












中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 162-170.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0650
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
黄小红1,2( ), 焦静1,3, 杜嵇华1,2,3(
), 焦静1,3, 杜嵇华1,2,3( ), 吴翼4(
), 吴翼4( ), 李尊香1,3, 刘信鹏1,3
), 李尊香1,3, 刘信鹏1,3
收稿日期:2023-08-31
接受日期:2023-11-13
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-02-04
通讯作者:
杜嵇华,吴翼
作者简介:黄小红 E-mail:xiaohong0611@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaohong HUANG1,2( ), Jing JIAO1,3, Jihua DU1,2,3(
), Jing JIAO1,3, Jihua DU1,2,3( ), Yi WU4(
), Yi WU4( ), Zunxiang LI1,3, Xinpeng LIU1,3
), Zunxiang LI1,3, Xinpeng LIU1,3
Received:2023-08-31
Accepted:2023-11-13
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-02-04
Contact:
Jihua DU,Yi WU
摘要:
为探究不同氮源对椰子叶堆肥腐殖化效果的影响,以鸡粪、猪粪、沼渣、尿素等不同氮源为控制变量,分别与椰子叶进行混合堆肥,对温度、发酵前后碳氮比的比值(T值)、腐殖质含量、腐殖化系数、腐殖化指数和腐殖化聚合度等指标进行分析。结果表明,各处理组的堆肥高温期(55.0 ℃以上)均超过15 d,达到无害化处理要求;T值均小于0.60,达到了腐熟要求;发酵后总有机碳含量下降,但各处理组的腐殖质碳含量上升,腐殖化程度增加。鸡粪处理组腐殖化效果最佳,其腐殖化系数增加19.28%、腐殖化指数增加65.80%,腐殖化聚合度达到2.38;猪粪处理组产品稳定性低于鸡粪处理,高于沼渣和尿素处理;沼渣处理组堆肥腐殖化系数最高,但腐殖化聚合度只有1.61,产品稳定性差;尿素处理组堆肥腐殖化指数和腐殖化聚合度降低,阻碍了其腐殖化进程。综上可知,鸡粪作为氮源添加对椰子叶堆肥的腐殖化效果最好,研究结果为海南地区椰子叶废弃物资源化利用提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
黄小红, 焦静, 杜嵇华, 吴翼, 李尊香, 刘信鹏. 不同氮源添加对椰子叶堆肥腐殖化效果的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 162-170.
Xiaohong HUANG, Jing JIAO, Jihua DU, Yi WU, Zunxiang LI, Xinpeng LIU. Effects of Different Nitrogen Sources Addition on Humification of Coconut Leaf Compost[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 162-170.
原料 Raw material | 含水率 Moisture content | 总氮 Total nitrogen | 总碳 Total carbon |
|---|---|---|---|
| 椰子叶Coconut leaf | 11.96 | 0.40 | 61.22 |
| 鸡粪Chicken manure | 68.28 | 3.23 | 24.35 |
| 猪粪Pig manure | 69.77 | 1.84 | 28.92 |
| 沼渣Biogas residue | 94.24 | 0.43 | 2.30 |
| 尿素Urea | — | 46.00 | — |
表1 原料基本性质 (%)
Table 1 Property of raw material
原料 Raw material | 含水率 Moisture content | 总氮 Total nitrogen | 总碳 Total carbon |
|---|---|---|---|
| 椰子叶Coconut leaf | 11.96 | 0.40 | 61.22 |
| 鸡粪Chicken manure | 68.28 | 3.23 | 24.35 |
| 猪粪Pig manure | 69.77 | 1.84 | 28.92 |
| 沼渣Biogas residue | 94.24 | 0.43 | 2.30 |
| 尿素Urea | — | 46.00 | — |

图1 不同处理的温度注:第7、14、21、35、42天为翻堆时间,温度下降。
Fig. 1 Temperature in different treatmentsNote: 7, 14, 21, 35 and 42 d are the turning time, and the temperature decrease.
| 处理 Treatment | 最高温度 Maximum temperature/℃ | 到达高温期(≥55 ℃)所需天数 Number of days required to reach the high temperature period (≥55 ℃)/d | 高温期(≥55 ℃)维持天数High temperature period (≥55 ℃) maintenance days/d | 堆肥积温 Accumulated temperature of compost/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 74.5 | 4 | 25 | 2 699.4 |
| T2 | 73.0 | 5 | 24 | 2 531.8 |
| T3 | 74.5 | 4 | 20 | 2 329.3 |
| T4 | 72.5 | 4 | 17 | 2 469.4 |
表2 不同处理下的温度变化
Table 2 Temperature changes in different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 最高温度 Maximum temperature/℃ | 到达高温期(≥55 ℃)所需天数 Number of days required to reach the high temperature period (≥55 ℃)/d | 高温期(≥55 ℃)维持天数High temperature period (≥55 ℃) maintenance days/d | 堆肥积温 Accumulated temperature of compost/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 74.5 | 4 | 25 | 2 699.4 |
| T2 | 73.0 | 5 | 24 | 2 531.8 |
| T3 | 74.5 | 4 | 20 | 2 329.3 |
| T4 | 72.5 | 4 | 17 | 2 469.4 |
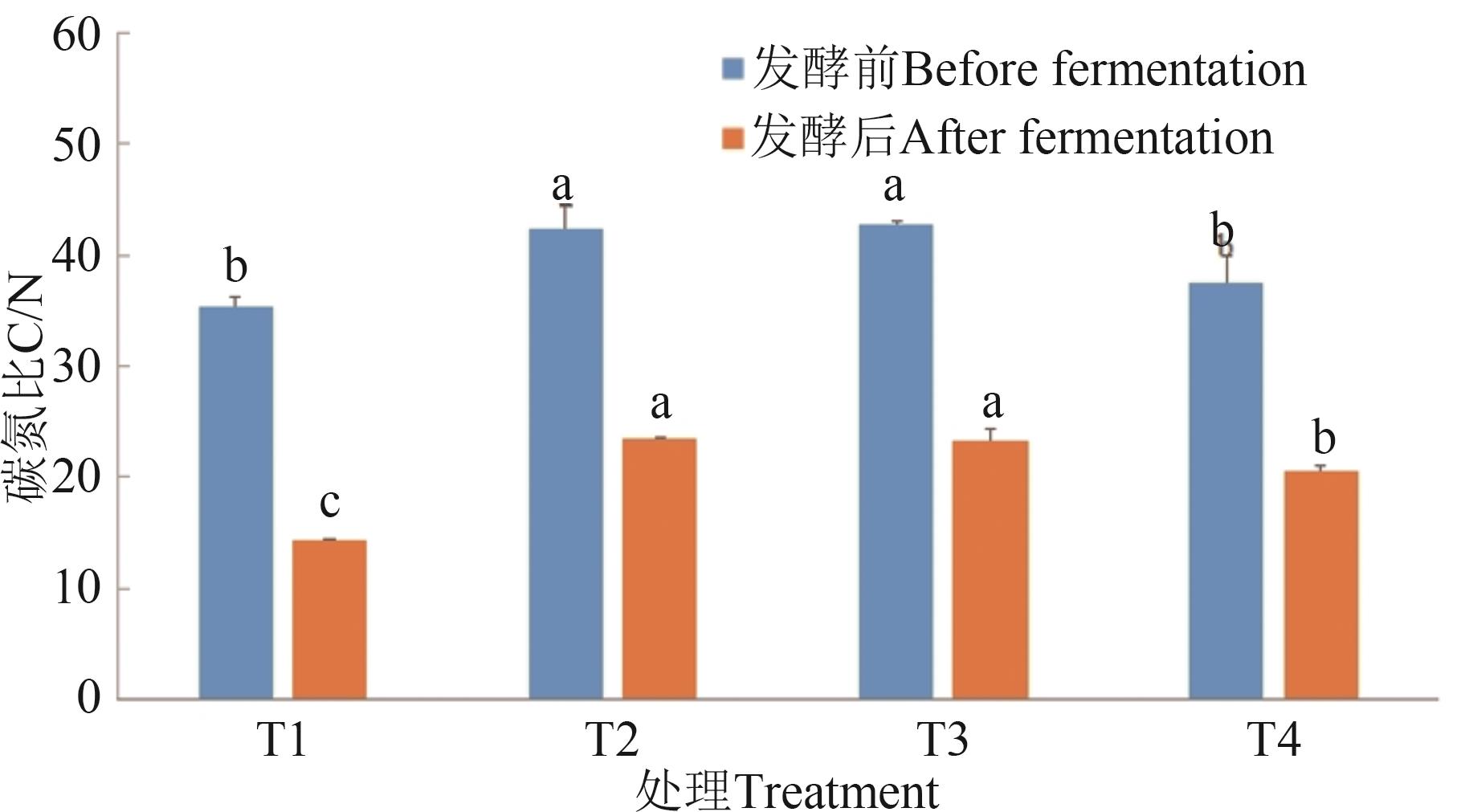
图 2 不同处理的碳氮比注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 C/N in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
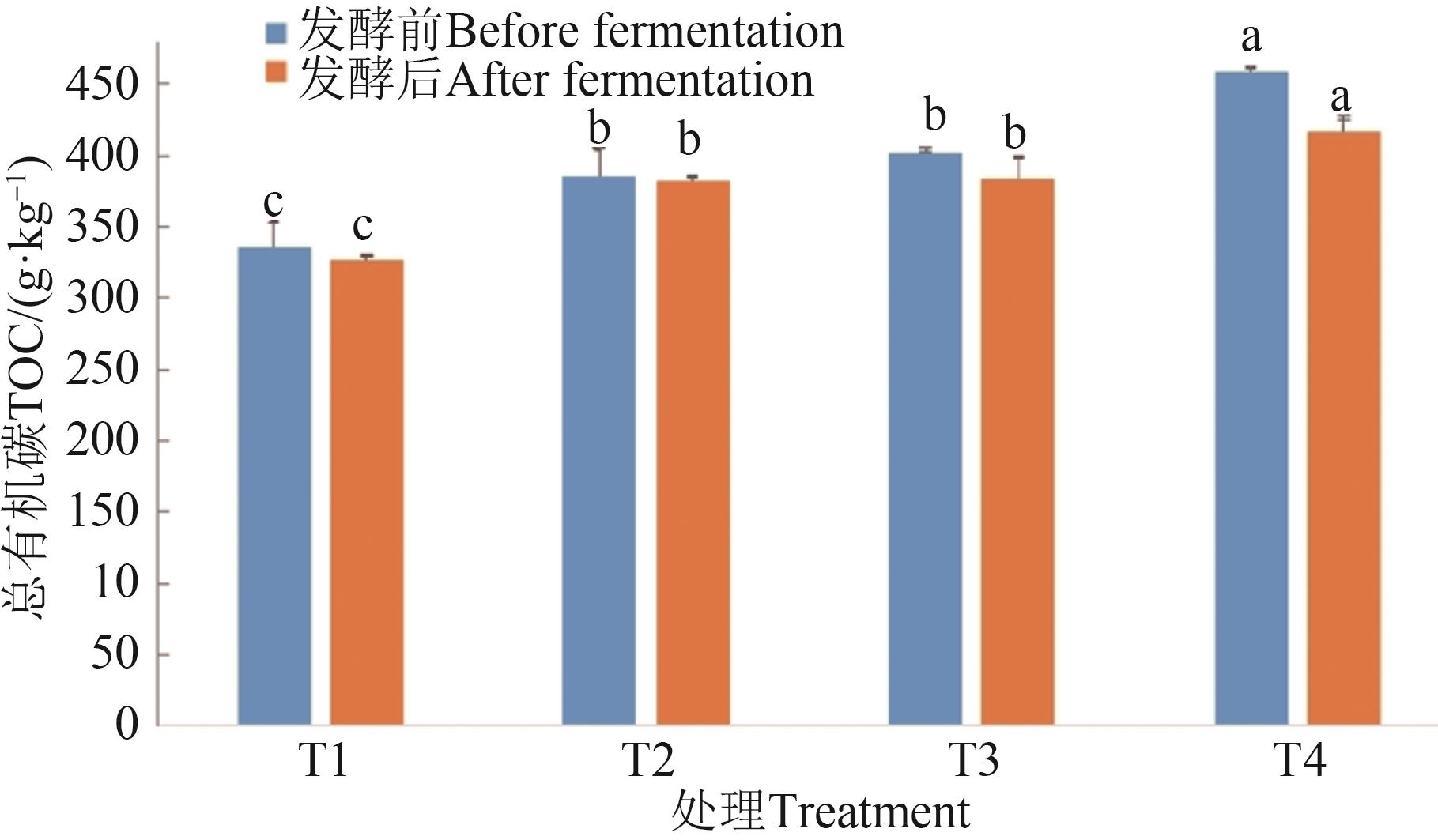
图 3 不同处理的总有机碳含量注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 TOC contents in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
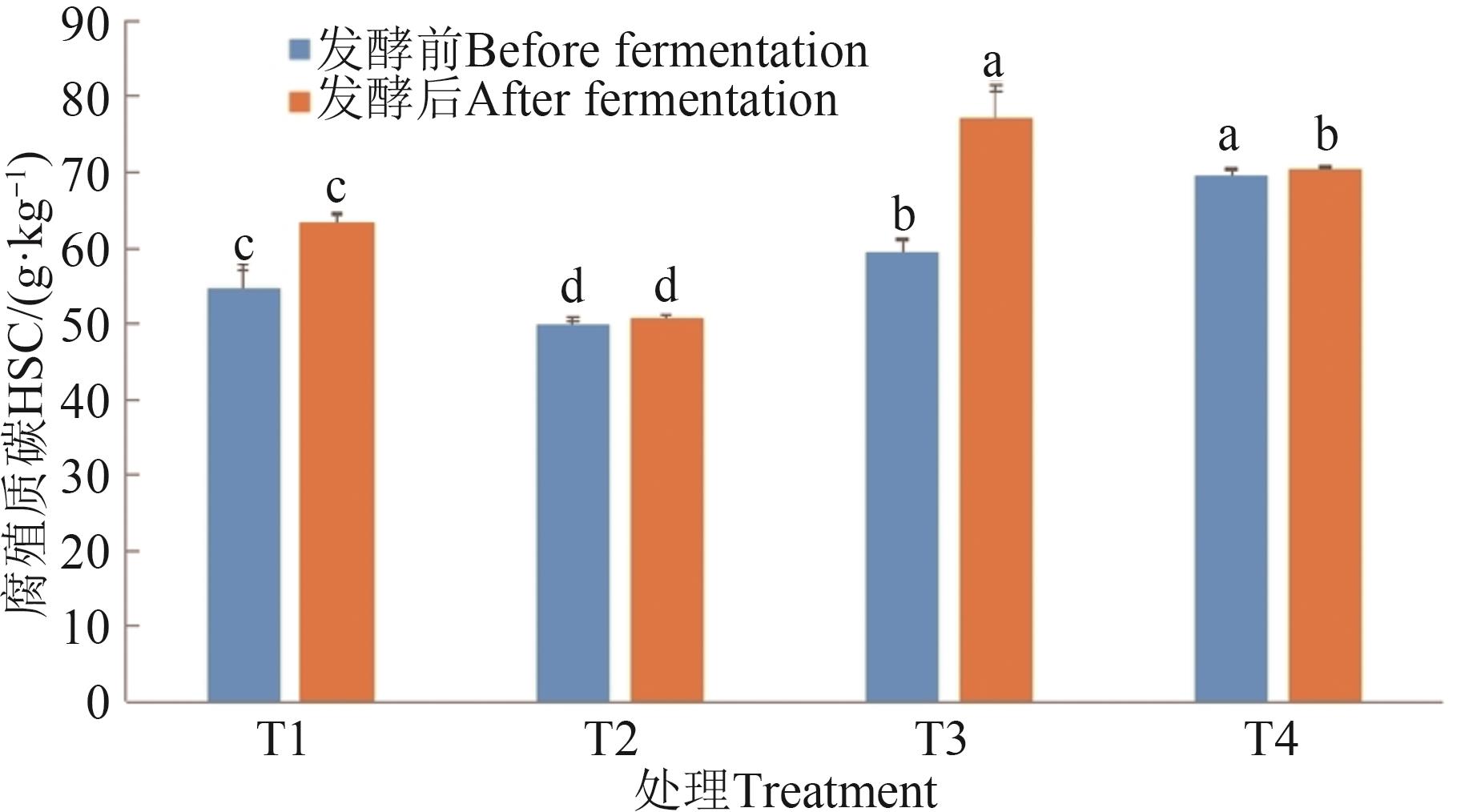
图 4 不同处理的腐殖质碳含量及增幅注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 4 HSC contents and increase in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
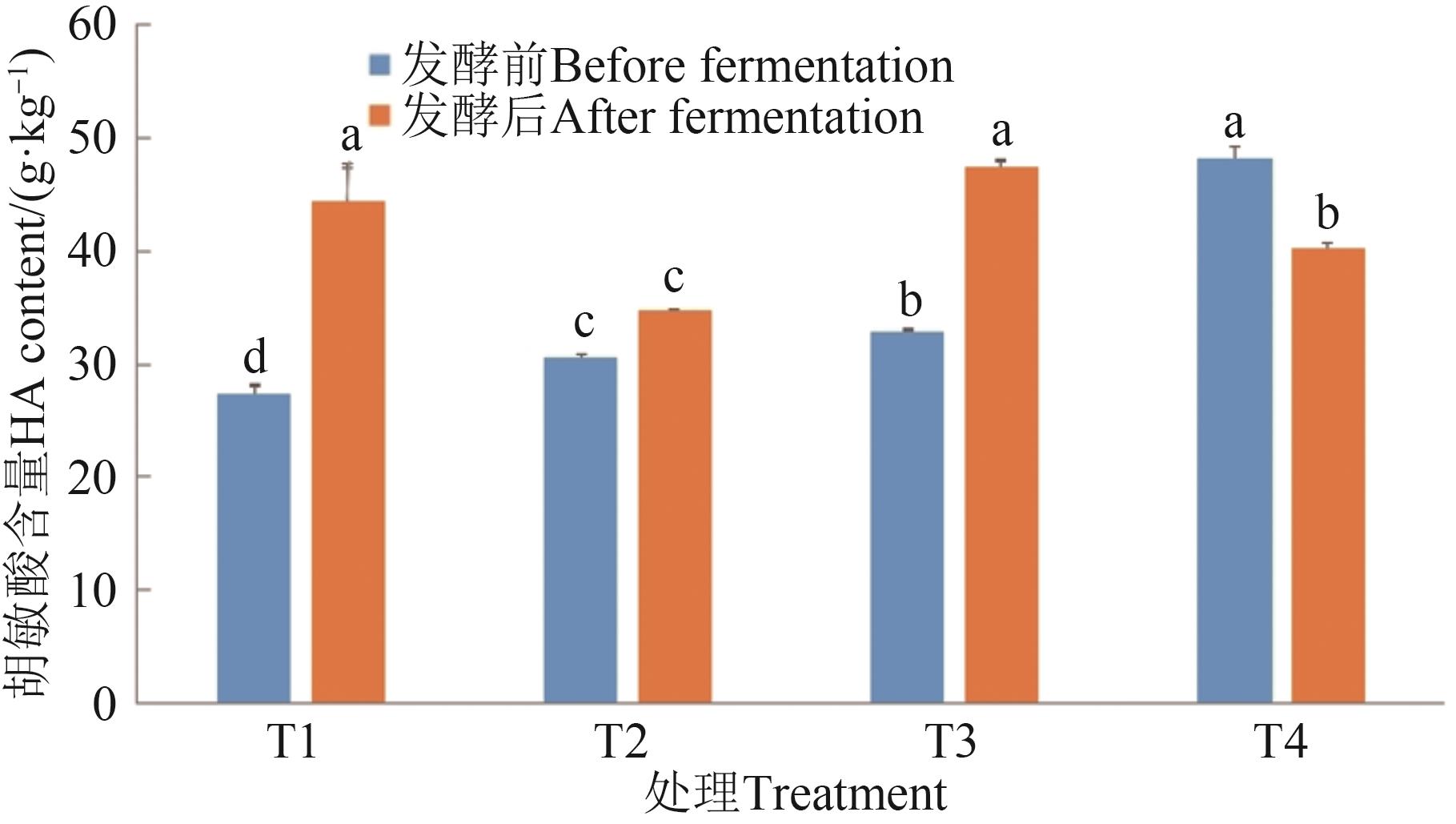
图 5 不同处理的胡敏酸含量及增幅注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 5 HA contents and increase in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
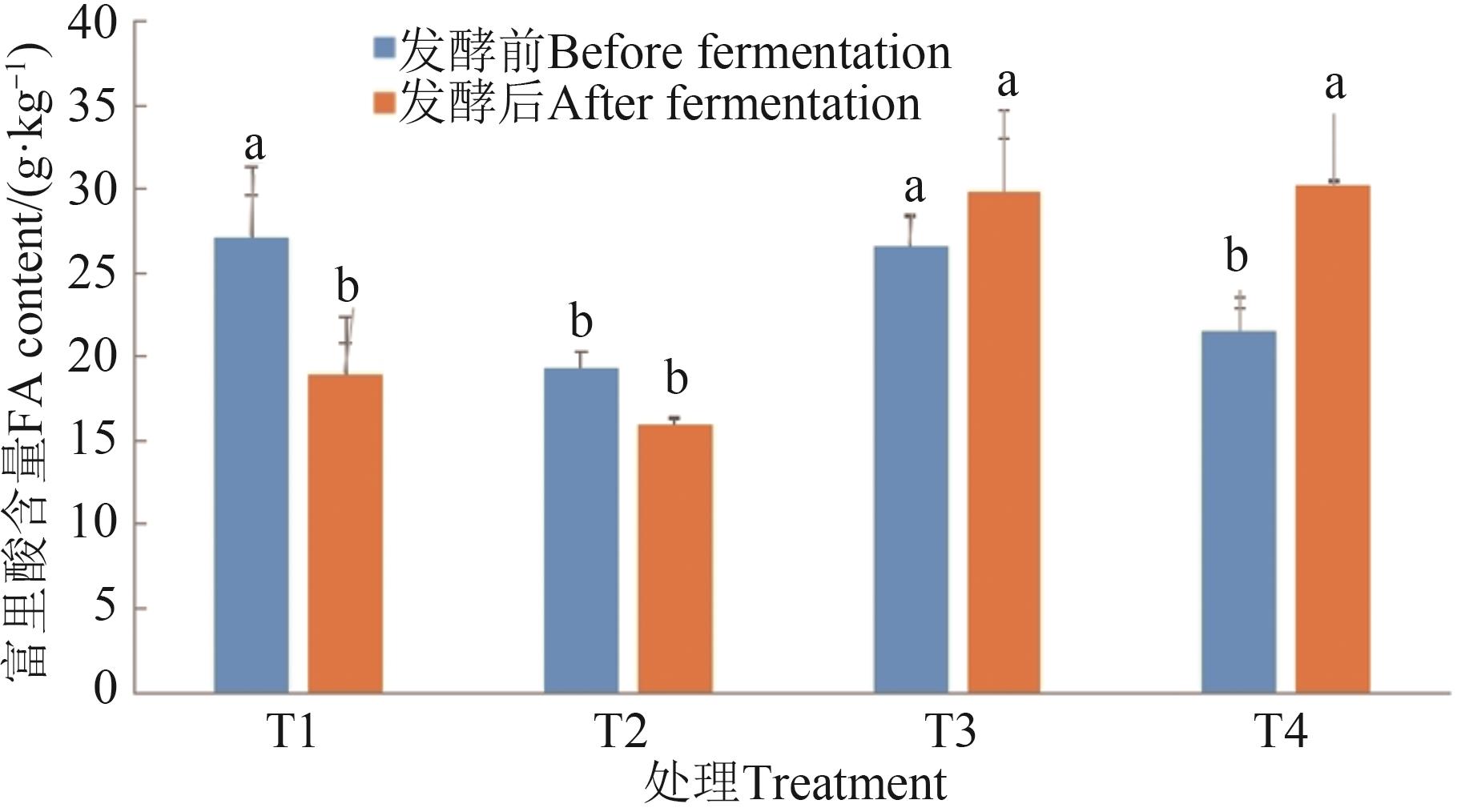
图 6 不同处理的富里酸含量及增幅注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 6 Content and increase of FA in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
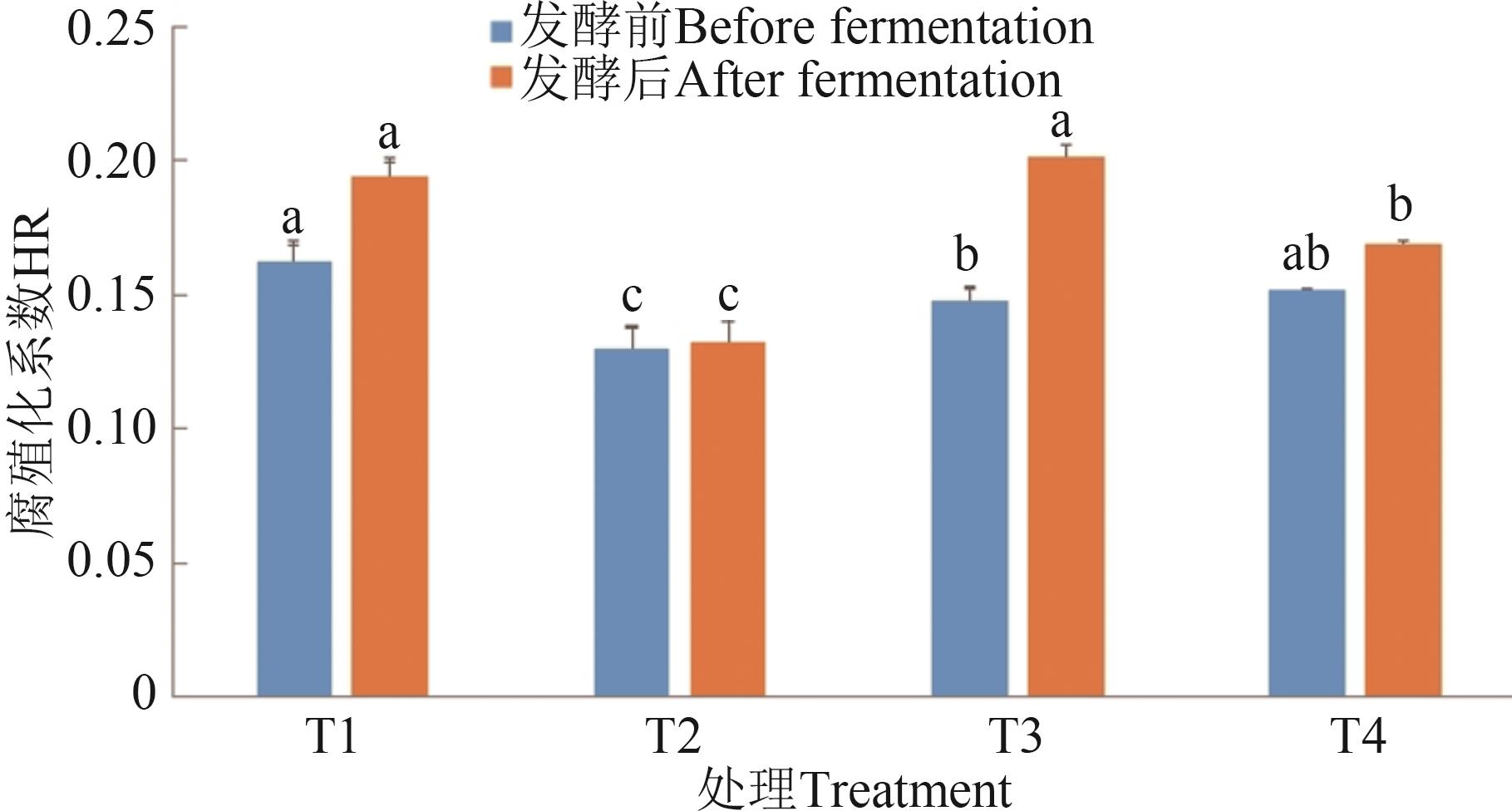
图7 不同处理的腐殖化系数注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 7 HR in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
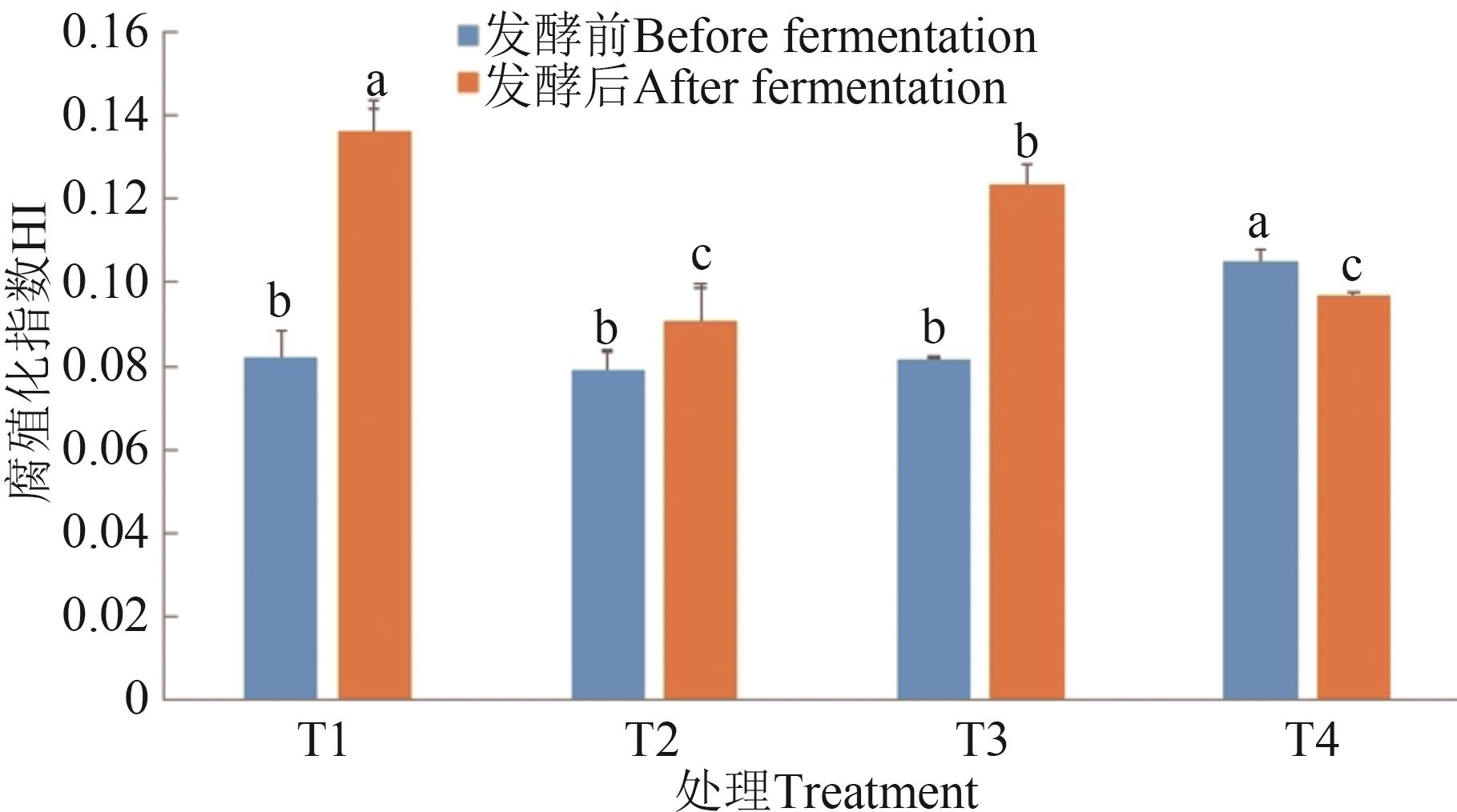
图8 不同处理的腐质化指数注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 8 HI in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
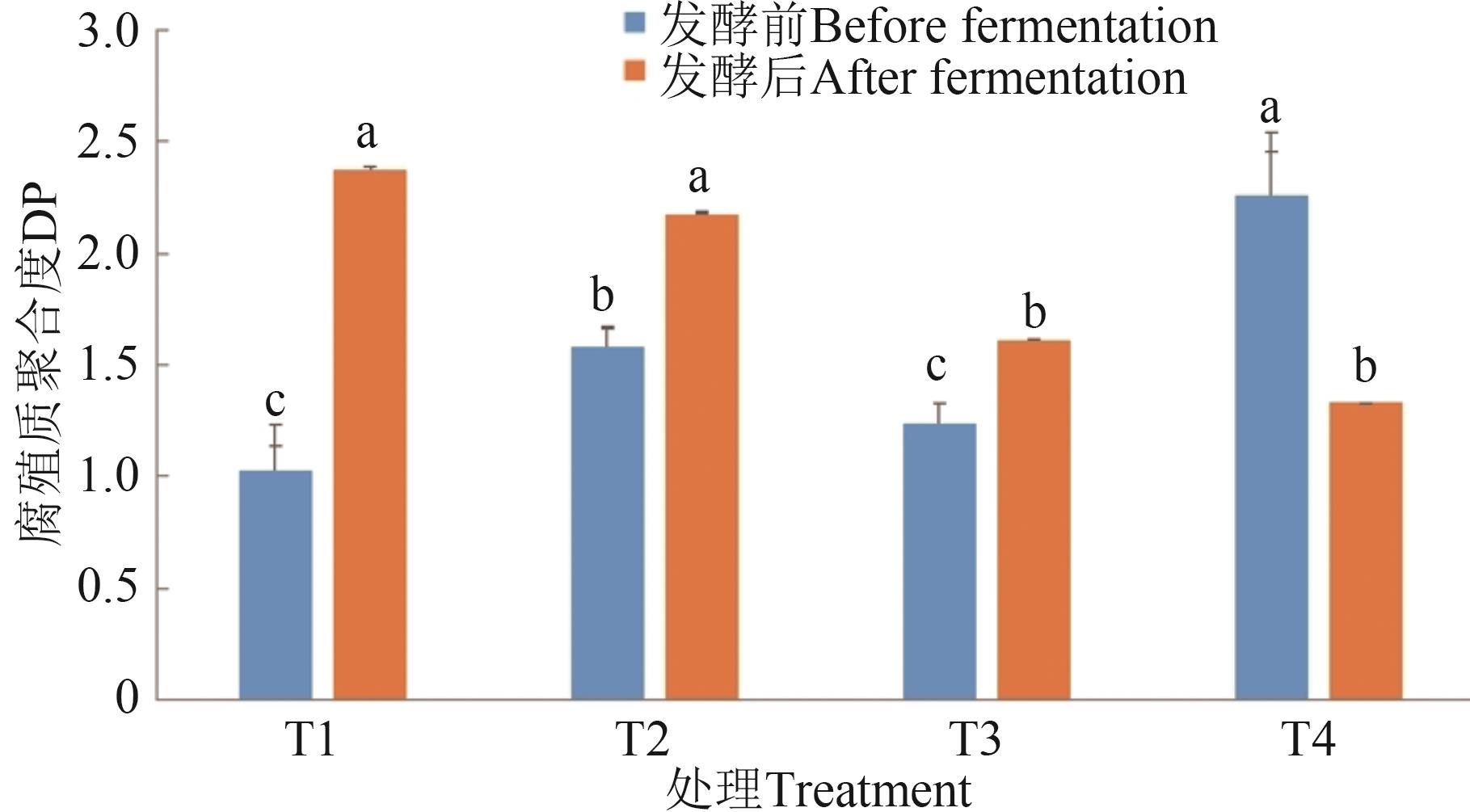
图9 不同处理的腐殖质聚合度注:同一指标不同字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 9 DP in different treatmentsNote: Different letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 卢琨, 侯媛媛. 海南省椰子产业分析与发展路径研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2020, 47(6): 145-151. |
| LU K, HOU Y Y. Analysis and development path of coconut industry in Hainan province [J]. Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2020, 47(6): 145-151. | |
| 2 | 张锋, 王俊峰, 汪汇源, 等. 乡村振兴背景下海南省椰子产业发展的SWOT分析[J]. 世界热带农业信息, 2023 (7): 92-94. |
| 3 | 郑侃, 梁栋, 张喜瑞. 椰子废弃物综合利用现状与分析[J]. 广东农业科学, 2013 (5): 175-177. |
| ZHENG K, LIANG D, ZHANG X R. Status and analysis of coconut waste’s comprehensive utilization [J]. Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2013 (5): 175-177. | |
| 4 | WANG Q, AWASTHI M K, ZHAO J C, et al.. Improvement of pig manure compost lignocellulose degradation, organic matter humification and compost quality with medical stone [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2017, 243: 771-777. |
| 5 | BERNAL M P, ALBURQUERQUE J A, MORAL R, et al.. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment: a review [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2009, 100: 5444-5453. |
| 6 | ZHANG X, MA D C, LYU J H, et al.. Food waste composting based on patented compost bins: carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions and the denitrifying community analysis [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2022, 346:126643 [2023-07-28]. . |
| 7 | WANG S G, ZENG Y. Ammonia emission mitigation in food waste composting: a review [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2018, 248: 13-19. |
| 8 | 雷仁清, 秦文婧, 刘佳, 等. 不同碳氮比猪粪沼渣堆肥及其产品对水稻种子萌发的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2022 (8): 205-211. |
| LEI R Q, QIN W J, LIU J, et al.. Research on composting of swine manure biogas residue and sawdust with different C/N and effects of the products on germination characteristics of rice seed [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2022 (8): 205-211. | |
| 9 | 常瑞雪, 甘晶晶, 陈清, 等. 碳源调理剂对黄瓜秧堆肥进程和碳氮养分损失的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(): 254-259. |
| CHANG R X, GAN J J, CHEN Q, et al.. Effect of carbon resources conditioner on composting process and carbon and nitrogen loss during composting of cucumber stalk [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016, 32(S2): 254-259. | |
| 10 | 常瑞雪, 王骞, 甘晶晶, 等. 易降解有机质含量对黄瓜秧堆肥腐熟和氮损失的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017,33(1): 231-237. |
| CHANG R X, WANG Q, GAN J J, et al.. Influence of easily-degraded organic matter content on maturity and nitrogen loss during composting of cucumber vine [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2017, 33(1): 231-237. | |
| 11 | 杜鹏祥. 碳源构成对堆肥进程与腐熟度的影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. |
| DU P X. Study on the effect of carbon source composition on composting process and maturity [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 12 | 王定美, 麦力文, 杨霞, 等. 粪便对食用菌渣堆肥中碳氮转化的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020,42(11): 1368-1374. |
| WANG D M, MAI L W, YANG X, et al.. Effect of animal manures on the conversion of carbon and nitrogen in edible fungi residue compost [J]. Environ. Pollut. Control, 2020,42(11): 1368-1374. | |
| 13 | 程文静. 椰子叶废弃物与畜禽粪便混合堆肥研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2012. |
| CHENG W J. Study on co-composting of coconut waste and livestock [D]. Haikou: Hainan university, 2012. | |
| 14 | 杨航波, 张韵, 郑威, 等. 竹醋添加时期对猪粪堆肥腐殖质形成的影响[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(9): 1-9. |
| YANG H B, ZHANG Y, ZHENG W, et al.. Effect of bamboo vinegar addition timing in humus formation in pig manure compost [J]. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 43(9): 1-9. | |
| 15 | YANG Y J, DU W, REN X N, et al.. Effect of dean dregs amendment on the organic matter degradation, humification, maturity and stability of pig manure composting [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020,708:134623 [2023-07-28]. . |
| 16 | 童善坤, 李方敏, 夏贤格, 等. 包菜废弃物好氧堆肥初始条件研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022 (11): 1-10. |
| TONG S K, LI F M, XIA X G, et al.. Study on aerobic composting of cabbage wastes under different initial conditions [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2022(11): 1-10. | |
| 17 | 李龙涛, 董春华, 饶中秀,等. 添加沼渣对餐厨垃圾堆肥腐殖化过程的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2023,42(5): 1148-1155. |
| LI L T, DONG C H, RAO Z X, et al.. Effects of biogas residue addition on humification of kitchen waste compost [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2023, 42(5): 1148-1155. | |
| 18 | 陶娟娟. 淮南市污水厂污泥资源化利用研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2012. |
| TAO J J. The research in sludge resources reuse of Huainan sewage processing plant [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2012. | |
| 19 | 廖新俤, 吴银宝, 汪植三, 等. 堆体大小对猪粪堆肥影响和袋装堆肥的研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2003, 19(4): 287-290. |
| LIAO X D, WU Y B, WANG Z S, et al.. Effects of pile size and packaging on swine manure composting [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2003, 19(4): 287-290. | |
| 20 | 董存明, 张曼, 邓小垦, 等. 不同碳氮比条件下鸡粪和椰糠高温堆肥腐熟过程研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2015, 31(3): 420-424. |
| DONG C M, ZHANG M, DENG X K, et al.. High-temperature composting of mixtures of chicken manure and coconut husk different in C/N ratio [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2015, 31(3): 420-424. | |
| 21 | 杨毓峰, 薛澄泽, 唐新保. 畜禽废弃物堆肥的腐熟指标[J]. 西北农业大学学报, 1999, 27(4): 62-66. |
| YANG Y F, XUE C Z, TANG X B. Maturity indices of poultry waste compost [J]. Acta Univ. Agric. Bor-Occid., 1999, 27(4): 62-66. | |
| 22 | GUO X X, LIU H T, WU S B. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 662:501-510. |
| 23 | QI H S, ZHAO Y, ZHAO X Y, et al.. Effect of manganese dioxide on the formation of humin during different agricultural organic wastes compostable environments: it is meaningful carbon sequestration [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2020, 299: 122596 [2023-07-28]. . |
| 24 | ZHAO X L, LI B Q, NI J P, et al.. Effect of four crop straws on transformation of organic matter during sewage sludge composting [J]. J. Integrative Agric., 2016,15(1): 232-240. |
| 25 | 徐成, 刘国涛, 王政, 等. 添加腐熟堆肥对厨余垃圾堆肥腐殖质形成的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(8): 122-127. |
| XU C, LIU G T, WANG Z, et al.. Effect of matured compost addition on the formation of humus in kitchen waste composting [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2020,43(8):122-127. | |
| 26 | ZHOU Y, SELVAM A, WONG J W C. Evaluation of humic substances during co-composting of food waste, sawdust and Chinese medicinal herbal residues [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2014, 168: 229-234. |
| 27 | ZHU N, ZHU Y Y, LIANG D, et al.. Enhanced turnover of phenolic precursors by Gloeophyllum trabeum pretreatment promotes humic substance formation during co-composting of pig manure and wheat straw [J/OL]. J. Cleaner Product., 2021, 315: 128211 [2023-07-28]. . |
| 28 | MA C, HU B, WEI M B, et al.. Influence of matured compost in-oculation on sewage sludge composting: enzyme activity, bacterial and fungal community succession [J/OL]. Bioresour. Technol., 2019, 294:122165 [2023-07-28]. . |
| 29 | 王玉军, 窦森, 张晋京, 等. 农业废弃物堆肥过程中腐殖质组成变化[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2009, 37(8): 79-81. |
| WANG Y J, DOU S, ZHANG J J, et al.. Changes of humus components during agricultural waste composting [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2009, 37(8): 79-81. | |
| 30 | 张勇, 陈宇鹏, 权秋梅, 等. 畜禽粪添加对菌糠堆肥过程中酶活性的影响[J]. 地球环境学报, 2019, 10(4):406-418. |
| ZHANG Y, CHEN Y P, QUAN Q M, et al.. Effects of manure addition on enzyme activities during spent mushroom substrate composting [J]. J. Earth Environ., 2019, 10(4): 406 -418. | |
| 31 | 李吉进, 郝晋珉, 邹国元, 等. 高温堆肥碳氮循环及腐殖质变化特征研究[J]. 生态环境, 2004,13(3): 332-334. |
| LI J J, HAO J M, ZOU G Y, et al.. Carbon and nitrogen circulation and humus characteristics of high-temperature composting [J]. Ecol. Environ., 2004,13(3): 332-334. | |
| 32 | 关松. 特定培养条件下土壤腐殖质形成与转化的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2005. |
| GUAN S. The study on formation and transformation of soil humus under special incubation condition [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2005. |
| [1] | 张智, 乔艳, 陈云峰, 胡诚, 刘东海, 李双来. 不同菌剂对鸡粪堆肥过程中有害气体排放的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 145-150. |
| [2] | 刘子乐1,白林1*,胡红文2. 超高温堆肥及其资源化与无害化研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 119-127. |
| [3] | 胡红文,夏运红,查琳,刘贵平,李清亮. 不同添料频率对蚯蚓堆肥的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 162-168. |
| [4] | 谭施北1,习金根1*,陈河龙2,郑金龙1,黄兴1,贺春萍1,吴伟怀1,梁艳琼1,张世清2,高建明2,李锐1,易克贤1*. 添加菌剂和石灰对剑麻麻渣堆肥腐熟效果及养分含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 166-172. |
| [5] | 仝利朋,赵京考*,吴德亮. 不同氮源对土壤无机氮、玉米产量和氮利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(6): 101-109. |
| [6] | 杨朝元,刘国涛*,李伟雨,李蕾,夏璇,李世博. 堆肥化过程木质素降解和腐殖质形成的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2): 148-154. |
| [7] | 张国占. 碳源调理剂对牛粪高温好氧堆肥发酵的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(12): 99-106. |
| [8] | 李冉1,2,赵立欣1,孟海波1,周海宾1,王健1,沈玉君1*. 有机废弃物堆肥过程重金属钝化研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(1): 121-129. |
| [9] | 张海滨1,2,孟海波1,沈玉君1,赵立欣1*. 好氧堆肥微生物研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(3): 1-8. |
| [10] | 赵秀玲1,朱新萍1,罗艳丽1,贾宏涛1*,余雄2. 添加不同秸秆对牛粪好氧堆肥的影响[J]. , 2014, 16(3): 119-125. |
| [11] | 候月卿1,2,沈玉君2,刘树庆1*. 我国畜禽粪便重金属污染现状及其钝化措施研究进展[J]. , 2014, 16(3): 112-118. |
| [12] | 习佳林,董红敏,朱志平,陶秀萍,黄宏坤. 死畜禽堆肥化处理研究进展死畜禽堆肥化处理研究进展[J]. , 2010, 12(2): 76-80. |
| [13] | 刘文 刘景辉 李立军. 城市垃圾粗堆肥对废沙坑土壤物理性状的影响[J]. , 2006, 8(2): 51-55. |
| [14] | 李吉进[1] 郝晋珉[2] 邹国元[1] 张有山[1] 王美菊[1]. 畜禽粪便高温堆肥及工厂化生产研究进展[J]. , 2004, 6(3): 50-53. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 555
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 187
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号