




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 52-62.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0783
周雨青1,2( ), 杨永飞1,2, 葛常伟2, 沈倩2, 张思平2, 刘绍东2, 马慧娟2, 陈静2, 刘瑞华2, 李士丛2, 赵新华2, 李存东1(
), 杨永飞1,2, 葛常伟2, 沈倩2, 张思平2, 刘绍东2, 马慧娟2, 陈静2, 刘瑞华2, 李士丛2, 赵新华2, 李存东1( ), 庞朝友2(
), 庞朝友2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-07
接受日期:2021-03-03
出版日期:2022-04-15
发布日期:2022-04-20
通讯作者:
李存东,庞朝友
作者简介:周雨青 E-mail: zhouyuqing0803@163.com
基金资助:
Yuqing ZHOU1,2( ), Yongfei YANG1,2, Changwei GE2, Qian SHEN2, Siping ZHANG2, Shaodong LIU2, Huijuan MA2, Jing CHEN2, Ruihua LIU2, Shicong LI2, Xinhua ZHAO2, Cundong LI1(
), Yongfei YANG1,2, Changwei GE2, Qian SHEN2, Siping ZHANG2, Shaodong LIU2, Huijuan MA2, Jing CHEN2, Ruihua LIU2, Shicong LI2, Xinhua ZHAO2, Cundong LI1( ), Chaoyou PANG2(
), Chaoyou PANG2( )
)
Received:2020-09-07
Accepted:2021-03-03
Online:2022-04-15
Published:2022-04-20
Contact:
Cundong LI,Chaoyou PANG
摘要:
权重基因共表达网络分析(weighted gene co-expression network analysis, WGCNA)是系统生物学的一种研究方法,在多样本转录组数据中挖掘与目标性状相关的基因模块应用较广泛。为深入探究棉花应对冷害胁迫的分子机制,以4 ℃低温处理不同时间点的2个棉花品种(新陆中16和新陆中32)幼苗子叶转录组数据为基础,过滤低表达量基因, 最终利用筛选的22 083个表达的基因来构建共表达矩阵, 得到9个共表达模块,其中2个为抗冷相关特异性模块(Blue模块与低温处理0、1和3 h时间点正相关,Brown模块与低温处理9和12 h时间点正相关)。GO和KEGG富集分析表明, 特异性模块可以富集到对刺激反应的调节(GO:0048583)、对胁迫反应的调节(GO:0080134)、对油菜素类固醇的反应(GO:0009741)等抗逆相关通路。通过计算模块内基因的连通性挖掘网络中的核心基因,功能注释表明这些基因可能在棉花抗冷过程中发挥着重要作用。该结果为进一步研究棉花抗冷调控机理提供数据支持。
中图分类号:
周雨青, 杨永飞, 葛常伟, 沈倩, 张思平, 刘绍东, 马慧娟, 陈静, 刘瑞华, 李士丛, 赵新华, 李存东, 庞朝友. 基于WGCNA的棉花子叶抗冷相关共表达模块鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 52-62.
Yuqing ZHOU, Yongfei YANG, Changwei GE, Qian SHEN, Siping ZHANG, Shaodong LIU, Huijuan MA, Jing CHEN, Ruihua LIU, Shicong LI, Xinhua ZHAO, Cundong LI, Chaoyou PANG. Identification of Cold-related Co-expression Modules in Cotton Cotyledon by WGCNA[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 52-62.
基因 ID Gene ID | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Gh_A11G0969 | GAAGGCATTCCACCTGACCAAC | CTTGACCTTCTTCTTCTTGTGCTTG |
| Gh_A05G1931 | TGCCCAATGGTGGAAAACCACT | CGGCTCATGCAGAACCCTTCAA |
| Gh_D13G0160 | CGAACATGATGCCAACCGATGC | TGCAATCGAGCTTCCGTAGGTG |
| Gh_A13G2112 | CCACAAGAGTTTCCCTACGGGC | CGTGGTTTCTTGGTCGGCAATG |
| Gh_A05G0483 | GCCGAGTGTGAGGATTATGCCA | TTCTTGACGGGACAACTTGGGG |
| Gh_A12G2357 | CGTGGCAGCTATAGCACTGA | TTCTGAAAGTCTCCGCCACC |
| Gh_D09G1773 | AATAGGGCTACCGAGGCTGGTT | AGCCCTCCCGTTGTAAAACACC |
| Gh_D05G2642 | GCAGCAACCCCAAAATCCCAAC | CCACATCCCCGTATTCAGCACC |
| Gh_A05G1554 | GCCTCAAGAGGAGGTGATCG | GCTGCTGCTATCTGATCGGT |
| Gh_D05G0600 | AAGGGCTTACGTCCGCACAAAT | GCACTTGAAGTATGCCCTCGGA |
| Gh_A13G0138 | AGGGTGCATGTCCTAAGGGTGA | GACCTCGGTGAAGGCATAGCAG |
表1 qRT-PCR 所用基因引物序列
Table 1 Specific primers for the selected genes
基因 ID Gene ID | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Gh_A11G0969 | GAAGGCATTCCACCTGACCAAC | CTTGACCTTCTTCTTCTTGTGCTTG |
| Gh_A05G1931 | TGCCCAATGGTGGAAAACCACT | CGGCTCATGCAGAACCCTTCAA |
| Gh_D13G0160 | CGAACATGATGCCAACCGATGC | TGCAATCGAGCTTCCGTAGGTG |
| Gh_A13G2112 | CCACAAGAGTTTCCCTACGGGC | CGTGGTTTCTTGGTCGGCAATG |
| Gh_A05G0483 | GCCGAGTGTGAGGATTATGCCA | TTCTTGACGGGACAACTTGGGG |
| Gh_A12G2357 | CGTGGCAGCTATAGCACTGA | TTCTGAAAGTCTCCGCCACC |
| Gh_D09G1773 | AATAGGGCTACCGAGGCTGGTT | AGCCCTCCCGTTGTAAAACACC |
| Gh_D05G2642 | GCAGCAACCCCAAAATCCCAAC | CCACATCCCCGTATTCAGCACC |
| Gh_A05G1554 | GCCTCAAGAGGAGGTGATCG | GCTGCTGCTATCTGATCGGT |
| Gh_D05G0600 | AAGGGCTTACGTCCGCACAAAT | GCACTTGAAGTATGCCCTCGGA |
| Gh_A13G0138 | AGGGTGCATGTCCTAAGGGTGA | GACCTCGGTGAAGGCATAGCAG |
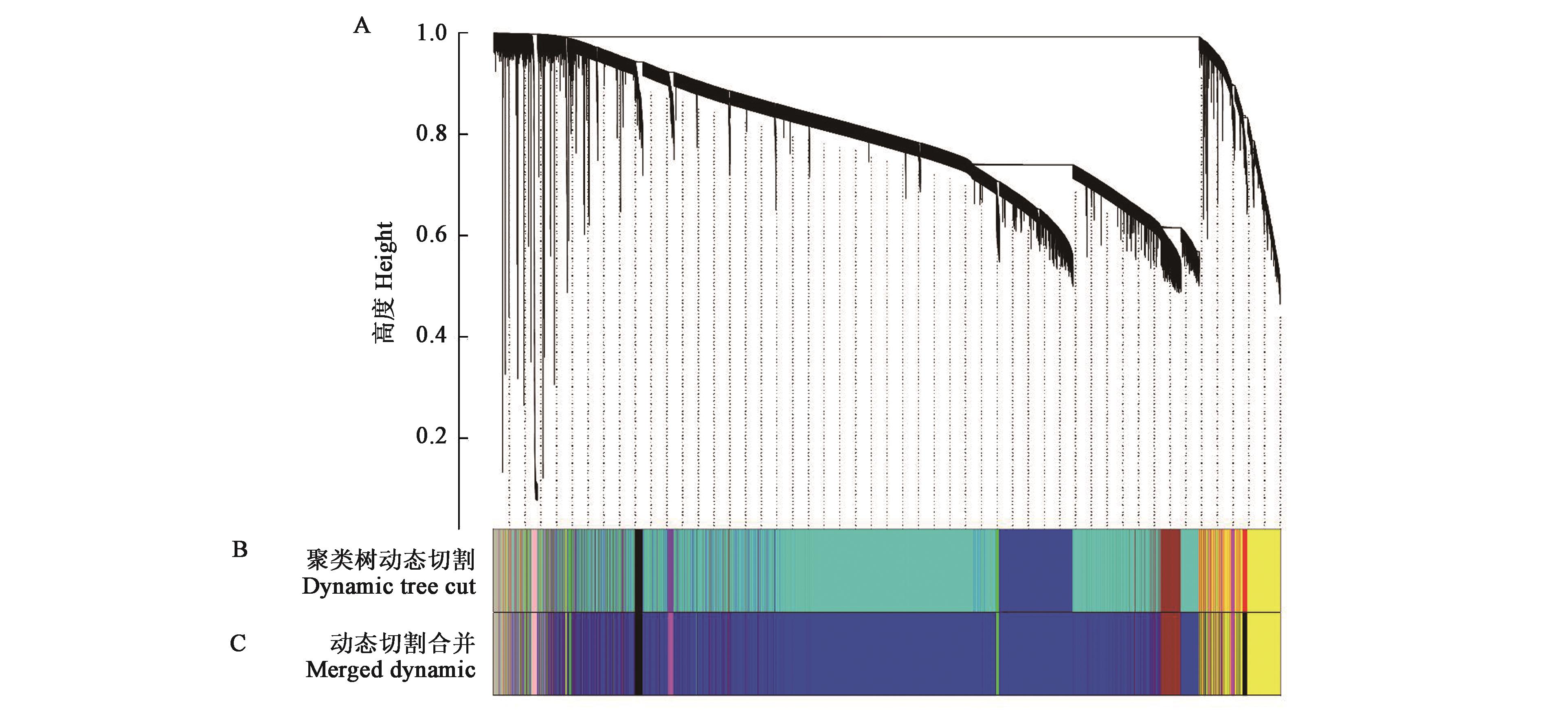
图2 基因聚类树和模块划分A:基于拓扑重叠构建的基因聚类树;B:动态剪切树法得到的基因模块,颜色代表模块;C:表达模式相似模块合并后的共表达模块
Fig.2 Gene cluster dendrograms and module divisionA: Clustering of genes based on the topological overlap; B: Gene modules obtained from the dynamic tree cut, and different colors represent different modules; C: Merged co-expression modules with similar expression pattern
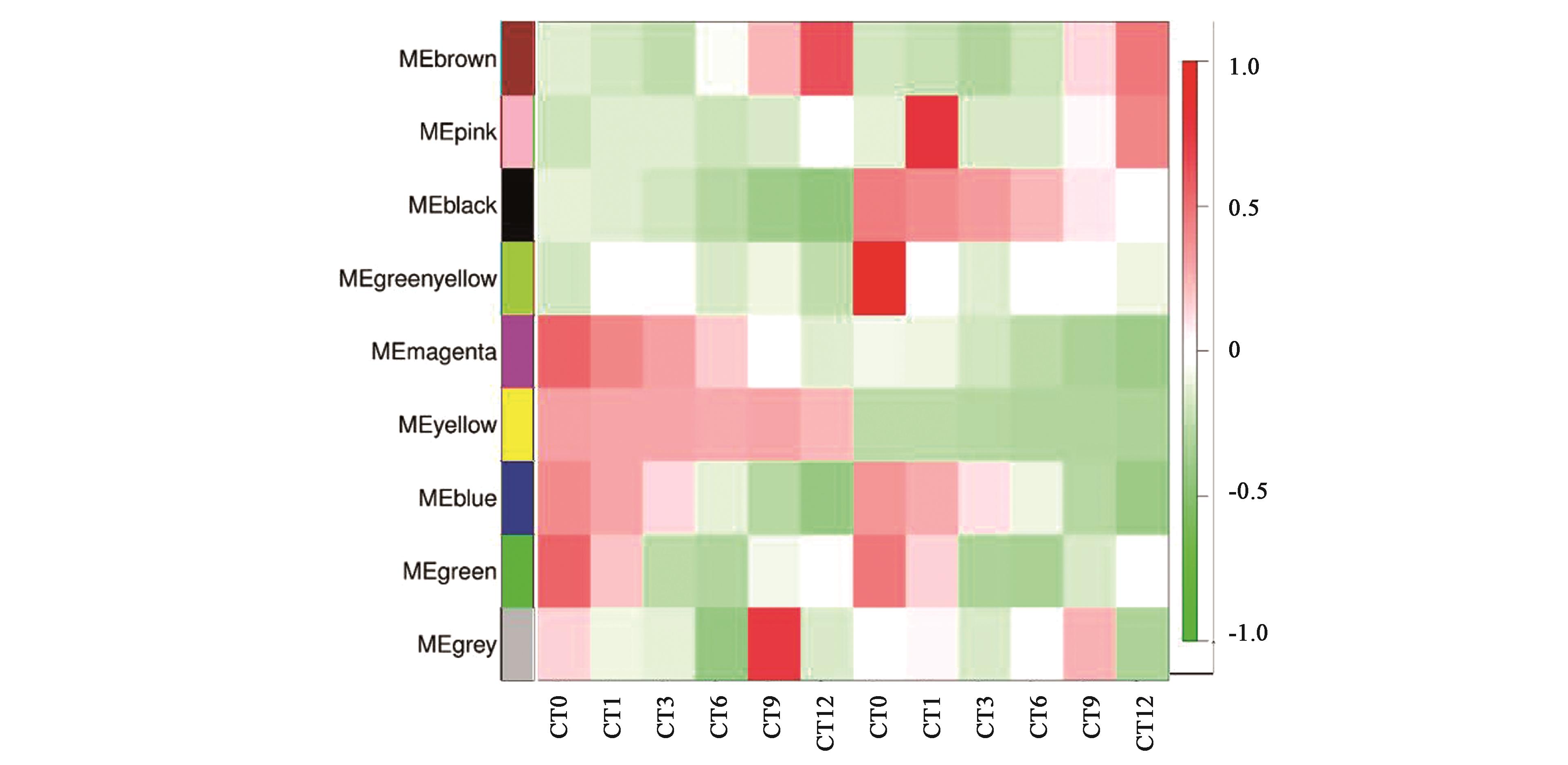
图4 基因共表达网络模块与不同样本的关联热图注:红色和绿色格分别代表性状与模块具有正相关性和负相关性。
Fig.4 Association analysis of gene co-expression network modules with different samplesNote: Red and green lattice represent positive correlation and negative correlation, respectively.
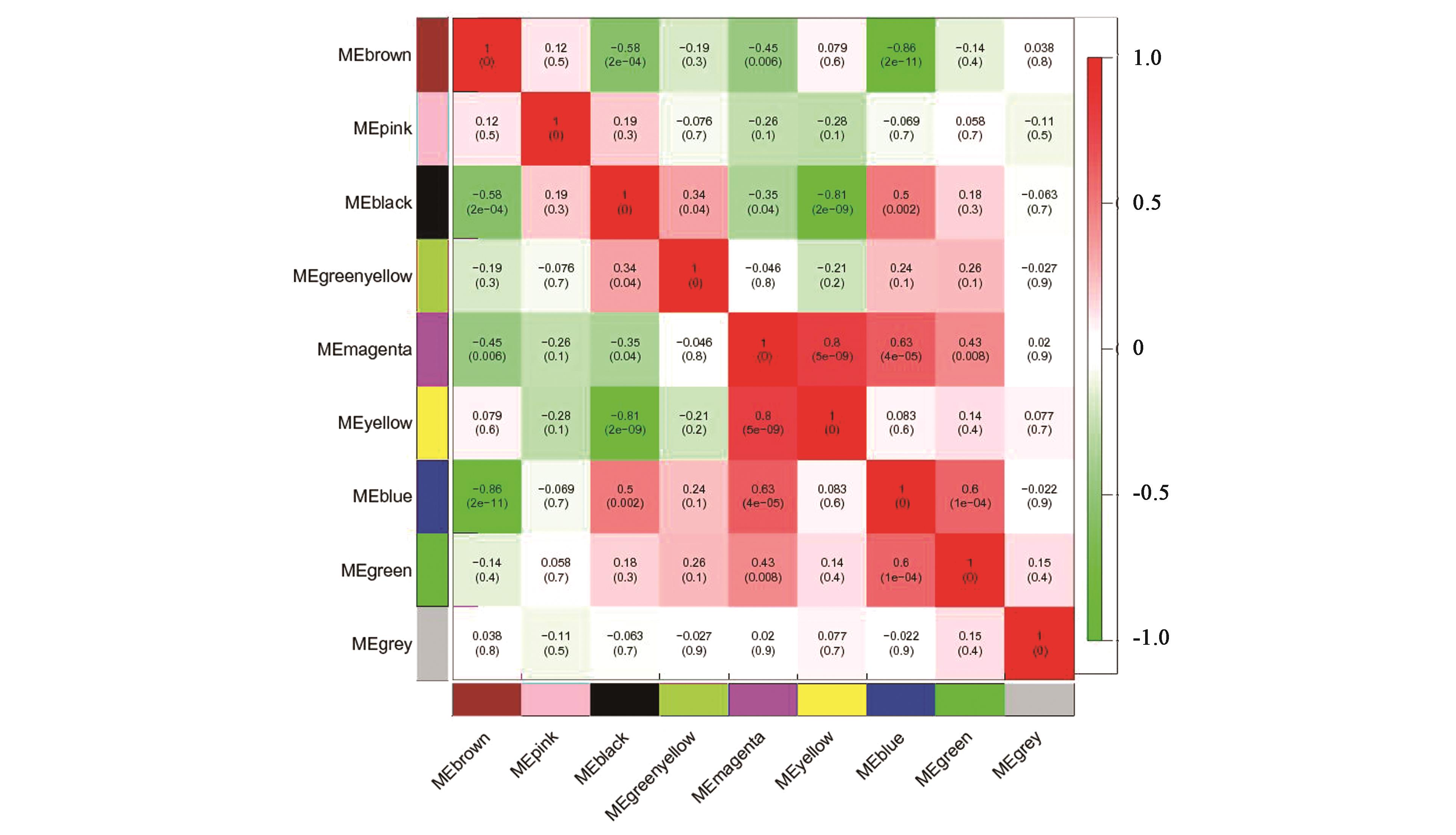
图5 不同模块两两之间 ME 的相关性注:红色和绿色格分别代表性状与模块具有正相关性和负相关性。格中数值代表模块与性状之间的相关系数和相应的P值(括号中)。
Fig.5 ME correlation between different modulesNote : Red and green lattice represent positive correlation and negative correlation, respectively. The numbers in the lattice show correlation coefficient and the corresponding P value (in the bracket).
模块 Module | GO条目 GO term | 基因本体 Ontology | 描述 Description | 基因数目 Genes No. | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
蓝色 Blue | GO:0048583 | P | 对刺激反应的调节Regulation of response to stimulus | 538 | 0.001 08 |
| GO:0080134 | P | 对胁迫反应的调节Regulation of response to stress | 282 | 0.000 45 | |
| GO:0031347P | P | 对防御反应的调节Regulation of defense response | 216 | 0.000 15 | |
| GO:0009738 | P | 脱落酸激活的信号通路 Abscisic acid-activated signaling pathway | 216 | 0.000 32 | |
| GO:0010200 | P | 对几丁质的反应Response to chitin | 166 | 0.000 15 | |
| GO:0009741 | P | 对油菜素类固醇的反应Response to brassinosteroid | 114 | 0.001 47 | |
| GO:0003700 | F | 转录因子活性,特异性DNA序列结合 Transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 1 275 | 0.000 68 | |
| GO:0005623 | C | 细胞Cell | 12 853 | 1.05e-06 | |
| GO:0043227 | C | 膜结合细胞器Membrane-bounded organelle | 10 326 | 7.51e-06 |
表2 特异性模块的部分GO富集分析结果
Table 2 Partial GO enrichment analysis of target module
模块 Module | GO条目 GO term | 基因本体 Ontology | 描述 Description | 基因数目 Genes No. | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
蓝色 Blue | GO:0048583 | P | 对刺激反应的调节Regulation of response to stimulus | 538 | 0.001 08 |
| GO:0080134 | P | 对胁迫反应的调节Regulation of response to stress | 282 | 0.000 45 | |
| GO:0031347P | P | 对防御反应的调节Regulation of defense response | 216 | 0.000 15 | |
| GO:0009738 | P | 脱落酸激活的信号通路 Abscisic acid-activated signaling pathway | 216 | 0.000 32 | |
| GO:0010200 | P | 对几丁质的反应Response to chitin | 166 | 0.000 15 | |
| GO:0009741 | P | 对油菜素类固醇的反应Response to brassinosteroid | 114 | 0.001 47 | |
| GO:0003700 | F | 转录因子活性,特异性DNA序列结合 Transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 1 275 | 0.000 68 | |
| GO:0005623 | C | 细胞Cell | 12 853 | 1.05e-06 | |
| GO:0043227 | C | 膜结合细胞器Membrane-bounded organelle | 10 326 | 7.51e-06 |
模块 Module | 核心基因编号 Hub gene ID | 模块内连通性 Connectivity | 拟南芥同源基因编号 Homologous gene ID in A. thaliana | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蓝色Blue | Gh_A05G1931 | 4 300.865 | AT4G08950 | 磷酸盐反应1家族蛋白 Phosphate-responsive 1 family protein |
| Gh_D13G0160 | 4 218.162 | AT2G40140 | 锌指(C3H型)蛋白家族 Zinc finger (C3H-type) family protein | |
| Gh_A13G2112 | 3 944.263 | AT1G27730 | 耐盐锌指Salt tolerance zinc finger | |
| Gh_A05G0483 | 3 864.472 | AT1G80840 | WRKY DNA结合蛋白40 WRKY DNA-binding protein 40 | |
| Gh_A12G2357 | 3 096.27 | AT5G51990 | C重复结合因子4 C-repeat-binding factor 4 | |
棕色 Brown | Gh_D09G1773 | 628.545 | AT3G49530 | 含有NAC结构域的蛋白质62 NAC domain containing protein 62 |
| Gh_D05G2642 | 601.582 | AT3G56400 | WRKY DNA结合蛋白70 WRKY DNA-binding protein 70 | |
| Gh_A05G1554 | 557.708 | AT1G20440 | 低温调节47 Cold-regulated 47 | |
| Gh_D05G0600 | 550.86 | AT1G80840 | WRKY DNA结合蛋白40 WRKY DNA-binding protein 40 | |
| Gh_A13G0138 | 517.077 | AT2G40140 | 锌指(C3H型)蛋白家族 Zinc finger (C3H-type) family protein
图8 核心基因的表达模式 Fig.8 Expression pattern of hub genes
图9 核心基因的 RT-qPCR 验证 Fig.9 qRT-PCR validation of hub genes |
表3 目标模块中核心基因的功能注释
Table 3 Annotation of hub genes in target module
模块 Module | 核心基因编号 Hub gene ID | 模块内连通性 Connectivity | 拟南芥同源基因编号 Homologous gene ID in A. thaliana | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蓝色Blue | Gh_A05G1931 | 4 300.865 | AT4G08950 | 磷酸盐反应1家族蛋白 Phosphate-responsive 1 family protein |
| Gh_D13G0160 | 4 218.162 | AT2G40140 | 锌指(C3H型)蛋白家族 Zinc finger (C3H-type) family protein | |
| Gh_A13G2112 | 3 944.263 | AT1G27730 | 耐盐锌指Salt tolerance zinc finger | |
| Gh_A05G0483 | 3 864.472 | AT1G80840 | WRKY DNA结合蛋白40 WRKY DNA-binding protein 40 | |
| Gh_A12G2357 | 3 096.27 | AT5G51990 | C重复结合因子4 C-repeat-binding factor 4 | |
棕色 Brown | Gh_D09G1773 | 628.545 | AT3G49530 | 含有NAC结构域的蛋白质62 NAC domain containing protein 62 |
| Gh_D05G2642 | 601.582 | AT3G56400 | WRKY DNA结合蛋白70 WRKY DNA-binding protein 70 | |
| Gh_A05G1554 | 557.708 | AT1G20440 | 低温调节47 Cold-regulated 47 | |
| Gh_D05G0600 | 550.86 | AT1G80840 | WRKY DNA结合蛋白40 WRKY DNA-binding protein 40 | |
| Gh_A13G0138 | 517.077 | AT2G40140 | 锌指(C3H型)蛋白家族 Zinc finger (C3H-type) family protein
图8 核心基因的表达模式 Fig.8 Expression pattern of hub genes
图9 核心基因的 RT-qPCR 验证 Fig.9 qRT-PCR validation of hub genes |
模块 Module | GO条目 GO term | 基因本体 Ontology | 描述 Description | 基因数目 Genes No. | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
棕色 Brown | GO:0050896 | P | 对刺激的反应Response to stimulus | 644 | 6.16e-10 |
| GO:0006950 | P | 对胁迫的反应Response to stress | 365 | 1.39e-05 | |
| GO:0009719 | P | 对内源性刺激的反应Response to endogenous stimulus | 269 | 7.26e-14 | |
| GO:0009628 | P | 对非生物刺激的反应Response to abiotic stimulus | 263 | 2.57e-07 | |
| GO:1901700 | P | 对含氧化合物的反应Response to oxygen-containing compound | 253 | 3.61e-14 | |
| GO:0009725 | P | 对激素的反应Response to hormone | 233 | 1.08e-08 | |
| GO:0048583 | P | 对刺激反应的调节Regulation of response to stimulus | 106 | 3.83e-08 | |
| GO:0009737 | P | 对脱落酸的反应Response to abscisic acid | 103 | 3.37e-08 | |
| GO:0009723 | P | 对乙烯的反应Response to ethylene | 68 | 6.83e-08 | |
| GO:0080134 | P | 对胁迫反应的调节Regulation of response to stress | 66 | 3.94e-09 | |
| GO:0010200 | P | 对几丁质的反应Response to chitin | 64 | 2.87e-20 | |
| GO:0009751 | P | 对水杨酸的反应Response to salicylic acid | 47 | 4.46e-08 | |
| GO:0031347 | P | 对防御反应的调节Regulation of defense response | 47 | 1.41e-06 | |
| GO:0009753 | P | 对茉莉酸的反应Response to jasmonic acid | 46 | 2.71e-05 | |
| GO:0003700 | F | 转录因子活性,特异性DNA序列结合 Transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 262 | 3.74e-20 | |
| GO:0005634 | C | 核nucleus | 797 | 1.94e-06 | |
| GO:0005887 | C | 质膜的组成部分Integral component of plasma membrane | 24 | 0.024 88 |
表2 特异性模块的部分GO富集分析结果 (续表Continued)
Table 2 Partial GO enrichment analysis of target module
模块 Module | GO条目 GO term | 基因本体 Ontology | 描述 Description | 基因数目 Genes No. | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
棕色 Brown | GO:0050896 | P | 对刺激的反应Response to stimulus | 644 | 6.16e-10 |
| GO:0006950 | P | 对胁迫的反应Response to stress | 365 | 1.39e-05 | |
| GO:0009719 | P | 对内源性刺激的反应Response to endogenous stimulus | 269 | 7.26e-14 | |
| GO:0009628 | P | 对非生物刺激的反应Response to abiotic stimulus | 263 | 2.57e-07 | |
| GO:1901700 | P | 对含氧化合物的反应Response to oxygen-containing compound | 253 | 3.61e-14 | |
| GO:0009725 | P | 对激素的反应Response to hormone | 233 | 1.08e-08 | |
| GO:0048583 | P | 对刺激反应的调节Regulation of response to stimulus | 106 | 3.83e-08 | |
| GO:0009737 | P | 对脱落酸的反应Response to abscisic acid | 103 | 3.37e-08 | |
| GO:0009723 | P | 对乙烯的反应Response to ethylene | 68 | 6.83e-08 | |
| GO:0080134 | P | 对胁迫反应的调节Regulation of response to stress | 66 | 3.94e-09 | |
| GO:0010200 | P | 对几丁质的反应Response to chitin | 64 | 2.87e-20 | |
| GO:0009751 | P | 对水杨酸的反应Response to salicylic acid | 47 | 4.46e-08 | |
| GO:0031347 | P | 对防御反应的调节Regulation of defense response | 47 | 1.41e-06 | |
| GO:0009753 | P | 对茉莉酸的反应Response to jasmonic acid | 46 | 2.71e-05 | |
| GO:0003700 | F | 转录因子活性,特异性DNA序列结合 Transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 262 | 3.74e-20 | |
| GO:0005634 | C | 核nucleus | 797 | 1.94e-06 | |
| GO:0005887 | C | 质膜的组成部分Integral component of plasma membrane | 24 | 0.024 88 |
| 1 | 付小琼,彭军.国家棉花区域试验工作十年回顾与展望[J].棉花学报,2017,29(S1):113-117. |
| FU X Q, PENG J. Prospect and retrospection of national cotton regional test of China in last decade [J]. Cotton Sci., 2017, 29(S1):113-117. | |
| 2 | 李俊义,王润珍,王宗洪,等.环境条件与棉苗冻害程度研究简报[J].新疆农垦科技,2000(1):19. |
| 3 | 龚双军,李国英,杨德松,等.不同棉花品种苗期抗寒性及其生理指标测定[J].中国棉花,2005,32(3):16-17. |
| GONG S J, LI G Y, YANG D S, et al.. Determination of cold resistance and physiological indexes of different cotton varieties at seedling stage [J]. China Cotton, 2005, 32(3):16-17. | |
| 4 | 秦天元,孙超,毕真真,等.基于WGCNA的马铃薯根系抗旱相关共表达模块鉴定和核心基因发掘[J].作物学报,2020,46(7):1033-1051. |
| QIN T Y, SUN C, BI Z Z, et al.. Identification of drought-related co-expression modules and hub genes in potato roots based on WGCNA [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2020, 46(7):1033-1051. | |
| 5 | 巨飞燕,张思平,刘绍东,等.利用WGCNA进行棉花果枝节间伸长相关基因共表达模块鉴定[J].棉花学报,2019,31(5)403-413. |
| JU F Y, ZHANG S P, LIU S D, et al.. Identification of co-expression modules of genes related to internode elongation of cotton fruiting branches by WGCNA [J]. Cotton Sci., 2019, 31(5)403-413. | |
| 6 | 傅明川,李浩,陈义珍,等.利用WGCNA鉴定棉花抗黄萎病相关基因共表达网络[J].作物学报,2020,46(5)668-679. |
| FU M C, LI H, CHEN Y Z, et al.. Identification of co-expressed modules of cotton genes responding to Verticillium dahliae infection by WGCNA [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2020, 46(5):668-679. | |
| 7 | 李旭凯,李任建,张宝俊.利用WGCNA鉴定非生物胁迫相关基因共表达网络[J].作物学报,2019,45(9)1349-1364. |
| LI X K, LI R J, ZHANG B J. Identification of rice stress-related gene co-expression modules by WGCNA [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(9)1349-1364. | |
| 8 | 秦梦凡,李浩东,左凯峰,等.利用WGCNA鉴定甘蓝型油菜低温胁迫的基因共表达网络[J].中国油料作物学报,2020,42(4)554-562. |
| QIN M F, LI H D, ZUO K F, et al.. Identification of co-expression networks responding to low-temperature stress by WGCNA in Brassica napus L. [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2020, 42(4)554-562. | |
| 9 | MORTAZAVI A, WILLIAMS B A, MCCUE K, et al.. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq [J]. Nat. Methods, 2008, 5(7):621-628. |
| 10 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408. |
| 11 | 谢勇军.水稻非生物逆境差异表达基因分析及共表达网络构建[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2018. |
| XIE Y J. Analysis of ifferentially expressed genes and construction of gene co-expression network in rice under abiotic stresses [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 12 | SHARMA N, CRAM D, HUEBERT T, et al.. Exploiting the wild crucifer Thlaspi arvense to identify conserved and novel genes expressed during a plant's response to cold stress [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2007, 63(2):171-184. |
| 13 | 赵娟 .反义抑制GhDET2对棉花生长发育的影响[D].重庆:西南大学,2009. |
| ZHAO J. Effects of down-regulation of GhDET2, a steroid 5α-reducase gene of cotton, on the growth and development of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2009. | |
| 14 | KAZAN K. Negative regulation of defence and stress genes by EAR-motif-containing repressors [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2006, 11(3):109-112. |
| 15 | SAKAMOTO H, MARUYAMA K, SAKUMA Y, et al.. Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger proteins function as transcription repressors under drought, cold, and high-salinity stress conditions [J]. Plant Physiol., 2004, 136(1):2734-2746. |
| 16 | OHTA M, MATSUI K, HIRATSU K, et al.. Repression domains of class Ⅱ ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression [J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(8):1959-1968. |
| 17 | SAKAMOTO H, ARAKI T, MESHI T, et al.. Expression of a subset of the Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger protein gene family under water stress [J]. Gene,2000,248(1):23-32. |
| 18 | ENGLBRECHT C C, SCHOOF H, BOHM S. Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2004, 5(1):39 [2021-06-21]. . |
| 19 | MITTLER R, KIM Y, SONG L, et al.. Gain-and loss-of-function mutations in Zat10 enhance the tolerance of plants to abiotic stress [J]. FEBS Lett., 2006, 580(28-29):6537-6542. |
| 20 | ROSSEL J B, WILSON P B, HUSSAIN D, et al.. Systemic and intracellular responses to photooxidative stress in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(12):4091-4110. |
| 21 | NGUYEN X C, KIM S H, LEE K, et al.. Identification of a C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor (ZAT10) from Arabidopsis as a substrate of MAP kinase [J]. Plant Cell Rep.,2012, 31(4):737-745. |
| 22 | DROILLARD M, BOUDSOCQ M, BARBIER-BRYGOO H, et al.. Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions. Involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6 [J]. FEBS Lett., 2002, 527(1-3):43-50. |
| 23 | LIU X M, KIM K E, KIM K C, et al.. Cadmium activates Arabidopsis MPK3 and MPK6 via accumulation of reactive oxygen species [J]. Phytochemistry, 2010, 71(56):614-618. |
| 24 | NAKAGAMI H, PITZSCHKE A, HIRT H. Emerging MAP kinase pathways in plant stress signalling [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2005, 10(7):339-346. |
| 25 | SAMUEL M A, MILES G P, ELLIS B E. Ozone treatment rapidly activates MAP kinase signalling in plants [J]. Plant J., 2000, 22(4):367-376. |
| 26 | TENA G, ASAI T, CHIU W L, et al.. Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades [J]. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2001, 4(5):392-400. |
| 27 | YUASA T, ICHIMURA K, MIZOGUCHI T, et al.. Oxidative stress activates ATMPK6, an Arabidopsis homologue of MAP kinase [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2001, 42(9):1012-1016. |
| 28 | 张丽丽,李景富,王傲雪.转录激活因子CBF基因在植物抗冷分子机制中的作用[J].园艺学报,2008,35(5):765-771. |
| ZHANG L L, LI J F, WANG A X. The role of the transcription factor CBF genes in cold-responsive molecular mechanism [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2008, 35(5):765-771. | |
| 29 | CAI X, MAGWANGA R O, XU Y, et al.. Comparative transcriptome, physiological and biochemical analyses reveal response mechanism mediated by CBF4 and ICE2 in enhancing cold stress tolerance in Gossypium thurberi [J]. AoB Plants, 2019:1-17. |
| 30 | HAAKE V, COOK D, RIECHMANN J L, et al.. Transcription factor CBF4 is a regulator of drought adaptation in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiol., 2002, 130(2):639-648. |
| 31 | CHAWADE A, BRAUTIGAM M, LINDLOF A, et al.. Putative cold acclimation pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana identified by a combined analysis of mRNA co-expression patterns, promoter motifs and transcription factors [J]. BMC Genomics, 2007, 8(1):304. |
| 32 | SEO P J, KIM M J, PARK J Y, et al.. Cold activation of a plasma membrane-tethered NAC transcription factor induces a pathogen resistance response in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant J., 2010, 61(4):661-671. |
| 33 | BOZOVIC V, SVENSSON J, SCHMITT J, et al.. Dehydrins (LTI29, LTI30, COR47) from Arabidopsis thaliana expressed in Escherichia coli protect thylakoid membrane during freezing [J]. J. Serb. Chem. Soc., 2013, 78(8):1149-1160. |
| 34 | HERNANDEZ-SANCHEZ I E, MARURI-LOPEZ I, GRAETHER S P, et al.. In vivo evidence for homo-and heterodimeric interactions of Arabidopsis thaliana dehydrins AtCOR 47, AtERD10, and AtRAB18 [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2019, 7(1):17036 [2021-06-21]. . |
| [1] | 李舒欣, 张浩, 郑厚胜, 郑培和, 逄世峰, 许世泉. 转录组分析二马牙和长脖类型林下参表型差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 56-68. |
| [2] | 李生梅, 张大伟, 迪丽拜尔·迪力买买提, 魏鑫, 芮存, 杨涛, 耿世伟, 高文伟. 减量灌溉对转ScALDH21基因棉花农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 152-159. |
| [3] | 刘源, 张秀妍, 徐妙云, 郑红艳, 邹俊杰, 张兰, 王磊. 水稻干旱胁迫的small RNA转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 23-32. |
| [4] | 张旭1,何俊峰1,陈佛文1,李继福1*,吴启侠1,谭京红1,邹家龙2. 麦秆还田对直播和移栽棉花产量及氮素吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 122-131. |
| [5] | 张特,康正华,赵强*,聂志勇,王蜜蜂,崔延楠. 施氮量及打顶方式对棉花营养积累与分配及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 139-147. |
| [6] | 马盼盼1,2,赵曾强1,2,祝建波2,孙国清3*. 棉花耐旱耐盐碱生理和分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 27-36. |
| [7] | 王国宁, 张艳, 宋俊丽, 杨君, 王省芬, 吴立强, 张桂寅. 黄萎病胁迫下抗病陆地棉茎组织lncRNA的鉴定与分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 29-41. |
| [8] | 吴雪琴, 崔延楠, 赵强. 化学打顶后使用外源物质对棉花脱叶催熟及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 151-160. |
| [9] | 李憬霖, 刘绍东, 张思平, 陈静, 刘瑞华, 沈倩, 李阳, 马慧娟, 赵新华, 庞朝友. 棉花品种资源全生育期抗旱性评价及抗旱指标筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 52-65. |
| [10] | 刘梦丽1,李进2,张军高2,周小云2,杜鹏程1,郭庆元1*,雷斌2*. 棉花红腐病菌不同致病力菌株间毒素活性差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 99-105. |
| [11] | 刘松涛1,田春丽1,曹雯梅1,郑贝贝1,李鹏程2,董合林2. 基于不同土壤质地棉花根际微生物和酶活性特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 73-79. |
| [12] | 段怡红,阎媛媛,陈丽婷,李青,张冬梅,孙正文,张艳,马峙英,王省芬*. 陆地棉开花时间相关基因GhMYB44的克隆与功能验证[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(12): 29-38. |
| [13] | 张文云1,张建诚2,姚景珍2*. 氮胁迫下小麦叶片转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(11): 26-34. |
| [14] | 王潭刚1§,马丽1§,李克富1,王冀川2*,李慧琴1,吉光鹏1,郝全有1,崔建强1,胡宝1. 不同密度下封顶方式对南疆棉花生长及产量性状的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(6): 110-116. |
| [15] | 赵婧文,张庆伟,李政,张文太*. 膜下滴灌施用生物有机肥对土壤盐分及棉花产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3): 102-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号