




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 164-171.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0731
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-08-20
Accepted:2020-10-14
Online:2022-01-15
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Shaoli HUANG
通讯作者:
黄劭理
作者简介:苏煜 E-mail:458243561@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yu SU, Shaoli HUANG. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer on Flue-cured Tobacco Photosynthetic Characteristics and Rhizosphere Soil Microorganism[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 164-171.
苏煜, 黄劭理. 增施生物有机肥对烤烟光合特性及根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 164-171.
| 处理 Treatment | SPAD值 SPAD value | 净光合速率Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度Gs/(mol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci/(μmol·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 35.1±0.3 b | 18.41±0.42 c | 5.28±0.26 b | 0.25±0.07 d | 309.16±3.18 c |
| T1 | 35.3±0.7 ab | 19.15±0.03 b | 5.43±0.20 b | 0.34±0.00 c | 316.28±4.46 b |
| T2 | 37.6±1.3 a | 21.17±0.52 ab | 5.85±0.17 a | 0.39±0.01 b | 320.73±1.46 b |
| T3 | 36.2±0.4 a | 22.03±0.11 a | 5.97±0.13 a | 0.48±0.00 a | 327.48±3.82 a |
Table 1 Photosynthetic characteristics of flue-cured tobacco with different treatment of bio-organic fertilizer
| 处理 Treatment | SPAD值 SPAD value | 净光合速率Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度Gs/(mol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci/(μmol·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 35.1±0.3 b | 18.41±0.42 c | 5.28±0.26 b | 0.25±0.07 d | 309.16±3.18 c |
| T1 | 35.3±0.7 ab | 19.15±0.03 b | 5.43±0.20 b | 0.34±0.00 c | 316.28±4.46 b |
| T2 | 37.6±1.3 a | 21.17±0.52 ab | 5.85±0.17 a | 0.39±0.01 b | 320.73±1.46 b |
| T3 | 36.2±0.4 a | 22.03±0.11 a | 5.97±0.13 a | 0.48±0.00 a | 327.48±3.82 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 细菌Bacteria /(104 CFU·g-1) | 真菌Fungi /(104 CFU·g-1) | 放线菌Actinomycetes /(104 CFU·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 91.8±10.2 d | 1.464±0.152 bc | 3.62±0.34 c |
| T1 | 105.3±9.8 c | 1.574±0.122 b | 5.48±0.45 b |
| T2 | 137.6±9.2 b | 1.735±0.134 a | 6.24±0.58 a |
| T3 | 178.2±11.0 a | 1.767±0.174 a | 6.74±0.55 a |
Table 2 The amount of microorganism in soil with different amount of bio-organic fertilizer
| 处理 Treatment | 细菌Bacteria /(104 CFU·g-1) | 真菌Fungi /(104 CFU·g-1) | 放线菌Actinomycetes /(104 CFU·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 91.8±10.2 d | 1.464±0.152 bc | 3.62±0.34 c |
| T1 | 105.3±9.8 c | 1.574±0.122 b | 5.48±0.45 b |
| T2 | 137.6±9.2 b | 1.735±0.134 a | 6.24±0.58 a |
| T3 | 178.2±11.0 a | 1.767±0.174 a | 6.74±0.55 a |
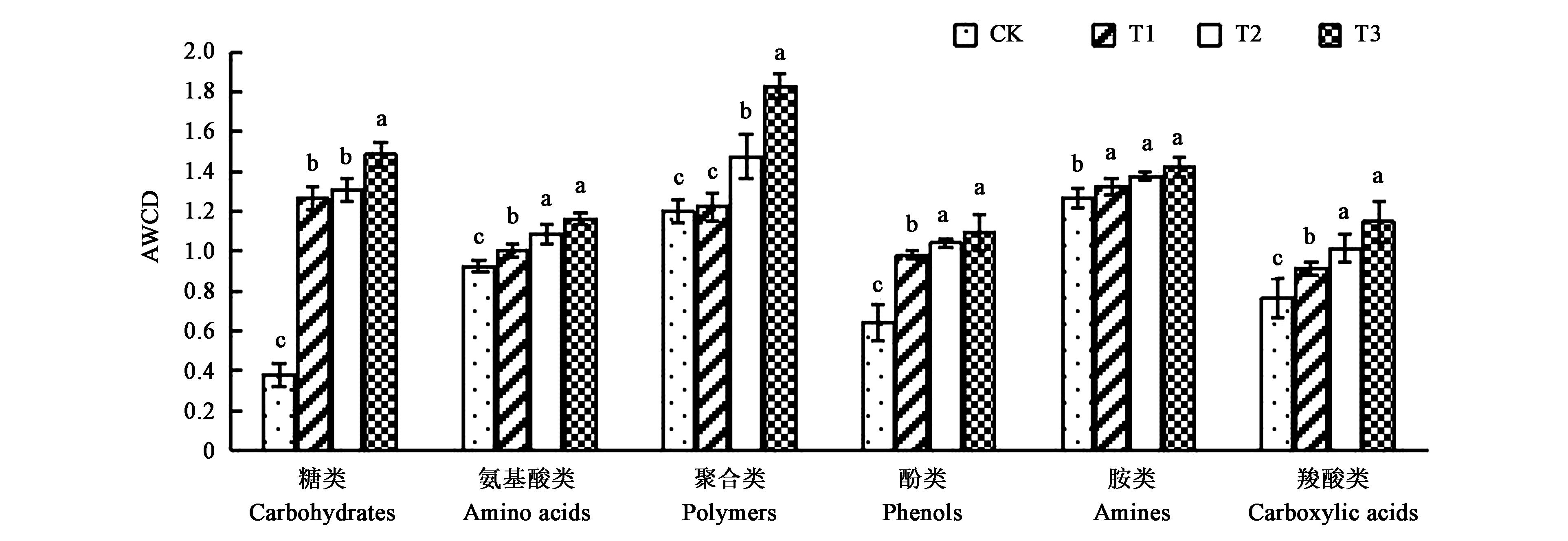
Fig.2 Utility for different types of carbon sources by rhizospheric microbes in soil with different amount ofbio-organic fertilizerNote:Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 主成份 Principal component | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64.705 | 64.705 |
| 2 | 14.544 | 79.249 |
| 3 | 9.996 | 89.245 |
| 4 | 4.105 | 93.350 |
Table 3 Contribution rate of principal component
| 主成份 Principal component | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64.705 | 64.705 |
| 2 | 14.544 | 79.249 |
| 3 | 9.996 | 89.245 |
| 4 | 4.105 | 93.350 |
| 碳源种类 Carbon substrate | 碳源名称 Name of the carbon source | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 糖类 Carbohydrate | D-甘露醇 D-mannitol | 0.923 | -0.173 |
| N-乙酰基-D-葡萄胺 N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | 0.901 | — | |
| D-纤维二糖 D-cellobiose | 0.877 | — | |
| D-木糖 D-xylose | 0.857 | — | |
| I-赤藻糖醇 I-erythritol | 0.832 | -0.433 | |
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸盐 Glucose-1-phosphate | 0.785 | 0.553 | |
| β-甲基D-葡萄糖苷 β-methyl-D-glucoside | 0.680 | 0.623 | |
| D,L-α-甘油 D,L-α-glycerol | 0.559 | 0.768 | |
| α-D-乳糖α-D-lactose | 0.378 | 0.517 | |
| 氨基酸类 Amino acids | L-天冬酰胺酸 L-asparagine | 0.944 | — |
| L-丝氨酸 L-serine | 0.837 | -0.280 | |
| 甘氨酰-L-谷氨酸 Glycyl-L-glutamic Acid | 0.823 | -0.543 | |
| L-精氨酸 L-arginine | 0.801 | 0.109 | |
| L-苏氨酸 L-threonine | 0.742 | — | |
聚合类 Polymers | α-环式糊精α-cyclodextrin | 0.852 | 0.360 |
| 肝糖 Glycogen | 0.841 | -0.417 | |
| 吐温40 Tween 40 | 0.834 | 0.329 | |
| 吐温80 Tween 80 | 0.778 | -0.491 | |
| L-苯基丙氨酸 L-phenylalanine | 0.759 | -0.597 | |
| 酚类 Phenols | 4-羟基苯甲酸 4-hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.879 | -0.275 |
| 2-羟苯甲酸 2-hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.850 | -0.237 | |
胺类 Amines | 苯乙基胺 Phenylethyl-amine | 0.913 | -0.293 |
| 腐胺 Putrescine | 0.751 | 0.514 | |
羧酸类 Carboxylic acids | α-丁酮酸α-ketobutyric acid | 0.925 | — |
| D-半乳糖内酯 D-galactonic acid y-lactone | 0.879 | -0.198 | |
| D-葡萄胺酸 D-glucosaminic acid | 0.855 | 0.385 | |
| D-半乳糖醛酸 D-galacturonic acid | 0.827 | — | |
| D-苹果酸 D-malic acid | 0.777 | -0.200 | |
| 衣康酸 Itaconic acid | 0.727 | 0.579 | |
| 丙酮酸甲脂 Pyruvic acid methyl ester | 0.727 | 0.394 | |
| γ-羟基丁酸 γ-hydroxybutyric acid | 0.539 | -0.342 |
Table 4 Loading values of principal components
| 碳源种类 Carbon substrate | 碳源名称 Name of the carbon source | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 糖类 Carbohydrate | D-甘露醇 D-mannitol | 0.923 | -0.173 |
| N-乙酰基-D-葡萄胺 N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | 0.901 | — | |
| D-纤维二糖 D-cellobiose | 0.877 | — | |
| D-木糖 D-xylose | 0.857 | — | |
| I-赤藻糖醇 I-erythritol | 0.832 | -0.433 | |
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸盐 Glucose-1-phosphate | 0.785 | 0.553 | |
| β-甲基D-葡萄糖苷 β-methyl-D-glucoside | 0.680 | 0.623 | |
| D,L-α-甘油 D,L-α-glycerol | 0.559 | 0.768 | |
| α-D-乳糖α-D-lactose | 0.378 | 0.517 | |
| 氨基酸类 Amino acids | L-天冬酰胺酸 L-asparagine | 0.944 | — |
| L-丝氨酸 L-serine | 0.837 | -0.280 | |
| 甘氨酰-L-谷氨酸 Glycyl-L-glutamic Acid | 0.823 | -0.543 | |
| L-精氨酸 L-arginine | 0.801 | 0.109 | |
| L-苏氨酸 L-threonine | 0.742 | — | |
聚合类 Polymers | α-环式糊精α-cyclodextrin | 0.852 | 0.360 |
| 肝糖 Glycogen | 0.841 | -0.417 | |
| 吐温40 Tween 40 | 0.834 | 0.329 | |
| 吐温80 Tween 80 | 0.778 | -0.491 | |
| L-苯基丙氨酸 L-phenylalanine | 0.759 | -0.597 | |
| 酚类 Phenols | 4-羟基苯甲酸 4-hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.879 | -0.275 |
| 2-羟苯甲酸 2-hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.850 | -0.237 | |
胺类 Amines | 苯乙基胺 Phenylethyl-amine | 0.913 | -0.293 |
| 腐胺 Putrescine | 0.751 | 0.514 | |
羧酸类 Carboxylic acids | α-丁酮酸α-ketobutyric acid | 0.925 | — |
| D-半乳糖内酯 D-galactonic acid y-lactone | 0.879 | -0.198 | |
| D-葡萄胺酸 D-glucosaminic acid | 0.855 | 0.385 | |
| D-半乳糖醛酸 D-galacturonic acid | 0.827 | — | |
| D-苹果酸 D-malic acid | 0.777 | -0.200 | |
| 衣康酸 Itaconic acid | 0.727 | 0.579 | |
| 丙酮酸甲脂 Pyruvic acid methyl ester | 0.727 | 0.394 | |
| γ-羟基丁酸 γ-hydroxybutyric acid | 0.539 | -0.342 |
| 处理Treatment | 丰富度指数Shannon index | 优势度指数Simpson index | 均匀度指数 McIntosh index |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.158 b | 0.952 b | 5.472 c |
| T1 | 3.263 a | 0.958 a | 7.057 b |
| T2 | 3.320 a | 0.962 a | 7.170 b |
| T3 | 3.333 a | 0.962 a | 8.066 a |
Table 5 The diversity of microbial community in soil
| 处理Treatment | 丰富度指数Shannon index | 优势度指数Simpson index | 均匀度指数 McIntosh index |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.158 b | 0.952 b | 5.472 c |
| T1 | 3.263 a | 0.958 a | 7.057 b |
| T2 | 3.320 a | 0.962 a | 7.170 b |
| T3 | 3.333 a | 0.962 a | 8.066 a |
| 关联参数 Correlation parameter | SPAD值 SPAD value | 净光合速率Pn | 丰富度指数Shannon index | 优势度指数Simpson index | 均一性指数McIntosh index | 碳源利用力Utility of carbon source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物有机肥 Bio-organic fertilizer | 0.170 3 | 0.191 6 | 0.183 4 | 0.172 6 | 0.190 3 | 0.180 4 |
| 真菌 Fungi | 0.366 9 | 0.473 4 | 0.402 5 | 0.338 3 | 0.542 2 | 0.409 5 |
| 细菌 Bacteria | 0.651 6 | 0.858 7 | 0.684 1 | 0.605 0 | 0.621 0 | 0.535 3 |
| 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 0.436 6 | 0.434 2 | 0.465 0 | 0.406 6 | 0.724 4 | 0.666 1 |
Table 6 Correlation between photosynthetic parameters and soil microbial diversity
| 关联参数 Correlation parameter | SPAD值 SPAD value | 净光合速率Pn | 丰富度指数Shannon index | 优势度指数Simpson index | 均一性指数McIntosh index | 碳源利用力Utility of carbon source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物有机肥 Bio-organic fertilizer | 0.170 3 | 0.191 6 | 0.183 4 | 0.172 6 | 0.190 3 | 0.180 4 |
| 真菌 Fungi | 0.366 9 | 0.473 4 | 0.402 5 | 0.338 3 | 0.542 2 | 0.409 5 |
| 细菌 Bacteria | 0.651 6 | 0.858 7 | 0.684 1 | 0.605 0 | 0.621 0 | 0.535 3 |
| 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 0.436 6 | 0.434 2 | 0.465 0 | 0.406 6 | 0.724 4 | 0.666 1 |
| 1 | 肖汉乾,李德清,徐双红,等.不同生物活性肥对烤烟生长影响的初步研究[J].中国烟草科学,2001,22(1):28-30. |
| XIAO H Q, LI D Q, XU S H, et al.. Effect of various activated bio-fertilizers on growth of flue-cured tobacco [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2001, 22(1):28-30. | |
| 2 | 蒋岁寒,刘艳霞,孟琳,等.生物有机肥对烟草青枯病的田间防效及根际土壤微生物的影响[J].南京农业大学学报,2016,39(5):784-790. |
| JIANG S H, LIU Y X, MENG L, et al.. Effects of biological organic fertilizer on field control efficiency of tobacco Ralstoniasolanacearum wilt and soil microbial in rhizosphere soil [J]. J. Nanjing Agric.Univ., 2016, 39(5):784-790. | |
| 3 | 吴晓宗,王岩.生物有机肥防治烟草青枯病及对土壤微生物多样性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2019(4):193-199. |
| WU X Z, WANG Y. Research of bio-organic fertilizer on prevention of tobacco bacterial wilt and its effects on soil microbial diversity [J]. China Soil Fert., 2019(4):193-199. | |
| 4 | 胡可,李华兴,卢维盛,等.生物有机肥对土壤微生物活性的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2010,18(2):303-306. |
| HU K, LI H X, LU W S, et al.. Effect of microbial organic fertilizer application on soil microbial activity [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2010, 18(2):303-306. | |
| 5 | 李红丽,郭夏丽,李清飞.抑制烟草青枯病生物有机肥的研制及其生防效果研究[J]. 土壤学报,2010,47(4):798-801. |
| LI H L, GUO X L, LI Q F, et al.. Tobacco wilt suppressing bio-manure and its bio-control effect [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2010, 47(4):798-801. | |
| 6 | 王玉,侯玉杰,付乃峰,等.生物有机肥对茶园土壤肥力、养分及土壤环境的影响[J].北方园艺,2011(17):171-173. |
| WANG Y, HOU Y J, FU N F, et al.. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer treatment on soil fertility, nutrient and soil environment of tea garden [J]. Northern Hortic., 2011(17):171-173. | |
| 7 | 赵军,窦玉青,宋付朋,等.有机和无机烟草专用肥配合施用对烟草生产效益和肥料氮素利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2014,20(3):613-619. |
| ZHAO J, DOU Y Q, SONG F P, et al.. Effects of combined application of biological organic fertilizer and inorganic compound fertilizer on the tobacco profit and nitrogen use efficiency [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2014, 20(3):613-619. | |
| 8 | 张云伟,徐智,汤利,等.生物有机肥对烤烟黑胫病及根际微生物代谢功能多样性的影响[J].中国烟草学报,2014,20(5):59-65. |
| ZHANG Y W, XU Z, TANG L, et al.. Effets of bio-organic fertilizer on flue-cured tobacco black shank and diversity of rhizospheric microbial metabolic function [J]. Acta Tab. Sin., 2014, 20(5):59-65. | |
| 9 | 赵兰凤,胡伟,刘小峰,等.生物有机肥对香蕉根际土壤生物多样性的影响[J].华南农业大学学报,2013,34(2):144-148. |
| ZHAO L F, HU W, LIU X F, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on biodiversity in rhizosphere soil of banana [J]. J. South Chin. Agric. Univ., 2013, 34(2):144-148. | |
| 10 | 黄玥.施肥和种植方式对烤烟、玉米根际微生物数量及细菌群落的影响[D]. 重庆:西南大学,2013. |
| HUANG Y. Influence of fertilization and cropping pattern on microbial numbers and bacteria community structures in flue-cured tobacco and maize soils [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2013. | |
| 11 | 林先贵.土壤微生物研究原理与方法[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2010:362-364. |
| LIN X G. Principles and Methods of Soil Microbiology Research [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2010:362-364. | |
| 12 | GARLAND J L, MILLS A L. Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1991, 57(8):2351-2359. |
| 13 | 靳辉勇,黎娟,朱益,等.土壤调理剂对烤烟根系活力及根际土壤微生物碳代谢特征的影响[J].核农学报,2019,33(1):158-165. |
| JING H Y, LI J, ZHU Y, et al.. Effects of soil conditioner on root vigor and carbon metabolism characteristics of rhizosphere soil microorganisms in Flue-cured tobacco [J]. Acta Agric.Nucl. Sin., 2019, 33(1):158-165. | |
| 14 | 程存刚,赵德英,吕德国,等.植物源有机物料对果园土壤微生物群落多样性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2014(4):913-922. |
| CHENG C G, ZHAO D Y, LV D G, et al.. Effects of plant-derived organic materials and humification driving forces on soil microbial cummunity diverity in orchards [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2014(4):913-922. | |
| 15 | 王通明,陈伟,潘文杰,等.有机肥和化肥对烟叶气体交换、叶绿素荧光特性及叶绿体超微结构的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(2):517-526. |
| WANG T M, CHEN W, PAN W J, et al.. Difference of leaf gas exchange traits, chlorophyⅡ fluorescence characteristics and chloroplast ultrastructure of Nicotianatabacum L. K326 under organic fertilization and chemical fertilization [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2015, 21(2):517-526. | |
| 16 | 杨海君,肖启明,刘安元.土壤微生物多样性及其作用研究进展[J].南华大学学报(自然科学版),2005,19(4):21-27. |
| YANG H J, XIAO Q M, LIU A Y. Soil microbial diversity and its action [J]. J. Nanhua Univ. (Nat. Technol.), 2005, 19(4):21-27. | |
| 17 | 杨旭初,龙莉,屠乃美,等.微生物肥料在不同节肥水平下对烟草根际微生物碳代谢指纹的影响[J].核农学报,2017,31(10): 2016-2022. |
| YANG X C, LONG L, TU N M, et al.. Effects of microbial fertilizer in the different fertilizer-saving levels on C Metabolic fingerprint of tobacco rizosphere microorganisms [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2017, 31(10):2016-2022. | |
| 18 | 宋蒙亚,李忠佩,吴萌,等.不同种植年限设施菜地土壤微生物量和群落结构的差异[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(18):3635-3644. |
| SONG M Y, LI Z P, WU M, et al.. Change in soil microbial biomass and community structure with cultivation chronosequence of greenhouse vegetable [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2015, 48(18):3635-3644. | |
| 19 | 陆雅海,张福锁.根际微生物研究进展[J].土壤,2006,38(2):113-121. |
| LU Y H, ZHANG F S. The advances in rhizospher microbiology [J]. Soils, 2006, 38(2):113-121. | |
| 20 | 张云伟,徐智,汤利,等.不同有机肥对烤烟根际土壤微生物的影响[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(9):2551-2556. |
| ZHANG Y W, XU Z, TANG L, et al.. Effects of different organic fertilizers on the microbes in rhizospheric soil of flue-cured tobacco [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2013, 24(9):2551-2556. | |
| 21 | 王辉,李小艳,云菲,等.微生物菌剂对烤烟光合特性及产质量的影响[J].江西农业学报,2018,30(6):52-56. |
| WANG H, LI X Y, YUN F, et al.. Effects of microbial agent on photosynthetic characteristics,yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2018, 30(6):52-56. | |
| 22 | 范黎.菌根真菌促进植物生长的光合生理研究[J].微生物学通报,2015,42(5):968-976. |
| FANG L. Influence of mycorrhizae on photothesis of plant [J]. Mocrobiology, 2015, 42(5):968-976. | |
| 23 | 李月灵,金则新,管铭,等.铜胁迫条件下土壤微生物对海州香薷光合特性和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J].植物研究,2013,33(6):684-689. |
| LI Y L, JIN Z X, GUAN M, et al.. Effects of soil microbes on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophⅡ fluorescence parameters of Elsholtziasplendens under copper stress condition [J]. Bull. Bot. Res., 2013, 33(6):684-689. |
| [1] | ZHANG Jie1,2, MA Yajun1, HE Zhibin1, GAO Fangfang1, ZHANG Shaohua1, WANG Chaoran1, ZHAO Danchen1. Application of Microbial Fertilizer Instead of Fertilizer in Apple Planting [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(7): 128-135. |
| [2] | GU Meiying1§, YANG Rong1§, XU Wanli2*, TANG Guangmu2, ZHANG Zhidong1, ZHANG Yunshu2, FENG Lei2, WANG Ning1, ZHAN Faqiang1. Effects of Cotton Stalk Biochar Combined with Bio-organic Fertilizer on Rhizosphere Soil Micro-ecology and Cotton Growth of Continuous Cropping Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(10): 47-57. |
| [3] | LI Diqin1, GONG Zhanwu1, LI Yuhui2, LIU Guanghui2*, CHEN Yifan1, . Effects of Compound Bio-organic Fertilizer on Flue-cured Tobacco Photosynthetic Physiological Characters & Soil Microbes [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(9): 109-116. |
| [4] | WANG Haibin1,2, ZHANG Qingxu1, CHEN Xiaoting1, MA Xiaomao1, ZHAO Hu1,YE Jianghua2,3, KONG Xianghai1. Effect of Animal Manure on Soil Acidity and Microbe of Tea Tree Rhizosphere [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(5): 115-122. |
| [5] | ZHANG Ming\|yan1, ZHANG Ji\|guang1*, SHEN Guo\|ming1, ZHANG Zhong\|feng1, CAI Xi. Present Research Status and Prospects of Microbial Communities Structure and Functional Microorganisms in Tobacco\|Planting Soil [J]. , 2014, 16(5): 115-122. |
| [6] | XIAO Bo1§, ZHOU Wen1§, LIU Wan\|xue1*, JIANG Zhi\|lin2, WAN Fang\|hao1. Feedback of Ageratina adenophora Soil Microbe on A. adenophora and Native Plants [J]. , 2014, 16(4): 151-158. |
| [7] | LUO Hui\|ying1, YAO Bin1*, FAN Yun\|liu2. Research Progress on Acidophilic Glycoside Hydrolase [J]. , 2013, 15(5): 1-7. |
| [8] | TIAN Jia1, SUN Chao1, YANG Ming-yan2, ZHANG Xiao-qi1*. Studies on the Activities of Three Kinds of Soil Enzyme, Organic Matters, Microbes and the Yields and Quality of Apple in Different Tree-aged Apple Orchards in Loess Plateau [J]. , 2012, 14(5): 115-122. |
| [9] |
SHAN Hong-bin1, LIANG Zhi2, WANG Chun-li1, JIA Hong-tao1, WANG Li1.
Effect of Continuous Cotton Cropping on the Microbes and Enzyme Activities in Soil [J]. , 2009, 11(1): 113-117. |
| [10] | . [J]. , 1999, 1(4): 53-58. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号 