of materials for the asorption of heavy metal ion and dyes [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2013. | |
| 2 | MAZEAU K, WYSZOMIRSKI M. Modeling of congo red adsorption on a surface of crystalline cellulose using molecular dynamics [J]. Cellulose, 2012, 19: 1495-1506. |
| 3 | WANG B, LIAN G Q, LEE X Q, et al.. Phosphogypsum as a novel modifier for distillers grains biochar removal of phosphate from water [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2020,238:124684 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 4 | FANG S, HUANG X, XIE S, et al.. Removal of chromium (VI) by a magnetic nanoscale zerovalent iron-assisted chicken manure-derived biochar:adsorption behavior and synergetic mechanism [J/OL]. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2022,10: 935525[2023-11-12]. . |
| 5 | ABDI S, NASIRI M, MESBAHI A, et al.. Investigation of uranium (VI) adsorption by polypyrrole [J]. J. Hazard. Mater.,2017,332:132-139. |
| 6 | 孙宇. 辣椒秸秆生物炭的制备, 改性及对有机染料的吸附性能研究 [D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2021. |
| SUN Y. Preparation and modification of biocharfrom pepper straw and its adsorption properties for organic dyes [D]. Handan: Hebei University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 7 | 丁华毅.生物炭的环境吸附行为及在土壤重金属镉污染治理中的应用[D].厦门:厦门大学,2014. |
| DING H Y. Environmental adsorption behavior of biochar and its application in remediation of cadmium contaminated soil [D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2014. | |
| 8 | 缪旭东,曹澄澄,陈颖,等.玉米秸秆生物炭吸附挥发性有机物的基本特性[J].环境科技,2021,34(1):24-29. |
| MIAO X D, CAO C C, CHEN Y, et al.. Basic properties of volatile organic compounds adsorption on straw-based biochar [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2021,34(1):24-29. | |
| 9 | QU J, CHE N J, NIU G L, et al.. Iron/manganese binary metal oxide-biochar nano-composites with high adsorption capacities of Cd2+:preparation and adsorption mechanisms [J/OL]. J. Water Process. Eng., 2023, 51:103332 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 10 | SOSZKA E, SNEKA-PŁATEK O, SKIBA E, et al.. Influence of the presence of impurities and of the biomass source on the performance of Ru catalysts in the hydrolytic hydrogenation of cellulose towards γ-valerolactone [J/OL]. Fuel, 2022,319:123646 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 11 | BUTNARU E, PAMFIL D, STOLERU E, et al.. Characterization of bark, needles and cones from silver fir (Abies alba mill.) towards valorization of biomass forestry residues [J/OL]. Biomass Bioenergy, 2022, 159: 106413[2023-11-12]. . |
| 12 | PÉREZ S, RENEDO C, ORTIZ A, et al.. Energy potential of waste from 10 forest species in the North of Spain (Cantabria) [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2008,99(14):6339-6345. |
| 13 | TERRY L M, LOY A C M, CHEW J J, et al.. Chemical engineering and the sustainable oil palm biomass industry—recent advances and perspectives for the future [J]. Chem. Eng.Res. Des., 2022,188: 729-735. |
| 14 | 江建方.城市生活垃圾外热式热解技术的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2006. |
| JIANG J F. Dissertation submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for th e degree of doctor of philosophy in engineering [D].Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2006. | |
| 15 | WYNN P A, PRESTON R. Hearing impairment in municipal refuse and glass recycling collection operatives [J]. Ann. Work.Expos. Health, 2021,65(6):727-731. |
| 16 | 李婷,李欣桐,李敏,等.山竹壳基生物质活性炭的制备及其吸附性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2018,46(2):213-216. |
| LI T, LI X T, LI M, et al.. Preparation and adsorption property of mangosteen shell based activated carbon [J]. New Chem. Mater., 2018,46(2):213-216. | |
| 17 | 单锐,谈莉,陈凤鸣,等.改性山竹壳炭对废水中Ni(Ⅱ)的吸附效果与机理研究[J].安全与环境学报,2022,22(6):3473-3483. |
| SHAN R, TAN L, CHEN F M, et al.. Study on the adsorption effect and mechanism of modified mangosteen charcoal on Ni(Ⅱ) in wastewater [J]. J. Saf. Environ., 2022,22(6):3473-3483. | |
| 18 | 单永芳,黄齐林,韩汝莲,等.山竹壳基活性炭的制备及性能研究[J].现代农业科技,2020(12):193-196. |
| SHAN Y F, HUANG Q L, HAN R L, et al.. Study on preparation and properties of mangosteen shell-based activated carbon [J]. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020(12):193-196. | |
| 19 | MARCELLO M, LORENZIN A, DE CAL M, et al.. Bilirubin removal by plasmafiltration-adsorption: ex vivo adsorption kinetics model and single case report [J]. Blood Purif., 2023,52(4):345-351. |
| 20 | GUO D L, HU D G, YAN Z Y, et al.. Preparation and characteristic of high surface area lignin-based porous carbon by potassium tartrate activation [J/OL]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2021,326:111340 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 21 | LANGMUIR I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass,mica and platinum [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1918,40(9):1361-1403. |
| 22 | 焦豫滨.核桃壳活性炭的制备及其对水中有机污染物的吸附性能研究[D].郑州: 郑州大学,2016. |
| JIAO Y B. Study on the adsorption performance of modified activated carbon prepared from nutshell [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2016. | |
| 23 | VYAVAHARE G, GURAV R, PATIL R, et al.. Sorption of brilliant green dye using soybean straw-derived biochar:characterization, kinetics, thermodynamics and toxicity studies [J]. Environ. Geochem. Health, 2021,43(8):2913-2926. |
| 24 | HWANG Y J, JEONG S K, SHIN J S, et al.. High capacity disordered carbons obtained from coconut shells as anode materials for lithium batteries [J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2008,448(1/2):141-147. |
| 25 | ALFATTANI R, SHAH M A, SIDDIQUI M I H, et al.. Bio-char characterization produced from walnut shell biomass through slow pyrolysis: Sustainable for soil amendment and an alternate bio-fuel [J/OL]. Energies, 2021, 15(1): 15010001 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 26 | ANEMANA T, ÓVÁRI M, VARGA M, et al.. Granular activated charcoal from peanut (Arachis hypogea) shell as a new candidate for stabilization of arsenic in soil [J/OL].Microchem. J., 2019, 149: 104030 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 27 | 张江南,黄正宏,徐成俊,等.竹基多孔炭用作超级电容器极板材料的研究[J].世界竹藤通讯,2008,6(4):13-16. |
| ZHANG J N, HUANG Z H, XU C J, et al.. Study on bamboo based porous carbon as material for supercapacitor [J]. World Bamboo Rattan, 2008,6(4):13-16. | |
| 28 | YAN S W, YU W, YANG T, et al.. The adsorption of corn stalk biochar for Pb and Cd: preparation characterization and batch adsorption study [J/OL]. Separations 2022, 9(2):22 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 29 | LYKOUDI A, FRONTISTIS Z, VAKROS J, et al.. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole with persulfate using spent coffee grounds biochar as activator [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manag., 2020,271:111022 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 30 | SUN Z J, WANG S J, YAN L L, et al.. Mesoporous carbon materials prepared from litchi shell as sulfur encapsulator for lithium-sulfur battery application [J]. J. Power Sources, 2016,324: 547-555. |
| 31 | 朱秀珍.有机钾盐活化法制备活性炭及其对氯霉素吸附性能的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2018. |
| ZHU X Z. Preparation of activated carbon by organic potassium salt activation for adsorption of chloramphenicol [D]. Ji'nan: Shandong University, 2018. | |
| 32 | YANG X M, XIE D, WANG W H, et al.. An activated carbon from walnut shell for dynamic capture of high concentration gaseous iodine [J/OL]. Chem. Eng. J., 2023,454:140365 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 33 | SINGH G, MARIA RUBAN A, GENG X, et al.. Recognizing the potential of K-salts, apart from KOH, for generating porous carbons using chemical activation [J/OL]. Chem. Eng. J., 2023,451:139045 [2023-11-12]. . |
| 34 | LUO H M, YANG Y F, ZHAO X, et al.. 3D sponge-like nanoporous carbons via a facile synthesis for high-performance supercapacitors:direct carbonization of tartrate salt [J].Electrochim. Acta, 2015,169:13-21. |
| 35 | WANG M X, HE D, ZHU M W, et al.. Green fabrication of hierarchically porous carbon microtubes from biomass waste via self-activation for high-energy-density supercapacitor [J/OL]. J. Power Sources, 2023,560:232703 [2023-11-12]. . |
| [1] | 吕志伟, 李冬梅, 金梅娟, 张燕辉, 陶玥玥, 周新伟, 王海候. 热解温度及时间对生物炭理化性质及吸附性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 211-217. |
| [2] | 王鑫宇1,2,张曦2,孟海波2,沈玉君2,解恒燕1*,周海宾2,程红胜2,宋立秋2. 温度对生物炭吸附重金属特性的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 150-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号