




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 66-76.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0657
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-13
通讯作者:
张芃芃
Xiaoting WANG( ), Pengpeng ZHANG(
), Pengpeng ZHANG( )
)
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Pengpeng ZHANG
About author:WANG XiaotingE-mail: xiaotingwang2021@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
生物的信号感知与传导过程与生物对外界环境的适应性密不可分。提及信号传导系统,真核生物和原核生物中普遍存在的是双元激酶系统和丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶系统,且关于这2种信号传导系统的研究已有诸多报道。作为一种典型的原核光合模式生物,集胞藻6803除了具有原核生物的双元信号传导系统之外,还具有由12个基因编码的真核类Ser/Thr激酶系统,根据它们的结构特点可以分为2大类,即PKN2亚家族和ABC1亚家族。编码属于PKN2亚家族的Ser/Thr激酶的基因大多数已有功能研究,而其他属于ABC1亚家族的基因大多数功能未知。对集胞藻6803中12个Ser/Thr蛋白激酶的保守域、基序以及蛋白细胞定位等进行分析,同时选取具有代表性的单子叶植物水稻和双子叶植物拟南芥作为参照对象,通过与水稻(15 ABC1Ks)和拟南芥(17 ABC1Ks)中的ABC1家族的蛋白激酶基因进行序列分析比较,从而对集胞藻6803中12个Ser/Thr蛋白激酶的潜在功能和进化关系进行了讨论分析,将为更全面地理解集胞藻6803中Ser/Thr蛋白激酶参与的信号传导过程提供新的见解和思路。
中图分类号:
王小婷, 张芃芃. 集胞藻6803中丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶系统发育和功能概述[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 66-76.
Xiaoting WANG, Pengpeng ZHANG. Phylogenic and Functional Profile of Ser/Thr Kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 66-76.
| Gene product | Gene ID | Category |
|---|---|---|
| SpkA | sll 1574~1575 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkB | slr 1697 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkC | slr 0599 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkD | sll 0776 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkE | slr 1443 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkF | slr 1225 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkG | slr 0152 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkH | sll 0005 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkI | sll 1770 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkJ | slr 0889 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkK | slr 1919 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkL | sll 0095 | ABC1 subfamily |
Table 1 12 Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
| Gene product | Gene ID | Category |
|---|---|---|
| SpkA | sll 1574~1575 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkB | slr 1697 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkC | slr 0599 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkD | sll 0776 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkE | slr 1443 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkF | slr 1225 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkG | slr 0152 | PKN2 subfamily |
| SpkH | sll 0005 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkI | sll 1770 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkJ | slr 0889 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkK | slr 1919 | ABC1 subfamily |
| SpkL | sll 0095 | ABC1 subfamily |
| Gene | Function description |
|---|---|
| spkA | Involved in cell motility[ |
| spkB | Participate in the oxidative stress response[ |
| spkC | Participate in the regulation of nitrogen metabolism[ |
| spkD | Involved in adjusting the pool of TCA cycle metabolites[ |
| spkE | Respond to cold stress[ |
| spkF | Involved in the phosphorylation of the GroES chaperone protein[ |
| spkG | Involved in high-salt acclimation[ |
| spkH | Involved in hyperosmotic stress response[ |
| spkK | Involved in the phosphorylation of the GroES chaperone protein[ |
Table 2 Partly published function descriptions among 12 Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
| Gene | Function description |
|---|---|
| spkA | Involved in cell motility[ |
| spkB | Participate in the oxidative stress response[ |
| spkC | Participate in the regulation of nitrogen metabolism[ |
| spkD | Involved in adjusting the pool of TCA cycle metabolites[ |
| spkE | Respond to cold stress[ |
| spkF | Involved in the phosphorylation of the GroES chaperone protein[ |
| spkG | Involved in high-salt acclimation[ |
| spkH | Involved in hyperosmotic stress response[ |
| spkK | Involved in the phosphorylation of the GroES chaperone protein[ |
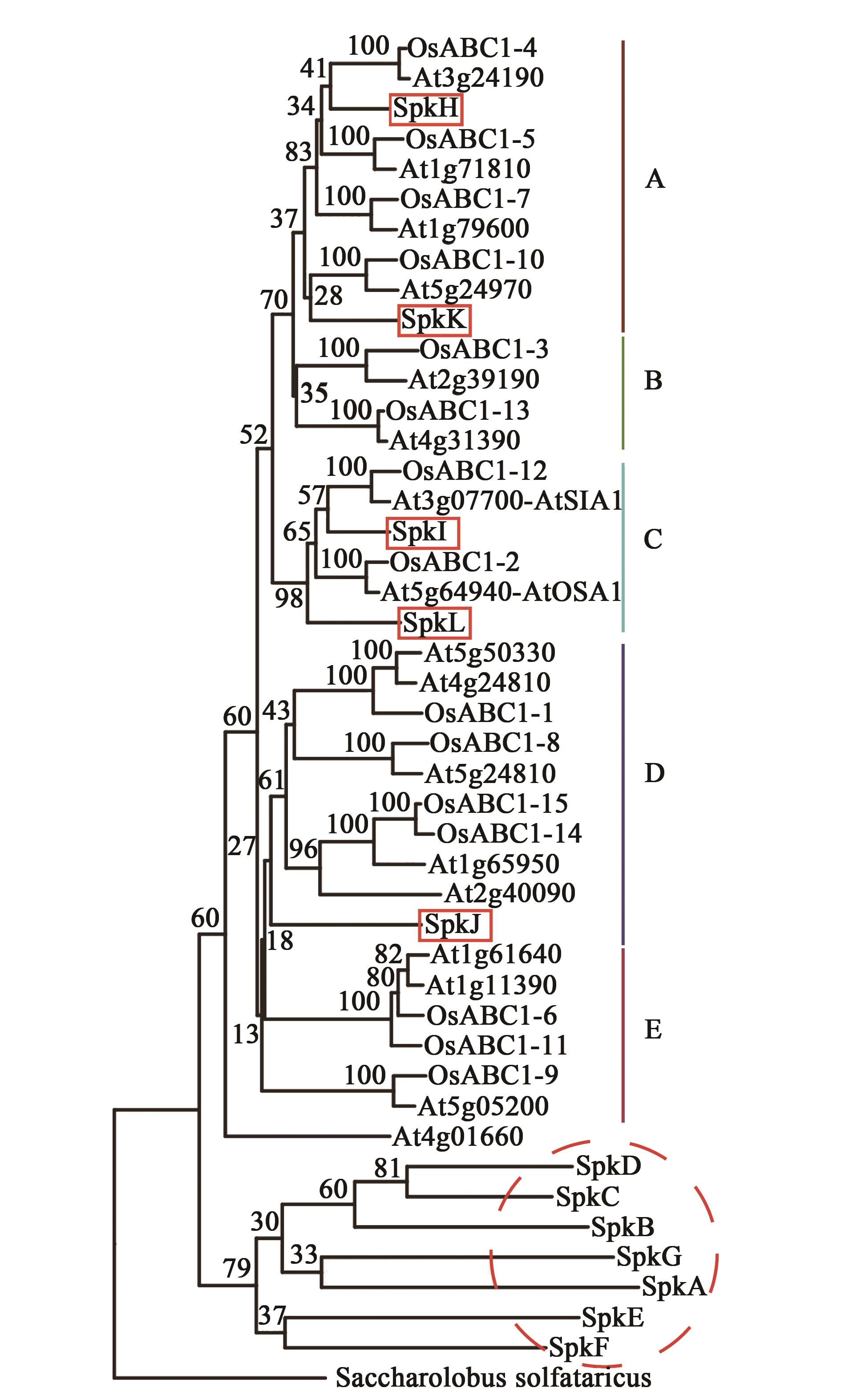
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic analysis of Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, rice and ArabidopsisNote:12 Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 used for construction of phylogenetic tree are listed in Table 1, amino acid sequences are derived from KEGG GENES database (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/genes.html); 15 ABC1Ks in rice are from RiceData; 17 ABC1Ks in Arabidopsis are derived from the Arabidopsis information resource(https://arabidopsis.org/). The rooted tree is generated using MEGA6 program by neighbor-joining method. The scale bar indicates 0.2 amino acid substitutions per synonymous site.

Fig. 2 Motif predictions of 12 Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803Note:Amino acid sequences are retrieved from KEGG GENES database (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/genes.html); motif prediction is conducted on MEME website (https://meme-suite.org/).
| Gene product | Rice | Arabidopsis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homolog | Location | Predicted function | Homolog | Location | Predicted function | |
| SpkH | OsABC1-4 | Chloroplast | Cold stress[ | At3g24190 | Chloroplast | Protein phosphorylation |
| SpkK | OsABC1-10 | Mitochondria | Salt stress[ | At5g24970 | Mitochondria | Protein phosphorylation |
| SpkI | OsABC1-12 | Chloroplast | Cold and salt stress; biosynthesis of isoprenoids[ | At3g07700 (AtSIA1; ABC1K7) | Chloroplast | Salt stress[ |
| SpkL | OsABC1-2 | Chloroplast | Salt, H2O2 and darkness; energy metabolism[ | At5g64940 (AtOSA1; ABC1K8) | Chloroplast | Cadmium and oxidative stresses; isoprenyl lipid synthesis; distribution of iron within chloroplast[ |
| SpkJ | OsABC1-14, -15 | Vacuole | H2O2, cold, drought, and darkness[ | At1g65950 (ABC1K14); At2g40090 (ABC1K15) | Extracellular region | Lipid homeostasis; protein phosphorylation |
Table 3 Homology of 5 Ser/Thr kinases (SpkH-SpkL)in rice and Arabidopsis, respectively
| Gene product | Rice | Arabidopsis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homolog | Location | Predicted function | Homolog | Location | Predicted function | |
| SpkH | OsABC1-4 | Chloroplast | Cold stress[ | At3g24190 | Chloroplast | Protein phosphorylation |
| SpkK | OsABC1-10 | Mitochondria | Salt stress[ | At5g24970 | Mitochondria | Protein phosphorylation |
| SpkI | OsABC1-12 | Chloroplast | Cold and salt stress; biosynthesis of isoprenoids[ | At3g07700 (AtSIA1; ABC1K7) | Chloroplast | Salt stress[ |
| SpkL | OsABC1-2 | Chloroplast | Salt, H2O2 and darkness; energy metabolism[ | At5g64940 (AtOSA1; ABC1K8) | Chloroplast | Cadmium and oxidative stresses; isoprenyl lipid synthesis; distribution of iron within chloroplast[ |
| SpkJ | OsABC1-14, -15 | Vacuole | H2O2, cold, drought, and darkness[ | At1g65950 (ABC1K14); At2g40090 (ABC1K15) | Extracellular region | Lipid homeostasis; protein phosphorylation |
| ID | Gene product | Peptide length | Number of predicted TM helix | Start and end position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| slr0599 | SpkC | 535 | 1 | 344~366 |
| sll0776 | SpkD | 505 | 1 | 326~348 |
| slr1225 | SpkF | 495 | 3 | 372~394, 399~416, 463~485 |
| sll1770 | SpkI | 585 | 2 | 530~549, 553~575 |
| sll0095 | SpkL | 567 | 3 | 27~46, 503~525, 530~552 |
Table 4 Transmembrane helix prediction of Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
| ID | Gene product | Peptide length | Number of predicted TM helix | Start and end position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| slr0599 | SpkC | 535 | 1 | 344~366 |
| sll0776 | SpkD | 505 | 1 | 326~348 |
| slr1225 | SpkF | 495 | 3 | 372~394, 399~416, 463~485 |
| sll1770 | SpkI | 585 | 2 | 530~549, 553~575 |
| sll0095 | SpkL | 567 | 3 | 27~46, 503~525, 530~552 |
| Gene product | Cellular compartment | Intensity (A. U.) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM | PM1 | PM2 | TM | SOL | ||
| SpkB | 3.5 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkC | 0.9 | 3 | 4.3 | 0.3 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkE | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1.9 | / | / | 1×106 |
| SpkF | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.2 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkH | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 2.1 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkI | / | 3.7 | 1.9 | 1.4 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkJ | 3.3 | 3.3 | 1.4 | / | / | 1×105 |
| SpkK | / | 1.9 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 1×107 |
| SpkL | / | 2.8 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 1×106 |
Table 5 Subcellular localization prediction of Ser/Thr kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
| Gene product | Cellular compartment | Intensity (A. U.) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM | PM1 | PM2 | TM | SOL | ||
| SpkB | 3.5 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkC | 0.9 | 3 | 4.3 | 0.3 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkE | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1.9 | / | / | 1×106 |
| SpkF | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.2 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkH | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 2.1 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkI | / | 3.7 | 1.9 | 1.4 | / | 1×107 |
| SpkJ | 3.3 | 3.3 | 1.4 | / | / | 1×105 |
| SpkK | / | 1.9 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 1×107 |
| SpkL | / | 2.8 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 1×106 |
| 1 | DUTTA R, QIN L, INOUYE M. Histidine kinases: diversity of domain organization [J]. Mol. Microbiol., 1999, 34(4): 633-640. |
| 2 | ALEX L A, SIMON M I. Protein kinase and signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes [J]. Trends Genet., 1994, 10(4): 133-138. |
| 3 | STOCK A M, ROBINSON V L, GOUDREAU P N. Two-component signal transduction [J]. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2000, 69:183-215. |
| 4 | KHORCHID A, IKURA M. Bacterial histidine kinase as signal sensor and transducer [J]. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 2006, 38(3): 307-312. |
| 5 | HANKS S K, HUNTER T. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: kinase (catalytic) domain structure and classification1 [J]. FASEB J., 1995, 9(8): 576-596. |
| 6 | HUNTER T. Signaling—2000 and beyond [J]. Cell, 2000, 100(1): 113-127. |
| 7 | MU OZ-DORADO J, INOUYE S, INOUYE M. A gene encoding a protein serine/threonine kinase is required for normal development of M. xanthus, a gram-negative bacterium [J]. Cell, 1991, 67(5): 995-1006. |
| 8 | ZHANG C C. Bacterial signaling involving eukaryotic-type protein kinases [J]. Mol. Microbiol., 1996, 20(1): 9-15. |
| 9 | KENNELLY P J, POTTS M. Fancy meeting you here! a fresh look at “prokaryotic” protein phosphorylation [J]. J. Bacteriol., 1996, 178(16): 4759-4764. |
| 10 | RIPPKA R. Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria [J]. Methods Enzymol., 1988, 167: 3-27. |
| 11 | MANN N H. Protein phosphorylation in cyanobacteria [J]. Microbiology, 1995, 140 (Pt 12): 3207-3215. |
| 12 | ZHANG X W, ZHAO F Q, GUAN X Y, et al.. Genome-wide survey of putative serine/threonine protein kinases in cyanobacteria [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2007, 8(1): 395 [2021-07-09]. . |
| 13 | YANG M K, QIAO Z X, ZHANG W Y, et al. . Global phosphoproteomic analysis reveals diverse functions of serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphorylation in the model cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp strain PCC 7002 [J]. J. Proteome Res., 2013, 12(4): 1909-1923. |
| 14 | CHEN Z, ZHAN J, CHEN Y, et al.. Effects of phosphorylation of beta subunits of phycocyanin on state transition in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp PCC 6803 [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2015, 56(10): 1997-2013. |
| 15 | SPÄT P, MAČEK B, FORCHHAMMER K. Phosphoproteome of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and its dynamics during nitrogen starvation [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2015, 6: 248 [2021-07-09]. . |
| 16 | ANGELERI M, MUTH-PAWLAK D, ARO E M, et al.. Study of O-phosphorylation sites in proteins involved in photosynthesis-related processes in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803: application of the SRM approach [J]. J. Proteome Res., 2016,15(12): 4638-4652. |
| 17 | ZHANG C C, JANG J C, SAKR S, et al.. Protein phosphorylation on Ser, Thr and Tyr residues in cyanobacteria [J]. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2006, 9(3-4): 154-166. |
| 18 | KANEKO T, SATO S, KOTANI H, et al.. Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. Ⅱ. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions [J]. DNA Res., 1996, 3(3): 109-136. |
| 19 | WILLIAMS J G K. Construction of specific mutations in PSII photosynthetic reaction center by genetic engineering [J]. Methods Enzymol., 1988,167:766-778. |
| 20 | XU W, WANG Y C. Sequences, domain architectures, and biological functions of the sserine/threonine and histidine kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [J]. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2019, 188: 1022-1065. |
| 21 | HAN G N, ZHANG C C. On the origin of Ser/Thr kinases in a prokaryote [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2001, 200(1): 79-84. |
| 22 | ZORINA A A. Eukaryotic protein kinase in cyanobacteria [J]. Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2013, 60(5): 589-596. |
| 23 | LEONARD C J, ARAVIND L, KOONIN E V. Novel families of putative protein kinases in bacteria and archaea: evolution of the “eukaryotic” protein kinase superfamily [J]. Genome Res., 1998, 8(10): 1038-1047. |
| 24 | LUNDQUIST P K, POLIAKOV A, GIACOMELLI L, et al.. Loss of plastoglobule kinases ABC1K1 and ABC1K3 causes conditional degreening, modified prenyl-lipids, and recruitment of the jasmonic acid pathway [J]. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(5): 1818-1839. |
| 25 | MANARA A, DALCORSO G, FURINI A. The role of the atypical kinases ABC1K7 and ABC1K8 in abscisic acid responses [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016, 7: 366 [2021-07-09]. . |
| 26 | HANKS S K, QUINN A M, HUNTER T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains [J]. Science, 1988, 241(4861): 42-52. |
| 27 | ZHANG C C. A gene encoding a protein related to eukaryotic protein kinases from the filamentous heterocystous cyanobacterium Anabaena PCC 7 120 [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1994, 90(24): 11840-11844. |
| 28 | MUELLER P R, COLEMAN T R, KUMAGAI A, et al.. Myt1: a membrane-associated inhibitory kinase that phosphorylates Cdc2 on both threonine-14 and tyrosine-15 [J]. Science, 1995, 270(5233): 86-90. |
| 29 | ZHANG C C, GONZALEZ L, PHALIP V. Survey analysis and genetic organization of genes encoding eukaryotic-like signaling proteins on a cyanobacterial genome [J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 1998, 26(16): 3619-3625. |
| 30 | KAMEI A, YOSHIHARA S, YUASA T, et al.. Biochemical and functional characterization of a eukaryotic-type protein kinase, SpkB, in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [J]. Curr. Microbiol., 2003, 46(4): 296-301. |
| 31 | KAMEI A, YUASA T, ORIKAWA K, et al.. A eukaryotic-type protein kinase, SpkA, is required for normal motility of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 [J]. J. Bacteriol., 2001, 183(5): 1505-1510. |
| 32 | PANICHKIN V B, ARAKAWA-KOBAYASHI S, KANASEKI T, et al.. Serine/threonine protein kinase SpkA in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 is a regulator of expression of three putative pilA operons, formation of thick pili, and cell motility [J]. J. Bacteriol., 2006, 188(21): 7696-7699. |
| 33 | ZORINA A A, STEPANCHENKO N, NOVIKOVA G V, et al.. Eukaryotic-like Ser/Thr protein kinases SpkC/F/K are involved in phosphorylation of GroES in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis [J]. DNA Res., 2011, 18(3): 137-151. |
| 34 | MATA-CABANA A, GARCÍA-DOMÍNGUEZ M, FLORENCIO F J, et al.. Thiol-based redox modulation of a cyanobacterial eukaryotic-type serine/threonine kinase required for oxidative stress tolerance [J]. Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2012, 17(4): 521-533. |
| 35 | SINETOVA M A, LOS D A. New insights in cyanobacterial cold stress responses: genes, sensors, and molecular triggers [J]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj., 2016, 1860: 2391-2403. |
| 36 | LAURENT S, JANG J, JANICKI A, et al. . Inactivation of spkD, encoding a Ser/Thr kinase, affects the pool of the TCA cycle metabolites in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 [J]. Microbiology, 2008, 154(7): 2161-2167. |
| 37 | WANG H L, POSTIER B L, BURNAP R L. Alterations in global patterns of gene expression in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in response to inorganic carbon limitation and the inactivation of ndhR, a LysR family regulator [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2004, 279(7): 5739-5751. |
| 38 | ZORINA A A, BEDBENOV V S, NOVIKOVA G V, et al. . Involvement of serine/threonine protein kinases in cold stress response in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: functional characterization of a protein kinase SpkE [J]. Mol. Biol. (Mosk), 2014, 48(3): 452-462. |
| 39 | GALKIN A N, MIKHEEVA L E, SHESTAKOV S V. The insertional inactivation of genes encoding eukaryotic-type serine/threonine protein kinases in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [J]. Microbiology, 2003, 72(1): 52-57. |
| 40 | LIANG C W, ZHANG X W, CHI X Y, et al. . Serine/threonine protein kinase SpkG is a candidate for high salt resistance in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(5): e18718 [2021-07-09]. . |
| 41 | ANGELERI M, ZORINA A, ARO E, et al.. Interplay of SpkG kinase and the Slr0151 protein in the phosphorylation of ferredoxin 5 in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 [J]. FEBS Lett., 2018, 592(3): 411-421. |
| 42 | PAITHOONRANGSARID K, SHOUMSKAYA M A, KANESAKI Y, et al. . Five histidine kinases perceive osmotic stress and regulate distinct sets of genes in Synechocystis [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2004, 279(51): 53078-53086. |
| 43 | CALZADILLA P I, ZHAN J, SÉTIF P, et al.. The cytochrome b6f complex is not involved in cyanobacterial state transitions [J]. Plant Cell, 2019, 31(4): 911-931. |
| 44 | XU W, WANG Y C. Post-translational modifications of serine/threonine and histidine kinases and their roles in signal transductions in Synechocystis Sp. PCC 6803 [J]. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2021, 193(3): 687-716. |
| 45 | KAMEI A, YUASA T, GENG X, et al. . Biochemical examination of the potential eukaryotic-type protein kinase genes in the complete genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [J]. DNA Res., 2002, 9(3): 71-78. |
| 46 | WANG L, SUN Y P, CHEN W L, et al.. Genomic analysis of protein kinases, protein phosphatases and two-component regulatory systems of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2002, 217(2): 155-165. |
| 47 | GALKIN A N, MIKHEEVA L E, SHESTAKOV S V. Insertional inactivation of genes encoding eukaryotic type serine/threonine protein kinases in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [J]. Mikrobiologiia, 2003, 72(1): 64-69. |
| 48 | GAO Q S, ZHANG D, XU L, et al. . Systematic identification of rice ABC1 gene family and its response to abiotic stress [J]. Rice Sci., 2011, 18(3): 167-177. |
| 49 | GAO Q S, ZANG H, GAO Y, et al. . Comprehensive molecular evolution and gene expression analyses of the ABC1 atypical kinase family in rice and Arabidopsis [J]. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 2015, 24(2): 210-217. |
| 50 | YANG S, ZHANG Q, LI T, et al. . AtSIA1, an ABC1-like kinase, regulates salt response in Arabidopsis [J]. Biologia, 2012, 67(6): 1107-1111. |
| 51 | JASINSKI M, SUDRE D, SCHANSKER G, et al.. AtOSA1, a member of the Abc1-like family, as a new factor in cadmium and oxidative stress response [J]. Plant Physiol., 2008, 147(2): 719-731. |
| 52 | YANG S G, ZENG X Q, LI Tet al.. AtACDO1, an ABC1-like kinase gene, is involved in chlorophyll degradation and the response to photooxidative stress in Arabidopsis [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2012, 63(10): 3959-3973. |
| 53 | MARTINIS J, GLAUSER G, VALIMAREANU S, et al.. ABC1K1/PGR6 kinase: a regulatory link between photosynthetic activity and chloroplast metabolism [J]. Plant J., 2014, 77(2): 269-283. |
| 54 | MARTINIS J, GLAUSER G, VALIMAREANU S, et al.. A chloroplast ABC1-like kinase regulates vitamin E metabolism in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiol., 2013, 162(2): 652-662. |
| 55 | LUNDQUIST P K, DAVIS J I, VAN WIJK K J. ABC1K atypical kinases in plants: filling the organellar kinase void [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2012, 17(9): 546-555. |
| [1] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [2] | 张叶, 张昊, 张芃芃. 不同光环境集胞藻循环电子传递与类梅勒反应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 78-95. |
| [3] | 代艾林, 张永刚, 艾强, 滕熙超, 杨利民. 不同光质对朝鲜淫羊藿生长、生理和黄酮类成分积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 85-92. |
| [4] | 郝正刚,赵会君,魏玉清*,曾周琦,王志恒. 甜高粱对镉胁迫的生理生化响应及镉富集研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 30-42. |
| [5] | 李猛,陈栋,李秀妮,李林林,王荣浩,时向东*. 盐胁迫下外源褪黑素对烟草幼苗抗氧化特性和光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2): 141-147. |
| [6] | 郝水源1,宝格日乐1,苏晓东2,苏康3,刘卓恩2,韩雪3,史瑞东3. 不同施肥措施对黄灌区枸杞光合特性及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(2): 101-107. |
| [7] | 宋云1,李林宣2,卓凤萍2,张雪妍1,任茂智2,李付广1* . 茉莉酸信号传导在植物抗逆性方面研究进展[J]. , 2015, 17(2): 17-24. |
| [8] | 秦晓克[1] 黄跃[1] 杨笑瑒[1] 蒋彦[1] 李旭锋[1] Erwin Grill[2] 杨毅[1]. 拟南芥中一个与ABA信号途径相关未知蛋白质的研究初报[J]. , 2007, 9(3): 112-117. |
| [9] | 吴向华 杨启银 刘五星 虞光华. 光合细菌的研究进展及其应用[J]. , 2004, 6(2): 35-38. |
| [10] | 袁永慧 邓西平 黄明丽 白登忠. 生物节水中的补偿效应与根系调控研究[J]. , 2003, 5(6): 24-28. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号