




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 143-152.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0132
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-02-26
接受日期:2024-03-07
出版日期:2025-03-15
发布日期:2025-03-14
通讯作者:
宋丽雅
作者简介:周瑾 E-mail:zhoujin_mail@163.com;
基金资助:
Jin ZHOU( ), Haiyun LIANG, Jiahui SUN, Shuhan ZHANG, Liya SONG(
), Haiyun LIANG, Jiahui SUN, Shuhan ZHANG, Liya SONG( )
)
Received:2024-02-26
Accepted:2024-03-07
Online:2025-03-15
Published:2025-03-14
Contact:
Liya SONG
摘要:
为了解黄连提取物对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌机理,通过生长曲线、氧化损伤试验、细胞壁膜分析、蛋白质分析和DNA分析,探讨黄连提取物对金黄色葡萄球菌的作用机制。结果表明,黄连提取物对金黄色葡萄球菌有明显的抑制效果,最小抑菌浓度为2.60 mg·mL-1。黄连提取物可引起金黄色葡萄球菌胞内活性氧水平增加506.90%,胞外β-半乳糖苷酶活性和核酸含量分别增加258.28%和23.82%,碘化丙啶荧光染色也明显多于对照;总蛋白合成量、细胞代谢活力以及琥珀脱氢酶活性分别降低30.83%、30.89%、54.05%。基因组DNA的紫外吸收光谱和竞争性荧光光谱显示,黄连提取物可以与金黄色葡萄球菌DNA进行小沟结合或静电结合。以上结果表明,黄连提取物主要通过增加胞内活性氧水平,破坏细胞壁膜完整性及通透性来达到抑菌效果。研究结果为黄连的综合开发利用及其在饲料添加剂领域的应用提供借鉴。
中图分类号:
周瑾, 梁海运, 孙佳慧, 张舒涵, 宋丽雅. 黄连提取物对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌活性及作用机理[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 143-152.
Jin ZHOU, Haiyun LIANG, Jiahui SUN, Shuhan ZHANG, Liya SONG. Bacteriostatic Activity and Mechanism of Action of Rhizoma Coptidis Extracts on Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 143-152.
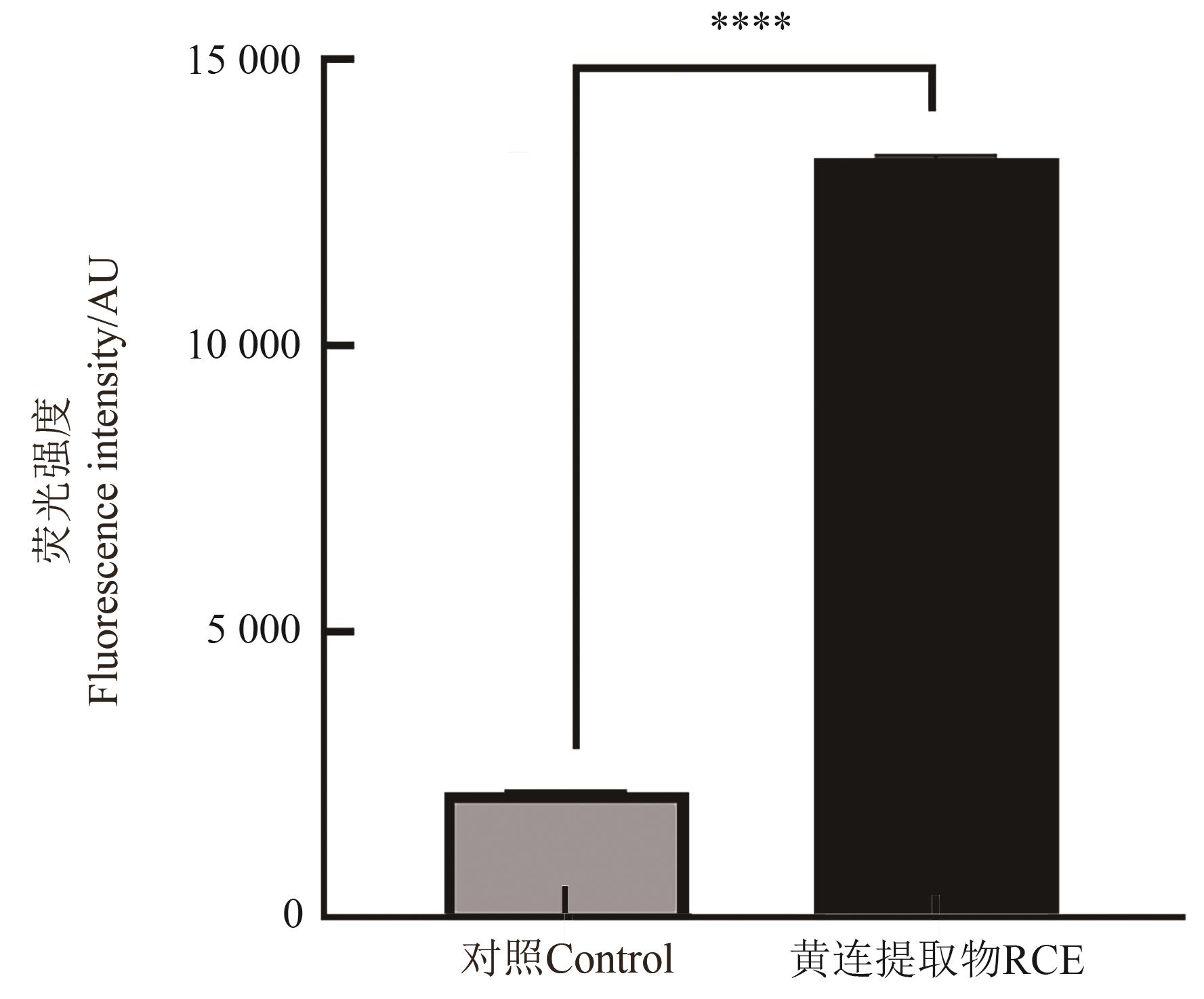
图2 RCE对金黄色葡萄球菌作用后的荧光强度注:****表示在P<0.000 1水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Fluorescence intebsity of Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to RCENote:**** indicates significant differences at P<0.000 1 level.
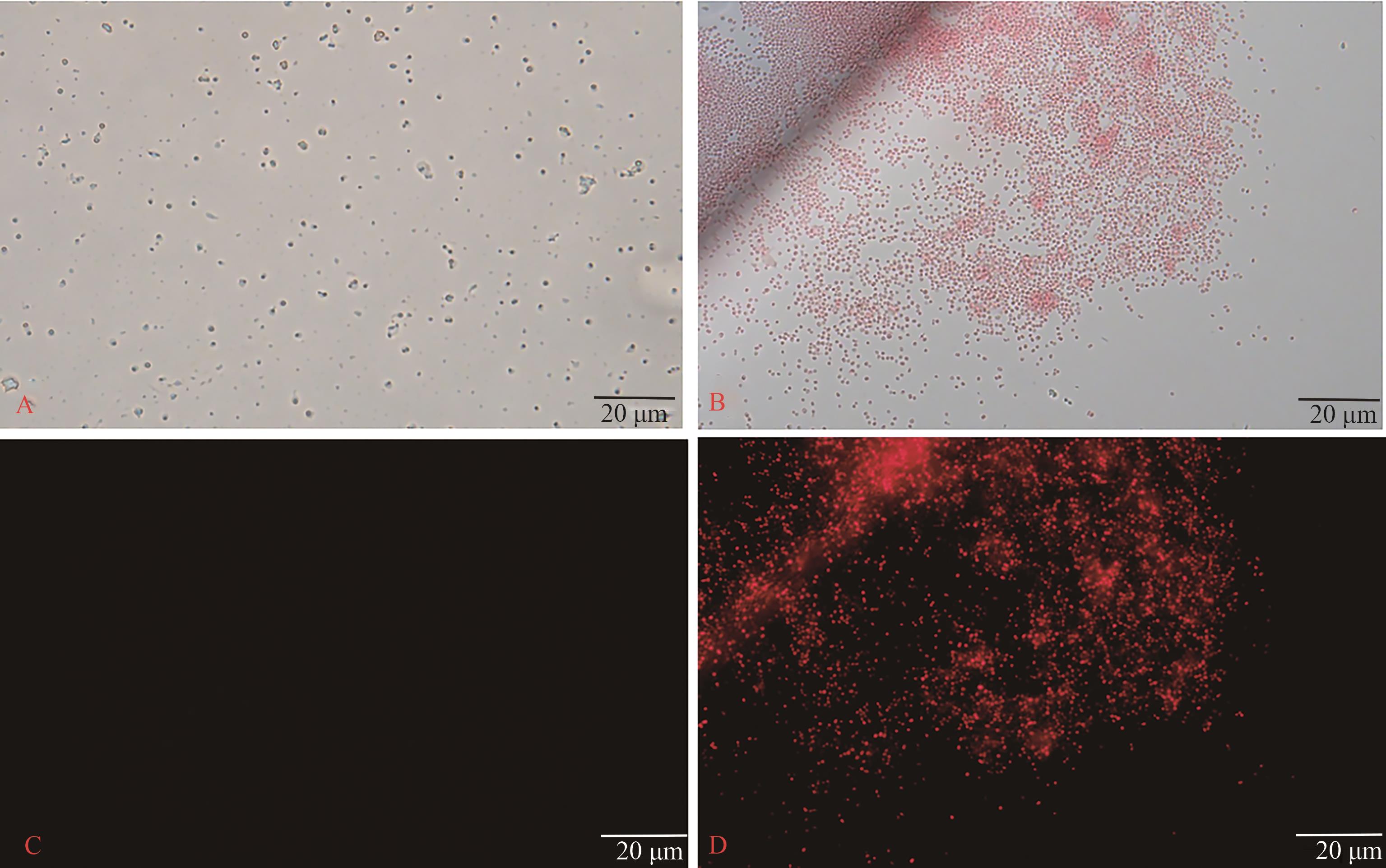
图3 PI标记结果A:对照组明场结果;B:RCE作用后的明场结果;C:对照组暗场结果;D:RCE作用后的暗场结果
Fig. 3 Result of PI-labeling experimentA: Bright field result of control group; B: Bright field result after RCE action; C: Dark field result of the control group; D: Dark field result after RCE
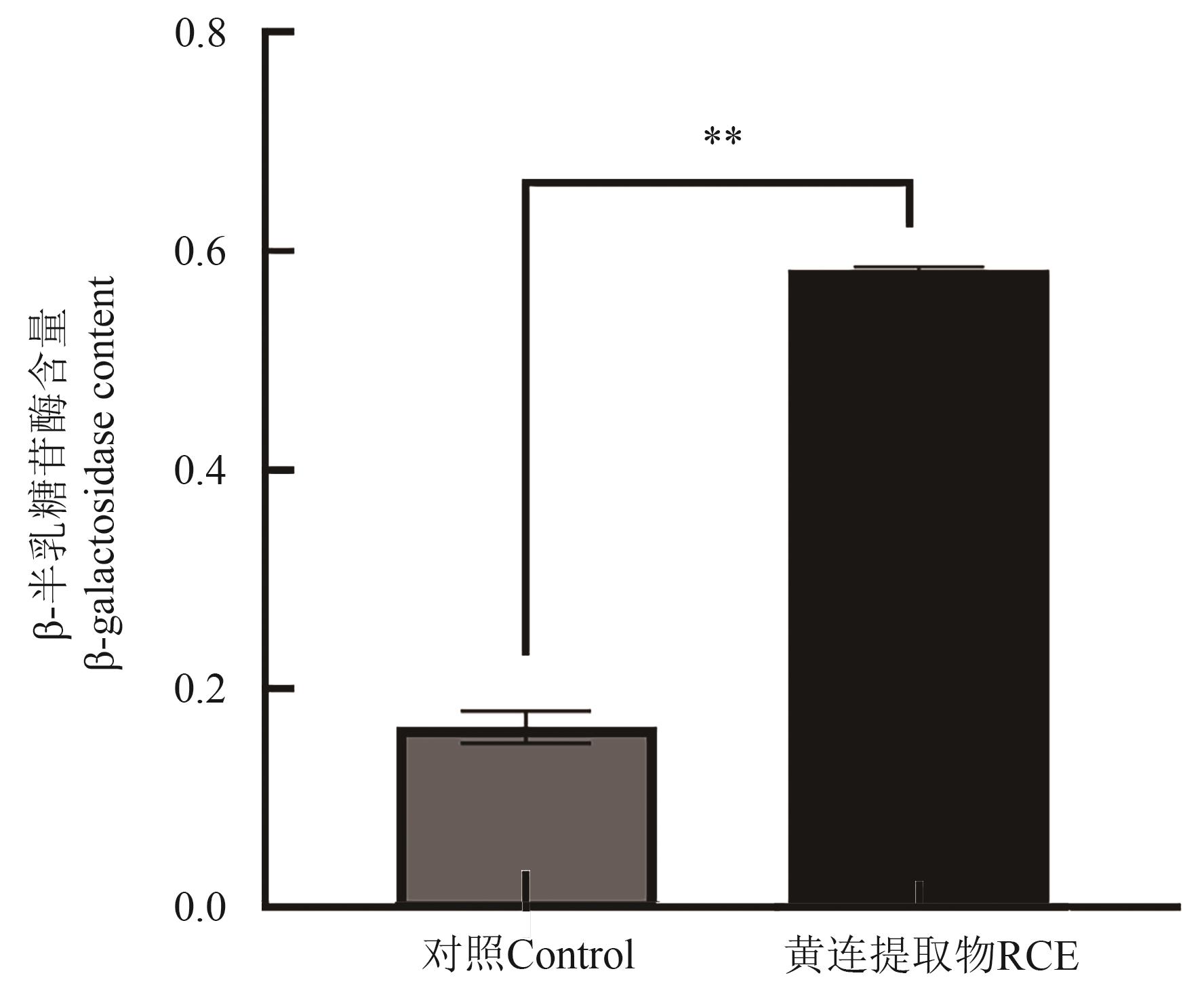
图4 RCE作用于金黄色葡萄球菌后胞外β-半乳糖苷酶含量注:**表示差异在P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 4 Content of β-galactosidase in Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to RCENote:** indicates significant difference at P<0.01 level.
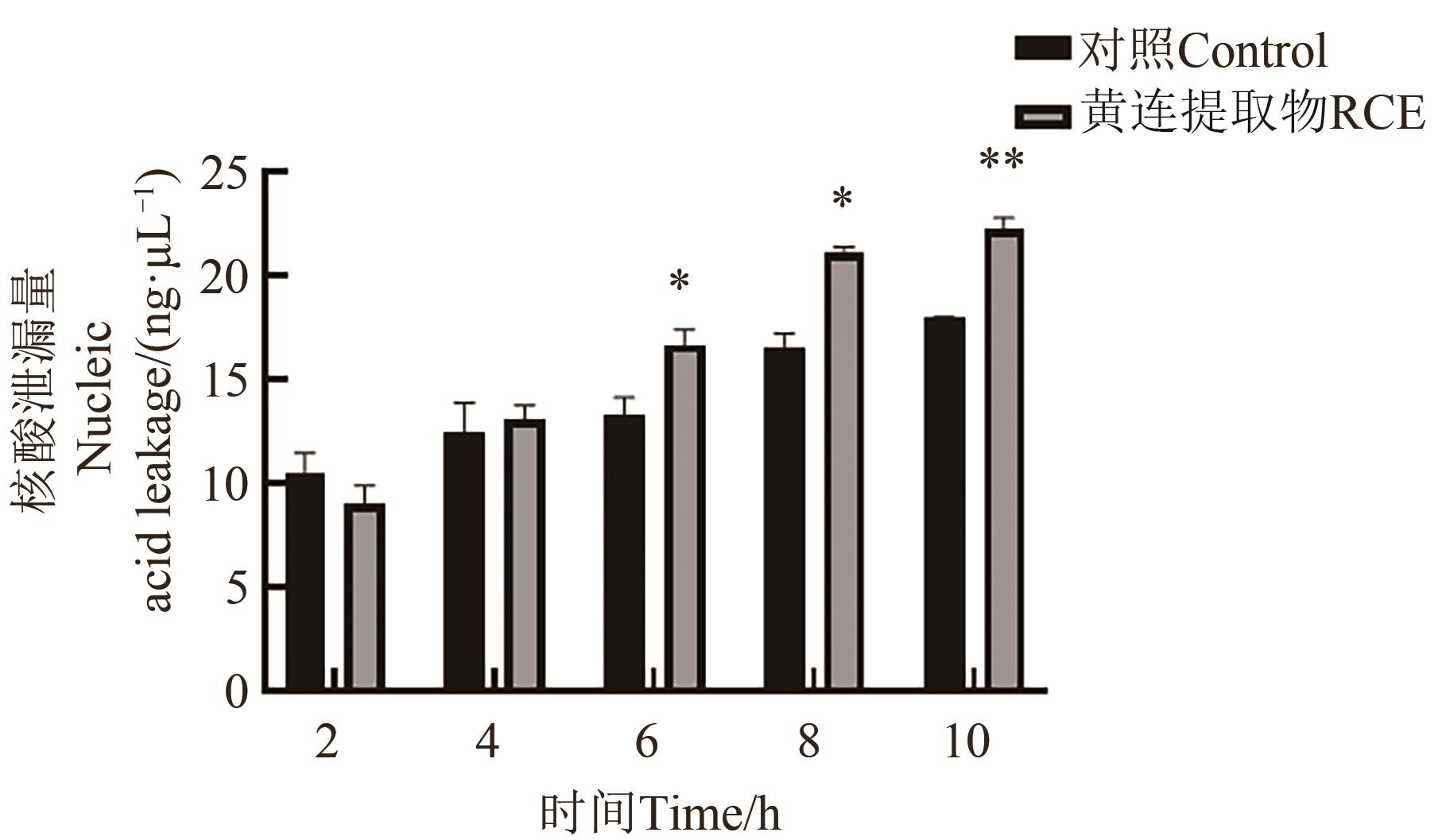
图5 RCE作用于金黄色葡萄球菌后的核酸泄漏量注:*和**分别表示两组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Amount of nucleic acid leakage from Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to RCENote:* and ** indicate significant differences between two groups at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels,respectively.
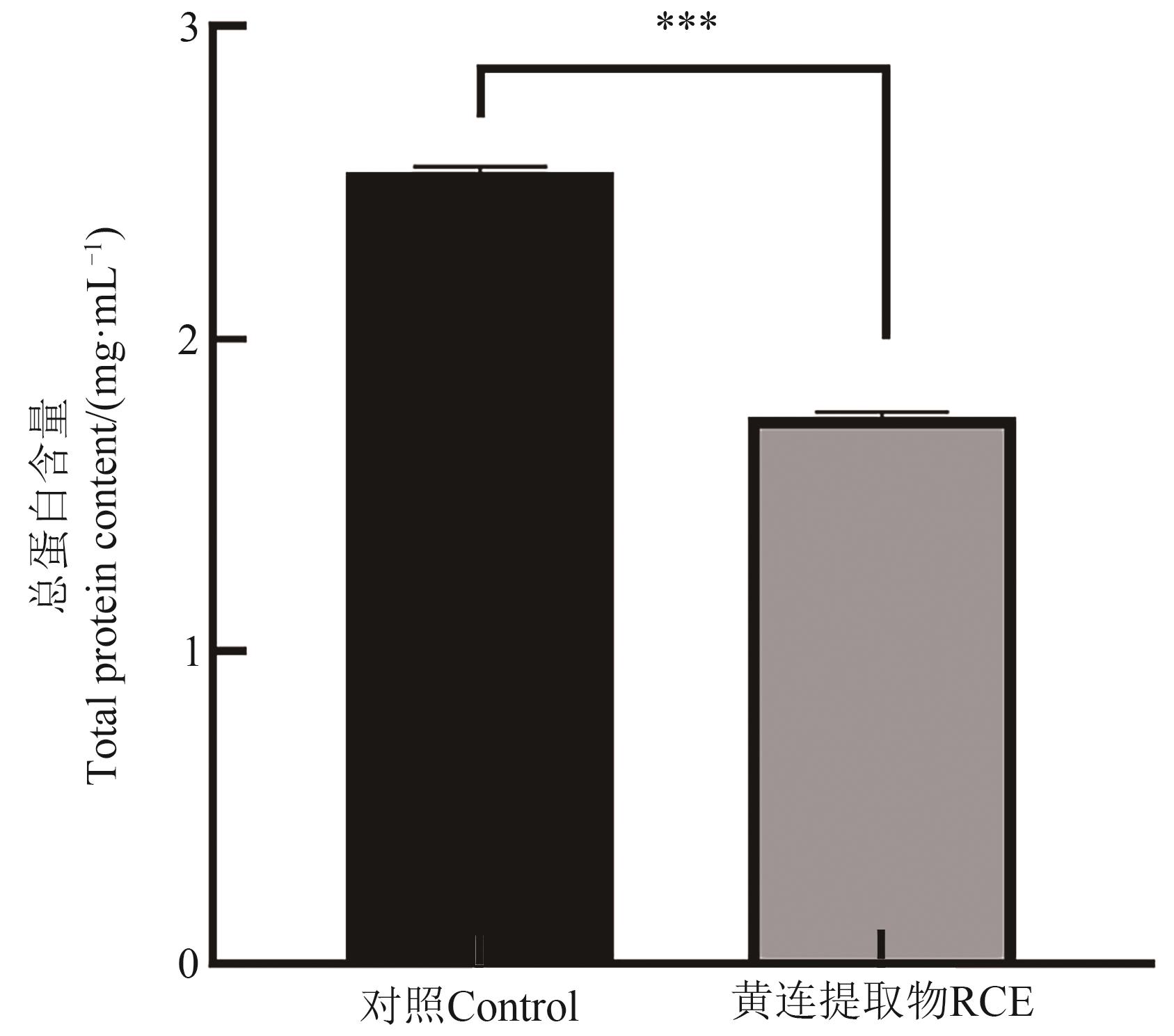
图6 RCE作用于金黄色葡萄球菌后细胞内总蛋白含量注:***表示差异在P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 6 Intracellular total protein content of Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to RCENote:*** indicates significant difference at P<0.001 level.
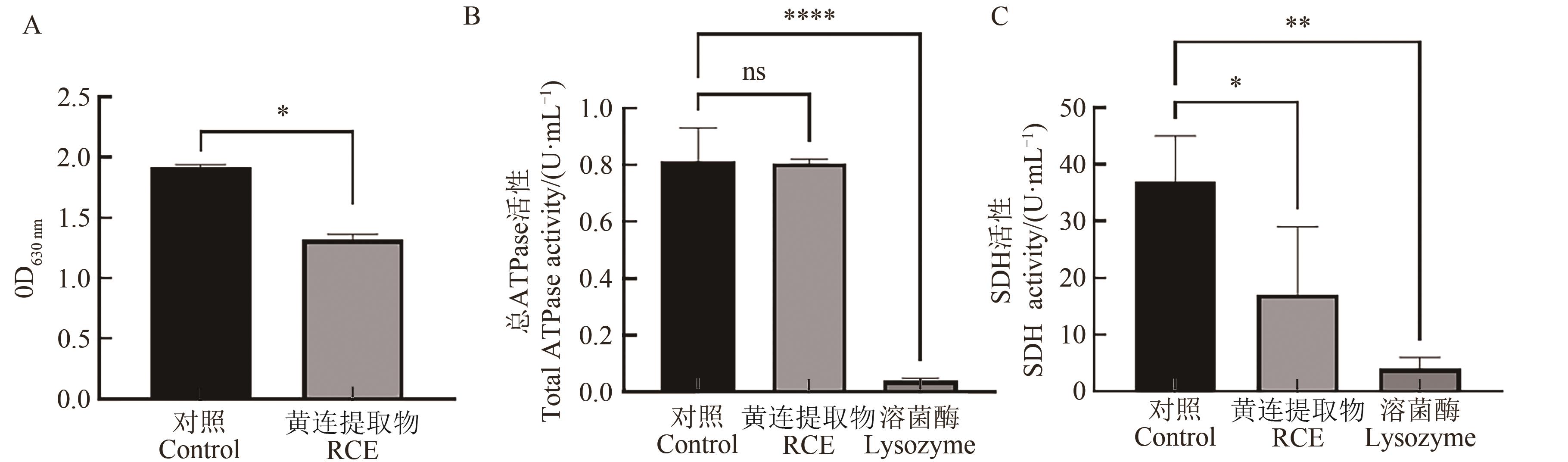
图7 RCE作用于金黄色葡萄球菌后细胞的代谢活力和酶活力A:细胞活力;B:细胞总ATPase活性;C:细胞SDH活性。*、**和****分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.000 1水平差异显著;ns表示差异不显著
Fig. 7 Activity of cellular metabolism and enzyme of Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to RCEA: Cell viability; B: Cellular total ATPase activity; C: Cellular SDH activity. *,**and **** indicate significant differences at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.000 1 levels,respectiveiy;ns indicates not significant
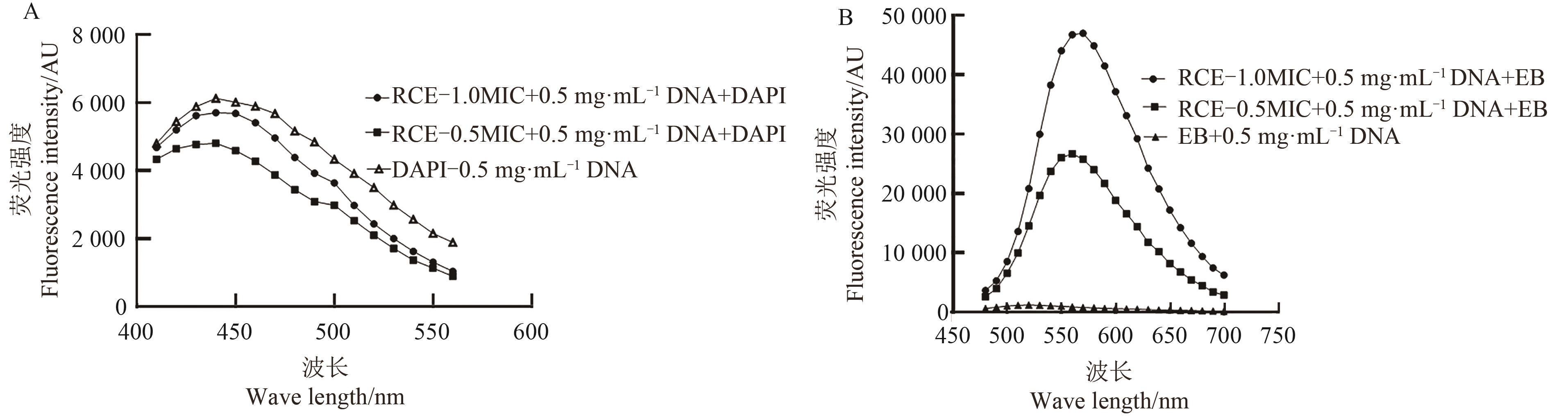
图 9 RCE与DAPI/EB竞争性结合DNA的荧光光谱图A:DAPI-DNA体系;B:EB-DNA体系
Fig. 9 Fluorescence emission spectra of DAPI/EB-DNA in the presence of RCEA:DAPI-DNA system; B:EB-DNA system
| 1 | FITZGERALD J R. Livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus:origin,evolution and public health threat [J]. Trends Microbiol., 2012,20(4):192-198. |
| 2 | PARK S, RONHOLM J. Staphylococcus aureus in agriculture:lessons in evolution from a multispecies pathogen [J/OL]. Clin.Microbiol. Rev., 2021,34(2):e00182-20 [2024-01-26].. |
| 3 | BEYER P, PAULIN S. Priority pathogens and the antibiotic pipeline:an update [J/OL]. Bull.World Health Rrgan., 2020,98(3):151 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 4 | WU J, LUO Y, DENG D, et al.. Coptisine from Coptis chinensis exerts diverse beneficial properties:a concise review [J]. J. Cell Mol. Med., 2019,23(12):7946-7960. |
| 5 | LI C, SRIDHARA M B, RAKESH K P, et al.. Multi-targeted dihydrazones as potent biotherapeutics [J]. Bioorg. Chem., 2018,81:389-395. |
| 6 | XU Z, FENG W, SHEN Q, et al.. Rhizoma coptidis and berberine as a natural drug to combat aging and aging-related diseases via anti-oxidation and AMPK activation [J]. Aging Dis., 2017,8(6):760-777. |
| 7 | WANG Y, DU P, JIANG D. Berberine functions as a negative regulator in lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis by suppressing NF-κB and IL-6 mediated STAT3 activation [J/OL]. Pathog. Dis., 2020,78(7):ftaa047 [2024-01-26].. |
| 8 | 王茹,关亮俊,陈两绵, 等. 黄连等6味中药中生物碱苷类成分的发现、分离和结构鉴定[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48 (17): 4598-4609. |
| WANG R, GUAN L J, CHEN L M, et al.. Discovery, isolation and structural identification of alkaloid glycosides in six traditional Chinese medicine such as Coptis chinensis [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2023,48(17):4598-4609. | |
| 9 | 周瑞,项昌培,张晶晶,等.黄连化学成分及小檗碱药理作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(19):4561-4573. |
| ZHOU R, XIANG C P, ZHANG J J, et al.. Research progress on chemical compositions of Coptidis Rhizomaand pharmacological effects of berberine [J]. China J.Chin.Mater. Med., 2020,45(19):4561-4573. | |
| 10 | LIN S J, CHEN C S, LIN S S, et al.. In vitro anti-microbial and in vivo cytokine modulating effects of different prepared Chinese herbal medicines [J]. Food Chem. Toxicol., 2006,44(12):2078-2085. |
| 11 | 周芳芳,杨温仪,王蕾.黄连解毒汤对100株临床多重耐药菌的体外抑菌效果研究[J].国际检验医学杂志,2018,39(24):3061-3065. |
| ZHOU F F, YANG W Y, WANG L. In vitro antibacterial effect of coptidis decoction on 100 isolates of multi-drug resistant bacteria [J]. Int. J. Lab. Med., 2018,39(24):3061-3065. | |
| 12 | XUE D F, ZOU Z Y, CHEN B, et al.. Study on membrane injury mechanism of total alkaloids and berberine from Coptidis Rhizoma on Aeromonas hydrophila [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2015,40(9):1787-1792. |
| 13 | ARAYA-CONTRERAS T, VEAS R, ESCOBAR C A, et al..Antibacterial effect of Luma apiculata (DC.) burret extracts in clinically important bacteria [J/OL]. Int. J. Microbiol., 2019,2019:7803726 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 14 | GOEL S, MISHRA P. Thymoquinone inhibits biofilm formation and has selective antibacterial activity due to ROS generation [J].Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2018,102(4):1955-1967. |
| 15 | XIANG Q S, KANG C D, NIU L Y, et al.. Antibacterial activity and a membrane damage mechanism of plasma-activated water against Pseudomonas deceptionensis CM2 [J]. LWT Food Sci. Technol., 2018, 96: 395-401. |
| 16 | LIU G R, SONG Z Q, YANG X L, et al.. Antibacterial mechanism of bifidocin A,a novel broad-spectrum bacteriocin produced by Bifidobacterium animalis BB04 [J]. Food Contr., 2016,62:309-316. |
| 17 | KIELKOPF C L, BAUER W, URBATSCH I L. Bradford assay for determining protein concentration [J/OL]. Cold Spring Har. Protoc., 2020(4):102269 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 18 | WU Y P, BAI J R, ZHONG K, et al.. A dual antibacterial mechanism involved in membrane disruption and DNA binding of 2R,3R-dihydromyricetin from pine needles of Cedrus deodara against Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Food Chem., 2017,218:463-470. |
| 19 | HEGDE A H, PRASHANTH S N, SEETHARAMAPPA J.Interaction of antioxidant flavonoids with calf Thymus DNA analyzed by spectroscopic and electrochemical methods [J]. J.Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2012,63:40-46. |
| 20 | LYU M X, WANG M W, LU K, et al.. DNA/Lysozyme-binding affinity study of novel peptides from TAT (47-57) and BRCA1 (782-786) in vitro by spectroscopic analysis [J]. Spectrochim.Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 2019,209:109-117. |
| 21 | 王欢, 王敏, 刘竹青, 等. 蓝莓黑醋栗枸杞决明子复合物对眼部细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2024,40(1):47-53. |
| WANG H, WANG M, LIU Z Q, et al.. Protective effect of a complex of blueberry, blackcurrant, medlar and Cassia obtusifolia against oxidative stress injury in retinal epithelial cells [J]. Mod. Food Sci. Technol., 2024, 40(1): 47-53. | |
| 22 | LEE B, LEE D G. Depletion of reactive oxygen species induced by chlorogenic acid triggers apoptosis-like death in Escherichia coli [J]. Free. Radic. Res., 2018,52(5):605-615. |
| 23 | LIU F, LIU Y, SUN Z, et al.. Preparation and antibacterial properties of epsilon-polylysine-containing gelatin/chitosan nanofiber films [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 164: 3376-3387. |
| 24 | 陈梦玲,蓝蔚青,李函笑,等.牛至精油对腐生葡萄球菌抑制作用机制[J].食品科学,2020,41(7):46-51. |
| CHEN M L, LAN W Q, LI H X, et al.. Action mechanism of oregano essential oil against Staphylococcus saprophyticus [J]. Food Sci., 2020,41(7):46-51. | |
| 25 | ZHU Y, ZHANG S.Antibacterial activity and mechanism of lacidophilin from Lactobacillus pentosus against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2020,11:582349 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 26 | SHU H, CHEN H, WANG X, et al.. Antimicrobial activity and proposed action mechanism of 3-Carene against Brochothrix thermosphacta and Pseudomonas fluorescens [J/OL]. Molecules, 2019,24(18):3246 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 27 | WU Y P, BAI J R, ZHONG K, et al.. Antibacterial effect of 2R,3R-dihydromyricetin on the cellular functions of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 2018,82(1):135-138. |
| 28 | 张舒涵,梁海运,孙佳慧,等. 甘草提取物对Staphylococcus aureus的抑菌活性及作用机理[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2024,50(10):259-265. |
| ZHANG S H, LIANG H Y, SUN J H, et al.. Antimicrobial activity of licorice extract against Staphylococcus aureus and its underlying mechanism of action [J]. Food Ferment. Ind., 2024, 50(10): 259-265. | |
| 29 | ZHOU C Q, LI C Z, SIVA S,et al..Chemical composition,antibacterial activity and study of the interaction mechanisms of the main compounds present in the Alpinia galanga rhizomes essential oil [J/OL]. Ind.Crops Prod., 2021,165:113441 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 30 | JIN Y S, LIN J X, SHI H Q, et al.. The active ingredients in Chinese peony pods synergize with antibiotics to inhibit MRSA growth and biofilm formation [J/OL]. Microbiol. Res., 2024,281:127625 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 31 | 黄梅,谭余庆,罗俊,等.植物类中药抗细菌耐药性的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(23):218-224. |
| HUANG M, TAN Y Q, LUO J, et al.. Antimicrobial resistance of Chinese herbal medicine [J].Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae, 2018,24(23):218-224. | |
| 32 | WANG J, WANG L, LOU G H, et al.. Coptidis rhizoma:a comprehensive review of its traditional uses,botany,phytochemistry,pharmacology and toxicology [J]. Pharm. Biol., 2019,57(1):193-225. |
| 33 | RUBFIARO A S, TSEGAY P S, LAI Y, et al.. Scanning ion conductance microscopy study reveals the disruption of the integrity of the human cell membrane structure by oxidative DNA damage [J]. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater., 2021,4(2):1632-1639. |
| 34 | WANG L H, WANG M S, ZENG X N, et al..An in vitro investigation of the inhibitory mechanism of β-galactosidase by cinnamaldehyde alone and in combination with carvacrol and thymol [J]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj., 2017,1861(1):3189-3198. |
| 35 | WANG J, RAN Q, ZENG H R, et al.. Cellular stress response mechanisms of rhizoma coptidis:a systematic review [J/OL].Chin. Med., 2018,13(1):27 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 36 | DHAMGAYE S, DEVAUX F, VANDEPUTTE P, et al.. Molecular mechanisms of action of herbal antifungal alkaloid berberine,in Candida albicans [J/OL].PLoS One,2014,9(8):e104554 [2024-01-26]. . |
| 37 | 杨维琴,钱亮亮,张宗艺,等.黄连提取物抗副溶血弧菌活性成分的鉴定及其作用机理[J].中国食品添加剂,2022,33(4):181-187. |
| YANG W Q, QIAN L L, ZHANG Z Y, et al.. Identification of the active components of Coptis chinensis extracts and its antibacterial mechanism on Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J]. China Food Addit., 2022,33(4):181-187. | |
| 38 | ZHANG R, TIAN S, ZHANG T, et al.. Antibacterial activity mechanism of coptisine against Pasteurella multocida [J/OL]. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 2023,13:1207855 [2024-01-26].. |
| [1] | 高思琦, 杨新建, 朱德琪, 关明玮, 寇云婷, 满程, 焦健. 抗菌肽PAJE对金黄色葡萄球菌及其SCVs的杀菌作用机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 156-166. |
| [2] | 纪蕾, 刘天红, 王颖, 李晓, 李红艳, 孙元芹, 姜晓东. 载银氧化壳聚糖的制备与抑菌性能研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 214-222. |
| [3] | 周宇, 李佳玉, 王乐, 贾晓爽, 高思琦, 王潇, 焦健. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变体诱导筛选及特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 147-157. |
| [4] | 梁艳琼, 李锐, 吴伟怀, 习金根, 谭施北, 黄兴, 陆英, 贺春萍, 易克贤. 枯草芽孢杆菌Czk1挥发物混合活性组分对橡胶灵芝菌的抑菌机理[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 152-159. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号