




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 205-217.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.1020
• 海洋农业 淡水渔业 • 上一篇
武博琼( ), 崔东遥, 焦仁和, 宋坚, 湛垚垚, 常亚青(
), 崔东遥, 焦仁和, 宋坚, 湛垚垚, 常亚青( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-30
接受日期:2022-04-12
出版日期:2022-07-15
发布日期:2022-08-15
通讯作者:
常亚青
作者简介:武博琼 E-mail: 18634710693@163.com;
基金资助:
Boqiong WU( ), Dongyao CUI, Renhe JIAO, Jian SONG, Yaoyao ZHAN, Yaqing CHANG(
), Dongyao CUI, Renhe JIAO, Jian SONG, Yaoyao ZHAN, Yaqing CHANG( )
)
Received:2021-11-30
Accepted:2022-04-12
Online:2022-07-15
Published:2022-08-15
Contact:
Yaqing CHANG
摘要:
为明确中间球海胆己糖激酶的序列信息和表达规律,了解高温-酸化胁迫对其表达和生物活性的影响,以中间球海胆为研究对象,利用cDNA末端快速扩增技术获得中间球海胆已糖激酶基因的全长cDNA序列(SiHK),并利用生物信息学软件分析其序列特征,分析高温-酸化胁迫下中间球海胆肠和性腺组织中SiHK基因的表达及其酶活力变化。结果表明,SiHK基因的cDNA全长2 041 bp,编码476个氨基酸,SiHK蛋白的理论等电点为6.44,蛋白质分子质量52.72 kD。生物信息学分析显示,SiHK蛋白氨基酸序列与紫球海胆HK氨基酸序列相似最高。实时荧光定量PCR结果显示,SiHK基因的表达具有组织特异性,其中,肠和性腺组织中SiHK基因的相对表达量较高,而在体腔液和管足中SiHK酶活力较高。高温-酸化胁迫处理60 d后,与对照组相比,处理组中间球海胆的肠和性腺组织中SiHK基因的相对表达量和SiHK酶活性均发生改变。由此表明,高温-酸化胁迫可能通过调控糖代谢关键酶活性对海胆的物质代谢过程产生影响。
中图分类号:
武博琼, 崔东遥, 焦仁和, 宋坚, 湛垚垚, 常亚青. 中间球海胆己糖激酶基因克隆及高温-酸化胁迫对其表达影响的初步研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 205-217.
Boqiong WU, Dongyao CUI, Renhe JIAO, Jian SONG, Yaoyao ZHAN, Yaqing CHANG. Cloning of Hexokinase Gene from Strongylocentrotus intermedius and Its Expression Response to High Temperature-acidification Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 205-217.
| 处理 Treatment | 温度 Temperature/℃ | pHNBS | 盐度 Salinaty/PPT | 总碱度 TA/(µmol·kg-1) | 二氧化碳分压 pCO2/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.10±0.30 | 8.10±0.03 | 31.21±0.20 | 2 360.45±24.18 | 53.44±2.55 |
| HC | 23.20±0.30 | 8.10±0.03 | 31.33±0.21 | 2 363.32±25.34 | 54.35±3.26 |
| LO | 20.30±0.30 | 7.62±0.04 | 31.25±0.12 | 2 360.88±20.33 | 179.87±5.44 |
| HO | 23.00±0.30 | 7.61±0.03 | 31.18±0.13 | 2 349.54±26.42 | 189.17±7.00 |
表1 各试验组的海水参数
Table1 Seawater parameters of each treatment
| 处理 Treatment | 温度 Temperature/℃ | pHNBS | 盐度 Salinaty/PPT | 总碱度 TA/(µmol·kg-1) | 二氧化碳分压 pCO2/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.10±0.30 | 8.10±0.03 | 31.21±0.20 | 2 360.45±24.18 | 53.44±2.55 |
| HC | 23.20±0.30 | 8.10±0.03 | 31.33±0.21 | 2 363.32±25.34 | 54.35±3.26 |
| LO | 20.30±0.30 | 7.62±0.04 | 31.25±0.12 | 2 360.88±20.33 | 179.87±5.44 |
| HO | 23.00±0.30 | 7.61±0.03 | 31.18±0.13 | 2 349.54±26.42 | 189.17±7.00 |
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequences(5’-3’) | 用途 Application | 退火温度Temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiHK-F1 | AATGCCTGGCGAACAAAATACAG | SiHK-1 | 54 |
| SiHK-R1 | ATCACTGCTACTATGTCAACTCG | ||
| SiHK-F2 | ATTCCCCTCGGTTTCACCTTTTC | SiHK-2 | 60 |
| SiHK-R2 | ATACCCGAGGCAATCAGTCTGGC | ||
| SiHK-F3 | GCCAGACTGATTGCCTCGGGTAT | SiHK-3 | 57 |
| SiHK-R3 | GTACGTCCTTACAGTCCAGCAGA | ||
| SiHK-5-out | TCACCCACATCACACGGAAGTTG | 5’RACE | 60 |
| SiHK-5-in | GCATTGAGAGCAGCCTTCAGACC | 5’RACE | 61 |
| SiHK-3-out | CAATACAACCATCTGCTGGACTG | 3’RACE | 56 |
| SiHK-3-in | TTCAATAAGCAAGAACATCAGGC | 3’RACE | 53 |
| UPM | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTAACAACGCAGAGT | RACE | 67 |
| NUP | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC | RACE | 52 |
| SiHK-F | ACTCCATCGTCTCCGAATGC | qPCR | 60 |
| SiHK-R | CAACGCCTGCTACATGGAAG | qPCR | 60 |
| β-actin-F | ACAGGGAAAAGATGGCACAGA | qPCR | 60 |
| β-actin-R | AGAGGCGTAGAGGGAAAGCAC | qPCR | 60 |
表2 本研究中使用的引物
Table 2 Primers used in this study
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequences(5’-3’) | 用途 Application | 退火温度Temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiHK-F1 | AATGCCTGGCGAACAAAATACAG | SiHK-1 | 54 |
| SiHK-R1 | ATCACTGCTACTATGTCAACTCG | ||
| SiHK-F2 | ATTCCCCTCGGTTTCACCTTTTC | SiHK-2 | 60 |
| SiHK-R2 | ATACCCGAGGCAATCAGTCTGGC | ||
| SiHK-F3 | GCCAGACTGATTGCCTCGGGTAT | SiHK-3 | 57 |
| SiHK-R3 | GTACGTCCTTACAGTCCAGCAGA | ||
| SiHK-5-out | TCACCCACATCACACGGAAGTTG | 5’RACE | 60 |
| SiHK-5-in | GCATTGAGAGCAGCCTTCAGACC | 5’RACE | 61 |
| SiHK-3-out | CAATACAACCATCTGCTGGACTG | 3’RACE | 56 |
| SiHK-3-in | TTCAATAAGCAAGAACATCAGGC | 3’RACE | 53 |
| UPM | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTAACAACGCAGAGT | RACE | 67 |
| NUP | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC | RACE | 52 |
| SiHK-F | ACTCCATCGTCTCCGAATGC | qPCR | 60 |
| SiHK-R | CAACGCCTGCTACATGGAAG | qPCR | 60 |
| β-actin-F | ACAGGGAAAAGATGGCACAGA | qPCR | 60 |
| β-actin-R | AGAGGCGTAGAGGGAAAGCAC | qPCR | 60 |

图1 中间球海胆SiHK的核苷酸序列及其所编码的氨基酸序列注:方框中的字母为起始密码子(ATG),*表示终止密码子(TGA);下划线表示SiHK蛋白编码的氨基酸序列; 灰色区域表示COG5026结构域;双下划线区域字母(AATAA)为3’-UTR中的不稳定因素。
Fig. 1 Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of SiHK in Strongylocentrotus intermediusNote:Letter in the frame is the starting codon (ATG); * indicates the terminating codon (TGA); underline represents the amino acid sequence encoded by the SiHK protein; grey region represents the COG5026 domain; double underlined area ( AATAA) is the unstable factor in 3’-UTR.
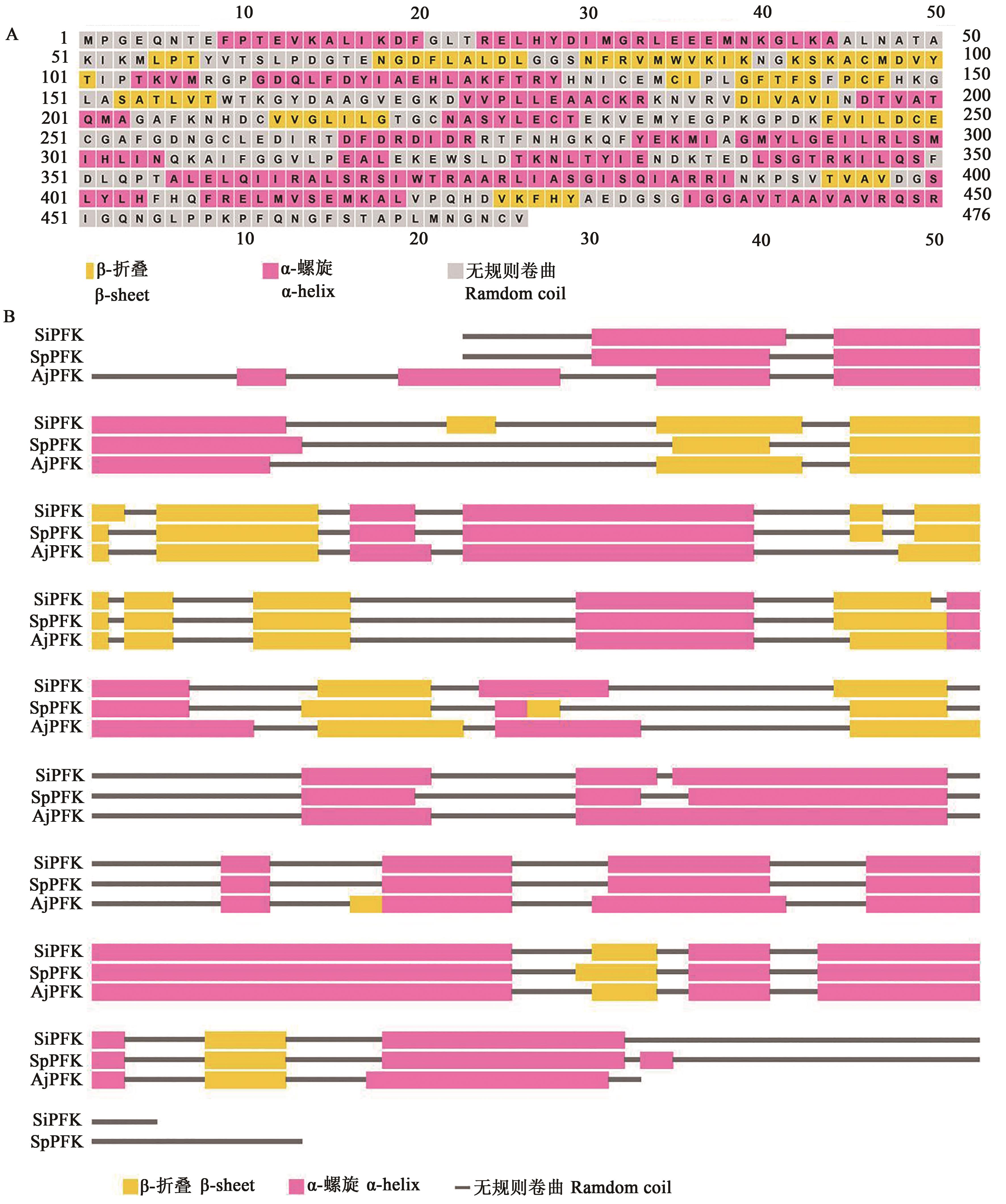
图2 中间球海胆SiHK二级结构预测及其与紫球海胆、仿刺参HK的二级结构比较A:中间球海胆SiHK二级结构;B:中间球海胆SiHK、紫球海胆SpHK、仿刺参AjHK的二级结构比对
Fig. 2 Secondary structure prediction and comparison of hexokinase betweenA:Predicted secondary structure of SiHK in Strongylocentrotus intermedius; B:Comparison of HK secondary structure among S. intermedius (SiHK), Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (SpHK) and Apostichopus japonicus (AjHK)
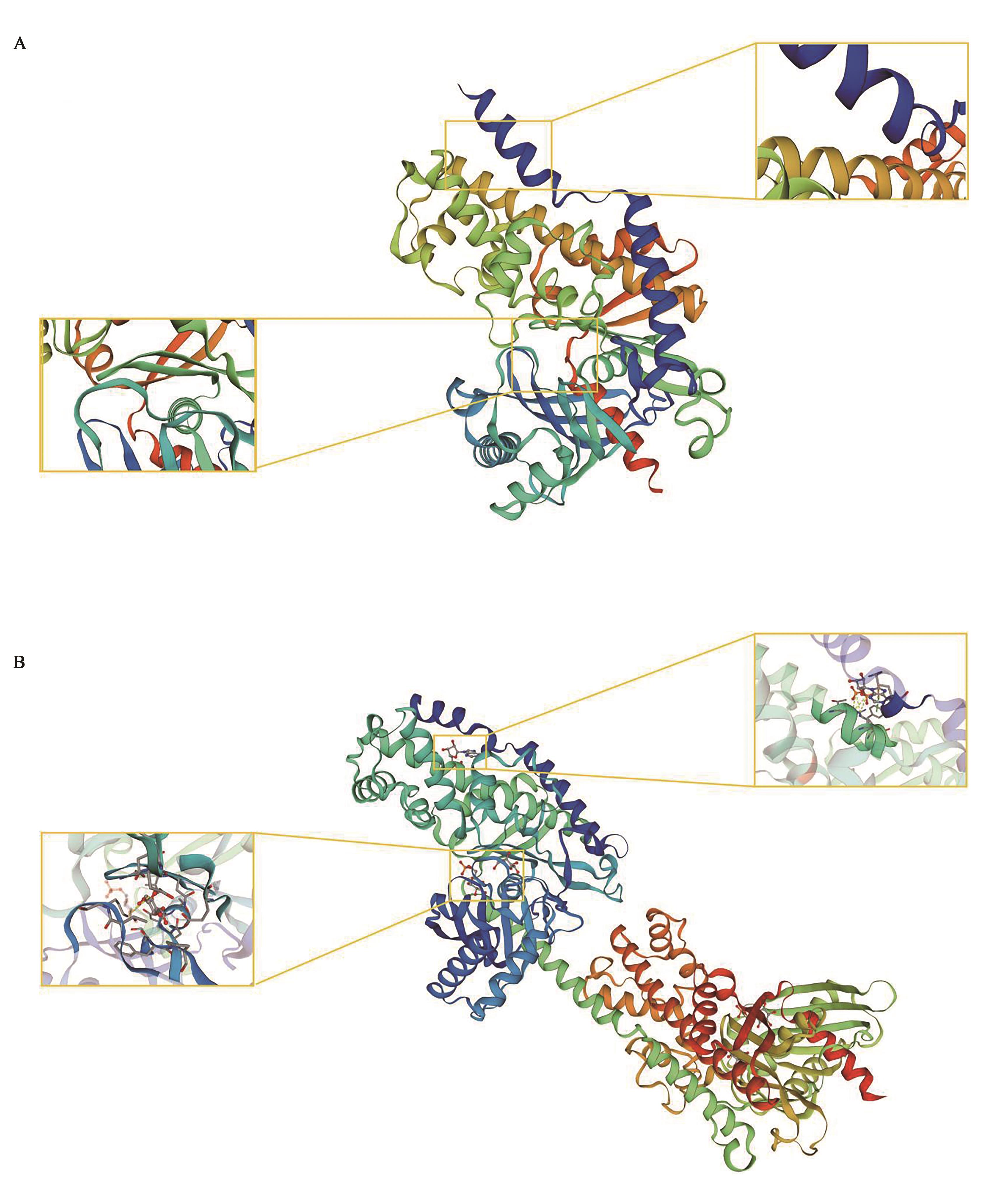
图3 中间球海胆SiHK蛋白质的三级结构A:中间球海胆SiHK蛋白;B:人HK蛋白;黄色框住区域中, 球棍结构表示磷酸基团识别位点, 周围蛋白质构成的结构为酶活性中心, 黄色虚线代表盐桥。
Fig. 3 3D structure prediction of SiHKA:SiHK protein from Strongylocentrotus intermedius;B:HK protein from Homo spains;in the yellow framed area, the club structure represents the phosphate group recognition site, the surrounding protein structure is the enzyme active center, and the yellow dotted line represents the salt bridge.
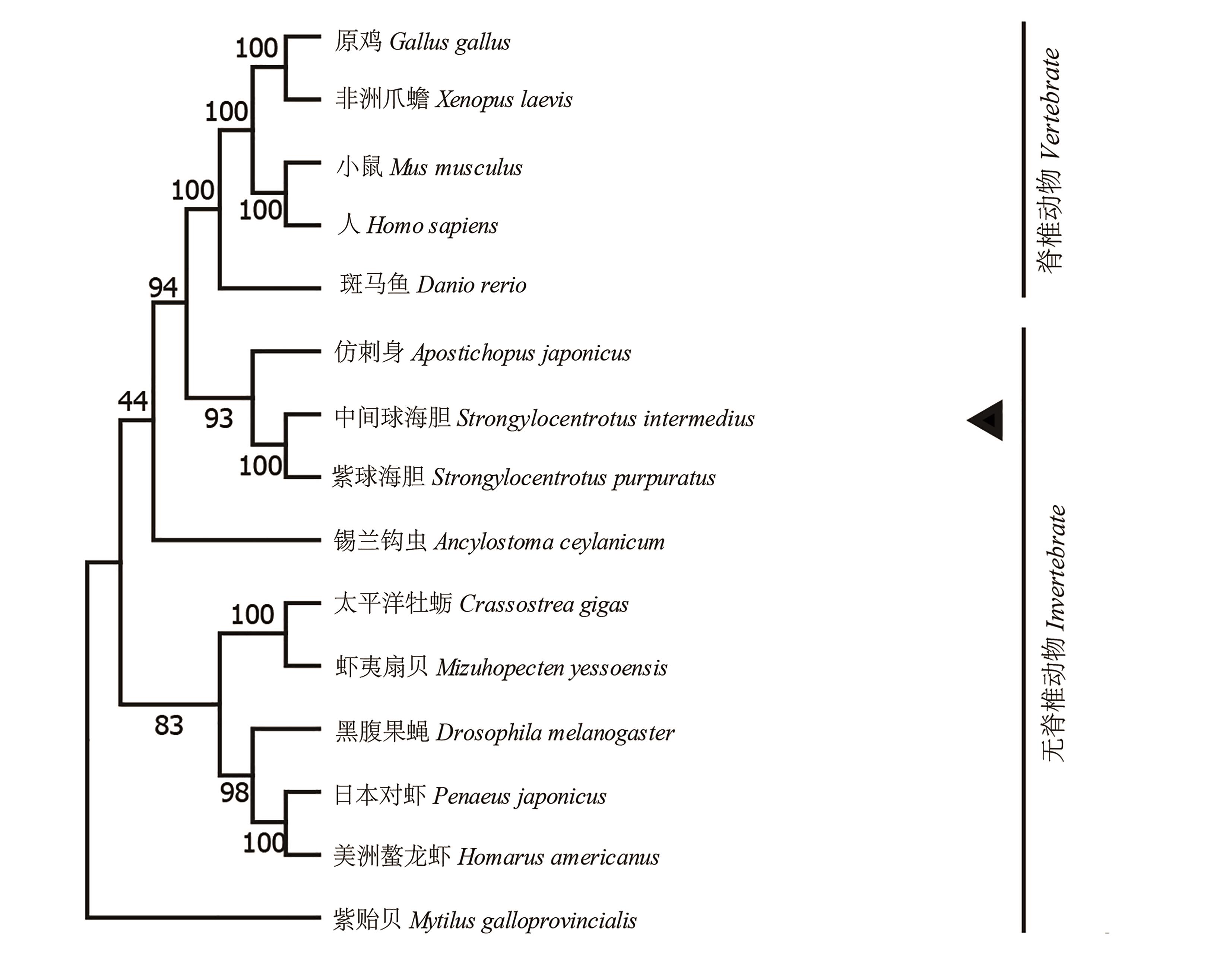
图 4 中间球海胆SiHK氨基酸序列系统进化分析注:黑色箭头指出中间球海胆SiHK,左侧数字代表迭代次数。
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic analysis of deduced amino acid sequences of SiHKNote:SiHK is marked with black arrow, the numbers at the tree nodes indicate the percentage of bootstrapping after 1 000 replicates.
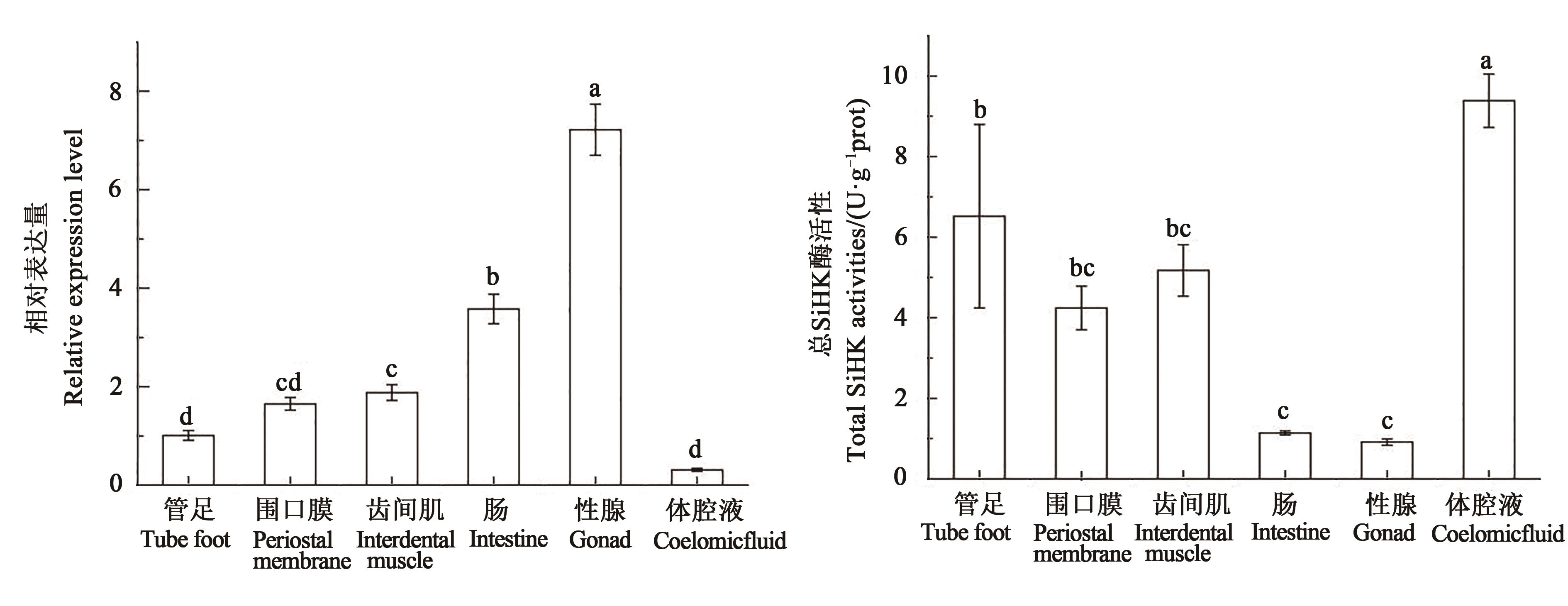
图5 中间球海胆不同组织SiHK基因表达量和总SiHK酶活力注:不同小写字母表示不同组织间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Relative expression of SiHK and total SiHK activities in different tissues of Strongylocentrotus intermediusNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different tissues at P<0.05 level.
| 指标 Index | 组织 Organ | 因子Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高温 High temperature | 酸化Acidification | 高温×酸化 High temperature×acidification | ||
SiHK表达量 Relative expression level of SiHK | 肠 Intestine | 77.918** | 85.696** | 117.932** |
| 性腺 Gonad | 0.320 | 4.173* | 29.133** | |
总SiHK酶活力 Total SiHK activity | 肠 Intestine | 9.217* | 2.553 | 3.690 |
| 性腺 Gonad | 13.046* | 0.486 | 101.034** | |
表3 高温和酸化对SiHK基因表达和总SiHK酶活力影响的双因素方差分析
Table 3 Two-way ANOVA of effects of high temperature-acidification stress on relative expression and total enzyme activities of SiHK
| 指标 Index | 组织 Organ | 因子Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高温 High temperature | 酸化Acidification | 高温×酸化 High temperature×acidification | ||
SiHK表达量 Relative expression level of SiHK | 肠 Intestine | 77.918** | 85.696** | 117.932** |
| 性腺 Gonad | 0.320 | 4.173* | 29.133** | |
总SiHK酶活力 Total SiHK activity | 肠 Intestine | 9.217* | 2.553 | 3.690 |
| 性腺 Gonad | 13.046* | 0.486 | 101.034** | |
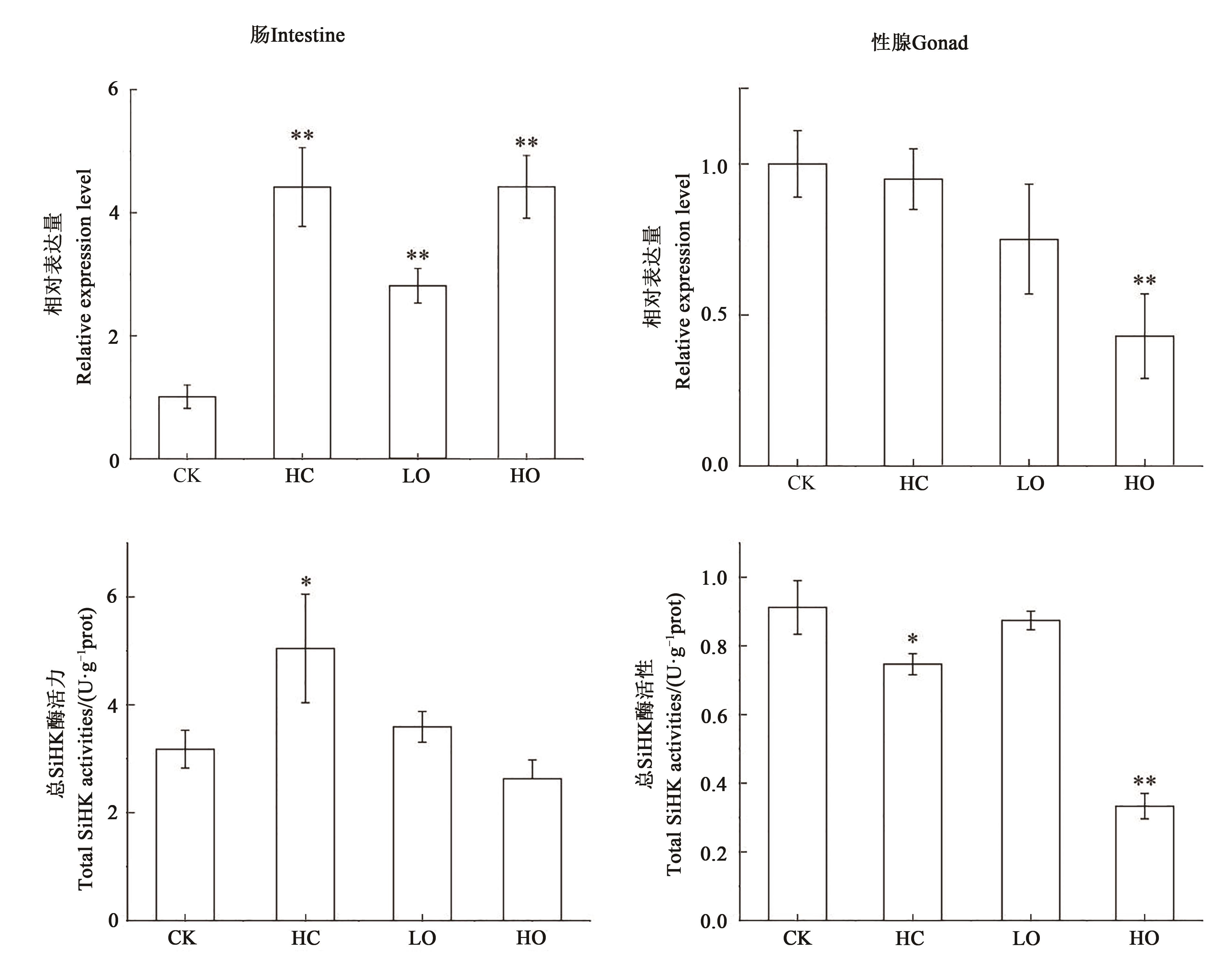
图6 不同处理下肠和性腺中SiHK基因的表达和总SiHK酶活力注:*和**分别表示处理与对照间差P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Relative expression level of SiHK and the total SiHK activities under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between treatment CK at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
| 1 | CALDEIRA K, WICKETT M E. Oceanography: anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH [J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6956):365-365. |
| 2 | 石莉,桂静,吴克勤.海洋酸化及国际研究动态[J].海洋科学进展,2011,29(1):122-128. |
| SHI L, GUI J, WU K Q. Developments in international studies on ocean acidification [J]. Adv. Mar. Sci., 2011, 29(1):122-128. | |
| 3 | HESTER K C, PELTZER E T, KIRKWOOD W J, et al.. Unanticipated consequences of ocean acidification: a noisier ocean at lower pH [J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 2008, 35(19):402-411. |
| 4 | RIEBESELL U. Climate change: acid test for marine biodiversity [J]. Nature, 2008, 454(7200):46-47. |
| 5 | 秦艳杰,宋晓楠,李霞,等.海洋酸化和升温对中间球海胆幼虫发育和生长的影响[J].大连海洋大学学报,2013,28(5):450-455. |
| QIN Y J, SONG X N, LI X, et al.. Effects of ocean acidification and warming on growth and development in larval sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius [J]. J. Dalian Ocean Univ., 2013, 28(5):450-455. | |
| 6 | 卢羽洁.海洋酸化及变暖对刺参主要生理生态过程和免疫的影响[D].大连:大连海洋大学, 2017. |
| LU Y J. Effects of ocean acidification and warming on physio-ecological process and immune responses of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) [D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2017. | |
| 7 | 尹文露,崔东遥,李莹莹,等.中间球海胆丙酮酸激酶(PK)基因克隆及其对海水酸化的响应[J].大连海洋大学学报,2020,35(3):360-367. |
| YIN W L, CUI D Y, LI Y Y, et al.. Cloning and response of pyruvate kinase (PK) gene to seawater acidification in sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius [J]. J. Dalian Ocean Univ., 2020, 35(3):360-367. | |
| 8 | 李笑.海水酸化和升温对日本鼓虾和马粪海胆氧化应激和能量代谢的影响[D].烟台:中国科学院大学,2020. |
| LI X. Effects of seawater acidification and thermal sterss on the antioxidant responses and energy metabolism of Alpheus japonicus miers [D]. Yantai: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. | |
| 9 | GREENBERG D M, MATSUO Y, ROTHSTEIN M. Metabolic pathways of homoserine in the mammal [J]. J. Biol. Chem.. 1956, 221(2):679-687. |
| 10 | 汝玉涛.柞蚕EcR、USP和HK基因的克隆及表达研究[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2018. |
| RU Y T. The clone and expression research of ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle and hexokinase gene of Antheraea pernyi [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 11 | 王倩.己糖激酶1(HK1)在鹅肥肝形成中的作用及调控研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2019. |
| WANG Q. Study on the expression of hexokinase-1 in the development of goose fatty liver and the regulation of its function [D]. Yanghzou: Yangzhou University, 2018 | |
| 12 | 刘雅,王庆恒,郑哲,等.马氏珠母贝(Pinctada fucata martensii)Pm-HK基因的克隆及其对温度胁迫的响应[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2019,38(2):503-510. |
| LI Y, WANG Q H, ZHENG Z, et al.. Cloning of Pm-HK gene of Pinctada fucata martensii and its response to temperature stress [J]. Gen. App. Biol., 2019, 38(2):503-510. | |
| 13 | 郭彪,王芳,侯纯强,等.温度突变对凡纳滨对虾己糖激酶和丙酮酸激酶活力以及热休克蛋白表达的影响[J].中国水产科学,2008,15(5):885-889. |
| GUO B, WANG F, HOU C Q, et al.. Effects of acute temperature fluctuation on HK and PK activity, HSP70 relative content in Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. J. Fish. Sci. China, 2008, 15(5):885-889. | |
| 14 | 常亚青,丁君,宋坚,等.海参海胆生物学研究与养殖[M].北京:海洋出版社,2004:211-216. |
| CHANG Y Q, DING J, SONG J, et al.. Biological Study and Breeding of Sea Cucumber and Sea Urchin [M].Beijing: Maritime Press, 2004:211-216. | |
| 15 | WANG H, ZHAO W F, DING B C, et al.. Comparative lipidomics profiling of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus intermedius [J/OL]. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D, 2021, 40:100900 [2021-10-05]. . |
| 16 | 湛垚垚,黄显雅,段立柱,等.实验室模拟海水酸化系统[P].中华人民共和国国家知识产权局,ZL201320267332.7 |
| 17 | STOCKER T F, QIN D, PLATTNER G K, et al.. Contribution of working group to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [C]// IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007. |
| 18 | 余舜武,刘鸿艳,罗利军.利用不同实时定量PCR方法分析相对基因表达差异[J].作物学报,2007,33(7):1214-1218. |
| YU S W, LIU H Y, LUO L J. Analysis of relative gene expression using different real-time quantitative PCR [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2007, 33(7):1214-1218. | |
| 19 | 崔东遥,任丽媛,邢冬飞,等.中间球海胆乳酸脱氢酶基因克隆及其对海水酸化的响应[J].水产学报,2019,43(6):1423-1437. |
| CUI D Y, REN L Y, XING D F, et al.. Identification and characterization of LDH gene and its response to seawater acidification in the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius) [J]. J. Fish. China, 2019, 43(6):1423-1437. | |
| 20 | HU M Y, KATHARINA M, KREISS C M, et al.. Temperature modulates the effects of ocean acidification on intestinal ion transport in Atlantic Cod, Gadus morhua [J/OL]. Front. Physiol., 2016, 7:198 [2021-10-05]. . |
| 21 | KURIHARA H, YIN R, NISHIHARA G N, et al.. Effect of ocean acidification on growth, gonad development and physiology of the sea urchin Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus [J]. Aquat. Biol., 2013, 18(3):281-292. |
| 22 | STUMPP M, WREN J, MELZNER F, et al.. CO2 induced seawater acidification impacts sea urchin larval development I: Elevated metabolic rates decrease scope for growth and induce developmental delay [J]. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol., 2011, 160(3):331-340. |
| 23 | YUAN X, SHAO S, DUPONT S, et al.. Impact of CO2-driven acidification on the development of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicas (Selenka) (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea) [J]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2015, 95(1):195-199. |
| 24 | WOOD H, SPICER J, WIDDICOMBE S. Ocean acidification may increase calcification rates, but at a cost [J]. Proc. Biol. Sci., 2008, 275(1644):1767-1773. |
| 25 | 郭蔼光.基础生物化学[M].第2版.北京:高等教育出版社,2009:151-158. |
| GUO A G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry [M]. 2nd Ed n. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009:151-158. | |
| 26 | KATZEN H M, SCHIMKE R T. Multiple forms of hexokinase in the rat: tissue distribution, age dependency, and properties [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1965, 54:1218-1225. |
| 27 | DOBRETSOV S, COUTINHO R, RITTSCHOF D, et al.. The oceans are changing: impact of ocean warming and acidification on biofouling communities [J]. Biofouling, 2019, 35(5):1-11. |
| 28 | 许冰,贾爱芳,赵文献.温度对酶活性的影响[J].临床合理用药杂志,2010,3(7):28-28. |
| 29 | 常亚青,王子臣,王国江.温度和藻类饵料对虾夷马粪海胆摄食及生长的影响[J].水产学报,1999,23(1):69-76. |
| CHANG Y Q, WANG Z C, WANG G J. Effect of temperature and algae on feeding and growth in sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius [J]. J. Fish. China, 1999, 23(1):69-76. | |
| 30 | 马红悦,李玲,李艳艳,等.沙葱萤叶甲己糖激酶基因的克隆、相对表达量及RNA干扰效应[J].植物保护学报,2020,47(6):1211-1218. |
| MA H Y, LI L, LI Y Y, et al.. Cloning, relative expression, and RNAi effects of the hexokinase gene in Galeruca daurica (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2020, 47(6):1211-1218. | |
| 31 | 童欢, AKIBER C W,袁海荣,等.酸化温度对玉米秸秆厌氧水解酸化性能的影响[J].可再生能源,2020,38(8):995-1000. |
| TONG H, AKIBER C W, YUAN H R, et al.. Effect of acidification temperature on anaerobic hydrolysis and acidogenesis of corn straw [J]. Renew. Energy Resour., 2020, 38(8):995-1000. | |
| 32 | ZHAN Y, CUI D, XING D, et al.. CO2-driven ocean acidification repressed the growth of adult sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius by impairing intestine function [J/OL]. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2020, 153:110944 [2021-10-05]. . |
| 33 | UTHICKE S, LIDDY M, NGUYEN H D, et al.. Interactive effects of near-future temperature increase and ocean acidification on physiology and gonad development in adult Pacific sea urchin, Echinometra sp. A [J]. Coral Reefs., 2014, 33(3):831-845. |
| [1] | 王帅, 宋伟, 王荣焕, 赵久然. 我国玉米生物学研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 23-31. |
| [2] | 刘鹏,韦杰1,杨毅清1,张娜1,温晓蕾1,2,范学锋1,杨文香1*,刘大群1*. 小麦类钙调素新亚型基因TaCML25/26调控抗叶锈性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(4): 120-128. |
| [3] | 张丽洁1,2,徐欣欣2,田健2,初晓宇2*,朱宝成1*,伍宁丰2. 特异腐质霉来源漆酶基因的克隆及其在毕赤酵母中的表达[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2): 46-53. |
| [4] | 葛建忠1,尹亚昕2,蒋肖1,刘伟娜1,姚斌1,罗会颖1*. Cladosporium tianshanense SL19来源的新型葡萄糖氧化酶的基因克隆及性质研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(12): 49-57. |
| [5] | 商艳鹏,田燚*,李晓雨,蒋亚男,常亚青. 仿刺参7个盐度相关基因在低盐胁迫下的表达模式[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(11): 145-153. |
| [6] | 蒲全明1,施松梅2,张林成2,高启国2*,任雪松2,向承勇1,. 结球甘蓝AUX/IAA家族基因BoIAA2与BoIAA19 的克隆与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(9): 24-33. |
| [7] | 李静1§,刘思敏1§,蔡丽静2,王昭玉1,董丽君1,刘建凤1,张书玲1*. 海岛棉GbWRKY53基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(11): 15-21. |
| [8] | 邹媛媛,刘洋,赵亮,刘琳,宋未*. 两种抗病性不同的水稻种子固有细菌群落的多样性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(4): 9-16. |
| [9] | 王丹霞,权瑞党*,黄荣峰. 水稻yl1黄叶突变体的基因克隆与功能分析[J]. , 2015, 17(2): 41-48. |
| [10] | 胡斌斌1,2§,吴萍2§,刘晓青2,丁伟1*,伍宁丰2*. 来源于土壤宏基因组中漆酶Lac13H9基因克隆及其酶学性质分析[J]. , 2015, 17(2): 64-71. |
| [11] | 余小霞,刘晓青,田健,伍宁丰*. 来源于枯草芽孢杆菌的漆酶cotA基因克隆与表达及其酶学性质研究[J]. , 2015, 17(1): 102-108. |
| [12] | 李雅楠1,余利红1,李昀楷1,马文康1,张伟2*. 特异腐质酶Humicola insolens Y1耐热型木聚糖酶基因的克隆及酶学性质分析[J]. , 2013, 15(4): 121-128. |
| [13] | 韩慧超1,黄逸群1,王劲2,左开井1*. 陆地棉LTP家族基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. , 2013, 15(3): 84-90. |
| [14] | 武英利,霍韶瑜. 饲用酶添加剂预混料中酸性蛋白酶活力测定方法研究[J]. , 2009, 11(S1): 52-55. |
| [15] | 刘小丹1,2,杨培龙2,刘永超3,许修宏1,孟昆2,姚斌2. 一种来源于Paenibacillus sp. A1的中性β-甘露 聚糖酶基因克隆及其酶学性质研究[J]. , 2009, 11(5): 60-65. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号