




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 63-70.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0873
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaochun SUN( ), Wenjing HUANG, Bo LI
), Wenjing HUANG, Bo LI
Received:2020-10-17
Accepted:2021-07-26
Online:2022-01-15
Published:2022-01-25
作者简介:孙晓春 Email: sunxiaochun08@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xiaochun SUN, Wenjing HUANG, Bo LI. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Physiological and Biochemical Indexes and Related Gene Expression in Platycodongrandiflorus Under Drought Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 63-70.
孙晓春, 黄文静, 李铂. 水杨酸对干旱胁迫下桔梗幼苗生理生化指标及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 63-70.
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’3’) |
|---|---|
| actinF | CTGAGAACAATGTTGCCATAAAGAT |
| actinR | CAGAAGTCCTTTTCCAGCCATC |
| PODF | CATTAAGATTCAAACCCGGGC |
| PODR | CTCGTGACTCAGTTGTTGCTCTT |
| P5CRF | TGGGTAGACGGATTGTGTGAA |
| P5CRR | GCCATGTTTGTGCGTGGAT |
| CAOF | TGCTGTAGAACTATCTTTATGACTT |
| CAOR | CTGTGTACAGTCCATAAGCATTCCC |
| CHLGF | TTCTTGCTTAGCTCCTTTGATTC |
| CHLGR | GCAAATGAAGCGGTTAAAGCG |
Table 1 Primer sequence
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’3’) |
|---|---|
| actinF | CTGAGAACAATGTTGCCATAAAGAT |
| actinR | CAGAAGTCCTTTTCCAGCCATC |
| PODF | CATTAAGATTCAAACCCGGGC |
| PODR | CTCGTGACTCAGTTGTTGCTCTT |
| P5CRF | TGGGTAGACGGATTGTGTGAA |
| P5CRR | GCCATGTTTGTGCGTGGAT |
| CAOF | TGCTGTAGAACTATCTTTATGACTT |
| CAOR | CTGTGTACAGTCCATAAGCATTCCC |
| CHLGF | TTCTTGCTTAGCTCCTTTGATTC |
| CHLGR | GCAAATGAAGCGGTTAAAGCG |
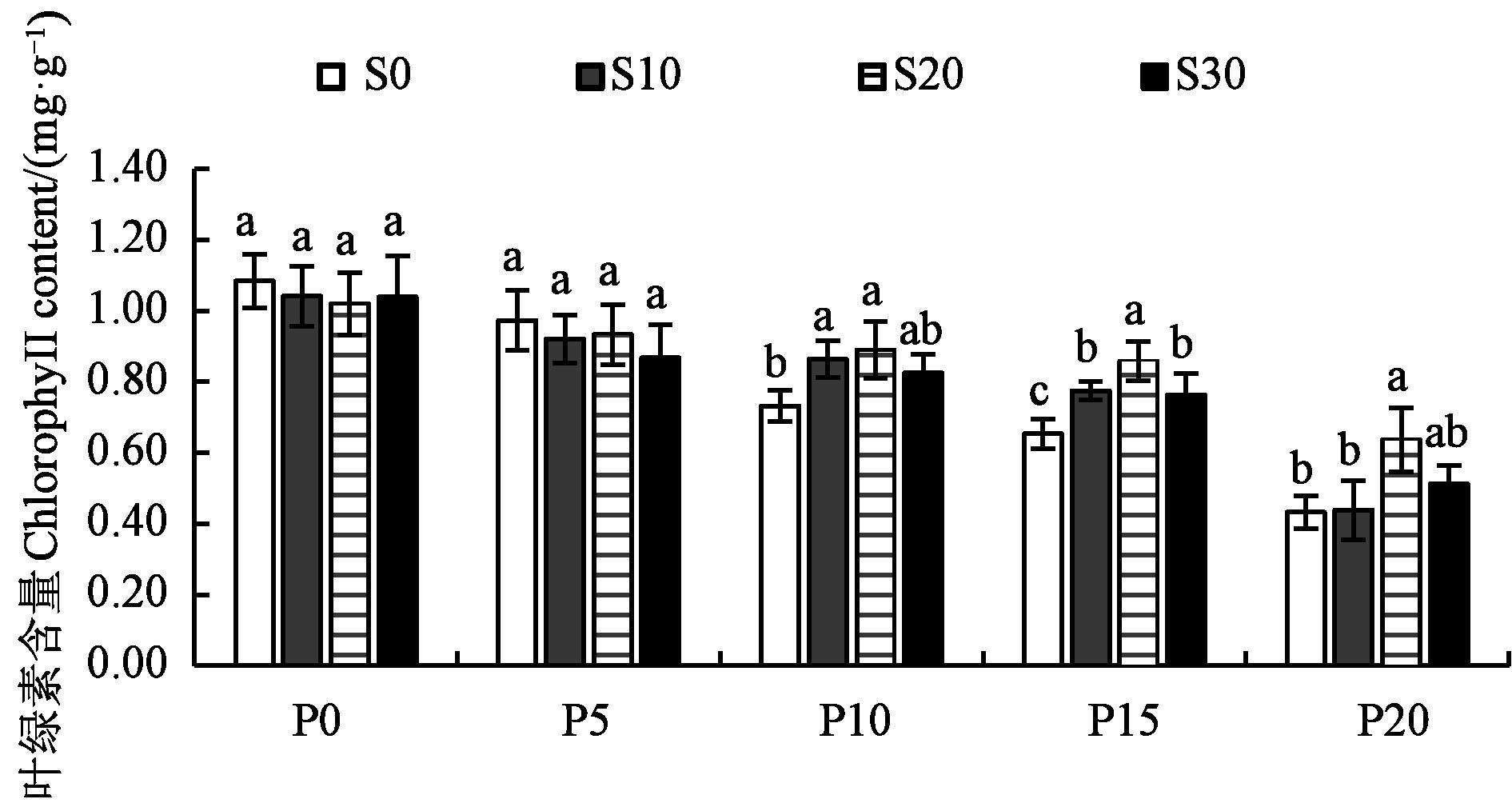
Fig.1 Chlorophyll contents in PlatycodongrandiflorusNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different SA treatments in same PEG treatment at P<0.05 level.leaves of different treatments
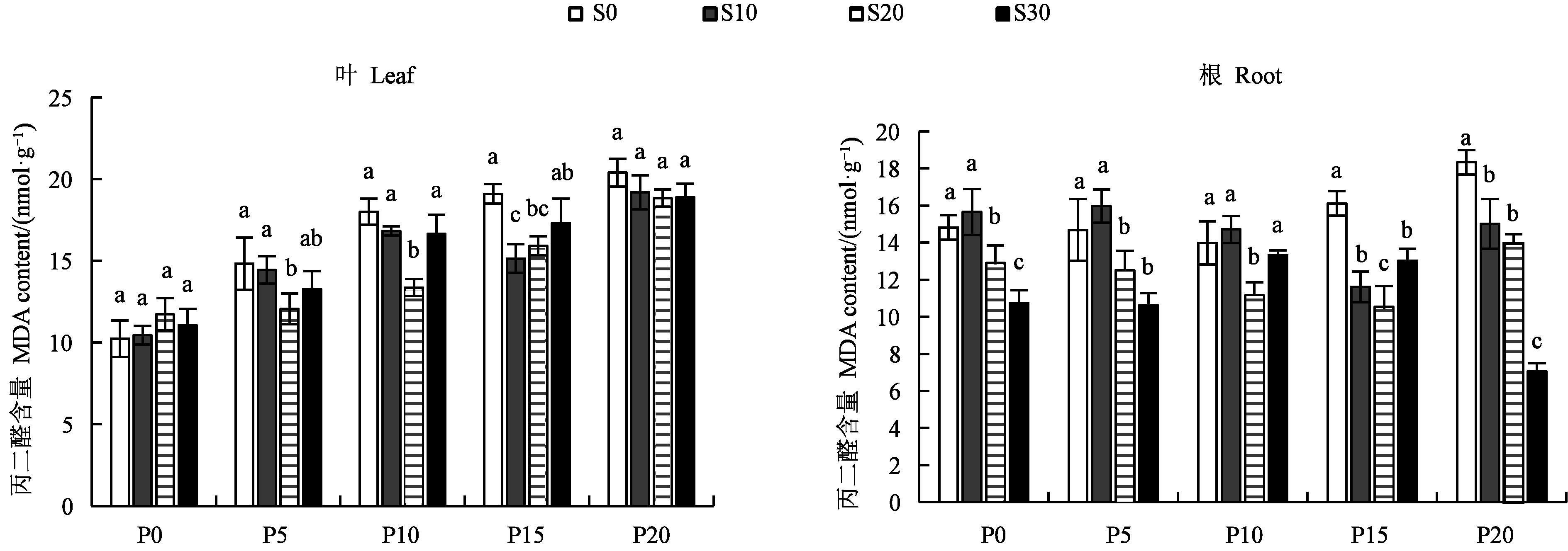
Fig.2 MDA contents in Platycodongrandiflorus leaves and roots of different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different SA treatments in same PEG treatment at P<0.05 level.
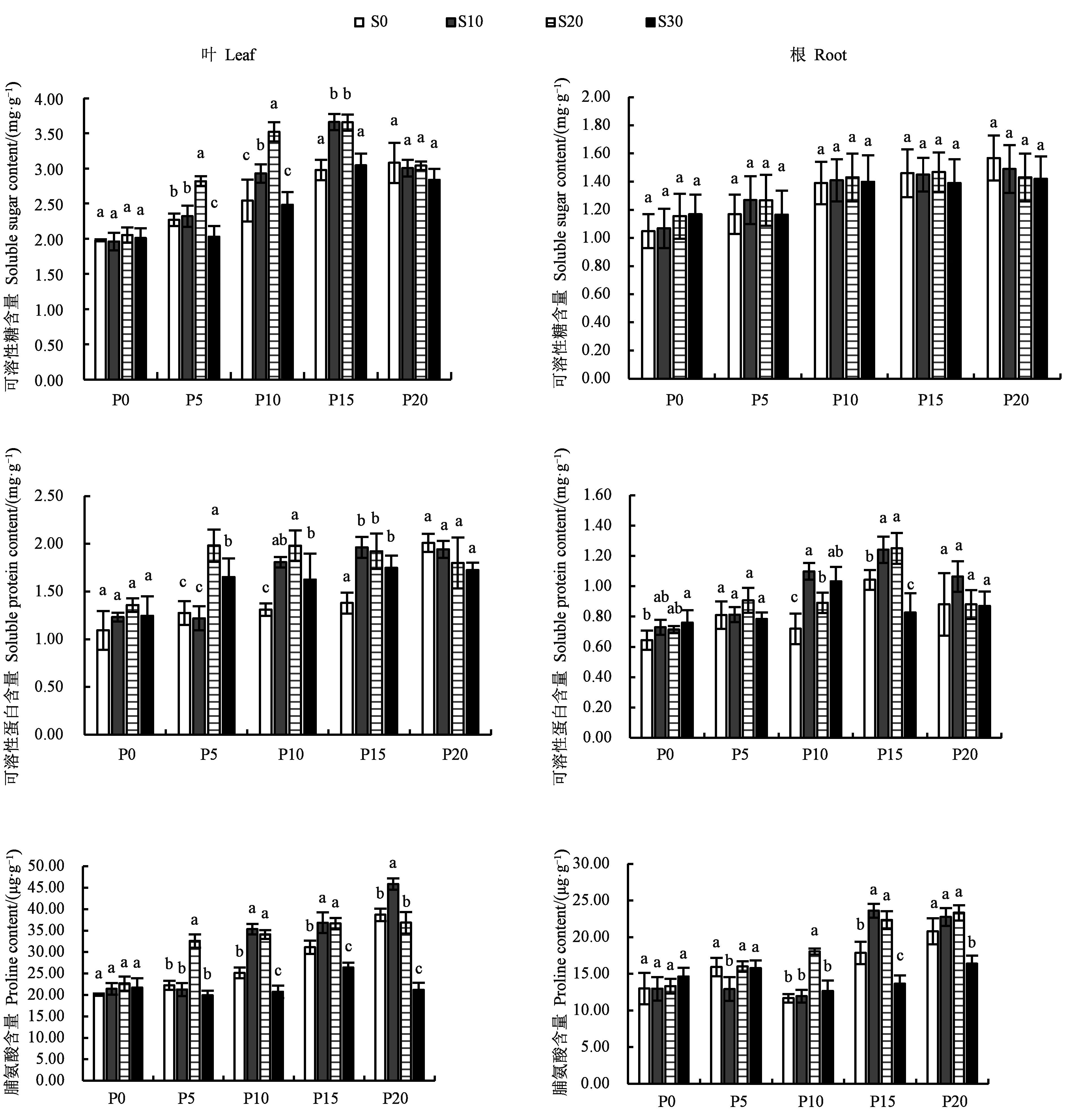
Fig.3 Contents of SS, SP and Pro in Platycodongrandiflorus leaves and roots of different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different SA treatments in same PEG treatment at P<0.05 level.
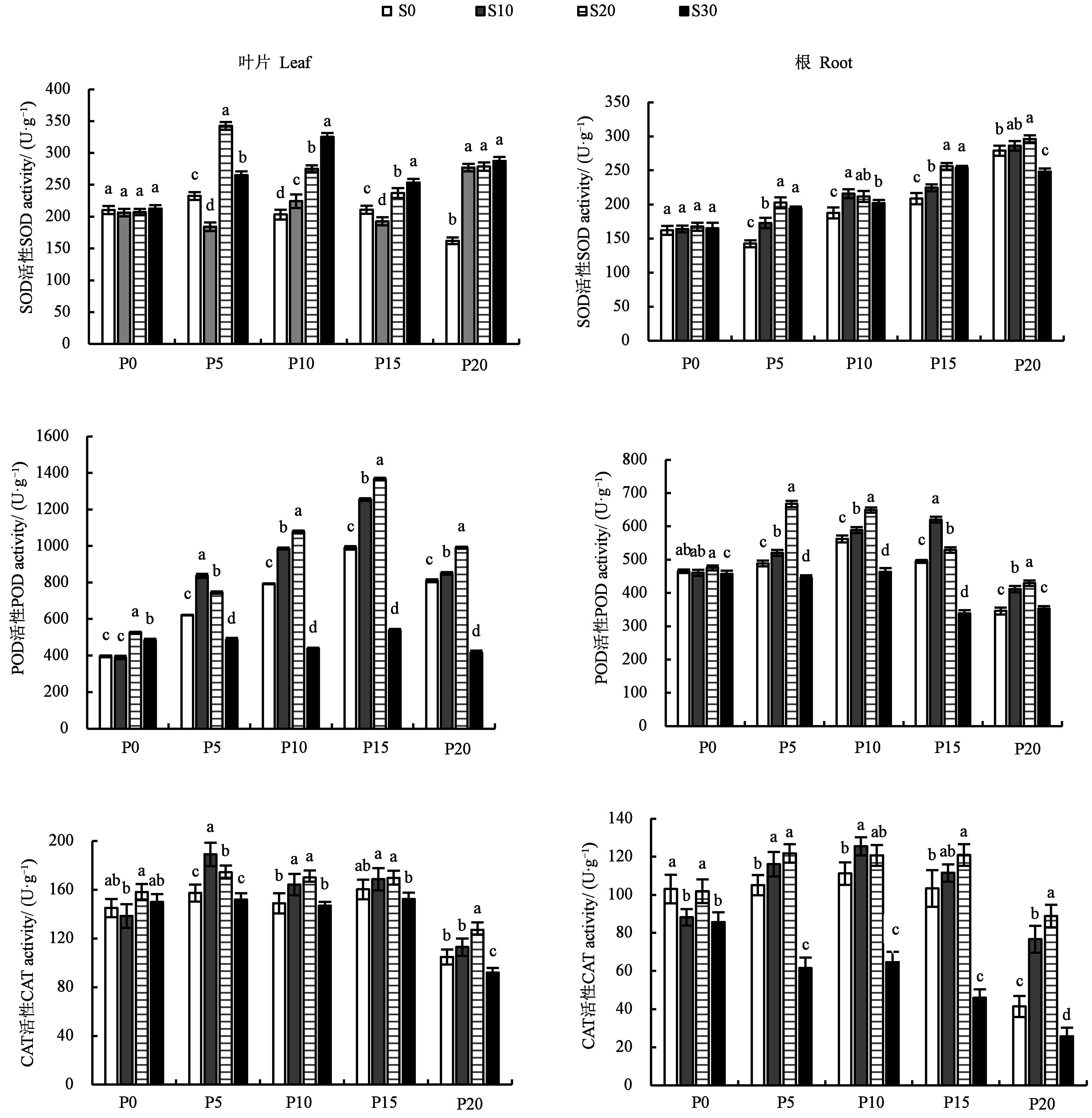
Fig.4 Activities of antioxidant enzymes in Platycodongrandiflorus leaves and roots of different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different SA treatments in same PEG treatment at P<0.05 level.
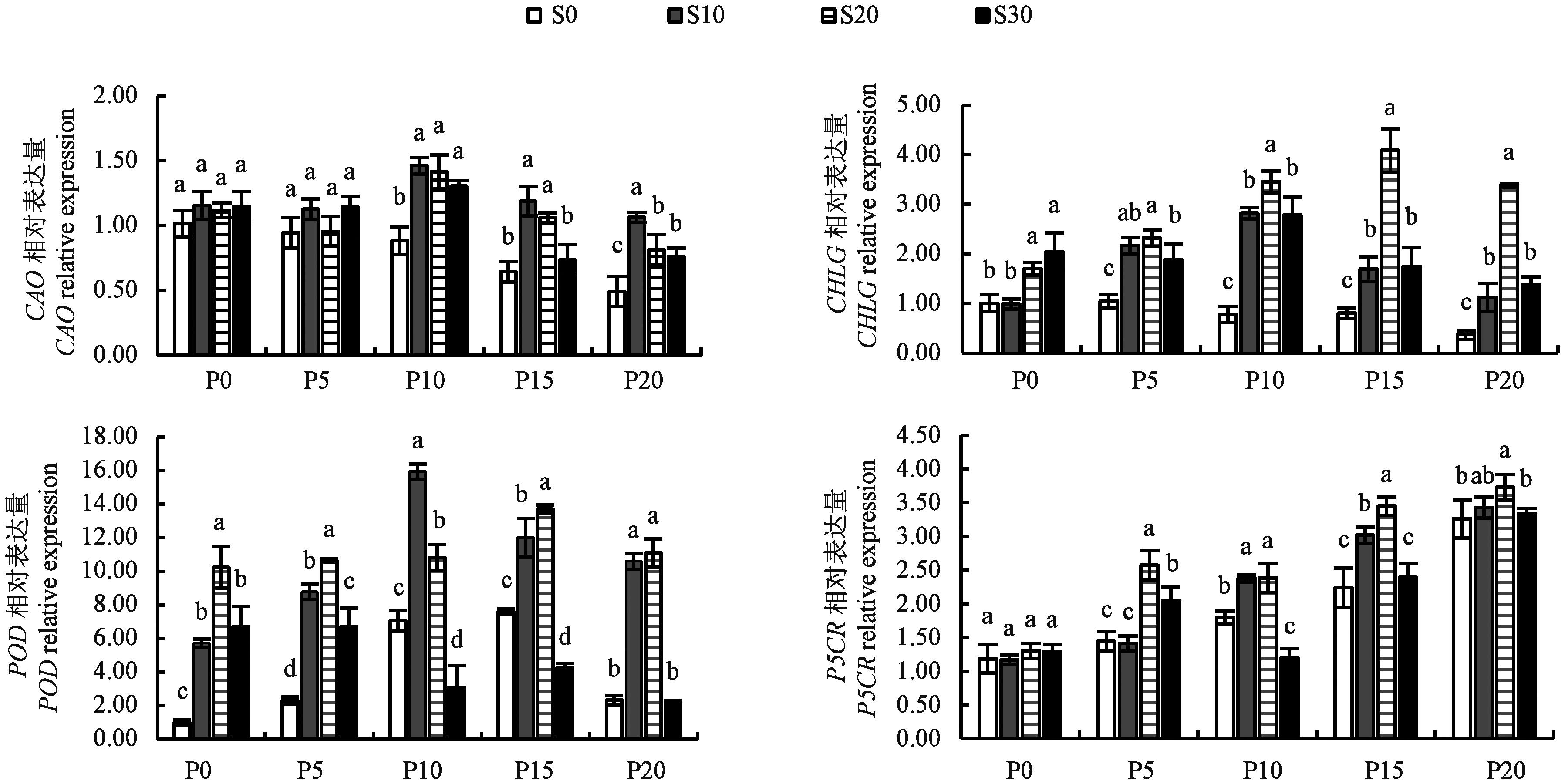
Fig.5 Related expression of COA, CHLG, POD and P5CR genes in Platycodongrandiflorus leavesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different SA treatments in same PEG treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | CHOI J H, SUN W J, CHOI C Y, et al.. Saponins from the roots of Platycodongrandiflorum ameliorate high fat dietinduced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [J]. Biomed. Pharmacotherapy, 2017, 86:205-212. |
| 2 | 郑繁慧,刘文丛,郑毅男,等.桔梗总皂苷与桔梗总次皂苷祛痰作用的比较[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2011,33(5):541-544. |
| ZHENG F H, LIU W C, ZHENG Y N, et al.. Comparation of expectorant effect of total platycosides and secondary saponin from the roots of platycodon grandiflorum [J]. J. Jilin Agric.Univ., 2011, 33(5):541-544. | |
| 3 | 赵璞,李梦,及增发,等.植物干旱响应生理对策研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016,32(15):86-92. |
| ZHAO P, LI M, JI Z F, et al.. Countermeasures of drought physiology response in plant [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016, 32(15):86-92. | |
| 4 | 吴自明,张欣,万建民.叶绿素生物合成的分子调控[J]. 植物生理学报,2008,44(6):1064-1070. |
| WU Z M, ZHANG X, WAN J M. Molecular regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2008, 44(6):1064-1070. | |
| 5 | 邓小艳,彭浩,贺红武.植物吡咯啉-5-羧酸还原酶-潜在的除草作用靶标[J]. 农 药,2013,52(2):87-89. |
| DENG X.Y, PENG H, HE H W. Pyrroline-5carboxylate reductase as potential target of herbicide [J]. Agrochemicals, 2013, 52(2):87-89. | |
| 6 | 梁艳荣,胡晓红,张颍力,等.植物过氧化物酶生理功能研究进展[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2003,24(2):110-113. |
| LIANG Y R, HU X H, ZHANG Y L, et al.. Progress on physiological function research of plant peroxidase [J]. J. Inner Mongolia Agric. Univ. (Nat.Sci.), 2003, 24(2):110-113. | |
| 7 | 周永海,杨丽萍,马荣雪,等.外源褪黑素对高温胁迫下甜瓜幼苗抗氧化特性及其相关基因表达的影响[J]. 西北农业学报,2020,29(5):745-751. |
| ZHOU Y H, YANG L P, MA R X, et al.. Effects of exogenous melatoninon antioxidant properties and related gene expression in melon seedlings under high temperature stress [J]. Acta Agric. Boroccid. Sin., 2020, 29(5):745-751. | |
| 8 | 田永强,聂国伟,李凯,等.5-氨基乙酰丙酸对甜樱桃花器官低温胁迫伤害的缓解效应[J]. 西北农业学报,2020,29(4):595-602. |
| TIAN Y Q, NIE G W, LI K, et al.. Ameliorating effects of 5aminolevulinic acid on damage to sweet cherry floral organ under low temperature stress [J]. Acta Agric. Boroccid. Sin., 2020, 29(4):595-602. | |
| 9 | 张艳军,赵江哲,张可伟.植物激素在叶片衰老中的作用机制研究进展[J].植物生理学报,2014, 50(9):1305-1309. |
| ZHANG Y J, ZHAO J Z, ZHANG K W. Research progress on mechanisms of phytohormones regulating leaf senescence [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2014, 50(9):1305-1309. | |
| 10 | 易小林,李名扬,池浩,等.水杨酸缓解干旱、高温及双重胁迫下对紫御谷内源激素及渗透调节物质的影响[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,36(2):62-67. |
| YI X L, LI M Y, CHI H, et al.. Influences of salicylic acid (SA) on the contents of endogenous hormones and osmotic adjustment substances in purple majesty under drought stress and/or high temperature [J]. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2014, 36(2):62-67. | |
| 11 | 马乐元,陈年来,韩国君,等.外源水杨酸对干旱胁迫下小冠花叶片活性氧水平及抗氧化系统的影响[J].草业学报,2017(10):132-142. |
| MA L Y, CHEN N L, HAN G J, et al.. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Coronillavaria under drought stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2017, 28(10):3274-3280. | |
| 12 | 蒋明敏,徐晟,夏冰,等.干旱胁迫下外源氯化钙、水杨酸和一氧化氮对石蒜抗旱性的影响[J].植物生理学报,2012,48(9):909-916. |
| JIANG M M, XU S, XIA B, et al.. Effects of exogenous calcium chloride, salicylic acid and nitric oxide on drought resistance of Lycorisradiata under drought stress [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2012, 48(9):909-916. | |
| 13 | 孙晓春,黄文静,李铂,等.外源水杨酸对干旱胁迫下桔梗幼苗生理生化指标的影响[J].北方园艺,2019 (16):121-125. |
| SUN X C, HUANG W J, LI B, et al.. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on physiological characteristics of seedlings under drought stress of Platycodongrandiflorus [J]. Nor. Hortic., 2019 (16):121-125. | |
| 14 | 张以顺,黄霞,陈云凤.植物生理学实验教程[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2009:135-136,139-142. |
| ZHANG Y S, HUANG X, CHEN Y F. Guide of Plant Physiological Experiments [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009:135-136,139-142. | |
| 15 | LIVAK K J,SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408. |
| 16 | 张宇,周自云,夏鹏国,等.干旱胁迫对柴胡中皂苷合成关键酶基因表达及皂苷含量的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2016,41(4):643-647. |
| ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z Y, XIA P G, et al.. Expression of key enzyme genes and content of saikosaponin in saikosaponin biosynthesis under drought stress in Bupleurum Chinense [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2016, 41(4):643-647. | |
| 17 | 唐艳萍,文涛,孙歆,等.水杨酸对植物光合作用影响的研究进展[J].西北植物学报,2015,35(8):1701-1708. |
| TANG Y P, WEN T, SUN X, et al.. Research progress on the impact of salicylic acid on plant photosynthesis [J]. Acta Bot. BorOccid. Sin., 2015, 35(8):1701-1708. | |
| 18 | CRAMER G R, ERGUL A, GRIMPLET J. Water and salinity stress in grapevines: early and late changes in transcript and metabolite profiles [J]. Funct. Integr. Genomics, 2007, 7:111-134. |
| 19 | SZABADOS L, SAVOURE A. Proline: a multifunctional amino acid [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2009, 15:89-97. |
| 20 | TROVATO M, MATTIOLI R, COSTANTINO P. Multiple roles of proline in plant stress tolerance and development [J]. Rend. Lincei, 2008, 19:325-346. |
| [1] | BAI Hao, LI Xiaofan, ZHONG Li, SONG Qianqian, LIU Benshuai, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Yang, WANG Zhixiu, JIANG Yong, XU Qi, CHANG Guobin, CHEN Guohong, . Mineral Element Depositions and Gene Expression Across Different Tissues of the Runzhou White Crested Ducks [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 63-73. |
| [2] | LIU Yuan, ZHANG Xiuyan, XU Miaoyun, ZHENG Hongyan, ZOU Junjie, ZHANG Lan, WANG Lei. Global Small RNA Transcriptome Profiling of Rice Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 23-32. |
| [3] | HU Yang, LI Gangtie, LI Xing, JIA Shouyi. Growth and Physiological Index of Tamarix leptostachys Bunge Seedlings Under Soil Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 43-50. |
| [4] | ZHANG Haoyang, JIN Yinan, SUN Yanxin, LI Ziwei, GUO Xiaoheng, XU Zicheng*. Research Progress of Plant microRNAs in Drought Stress Response [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 27-36. |
| [5] | WANG Deyun1,2, LIU Peipei1, CHEN Yunting1, XU Yueying1, ZHOU Li1, LUO Guangming1*. Effect of Drought Stress on Endogenous Hormone Content of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 58-63. |
| [6] | SU Yumeng§, ZHANG Xuting§, Terigele, TIAN Min, SHANG Xiaorui, LI Guojing, WANG Ruigang*. Identification of microRNAs in Caragana intermedia Kuang by High Throughput Sequencing Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 51-57. |
| [7] | FAN Ningbo1, ZHOU Junxue2, JIANG Kai2, WANG Hong2, SHI Longfei2, GAO Yulong3*, CHEN Yi3*. Membrane Lipid Peroxidation and Its Relationship with Senescence-Related Genes in Main Veins of Flue-Cured Tobacco at Different Maturity Stages#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 66-72. |
| [8] | ZHANG Luxiang1, CHEN Simeng1, ZHENG Cong2, JIN Yinan1, HAN Yi3, XU Zicheng1, HUANG Wuxing1, SHAO Huifang1*. Influences of Different Deacclimation Duration on Drought Resistance of Tobacco Seedlings#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 57-64. |
| [9] | BAO Zhijuan, JIN Rong, YANG Jinqing, ZHANG Qi, ZHU Yongli, ZHAO Zhengxiong*. Effects of Pb and Zn Combination on Antioxidant Enzymes and Carbon-nitrogen Metabolism of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 65-72. |
| [10] | GUAN Sijing, WANG Nan, XU Rongrong, GE Tiantian, GAO Jing, YAN Yonggang, ZHANG Gang, CHEN Ying, ZHANG Mingying. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(12): 66-75. |
| [11] | HAO Zhenggang, ZHAO Huijun, WEI Yuqing*, ZENG Zhouqi, WANG Zhiheng. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Sweet Sorghum to Cadmium Stress and Its Cadmium Accumulation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 30-42. |
| [12] | LUO Yong1, JIAO Guizhen1, LIU Shengbo2*, WEI Yuewei1, SHAO Huifang1, JIA Hongfang1*. Effects of Cadmium with Different Concentrations on Seeding Growth and Auxin-related Gene Expression of Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 58-65. |
| [13] | WANG Zhiheng, HUANG Siqi, ZOU Fang, YANG Xiuliu, WEI Yuqing*. Effects of Temperature and NaCl on Seed Germination and Seedling Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Sweet Sorghum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(9): 42-51. |
| [14] | YANG Ruiping1, LIU Ruixiang1, MA Yingmei1*, Guo Zhanbin2, ZHANG Hongwu2, BAI Yu1, ZHAO Xinyu1. Evaluation of Different Chenopodium quinoa Resources and Effects of Osmotic Regulators on Their Drought Resistance [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(9): 52-60. |
| [15] | SONG Jinhui, WENG Qiaoyun, LYU Aizhi, YUAN Jincheng, LIU Yinghui*. Influence of Drought Stress on Growth and Quality of Silage Corn at Jointing Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(6): 161-167. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号