




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 197-206.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0931
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-11-02
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2023-07-15
发布日期:2023-08-25
通讯作者:
井长青
作者简介:赵苇康 E-mail: zhaoweikang1997@126.com;
基金资助:
Weikang ZHAO1( ), Changqing JING1(
), Changqing JING1( ), Chen CHEN2
), Chen CHEN2
Received:2021-11-02
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-07-15
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
Changqing JING
摘要:
基于植被净初级生产力(net primary productivity,NPP)、归一化植被指数(normal difference vegetation index, NDVI)、气候因子(气温和降水量)等遥感数据,并借助于一元线性回归模型、相关性分析等方法,对新疆天然年草地NPP、NDVI的时空变化及其对气候因子的响应进行了分析。结果表明,新疆草地NPP和NDVI的年均值呈上升趋势,其中草地NPP的多年空间分布呈北高南低的趋势;草地NDVI由西北向东南呈逐渐降低的趋势。1985—2015年年均气温和降水量均呈上升趋势,总体表现为盆地年均气温高于山区,而山区年均降水量多于盆地。从空间分布来看,草地NPP和NDVI均表现为与降水量呈正相关的草地面积大于与气温呈正相关的草地面积,且与降水量的相关系数均高于与气温的相关系数。由此表明,降水量是新疆草地植被的主要影响因子,为应对气候变化提供了数据支撑。
中图分类号:
赵苇康, 井长青, 陈宸. 新疆天然草地时空变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 197-206.
Weikang ZHAO, Changqing JING, Chen CHEN. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Xinjiang Natural Grassland and Their Responses to Climate Factors[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 197-206.
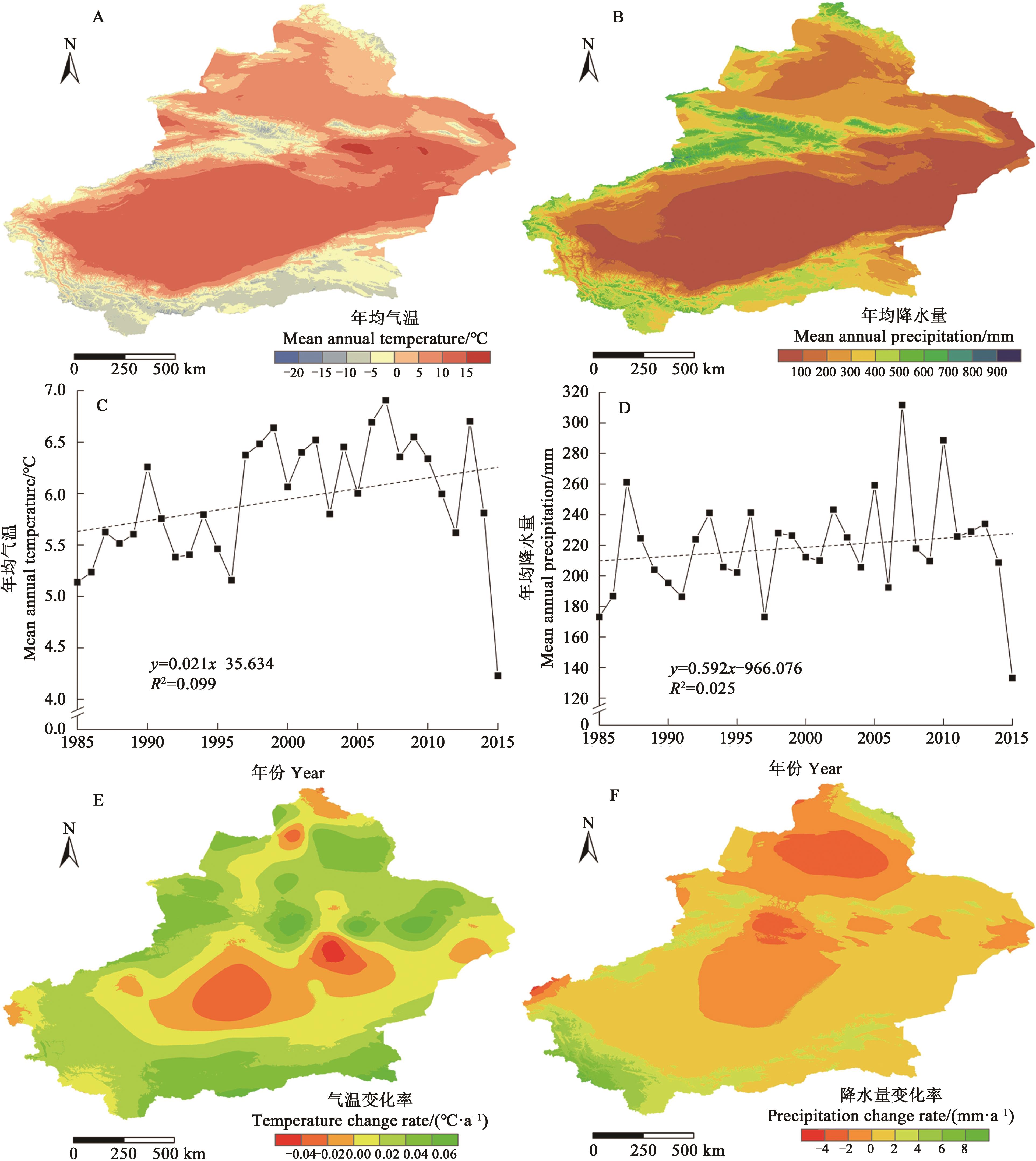
图2 1985—2015年新疆年均气温、年均降水量空间分布及时空变化A:年均气温的空间分布;B:年均降水的空间分布;C:年均气温的时间变化;D:年均降水的时间变化;E:气温变化率的空间分布;F:降水变化率的空间分布
Fig. 2 Spatial distribution and spatial variation of mean annual temperature and annual precipitation in Xinjiang from 1985 to 2015A: Spatial distribution of mean annual temperature; B: Spatial distribution of mean annual precipitation; C: Temporal variation of mean annual temperature; D: Temporal variation of mean annual precipitation; E: Spatial distribution of temperature change rate; F: Spatial distribution of precipitation change rate
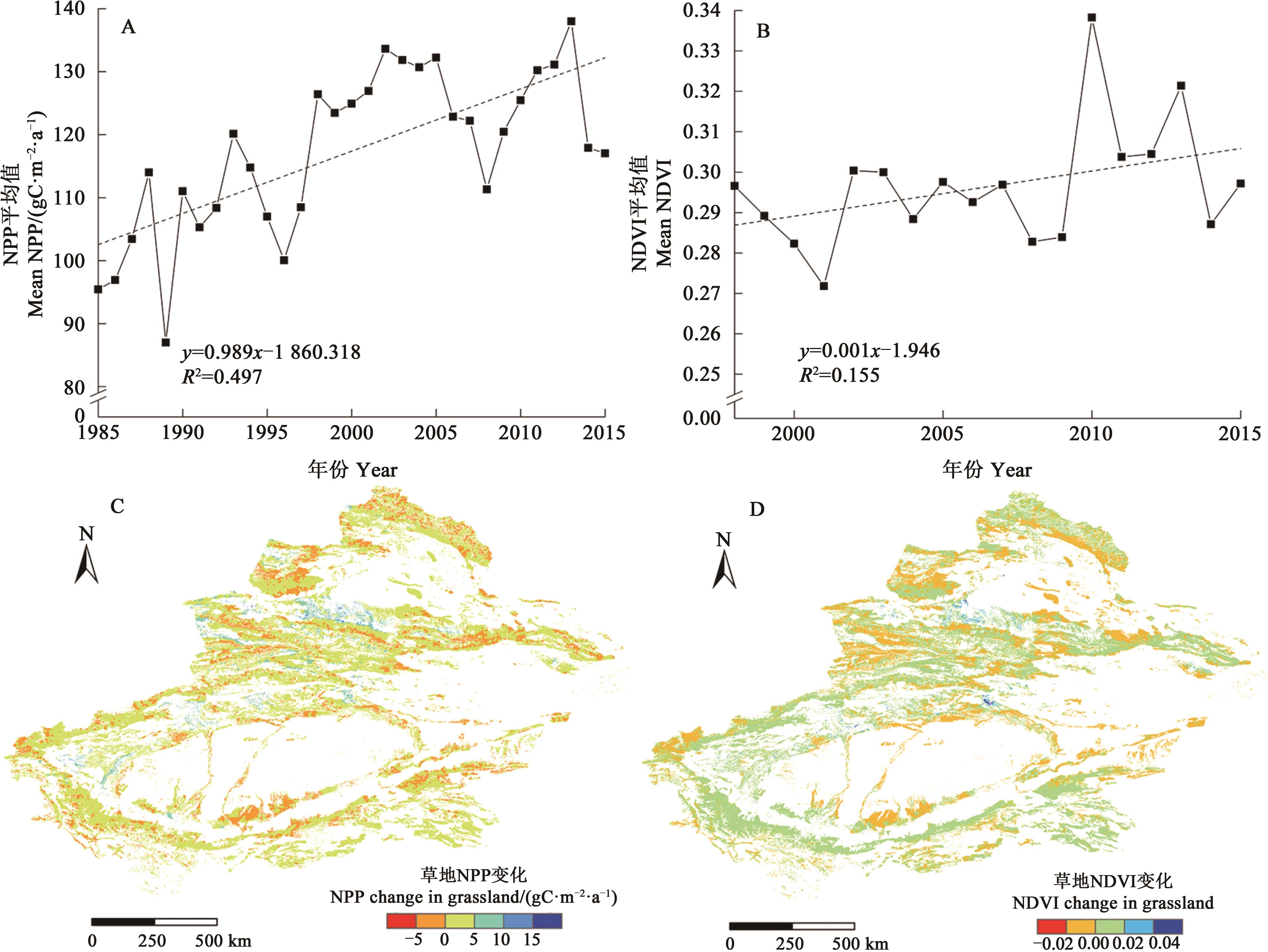
图4 新疆草地NPP、NDVI的时空变化A:NPP的时间变化;B:NDVI的时间变化;C:NPP变化的空间分布; D:NDVI变化的空间分布
Fig. 4 Temporal and spatial variation of NPP and NDVI of Xinjiang grasslandA: Temporal variation of NPP; B: Temporal variation of NDVI; C: Spatial distribution of NPP change; D: Spatial distribution of NDVI change
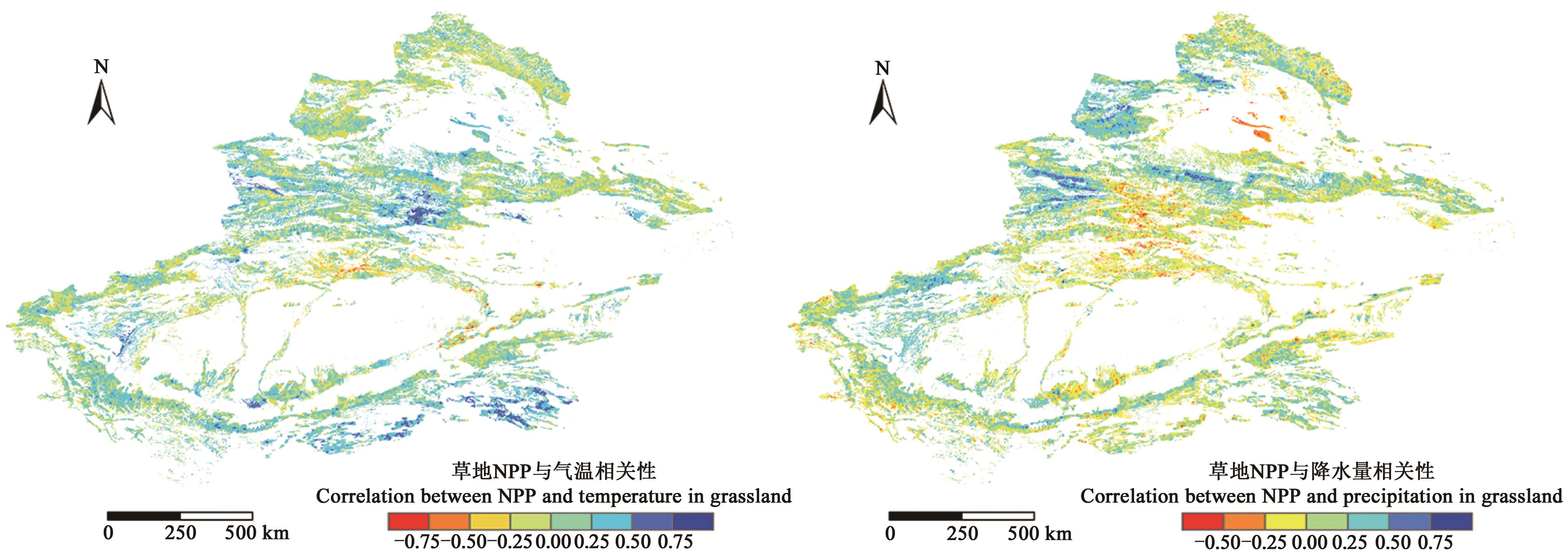
图 5 1985—2015年新疆草地NPP与气温、降水量相关性的空间分布
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution of correlation between NPP and temperature and precipitation in Xinjiang grassland from 1985 to 2015
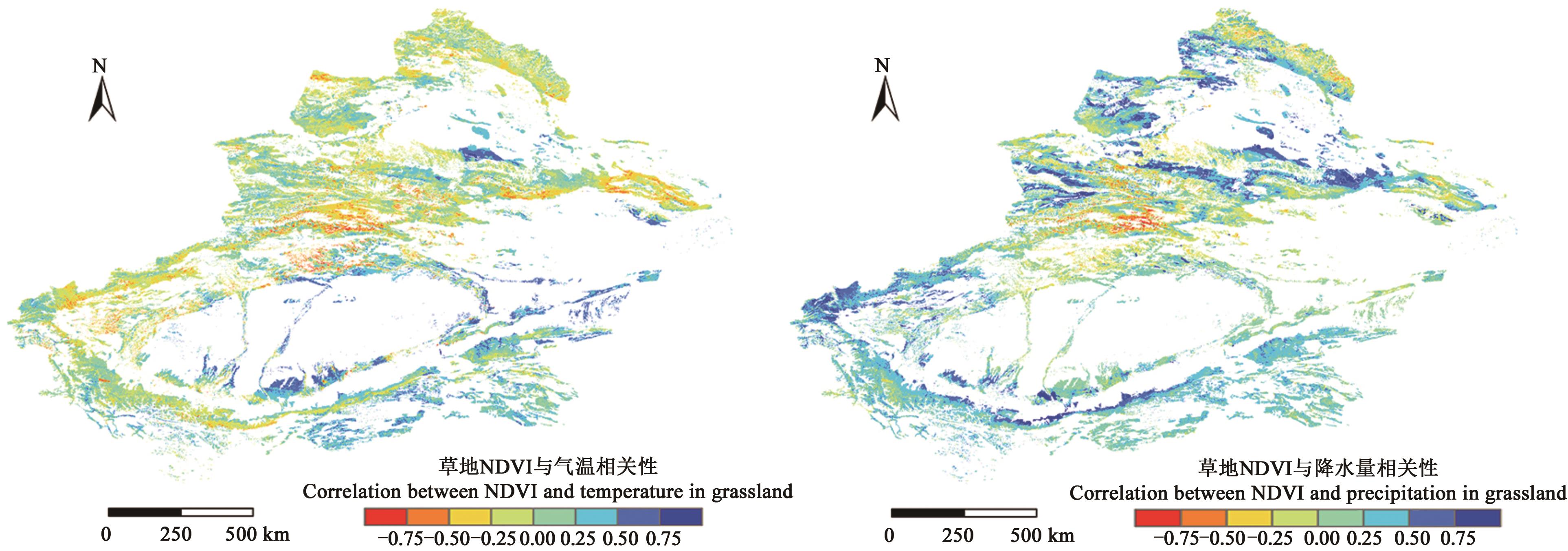
图6 1998—2015年新疆草地NDVI与气温、降水量的相关性空间分布
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution of correlation between NDVI and temperature and precipitation in Xinjiang grassland from 1998 to 2015
| 1 | 吴金凤,刘鞠善,李梓萌,等.草地土壤磷循环及其对全球变化的响应[J].中国草地学报,2021,43(6):102-111. |
| WU J F, LIU J S, LI Z M, et al.. Grassland soil phosphorus cycle and its response to global change [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2021, 43(6):102-111. | |
| 2 | 杨红飞,刚成诚,穆少杰,等.近10年新疆草地生态系统净初级生产力及其时空格局变化研究[J].草业学报,2014,23(3):39-50. |
| YANG H F, GANG C C, MU S J, et al.. Analysis of the spatio-temporal variation in net primary productivity of grassland during the past 10 years in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2014, 23(3):39-50. | |
| 3 | FIELD C B, BEHRENFELD M J, RANDERSON J T, et al.. Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components [J]. Science, 1998, 281(5374):237-240. |
| 4 | FANG J Y, PIAO S L, FIELD C B, et al.. Increasing net primary production in China from 1982 to 1999 [J]. Front. Ecol. Environ., 2003, 1:293-297. |
| 5 | 边多,杨秀海,普布次仁,等.西藏NPP时空格局与气候因子的关系[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(3):830-836. |
| BIAN D, YANG X H, PUBUCIREN, et al.. Spatial and temporal pattern of NPP and its relationship with climate factors in Tibet, China [J]. J. Desert Res., 2015, 35(3):830-836. | |
| 6 | 孙政国,陈奕兆,居为民,等.我国南方不同类型草地生产力及对气候变化的响应[J].长江流域资源与环境,2015,24(4):609-616. |
| SUN Z G, CHEN Y Z, JU W M, et al.. Productivity of different types of grassland plots and their responses to climate change in the southern China [J]. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin, 2015, 24(4):609-616. | |
| 7 | 高清竹,万运帆,李玉娥,等.藏北高寒草地NPP变化趋势及其对人类活动的响应[J].生态学报,2007,27(11):4612-4619. |
| GAO Q Z, WAN Y F, LI Y E, et al.. Trends of grassland NPP and its response to human activity in Northern Tibet [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2007, 27(11):4612-4619. | |
| 8 | GAO J B, JIAO K W, WU S H, et al.. Past and future effects of climate change on spatially heterogeneous vegetation activity in China [J]. Earth’s Future, 2017, 5(7):679-692. |
| 9 | ANDREW R L, GUAN H D, BATELAAN O. Large-scale vegetation responses to terrestrial moisture storage changes [J]. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 2017, 21(9):4469-4478. |
| 10 | 李金珂,杨玉婷,张会茹,等.秦巴山区近15年植被NPP时空演变特征及自然与人为因子解析[J].生态学报,2019,39(22):8504-8515. |
| LI J K, YANG Y T, ZHANG H R, et al.. Spatio-temporal variations of net primary productivity and its natural and human factors analysis in Qinling-Daba mountains in the past 15 years [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(22):8504-8515. | |
| 11 | 田义超,黄远林,张强,等.北部湾南流江流域植被净初级生产力时空分布及其驱动因素[J].生态学报,2019,39(21):8156-8171. |
| TIAN Y C, HUANG Y L, ZHANG Q, et al.. Spatiotemporal distribution of net primary productivity and its driving factors in the Nanliu river basin in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019, 39(21):8156-8171. | |
| 12 | 罗敏,古丽·加帕尔,郭浩,等.2000-2013年塔里木河流域生长季NDVI时空变化特征及其影响因素分析[J].自然资源学报,2017,32(1):50-63. |
| LUO M, Jiapaer Guli, GUO H, et al.. Spatial-temporal variation of growing-season NDVI and its responses to hydrothermal condition in the Tarim river basin from 2000 to 2013 [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2017, 32(1):50-63. | |
| 13 | 郭金停,胡远满,熊在平,等.中国东北多年冻土区植被生长季NDVI时空变化及其对气候变化的响应[J].应用生态学报,2017,28(8):2413-2422. |
| GUO J T, HU Y M, XIONG Z P, et al.. Spatiotemporal variations of growing-season NDVI and response to climate change in permafrost zone of Northeast China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2017, 28(8):2413-2422. | |
| 14 | 朱莹莹,韩磊,赵永华,等.中国西北地区NPP模拟及其时空格局[J].生态学杂志,2019,38(6):1861-1871. |
| ZHU Y Y, HAN L, ZHAO Y H, et al.. Simulation and spatio-temporal pattern of vegetation NPP in northwest China [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2019, 38(6):1861-1871. | |
| 15 | ZHOU W, GANG C C, ZHOU F C, et al.. Quantitative assessment of the individual contribution of climate and human factors to desertification in northwest China using net primary productivity as an indicator [J]. Ecol. Indic., 2015, 48:560-569. |
| 16 | 韩王亚,张超,曾源,等.2000—2015年拉萨河流域NPP时空变化及驱动因子[J].生态学报,2018,38(24):8787-8798. |
| HAN W Y, ZHANG C, ZENG Y, et al.. Spatio-temporal changes and driving factors in the net primary productivity of Lhasa river basin from 2000 to 2015 [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2018, 38(24):8787-8798. | |
| 17 | WANG H, LIU G H, LI Z S, et al.. Impacts of climate change on net primary productivity in arid and semiarid regions of China [J]. Chin. Geogr. Sci., 2016, 26(1):35-47. |
| 18 | ZHAO M S, RUNNING S W. Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009 [J]. Science, 2010, 329(5994):940-943. |
| 19 | LI Z, CHEN Y N, LI W H, et al.. Potential impacts of climate change on vegetation dynamics in Central Asia [J]. J. Geophys. Res. (Atmos.), 2015, 120(24):12345-12356. |
| 20 | 王桂钢,周可法,孙莉,等.近10a新疆地区植被动态与R/S分析[J].遥感技术与应用,2010,25(1):84-90. |
| WANG G G, ZHOU K F, SUN L, et al.. Study on the vegetation dynamic change and R/S analysis in the past ten years in Xinjiang [J]. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl., 2010, 25(1):84-90. | |
| 21 | 李秀花,师庆东,常顺利,等.1981—2001年中国西北干旱区NDVI变化分析[J].干旱区地理,2008,31(6):940-945. |
| LI X H, SHI Q D, CHANG S L, et al.. Change of NDVI based on NOAA image in northwest arid area of China in 1981—2001 [J]. Arid Land Geogr., 2008, 31(6):940-945. | |
| 22 | 侯小丽.基于MODIS数据的全球干旱区植被变化及其与气候关系的研究(2002—2011年)[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2016. |
| HOU X L. The change of vegetation greenness (2002—2011) in globe drylands and its climate responses with remote sensing information of MODIS [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 23 | 郑艺,张丽,周宇,等.1982—2012年全球干旱区植被变化及驱动因子分析[J].干旱区研究,2017,34(1):59-66. |
| ZHENG Y, ZHANG L, ZHOU Y, et al.. Vegetation change and its driving factors in global drylands during the period of 1982—2012 [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2017, 34(1):59-66. | |
| 24 | 赵鹏,陈桃,王茜,等.气候变化和人类活动对新疆草地生态系统NPP影响的定量分析[J].中国科学院大学学报,2020,37(1):51-62. |
| ZHAO P, CHEN T, WANG Q, et al.. Quantitative analysis of the impact of climate change and human activities on grassland ecosystem NPP in Xinjiang [J]. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci., 2020, 37(1):51-62. | |
| 25 | 蔡朝朝,淮永建,白涛,等.基于NDVI的新疆草地覆盖变化特征[J].应用基础与工程科学学报,2020,28(6):1369-1381. |
| CAI Z Z, HUAI Y J, BAI T, et al.. Recent changes of grassland cover in Xinjiang based on NDVI analysis [J]. J. Basic Sci. Eng., 2020, 28(6):1369-1381. | |
| 26 | 黄敬峰,王秀珍,王人潮,等.天然草地牧草产量与气象卫星植被指数的相关分析[J].农业现代化研究,2000,21(1):33-36. |
| HUANG J F, WANG X Z, WANG R C, et al.. Relation analysis between the production of natural grassland and satallite vegetation indices [J]. Res. Agric. Mod., 2000, 21(1):33-36. | |
| 27 | 穆少杰,李建龙,周伟,等.2001—2010年内蒙古植被净初级生产力的时空格局及其与气候的关系[J].生态学报,2013,33(12):3752-3764. |
| MU S J, LI J L, ZHOU W, et al.. Spatial-temporal distribution of net primary productivity and its relationship with climate factors in Inner Mongolia from 2001 to 2010 [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2013, 33(12):3752-3764. | |
| 28 | 尹锴,田亦陈,袁超,等.基于CASA模型的北京植被NPP时空格局及其因子解释[J].自然资源遥感,2015,27(1):133-139. |
| YIN K, TIAN Y C, YUAN C, et al.. NPP spatial and temporal pattern of vegetation in Beijing and its factor explanation based on CASA model [J]. Remote Sens. Nat. Res., 2015, 27(1):133-139. | |
| 29 | 刘卫国,魏文寿,刘志辉.新疆气候变化下植被净初级生产力格局分析[J].干旱区研究,2009,26(2):206-211. |
| LIU W G, WEI W S, LIU Z H, et al.. NPP change in vegetation in Xinjiang under climate change [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2009, 26(2):206-211. | |
| 30 | 姜萍,丁文广,肖静,等.新疆植被NPP及其对气候变化响应的海拔分异[J].干旱区地理,2021,44(3):849-857. |
| JIANG P, DING W G, XIAO J, et al.. Altitudinal difference of vegetation NPP and its response to climate change in Xinjiang [J]. Arid Land Geogr., 2021, 44(3):849-857. | |
| 31 | 焦伟,陈亚宁,李稚.西北干旱区植被净初级生产力的遥感估算及时空差异原因[J].生态学杂志,2017,36(1):181-189. |
| JIAO W, CHEN Y N, LI Z, et al.. Remote sensing estimation and the reasons for temporal-spatial differences of vegetation net primary productivity in arid region of Northwest China [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2017, 36(1):181-189. | |
| 32 | 同琳静,刘洋洋,王倩,等.西北植被净初级生产力时空变化及其驱动因素[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(4):367-374. |
| TONG L J, LIU Y Y, WANG Q, et al.. Spatial and temporal dynamics of net primary productivity and its driving factors in Northwest China [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2019, 26(4):367-374. | |
| 33 | 耿元波,王松,胡雪荻.高寒草甸草原净初级生产力对气候变化响应的模拟[J].草业学报,2018,27(1):1-13. |
| GENG Y B, WANG S, HU X D. Responses of aboveground net primary productivity of the alpine meadow steppe to climate change: simulations based on the CENTURY model [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2018, 27(1):1-13. | |
| 34 | 慈晖,张强.新疆NDVI时空特征及气候变化影响研究[J].地球信息科学学报,2017,19(5):662-671. |
| CI H, ZHANG Q. Spatio-temporal patterns of NDVI variations and possible relations with climate changes in Xinjiang province [J]. J. Geo-Inform. Sci., 2017, 19(5):662-671. | |
| 35 | 张扬,楚新正,杨少敏,等.近56年新疆北部地区气候变化特征[J].干旱区研究,2019,36(1):212-219. |
| ZHANG Y, CHU X Z, YANG S M, et al.. Climate change in North Xinjiang in recent 56 years [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2019, 36(1):212-219. | |
| 36 | 贾璎,祁正鹏.草地净初级生产力对气候变化的响应[J].畜牧兽医杂志,2016,35(6):87-89. |
| JIA Y, QI Z P. The response of grassland net primary productivity to climate change [J]. J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med., 2016, 35(6):87-89. | |
| 37 | 陈宸,井长青,邢文渊,等.近20年新疆荒漠草地动态变化及其对气候变化的响应[J].草业学报,2021,30(3):1-14. |
| CHEN C, JING C Q, XING W Y, et al.. Desert grassland dynamics in the last 20 years and its response to climate change in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2021, 30(3):1-14. | |
| 38 | TRUJILLO E, MOLOTCH N P, GOULDEN M L, et al.. Elevation-dependent influence of snow accumulation on forest greening [J]. Nat. Geogr-Sci., 2012, 5(10):705-709. |
| 39 | 戴声佩,张勃,王海军,等.中国西北地区植被覆盖变化驱动因子分析[J].干旱区地理,2010,33(4):636-643. |
| DAI S P, ZHANG B, WANG H J, et al.. Vegetation cover change and its driving factors over northwest China [J]. Arid Land Geogr., 2010, 33(4):636-643. | |
| 40 | 刘春静,张丽,周宇,等.中国新疆及中亚五国干旱区草地覆盖度反演与分析[J].草业科学,2016,33(5):861-870. |
| LIU C J, ZHANG L, ZHOU Y, et al.. Retrieval and analysis of grassland coverage in arid Xinjiang, China and five countries of Central Asia [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2016, 33(5):861-870. | |
| 41 | CHEN C, PARK T, WANG X H, et al.. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management [J]. Nat. Sustain., 2019, 2(2):122-129. |
| 42 | 何航,张勃,侯启,等.1982—2015年中国北方归一化植被指数(NDVI)变化特征及对气候变化的响应[J].生态与农村环境学报,2020,36(1):70-80. |
| HE H, ZHANG B, HOU Q, et al.. Variation characteristic of NDVI and its response to climate change in Northern China from 1982 to 2015 [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2020, 36(1):70-80. | |
| 43 | 张晋霞,徐长春,杨秋萍.2001—2017年新疆NDVI变化及其对极端气候的响应[J].水土保持通报,2020,40(5):250-256, 275,341. |
| ZHANG J X, XU C C, YANG Q P. NDVI variations and its response to extreme climate in Xinjiang during 2001—2007 [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2020, 40(5):250-256, 275,341. | |
| 44 | 邓兴耀,姚俊强,刘志辉.基于GIMMS NDVI的中亚干旱区植被覆盖时空变化[J].干旱区研究,2017,34(1):10-19. |
| DENG X Y, YAO J Q, LIU Z H, et al.. Spatiotemporal dynamic change of vegetation coverage in arid regions in central Asia based on GIMMS NDVI [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2017, 34(1):10-19. | |
| 45 | 李佳秀,陈亚宁,刘志辉.新疆不同气候区的气温和降水变化及其对地表水资源的影响[J].中国科学院大学学报,2018,35(3):370-381. |
| LI J X, CHEN Y N, LIU Z H. Variations in temperature and precipitation and their influences on surface water resource in different climate zones of Xinjiang [J]. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci., 2018, 35(3):370-381. | |
| 46 | 祝稳.西北干旱区植被覆盖动态及其对极端气温和降水过程的响应[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2015. |
| ZHU W. Spatial-temporal dynamics of vegetation coverage and its response to extreme temperature and precipitation processes over the arid region of northwest China [D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2015. |
| [1] | 郝需婷, 黄雅茹, 马迎宾, 张帅, 韩春霞, 庞嘉诚, 徐光甫, 郝惠忠, 刘雅婧. 乌兰布和沙漠固沙梭梭林生长季土壤水分动态研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 187-196. |
| [2] | 侯志雄, 井长青, 王公鑫, 郭文章, 赵苇康. 1998—2018年北疆天然草地植被覆盖度时空变化及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 140-151. |
| [3] | 梁艳1,干珠扎布1,张伟娜1,高清竹1*,旦久罗布2, 西饶卓玛2,白马玉珍2 . 气候变化对中国草原生态系统影响研究综述[J]. , 2014, 16(2): 1-8. |
| [4] | 司文才,刘峻明. 冬小麦关键物候空间分布遥感监测方法研究[J]. , 2011, 13(6): 82-89. |
| [5] | 司亚辉,张玮. 基于MODIS-NDVI的草地长势变化监测——以锡林郭勒盟为例[J]. , 2008, 10(5): 66-70. |
| [6] | 孙玲[1] 朱泽生[2]. 江苏省小麦综合比较优势时空特征动态变化研究[J]. , 2006, 8(1): 26-30. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号