




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 221-233.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0498
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
申云鑫1,2( ), 施竹凤2(
), 施竹凤2( ), 韩天华3, 周旭东1,2, 贺彪3, 赵文山3, 和强3, 马斌3, 陈齐斌1(
), 韩天华3, 周旭东1,2, 贺彪3, 赵文山3, 和强3, 马斌3, 陈齐斌1( ), 杨佩文2(
), 杨佩文2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-14
接受日期:2022-11-10
出版日期:2023-10-15
发布日期:2023-10-27
通讯作者:
陈齐斌,杨佩文
作者简介:申云鑫 E-mail:1437466844@qq.com基金资助:
Yunxin SHEN1,2( ), Zhufeng SHI2(
), Zhufeng SHI2( ), Tianhua HAN3, Xudong ZHOU1,2, Biao HE3, Wenshan ZHAO3, Qiang HE3, Bin MA3, Qibin CHEN1(
), Tianhua HAN3, Xudong ZHOU1,2, Biao HE3, Wenshan ZHAO3, Qiang HE3, Bin MA3, Qibin CHEN1( ), Peiwen YANG2(
), Peiwen YANG2( )
)
Received:2022-06-14
Accepted:2022-11-10
Online:2023-10-15
Published:2023-10-27
Contact:
Qibin CHEN,Peiwen YANG
摘要:
为探究土壤微生物多样性对有机碳源物料输入的响应特征,揭示土壤微生物多样性变化趋势与有机碳源物料输入的关系,筛选我国施用动物类粪便肥的长期定位试验中具有代表性的文章69篇,提取土壤细菌Shannon多样性指数数据120组和Chao l丰富度指数数据90组,纳入Meta分析,以不施肥和单施无机肥为对照,评估不同类型动物类粪便肥及施用方式对土壤细菌多样性指数的效应量,进一步分析不同区域、年均降水量、年均温度等条件下施用动物类粪便对土壤细菌群落变化的影响。结果表明,施用动物类粪便可显著提高根际细菌Shannon多样性指数和Chao l丰富度指数(P<0.05),促进效果依次为牛粪、鸡粪和猪粪;从作物类型看,种植茄科、豆科、禾本科作物及蔷薇科、葫芦科植物的土壤微生物多样性对动物类粪便施用的响应呈显著正效应(P<0.05);从施用方式看,单施动物类粪便与动物类粪便配施无机肥均对土壤细菌多样性的提高具有显著的正效应(P<0.05);从气候条件看,施用动物类粪便处理下土壤细菌多样性随降水量的增多、温度的升高显著提高(P<0.05),且年均降水量500~1 500 mm、年均温度5~15 ℃时促进作用最佳。可见施用动物类粪便可显著提高土壤细菌群落多样性,建议在茄科、豆科和禾本科等作物上推广应用以牛粪和鸡粪等为核心的单施动物类粪便或动物类粪便配施无机肥的施肥技术。此外,年均降水量及年均温度显著影响土壤细菌多样性对动物类粪便施用的响应,应进一步结合气象因素优化施肥技术,以实现构建土壤健康微生态,最终实现有效利用肥料资源、提高土壤生产力的目的。
中图分类号:
申云鑫, 施竹凤, 韩天华, 周旭东, 贺彪, 赵文山, 和强, 马斌, 陈齐斌, 杨佩文. 土壤微生物多样性对有机碳源物料输入的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 221-233.
Yunxin SHEN, Zhufeng SHI, Tianhua HAN, Xudong ZHOU, Biao HE, Wenshan ZHAO, Qiang HE, Bin MA, Qibin CHEN, Peiwen YANG. Responses of Soil Microbial Diversity to Input of Organic Carbon Source Materials[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 221-233.
指数 Index | 处理与对照 Treatment vs control | 模型 Model | 异质性检验Heterogeneity | 发表偏倚检验 Publication bias test | 数量 Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | P | 潜在值 Potential size | 临界值 Critical size | ||||
Shannon指数 Shannon index | AM vs NF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 83.063 | 0.000 01 | 36 658.9 | 280 | 54 |
| AM vs IF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 118.620 | 0.000 06 | 56 517.5 | 340 | 66 | |
Chao l指数 Chao l index | AM vs NF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 76.189 | 0.000 69 | 25 495.6 | 220 | 42 |
| AM vs IF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 79.615 | 0.002 08 | 45 977.9 | 250 | 48 | |
表1 施用动物类粪便对 Shannon 和 Chao l 指数数据的异质性及正态性检验
Table 1 Heterogeneity and normality test of Shannon and Chao l index after application of animal manure
指数 Index | 处理与对照 Treatment vs control | 模型 Model | 异质性检验Heterogeneity | 发表偏倚检验 Publication bias test | 数量 Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | P | 潜在值 Potential size | 临界值 Critical size | ||||
Shannon指数 Shannon index | AM vs NF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 83.063 | 0.000 01 | 36 658.9 | 280 | 54 |
| AM vs IF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 118.620 | 0.000 06 | 56 517.5 | 340 | 66 | |
Chao l指数 Chao l index | AM vs NF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 76.189 | 0.000 69 | 25 495.6 | 220 | 42 |
| AM vs IF | 随机效应模型 Random effect model | 79.615 | 0.002 08 | 45 977.9 | 250 | 48 | |

图1 施用不同动物类粪便对土壤细菌多样性指数的影响注:图中菱形点对应横轴的值代表效应值(lnR++);横直线上下限对应的值代表95%置信区间;右侧括号中数字为数据统计量。
Fig. 1 Effect of manure application on soil bacterial diversity indexNote: The value of the horizontal axis corresponding to the diamond points in the figure represents the effect value (lnR++); the upper and lower bound of the horizontal line represents the 95% confidence interval; the numbers in the brackets on the right are data statistics.
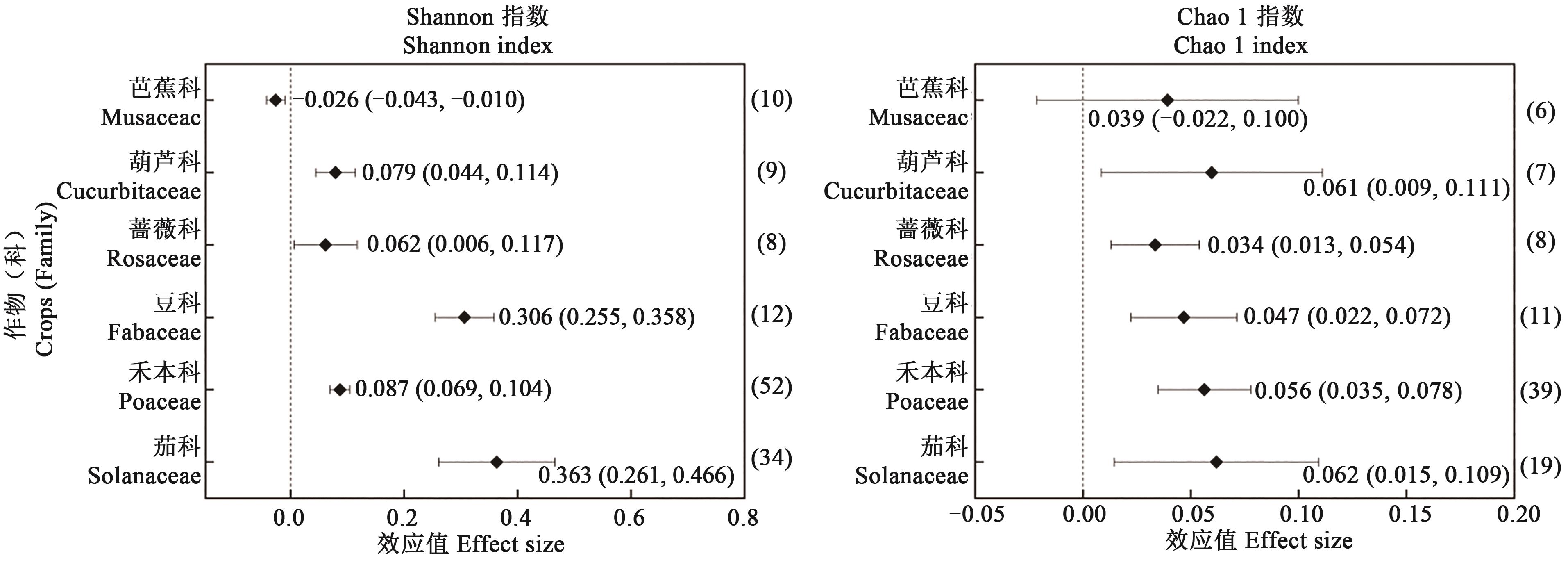
图2 不同作物类型下施用动物粪便对土壤细菌多样性指数的影响注:图中菱形点对应横轴的值代表效应值(lnR++);横直线上下限对应的值代表95%置信区间;右侧括号中数字为数据统计量。
Fig. 2 Effects of animal manure application on soil bacterial diversity index under different crop typesNote: The value of the horizontal axis corresponding to the diamond points in the figure represents the effect value (lnR++); the upper and lower bound of the horizontal line represents the 95% confidence interval; the numbers in the brackets on the right are data statistics.
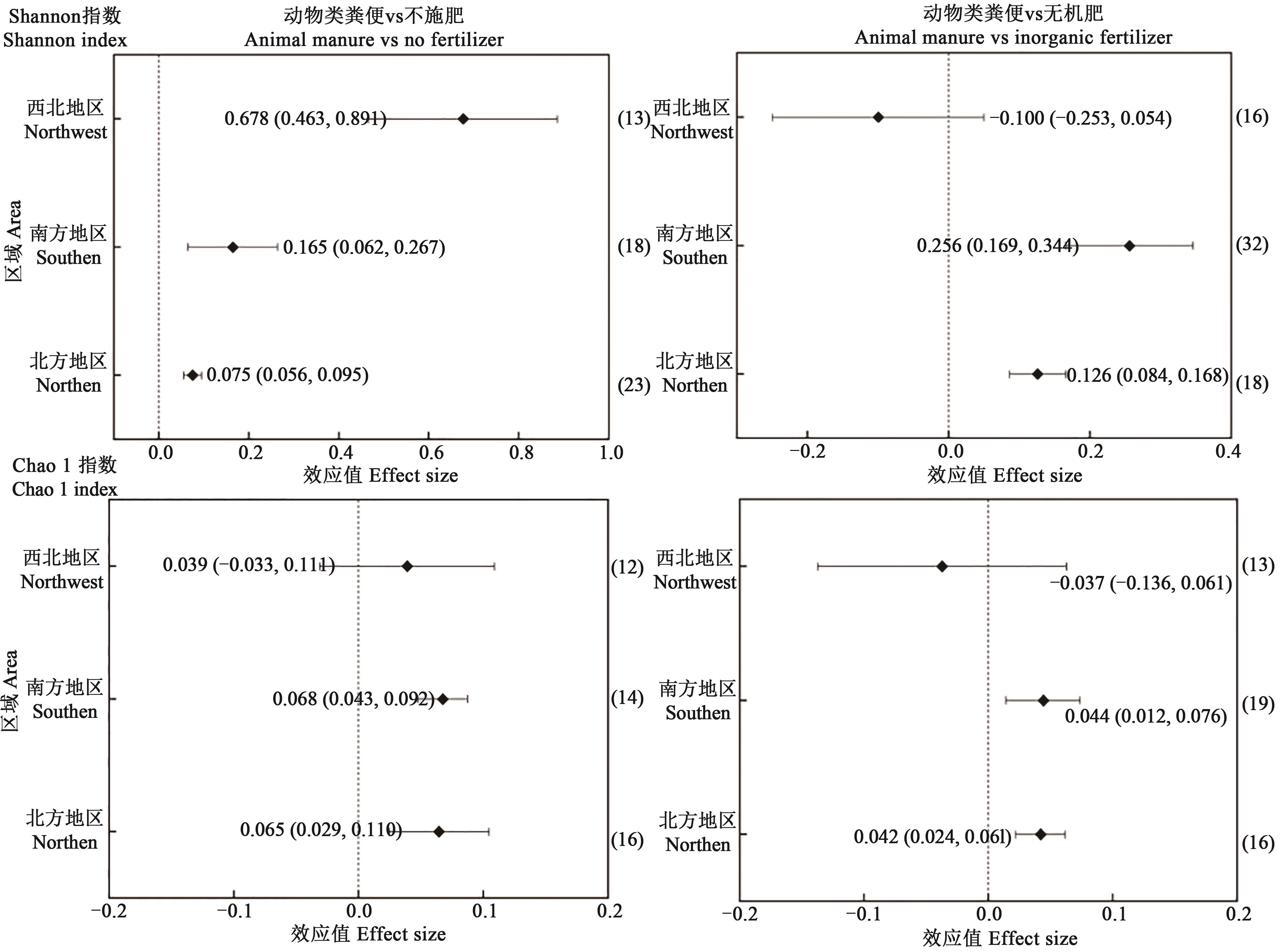
图4 不同区域施用动物粪便对土壤细菌多样性指数的影响注:图中菱形点对应横轴的值代表效应值(lnR++);横直线上下限对应的值代表95%置信区间;右侧括号中数字为数据统计量。
Fig. 4 Effects of animal manure application on soil bacterial diversity index in different areasNote: The value of the horizontal axis corresponding to the diamond points in the figure represents the effect value (lnR++); the upper and lower bound of the horizontal line represents the 95% confidence interval; the numbers in the brackets on the right are data statistics.

图5 不同降水量下施用动物粪便对土壤细菌多样性指数的影响注:图中菱形点对应横轴的值代表效应值(lnR++);横直线上下限对应的值代表95%置信区间;右侧括号中数字为数据统计量。
Fig. 5 effect of animal manure application on soil bacterial diversity index under different precipitationNote:The value of the horizontal axis corresponding to the diamond points in the figure represents the effect value (lnR++);the upper and lower bound of the horizontal line represents the 95% confidence interval; the numbers in the brackets on the right are data statistics.
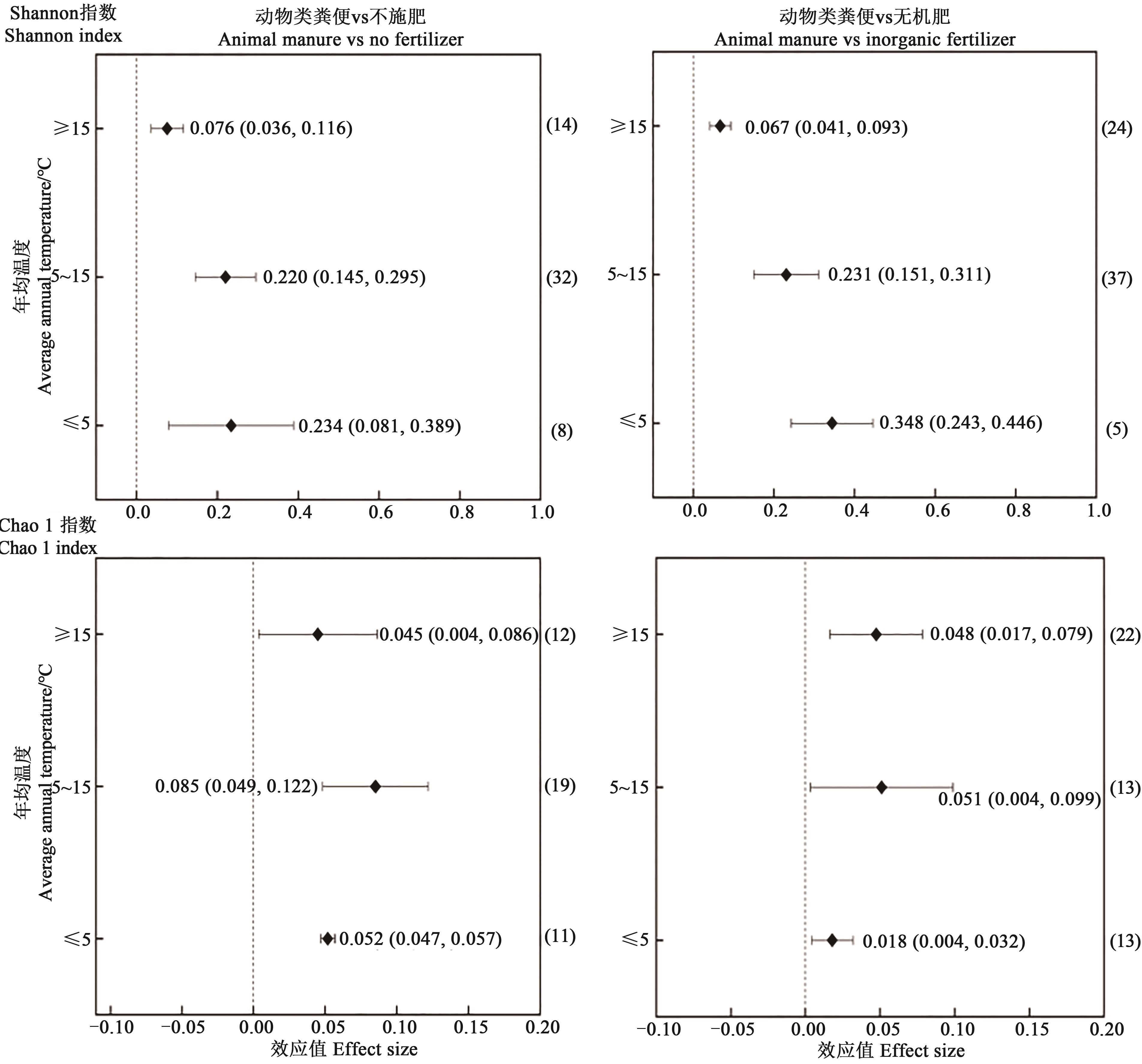
图6 不同年均温度下施用动物粪便对土壤细菌多样性指数的影响注:图中菱形点对应横轴的值代表效应值(lnR++);横直线上下限对应的值代表95%置信区间;右侧括号中数字为数据统计量。
Fig. 6 Effects of animal manure application on soil bacterial diversity index at different annual temperaturesNote:The value of the horizontal axis corresponding to the diamond points in the figure represents the effect value (lnR++);the upper and lower bound of the horizontal line represents the 95% confidence interval; the numbers in the brackets on the right are data statistics.
| 1 | RANVA S, SINGH Y V, JAIN N, et al.. Impact of safe rock® minerals, mineral fertilizers, and manure on the quantity and quality of the wheat yield in the rice-wheat cropping system [J]. Plants, 2022, 11(2): 183-198. |
| 2 | 赵秀东,陈晓芳,袁自然, 等. 有机肥替代对土壤养分的影响[J].中国农学通报,2022,38(16):74-80. |
| ZHAO X D, CHEN X F, YUAN Z R, et al.. Organic fertilizer substitution: effects on soil nutrients [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull.,2022,38(16):74-80. | |
| 3 | 安祥瑞,江尚焘,谢昶琰, 等. 减施化肥配施有机肥对荔枝园土壤微生物区系的影响[J].应用生态学报,2022,33(4):1099-1108. |
| AN X R, JIANG S T, XIE C Y, et al.. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizers combined with organic fertilizers on soil microbial community in litchi orchards [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2022,33( 4):1099-1108. | |
| 4 | SCHLOTER M, DILLY O, MUNCH J C. Indicators for evaluating soil quality [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2003, 98(1-3): 255-262. |
| 5 | 李玉林,徐承昱,胡雪, 等. 有机和常规施肥模式的土壤养分特征及对不同食味型粳稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2022,36(2):445-455. |
| LI Y L, XU C Y, HU X, et al.. Soil nutrition characteristic of organic and conventional fertilization models and effects on yields and qualities of japonica rice of different palatability types [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2022,36(2):445-455. | |
| 6 | 郝海婷, 王若愚, 赵霞, 等. 基于高通量测序技术的堆肥对兰州百合根际微生物多样性的影响 [J]. 西北农业学报, 2017, 26(3): 437-447. |
| HAO H T, WANG R Y, ZHAO X, et al.. Effect of compost on rhizosphere microbial community of Lanzhou-Lily based on high throughput sequencing [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2017, 26(3): 437-447. | |
| 7 | GEISSELER D, SCOW K M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms–a review [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2014, 75: 54-63. |
| 8 | STEWART W M, DIBB D W, JOHNSTON A E, et al.. The contribution of commercial fertilizer nutrients to food production [J]. Agron. J., 2005, 97(1): 1-6. |
| 9 | 李琳,向丹,武亚芬, 等. 长期不同施肥方式对日光温室番茄土壤养分和微生物群落结构的影响 [J].应用生态学报,2022,33(2):415-422. |
| LI L, XIANG D, WU Y F, et al.. Effects of long-term different fertilization patterns on soil nutrients and microbial community structure of tomato in a solar greenhouse [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2022, 33(2):415-422 | |
| 10 | 张慧,余端,卢文才, 等. 不同减氮施肥模式对水稻土壤养分及可培养微生物数量的影响[J].农学学报,2021,11(9):33-37. |
| ZHANG H, YU D, LU W C, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen reduction fertilization models on rice soil nutrients and the number of cultivable microorganism [J]. J. Agric. Sci., 2021,11(9):33-37. | |
| 11 | NADA R S, ASHMAWI A E, MADY E, et al.. Effect of organic manure and plant growth promoting microbes on yield, quality and essential oil constituents of fennel bulb (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) [J]. J. Ecol. Eng., 2022, 23(5): 149-164. |
| 12 | MI W, CHEN C, MA Y, et al.. The combined application of mineral fertilizer and organic amendments improved the stability of soil water-stable aggregates and C and N accumulation [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(2): 469 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 13 | 郭雨浓,刘宝玉,郑直, 等. 不同施肥对河套灌区瓜田土壤养分及甜瓜生长和养分利用的影响[J].水土保持学报,2021,35(4):230-236. |
| GUO Y N, LIU B Y, ZHENG Z, et al.. Effects of different fertilizations on soil nutrients and muskmelon growth and nutrient utilization in the Hetao irrigation district [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2021,35(4):230-236. | |
| 14 | BOUHIA Y, HAFIDI M, OUHDOUCH Y, et al.. Conversion of waste into organo-mineral fertilizers: current technological trends and prospects [J]. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., 2022, 21: 425-446. |
| 15 | 刘强,穆兴民,王新民, 等. 长期不同施肥方式对旱地轮作土壤养分和作物产量的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2021,39(3):122-128. |
| LIU Q, MU X M, WANG X M, et al.. Effects of different long-term fertilization on crop yield and soil nutrients under rotation planting in arid region [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas,2021,39(3):122-128. | |
| 16 | ZHOU J, GUAN D, ZHOU B, et al.. Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in northeast China [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2015, 90: 42-51. |
| 17 | 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 吐尔逊·吐尔洪, 山其米克, 等. 施肥对不同生育期甜高粱土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 草地学报,2021,29(1):103-113. |
| Kuerban Zaituniguli, Tuerhong Tuerxun, Shanqimike, et al.. Study on the change of soil nutrient content in the growth period of sweet sorghum under different fertilization [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021,29(1):103-113. | |
| 18 | BEBBER D P, RICHARDS V R. A meta-analysis of the effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil microbial diversity [JOL]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2022, 175: 104450 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 19 | BORENSTEIN M, HEDGES L V, HIGGINS J P T, et al.. Introduction to Meta-analysis [M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 2021:1-452. |
| 20 | WANG C, LIU D, BAI E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2018, 120: 126-133. |
| 21 | WANG S, AUGÉ R M, TOLER H D. Arbuscular mycorrhiza formation and its function under elevated atmospheric O3: a meta-analysis [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2017, 226: 104-117. |
| 22 | TRESEDER K K. Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: a Meta-analysis of ecosystem studies [J]. Ecol. Lett., 2008, 11(10): 1111-1120. |
| 23 | WITTIG V E, AINSWORTH E A, NAIDU S L, et al.. Quantifying the impact of current and future tropospheric ozone on tree biomass, growth, physiology and biochemistry: a quantitative Meta-analysis [J]. Glob. Chang. Biol., 2009, 15(2): 396-424. |
| 24 | ZHANG H Y, LÜ X T, HARTMANN H, et al.. Foliar nutrient resorption differs between arbuscular mycorrhizal and ectomycorrhizal trees at local and global scales [J]. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr., 2018, 27(7): 875-885. |
| 25 | 王晓娇, 张仁陟, 齐鹏, 等. Meta 分析有机肥施用对中国北方农田土壤CO2排放的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019,35(10):99-107. |
| WANG X J, ZHANG R S, QI P, et al.. Meta-analysis on farmland soil CO2 emission in Northern China affected by organic fertilizer [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2019, 35(10): 99 -107. | |
| 26 | ROSENBERG M S, ADAMS D C, GUREVITCH J. MetaWin: Statistical Software for Meta-analysis with Resampling Tests [M]. Sunderland :Sinauer Associates, 1997. |
| 27 | QIU M, ZHANG R, XUE C, et al.. Application of bio-organic fertilizer can control fusarium wilt of cucumber plants by regulating microbial community of rhizosphere soil [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2012, 48(7): 807-816. |
| 28 | 申云鑫,沈广材,包玲凤, 等. 烟草青枯病病株根际土壤可培养细菌多样性特征分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(4):871-878. |
| SHEN Y X, SHEN G C, BAO L F,et al.. Diversity of culturable bacteria in rhizosphere soil of tobacco with bacterial wilt disease [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2022, 35(4):871-878. | |
| 29 | 王明友,张红,张桂祥.鸡粪配施尿素对扁豆根际微环境特征及产量、品质的影响[J].水土保持通报,2017,37(6):101-105, 112. |
| WANG M Y, ZHANG H, ZHANG G X, et al.. Effect of chicken manure co-applied with urea on rhizospheric characteristics and yield, quality of Lablab Purpureus [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2017,37(6):101-105, 112. | |
| 30 | 郭莹,王一明,巫攀, 等. 长期施用粪肥对水稻土中微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J].应用与环境生物学报,2019,25(3):593-602. |
| GUO Y, WANG Y M, WU P, et al.. Influence of long-term manure application in paddy soil on the functional diversity of microbial community [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Environ., 2019, 25(3): 593-602. | |
| 31 | 付修勇,井大炜,段晓尘, 等. 不同施肥措施对德州市农田土壤生物学性状的影响[J].水土保持通报,2017,37(5):76-80, 85. |
| FU X Y, JIN D W, DUAN X C, et al.. Effect of different fertilization measures on soil biological characteristics in farmland of Dezhou city [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 37(5):76-80, 85. | |
| 32 | CAI F, PANG G, LI R X, et al.. Bioorganic fertilizer maintains a more stable soil microbiome than chemical fertilizer for monocropping [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2017, 53(8): 861-872. |
| 33 | 李焕苓,查晋燕,魏志远, 等. 化肥减施对荔枝园土壤微生物功能多样性的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2022(2):25-33. |
| LI H L, ZHA J Y, WEI Z Y, et al.. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction on the function diversity of soil microbial community in litchi orchard [J]. China Soils Fert., 2022(2):25-33. | |
| 34 | SHEN Z, WANG D, RUAN Y, et al.. Deep 16S rRNA pyrosequencing reveals a bacterial community associated with banana fusarium wilt disease suppression induced by bio-organic fertilizer application [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e98420 [2022-05-12] .. |
| 35 | CHANG H, ZHU X, JIE W U, et al.. Dynamics of microbial diversity during the composting of agricultural straw [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2021, 20(5): 1121-1136. |
| 36 | 孔云, 张婷, 李刚, 等. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2018, 33(6): 205-211. |
| KONG Y, ZHANG T, LI G, et al.. Effects of different fertilization regimes on maize field nematode community in fluvo-aquic soil in North China [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2018, 33(6): 205-211. | |
| 37 | 刘振香, 刘鹏, 贾绪存, 等. 不同水肥处理对夏玉米田土壤微生物特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(1): 113-121. |
| LIU Z X, LIU P, JIA X C, et al.. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on soil microbial properties in summer maize field [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2015, 26(1): 113-121. | |
| 38 | 李江涛, 罗甜甜, 杜满聪, 等. 畜禽粪肥添加及干湿交替强度对土壤微生物功能多样性的影响 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2018, 45(6): 68-77. |
| LI J T, LUO T T, DU M C, et al.. Effects of livestock and poultry manure amendment and wetting-drying cycle on functional diversity of soil microbial community [J]. Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2018, 45(6): 68-77. | |
| 39 | WU L, CHEN J, WU H, et al.. Insights into the regulation of rhizosphere bacterial communities by application of bio-organic fertilizer in Pseudostellaria heterophylla monoculture regime [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2016, 7: 1788[2022-05-12]. . |
| 40 | LIU Z, GUO Q, FENG Z, et al.. Long-term organic fertilization improves the productivity of kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis Planch.) through increasing rhizosphere microbial diversity and network complexity [J/OL]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2020, 147: 103426 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 41 | ZHAO J, LIU J, LIANG H, et al.. Manipulation of the rhizosphere microbial community through application of a new bio-organic fertilizer improves watermelon quality and health [J/OL]. PloS One, 2018, 13(2): e0192967 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 42 | CHEN X, LI Z, LIU M, et al.. Microbial community and functional diversity associated with different aggregate fractions of a paddy soil fertilized with organic manure and/or NPK fertilizer for 20 years [J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2015, 15(2): 292-301. |
| 43 | 张超, 周旭, 张海, 等. 苹果专用肥对旱地果园土壤酶活性以及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(12): 3485-3492. |
| ZHANG C, ZHOU X, ZHANG H, et al.. Effect of apple special fertilizer on soil enzyme activities and functional diversity of microbial community in a non-irrigated apple orchard [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2017, 36(12): 3485-3492. | |
| 44 | QIU M, ZHANG R, XUE C, et al.. Application of bio-organic fertilizer can control fusarium wilt of cucumber plants by regulating microbial community of rhizosphere soil [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2012, 48(7): 807-816. |
| 45 | ZHAOXIANG W, HUIHU L, QIAOLI L, et al.. Application of bio-organic fertilizer, not biochar, in degraded red soil improves soil nutrients and plant growth [J/OL]. Rhizosphere, 2020, 16: 100264 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 46 | ZHU L, JIA X, LI M, et al.. Associative effectiveness of bio-organic fertilizer and soil conditioners derived from the fermentation of food waste applied to greenhouse saline soil in Shandong province, China [J/OL]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2021, 167: 104006 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 47 | LI W, ZHANG F, CUI G, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility, microbial community composition, and potato growth [J/OL]. Sci. Asia, 2021, 47: 347 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 48 | TRIPATHI B M, STEGEN J C, KIM M, et al.. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria [J]. ISME J., 2018, 12(4): 1072-1083. |
| 49 | LIU S, WANG Z, NIU J, et al.. Changes in physicochemical properties, enzymatic activities, and the microbial community of soil significantly influence the continuous cropping of Panax quinquefolius L. (American ginseng) [J]. Plant Soil, 2021, 463(1): 427-446. |
| 50 | WU L, NING D, ZHANG B, et al.. Global diversity and biogeography of bacterial communities in wastewater treatment plants [J]. Nat. Microbiol., 2019, 4(7): 1183-1195. |
| 51 | BURNS R G, DEFOREST J L, MARXSEN J, et al.. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2013, 58: 216-234. |
| 52 | 井大炜, 王明友, 张红, 等. 蚯蚓粪配施尿素对豇豆根系特征与根际土腐殖质的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(1): 212-219. |
| JING D W, WANG M Y, ZHANG H, et al.. Effects of vermicompost co-applied with urea on root characteristics and humus in rhizosphere soil of cowpea [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2017, 48(1): 212-219. | |
| 53 | NEMERGUT D R, COSTELLO E K, MEYER A F, et al.. Structure and function of alpine and arctic soil microbial communities [J]. Res. Microbiol., 2005, 156(7): 775-784. |
| 54 | 侯萌,陈一民,焦晓光, 等. 两种气候条件下不同有机质含量农田黑土真菌群落结构特征[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(9):2822-2832. |
| HOU M, CHEN Y M, JIAO X G, et al.. Characteristics of fungal community structure in arable mollisols with different organic matter content under two climatic conditions [J]. Mocrobiology, 2020,47(9):2822-2832. |
| [1] | 孟亚轩, 马玮, 姚旭航, 孙颖琦, 钟鑫, 黄山, 瓮巧云, 刘颖慧, 袁进成. 玉米产量对氮肥的响应因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号