




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 167-176.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0998
收稿日期:2021-10-20
接受日期:2021-11-24
出版日期:2022-07-15
发布日期:2022-08-15
通讯作者:
甄文超
作者简介:刘雪静 E-mail: liuxuejing830527@163.com;
基金资助:
Xuejing LIU( ), Xiaoyuan BAO, Xiaoyang HOU, Wenchao ZHEN(
), Xiaoyuan BAO, Xiaoyang HOU, Wenchao ZHEN( )
)
Received:2021-10-20
Accepted:2021-11-24
Online:2022-07-15
Published:2022-08-15
Contact:
Wenchao ZHEN
摘要:
海河平原冬小麦生产与水资源匮乏的矛盾十分突出,亟需建立限水灌溉制度,实现丰产与水分高效的协调统一。于2018—2020年冬小麦生长季,选取旱地组(石麦22、衡观35和冀麦418)和水地组(石农086、冀麦585和石新828)2种类型小麦品种,设置适期播种和晚播2个播期以及春季2次灌水、不灌水和春3、4、5、6叶龄1次灌水处理。研究不同处理土壤水分动态变化及冬小麦产量形成特征。结果表明: 春季限水灌溉下,0—60 cm土层为主要供水层,其含水量(SWC60)变化显著影响小麦产量形成;春4叶龄为冬小麦春季1次灌水的最佳灌溉时期,灌水前干旱程度较轻,灌水后直至乳熟末期SWC60才低于60%,干旱胁迫也相对较轻;春季限水灌溉下,冬小麦产量显著降低,旱地组品种产量降幅低于水地组品种。不同春季叶龄1次灌水处理总体表现为春4叶龄灌水产量降幅最小,平均减产约10%。春季1次灌水晚播处理的产量水平与对应的适期播种处理无显著差异。春4叶龄灌水处理产量和水分利用效率(WUE)显著高于其他春季1次灌水处理,其单位面积穗数、穗粒数和千粒重更为均衡协调,最终在实现7 502.9~8 050.0 kg·hm?2产量水平的同时,WUE达17.5 ~20.1 kg·hm?2·mm?1,较春季2次灌水节水70.1 mm。上述研究结果为构建精量高效的小麦春季限水灌溉制度提供了依据。
中图分类号:
刘雪静, 鲍晓远, 候晓阳, 甄文超. 海河平原春季限水灌溉下冬小麦农田水分动态及产量形成特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 167-176.
Xuejing LIU, Xiaoyuan BAO, Xiaoyang HOU, Wenchao ZHEN. Dynamics of Soil Water Content and Yield Formation Characteristics of Winter Wheat Under Water Limited Irrigation in Spring in Haihe Plain[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 167-176.
土层 Soil layer/cm | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density/(g·cm‒3) | 田间持水量 Field capacity/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辛集Xinji | 深州Shenzhou | 辛集Xinji | 深州Shenzhou | |
| 0—20 | 1.44 | 1.50 | 35.2 | 35.5 |
| 20—40 | 1.39 | 1.34 | 35.1 | 34.8 |
| 40—60 | 1.44 | 1.37 | 37.6 | 38.6 |
| 60—80 | 1.42 | 1.40 | 37.5 | 41.8 |
| 80—100 | 1.44 | 1.39 | 38.0 | 39.5 |
| 100—120 | 1.31 | 1.60 | 37.9 | 41.5 |
| 120—140 | 1.39 | 1.42 | 38.9 | 42.3 |
| 140—160 | 1.39 | 1.34 | 38.9 | 37.2 |
| 160—180 | 1.38 | 1.47 | 39.2 | 40.7 |
| 180—200 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 39.4 | 41.6 |
表1 土壤容重和田间持水量
Table 1 Soil bulk density and field capacity
土层 Soil layer/cm | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density/(g·cm‒3) | 田间持水量 Field capacity/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辛集Xinji | 深州Shenzhou | 辛集Xinji | 深州Shenzhou | |
| 0—20 | 1.44 | 1.50 | 35.2 | 35.5 |
| 20—40 | 1.39 | 1.34 | 35.1 | 34.8 |
| 40—60 | 1.44 | 1.37 | 37.6 | 38.6 |
| 60—80 | 1.42 | 1.40 | 37.5 | 41.8 |
| 80—100 | 1.44 | 1.39 | 38.0 | 39.5 |
| 100—120 | 1.31 | 1.60 | 37.9 | 41.5 |
| 120—140 | 1.39 | 1.42 | 38.9 | 42.3 |
| 140—160 | 1.39 | 1.34 | 38.9 | 37.2 |
| 160—180 | 1.38 | 1.47 | 39.2 | 40.7 |
| 180—200 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 39.4 | 41.6 |
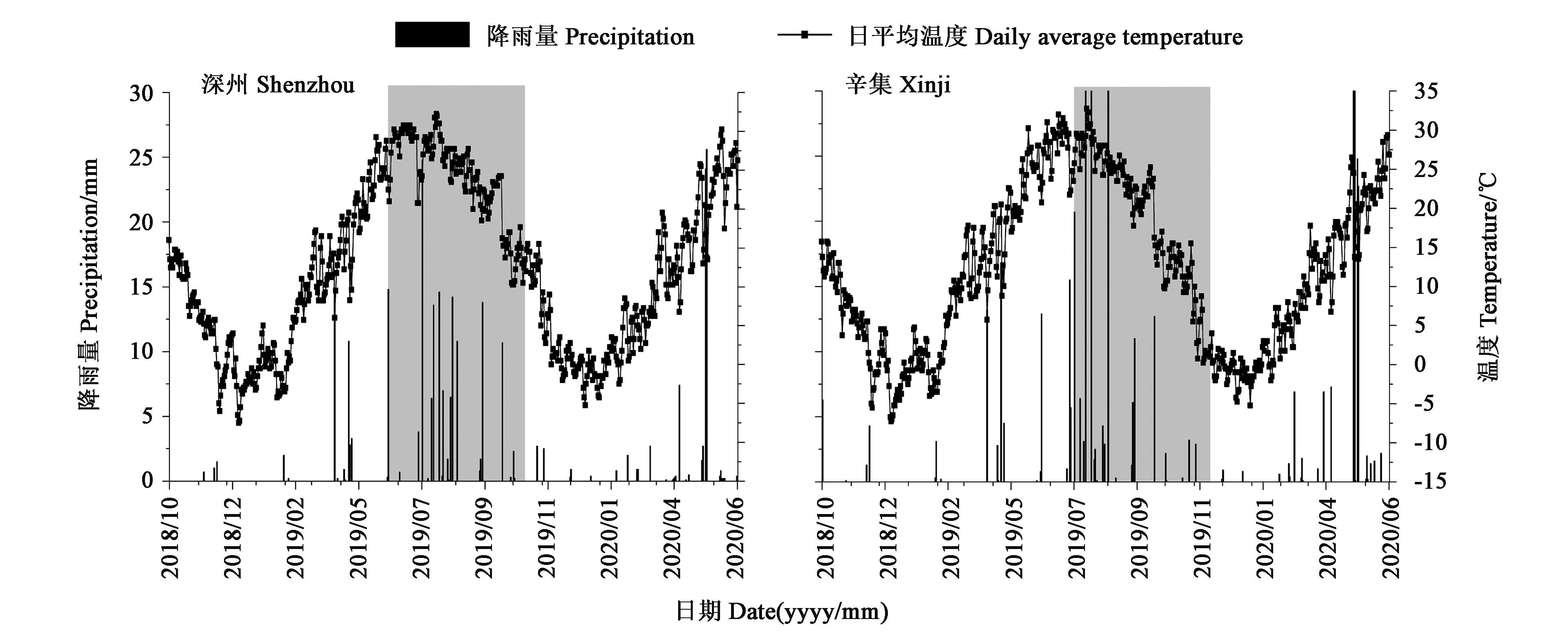
图1 2018—2020年小麦生长季降水量和日平均温度数据来源:国家气象科学数据中心(http://data. cma.cn/)。
Fig. 1 Precipitation and daily average temperature in wheat growing season from 2018 to 2020Data source: National Meteorological Information Centre (http://data. cma.cn/).
处理 Treatment | 播期类型 Sowing date type | 灌水时期 Irrigation period | 灌水次数 Irrigation times | 处理 Treatment | 播期类型 Sowing date type | 灌水时期 Irrigation period | 灌水次数 Irrigation times |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKⅡ | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春3叶龄+开花 Spring 3-leaf age and anthesis stage | 2 | WCKⅡ | 晚播 Late sowing | 春3叶龄+开花 Spring 3-leaf age and anthesis stage | 2 |
| CK0 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春季0水 No irrigation at spring | 0 | WCK0 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春季0水 No irrigation at spring | 0 |
| L3 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春3叶龄 Spring 3-leaf age | 1 | WL3 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春3叶龄 Spring 3-leaf age | 1 |
| L4 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春4叶龄 Spring 4-leaf age | 1 | WL4 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春4叶龄 Spring 4-leaf age | 1 |
| L5 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春5叶龄 Spring 5-leaf age | 1 | WL5 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春5叶龄 Spring 5-leaf age | 1 |
| L6 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春6叶龄 Spring 6-leaf age | 1 | WL6 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春6叶龄 Spring 6-leaf age | 1 |
表2 试验处理设置
Table 2 Experimental treatment
处理 Treatment | 播期类型 Sowing date type | 灌水时期 Irrigation period | 灌水次数 Irrigation times | 处理 Treatment | 播期类型 Sowing date type | 灌水时期 Irrigation period | 灌水次数 Irrigation times |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKⅡ | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春3叶龄+开花 Spring 3-leaf age and anthesis stage | 2 | WCKⅡ | 晚播 Late sowing | 春3叶龄+开花 Spring 3-leaf age and anthesis stage | 2 |
| CK0 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春季0水 No irrigation at spring | 0 | WCK0 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春季0水 No irrigation at spring | 0 |
| L3 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春3叶龄 Spring 3-leaf age | 1 | WL3 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春3叶龄 Spring 3-leaf age | 1 |
| L4 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春4叶龄 Spring 4-leaf age | 1 | WL4 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春4叶龄 Spring 4-leaf age | 1 |
| L5 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春5叶龄 Spring 5-leaf age | 1 | WL5 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春5叶龄 Spring 5-leaf age | 1 |
| L6 | 适期播种 Suitable sowing date | 春6叶龄 Spring 6-leaf age | 1 | WL6 | 晚播 Late sowing | 春6叶龄 Spring 6-leaf age | 1 |

图2 不同叶龄灌水后麦田土壤含水量动态A:深州2018—2019;B:深州2019—2020;C:辛集2019—2020
Fig.2 Dynamics of soil water content in wheat field after irrigation at different leaf ages.A: Shenzhou 2018—2019; B: Shenzhou 2019—2020; B: Xinji 2019—2020;
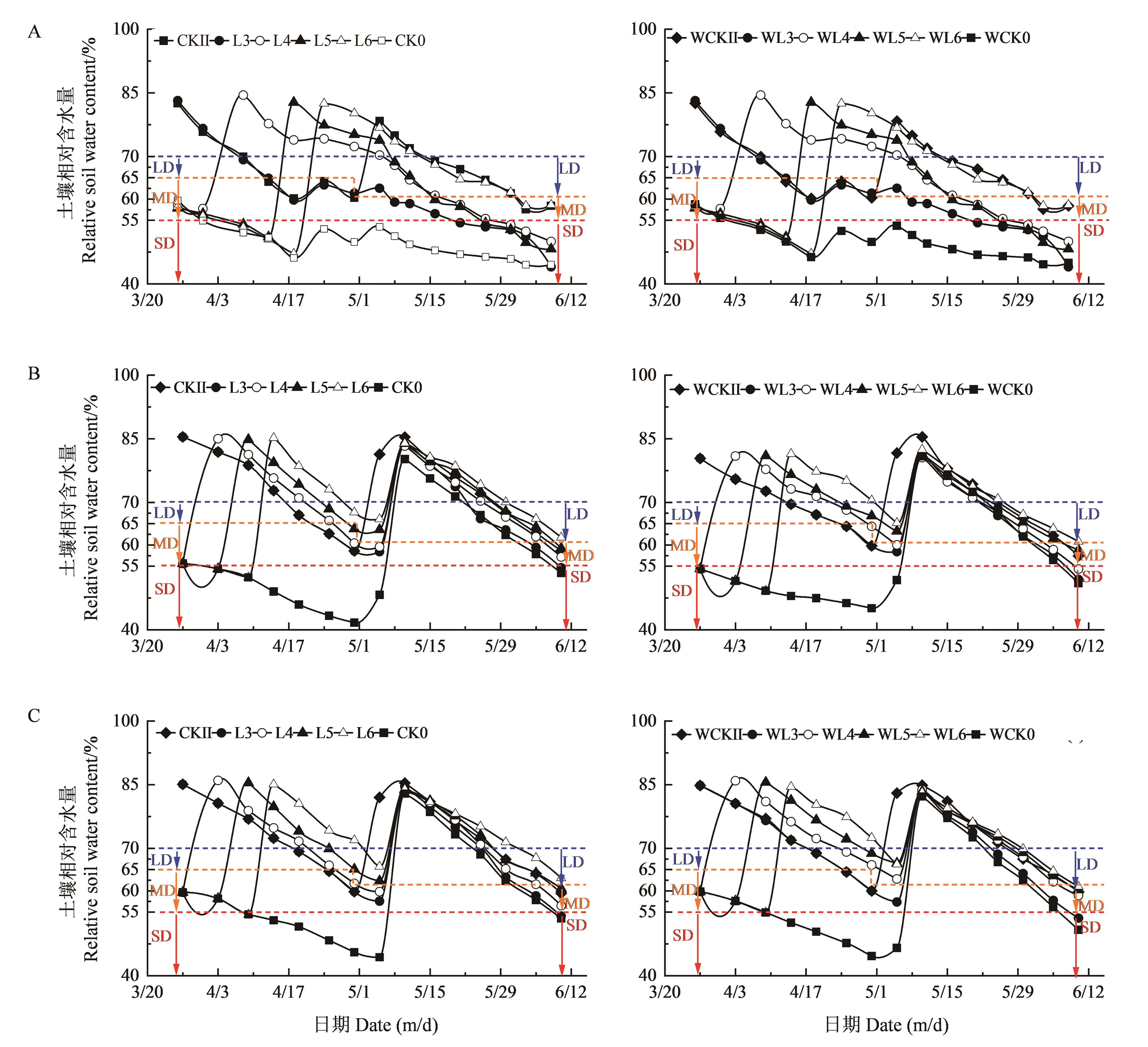
图3 不同叶龄灌水条件下冬小麦土壤干旱程度A:深州2018—2019;B:深州2019—2020;C:辛集2019—2020。LD—轻度干旱;MD—重度干旱;SD—重度干旱。起身?开花期土壤含水量为0—60 cm均值;开花?成熟期土壤含水量为0—80 cm均值。
Fig. 3 Soil drought degree of winter wheat under irrigation at different leaf agesA: Shenzhou 2018—2019; B: Shenzhou 2019—2020; B: Xinji 2019—2020. LD—Mild drought; MD—Severe drought; SD——Severe drought. Soil water content from late rising to flowering is the average value of 0—60 cm; soil water content from flowering to maturity is the average value of 0—80 cm.
品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm‒2) | 水分利用效率 WUE/(kg·hm‒2·mm‒1) | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm‒2) | 水分利用效率 WUE/(kg·hm‒2·mm‒1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | 深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | 深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | 深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | |||
衡观35 Hengguan 35 | CKⅡ | 8 790.6 a | 8 808.5 a | 8 577.8 a | 20.3 a | 20.1 a | 17.8 a | WCKⅡ | 8 764.9 a | 8 268.1 a | 8 401.5 a | 20.5 a | 19.0 a | 17.8 a |
| L3 | 7 207.9 c | 7 294.2 c | 7 201.3 c | 17.7 b | 17.9 b | 15.9 b | WL3 | 7 094.9 c | 7 088.6 c | 7 284.1 b | 17.8 b | 17.1 b | 16.3 b | |
| L4 | 8 050.8 b | 7 900.2 b | 7 877.5 b | 20.1 a | 19.6 a | 18.0 a | WL4 | 7 946.9 b | 7 804.1 b | 7 759.4 b | 20.5 a | 19.2 a | 17.9 a | |
| L5 | 6 302.9 d | 6 109.9 d | 6 317.7 d | 16.4 c | 15.6 c | 14.6 c | WL5 | 6 455.8 d | 6 199.8 d | 6 034.5 c | 16.3 b | 16.3 b | 14.2 c | |
| L6 | 5 323.3 e | 5 463.9 e | 5 438.8 e | 13.9 d | 14.2 d | 12.5 d | WL6 | 5 528.1 e | 5 052.7 e | 5 074.1 d | 14.2 c | 13.6 c | 12.1 d | |
冀麦418 Jimai 418 | CKⅡ | 8 886.7 a | 8 783.7 a | 8 558.0 a | 20.5 a | 20.0 a | 17.7 a | WCKⅡ | 8 301.2 a | 8 362.3 a | 8 634.1 a | 19.4 a | 19.2 a | 18.3 a |
| L3 | 6 864.5 c | 6 847.6 c | 6 525.9 c | 16.8 c | 16.8 b | 14.4 b | WL3 | 6 720.1 c | 6 916.0 c | 6 929.5 c | 16.9 b | 16.7 b | 15.5 b | |
| L4 | 7 543.4 b | 7 836.6 b | 7 684.4 b | 18.9 b | 19.5 a | 17.5 a | WL4 | 7 582.6 b | 7 552.0 b | 7 785.9 b | 19.5 a | 18.6 a | 18.0 a | |
| L5 | 5 917.1 d | 6 210.6 d | 6 155.4 c | 15.4 c | 15.9 b | 14.2 b | WL5 | 5 669.1 d | 6 053.5 d | 5 914.1 d | 14.3 c | 15.9 c | 14.0 c | |
| L6 | 5 077.1 e | 5 084.0 e | 4 898.5 d | 13.2 d | 13.2 c | 11.3 c | WL6 | 4 859.3 e | 4 990.0 e | 5 086.8 e | 12.4 d | 13.4 d | 12.1 d | |
石麦22 Shimai 22 | CKⅡ | 8 377.4 a | 8 476.2 a | 8 548.5 a | 19.3 a | 19.3 a | 17.7 a | WCKⅡ | 8 233.5 a | 8 231.6a | 8 444.9 a | 19.3 a | 18.9 a | 17.9 a |
| L3 | 6 793.2 c | 6 901.5 c | 6 923.9 c | 16.6 b | 16.9 b | 15.3 b | WL3 | 6 715.2 c | 6 791.6 c | 6 670.2 c | 16.9 b | 16.4 b | 14.9 b | |
| L4 | 7 463.1 b | 7 502.9 b | 7 450.1 b | 18.7 a | 18.6 a | 17.0 a | WL4 | 7 734.9 b | 7 326.7 b | 7 548.9 b | 19.9 a | 18.1 a | 17.4 a | |
| L5 | 6 070.0 d | 6 240.9 d | 5 646.4 d | 15.8 b | 15.9 c | 13.0 c | WL5 | 6 064.5 d | 6 116.9 d | 5 679.1 d | 15.3 c | 16.1 b | 13.4 c | |
| L6 | 5 568.2 e | 5 513.7 e | 5 297.3 d | 14.5 c | 14.3 d | 12.2 c | WL6 | 5 573.1 e | 5 497.2 e | 5 283.7 d | 14.3 d | 14.8 c | 12.6 d | |
石农086 Shinong 086 | CKⅡ | 8 497.1 a | 8 455.2 a | 8 404.1 a | 19.6 a | 19.3 a | 17.4 a | WCKⅡ | 8 561.6 a | 8 107.5 a | 8 109.0 a | 20.0 a | 18.6 a | 17.2 a |
| L3 | 6 962.1 b | 6 881.6 b | 6 991.7 b | 17.0 b | 16.9 b | 15.4 b | WL3 | 6 838.3 b | 6 763.9 b | 6 929.2 b | 17.2 b | 16.3 b | 15.5 b | |
| L4 | 6 300.7 c | 6 143.8 c | 6 263.8 c | 15.7 bc | 15.2 c | 14.3 c | WL4 | 5 906.4 c | 5 896.8 c | 6 324.1 c | 15.2 c | 14.5 d | 14.6 c | |
| L5 | 5 537.2 d | 5 697.6 d | 5 402.0 d | 14.4 c | 14.5 cd | 12.5 d | WL5 | 5 681.1 c | 5 744.9 c | 5 590.7 d | 14.3 c | 15.1 c | 13.2 d | |
| L6 | 4 926.5 e | 5 221.7 e | 4 642.3 e | 12.8 d | 13.6 d | 10.7 e | WL6 | 4 643.1 d | 5 150.1 d | 4 792.1 e | 11.9 d | 13.8 e | 11.4 e | |
冀麦585 Jimai 585 | CKⅡ | 8 365.9 a | 8 473.8 a | 8 610.4 a | 19.3 a | 19.3 a | 17.8 a | WCKⅡ | 8 453.6 a | 8 223.2 a | 8 202.9 a | 19.8 a | 18.9 a | 17.4 a |
| L3 | 6 229.7 c | 6 817.4 b | 6 426.4 c | 11.9 d | 16.7 bc | 14.2 b | WL3 | 6 624.1 c | 6 764.3 c | 6 885.8 c | 16.6 b | 16.3 c | 15.4 b | |
| L4 | 7 622.7 b | 7 196.3 b | 7 691.6 b | 19.1 a | 17.9 b | 17.5 a | WL4 | 7 193.9 b | 7 121.4 b | 7 347.9 b | 18.5 a | 17.6 b | 17.0 a | |
| L5 | 5 391.7 d | 6 184.3 c | 6 149.0 c | 16.2 b | 15.8 c | 14.2 b | WL5 | 6 525.6 c | 5 941.6 d | 5 901.9 d | 16.5 b | 15.6 c | 13.9 c | |
| L6 | 4 850.8 d | 5 509.8 d | 5 518.1 d | 14.1 c | 14.3 d | 12.7 c | WL6 | 5 363.9 d | 5 143.1 e | 5 057.8 e | 13.7 c | 13.8 d | 12.0 d | |
石新828 Shinxin 828 | CKⅡ | 8 328.8 a | 8 461.3 a | 8 203.0 a | 19.2 a | 19.3 a | 17.0 a | WCKⅡ | 8 165.1 a | 8 097.2 a | 8 119.5 a | 19.1 a | 18.6 a | 17.2 a |
| L3 | 6 819.2 b | 6 918.2 c | 6 762.9 c | 16.7 c | 16.9 b | 14.9 b | WL3 | 6 713.1 b | 6 728.4 b | 6 746.3 c | 16.9 b | 16.2 b | 15.1 b | |
| L4 | 7 186.4 b | 7 386.4 b | 7 460.8 b | 18.0 b | 18.3 ab | 17.0 a | WL4 | 7 171.6 b | 7 157.5 b | 7 355.1 b | 18.5 a | 17.6 ab | 17.0 a | |
| L5 | 5 516.6 c | 5 696.7 d | 5 623.8 d | 14.4 d | 14.5 c | 13.0 c | WL5 | 5 467.3 c | 5 501.1 c | 5 397.2 d | 13.8 c | 14.5 c | 12.7 c | |
| L6 | 5 178.5 c | 5 045.0 e | 4 919.6 e | 13.5 d | 13.1 c | 11.3 d | WL6 | 5 006.1 c | 4 834.0 d | 5 096.4 d | 12.8 c | 13.0 d | 12.1 c | |
表3 不同处理冬小麦产量、水分利用效率
Table 3 Yield, water use efficiency of winter wheat under different treatment
品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm‒2) | 水分利用效率 WUE/(kg·hm‒2·mm‒1) | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm‒2) | 水分利用效率 WUE/(kg·hm‒2·mm‒1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | 深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | 深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | 深州Shenzhou 2019 | 深州Shenzhou 2020 | 辛集Xinji 2020 | |||
衡观35 Hengguan 35 | CKⅡ | 8 790.6 a | 8 808.5 a | 8 577.8 a | 20.3 a | 20.1 a | 17.8 a | WCKⅡ | 8 764.9 a | 8 268.1 a | 8 401.5 a | 20.5 a | 19.0 a | 17.8 a |
| L3 | 7 207.9 c | 7 294.2 c | 7 201.3 c | 17.7 b | 17.9 b | 15.9 b | WL3 | 7 094.9 c | 7 088.6 c | 7 284.1 b | 17.8 b | 17.1 b | 16.3 b | |
| L4 | 8 050.8 b | 7 900.2 b | 7 877.5 b | 20.1 a | 19.6 a | 18.0 a | WL4 | 7 946.9 b | 7 804.1 b | 7 759.4 b | 20.5 a | 19.2 a | 17.9 a | |
| L5 | 6 302.9 d | 6 109.9 d | 6 317.7 d | 16.4 c | 15.6 c | 14.6 c | WL5 | 6 455.8 d | 6 199.8 d | 6 034.5 c | 16.3 b | 16.3 b | 14.2 c | |
| L6 | 5 323.3 e | 5 463.9 e | 5 438.8 e | 13.9 d | 14.2 d | 12.5 d | WL6 | 5 528.1 e | 5 052.7 e | 5 074.1 d | 14.2 c | 13.6 c | 12.1 d | |
冀麦418 Jimai 418 | CKⅡ | 8 886.7 a | 8 783.7 a | 8 558.0 a | 20.5 a | 20.0 a | 17.7 a | WCKⅡ | 8 301.2 a | 8 362.3 a | 8 634.1 a | 19.4 a | 19.2 a | 18.3 a |
| L3 | 6 864.5 c | 6 847.6 c | 6 525.9 c | 16.8 c | 16.8 b | 14.4 b | WL3 | 6 720.1 c | 6 916.0 c | 6 929.5 c | 16.9 b | 16.7 b | 15.5 b | |
| L4 | 7 543.4 b | 7 836.6 b | 7 684.4 b | 18.9 b | 19.5 a | 17.5 a | WL4 | 7 582.6 b | 7 552.0 b | 7 785.9 b | 19.5 a | 18.6 a | 18.0 a | |
| L5 | 5 917.1 d | 6 210.6 d | 6 155.4 c | 15.4 c | 15.9 b | 14.2 b | WL5 | 5 669.1 d | 6 053.5 d | 5 914.1 d | 14.3 c | 15.9 c | 14.0 c | |
| L6 | 5 077.1 e | 5 084.0 e | 4 898.5 d | 13.2 d | 13.2 c | 11.3 c | WL6 | 4 859.3 e | 4 990.0 e | 5 086.8 e | 12.4 d | 13.4 d | 12.1 d | |
石麦22 Shimai 22 | CKⅡ | 8 377.4 a | 8 476.2 a | 8 548.5 a | 19.3 a | 19.3 a | 17.7 a | WCKⅡ | 8 233.5 a | 8 231.6a | 8 444.9 a | 19.3 a | 18.9 a | 17.9 a |
| L3 | 6 793.2 c | 6 901.5 c | 6 923.9 c | 16.6 b | 16.9 b | 15.3 b | WL3 | 6 715.2 c | 6 791.6 c | 6 670.2 c | 16.9 b | 16.4 b | 14.9 b | |
| L4 | 7 463.1 b | 7 502.9 b | 7 450.1 b | 18.7 a | 18.6 a | 17.0 a | WL4 | 7 734.9 b | 7 326.7 b | 7 548.9 b | 19.9 a | 18.1 a | 17.4 a | |
| L5 | 6 070.0 d | 6 240.9 d | 5 646.4 d | 15.8 b | 15.9 c | 13.0 c | WL5 | 6 064.5 d | 6 116.9 d | 5 679.1 d | 15.3 c | 16.1 b | 13.4 c | |
| L6 | 5 568.2 e | 5 513.7 e | 5 297.3 d | 14.5 c | 14.3 d | 12.2 c | WL6 | 5 573.1 e | 5 497.2 e | 5 283.7 d | 14.3 d | 14.8 c | 12.6 d | |
石农086 Shinong 086 | CKⅡ | 8 497.1 a | 8 455.2 a | 8 404.1 a | 19.6 a | 19.3 a | 17.4 a | WCKⅡ | 8 561.6 a | 8 107.5 a | 8 109.0 a | 20.0 a | 18.6 a | 17.2 a |
| L3 | 6 962.1 b | 6 881.6 b | 6 991.7 b | 17.0 b | 16.9 b | 15.4 b | WL3 | 6 838.3 b | 6 763.9 b | 6 929.2 b | 17.2 b | 16.3 b | 15.5 b | |
| L4 | 6 300.7 c | 6 143.8 c | 6 263.8 c | 15.7 bc | 15.2 c | 14.3 c | WL4 | 5 906.4 c | 5 896.8 c | 6 324.1 c | 15.2 c | 14.5 d | 14.6 c | |
| L5 | 5 537.2 d | 5 697.6 d | 5 402.0 d | 14.4 c | 14.5 cd | 12.5 d | WL5 | 5 681.1 c | 5 744.9 c | 5 590.7 d | 14.3 c | 15.1 c | 13.2 d | |
| L6 | 4 926.5 e | 5 221.7 e | 4 642.3 e | 12.8 d | 13.6 d | 10.7 e | WL6 | 4 643.1 d | 5 150.1 d | 4 792.1 e | 11.9 d | 13.8 e | 11.4 e | |
冀麦585 Jimai 585 | CKⅡ | 8 365.9 a | 8 473.8 a | 8 610.4 a | 19.3 a | 19.3 a | 17.8 a | WCKⅡ | 8 453.6 a | 8 223.2 a | 8 202.9 a | 19.8 a | 18.9 a | 17.4 a |
| L3 | 6 229.7 c | 6 817.4 b | 6 426.4 c | 11.9 d | 16.7 bc | 14.2 b | WL3 | 6 624.1 c | 6 764.3 c | 6 885.8 c | 16.6 b | 16.3 c | 15.4 b | |
| L4 | 7 622.7 b | 7 196.3 b | 7 691.6 b | 19.1 a | 17.9 b | 17.5 a | WL4 | 7 193.9 b | 7 121.4 b | 7 347.9 b | 18.5 a | 17.6 b | 17.0 a | |
| L5 | 5 391.7 d | 6 184.3 c | 6 149.0 c | 16.2 b | 15.8 c | 14.2 b | WL5 | 6 525.6 c | 5 941.6 d | 5 901.9 d | 16.5 b | 15.6 c | 13.9 c | |
| L6 | 4 850.8 d | 5 509.8 d | 5 518.1 d | 14.1 c | 14.3 d | 12.7 c | WL6 | 5 363.9 d | 5 143.1 e | 5 057.8 e | 13.7 c | 13.8 d | 12.0 d | |
石新828 Shinxin 828 | CKⅡ | 8 328.8 a | 8 461.3 a | 8 203.0 a | 19.2 a | 19.3 a | 17.0 a | WCKⅡ | 8 165.1 a | 8 097.2 a | 8 119.5 a | 19.1 a | 18.6 a | 17.2 a |
| L3 | 6 819.2 b | 6 918.2 c | 6 762.9 c | 16.7 c | 16.9 b | 14.9 b | WL3 | 6 713.1 b | 6 728.4 b | 6 746.3 c | 16.9 b | 16.2 b | 15.1 b | |
| L4 | 7 186.4 b | 7 386.4 b | 7 460.8 b | 18.0 b | 18.3 ab | 17.0 a | WL4 | 7 171.6 b | 7 157.5 b | 7 355.1 b | 18.5 a | 17.6 ab | 17.0 a | |
| L5 | 5 516.6 c | 5 696.7 d | 5 623.8 d | 14.4 d | 14.5 c | 13.0 c | WL5 | 5 467.3 c | 5 501.1 c | 5 397.2 d | 13.8 c | 14.5 c | 12.7 c | |
| L6 | 5 178.5 c | 5 045.0 e | 4 919.6 e | 13.5 d | 13.1 c | 11.3 d | WL6 | 5 006.1 c | 4 834.0 d | 5 096.4 d | 12.8 c | 13.0 d | 12.1 c | |
| 1 | 黄峰,杜太生,王素芬,等.华北地区农业水资源现状和未来保障研究[J].中国工程科学, 2019, 21(5): 28-37. |
| HUANG F, DU T S, WANG S F, et al.. Current situation and future security of agricultural water resources in North China [J]. Strategic Study CAE, 2019, 21(5): 28-37. | |
| 2 | MENG Q, SUN Q, CHEN X, et al.. Alternative cropping systems for sustainable water and nitrogen use in the North China Plain [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2012, 146(1): 93-102. |
| 3 | ZHANG A, ZHANG D, LI R, et al.. Evaluation of limited irrigation strategies to improve water use efficiency and wheat yield in the North China Plain [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1): e0189989 [2021-11-24]. . |
| 4 | 袁再健,许元则,谢栌乐.河北平原农田耗水与地下水动态及粮食生产相互关系分析[J].中国生态农业学报, 2014, 22(8): 904-910. |
| YUAN Z J, XU Y Z, XIE L Y. Correlation among farmland water consumption, grain yield and groundwater dynamics in the Hebei Plain [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2014, 22(8): 904-910. | |
| 5 | BROWN M E, FUNK C C. Climate food security under climate change [J]. Science, 2008, 319(5863): 580-581. |
| 6 | WANG X, LI L, DING Y, et al.. Adaptation of winter wheat varieties and irrigation patterns under future climate change conditions in Northern China [J/OL]. Agric. Water Manage., 2021, 243: e106409 [2021-11-25]. . |
| 7 | 刘涛,周广胜,谭凯炎,等.华北地区冬小麦灌溉制度及其环境效应研究进展[J].生态学报,2016, 36(19): 59, 79-86. |
| LIU T, ZHOU G S, TAN K Y, et al.. Review on research of irrigation regime and its environmental effect in winter wheat field of North China Plain [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin.,2016, 36(19): 59,79-86. | |
| 8 | 张凯,曾昭海,赵杰,等.华北平原压采地下水对小麦生产的影响分析[J].中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(5): 111-117. |
| ZHANG K, ZENG Z H, ZHAO J, et al.. Impact analysis of reduce the extraction of groundwater on wheat production in North China Plain [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2016, 18(5): 111-117. | |
| 9 | WANG Z, WU P, ZHAO X, et al.. Water use and crop coefficient of the wheat-maize strip intercropping system for an arid region in northwestern China [J]. Agric. Water Manage., 2015, 161: 77-85. |
| 10 | YU L, ZHAO X, GAO X, et al.. Improving/maintaining water-use efficiency and yield of wheat by deficit irrigation: a global meta-analysis [J/OL]. Agric. Water Manage., 2020, 228: e105906 [2021-11-25]. . |
| 11 | 康绍忠,杜太生,孙景生,等.基于生命需水信息的作物高效节水调控理论与技术[J].水利学报, 2007 (6):661-667. |
| KANG S Z, DU T S, SUN J S, et al.. Theory and technology of crop efficient water saving regulation based on life water demand information [J]. J. Hydraulic Eng., 2007 (6): 661-667. | |
| 12 | 王书吉,康绍忠,李涛.基于节水高产优质目标的冬小麦适宜水分亏缺模式[J].农业工程学报, 2015, 31(12): 111-118. |
| WANG S J, KANG S Z, LI T. Suitable water deficit mode for winter wheat basing objective of water saving as well as high yield and quality [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2015, 31(12): 111-118. | |
| 13 | 周青云,燕琪琦,张宝忠,等.冬小麦不同冠层叶片光合蒸腾和水分利用效率变化特征及对灌溉的响应[J].麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(10): 1247-1255. |
| ZHOU Q Y, YAN Q Q, ZHANG B Z, et al.. Variation characteristics of photosynthetic transpiration and water use efficiency of different canopy leaves of winter wheat and their response to irrigation [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2021, 41(10):1247-1255. | |
| 14 | 崔亚坤,王妮妮,田中伟,等.分蘖和拔节期干旱对小麦植株氮素积累转运的影响[J].麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(3): 322-328. |
| CUI Y K, WANG N N, TIAN Z W, et al.. Effect of srought in tillering and jointing stages on nitrogen accumulation and translocation in wheat plants [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(3): 322-328. | |
| 15 | FAN Y, LIU J, ZHAO J, et al.. Effects of delayed irrigation during the jointing stage on the photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat under different planting patterns [J]. Agric. Water Manage., 2019, 221: 371-376. |
| 16 | WU D, FANG S, LI X, et al.. Spatial-temporal variation in irrigation water requirement for the winter wheat-summer maize rotation system since the 1980s on the North China Plain [J]. Agric. Water Manage., 2019, 214: 78-86. |
| 17 | 江梦圆,薛晓萍,杨再强,等.开花期复水对受旱冬小麦叶片状态和产量结构的补偿效应[J].中国农业气象, 2020, 41(4): 253-262. |
| JIANG M Y, XUE X P, YANG Z Q, et al.. Compensation effects of rewatering at flowering stage on leaf state and yield structure of winter wheat under drought [J]. Chin. J. Agrometeorol., 2020, 41(4): 253-262. | |
| 18 | JOHNSON K M, JORDAN G J, BRODRIBB T J. Wheat leaves embolized by water stress do not recover function upon rewatering [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2018, 41(11): 2704-2014. |
| 19 | 曹彩云,党红凯,李科江,等. 冬小麦测墒灌溉技术规程: [S]. 河北省地方标准,2016. |
| 20 | 何昕楠,林祥,谷淑波,等.微喷补灌对麦田土壤物理性状及冬小麦耗水和产量的影响[J].作物学报, 2019, 45(6): 879-892. |
| HE X N, LIN X, GU S B, et al.. Effects of supplemental irrigation with micro-sprinkling hoses on soil physical properties, water consumption and grain yield of winter wheat [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(6): 879-892. | |
| 21 | LILLEY J M, KIRKEGAARD J A. Benefits of increased soil exploration by wheat roots [J]. Field Crops Res., 2011, 122(2): 118-130. |
| 22 | 姚宁,宋利兵,刘健,等.不同生长阶段水分胁迫对旱区冬小麦生长发育和产量的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2015, 48(12): 2379-2389. |
| YAO N, SONG L B, LIU J, et al.. Effects of water stress at different growth stages on the development and yields of winter aheat in arid region [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2015, 48(12): 2379-2389. | |
| 23 | 冉文星,王冀川,王璞.小麦水分高效利用研究进展[J].中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(1): 103-111. |
| RAN W X, WANG J C, WANG P. Research progress on high efficient water utilization of wheat [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2016, 18(1): 103-111. | |
| 24 | 刘帅康,林祥,谷淑波,等.拔节后补灌对不同穗型冬小麦耗水和籽粒产量的影响[J].麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(12): 1501-1513. |
| LIU S K, LIN X, GU S B, et al.. Effects of supplemental irrigation after jointing on water consumption and grain yield of winter wheat with different spike types [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(12): 1501-1513. | |
| 25 | WANG D. Water use efficiency and optimal supplemental irrigation in a high yield wheat field [J]. Field Crops Res., 2017, 213: 213-220. |
| 26 | LIU X W, FEIKE T, CHEN S Y, et al.. Effects of saline irrigation on soil salt accumulation and grain yield in the winter wheat-summer maize double cropping system in the low plain of North China [J]. J. Integrative Agric., 2016, 15(12): 2886-2898. |
| 27 | 李萍.返青期和拔节期土壤水分对冬小麦茎蘖成穗和产量的调控及其生理特性[D].泰安:山东农业大学, 2020. |
| LI P. Effect of siol misture during returning green and jointing stages on spike formation and yield of main stem and tillers in winter wheat and its physiolical character [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. |
| [1] | 王健, 许爱玲, 卫晓东, 席吉龙, 杨娜, 王珂, 席天元, 张建诚. 运城盆地不同播期小麦春季冻害风险评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 137-147. |
| [2] | 郭佳晖, 白雄辉, 王爱东, 李瑞杰, 石晓鑫, 史勇峰, 李爱莲, 王西成, 王宏富, 郭杰. 黄淮北片冬麦区国家区试冬小麦品种抗寒性鉴定与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 25-34. |
| [3] | 张胜男1,聂兆君1*,赵鹏1,李金峰1,李永革2,刘红恩1*,秦晓明1,秦世玉1. 磷硫配施对冬小麦硒吸收及转运的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 137-144. |
| [4] | 尹焕丽1,岳艳军2,常凤1,王海标1,苗玉红1,王宜伦1*. 新型尿素对冬小麦产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 145-152. |
| [5] | 李华伟1,陈昱利2,禚其翠1,张宾1*. 施氮对冬小麦生长及产量影响的模拟研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(12): 119-127. |
| [6] | 程婉莹1,王春艳1*,任徳超2,崔三荣1,耿金剑1. 不同穗分化时期冬小麦形态抗冻性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(7): 83-90. |
| [7] | 李书钦1,2,诸叶平2*,刘海龙2,李世娟2,刘升平2. 冬小麦返青后叶片高度模型构建及三维可视化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(11): 59-67. |
| [8] | 杨敏1,刘峻明1*,王鹏新1,胡新2,黄健熙1,汪念1. 基于MODIS大气廓线产品分析晚霜冻对冬小麦产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(2): 78-85. |
| [9] | 吴超,崔克辉*. 高温影响水稻产量形成研究进展[J]. , 2014, 16(3): 103-111. |
| [10] | 孙苏阳,王永军,李海军,李丽丽. 高产广适小麦品种淮麦25产量形成分析[J]. , 2014, 16(1): 98-103. |
| [11] | 胡乔玲1,刘峻明1*,王春艳2,王鹏新1,黄健熙1. 冬小麦拔节期遥感监测方法研究[J]. , 2013, 15(6): 152-157. |
| [12] | 秦欣,刘克,周顺利*. 华北地区冬小麦节水栽培氮素吸收利用特征研究[J]. , 2012, 14(5): 96-101. |
| [13] | 司文才,刘峻明. 冬小麦关键物候空间分布遥感监测方法研究[J]. , 2011, 13(6): 82-89. |
| [14] | 李卫国1,李正金1,2,杨澄2. 基于CBERS遥感的冬小麦长势分级监测[J]. , 2010, 12(3): 79-83. |
| [15] | 史占良,郭进考,何明琦,蔡欣,底瑞耀,刘彦军,张士昌. 高产抗倒广适冬小麦新品种石麦18号[J]. , 2009, 11(S2): 102-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号