




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 224-239.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0329
• MARINE AGRICULTURE & FRESHWATER FISHERIES • Previous Articles
Feng CUI1( ), Jingzhou LIU1(
), Jingzhou LIU1( ), Yixin QIAN2, Guiying CHEN2
), Yixin QIAN2, Guiying CHEN2
Received:2024-04-24
Accepted:2024-10-30
Online:2025-09-15
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
Jingzhou LIU
通讯作者:
刘荆州
作者简介:崔凤 E-mail:fcui@shou.edu.cn;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Feng CUI, Jingzhou LIU, Yixin QIAN, Guiying CHEN. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Marine Fishery Ecological Security in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 224-239.
崔凤, 刘荆州, 钱易鑫, 陈桂莹. 中国海洋渔业生态安全时空演变与驱动因素分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 224-239.
准则层 Criterion level | 指标层 Indicator level | 指标解释 Indicator interpretation |
|---|---|---|
D:探测器- 驱动 Detector- drive | C1:海洋渔业经济产值/(104 元) Marine fishery economic output value/(104 yuan) | 海洋捕捞和养殖生产的经济发展程度 Economic development level of marine fishing and aquaculture production |
C2:海洋渔业产值年增长率 Annual growth rate of marine fishery output value/% | 海洋渔业经济效益提升潜力 Potential for improving economic benefits of marine fishery | |
C3:海产品国际贸易水平 International trade level of seafood/(104 $) | 海洋渔业生产的水产品进出口产值效益 Import and export value benefit of aquatic products in marine fishery production | |
C4:海产品加工总量 Total processing volume of seafood/t | 海洋渔业资源开发利用效益 Benefit of development and utilization of marine fishery resources | |
C5:海洋渔业产值占农产值比重 Proportion of marine fishery output value in agricultural output value/% | 海洋捕捞和养殖的产业地位 Industrial status of marine fishing and aquaculture | |
P:主体适应- 压力 Subject adaptation- pressure | C6:海洋渔业人口从业率 Employment rate of marine fishery population/% | 海洋从业人口对海洋渔业生态安全产生的胁迫作用 Coercive effect of marine employed population on marine fishery ecological security |
C7:单船海洋捕捞效率 Single-vessel marine fishing efficiency/t | 单船海洋捕捞生产效率对海洋捕捞强度压力 Pressure of single-vessel marine fishing production efficiency on marine fishing intensity | |
C8:废水排放主要污染物总量 Total amount of major pollutants in wastewater discharge/(104 t) | 陆源污染物对海洋渔业安全造成的生境破坏强度 Intensity of habitat destruction caused by terrestrial pollutants to marine fishery safety | |
C9:海洋机动渔船年末总功率 Total power of marine motor fishing vessels at the end of the year/kW | 生产要素投入强度对海洋渔业资源安全造成的影响 Impact of input intensity of production factors on marine fishery resource security | |
C10:海洋渔业灾害造成经济损失/(104 元) Economic losses caused by marine fishery disasters/(104 yuan) | 海洋渔业灾害影响下海洋渔业生态安全持续运行能力 Sustainable operation capacity of marine fishery ecological security under the influence of marine fishery disasters | |
C11:直排海污水总量 Total amount of sewage directly discharged into the sea/(104 t) | 陆源污水对近海鱼类生存水质的破坏强度 Destruction intensity of terrestrial sewage on water quality for offshore fish survival | |
S:鱼类生境- 状态 Fish habitat- status | C12:海洋渔业资源集约利用指数 Index of intensive utilization of marine fishery resources | 海洋渔业资源开发状况 Development status of marine fishery resources |
C13:近海香农多样性指数 Offshore Shannon diversity index | 海洋鱼类种群生境中的生物多样性状况Biodiversity status in the habitat of marine fish populations |
Table 1 CAS-DPSIR evaluation indicator system for marine fishery ecological security
准则层 Criterion level | 指标层 Indicator level | 指标解释 Indicator interpretation |
|---|---|---|
D:探测器- 驱动 Detector- drive | C1:海洋渔业经济产值/(104 元) Marine fishery economic output value/(104 yuan) | 海洋捕捞和养殖生产的经济发展程度 Economic development level of marine fishing and aquaculture production |
C2:海洋渔业产值年增长率 Annual growth rate of marine fishery output value/% | 海洋渔业经济效益提升潜力 Potential for improving economic benefits of marine fishery | |
C3:海产品国际贸易水平 International trade level of seafood/(104 $) | 海洋渔业生产的水产品进出口产值效益 Import and export value benefit of aquatic products in marine fishery production | |
C4:海产品加工总量 Total processing volume of seafood/t | 海洋渔业资源开发利用效益 Benefit of development and utilization of marine fishery resources | |
C5:海洋渔业产值占农产值比重 Proportion of marine fishery output value in agricultural output value/% | 海洋捕捞和养殖的产业地位 Industrial status of marine fishing and aquaculture | |
P:主体适应- 压力 Subject adaptation- pressure | C6:海洋渔业人口从业率 Employment rate of marine fishery population/% | 海洋从业人口对海洋渔业生态安全产生的胁迫作用 Coercive effect of marine employed population on marine fishery ecological security |
C7:单船海洋捕捞效率 Single-vessel marine fishing efficiency/t | 单船海洋捕捞生产效率对海洋捕捞强度压力 Pressure of single-vessel marine fishing production efficiency on marine fishing intensity | |
C8:废水排放主要污染物总量 Total amount of major pollutants in wastewater discharge/(104 t) | 陆源污染物对海洋渔业安全造成的生境破坏强度 Intensity of habitat destruction caused by terrestrial pollutants to marine fishery safety | |
C9:海洋机动渔船年末总功率 Total power of marine motor fishing vessels at the end of the year/kW | 生产要素投入强度对海洋渔业资源安全造成的影响 Impact of input intensity of production factors on marine fishery resource security | |
C10:海洋渔业灾害造成经济损失/(104 元) Economic losses caused by marine fishery disasters/(104 yuan) | 海洋渔业灾害影响下海洋渔业生态安全持续运行能力 Sustainable operation capacity of marine fishery ecological security under the influence of marine fishery disasters | |
C11:直排海污水总量 Total amount of sewage directly discharged into the sea/(104 t) | 陆源污水对近海鱼类生存水质的破坏强度 Destruction intensity of terrestrial sewage on water quality for offshore fish survival | |
S:鱼类生境- 状态 Fish habitat- status | C12:海洋渔业资源集约利用指数 Index of intensive utilization of marine fishery resources | 海洋渔业资源开发状况 Development status of marine fishery resources |
C13:近海香农多样性指数 Offshore Shannon diversity index | 海洋鱼类种群生境中的生物多样性状况Biodiversity status in the habitat of marine fish populations |
准则层 Criterion level | 指标层 Indicator level | 指标解释 Indicator interpretation |
|---|---|---|
S:鱼类生境- 状态 Fish habitat- status | C14:海洋渔获物种类多样性指数 Species diversity index of marine catches | 以每年海洋渔获物多样性反映目前海洋渔业资源状况 Reflecting the current status of marine fishery resources with annual diversity of marine catches |
C15:近岸海域一、二类海水比例 Proportion of Class I and II seawater in offshore waters/% | 维持海洋渔业资源生境持续性的水质状况 Water quality status for maintaining the sustainability of marine fishery resource habitats | |
C16:人均湿地面积占比 Ratio of per capita wetland area/% | 提供保护滨海生物多样性和涵养水源等生态系统服务状况 Providing ecosystem services such as protecting coastal biodiversity and conserving water resources | |
I:效应器-影响 Effector- impact | C17:沿海渔民人均收入质量 Quality of per capita income of coastal fishermen | 海洋渔业开发对沿海渔民生计资本积累影响 Impact of marine fishery development on the accumulation of livelihood capital of coastal fishermen |
C18:海洋渔业产业升级水平 Upgrading level of marine fishery industry | 海洋渔业高质量发展战略对产业结构优化的影响 Impact of high-quality development strategy of marine fishery on industrial structure optimization | |
C19:万人均海洋捕捞和养殖产量 Capita marine fishing and aquaculture production per 10 000 people/kg | 海洋捕捞和养殖生产对海洋渔业资源生物量的影响 Impact of marine fishing and aquaculture production on biomass of marine fishery resources | |
C20:海洋渔业劳均产值(104 元) Average output value of marine fishery labor/(104 yuan) | 海洋渔业开发对海洋从业人员的获利影响 Impact of marine fishery development on profitability of marine practitioners | |
C21:海洋水产科技支持力度 Support for marine aquaculture science and technology | 绿色科技创新对海洋渔业的影响 Impact of green technological innovation on marine fishery | |
R:行为调整- 响应 Behavioral adjustment- response | C22:海洋渔业资源保护水平 Protection level of marine fishery resources | 以国家水产种质资源保护区建设数量表征保护水平Representing the protection level with the number of national aquatic germplasm resource conservation areas established |
C23:海洋渔业政策规制力度 Regulation intensity of marine fishery policies | 对海洋鱼类种群生境和绿色生产等问题的政策治理能力 Policy governance capacity for issues such as marine fish population habitats and green production | |
C24:海洋渔业执法能力 Law enforcement capacity of marine fishery | 海洋渔业执法投入对落实海洋渔业规制性政策的保障能力Safeguard capability of marine fishery law enforcement investment in implementing regulatory policies for marine fishery | |
C25:海洋渔业捕捞压力缓解力度 Intensity of relief of fishing pressure in marine fishery | 以拓展远洋和实行“双转”实现对近海渔业资源养护效果 Achieving the conservation effect of offshore fishery resources by expanding ocean fishing and implementing the “dual transformation” strategy | |
C26:海洋渔政管理水平 Management level of marine fishery administration | 能够高水平促进海洋渔业资源和保护海洋生态环境的行政资源Administrative resources capable of promoting marine fishery resources and protecting marine ecological environment at a high level | |
C27:海洋工业污染治理完成投资/(104 元) Investment completed for marine industrial pollution control/(104 yuan) | 通过调整海域污染修复海洋鱼类种群生境 Restoring marine fish population habitats by adjusting sea area pollution | |
C28:海洋工业固体废物综合利用率 Comprehensive utilization rate of solid waste from marine industry/% | 降低对海洋生态环境的污染风险 Reduce pollution risks to the marine ecological environment |
Table 1 CAS-DPSIR evaluation indicator system for marine fishery ecological security
准则层 Criterion level | 指标层 Indicator level | 指标解释 Indicator interpretation |
|---|---|---|
S:鱼类生境- 状态 Fish habitat- status | C14:海洋渔获物种类多样性指数 Species diversity index of marine catches | 以每年海洋渔获物多样性反映目前海洋渔业资源状况 Reflecting the current status of marine fishery resources with annual diversity of marine catches |
C15:近岸海域一、二类海水比例 Proportion of Class I and II seawater in offshore waters/% | 维持海洋渔业资源生境持续性的水质状况 Water quality status for maintaining the sustainability of marine fishery resource habitats | |
C16:人均湿地面积占比 Ratio of per capita wetland area/% | 提供保护滨海生物多样性和涵养水源等生态系统服务状况 Providing ecosystem services such as protecting coastal biodiversity and conserving water resources | |
I:效应器-影响 Effector- impact | C17:沿海渔民人均收入质量 Quality of per capita income of coastal fishermen | 海洋渔业开发对沿海渔民生计资本积累影响 Impact of marine fishery development on the accumulation of livelihood capital of coastal fishermen |
C18:海洋渔业产业升级水平 Upgrading level of marine fishery industry | 海洋渔业高质量发展战略对产业结构优化的影响 Impact of high-quality development strategy of marine fishery on industrial structure optimization | |
C19:万人均海洋捕捞和养殖产量 Capita marine fishing and aquaculture production per 10 000 people/kg | 海洋捕捞和养殖生产对海洋渔业资源生物量的影响 Impact of marine fishing and aquaculture production on biomass of marine fishery resources | |
C20:海洋渔业劳均产值(104 元) Average output value of marine fishery labor/(104 yuan) | 海洋渔业开发对海洋从业人员的获利影响 Impact of marine fishery development on profitability of marine practitioners | |
C21:海洋水产科技支持力度 Support for marine aquaculture science and technology | 绿色科技创新对海洋渔业的影响 Impact of green technological innovation on marine fishery | |
R:行为调整- 响应 Behavioral adjustment- response | C22:海洋渔业资源保护水平 Protection level of marine fishery resources | 以国家水产种质资源保护区建设数量表征保护水平Representing the protection level with the number of national aquatic germplasm resource conservation areas established |
C23:海洋渔业政策规制力度 Regulation intensity of marine fishery policies | 对海洋鱼类种群生境和绿色生产等问题的政策治理能力 Policy governance capacity for issues such as marine fish population habitats and green production | |
C24:海洋渔业执法能力 Law enforcement capacity of marine fishery | 海洋渔业执法投入对落实海洋渔业规制性政策的保障能力Safeguard capability of marine fishery law enforcement investment in implementing regulatory policies for marine fishery | |
C25:海洋渔业捕捞压力缓解力度 Intensity of relief of fishing pressure in marine fishery | 以拓展远洋和实行“双转”实现对近海渔业资源养护效果 Achieving the conservation effect of offshore fishery resources by expanding ocean fishing and implementing the “dual transformation” strategy | |
C26:海洋渔政管理水平 Management level of marine fishery administration | 能够高水平促进海洋渔业资源和保护海洋生态环境的行政资源Administrative resources capable of promoting marine fishery resources and protecting marine ecological environment at a high level | |
C27:海洋工业污染治理完成投资/(104 元) Investment completed for marine industrial pollution control/(104 yuan) | 通过调整海域污染修复海洋鱼类种群生境 Restoring marine fish population habitats by adjusting sea area pollution | |
C28:海洋工业固体废物综合利用率 Comprehensive utilization rate of solid waste from marine industry/% | 降低对海洋生态环境的污染风险 Reduce pollution risks to the marine ecological environment |
变量类型 Variable type | 变量名称 Variable name | 具体指标 Specific indicator |
|---|---|---|
解释变量 Explanatory variable | MFES:海洋渔业生态安全水平 Marine fishery ecological security | 灰色关联-TOPSIS计算结果 Grey relational analysis-TOPSIS calculation results |
被解释变量 Explained variable | MFEDL:海洋渔业经济发展水平 Marine fishery economic development level | 海洋渔业经济生产总值占农产值比重(对数) The proportion of marine fishery economic output value to agricultural output value (logarithm) |
MFR:海洋渔业资源状态 Marine fishery resources | 香农多样性指数 Shannon diversity index | |
MELL:海洋环境负荷水平 Marine environmental load level | 直排海污水总量(对数) Total amount of sewage discharged directly into the sea (logarithm) | |
FC:捕捞能力 Fishing capacity | 单船海洋捕捞效率与人均海洋捕捞产量的综合表征(对数) Comprehensive representation of single-vessel marine fishing efficiency and per capita marine fishing yield (logarithm) | |
TP:技术进步 Technological progress | 水产技术推广人员经费/水产技术推广人员数量 Funding for aquatic technology extension personnel / Number of aquatic technology extension personnel | |
MER:海洋环境规制 Marine environmental regulation | 财政环保相关支出占财政总支出比重 The proportion of fiscal expenditure related to environmental protection in total fiscal expenditure | |
FAMC:渔政管理能力 Fishery administration and management capability | 渔政管理中大学本科及以上人数占比(对数) The proportion of university graduates and above in fishery administration (logarithm) |
Table 2 Summary table of influencing factor variables selection
变量类型 Variable type | 变量名称 Variable name | 具体指标 Specific indicator |
|---|---|---|
解释变量 Explanatory variable | MFES:海洋渔业生态安全水平 Marine fishery ecological security | 灰色关联-TOPSIS计算结果 Grey relational analysis-TOPSIS calculation results |
被解释变量 Explained variable | MFEDL:海洋渔业经济发展水平 Marine fishery economic development level | 海洋渔业经济生产总值占农产值比重(对数) The proportion of marine fishery economic output value to agricultural output value (logarithm) |
MFR:海洋渔业资源状态 Marine fishery resources | 香农多样性指数 Shannon diversity index | |
MELL:海洋环境负荷水平 Marine environmental load level | 直排海污水总量(对数) Total amount of sewage discharged directly into the sea (logarithm) | |
FC:捕捞能力 Fishing capacity | 单船海洋捕捞效率与人均海洋捕捞产量的综合表征(对数) Comprehensive representation of single-vessel marine fishing efficiency and per capita marine fishing yield (logarithm) | |
TP:技术进步 Technological progress | 水产技术推广人员经费/水产技术推广人员数量 Funding for aquatic technology extension personnel / Number of aquatic technology extension personnel | |
MER:海洋环境规制 Marine environmental regulation | 财政环保相关支出占财政总支出比重 The proportion of fiscal expenditure related to environmental protection in total fiscal expenditure | |
FAMC:渔政管理能力 Fishery administration and management capability | 渔政管理中大学本科及以上人数占比(对数) The proportion of university graduates and above in fishery administration (logarithm) |
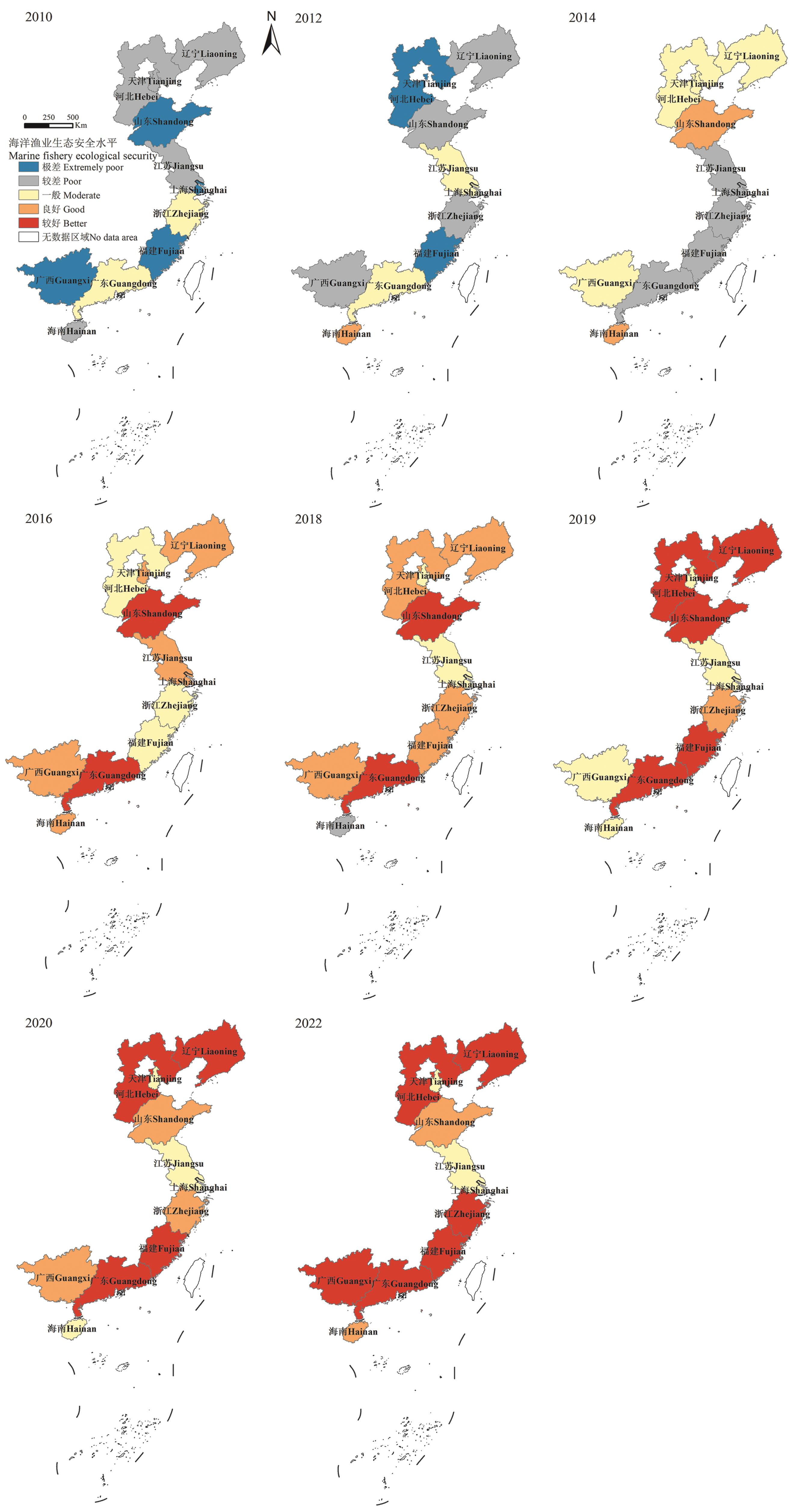
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution of China’s marine fishery ecological security from 2010 to 2022Note:Based on the standard map GS(2024)0650 of the National Resources Ministry's standard map service website, the base map boundary has not been modified.
年份 Year | 总体泰尔指数General Theil Index | 区域间差异 Inter-regional disparity | 区域内差异Intra-regional disparity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
总体 General | 环渤海 Bohai Rim region | 长三角 Yangtze River Delta region | 泛珠三角 Pan-Pearl River Delta region | |||
| 2010 | 0.001 31 | 0.000 29 | 0.001 02 | 0.000 31 | 0.001 43 | 0.002 23 |
| 2011 | 0.001 71 | 0.000 53 | 0.001 18 | 0.001 96 | 0.000 82 | 0.000 67 |
| 2012 | 0.002 30 | 0.000 78 | 0.001 52 | 0.001 89 | 0.000 93 | 0.001 61 |
| 2013 | 0.000 49 | 0.000 02 | 0.000 47 | 0.000 64 | 0.000 41 | 0.000 36 |
| 2014 | 0.001 85 | 0.000 32 | 0.001 52 | 0.001 05 | 0.000 07 | 0.003 01 |
| 2015 | 0.002 10 | 0.000 85 | 0.001 25 | 0.001 44 | 0.001 00 | 0.001 24 |
| 2016 | 0.000 72 | 0.000 28 | 0.000 44 | 0.000 48 | 0.000 08 | 0.000 65 |
| 2017 | 0.002 05 | 0.000 09 | 0.001 96 | 0.003 77 | 0.000 31 | 0.001 42 |
| 2018 | 0.002 63 | 0.000 27 | 0.002 36 | 0.001 42 | 0.000 78 | 0.004 40 |
| 2019 | 0.002 91 | 0.000 34 | 0.002 57 | 0.004 06 | 0.002 27 | 0.002 16 |
| 2020 | 0.002 06 | 0.000 08 | 0.001 98 | 0.002 65 | 0.001 46 | 0.001 72 |
| 2021 | 0.002 45 | 0.000 31 | 0.002 14 | 0.003 11 | 0.003 08 | 0.001 32 |
| 2022 | 0.002 32 | 0.000 11 | 0.002 21 | 0.004 08 | 0.001 96 | 0.000 59 |
Table 3 Theil index of China’s marine fishery ecological security level
年份 Year | 总体泰尔指数General Theil Index | 区域间差异 Inter-regional disparity | 区域内差异Intra-regional disparity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
总体 General | 环渤海 Bohai Rim region | 长三角 Yangtze River Delta region | 泛珠三角 Pan-Pearl River Delta region | |||
| 2010 | 0.001 31 | 0.000 29 | 0.001 02 | 0.000 31 | 0.001 43 | 0.002 23 |
| 2011 | 0.001 71 | 0.000 53 | 0.001 18 | 0.001 96 | 0.000 82 | 0.000 67 |
| 2012 | 0.002 30 | 0.000 78 | 0.001 52 | 0.001 89 | 0.000 93 | 0.001 61 |
| 2013 | 0.000 49 | 0.000 02 | 0.000 47 | 0.000 64 | 0.000 41 | 0.000 36 |
| 2014 | 0.001 85 | 0.000 32 | 0.001 52 | 0.001 05 | 0.000 07 | 0.003 01 |
| 2015 | 0.002 10 | 0.000 85 | 0.001 25 | 0.001 44 | 0.001 00 | 0.001 24 |
| 2016 | 0.000 72 | 0.000 28 | 0.000 44 | 0.000 48 | 0.000 08 | 0.000 65 |
| 2017 | 0.002 05 | 0.000 09 | 0.001 96 | 0.003 77 | 0.000 31 | 0.001 42 |
| 2018 | 0.002 63 | 0.000 27 | 0.002 36 | 0.001 42 | 0.000 78 | 0.004 40 |
| 2019 | 0.002 91 | 0.000 34 | 0.002 57 | 0.004 06 | 0.002 27 | 0.002 16 |
| 2020 | 0.002 06 | 0.000 08 | 0.001 98 | 0.002 65 | 0.001 46 | 0.001 72 |
| 2021 | 0.002 45 | 0.000 31 | 0.002 14 | 0.003 11 | 0.003 08 | 0.001 32 |
| 2022 | 0.002 32 | 0.000 11 | 0.002 21 | 0.004 08 | 0.001 96 | 0.000 59 |
变量 Variable | 系数值Coefficient value | 标准值 Standard value | Z值 Z value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
海洋渔业生态安全水平 MFES | 0.535 591 | 0.070 243 | 7.62 | 0.000** |
海洋渔业经济发展水平 MFEDL | 0.004 414 | 0.003 046 | 1.45 | 0.147 |
海洋渔业资源状态 MFR | 0.013 000 | 0.005 405 | 2.41 | 0.016* |
海洋环境负荷水平 MELL | 0.003 674 | 0.002 989 | -1.23 | 0.219 |
捕捞能力 FC | 0.006 746 | 0.002 516 | 2.68 | 0.007** |
技术进步 TP | 0.000 011 | 0.000 225 | 0.05 | 0.958 |
海洋环境规则 MER | 0.721 371 | 0.194 434 | 3.71 | 0.000** |
渔政管理能力 FAMC | 0.057 123 | 0.009 233 | 6.19 | 0.000** |
Table 4 System GMM regression results
变量 Variable | 系数值Coefficient value | 标准值 Standard value | Z值 Z value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
海洋渔业生态安全水平 MFES | 0.535 591 | 0.070 243 | 7.62 | 0.000** |
海洋渔业经济发展水平 MFEDL | 0.004 414 | 0.003 046 | 1.45 | 0.147 |
海洋渔业资源状态 MFR | 0.013 000 | 0.005 405 | 2.41 | 0.016* |
海洋环境负荷水平 MELL | 0.003 674 | 0.002 989 | -1.23 | 0.219 |
捕捞能力 FC | 0.006 746 | 0.002 516 | 2.68 | 0.007** |
技术进步 TP | 0.000 011 | 0.000 225 | 0.05 | 0.958 |
海洋环境规则 MER | 0.721 371 | 0.194 434 | 3.71 | 0.000** |
渔政管理能力 FAMC | 0.057 123 | 0.009 233 | 6.19 | 0.000** |
| [1] | 韩杨.1949年以来中国海洋渔业资源治理与政策调整[J].中国农村经济,2018(9):14-28. |
| HAN Y. Marine fishery resources management and policy adjustment in China since 1949 [J]. Chin. Rural Econ., 2018 (9):14-28. | |
| [2] | 陈东景.基于能值相图的海洋渔业生态经济系统可持续发展评价:以山东省为例[J].生态经济,2019,35(4):65-70. |
| CHEN D J. Research on sustainable development of marine fishery eco-economic system based on emergy ternary: a case of Shandong province [J]. Ecol. Econ., 2019, 35(4):65-70. | |
| [3] | 王建友.政策、制度供给视角下的海洋捕捞渔业供给侧结构改革研究[J].农业经济问题,2019(11):25-31. |
| WANG J Y. Research on the supply side structure reform of marine capture fisheries from the perspective of policy and institutional supply [J]. Issues Agric. Econ., 2019, 40(11):25-31. | |
| [4] | 黄硕琳,邵化斌.全球海洋渔业治理的发展趋势与特点[J].太平洋学报, 2018, 26(4): 65-78. |
| HUANG S L, SHAO H B. Development trends and features of global marine fisheries governance [J]. Pac. J., 2018, 26(4):65-78. | |
| [5] | AGURDY T. Effects of fisheries on marine ecosystems: a conservationist’s perspective [J]. ICES J. Mar. Sci., 2000, 57(3):761-765. |
| [6] | 李博,金校名,杨俊,等.中国海洋渔业产业生态系统脆弱性时空演化及影响因素[J].生态学报,2019,39(12):4273-4283. |
| LI B, JIN X M, YANG J, et al.. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors for marine fisheries industry ecosystem vulnerability in China [J].Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019,39(12):4273-4283. | |
| [7] | 王泽宇,曹江琦,王焱熙.中国海洋渔业生态效率的时空分异及其影响因素[J].海洋开发与管理,2021,38(8):36-43. |
| WANG Z Y, CAO J Q, WANG Y X. Spatial-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of ecological efficiency of China’s marine fisheries [J]. Ocean Dev. Manage., 2021, 38(8):36-43. | |
| [8] | 纪建悦,郭昕,张懿.生态-经济共生视角下的中国海洋渔业生态安全评价研究[J].中国海洋大学学报(社会科学版),2020(1):58-66. |
| JI J Y, GUO X, ZHANG Y. Ecological security assessment of China’s marine fishery from the perspective of ecological economic symbiosis [J]. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Soc. Sci.), 2020(1):58-66. | |
| [9] | CAMPBELLMARNIE L, GALLAGHER C. Assessing the relative effects of fishing on the New Zealand marine environment through risk analysis [J]. ICES J. Mar. Sci., 2007,62(2): 256-270. |
| [10] | RAMOS J E, TAM J, ARAMAYO V, et al.. Climate vulnerability assessment of key fishery resources in the Northern Humboldt current system [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2022, 12(1):4800 [2024-03-20].. |
| [11] | LI Y Z, SUN M, KLEISNER K M, et al.. A global synthesis of climate vulnerability assessments on marine fisheries:methods,scales, and knowledge co-production [J]. Glob. Chang. Biol., 2023, 29(13): 3545-3561. |
| [12] | LI Y, JI J. Evaluation of marine fisheries vulnerability in China and its spatial effects: evidence from coastal regions [J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(6):809-817. |
| [13] | DIANA C. RESTREPO G, MANUELJ, et al.. Trends in marine fisheries social-ecological systems studies [J/OL]. Ocean Coast. Manage., 2022, 220(3):106076 [2024-03-20].. |
| [14] | KASPERSKI S, DEPIPER G S, HAYNIE A C, et al.. Assessing the state of coupled social-ecological modeling in support of ecosystem based fisheries management in the United States [J/OL]. Front. Mar. Sci., 2021, 8:631400 [2024-03-20] .. |
| [15] | ZHU W, SUN W, LI D, et al.. Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of marine fishery eco-efficiency in China: evidence from coastal regions [J]. Fishes, 2023, 8(9):438-446. |
| [16] | ZHANG X X, SUN D, ZHANG X F, et al.. Regional ecological efficiency and future sustainable development of marine ranch in China:an empirical research using DEA and system dynamics [J/OL]. Aquaculture, 2021,534:736339 [2024-03-20].. |
| [17] | 乔瑞琪.我国海洋渔业生态安全评价体系实证研究[D].湛江:广东海洋大学,2016. |
| QIAO R Q. Empirical research on marine fishery ecological security evaluation system in our country [D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2016. | |
| [18] | 徐志泉.浙江省海洋渔业生态安全评价研究[D].舟山:浙江海洋大学,2021. |
| XU Z Q. Evaluation of marine fishery ecological security in Zhejiang province [D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2021. | |
| [19] | JIAO M Y, YUE W Z, SUO A N, et al.. Construction and influencing factors of an early warning system for marine ranching ecological security:experience from China’s coastal areas [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manage., 2023,335:117515 [2024-03-20]. . |
| [20] | DU Y W, CAO W M. DEPD model for evaluating marine ranching ecological security and its application in Shandong,China [J/OL]. Ocean. Coast. Manage., 2022,224:106206 [2024-03-20]. . |
| [21] | 杜元伟,王一凡,孙浩然.不确定环境下海洋牧场生态安全评价:以荣成市国家级海洋牧场示范区为例[J].资源科学,2021,43(10):2055-2067. |
| DU Y W, WANG Y F, SUN H R. Ecological security evaluation of marine ranching under uncertainty:a case study of national marine ranching demonstration zones in Rongcheng [J]. Resour. Sci., 2021,43(10): 2055-2067. | |
| [22] | 仇保兴.城市规划学新理性主义思想初探:复杂自适应系统(CAS)视角[J].城市发展研究,2017,24(1):1-8. |
| QIU B X.A preliminary research on the neo-rationality in urban planning:from the perspective of complex adaptive system (CAS) [J]. Urban Dev. Stud., 2017, 24(1):1-8. | |
| [23] | 张智光.人类文明与生态安全:共生空间的演化理论[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2013,23(7):1-8. |
| ZHANG Z G.Evolutionary theory of human civilization and ecological security in symbiotic space [J]. China Popul. Resour. Environ., 2013, 23(7):1-8. | |
| [24] | 韩增林,仝燕波,王耕.中国海洋生态安全时空分异及演化趋势研究[J].地理科学,2022,42(7):1166-1175. |
| HAN Z L, TONG Y B, WANG G. Spatial-temporal differentiation and evolution trend of marine ecological security in China [J]. Sci. Geogr. Sin., 2022, 42(7):1166-1175. | |
| [25] | HOLLAND J.隐秩序——适应性就是复杂性[M].上海:上海科技教育出版社, 2000:1-168. |
| [26] | SINGH K R, MURTY H R, GUPTA S K, et al.. An overview of sustainability assessment methodologies [J]. Ecol. Indicators, 2009, 9:189-212. |
| [27] | MA S Y, KANG B, LI J C, et al.. Climate risks to fishing species and fisheries in the China Seas [J/OL].Sci.Total Environ.,2023,857(Pt 1):159325 [2024-03-20].. |
| [28] | 谢明.公共政策导论[M].第4版.北京:中国人民大学出版社, 2017: 5-6. |
| [29] | 穆学青,郭向阳,明庆忠,等.黄河流域旅游生态安全的动态演变特征及驱动因素[J].地理学报,2022,77(3):714-735. |
| MU X Q, GUO X Y, MING Q Z, et al.. Dynamic evolution characteristics and driving factors of tourism ecological security in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Acta Geogr. Sin., 2022,77(3):714-735. | |
| [30] | 崔凤, 刘荆州.海岸带区域可持续发展综合评价及障碍因子诊断:以浙江省为例[J].海洋湖沼通报,2022,44(6):140-148. |
| CUI F, LIU J Z. Comprehensive evaluation of coastal zone and identification of obstacle factors to its sustainable development:Zhejiang as a case [J]. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol., 2022, 44(6):140-148. | |
| [31] | 朱红根,陈晖.中国数字乡村发展的水平测度、时空演变及推进路径[J].农业经济问题,2023,44(3):21-33. |
| ZHU H G, CHEN H. Measurement,spatial-temporal evolution and promotion path of digital village development in China [J].Issues Agric. Econ., 2023, 44(3):21-33. | |
| [32] | 孙康,李丽丹.我国海域污染与渔业经济EKC关系研究:基于日本海洋渔业发展的启示[J].当代经济管理,2017,39(4):90-97. |
| SUN K, LI L D. A EKC relationship study on between the marine pollution and fishery economic in China: based on the enlightenments from the marine economy development in Japan [J]. Contemp. Econ. Manage., 2017, 39(4):90-97. | |
| [33] | 高源,王钧丹.环渤海地区海洋渔业生态系统脆弱性的时空演变及影响因素分析[J].经济论坛,2020(4):95-102. |
| GAO Y, WANG J D. Spatiotemporal evolution of marine fishery ecosystem vulnerability and its influencing factors in Bohai rim region [J]. Econ. Forum, 2020(4):95-102. | |
| [34] | 韩增林,计雪晴,胡盈,等.基于SBM模型的我国海洋渔业生态效率的时空演变[J].海洋开发与管理, 2019, 36(12): 3-8. |
| HAN Z L, JI X Q, HU Y, et al.. The spatial-temporal evolution of marine fishery eco-efficiency based on SBM model in China [J]. Ocean. Dev. Manage., 2019, 36(12): 3-8. | |
| [35] | 孙康,季建文,李丽丹,等.基于非期望产出的中国海洋渔业经济效率评价与时空分异 [J].资源科学,2017,39 (11):2040-2051. |
| SUN K, JI J W, LI L D, et al.. Marine fishery economic efficiency and its spatio-temporal differences based on undesirable outputs in China [J]. Resour. Sci., 2017, 39 (11):2040-2051. | |
| [36] | BRITES N M, BRAUMANN C A. Fisheries management in random environments:comparison of harvesting policies for the logistic model [J]. Fish. Res., 2017, 195: 238-246. |
| [37] | 许罕多.资源衰退下的我国海洋捕捞业产量增长:基于1956年—2011年渔业数据的实证分析[J].山东大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2013(5):86-93. |
| XU H D. The growth of the production of China’s marine fishing industry under the condition of resource recession—an empirical analysis based on the 1956 to 2011 fisheries data [J]. J.Shandong Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.), 2013(5):86-93. | |
| [38] | 沈金生,张杰.我国主要海洋产业发展要素的贡献测度与经济分析[J].中国海洋大学学报(社会科学版),2013(1):35-40. |
| SHEN J S, ZHANG J.The contribution measurement and economic analysis of the development elements of China’s major marine industries [J]. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Soc.Sci.),2013(1):35-40. | |
| [39] | 郑莉,林香红,付瑞全.区域海洋渔业科技进步贡献率的测度与分析:基于面板数据模型的实证[J].科技管理研究,2019,39(12):85-90. |
| ZHENG L, LIN X H, FU R Q. Measure and analysis on contribution rate of scientific and technological progress of regional marine fisheries in China:empirical evidence based on panel data model [J]. Sci. Technol. Manage. Res., 2019, 39(12):85-90. | |
| [40] | 杜军, 寇佳丽,赵培阳. 海洋环境规制、海洋科技创新与海洋经济绿色全要素生产率:基于DEA-Malmquist指数与PVAR模型分析 [J]. 生态经济, 2020, 36 (1):144-153, 197. |
| DU J, KOU J L, ZHAO P Y. Marine environmental regulation, marine science and technology innovation and marine economic green total factor productivity: an analysis based on DEA-Malmquist index and PVAR model [J]. Ecol. Econ., 2020, 36 (1):144-153, 197. | |
| [41] | 吕鸣.普遍管辖权在海洋命运共同体时代面临的新挑战与法律对策[J].上海大学学报(社会科学版),2022,39(6):109-121. |
| LYU M. Universal jurisdiction in the era of the maritime community with a shared future:new challenges and legal countermeasures [J]. J. Shanghai Univ. (Soc.Sci.), 2022,39(6):109-121. | |
| [42] | 程显宏,杨珺涵,姜国刚.对外直接投资对我国外贸高质量发展的影响研究[J].世界地理研究,2024,33(10):83-99. |
| CHENG X H, YANG J H, JIANG G G. Research on the influence of outward foreign direct investment on the high-quality development of Chinese foreign trade [J]. World Regional Studies, 2024, 33(10):83-99. | |
| [43] | 毛伟, 梁贝贝. 海洋渔业中国式现代化时空分异及障碍因素研究[J/OL].中国农业资源与区划,2024:1-15[2024-03-20].. |
| MAO W, LAING B B. Study on the spatiotemporal differentiation and obstacle factors of Chinese-style modernisation of marine fisheries [J/OL]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan., 2024:1-15 [2024-03-20]. . |
| [1] | Weiming WANG, Xin PAN, Deping KONG, Yu AN, Shuang GUO, Zhimei SUN, Cheng XUE, Rongjun SUN, Wenqi MA, Huasen XU. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Influencing Factors of Crop Diversification in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 16-27. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号