




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 153-160.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.1032
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
孟亚轩1( ), 马玮2, 姚旭航1, 孙颖琦1, 钟鑫1, 黄山1, 瓮巧云1, 刘颖慧1, 袁进成1(
), 马玮2, 姚旭航1, 孙颖琦1, 钟鑫1, 黄山1, 瓮巧云1, 刘颖慧1, 袁进成1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-03
接受日期:2022-10-24
出版日期:2023-07-15
发布日期:2023-08-25
通讯作者:
袁进成
作者简介:孟亚轩 E-mail:bbbryant@126.com;
基金资助:
Yaxuan MENG1( ), Wei MA2, Xuhang YAO1, Yingqi SUN1, Xin ZHONG1, Shan HUANG1, Qiaoyun WENG1, Yinghui LIU1, Jincheng YUAN1(
), Wei MA2, Xuhang YAO1, Yingqi SUN1, Xin ZHONG1, Shan HUANG1, Qiaoyun WENG1, Yinghui LIU1, Jincheng YUAN1( )
)
Received:2021-12-03
Accepted:2022-10-24
Online:2023-07-15
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
Jincheng YUAN
摘要:
为明确不同生态条件下施氮对我国玉米产量的影响特征,通过中国知网、维普资讯、万方数据库进行文献检索,共获得78篇文献,构建了525个独立数据集,利用整合分析方法,以不施氮为对照,增产率为量度,定量分析不同氮肥运筹(施氮量,N;基追比,DR)、不同地域、不同气象因子(平均气温,Ta;生长季平均气温,Tg;年平均降雨量,Pa;生长季平均降雨量,Pg)、不同土壤有机质(soil organic matter,SOM)条件下施氮对玉米产量的影响。Meta分析结果表明,施氮可以显著提升玉米产量,增产率为17.64%。当以250<N≤300 kg·hm-2且DR=1∶2的方式施氮对玉米增产效果最佳。不同试验区域中,西南地区施氮处理增产率最高(28.15%),东南地区增产率最低(7.86%)。不同气象因子条件下氮素对玉米的增产效率不同,当5<Ta≤10 ℃、400<Pa≤800 mm、Tg≤25 ℃、Pg>400 mm时施氮的增产效应最高。施氮效果与土壤有机质含量密切相关,在15<SOM≤25 g·kg-1时,施氮对玉米的增产率最高,为18.36%。综上所述,生长季降雨量和土壤有机质含量较高、气温适宜的区域有利于发挥施氮的增产效应;因此,西南、西北地区为施氮的适宜区域;基追比为1∶2施入250~300 kg·hm-2氮肥为较高效的施氮模式。
中图分类号:
孟亚轩, 马玮, 姚旭航, 孙颖琦, 钟鑫, 黄山, 瓮巧云, 刘颖慧, 袁进成. 玉米产量对氮肥的响应因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 153-160.
Yaxuan MENG, Wei MA, Xuhang YAO, Yingqi SUN, Xin ZHONG, Shan HUANG, Qiaoyun WENG, Yinghui LIU, Jincheng YUAN. Study on the Response Factors of Maize Yield to Nitrogen Fertilizer[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 153-160.
| 解释变量Categorical explanatory variable | 分组Group |
|---|---|
| N:氮肥施用量 N application rate/(kg·hm-2) | N≤100; 100<N≤150; 150<N≤200; 200<N≤250; 250<N≤300; N>300 |
试验区域 Experiment region | 东北、华北、西北、东南、西南 、华中、华东 Northeast, North, Northwest, Southeast, Southwest, Central of China, East of China |
Ta:年平均气温 Average annual temperature/℃ | Ta≤5; 5<Ta≤10; 10<Ta≤15 |
Pa:年平均降雨量 Average annual precipitation/mm | Pa≤400; 400<Pa≤800; 800<Pa≤1 200;Pa>1 200 |
Tg:生长季平均气温 Average growing season temperature/℃ | Tg≤25; Tg>25 |
Pg:生长季平均降雨量 Average precipitation during the growing season/mm | Pg≤400; Pg>400 |
DR:基追比 Dressing ratio | 全基施; DR≤1;1<DR≤2;DR>2;全追施 All base; DR≤1;1<DR≤2; DR>2; All topdressing |
| SOM:土壤有机质含量Soil organic matter/(g·kg-1) | SOM≤15; 15<SOM≤25; SOM>25 |
表1 试验解释变量分类
Table 1 Classification of experiment data
| 解释变量Categorical explanatory variable | 分组Group |
|---|---|
| N:氮肥施用量 N application rate/(kg·hm-2) | N≤100; 100<N≤150; 150<N≤200; 200<N≤250; 250<N≤300; N>300 |
试验区域 Experiment region | 东北、华北、西北、东南、西南 、华中、华东 Northeast, North, Northwest, Southeast, Southwest, Central of China, East of China |
Ta:年平均气温 Average annual temperature/℃ | Ta≤5; 5<Ta≤10; 10<Ta≤15 |
Pa:年平均降雨量 Average annual precipitation/mm | Pa≤400; 400<Pa≤800; 800<Pa≤1 200;Pa>1 200 |
Tg:生长季平均气温 Average growing season temperature/℃ | Tg≤25; Tg>25 |
Pg:生长季平均降雨量 Average precipitation during the growing season/mm | Pg≤400; Pg>400 |
DR:基追比 Dressing ratio | 全基施; DR≤1;1<DR≤2;DR>2;全追施 All base; DR≤1;1<DR≤2; DR>2; All topdressing |
| SOM:土壤有机质含量Soil organic matter/(g·kg-1) | SOM≤15; 15<SOM≤25; SOM>25 |
模型 Model | 增产率 Increase rate/% | 置信区间Confidence interval/% | P值 P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限Lower limit | 上限Upper limit | |||
随机效应模型 Random effect model | 17.64 | 16.25 | 19.05 | 0.000 |
表2 施氮量对玉米产量的平均效应值
Table 2 Average effect size of maize yield under nitrogen application
模型 Model | 增产率 Increase rate/% | 置信区间Confidence interval/% | P值 P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限Lower limit | 上限Upper limit | |||
随机效应模型 Random effect model | 17.64 | 16.25 | 19.05 | 0.000 |
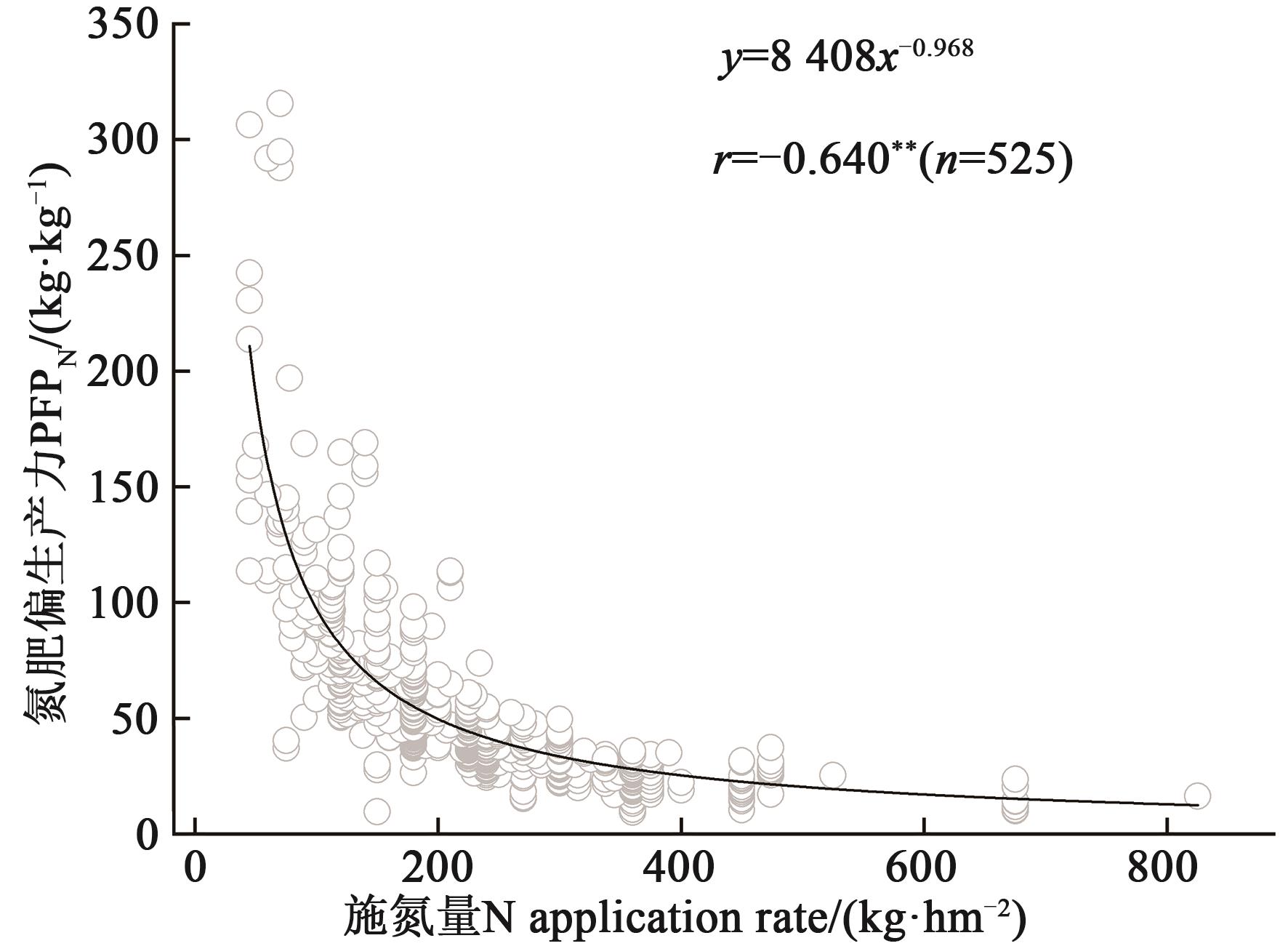
图1 玉米氮肥偏生产力与施氮量的相关关系注: **表示在P<0.01水平相关显著;n表示样本量。
Fig. 1 Relationship between PFPN and N ratesNote: ** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level; n indicates sample size.
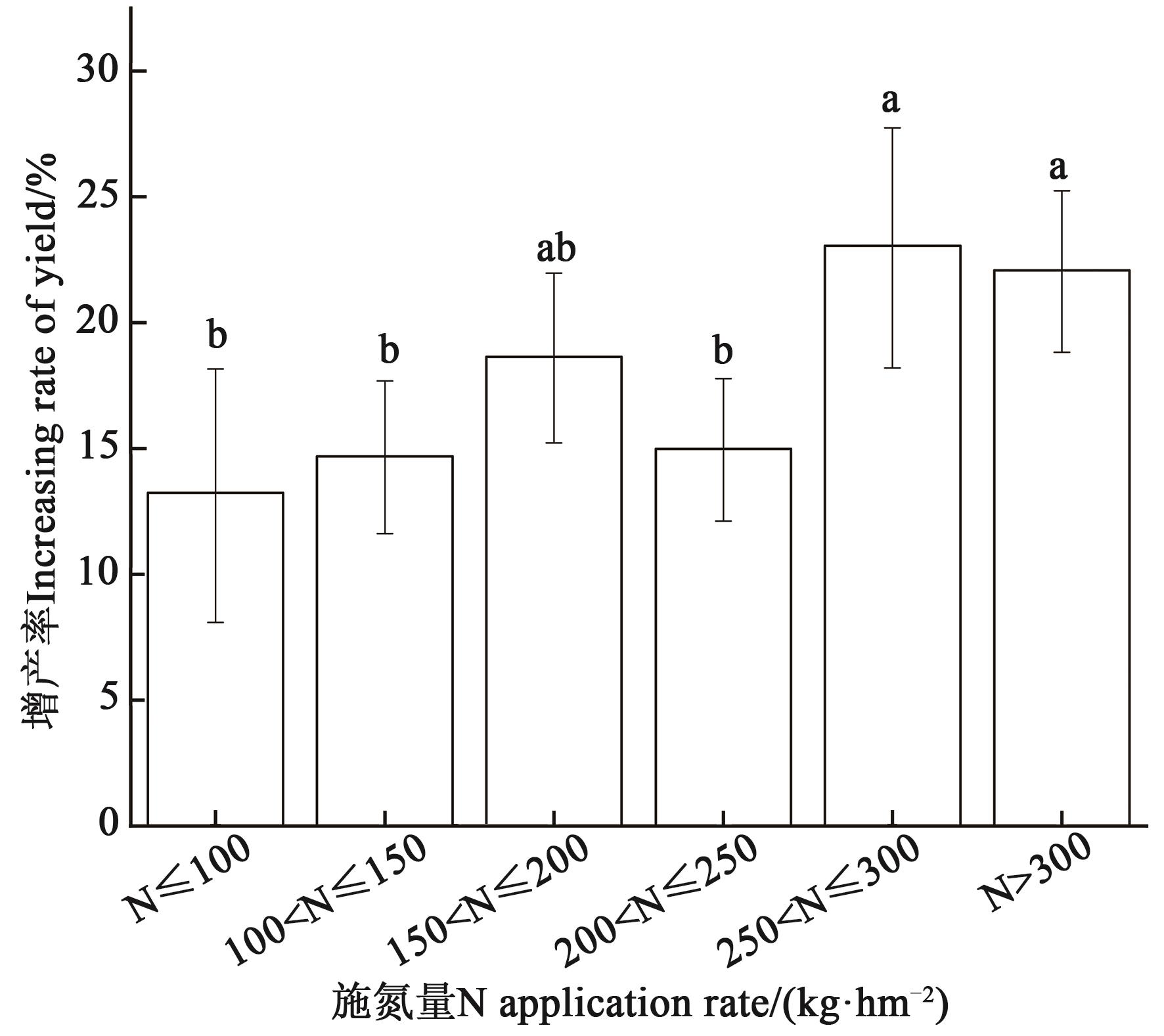
图2 不同氮肥用量玉米的增产率注:不同小写字母表示不同组间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Yield increase rate of maize under different nitrogen fertilizer ratesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
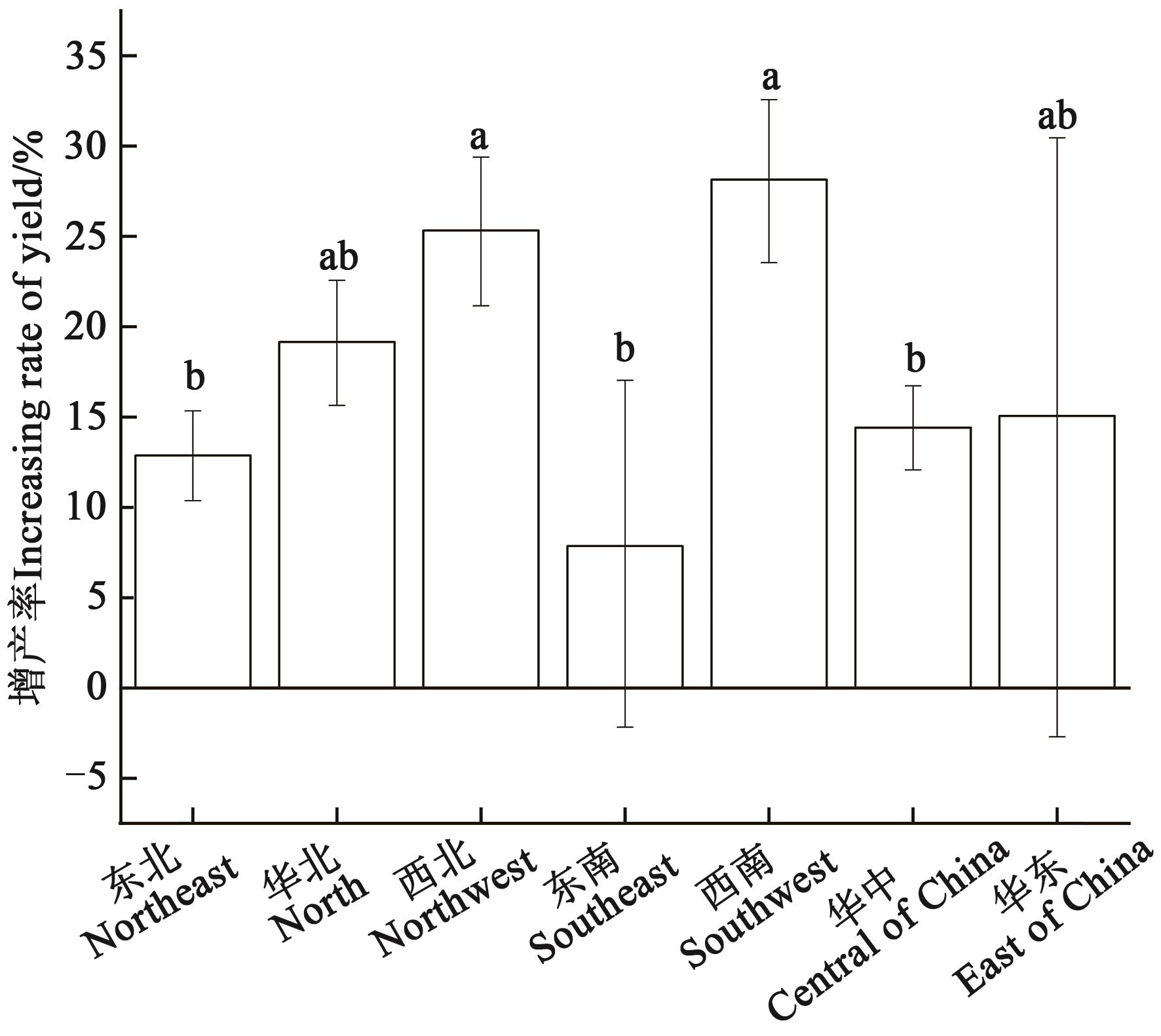
图3 不同试验区域条件下玉米的增产率注:不同小写字母表示不同组间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Yield increase rate of maize under different regionNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.

图4 不同气温条件下玉米的增产率注:不同小写字母表示不同组间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Yield increase rate of maize under different temperature conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
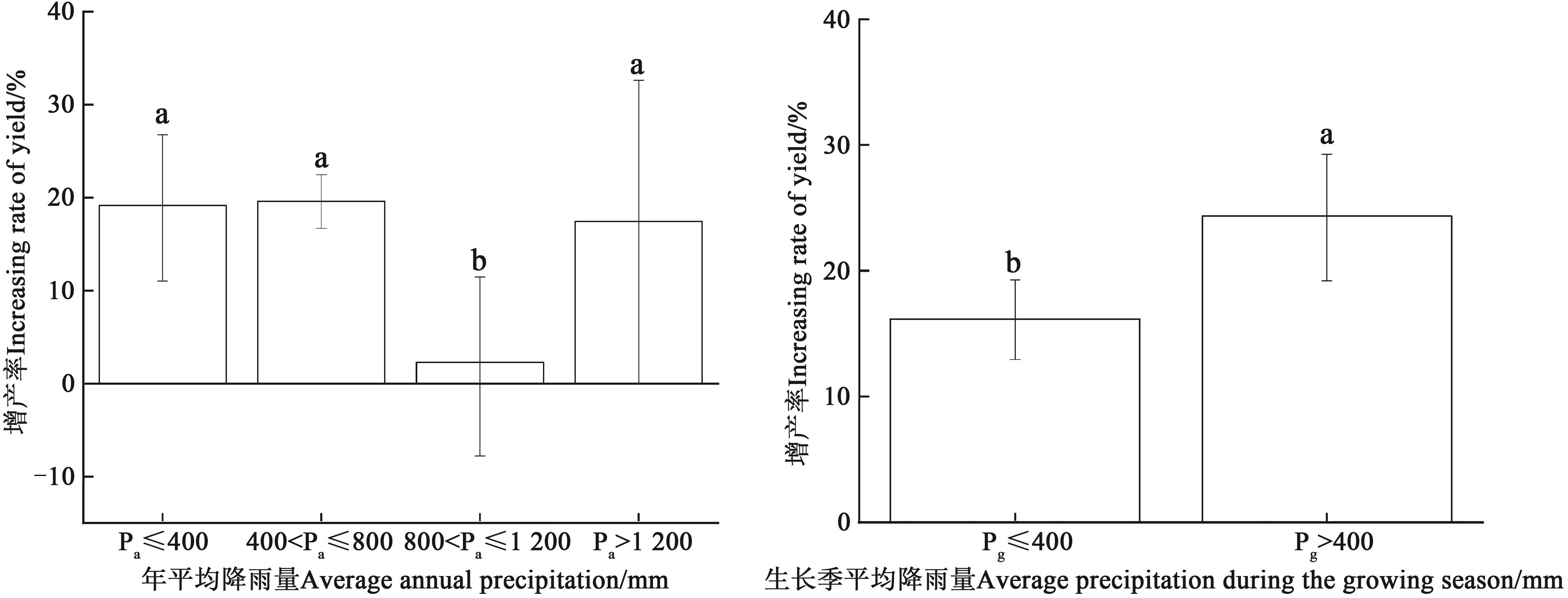
图5 不同年平均降水量条件下玉米的增产率注:不同小写字母表示不同组间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Yield increase rate of maize under different annual average precipitationNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
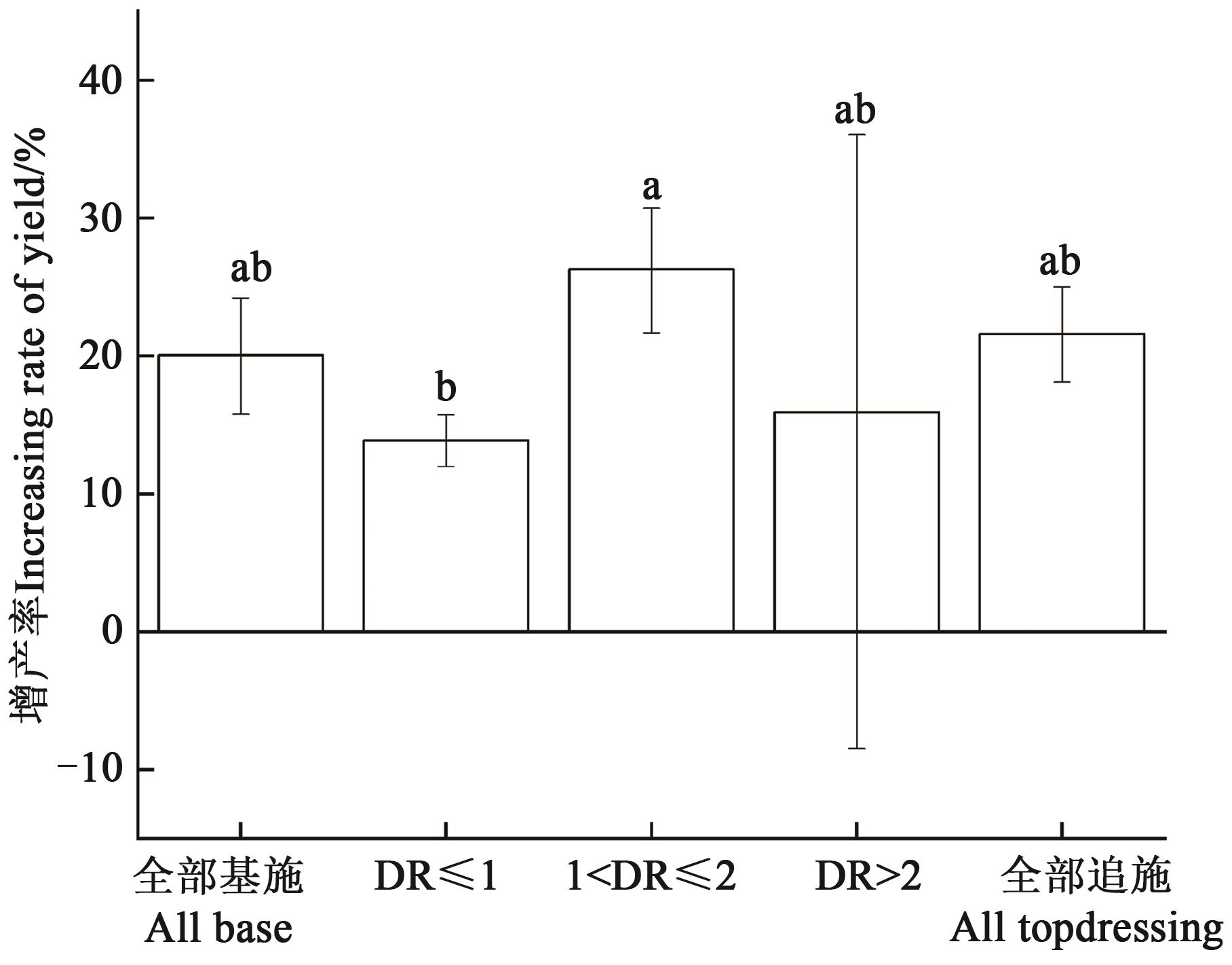
图6 不同施氮方式下玉米的增产率注:不同小写字母表示不同组间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Yield increase of maize under different nitrogen application methodsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
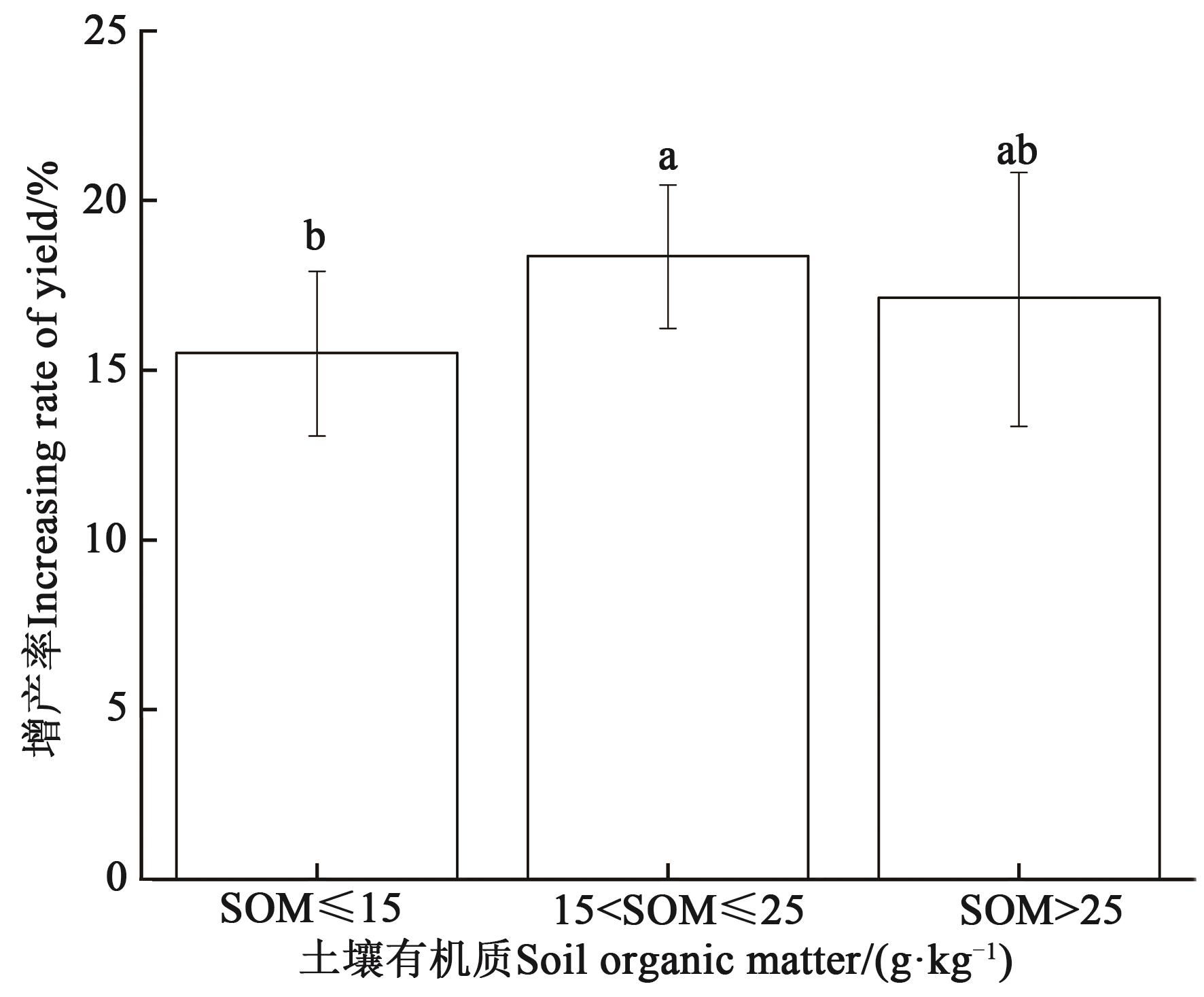
图7 不同土壤有机质条件下玉米的增产率注:不同小写字母表示不同组间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 7 Yield increase of maize under different soil organic matter conditionsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different groups at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 刘海光, 罗振, 董合忠. 植物硝态氮吸收和转运的调控研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(6): 192-201. |
| LIU H G, LUO Z, DONG H Z. Research progress on the regulation of N O 3 - uptake and transport in plant [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2021, 37(6): 192-201. | |
| 2 | 李姗, 黄允智, 刘学英, 等. 作物氮肥利用效率遗传改良研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(7): 629-640. |
| LI S, HUANG Y Z, LIU X Y, et al.. Genetic improvement of nitrogen use efficiency in crops [J]. Hereditas, 2021, 43(7):629-640. | |
| 3 | 胡春胜, 张玉铭, 秦树平, 等. 华北平原农田生态系统氮素过程及其环境效应研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(10): 1501-1514. |
| HU C S, ZHANG Y M, QIN S P, et al.. Nitrogen processes and related environmental effects on agro-ecosystem in the North China Plain [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2018, 26(10): 1501-1514. | |
| 4 | 李婷婷, 李文娟. 我国玉米空间格局演变及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2021, 42(2): 87-95. |
| LI T T, LI W J. Resrarch progress on the evoltion of maize spatial pattern and its infulencing factors in China [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region Plan., 2021, 42(2):87-95. | |
| 5 | 丁相鹏, 李广浩, 张吉旺, 等. 控释尿素基施深度对夏玉米产量和氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(21): 4342-4354. |
| DING X P, LI G H, ZHANG J W, et al.. Effects of base application depths of controlled release urea on yield and nitrogen utilization of summer maize [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2020, 53(21): 4342-4354 . | |
| 6 | 张雨珊, 杨恒山, 葛选良, 等. 水氮调控对作物碳代谢影响的研究进展[J]. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 36(3): 253-257. |
| ZHANG Y S, YANG H S, GE X L, et al.. Research progress on effects of water and nitrogen regulation on crop carbon metabolism [J]. J. Inner Mongolia Minzu Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 36(3):253-257. | |
| 7 | 李明悦, 金修宽, 高伟, 等. 不同施氮水平对鲜食玉米产量及氮素吸收的影响[J]. 天津农业科学, 2020, 26(8): 53-55. |
| LI M Y, JIN X K, GAO W, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen apphcation on fresh com yield and nitrogen absorption [J].Tianjin Agric. Sci., 2020, 26(8):53-55. | |
| 8 | 宁芳, 张元红, 温鹏飞, 等. 不同降水状况下旱地玉米生长与产量对施氮量的响应[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(5): 777-791. |
| NING F, ZHANG Y H, WEN P F, et al.. Responses of maize growth and yield to nitrogen application in dryland under different precipitation conditions [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(5):777-791. | |
| 9 | 张学林, 徐钧, 安婷婷, 等. 不同氮肥水平下玉米根际土壤特性与产量的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(14): 2687-2699. |
| ZHANG X L, XU J, AN T T, et al.. Relationship between rhizosphere soil properties and yield of maize at different nitrogen levels [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2016, 49(14): 2687-2699. | |
| 10 | 邬小春, 杨晓军, 高荣嵘, 等. 不同氮肥处理对西北区春玉米产量的影响[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2020, 66(8): 44-48. |
| WU X C, YANG X J, GAO R R, et al.. Effect of different nitrogn treatments on spring maize yield in Northwest China [J]. Shaanxi J. Agric. Sci., 2020, 66(8): 44-48. | |
| 11 | 费永红, 钟维, 韦德斌, 等. 施氮水平对不同玉米品种产量的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2016(11): 9-10. |
| FEI Y H, ZHONG W, WEI D B, et al.. Effects of N-fertilizer levels on yield of different m aize varietie [J]. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2016(11): 9-10. | |
| 12 | 刘永花, 郝建平, 杜天庆, 等. 施氮水平和追氮时间对玉米子粒产量的影响[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 32(6): 498-501. |
| LIU Y H, HAO J P, DU T Q, et al.. Effect of nitrogen appllication levels and top application time on grain yield of maize (Zea mays L.) [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2012, 32(6): 498-501. | |
| 13 | 魏欢欢. 耕作措施对黄土高原旱地春玉米和冬小麦产量及水分利用效率影响的整合分析[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017. |
| WEI H H. Meta analysis on impact of tillage practices on yield and water use efficiency of spring maize and winter wheat on the Loess plateau [D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. | |
| 14 | 王成宝, 霍琳, 温美娟, 等. 灌耕灰钙土耕层物理性质及其对玉米产量的影响[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2021, 52(7):24-32. |
| WANG C B, HO L, WEN M J, et al.. Soil physical properties and their effects on corn yield in irrigated farming sierozem [J]. Gansu Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 52(7):24-32. | |
| 15 | HEDGES L V, GUREVITCH J, CURTIS P S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology [J]. Ecology, 1999, 80:1150-1156. |
| 16 | ZHANG T A, CHEN-HAN Y H, RUAN H H. Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes [J]. ISME J., 2018, 12(7):1817-1825. |
| 17 | DARYANTO S, WANG L, JACINTHE P. Impacts of no-tillage management on nitrate loss from corn, soybean and wheat cultivation: a meta-analysis [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1):12117 [2021-11-03]. . |
| 18 | EGGER M, DAVEY S G, SCHNEIDER M, et al.. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test [J]. BMJ, 1997, 315(7109):629-634. |
| 19 | SIMONS M, SAHA R, GUILLARD L, et al.. Nitrogen-use efficiency in maize (Zea mays L.): from ‘omics’ studies to metabolic modelling [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2014, 65(19):5657-5671. |
| 20 | DAVIES B, COULTER J A, PAGLIARI P H. Timing and rate of nitrogen fertilization influence maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(5): e233674 [2021-11-03]. . |
| 21 | DECHORGNAT J, FRANCIS K L, DHUGGA K S, et al.. Tissue and nitrogen-linked expression profiles of ammonium and nitrate transporters in maize [J]. BMC Plant Biol., 2019, 19(1):206-219. |
| 22 | WEI S, WANG X, LI G, et al.. Maize canopy apparent photosynthesis and 13C-photosynthate reallocation in response to different density and N rate combinations [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2019, 10:1113 [2021-11-03]. . |
| 23 | 许国春, 纪荣昌, 邱永祥, 等. 我国马铃薯产量对施氮的响应及其影响因素分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(4): 727-737. |
| XU G C, JI R C, QIU Y X, et al.. Responses of potato yields to nitrogen application and associated driving factors in China [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26(4):727-737. | |
| 24 | YAN L, ZHANG Z, ZHANG J, et al.. Effects of improving nitrogen management on nitrogen utilization, nitrogen balance, and reactive nitrogen losses in a Mollisol with maize monoculture in Northeast China [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2016, 23(5):4576-4584. |
| 25 | LIU S, WANG X, YIN X, et al.. Ammonia volatilization loss and corn nitrogen nutrition and productivity with efficiency enhanced UAN and erea under no-tillage [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1):6610 [2021-11-03]. . |
| 26 | BANGER K, NAFZIGER E D, WANG J, et al.. Simulating nitrogen management impacts on maize production in the U.S. Midwest [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(10): e201825 [2021-11-03]. . |
| 27 | 山楠, 赵同科, 杜连凤, 等. 华北平原中部夏玉米农田不同施氮水平氨挥发规律[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(4): 32-40. |
| SHAN N, ZHAO T K, DU L F, et al.. Ammonia volatilization from maize cropland under different N applications at a rural area of central Northern China plain [J]. Chin. Soils Fert., 2020(4):32-40. | |
| 28 | 杨宇, 李霞, 潘晨, 等. 水氮互作对玉米生长和产量影响的研究进展[J]. 节水灌溉, 2021(5): 41-45. |
| YANG Y, LI X, PAN C, et al.. Research progresses on coupling effects of water and nitrogen on growth and grain yield of maize [J]. Water Saving Irri., 2021(5):41-45. | |
| 29 | 宁芳, 张元红, 温鹏飞, 等. 不同降水状况下旱地玉米生长与产量对施氮量的响应[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(5): 777-791. |
| NING F, ZHANG Y H, WEN P F, et al.. Responses of maize growth and yield to nitrogen application in dryland under different precipitation conditions [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(5): 777-791. | |
| 30 | 郭媛, 李宜联, 郭策, 等. 不同氮素添加对不同土地利用方式黑土氮素转化特征的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(1): 236-243. |
| GUO Y, LI Y L, GUO C, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen additions on nitrogen conversion characteristics of black soil with different land use patterns [J]. J. Soli Water Conserv., 2021, 35(1):236-243. | |
| 31 | 朱洪芬, 南锋, 徐占军, 等. 黄土高原盆地土壤有机质与影响因子的空间多尺度关系[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24):8348-8360. |
| ZHU H F, NAN F, XU Z J, et al.. Multi-scale spatial relationships between soil organic matter and influencing factors in basins of the Chinese Loess plateau [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(24):8348-8360. |
| [1] | 郑志刚, 向丽, 刘功义, 徐彩, 覃斌, 王慰亲, 郑华斌, 唐启源. 施氮量和密度对有序机抛早稻生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 132-143. |
| [2] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [3] | 张盼盼, 李川, 张美微, 赵霞, 牛军, 乔江方. 氮肥减施下添加硝化抑制剂对夏玉米氮素累积转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [4] | 赵威, 马睿, 王佳, 郭宏杰, 许金普. 基于果穗图像的玉米品种分类识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 97-106. |
| [5] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [6] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [7] | 孙正冉, 张翠萍, 张晋丽, 吴昊, 刘秀艳, 王振凯, 杨玉珍, 贺道华. 喷施化学打顶剂对关中棉区棉花植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 167-177. |
| [8] | 赵文军, 杨继周, 尹梅, 陈检锋, 薛开政, 胡保文, 付利波, 王伟, 王志远, 杨艳鲜, 陈华. 绿肥模式下减量施氮对烤烟产量与品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 189-196. |
| [9] | 韦海龙, 程乙, 宋碧, 邹军, 左晋, 李蕾, 张军, 刘代铃, 曾涛, 付敬锋, 魏盛. 不同播期下鲜食糯玉米籽粒灌浆特性及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 45-55. |
| [10] | 王向东, 宋玥, 马艳芝. 不同生姜品种的品质比较与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 56-66. |
| [11] | 姚佳, 刘加欣, 苏焱, 苏小娟. 烟杆炭配施氮肥对玉米苗期生长及土壤特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [12] | 杨玲, 张富仓, 孙鑫, 张少辉, 王海东, ABDELGHANY Ahmed Elsayed, 陈占飞, 方玉川. 生物炭和滴灌量对陕北榆林沙土性质和马铃薯生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 221-233. |
| [13] | 王洪波, 樊志鹏, 乌兰图雅, 王春光, 马哲. 揉碎玉米秸秆螺旋输送仿真离散元模型参数标定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 96-106. |
| [14] | 郑云珠, 孙树臣. 秸秆生物炭和秸秆对麦玉轮作系统土壤养分及作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [15] | 黄巧义, 吴永沛, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 张木, 逄玉万, 曾招兵, 唐拴虎. 控释尿素与尿素配施对甜玉米产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 163-173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号