




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 87-98.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0090
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qilin LIU( ), Jinze LI, Jiayu DING, Shuoli WANG, Ziming CHENG, Kangyuan GU, Guangyan FENG(
), Jinze LI, Jiayu DING, Shuoli WANG, Ziming CHENG, Kangyuan GU, Guangyan FENG( )
)
Received:2024-02-01
Accepted:2024-05-29
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Guangyan FENG
刘起麟( ), 李金泽, 丁佳渝, 王烁理, 程子铭, 古康圆, 冯光燕(
), 李金泽, 丁佳渝, 王烁理, 程子铭, 古康圆, 冯光燕( )
)
通讯作者:
冯光燕
作者简介:刘起麟 E-mail:1208859463@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Qilin LIU, Jinze LI, Jiayu DING, Shuoli WANG, Ziming CHENG, Kangyuan GU, Guangyan FENG. Analysis and Comparative Characteristics of Codon Preference in Chloroplast Genome of Polygonum genus[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 87-98.
刘起麟, 李金泽, 丁佳渝, 王烁理, 程子铭, 古康圆, 冯光燕. 蓼属叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性分析及比较特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 87-98.
物种 Species | 登陆号 Accession No. | 密码子适应指数 CAI | 最优密码子使用频率FOP | 有效密码 子数 ENC | GC含量GC content/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCall | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | |||||
| 香蓼 P. viscosa | NC_071834.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.30 | 38.38 | 45.91 | 37.75 | 31.49 |
| 粘蓼 P. viscofera | NC_082263.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.15 | 38.35 | 45.91 | 37.77 | 31.38 |
| 蓼蓝 P. tinctoria | OR730799.1 | 0.165 | 0.354 | 51.31 | 39.26 | 47.12 | 38.96 | 31.68 |
| 戟叶蓼 P. thunbergii | NC_082262.1 | 0.164 | 0.353 | 51.32 | 38.38 | 45.92 | 37.82 | 31.40 |
| 刺蓼 P. senticosa | NC_067968.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.04 | 38.26 | 45.74 | 37.88 | 31.15 |
| 伏毛蓼 P. pubescens | MK234901.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 51.18 | 38.36 | 45.94 | 37.74 | 31.39 |
| 丛枝蓼 P. posumbu | NC_082260.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.23 | 38.36 | 45.89 | 37.76 | 31.42 |
| 扛板归 P. perfoliata | OR730805.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 50.88 | 38.09 | 45.64 | 37.67 | 30.96 |
| 红蓼 P. orientalis | NC_065785.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.25 | 38.39 | 46.00 | 37.74 | 31.44 |
| 尼泊尔蓼 P. nepalensis | NC_082259.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.37 | 45.93 | 37.75 | 31.42 |
| 春蓼 P. maculosa | NC_082258.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.22 | 45.93 | 37.75 | 31.42 |
| 长戟叶蓼 P. maackiana | NC_061657.1 | 0.165 | 0.353 | 51.23 | 38.45 | 46.17 | 37.82 | 31.36 |
| 长鬃蓼 P. longiseta | OR730801.1 | 0.165 | 0.353 | 51.23 | 38.45 | 46.17 | 37.82 | 31.36 |
| 酸模叶蓼 P. lapathifolia | OR730804.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.23 | 38.38 | 45.96 | 37.78 | 31.42 |
| 柔茎蓼 P. kawagoeana | NC_082256.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.21 | 38.35 | 45.90 | 37.75 | 31.40 |
| 愉悦蓼 P. jucunda | NC_084112.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.30 | 38.43 | 46.04 | 37.77 | 31.48 |
| 蚕茧草 P. japonica | ON229577.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.18 | 38.33 | 45.85 | 37.76 | 31.37 |
| 水蓼 P. hydropiper | MK234902.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.08 | 38.23 | 45.80 | 37.74 | 31.15 |
| 长箭叶蓼 P. hastatosagittata | OR730803.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.08 | 38.23 | 45.80 | 37.74 | 31.15 |
| 冰川蓼 P. glacialis | NC_082254.1 | 0.163 | 0.350 | 50.88 | 38.20 | 45.80 | 37.74 | 31.04 |
| 光蓼 P. glabra | OR730797.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.31 | 38.45 | 46.11 | 37.77 | 31.48 |
| 多叶蓼 P. foliosa | ON229572.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.35 | 45.90 | 37.75 | 31.41 |
| 稀花蓼 P. dissitiflora | ON229570.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.02 | 38.23 | 45.82 | 37.76 | 31.11 |
| 蓼子草 P. criopolitana | NC_079578.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.39 | 45.99 | 37.72 | 31.44 |
| 火炭母 P. chinensis | NC_050358.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 50.99 | 38.24 | 45.92 | 37.69 | 31.11 |
| 头花蓼 P. capitata | OR730796.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 50.99 | 38.26 | 45.94 | 37.74 | 31.10 |
| 柳叶刺蓼 P. bungeana | ON229568.1 | 0.163 | 0.350 | 51.06 | 38.31 | 45.91 | 37.77 | 31.25 |
| 两栖蓼 P. amphibia | ON229566.1 | 0.163 | 0.350 | 51.06 | 38.31 | 45.91 | 37.77 | 31.25 |
Table 1 Codon related parameters of Polygonum plants
物种 Species | 登陆号 Accession No. | 密码子适应指数 CAI | 最优密码子使用频率FOP | 有效密码 子数 ENC | GC含量GC content/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCall | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | |||||
| 香蓼 P. viscosa | NC_071834.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.30 | 38.38 | 45.91 | 37.75 | 31.49 |
| 粘蓼 P. viscofera | NC_082263.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.15 | 38.35 | 45.91 | 37.77 | 31.38 |
| 蓼蓝 P. tinctoria | OR730799.1 | 0.165 | 0.354 | 51.31 | 39.26 | 47.12 | 38.96 | 31.68 |
| 戟叶蓼 P. thunbergii | NC_082262.1 | 0.164 | 0.353 | 51.32 | 38.38 | 45.92 | 37.82 | 31.40 |
| 刺蓼 P. senticosa | NC_067968.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.04 | 38.26 | 45.74 | 37.88 | 31.15 |
| 伏毛蓼 P. pubescens | MK234901.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 51.18 | 38.36 | 45.94 | 37.74 | 31.39 |
| 丛枝蓼 P. posumbu | NC_082260.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.23 | 38.36 | 45.89 | 37.76 | 31.42 |
| 扛板归 P. perfoliata | OR730805.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 50.88 | 38.09 | 45.64 | 37.67 | 30.96 |
| 红蓼 P. orientalis | NC_065785.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.25 | 38.39 | 46.00 | 37.74 | 31.44 |
| 尼泊尔蓼 P. nepalensis | NC_082259.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.37 | 45.93 | 37.75 | 31.42 |
| 春蓼 P. maculosa | NC_082258.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.22 | 45.93 | 37.75 | 31.42 |
| 长戟叶蓼 P. maackiana | NC_061657.1 | 0.165 | 0.353 | 51.23 | 38.45 | 46.17 | 37.82 | 31.36 |
| 长鬃蓼 P. longiseta | OR730801.1 | 0.165 | 0.353 | 51.23 | 38.45 | 46.17 | 37.82 | 31.36 |
| 酸模叶蓼 P. lapathifolia | OR730804.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.23 | 38.38 | 45.96 | 37.78 | 31.42 |
| 柔茎蓼 P. kawagoeana | NC_082256.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.21 | 38.35 | 45.90 | 37.75 | 31.40 |
| 愉悦蓼 P. jucunda | NC_084112.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.30 | 38.43 | 46.04 | 37.77 | 31.48 |
| 蚕茧草 P. japonica | ON229577.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.18 | 38.33 | 45.85 | 37.76 | 31.37 |
| 水蓼 P. hydropiper | MK234902.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.08 | 38.23 | 45.80 | 37.74 | 31.15 |
| 长箭叶蓼 P. hastatosagittata | OR730803.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.08 | 38.23 | 45.80 | 37.74 | 31.15 |
| 冰川蓼 P. glacialis | NC_082254.1 | 0.163 | 0.350 | 50.88 | 38.20 | 45.80 | 37.74 | 31.04 |
| 光蓼 P. glabra | OR730797.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.31 | 38.45 | 46.11 | 37.77 | 31.48 |
| 多叶蓼 P. foliosa | ON229572.1 | 0.163 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.35 | 45.90 | 37.75 | 31.41 |
| 稀花蓼 P. dissitiflora | ON229570.1 | 0.164 | 0.352 | 51.02 | 38.23 | 45.82 | 37.76 | 31.11 |
| 蓼子草 P. criopolitana | NC_079578.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 51.22 | 38.39 | 45.99 | 37.72 | 31.44 |
| 火炭母 P. chinensis | NC_050358.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 50.99 | 38.24 | 45.92 | 37.69 | 31.11 |
| 头花蓼 P. capitata | OR730796.1 | 0.164 | 0.351 | 50.99 | 38.26 | 45.94 | 37.74 | 31.10 |
| 柳叶刺蓼 P. bungeana | ON229568.1 | 0.163 | 0.350 | 51.06 | 38.31 | 45.91 | 37.77 | 31.25 |
| 两栖蓼 P. amphibia | ON229566.1 | 0.163 | 0.350 | 51.06 | 38.31 | 45.91 | 37.77 | 31.25 |

Fig. 2 Correlation of codon parameters in Polygonum plantsNote: Blue indicates a positive correlation; orange shows the negative correlation; the darker the color and the larger the circle, the higher the correlation. GN—Genes number; ENC—Effective number of codon.
| 指标 Index | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC3s | GCall | 有效密码子数ENC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC2 | 0.475** | |||||
| GC3 | 0.171 | 0.223 | ||||
| GC3s | 0.177 | 0.252 | 0.985** | |||
| GCall | 0.829** | 0.812** | 0.505** | 0.517** | ||
| 有效密码子数ENC | 0.094 | -0.071 | 0.343* | 0.348* | 0.121 | |
| 基因数量Genes number | -0.076 | -0.211 | 0.201 | 0.199 | -0.083 | 0.213 |
Table 2 Correlation analysis of GC contents and related parameters in codons of Polygonum L.
| 指标 Index | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC3s | GCall | 有效密码子数ENC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC2 | 0.475** | |||||
| GC3 | 0.171 | 0.223 | ||||
| GC3s | 0.177 | 0.252 | 0.985** | |||
| GCall | 0.829** | 0.812** | 0.505** | 0.517** | ||
| 有效密码子数ENC | 0.094 | -0.071 | 0.343* | 0.348* | 0.121 | |
| 基因数量Genes number | -0.076 | -0.211 | 0.201 | 0.199 | -0.083 | 0.213 |
| 物种Species | 最优密码子Optimal codon |
|---|---|
| 扛板归 P. perfoliata | |
| 两栖蓼 P. amphibia | |
| 光蓼 P. glabra | |
| 火炭母 P. chinensis | |
| 柔茎蓼 P. kawagoeana | |
| 蚕茧草 P. japonica | |
| 冰川蓼 P. glacialis | |
| 头花蓼 P. capitata |
Table 3 Optimal codon of Polygonum plants
| 物种Species | 最优密码子Optimal codon |
|---|---|
| 扛板归 P. perfoliata | |
| 两栖蓼 P. amphibia | |
| 光蓼 P. glabra | |
| 火炭母 P. chinensis | |
| 柔茎蓼 P. kawagoeana | |
| 蚕茧草 P. japonica | |
| 冰川蓼 P. glacialis | |
| 头花蓼 P. capitata |
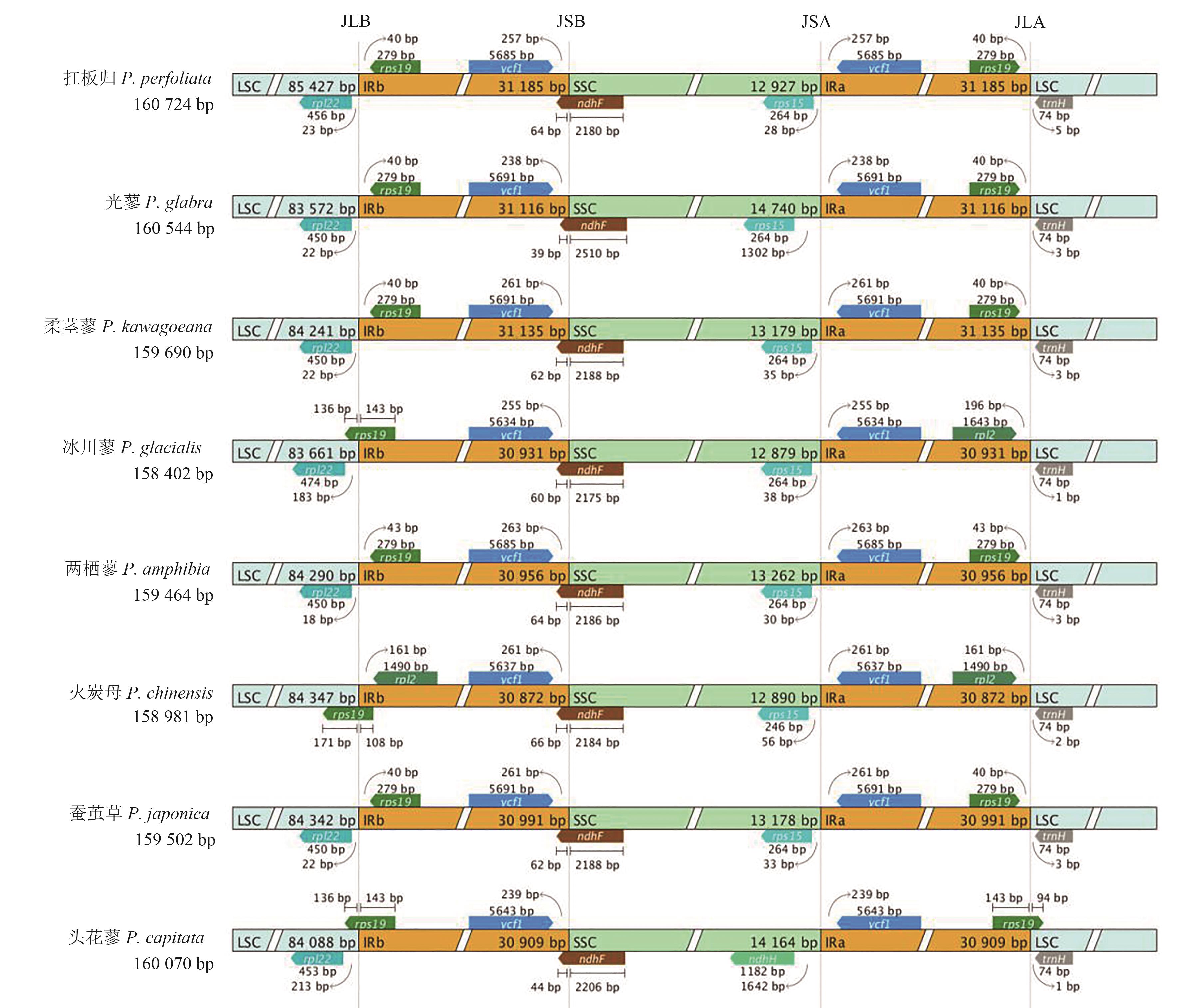
Fig. 6 Analysis of Boundary Differences in Polygonum plantsNot: LSC—Large single copy; SSC—Small single copy; IRA—Inverted repeats A; IRB—Inverted repeats B; JLA—Junction of LSC and IRA; JLB—Junction of LSC and IRB; JSA—Junction of SSC and IRA; JSB—Junction of SSC and IRB.

Fig. 9 Phylogenetic trees of Polygonum plants constructed using matk and rbcl sequencesA: Based on chloroplast matk sequence;B: Based on chloroplast rbcl sequence. Blue—Polygonum group; Green—P. senticosa group; Red—P. alatum group; Purple—P. kawagoeana group
| 1 | 朱晓宇,赵楚,辛建攀,等.江苏省蓼属植物资源及应用前景分析[J].中国野生植物资源,2020,39(5):72-78. |
| ZHU X Y, ZHAO C, XIN J P,et al..Plant resources and application prospects of Polygonum in Jiangsu [J].Chin.Wild Plant Resour.,2020,39(5):72-78. | |
| 2 | 沈冰冰,王敏,罗娟,等.蓼属药用植物的化学成分及其药理活性研究进展[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2015,35(7):63-70. |
| SHEN B B, WANG M, LUO J,et al..Research progress of chemical constituents and its pharmacological activities from the medicinal plants of genus Polygonum [J].J.Hunan Univ.Chin. Med., 2015,35(7):63-70. | |
| 3 | BAKER A J M, MCGSRATH S P, SIDOLI C, et al.. The possibility of insitu heavy metal decontamination of polluted soils using crops of metal accumulating plants [J]. Resour. Conserv. Re-cycling, 1994, 11(1-4):41-49. |
| 4 | LIU K, YU F, CHEN M,et al..A newly found manganese hyperaccumulator:Polygonum lapathifolium Linn [J].Int. J. Phytorem., 2016,18(4):348-353. |
| 5 | 赵月梅,杨振艳,赵永平,等.木犀科植物叶绿体基因组结构特征和系统发育关系[J].植物学报,2019,54(4):441-454. |
| ZHAO Y M, YANG Z Y, ZHAO Y P,et al..Chloroplast genome structural characteristics and phylogenetic relationships of Oleaceae [J]. Chin. Bull. Bot., 2019,54(4):441-454. | |
| 6 | 黄祥,楚光明,郑新开,等.睡莲属叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性及系统发育分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(4):75-84. |
| HUANG X, CHU G M, ZHENG X K, et al..Analysis of codon usage bias and phylogenetic of chloroplast genome in Nymphaea [J].J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022,24(4):75-84. | |
| 7 | ROBERTS R J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences [J]. Gene, 1980,8(4):329-343. |
| 8 | HERSHBERG R, PETROV D A. Selection on codon bias [J]. Annu. Rev. Genetics, 2008, 42(1):287-299. |
| 9 | 侯哲,娄晓鸣,李昂,等.11种唐松草属(Thalictrum)rbcL基因的密码子偏好性研究[J].江苏农业科学,2023,51(3):46-53. |
| 10 | 郭佳星,黄祥,杨梅花,等.桦木科叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性及系统发育分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2023,25(10):74-83. |
| GUO J X, HUANG X, YANG M H, et al.. Analysis of codon usage bias and phylogenetic in chloroplast genome of Betulaceae [J].J.Agric. Sci. Technol., 2023,25(10):74-83. | |
| 11 | LI N, LI Y Y, ZHENG C C, et al.. Genome-wide comparative analysis of the codon usage patterns in plants [J].Genes Genom., 2016,38(8):723-731. |
| 12 | YENGKHOM S, UDDIN A, CHAKRABORTY S. Deciphering codon usage patterns and evolutionary forces in chloroplast genes of Camellia sinensis var.assamica and Camellia sinensis var.sinensis in comparison to Camellia pubicosta [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2019,18(12):2771-2785. |
| 13 | 翟偲偲.中国春寥属植物分类和系统发育研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2021. |
| ZHAI S S. Study on taxonomy and phylogeny of Persicaria in China [D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2021. | |
| 14 | 王冰.广义蓼属(Polygonum L.s.l.)的系统发育研究进展及学名整理[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019. |
| WANG B. Phylogenetic progress in Polygonum L. s.l. and the re-arrangement of its scientific names [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019. | |
| 15 | 曹董玲.蓼亚科(蓼科)分类及系统发育研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2023. |
| CAO D L.Taxonomic and phylogenetic studies on the Polygonoideae (Polygonaceae) [D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2023. | |
| 16 | MENG J, LI X, LI H, et al.. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of four Aconitum medicinal species [J/OL].Molecules,2018,23(5):E101510 [2024-01-10]. . |
| 17 | SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O,et al..Cytoscape:a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks [J].Genome Res., 2003,13(11):2498-2504. |
| 18 | 尚明照,刘方,华金平,等.陆地棉叶绿体基因组密码子使用偏性的分析[J].中国农业科学,2011,44(2):245-253. |
| SHANG M Z, LIU F, HUA J P, et al.. Analysis on codon usage of chloroplast genome of Gossypium hirsutum [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2011,44(2):245-253. | |
| 19 | SUEOKA N. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerprints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses [J]. J. Mol. Evol., 2001,53(4):469-476. |
| 20 | 叶友菊,倪州献,白天道,等.马尾松叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性分析[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2018,37(10):4464-4471. |
| YE Y J, NI Z X, BAI T D, et al.. The analysis of chloroplast genome codon usage bais in Pinus massoniana [J]. Genom. Appl. Biol., 2018,37(10):4464-4471. | |
| 21 | 丁锐,胡兵,宗小雁,等.杓兰叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性分析[J].林业科学研究,2021,34 (5):177-185. |
| DING R, HU B, ZONG X Y, et al.. Analysis of codon usage in the chloroplast genome of Cypripedium calceolus [J]. For. Res., 2021, 34 (5):177-185. | |
| 22 | DIERCKXSENS N, MARDULYN P, SMITS G. NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data [J/OL].Nucl. Acids Res.,2017,45(4):e18 [2024-01-10]. . |
| 23 | FRAZER K A, PACHTER L, POLIAKOV A,et al..VISTA:computational tools for comparative genomics [J]. Nucl. Acids Res.,2004,32(S2):W273-W279. |
| 24 | TAMURA K, STECHER G, KUMAR S.MEGA11:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11 [J]. Mol. Boil. Evol.,2021,38(7):3022-3027. |
| 25 | 吴征镒.中国植物志[M].北京:科学出版社,1998:69. |
| 26 | 赵森,邓力华,陈芬.秋茄叶绿体基因组密码子使用偏好性分析[J].森林与环境学报, 2020, 40(5):534-541. |
| ZHAO S, DENG L H, CHEN F, et al.. Analysis of codon usepreference in the chloroplast genome of Kandelia [J]. J. For. Environ., 2020, 40(5):534-541. | |
| 27 | 王占军,李豹,姜行舟,等.两种茶树全基因组数据的密码子偏好性比较分析[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2018,40(12):2028-2039. |
| WANG Z J, LI B, JIANG X Z, et al.. Comparative analysis of the codon preference patterns in two species of Camellia sinensis based on genome data [J]. Chin. J. Cell Biol.,2018,40(12):2028-2039. | |
| 28 | 杨秀瑶,张梦洁,尹拓,等.蒲桃属叶绿体基因组特征及密码子偏好性分析[J].西南农业学报,2023,36(9):1869-1880. |
| YANG X Y, ZHANG M J, YIN T,et al..Chloroplast genome characteristics and codon preferences analysis in Syzygium [J].Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2023,36(9):1869-1880. | |
| 29 | 丁淑金,魏健生,陆莹玲,等.油麦吊云杉叶绿体基因组特征及密码子偏性分析[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2023,43(4):156-163. |
| DING S J, WEI J S, LU Y L, et al.. Characteristics and codon usage bias of Picea brachytyla var. Complanata chloroplast genome [J]. J. Central South Univ. For. Technol., 2023, 43(4):156-163. | |
| 30 | 童一涵,郑倩,杜新明,等.多齿红山茶叶绿体基因组序列特征分析[J].植物资源与环境学报,2022,31(5):27-36. |
| TONG Y H, ZHENG Q, DU X M, et al.. Analysis on sequence characteristics of chloroplast genome of Camellia polyodonta [J]. J.Plant Resour. Environ., 2022,31(5):27-36. | |
| 31 | DOBROGOJSKI J, ADAMIEC M, LUCIŃSKI R. The chloroplast genome:a review [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant., 2020,42(6):98-109. |
| 32 | FREUDENTHAL J A, PFAFF S, TERHOEVEN N,et al..A systematic comparison of chloroplast genome assembly tools [J/OL].Genome Biol.,2020,21(1):6 [2024-01-10]. . |
| 33 | ZHOU H, WANG H, HUANG L F, et al.. Heterogeneity in codon usages of sobemovirus genes [J]. Arch.Virol., 2005,150(8):1591-1605. |
| 34 | 张家格,雷万钧.18 种苔藓植物 rbcL 基因的密码子偏性及聚类分析[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(6):1-12. |
| ZHANG J G, LEI W J. Cluster analysis and codon usage bias studies of rbcL genes in 18 Bryophytes [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2020, 40(6):1-12. |
| [1] | Liangcai DA, Shanshan LIU, Junlin LIU, Lijuan ZHANG. Analysis of Codon Preference in Vitis vinifera Genome [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 78-86. |
| [2] | Chunlian LI, Peng ZHANG, Chuping CAI, Shuifeng QIN, Shanfang XIAO, Qiuxiang LUO, Song GUO, Junfeng LAN. Genomic Characteristics and Codon Preference Analysis of Schefflera octophylla (Lour.) Harms Chloroplasts [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(12): 63-76. |
| [3] | Dongdong ZHANG, Hongwei HAN, Zhenfan YU, Bin ZENG, Jiahui YANG, Wenwen GAO, Xintong MA. Codon Preference Analysis of Chloroplast Genome in 12 Rosaceae Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 65-75. |
| [4] | Jiaxing GUO, Xiang HUANG, Meihua YANG, Leilei WANG, Yanqi HAN, Zhuoyi LI. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias and Phylogenetic in Chloroplast Genome of Betulaceae [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 74-83. |
| [5] | Qiwei YAN, Xianglan LIANG, Qiuyun TAO, Qiuxiang LUO, Song GUO. Analysis of Chloroplast Genome Characteristics and Codon Usage Bias of Fissisfigma polyanthum Merr. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 74-86. |
| [6] | Xiang HUANG, Guangming CHU, Xinkai ZHENG, Jintao CHENG, Jianhao CHEN, Yingchun XU, Qijiang JIN, Meihua YANG. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias and Phylogenetic of Chloroplast Genome in Nymphaea [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 75-84. |
| [7] | SU Yue§, LIU Juanjuan§, WAN Bin, ZHANG Pengju, CHEN Zhenggen, SU Junji, WANG Caixiang. Chloroplast Genome Structure Characteristic and Phylogenetic Analysis of Mulgedium tataricum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 33-42. |
| [8] | JI Kaikai1, SONG Xiqiang1, CHEN Chunguo2, LI Ge2, XIE Shangqian1*. Codon Usage Profiling of Chloroplast Genome in Magnoliaceae [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(11): 52-62. |
| [9] | ZHOU Ziwei1,2§, CHANG Xiaojun1,2§, YOU Fangning1,2, . Analysis of Molecular Evolution and Codon Bias of Lipoxygenase (LOX) Gene Family in Tea Tree [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(12): 43-51. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号