




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 173-182.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0047
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Yuanjie YU1( ), Qingqing ZHANG1(
), Qingqing ZHANG1( ), Jianguo MA1, Kangwei JIANG2, Hong LI2
), Jianguo MA1, Kangwei JIANG2, Hong LI2
Received:2022-01-22
Accepted:2023-10-07
Online:2024-09-15
Published:2024-09-13
Contact:
Qingqing ZHANG
于远介1( ), 张青青1(
), 张青青1( ), 马建国1, 江康威2, 李宏2
), 马建国1, 江康威2, 李宏2
通讯作者:
张青青
作者简介:于远介 E-mail:3310395798@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuanjie YU, Qingqing ZHANG, Jianguo MA, Kangwei JIANG, Hong LI. Comparative Study on Soil Organic Carbon and Its Components in Different Plant Community Types[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 173-182.
于远介, 张青青, 马建国, 江康威, 李宏. 不同植物群落土壤有机碳及其组分的差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 173-182.
植物群落 Plant community | 代码 Code | 总盖度 Total coverage/% | 总生物量 Total biomass/gm3 | 优势种 Dominant species | 优势度 Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
雪林云杉林下植物群落 Understory of Picea schrenkiana plant community | X | 26.0 | 40.12 | 唐松草Thalictrum aquilegifolium | 54.65 |
紫苞鸢尾植物群落 Iris ruthenica plant community | W | 29.4 | 62.80 | 紫苞鸢尾Iris loczyi | 64.08 |
醉马草植物群落 Achnatherum inebrians plant community | Z | 32.2 | 101.05 | 醉马草Achnatherum inebrians | 125.23 |
圆叶锦葵植物群落 Malva pusilla plant community | Y | 33.6 | 110.87 | 圆叶锦葵Malva rotundifoli | 182.50 |
Table 1 Basic information of 4 typical plant communities
植物群落 Plant community | 代码 Code | 总盖度 Total coverage/% | 总生物量 Total biomass/gm3 | 优势种 Dominant species | 优势度 Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
雪林云杉林下植物群落 Understory of Picea schrenkiana plant community | X | 26.0 | 40.12 | 唐松草Thalictrum aquilegifolium | 54.65 |
紫苞鸢尾植物群落 Iris ruthenica plant community | W | 29.4 | 62.80 | 紫苞鸢尾Iris loczyi | 64.08 |
醉马草植物群落 Achnatherum inebrians plant community | Z | 32.2 | 101.05 | 醉马草Achnatherum inebrians | 125.23 |
圆叶锦葵植物群落 Malva pusilla plant community | Y | 33.6 | 110.87 | 圆叶锦葵Malva rotundifoli | 182.50 |
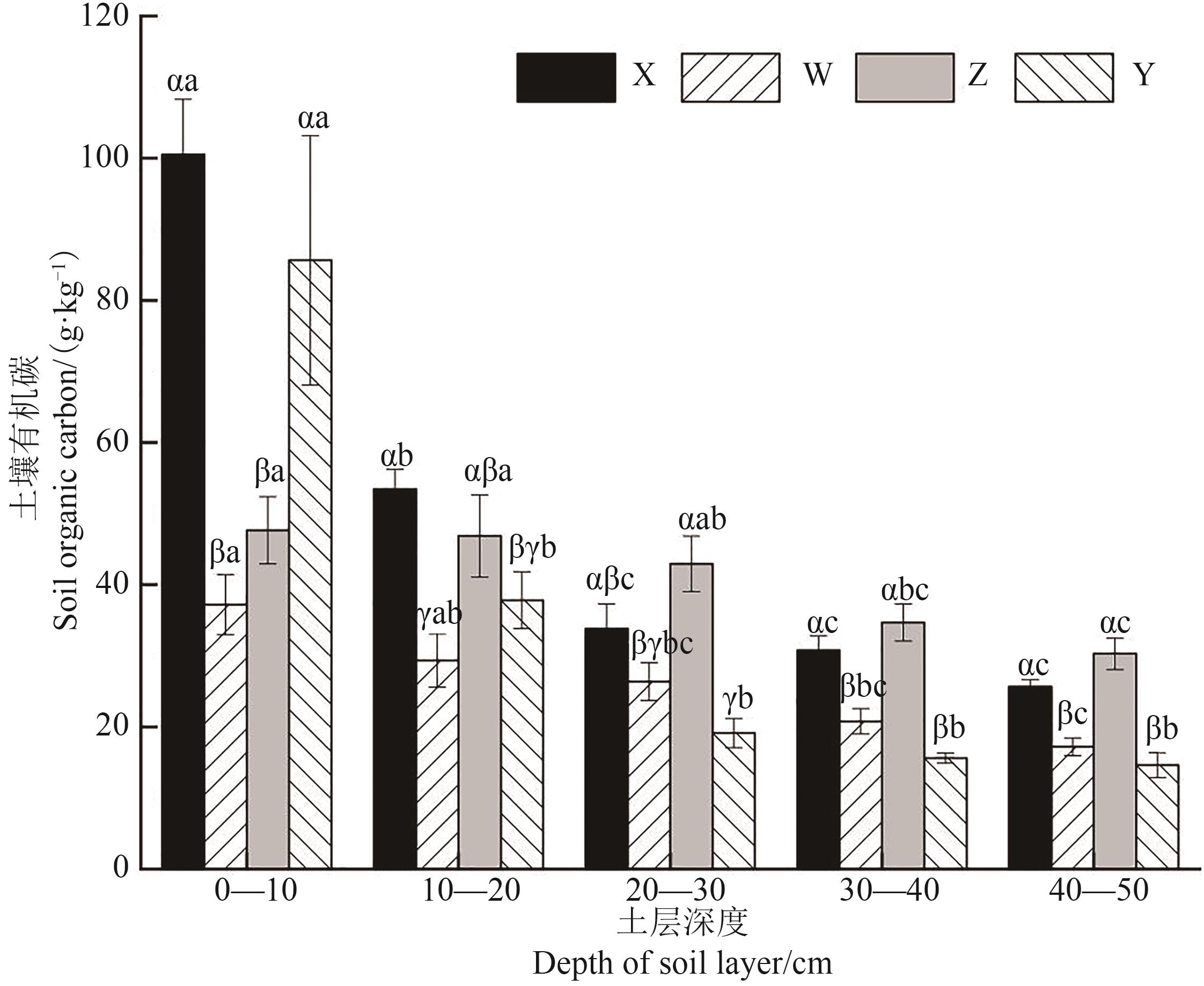
Fig. 1 Soil organic carbon content at different depths in 4 plant communitiesNote: Different Greece letters indicate significant differences between different plant communities of same soil layer at P<0.05 level; different English letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers of same plant community at P<0.05 level.
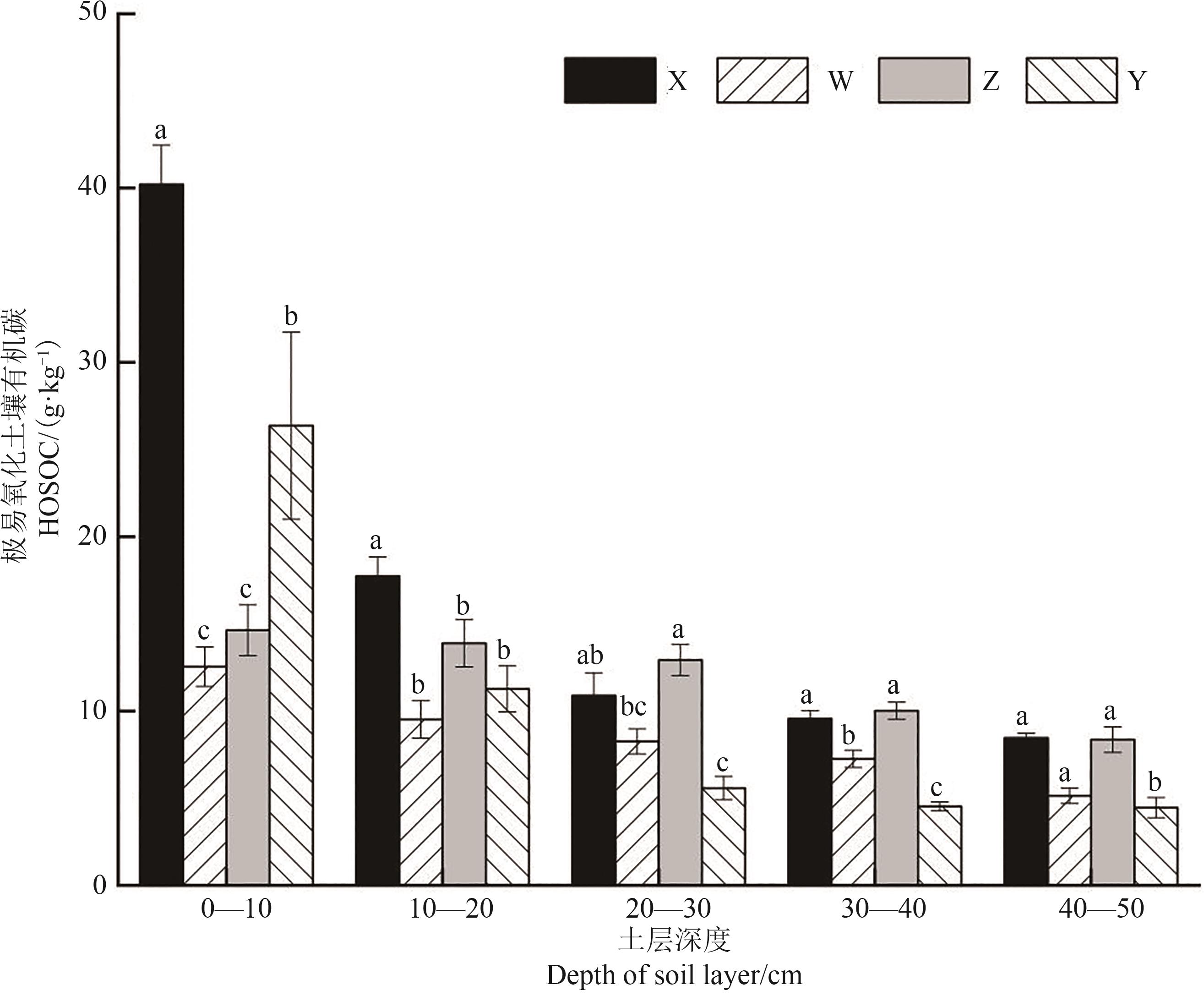
Fig. 3 Soils highly susceptible oxidizing organic carbon of 4 typical plant communitiesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different plant communities of same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
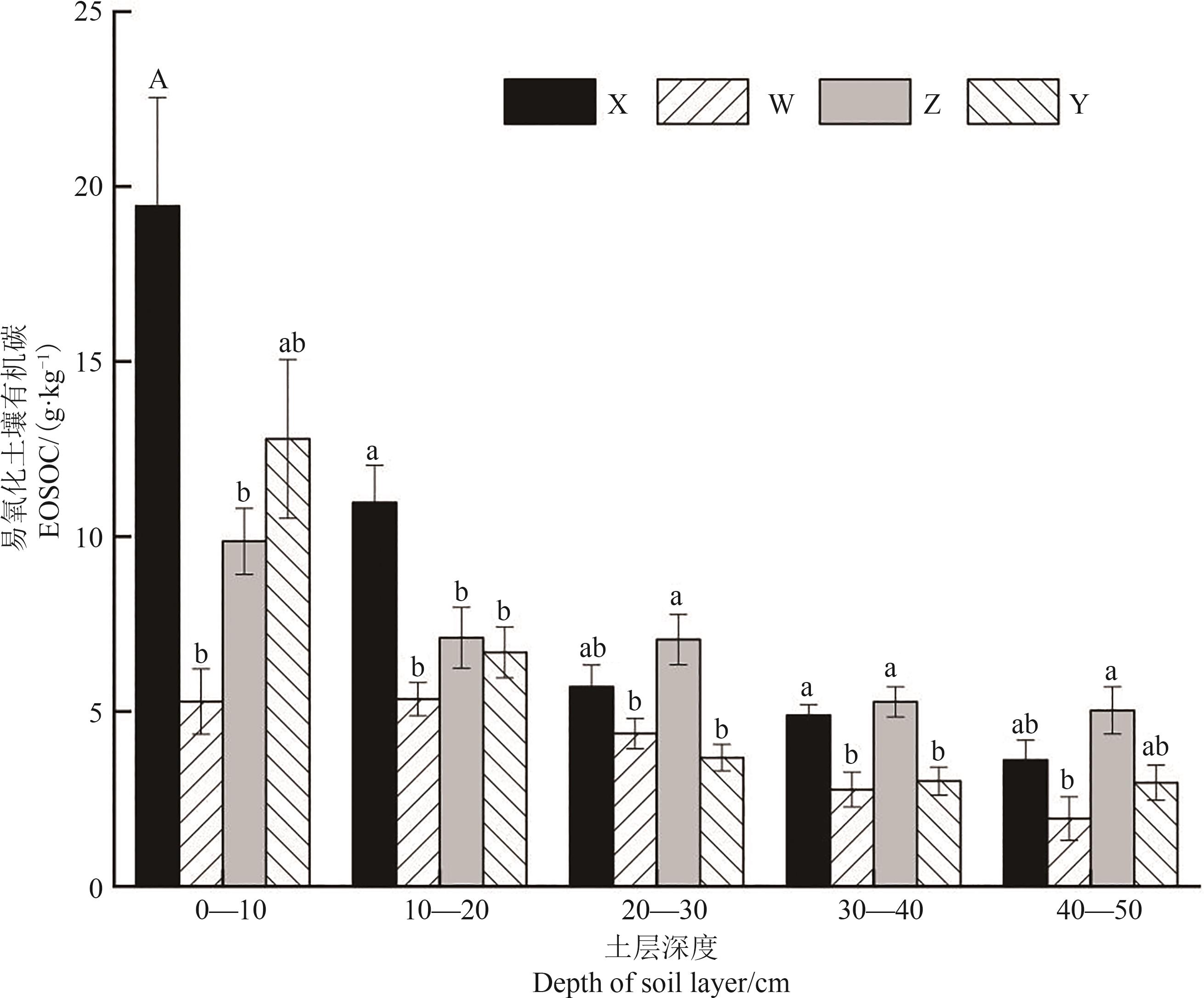
Fig. 4 Soil easily oxidized organic carbon in 4 typical plant communitiesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different plant communities of same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
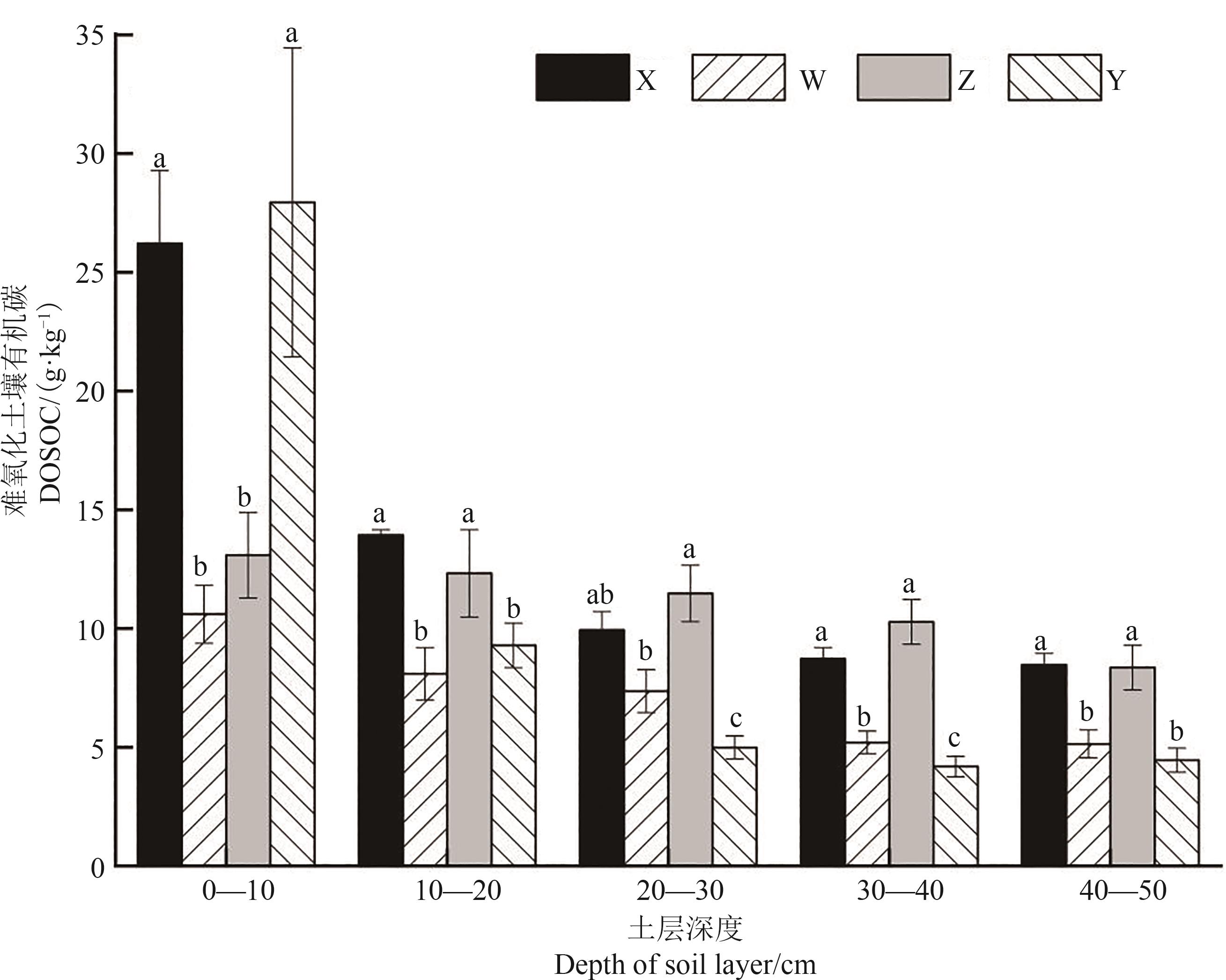
Fig. 5 Soil refractory organic carbon in 4 typical plant communitiesNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different plant communities of same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 解宪丽,孙波,周慧珍,等.中国土壤有机碳密度和储量的估算与空间分布分析[J].土壤学报,2004,41(1):35-43. |
| XIE X L, SUN B, ZHOU H Z, et al.. Organic carbon density and storage in soils of China and spatial analysis [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2004, 41(1):35-43. | |
| 2 | 刁二龙,曹广超,曹生奎,等.祁连山南坡不同土地利用方式下土壤碳氮含量及通径分析[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(5):1346-1354. |
| DIAO E L, CAO G C, CAO S K, et al.. Soil carbon and nitrogen content and path analysis under different land use patterns on the southern slope of Qilian mountains [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2021, 38(5):1346-1354. | |
| 3 | 周莉,李保国,周广胜.土壤有机碳的主导影响因子及其研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2005,20(1):99-105. |
| ZHOU L, LI B G, ZHOU G S. Advances in controlling factors of soil organic carbon [J]. Adv. Earth Sci., 2005, 20(1):99-105. | |
| 4 | 王绍强,周成虎.中国陆地土壤有机碳库的估算[J].地理研究,1999,18(4):349-356. |
| WANG S Q, ZHOU C H. Estimating soil carbon reservior of terrestrial ecosystem in China [J]. Geogr. Res., 1999, 18(4):349-356. | |
| 5 | 解宪丽,孙波,周慧珍,等.不同植被下中国土壤有机碳的储量与影响因子[J].土壤学报,2004,41(5):687-699. |
| XIE X L, SUN B, ZHOU H Z, et al.. Soil carbon stocks and their infuencing factors under native vegetations in China [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2004, 41(5):687-699. | |
| 6 | 丁越岿,杨劼,宋炳煜,等.不同植被类型对毛乌素沙地土壤有机碳的影响[J].草业学报,2012,21(2):18-25. |
| DING Y K, YANG J, SONG B Y, et al.. Effect of different vegetation types on soil organic carbon in Mu US desert [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2012, 21(2):18-25. | |
| 7 | 季波,何建龙,吴旭东,等.宁夏典型天然草地土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化特征[J].草业学报,2021,30(1):24-35. |
| JI B, HE J L, WU X D, et al.. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and active organic carbon in typical natural grassland in Ningxia [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2021, 30(1):24-35. | |
| 8 | NI J. Carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems of China:estimates at different resolutions and their responses to climate change [J]. Climate Change, 2001, 49(3):339-358. |
| 9 | 杨洪晓,吴波,张金屯,等.森林生态系统的固碳功能和碳储量研究进展[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2005,41(2):172-177. |
| YANG H X, WU B, ZHANG J T, et al.. Progress of research into carbon fixation and storage of forest ecosystems [J]. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2005, 41(2):172-177. | |
| 10 | 仝川,曾从盛.湿地生态系统碳循环过程及碳动态模型[J].亚热带资源与环境学报,2006,1(1):84-92. |
| TONG C, ZENG C S. Review and analysis on carbon cycling and carbon balance model in wetlands ecosystem [J]. J. Subtrop. Resour. Environ., 2006, 1(1):84-92. | |
| 11 | 汪业勖,赵士洞,牛栋.陆地土壤碳循环的研究动态[J].生态学杂志,1999,18(5):29-35. |
| WANG Y X, ZHAO S D, NIU D. Research state of soil carbon cycling in terrestrial ecosystem [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 1999, 18(5):29-35. | |
| 12 | 徐侠,陈月琴,汪家社,等.武夷山不同海拔高度土壤活性有机碳变化[J].应用生态学报,2008,19(3):539-544. |
| XU X, CHEN Y Q, WANG J S, et al.. Changes of soil active organic carbon at different altitudes in Mount Wuyi [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2008, 19(3):539-544. | |
| 13 | 葛楠楠,石芸,杨宪龙,等.黄土高原不同土壤质地农田土壤碳、氮、磷及团聚体分布特征[J].应用生态学报,2017, 28(5):1626-1632. |
| GE N N, SHI Y, YANG X L, et al.. Distribution of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen,total phosphorus and water stable aggregates of cropland with different soil textures on the Loess Plateau, northwest China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2017, 28(5):1626-1632. | |
| 14 | 杨丽霞,潘剑君.土壤活性有机碳库测定方法研究进展[J].土壤通报, 2004,35(4):502-506. |
| YANG L X, PAN J J. Progress in the study of measurements of soil active organic carbon pool [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2004, 35(4): 502-506. | |
| 15 | 徐广平,李艳琼,沈育伊,等.桂林会仙喀斯特湿地水位梯度下不同植物群落土壤有机碳及其组分特征[J].环境科学,2019,40(3):1491-1503. |
| XU G P, LI Y Q, SHEN Y Y, et al.. Soil organic carbon distribution and components in different plant communities along a water table gradient in the Huixian Karst wetland in Guilin [J]. Environ. Sci.,2020,26(3):658-666. | |
| 16 | 罗海波,刘方,刘元生,等.喀斯特石漠化地区不同植被群落的土壤有机碳变化[J].林业科学,2009,45(9):24-28. |
| LUO H B, LIU F, LIU Y S, et al.. Variation of forest soil organic carbon in Karst rocky desertification area [J]. Sci. Silvae Sin., 2009, 45(9):24-28. | |
| 17 | 金奇,吴琴,钟欣孜,等.鄱阳湖湿地水位梯度下不同植物群落类型土壤有机碳组分特征[J].生态学杂志,2017,36(5):1180-1187. |
| JIN Q, W Q, ZHONG X Z, et al.. Soil organic carbon and its components under different plant communities along a water table gradient in the Poyang Lake wetland [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2017, 36(5):1180-1187. | |
| 18 | 习盼,董倩,张亚楠,等.盐城滩涂湿地典型植物群落土壤活性有机碳组分分布特征[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(11):3623-3632. |
| XI P, DONG Q, ZHANG Y N, et al.. Distribution characteristics of active components in soil organic carbon across typical plant communities in Yancheng coastal wetlands [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2020, 39(11):3623-3632. | |
| 19 | 朱浩宇,王子芳,陆畅,等.缙云山5种植被下土壤活性有机碳及碳库变化特征[J].土壤,2021,53(2):354-360. |
| ZHU H Y, WANG Z F, LU C, et al.. Variation characteristics of soil active organic carbon and carbon pools under five vegetation types in Jinyun mountain [J]. Soils, 2021, 53(2):354-360. | |
| 20 | 周正虎,刘琳,侯磊.土壤有机碳的稳定和形成:机制和模型[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2022,44(10):11-22. |
| ZHOU Z H, LIU L, HOU L. Soil organic carbon stabilization and formation: mechanism and model [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2022, 44(10):11-22. | |
| 21 | 周国逸,熊鑫.土壤有机碳形成机制的探索历程[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2019,27(5):481-490. |
| ZHOU G Y, XIONG X. Exploration history of soil organic carbon formation mechanisms [J]. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot., 2019, 27(5):481-490. | |
| 22 | 何艳,黄昌勇,黄巧云,等.土壤学[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2021:29-43. |
| 23 | 张鲜花,朱进忠,吴咏梅.天山北坡羊茅草原群落结构与数量特征的动态变化[J].草地学报,2012,20(5):819-824. |
| ZHANG X H, ZHU J Z, WU Y M. Dynamic of community structure and quantitative characteristics of festuca ovin grassland in the northern slope of Tianshan mountains [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2012, 20(5):819-824. | |
| 24 | 李典鹏,孙涛,贾宏涛,等.利用方式对高寒草地土壤有机碳组分的影响[J].新疆农业大学学报,2018,41(1):55-60. |
| LI D P, SUN T, JIA H T, et al.. Effects of utilization modes on soil organic carbon components in alpine meadow [J]. J. Xinjiang Agric. Univ., 2018, 41(1):55-60. | |
| 25 | 王幼奇,夏子书,包维斌,等.银川鸣翠湖国家湿地公园香蒲、荷花、石菖蒲和芦苇生长区土壤有机碳及其组分含量对比研究[J].湿地科学,2020,18(3):294-302. |
| WANG Y Q, XIA Z S, BAO W B, et al.. Comparison of contents of soil organic carbon and its components in growth regions of Typha angustata, Nelumbo nucifera, Acorus tatarinowii and Phragmites australis in Yinchuan Mingcui lake national wetland park [J]. Wetland Sci., 2020, 18(3):294-302. | |
| 26 | 王慧杰,常顺利,张毓涛,等.天山雪岭云杉林土壤有机碳密度空间分异及其与森林发育的关系[J].山地学报,2017,35(3):300-307. |
| WANG H J, CHANG S L, ZHANG Y T, et al.. Spatial variation of the density of SOC of Picea schrenkiana forest and relationships with forest development [J]. Mountain Res., 2017, 35(3):300-307. | |
| 27 | 李菲,李娟,龙健,等.典型喀斯特山区植被类型对土壤有机碳、氮的影响[J].生态学杂志,2015,34(12):3374-3381. |
| LI F, LI J, LONG J, et al.. Effect of vegetation types on soil organic carbon and nitrogen in typical Karst mountainous area [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2015, 34(12):3374-3381. | |
| 28 | 王邵军,曹子林,李小英,等.滇池湖滨带不同植被类型土壤碳、氮时空分布特征[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2013,37(5):55-59. |
| WANG S J, CAO Z L, LI X Y, et al.. Spatiotemporal distributions of soil carbon and nitrogen under the four riparian zones in the Dianchi lake [J]. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2013, 37(5):55-59. | |
| 29 | 岳永寰,靳瑰丽,宫珂,等.小尺度下醉马草生长动态与土壤养分的关系[J].新疆农业科学,2019,56(6):1142-1150. |
| YUE Y H, JIN G L, GONG K, et al.. Study on the relationship between the growth dynamics and soil nutrients of Achnatherum inebrians on a small-scale [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2019, 56(6):1142-1150. | |
| 30 | 华娟,赵世伟,张扬,等.云雾山不同草地群落土壤活性有机碳分布特征[J].草地学报,2009,17(3):315-320. |
| HUA J, ZHAO S W, ZHANG Y, et al.. Distribution characteristics of soil labile organic carbon of different grassland communities in Yunwu mountain [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2009, 17(3):315-320. | |
| 31 | 张海东,于东升,王宁,等.植被恢复过程中侵蚀红壤有机质变化研究[J].土壤,2013,45(5):856-861. |
| ZHANG H D, YU D S, WANG N, et al.. The change of soil organic matter under vegetation restoration on the eroded red soil [J]. Soils, 2013, 45(5):856-861. | |
| 32 | 杨昊天,王增如,贾荣亮.腾格里沙漠东南缘荒漠草地不同群落类型土壤有机碳分布及储量特征[J].植物生态学报,2018,42(3):288-296. |
| YANG H T, WANG Z R, JIA R L. Distribution and storage of soil organic carbon across the desert grasslands in the southeastern fringe of the Tengger desert, China [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2018, 42(3):288-296. | |
| 33 | 张文敏,吴明,王蒙,等.杭州湾湿地不同植被类型下土壤有机碳及其组分分布特征[J].土壤学报,2014,51(6):1351-1360. |
| ZHANG W M, WU M, WANG M, et al.. Distribution character ristics of organic carbon and its components in soils under different types of vegetation in wetland of Hangzhou Bay [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2014, 51(6):1351-1360. | |
| 34 | BLAIR B J, LEFROY R D. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the developments of a carbon managemen index for agricultural systems [J]. Aust. J. Agric. Res., 1995, 46(7):1456-1466. |
| 35 | 阎欣,刘任涛,安慧.土壤易氧化有机碳与溶解性有机碳对荒漠草地沙漠化过程中土壤碳库变异的表征[J].草业学报,2018,27(11):15-25. |
| YAN X, LIU R T, AN H. Characterzation of readily oxidiable carbon andissolved organic carbon within the soil carbon pool during desertification of grassland in central China [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2018, 27(11):15-25. | |
| 36 | 张雪,韩士杰,王树起,等.长白山白桦林不同演替阶段土壤有机碳组分的变化[J].生态学杂志,2016,35(2):282-289. |
| ZHANG X, HAN S J, WANG S Q, et al.. Change of soil organic carbon fractions at different successional stages of Betula platyphylla forest in Changbai mountains [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2016, 35(2):282-289. | |
| 37 | 张哲,王邵军,李霁航,等.土壤易氧化有机碳对西双版纳热带森林群落演替的响应[J].生态学报,2019,39(17):6257-6263. |
| ZHANG Z, WANG S J, LI J H, et al.. Response of soil readily oxidizable carbon to community succession of Xishuangbanna tropical forests [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(17):6257-6263. |
| [1] | Linlin DONG, Jinfang ZHA, Mingxing SHEN, Haihou WANG, Linlin SHI, Yueyue TAO, Xinwei ZHOU, Changying LU. Effect of Long-term Straw Returning on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions Composition in Rice-Wheat Rotation Ecosystem [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 166-175. |
| [2] | LIU Huixia, SUN Zongjiu, SHI Yukun, WU Wenchao, ZHENG Li, AI Tijian. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(11): 147-155. |
| [3] | LI Long1, QIN Fucang1*, JIANG Lina2, YAO Xueling3. Spatio-temporal Variability of Soil Organic Carbon in Semi-arid Area [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(3): 100-107. |
| [4] | CHEN Zhuo, SHI Kun . Relation of Clay Organic Carbon and Proportion of Different |Soil Layers in Two Hilly Clay Sections [J]. , 2008, 10(2): 119-122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号