




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 44-53.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0885
赵贵元1,2( ), 王永强2, 刘建光2, 耿昭2, 张寒霜2, 吴立强1, 王省芬1(
), 王永强2, 刘建光2, 耿昭2, 张寒霜2, 吴立强1, 王省芬1( ), 张桂寅1(
), 张桂寅1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-28
接受日期:2024-11-27
出版日期:2025-07-15
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
王省芬,张桂寅
作者简介:赵贵元 E-mail:zhaogy0302@163.com
基金资助:
Guiyuan ZHAO1,2( ), Yongqiang WANG2, Jianguang LIU2, Zhao GENG2, Hanshuang ZHANG2, Liqiang WU1, Xingfen WANG1(
), Yongqiang WANG2, Jianguang LIU2, Zhao GENG2, Hanshuang ZHANG2, Liqiang WU1, Xingfen WANG1( ), Guiyin ZHANG1(
), Guiyin ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-10-28
Accepted:2024-11-27
Online:2025-07-15
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Xingfen WANG,Guiyin ZHANG
摘要:
外源基因的插入位点能影响受体材料的基因表达及性状表现。为明确外源基因插入位点对抗虫棉Bt蛋白含量的影响,选用29个抗虫棉品系进行Bt蛋白含量测定以及全基因组重测序分析。结果表明,不同品系间的Bt蛋白含量存在显著差异,其中K3品系蛋白含量最高。通过全基因组重测序分析和PCR鉴定发现,Bt基因在29个品系均为单拷贝但插入位点存在差异,其中K3品系的Bt基因位于A02染色体2 791 303~2 791 335 bp(A02型),而其他品系的Bt基因则位于D12染色体(D12型)。为进一步验证插入位点对Bt蛋白含量的影响,利用K3品系与对照新棉33B进行杂交并构建F2群体,进一步分析F2群体的Bt蛋白含量发现,Bt基因插入位点位于A02染色体的F2单株(A02型)Bt蛋白含量极显著高于D12型单株。综上所述,Bt抗虫蛋白含量受插入位点影响,其位于A02染色体更利于Bt基因的高效表达。以上结果可为培育抗虫棉新品种提供种质资源和理论支撑。
中图分类号:
赵贵元, 王永强, 刘建光, 耿昭, 张寒霜, 吴立强, 王省芬, 张桂寅. 外源基因插入位点对抗虫棉Bt蛋白含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 44-53.
Guiyuan ZHAO, Yongqiang WANG, Jianguang LIU, Zhao GENG, Hanshuang ZHANG, Liqiang WU, Xingfen WANG, Guiyin ZHANG. Effect of Exogenous Gene Insertion Site on Bt Protein Content in Insect-resistant Cotton[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 44-53.
品系 Line | 亲本 Parent | Bt基因 Bt gene | 品系 Line | 亲本 Parent | Bt基因 Bt gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | ND0901×33B | + | K21 | ND0921×33B | + |
| K3 | ND0903×33B | + | K22 | ND0922×33B | + |
| K4 | ND0904×33B | + | K23 | ND0923×33B | + |
| K5 | ND0905×33B | + | K24 | ND0924×33B | + |
| K6 | ND0906×33B | + | K27 | ND0927×33B | + |
| K8 | ND0908×33B | + | K28 | ND0928×33B | + |
| K9 | ND0909×33B | + | K29 | ND0929×33B | + |
| K10 | ND0910×33B | + | K30 | ND0930×33B | + |
| K11 | ND0911×33B | + | K31 | ND0931×33B | + |
| K12 | ND0912×33B | + | K32 | ND0932×33B | + |
| K13 | ND0913×33B | + | K33 | ND0933×33B | + |
| K17 | ND0917×33B | + | K34 | ND0934×33B | + |
| K18 | ND0918×33B | + | K35 | ND0935×33B | + |
| K19 | ND0919×33B | + | K26(33B) | 爱字90×岱字50 Aizi 90×Daizi 50 | + |
| K20 | ND0920×33B | + | CCRI12 | 乌干达4号×邢台6871 Wuganda 4×Xingtai 6871 | - |
表1 供试材料信息
Table 1 Information of the tested materials
品系 Line | 亲本 Parent | Bt基因 Bt gene | 品系 Line | 亲本 Parent | Bt基因 Bt gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | ND0901×33B | + | K21 | ND0921×33B | + |
| K3 | ND0903×33B | + | K22 | ND0922×33B | + |
| K4 | ND0904×33B | + | K23 | ND0923×33B | + |
| K5 | ND0905×33B | + | K24 | ND0924×33B | + |
| K6 | ND0906×33B | + | K27 | ND0927×33B | + |
| K8 | ND0908×33B | + | K28 | ND0928×33B | + |
| K9 | ND0909×33B | + | K29 | ND0929×33B | + |
| K10 | ND0910×33B | + | K30 | ND0930×33B | + |
| K11 | ND0911×33B | + | K31 | ND0931×33B | + |
| K12 | ND0912×33B | + | K32 | ND0932×33B | + |
| K13 | ND0913×33B | + | K33 | ND0933×33B | + |
| K17 | ND0917×33B | + | K34 | ND0934×33B | + |
| K18 | ND0918×33B | + | K35 | ND0935×33B | + |
| K19 | ND0919×33B | + | K26(33B) | 爱字90×岱字50 Aizi 90×Daizi 50 | + |
| K20 | ND0920×33B | + | CCRI12 | 乌干达4号×邢台6871 Wuganda 4×Xingtai 6871 | - |
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Sequence (5’-3’) | 扩增片段长度 Amplified fragment length/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| D12-LB-F | CACCAAAGAGAAACCCCAATC | 456 | 59.7 |
| D12-LB-R | CGCTGATTGTTCTGTTCCTCC | ||
| D12-RB-F | GTCAATACCGCAGGGCACTTA | 639 | 59.0 |
| D12-RB-R | AGTCAAAGGAGCTTCATGGGT | ||
| A02-LB-F | CACCAAAGAGAAACCCCAATC | 289 | 58.6 |
| A02-LB-R | CACGGACAACTCAGGCAAGTA | ||
| A02-RB-F | CCCAGGCTTGTCCACATCATC | 692 | 57.1 |
| A02-RB-R | TCCCTCCTGAGCTACCATGTC |
表2 插入位点验证所用引物序列
Table 2 Primer sequences used for insertion site validation
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Sequence (5’-3’) | 扩增片段长度 Amplified fragment length/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| D12-LB-F | CACCAAAGAGAAACCCCAATC | 456 | 59.7 |
| D12-LB-R | CGCTGATTGTTCTGTTCCTCC | ||
| D12-RB-F | GTCAATACCGCAGGGCACTTA | 639 | 59.0 |
| D12-RB-R | AGTCAAAGGAGCTTCATGGGT | ||
| A02-LB-F | CACCAAAGAGAAACCCCAATC | 289 | 58.6 |
| A02-LB-R | CACGGACAACTCAGGCAAGTA | ||
| A02-RB-F | CCCAGGCTTGTCCACATCATC | 692 | 57.1 |
| A02-RB-R | TCCCTCCTGAGCTACCATGTC |
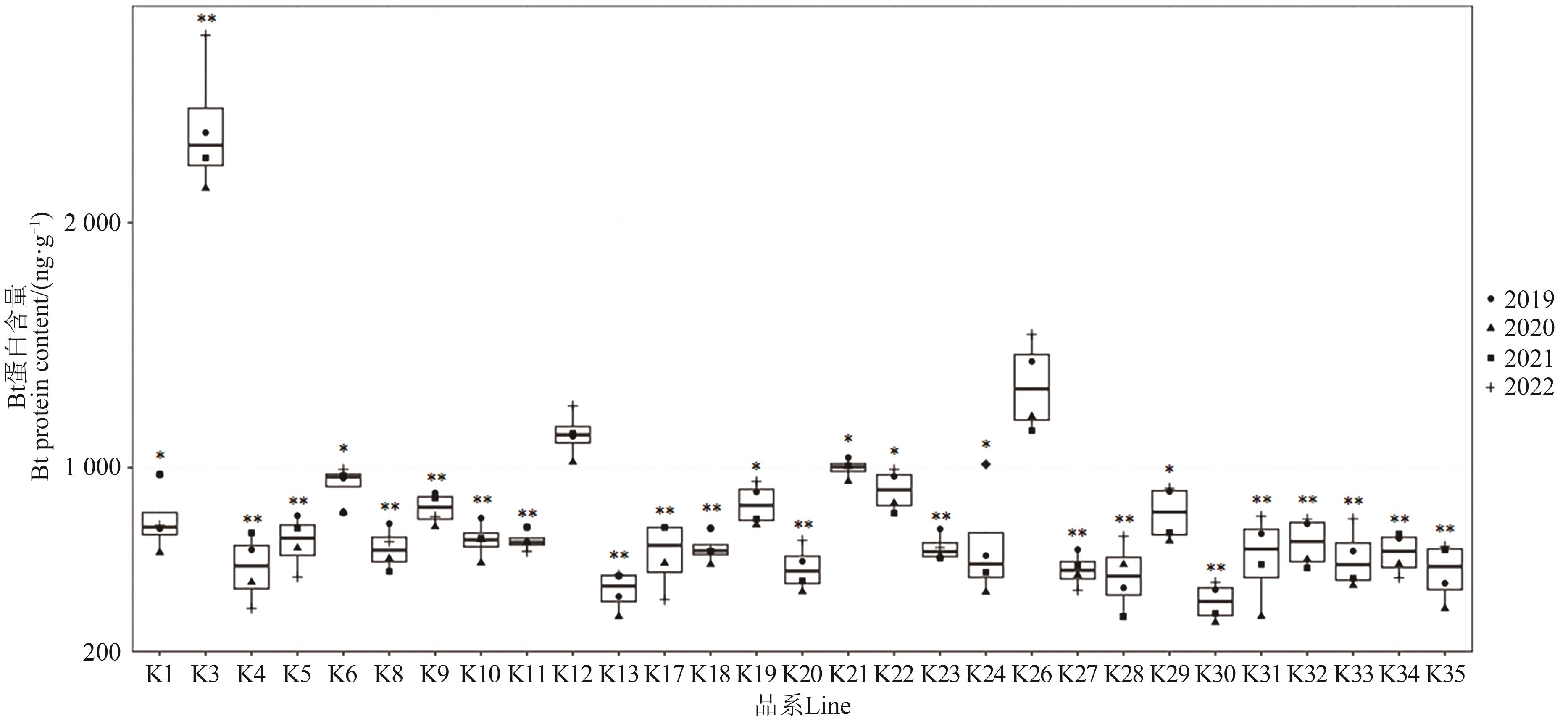
图1 2019—2022年各抗虫棉品系Bt蛋白含量注:*和**分别表示与K26(新棉33B)在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Bt protein content in different insect-resistant cotton lines from 2019 to 2022Note:* and ** indicate significant differences with K26 (Xinmian 33B) at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
品系 Line | 染色体 Chromosome | 插入起点 Insert starting point/bp | 插入终点 Insertion end point/bp | 碱基缺失 Base deletion/bp | 拷贝数 Copies number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K3 | ChrA02 | 2 791 303 | 2 791 335 | 32 | 1 |
| K4 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K5 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K6 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K8 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K9 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K10 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K11 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K12 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K13 | ChrD12 | 49 127 433 | 49 127 527 | 94 | 1 |
| K17 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K18 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K19 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K20 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K21 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K22 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K23 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 550 | 103 | 1 |
| K24 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K27 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K28 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K29 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K30 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K31 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K32 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K33 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K34 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K35 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K26(33B) | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
表3 Bt 基因拷贝数和插入位点整合信息
Table 3 Copy number and insertion site integrate information of Bt gene
品系 Line | 染色体 Chromosome | 插入起点 Insert starting point/bp | 插入终点 Insertion end point/bp | 碱基缺失 Base deletion/bp | 拷贝数 Copies number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K3 | ChrA02 | 2 791 303 | 2 791 335 | 32 | 1 |
| K4 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K5 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K6 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K8 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K9 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K10 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K11 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K12 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K13 | ChrD12 | 49 127 433 | 49 127 527 | 94 | 1 |
| K17 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K18 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K19 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K20 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K21 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K22 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K23 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 550 | 103 | 1 |
| K24 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K27 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K28 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K29 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K30 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K31 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K32 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K33 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K34 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K35 | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
| K26(33B) | ChrD12 | 49 127 447 | 49 127 527 | 80 | 1 |
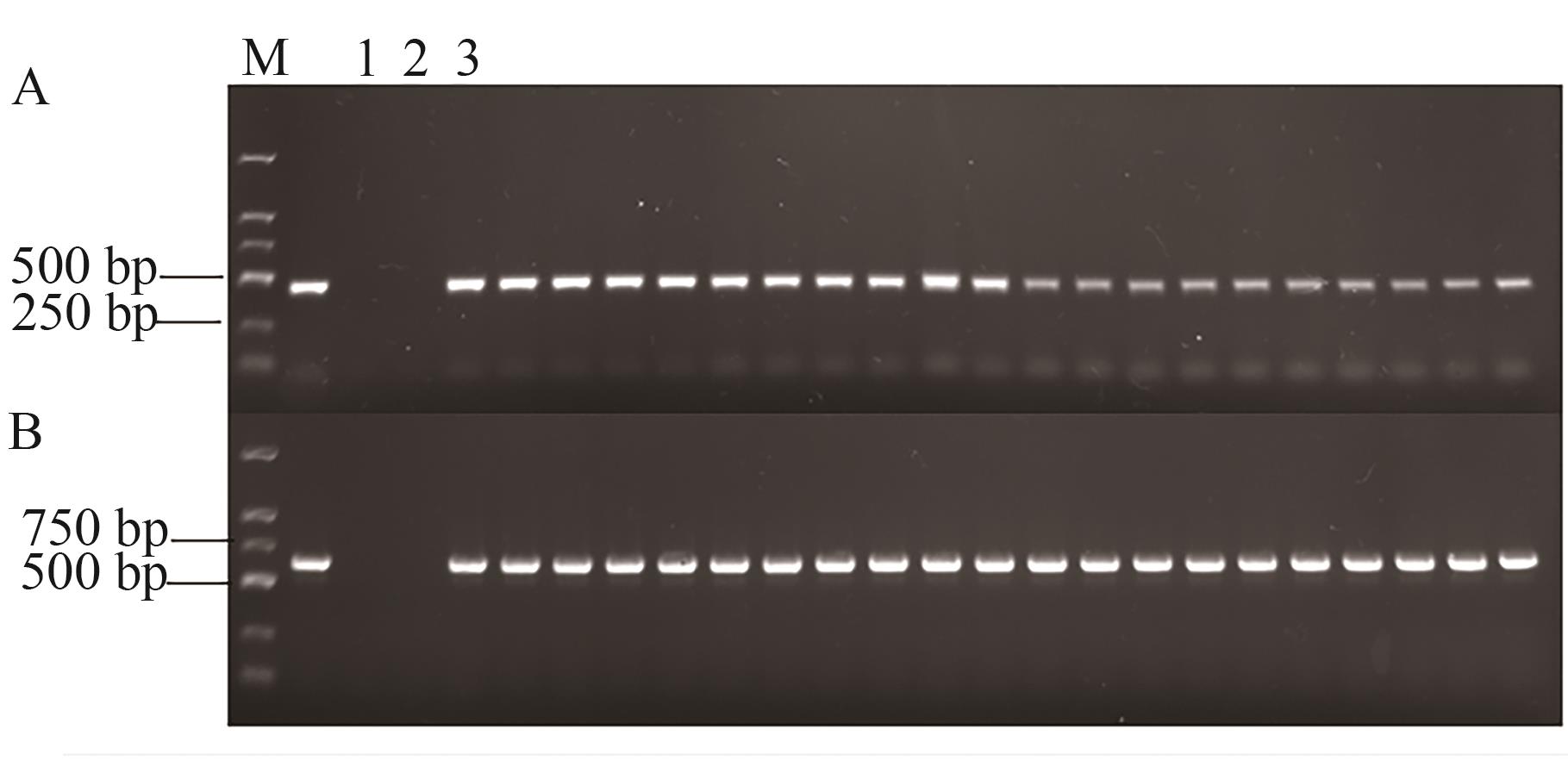
图2 D12染色体插入位点的检测A:D12-LB引物检测结果;B:D12-RB检测结果。1—水;2—K3;3—新棉33B;M—DL2000 DNA marker;其余甬道为其他品系
Fig. 2 Detection of ChrD12 insertion siteA: D12-LB primer detection results; B: D12-RB primer detection results. 1—Water; 2—K3; 3—Xinmian 33B; M—DL2000 DNA marker; other lanes are other lines
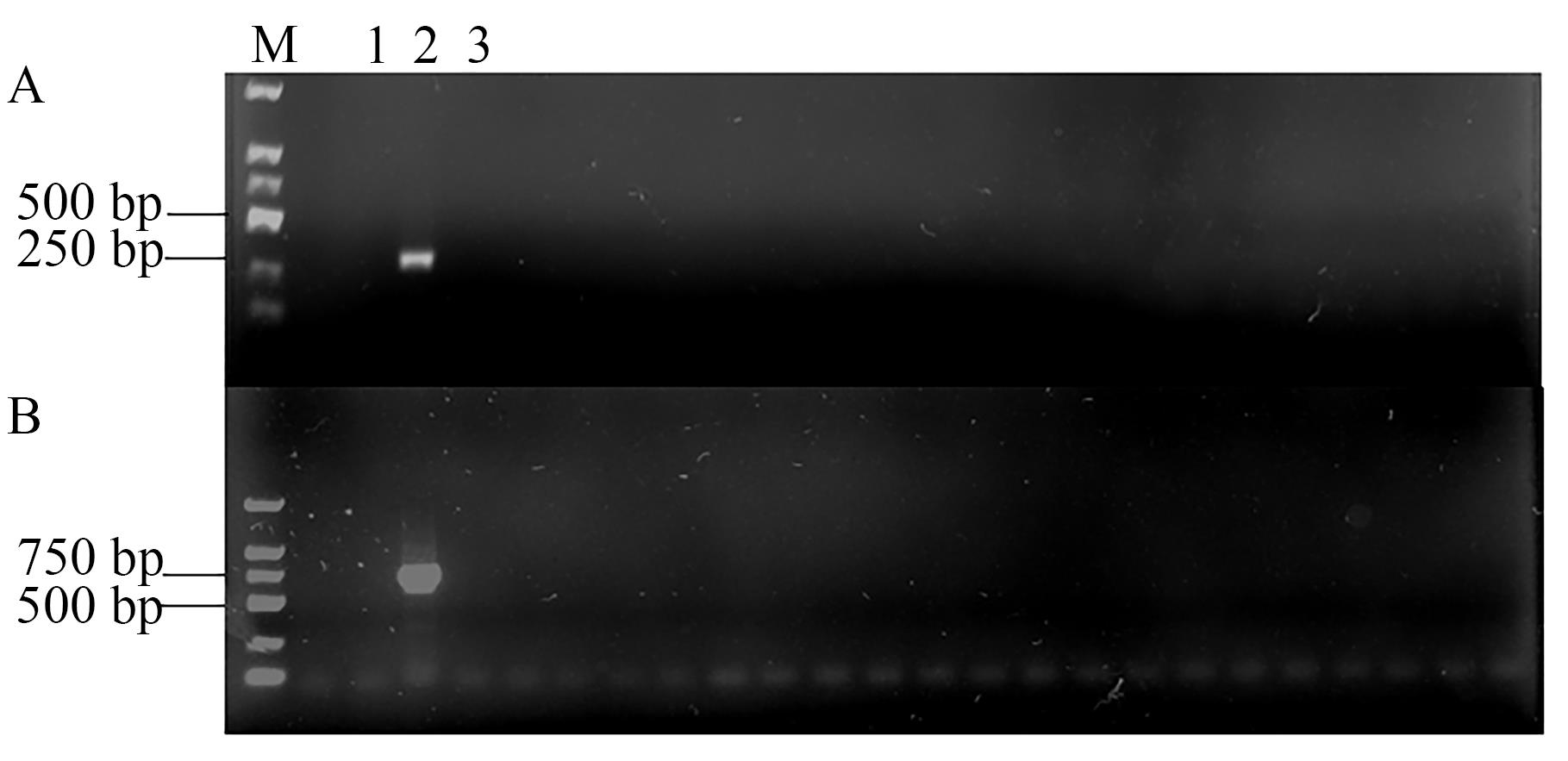
图3 A02染色体插入位点检测A: A02-LB引物检测结果;B: A02-RB检测结果。1—水;2—K3;3—新棉33B;M—DL2000 DNA marker;其余甬道为其他品系
Fig. 3 Detection of ChrA02 insertion siteA: A02-LB primer detection results; B: A02-RB primer detection results; 1—Water; 2—K3; 3—Xinmian 33B; M—DL2000 DNA marker; other lanes are other lines
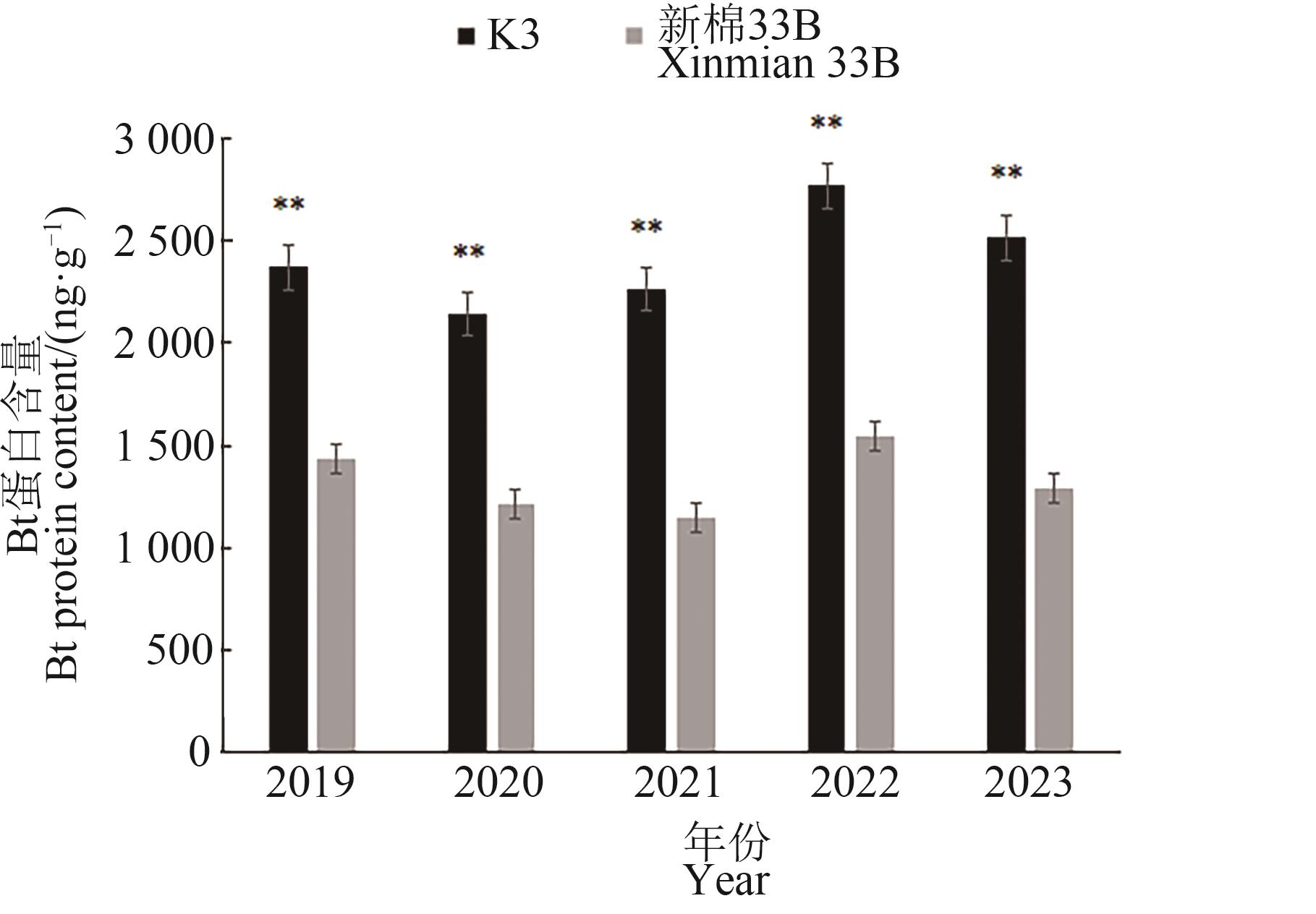
图4 2019—2023年K3与新棉33B Bt蛋白含量注:**表示K3和新棉33B间在P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 K3 and Xinmian 33B Bt protein contentfrom 2019 to 2023Note:** indicates significant difference between K3 and Xinmian 33B at P<0.01 level.
F1单株 F1 individual line | Bt蛋白含量 Bt protein content/(ng·g-1) | F1单株代号 F1 individual line | Bt蛋白含量 Bt protein content/(ng·g-1) | F1单株 F1 individual line | Bt蛋白含量 Bt protein content/(ng·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 620.96 | 35 | 1 900.34 | 69 | 1 959.75 |
| 2 | 2 343.26 | 36 | 2 620.28 | 70 | 2 282.87 |
| 3 | 2 080.38 | 37 | 2 003.94 | 71 | 2 375.58 |
| 4 | 1 719.96 | 38 | 2 708.17 | 72 | 2 582.07 |
| 5 | 1 901.95 | 39 | 2 509.09 | 73 | 2 681.05 |
| 6 | 1 567.73 | 40 | 1 739.91 | 74 | 1 778.00 |
| 7 | 2 710.37 | 41 | 1 986.55 | 75 | 1 979.19 |
| 8 | 2 160.84 | 42 | 2 003.78 | 76 | 2 425.47 |
| 9 | 2 458.44 | 43 | 2 452.15 | 77 | 2 592.63 |
| 10 | 2 206.88 | 44 | 2 689.70 | 78 | 2 749.04 |
| 11 | 2 030.17 | 45 | 2 006.63 | 79 | 2 552.07 |
| 12 | 2 616.94 | 46 | 1 740.00 | 80 | 2 032.94 |
| 13 | 1 804.79 | 47 | 2 092.82 | 81 | 1 752.55 |
| 14 | 2 380.22 | 48 | 2 293.19 | 82 | 2 506.93 |
| 15 | 2 519.91 | 49 | 2 493.81 | 83 | 1 766.27 |
| 16 | 2 521.00 | 50 | 1 569.09 | 84 | 2 384.92 |
| 17 | 1 839.19 | 51 | 1 937.93 | 85 | 2 458.43 |
| 18 | 2 658.52 | 52 | 1 600.92 | 86 | 2 156.09 |
| 19 | 1 980.21 | 53 | 2 034.36 | 87 | 2 629.90 |
| 20 | 2 159.45 | 54 | 2 320.95 | 88 | 1 717.48 |
| 21 | 1 589.29 | 55 | 2 641.93 | 89 | 1 983.71 |
| 22 | 2 728.60 | 56 | 1 710.80 | 90 | 2 697.81 |
| 23 | 1 904.49 | 57 | 1 846.32 | 91 | 2 124.19 |
| 24 | 1 786.33 | 58 | 2 500.14 | 92 | 2 477.61 |
| 25 | 2 058.37 | 59 | 2 240.53 | 93 | 2 530.88 |
| 26 | 2 744.91 | 60 | 2 588.66 | 94 | 2 214.65 |
| 27 | 2 762.57 | 61 | 2 657.60 | 95 | 2 265.45 |
| 28 | 2 133.94 | 62 | 2 463.61 | 96 | 2 119.77 |
| 29 | 1 591.75 | 63 | 1 885.70 | 97 | 1 962.63 |
| 30 | 1 710.46 | 64 | 2 138.93 | 98 | 1 747.97 |
| 31 | 2 150.90 | 65 | 2 274.05 | 99 | 1 857.94 |
| 32 | 2 238.87 | 66 | 1 957.03 | 100 | 2 001.26 |
| 33 | 2 691.36 | 67 | 2 034.69 | 101 | 2 410.54 |
| 34 | 1 790.58 | 68 | 2 470.77 | 102 | 2 401.90 |
表4 F1群体单株 Bt蛋白含量
Table 4 Bt protein content of individual lines in F1 population
F1单株 F1 individual line | Bt蛋白含量 Bt protein content/(ng·g-1) | F1单株代号 F1 individual line | Bt蛋白含量 Bt protein content/(ng·g-1) | F1单株 F1 individual line | Bt蛋白含量 Bt protein content/(ng·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 620.96 | 35 | 1 900.34 | 69 | 1 959.75 |
| 2 | 2 343.26 | 36 | 2 620.28 | 70 | 2 282.87 |
| 3 | 2 080.38 | 37 | 2 003.94 | 71 | 2 375.58 |
| 4 | 1 719.96 | 38 | 2 708.17 | 72 | 2 582.07 |
| 5 | 1 901.95 | 39 | 2 509.09 | 73 | 2 681.05 |
| 6 | 1 567.73 | 40 | 1 739.91 | 74 | 1 778.00 |
| 7 | 2 710.37 | 41 | 1 986.55 | 75 | 1 979.19 |
| 8 | 2 160.84 | 42 | 2 003.78 | 76 | 2 425.47 |
| 9 | 2 458.44 | 43 | 2 452.15 | 77 | 2 592.63 |
| 10 | 2 206.88 | 44 | 2 689.70 | 78 | 2 749.04 |
| 11 | 2 030.17 | 45 | 2 006.63 | 79 | 2 552.07 |
| 12 | 2 616.94 | 46 | 1 740.00 | 80 | 2 032.94 |
| 13 | 1 804.79 | 47 | 2 092.82 | 81 | 1 752.55 |
| 14 | 2 380.22 | 48 | 2 293.19 | 82 | 2 506.93 |
| 15 | 2 519.91 | 49 | 2 493.81 | 83 | 1 766.27 |
| 16 | 2 521.00 | 50 | 1 569.09 | 84 | 2 384.92 |
| 17 | 1 839.19 | 51 | 1 937.93 | 85 | 2 458.43 |
| 18 | 2 658.52 | 52 | 1 600.92 | 86 | 2 156.09 |
| 19 | 1 980.21 | 53 | 2 034.36 | 87 | 2 629.90 |
| 20 | 2 159.45 | 54 | 2 320.95 | 88 | 1 717.48 |
| 21 | 1 589.29 | 55 | 2 641.93 | 89 | 1 983.71 |
| 22 | 2 728.60 | 56 | 1 710.80 | 90 | 2 697.81 |
| 23 | 1 904.49 | 57 | 1 846.32 | 91 | 2 124.19 |
| 24 | 1 786.33 | 58 | 2 500.14 | 92 | 2 477.61 |
| 25 | 2 058.37 | 59 | 2 240.53 | 93 | 2 530.88 |
| 26 | 2 744.91 | 60 | 2 588.66 | 94 | 2 214.65 |
| 27 | 2 762.57 | 61 | 2 657.60 | 95 | 2 265.45 |
| 28 | 2 133.94 | 62 | 2 463.61 | 96 | 2 119.77 |
| 29 | 1 591.75 | 63 | 1 885.70 | 97 | 1 962.63 |
| 30 | 1 710.46 | 64 | 2 138.93 | 98 | 1 747.97 |
| 31 | 2 150.90 | 65 | 2 274.05 | 99 | 1 857.94 |
| 32 | 2 238.87 | 66 | 1 957.03 | 100 | 2 001.26 |
| 33 | 2 691.36 | 67 | 2 034.69 | 101 | 2 410.54 |
| 34 | 1 790.58 | 68 | 2 470.77 | 102 | 2 401.90 |
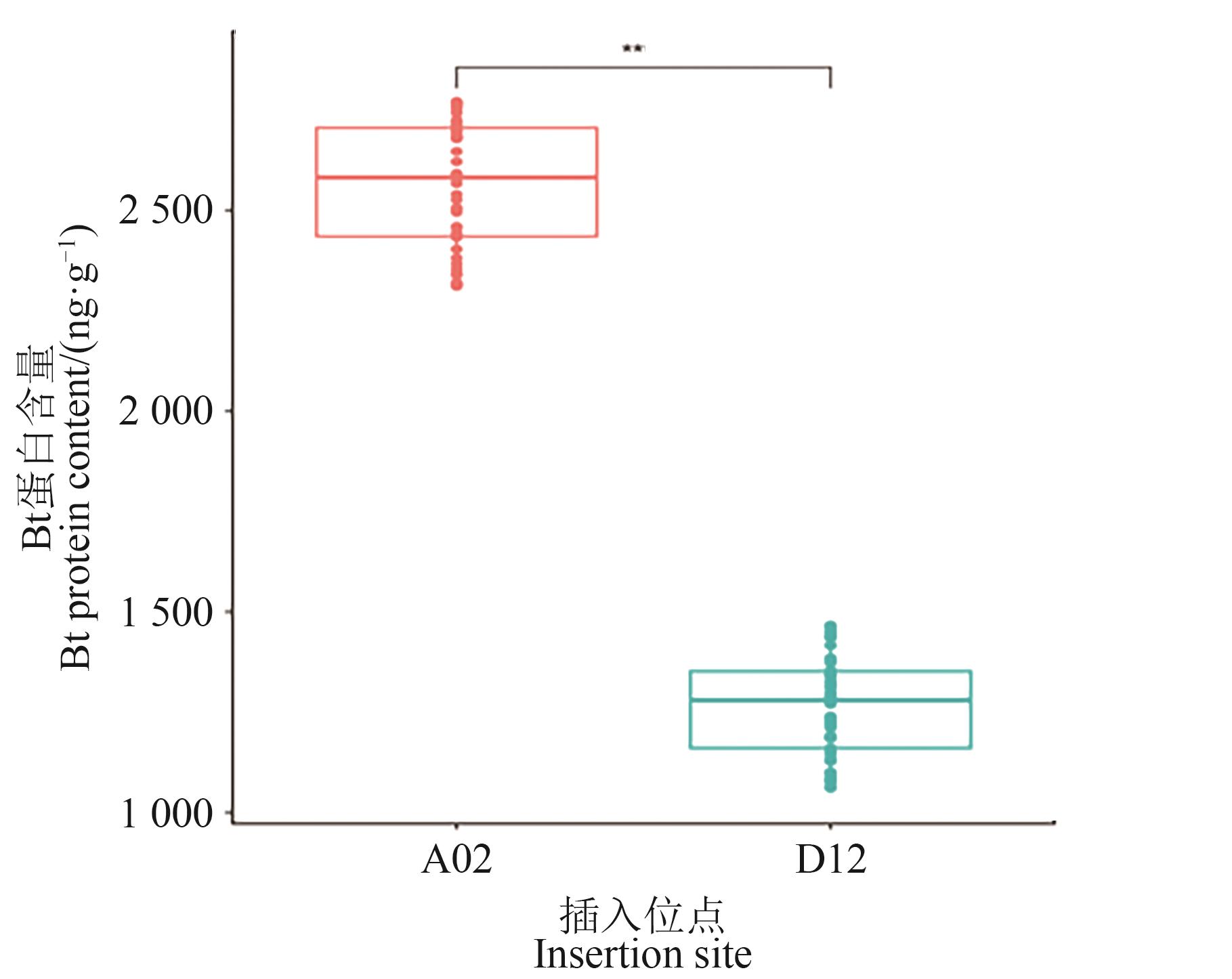
图5 两类单株的Bt蛋白含量注:**表示在P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Bt protein content in two types of individual plantsNote:** indicates significant difference at P<0.01 level.
| [1] | 夏荟菁.转Cry1C*基因棉花材料的抗虫性鉴定与评价[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2023. |
| XIA H J. Insect-resistant identification and evaluation of transgenic Cry1C* cotton [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| [2] | 文学,张宝红.转基因抗虫棉研究现状与展望[J].农业生物技术学报,2000, 8(2):194-199. |
| WEN X, ZHANG B H. Progress and prospects for insect-resistant transgenic cotton [J]. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2000, 8(2):194-199. | |
| [3] | 张京飞.转Bt基因抗虫棉抗虫性研究与新品系筛选[D].保定:河北农业大学,2014. |
| ZHANG J F. Identification of insect resisitance and new variety screening in Bt transgenic cotton [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| [4] | 邹奎.我国转基因抗虫棉品种现状分析[J].中国棉花,2003,30(8):2-4. |
| [5] | 徐泽俊,聂以春,张献龙,等.转双价抗虫基因棉花的主要农艺性状的遗传变异[J].植物遗传资源学报,2011,12(1):125-130. |
| XU Z J, NIE Y C, ZHANG X L, et al.. Genetic variation of main agronomic traits of transgenic insect resistant lines in cotton [J].J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2011,12(1):125-130. | |
| [6] | 李浩辉,刘彩月,张海文,等.2022年度全球转基因作物产业化发展现状及趋势分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2023,25(12):6-16. |
| LI H H, LIU C Y, ZHANG H W,et al..Global genetically modified crop industrialization trends in 2022 [J]. J. Agric. Sci.Technol., 2023, 25(12):6-16. | |
| [7] | 谷淇深,李志坤,王省芬,等. Bt抗虫棉新品系毒蛋白表达差异分析[J].棉花学报,2016,29(2):128-137. |
| GU Q S, LI Z K, WANG X F, et al.. Differential expression analysis of Bt protein in new Bt cotton lines [J]. Cott. Sci., 2016, 29(2):128-137. | |
| [8] | 周冬生,吴振延,王学林,等.转Bt基因棉的抗棉铃虫性及其生理作用研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2000,28(1):65-68. |
| ZHOU D S, WU Z Y, WANG X L, et al.. Progress and prospects of the resistance to cotton boll worm and physiological action of Bt transgenic cotton [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2000, 28(1):65-68. | |
| [9] | 陈源,顾超,王桂霞,等.蕾期低温及湿度胁迫对Bt棉杀虫蛋白表达量的影响[J].作物学报,2013,39(1):184-189. |
| CHEN Y, GU C, WANG G X, et al.. Effect on stresses of 18 ℃ and different relative humidities on Bt protein ex-pression at squaring stage in Bt cotton [J].Acta Agron. Sin., 2013,39(1):184-189. | |
| [10] | JIANG L J, DUAN L S, TIAN X L, et al.. NaCl salinity stress decreased Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) protein content of transgenic Bt cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) seedlings [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2006, 55(3):315-320. |
| [11] | 赵红霞,王士杰,朱继杰,等.不同遗传背景转基因抗虫棉Bt蛋白表达与氮代谢关系研究[J].棉花学报,2018,30(6):498-504. |
| ZHAO H X, WANG S J, ZHU J J, et al.. Relationship between Bt protein expression and nitrogen metabolism in insect-resistant transgenic cotton lines with different genetic backgrounds [J]. Cott. Sci., 2018, 30(6):498-504. | |
| [12] | HIMANEN S J, NERG A M, NISSINEN A, et al.. Elevated atmospheric ozone increases concentration of insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Cry1Ac protein in Bt Brassica napus and reduces feeding of a Bt target herbivore on the non-transgenic parent [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2009, 157(1):181-185. |
| [13] | 王家宝,王留明,沈法富,等.环境因素对转Bt基因棉Bt杀虫蛋白表达量的影响[J].山东农业科学,2000,32(6):4-6. |
| WANG J B, WANG L M, SHEN F F, et al.. Effect of environment elements on Bt-protein content in transgenic Bt cotton [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2000, 32(6):4-6. | |
| [14] | LI R, QUAN S, YAN X F, et al.. Molecular characterization of genetically-modified crops:challenges and strategies [J]. Biotechnol. Adv., 2017, 35(2):302-309. |
| [15] | 王翠云,刘艳,刘允军.外源基因在转基因玉米中的整合位点分析[J].生物技术通报,2019,35(3):1-5. |
| WANG C Y, LIU Y, LIU Y J. Analysis of the integration site of exogenous gene in transgenic maize [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2019, 35(3):1-5. | |
| [16] | 郭旺珍,孙敬,郭玉芳,等.转基因抗虫棉Bt基因不同剂量的聚合与抗虫性表现[J].遗传学报,2001,28(7):668-676. |
| GUO W Z, SUN J, GUO Y F, et al.. Investigation of different dosages of inserted Bt genes and their insect-resistance in transgenic Bt cotton [J]. J. Genet. Genom., 2001, 28(7):668-676. | |
| [17] | 赵梅香.转基因大麦的gfp基因遗传表达及整合位点结构[D].扬州:扬州大学,2007. |
| ZHAO M X. Integration loci structure and genetic expression of green fluorescent protein gfp gene in transgenic barley (Horsdeum vulgare L.) [D]. Yangzhou:Yangzhou University, 2007. | |
| [18] | 夏兰芹,王远,郭三堆.外源基因在转基因植物中的表达与稳定性[J].生物技术通报,2000(3):8-12. |
| XIA L Q, WANG Y, GUO S D. The stability of the expression of foreign genes in transgenic plants [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2000(3):8-12. | |
| [19] | 董美. NGS在生物技术作物分子特征解析中的应用[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2018. |
| DONG M. Application of NGS for molecular characterization of biotech crops [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. | |
| [20] | 陈天子,凌溪铁,杨郁文,等.转GbVe1基因在棉花基因组中的整合与定位分析[J].棉花学报,2019,31(1):1-11. |
| CHEN T Z, LING X T, YANG Y W, et al.. The integration and insertion site of GbVe1 gene in the genome of transgenic cotton(Gossypium hirsutum) [J]. Cott. Sci., 2019, 31(1):1-11. | |
| [21] | 金永梅,马瑞,于志晶,等.转cry1C基因抗虫水稻吉生粳3号外源基因整合分析与品系特异性检测[J].生物技术通报,2019,35(3):6-12. |
| JIN Y M, MA R, YU Z J, et al.. Integration analysis of exogenous gene and line-specific detection in the insect-resistant cry1C-transgenic rice Jishengjing3 [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2019, 35(3):6-12. | |
| [22] | PEDERSEN C, ZIMNY J, BECKER D, et al.. Localization of introduced genes on the chromosomes of transgenic barley,wheat and Triticale by fluorescence in situ hybridization [J].Theor. Appl. Genet., 1997, 94(6):749-757. |
| [23] | 李亚丽,刘中来,周洁,等.转mCherry基因水稻的遗传分析及T-DNA整合位点的研究[J].分子植物育种,2012,10(2):121-130. |
| LI Y L, LIU Z L, ZHOU J, et al.. Genetic analysis of mCherry transgenic rice and molecular characterization of T-DNA integration sites in the rice genome [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2012, 10(2):121-130. | |
| [24] | PATERSON A H, BRUBAKER C L, WENDEL J F. A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis [J]. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 1993, 11(2):122-127. |
| [25] | MA Z Y, HE S P, WANG X F, et al.. Resequencing a core collection of upland cotton identifies genomic variation and loci influencing fiber quality and yield [J]. Nat. Genet., 2018, 50(6): 803-813. |
| [26] | KERSTEN B, LEITE MONTALVÃO A P, HOENICKA H, et al.. Sequencing of two transgenic early-flowering poplar lines confirmed vector-free single-locus T-DNA integration [J].Transgenic Res., 2020, 29(3):321-337. |
| [27] | 魏嘉,王秀东,卜显峰,等.基于重测序鉴定耐盐转基因大豆事件外源T-DNA整合位点及特异性检测[J].南京农业大学学报,2023, 46(4):710-717. |
| WEI J, WANG X D, BU X F, et al.. Identification of T-DNA insertion and specific detection of transgenic soybean event based on re-sequencing technology [J]. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ., 2023, 46(4):710-717. | |
| [28] | 张伟.玉米超表达突变体生成系统的完善与突变体筛选鉴定[D].武汉:华中农业大学, 2023. |
| ZHANG W. Improvement of maize overexpression mutant generation system and identification of mutants [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| [29] | 周星鲁.转双Bt基因107杨T-DNA整合及对基因表达的影响[D].保定:河北农业大学, 2021. |
| ZHOU X L.T-DNA integration information of double Bt gene populus×euramericana “Neva” and its response to Bt gene [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [30] | 程俊凌,赵亮,徐剑文,等.基于重测序鉴定GbTMEM214基因在陆地棉基因组的插入位点[J].棉花学报,2024,36(4):285-295. |
| CHENG J L, ZHAO L, XU J W. Identification of GbTMEM214 insertion site in Gossypium hirsutum genome based on resequencing [J]. Cott. Sci., 2024, 36(4):285-295. | |
| [31] | 张美冬,孙玲,熊秋芳.转基因作物的安全性及其评价[J].湖北农业科学,2015,54(5):1025-1030. |
| ZHANG M D, SUN L, XIONG Q F. Safety and evaluation of transgenic crops [J]. Hubei Agric. Sci., 2015, 54(5):1025-1030. | |
| [32] | CADE R, BURGIN K, SCHILLING K, et al.. Evaluation of whole genome sequencing and an insertion site characterization method for molecular characterization of GM maize [J]. J. Regul. Sci., 2018, 6(1):1-14. |
| [33] | PARK D, PARK S H, BAN Y W, et al.. A bioinformatics approach for identifying transgene insertion sites using whole genome sequencing data [J/OL]. BMC Biotechnol., 2017,17(1):67 [2024-09-20]. . |
| [34] | SCHOUTEN H J, VANDE GEEST H, PAPADIMITRIOU S, et al.. Re-sequencing transgenic plants revealed rearrangements at T-DNA inserts,and integration of a short T-DNA fragment,but no increase of small mutations elsewhere [J]. Plant Cell Rep., 2017, 36(3):493-504. |
| [35] | 魏强,奥岩,杨漫漫,等.利用全基因组重测序技术鉴定五指山猪GHR突变体转基因插入位点[J].遗传, 2021,43(12):1149-1158. |
| WEI Q, AO Y, YANG M M, et al.. Identification of genomic insertion of dominant-negative GHR mutation transgenes in Wuzhishan pig using whole genome sequencing method [J]. Hereditas, 2021, 43(12):1149-1158. | |
| [36] | 徐纪明,胡晗,毛文轩,等.利用重测序技术获取转基因植物T-DNA插入位点[J].遗传,2018,40(8):676-682. |
| XU J M, HU H, MAO W X, et al.. Identifying T-DNA insertion site(s) of transgenic plants by whole-genome resequencing [J].Hereditas, 2018, 40(8):676-682. | |
| [37] | TIRNAZ S, BATLEY J. DNA methylation:toward crop disease resistance improvement [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2019,24(12):1137-1150. |
| [38] | GALLEGO-BARTOLOMÉ J.DNA methylation in plants:mechanisms and tools for targeted manipulation [J]. New Phytol., 2020, 227(1):38-44. |
| [39] | DELERIS A, HALTER T, NAVARRO L. DNA methylation and demethylation in plant immunity [J]. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2016, 54:579-603. |
| [40] | PERTEA M, KIM D, PERTEA G M, et al.. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT,StringTie and Ballgown [J]. Nat. Protoc., 2016, 11(9):1650-1667. |
| [41] | 孟彩凤,周颖.DNA甲基化对植物生长发育的调控研究[J].安徽农学通报,2015,21(10):29-32. |
| MENG C F, ZHOU Y. Regulation effect of DNA methylation on the growth and development of plant [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull., 2015, 21(10):29-32. | |
| [42] | ZHANG X Y, YAZAKI J, SUNDARESAN A, et al.. Genome-wide high-resolution mapping and functional analysis of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis [J]. Cell, 2006, 126(6):1189-1201. |
| [43] | 夏兰芹,徐琼芳,郭三堆.抗虫棉生长发育过程中Bt杀虫基因及其表达的变化[J].作物学报,2005,31(2):197-202. |
| XIA L Q, XU Q F, GUO S D. Bt insecticidal gene and its temporal expression in transgenic cotton plants [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2005, 31(2):197-202. | |
| [44] | CHEN Z Y,RIU E, HE C Y, et al.. Silencing of episomal transgene expression in liver by plasmid bacterial backbone DNA is independent of CpG methylation [J]. Mol. Ther., 2008,16(3):548-556. |
| [45] | 朱婷. m6A甲基化修饰调控YS型小麦温敏雄性不育系花药育性的分子机制[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2023. |
| ZHU T. The molecular regulation mechanism of m6A modification on anther fertility of YS-type thermo-sensitive male sterile line in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2023. | |
| [46] | AKHTAR J, LUGOBONI M, JUNION G.m~6A RNA modification in transcription regulation [J]. Transcription, 2021, 12(5):266-276. |
| [47] | SONG P Z, TAYIER S, CAI Z H, et al.. RNA methylation in mammalian development and cancer [J]. Cell Biol. Toxicol., 2021, 37(6):811-831. |
| [1] | 陈媛, 刘震宇, 周明园, 张晨霞, 田巧凤, 张中宁, 张祥, 陈德华. 种植密度对转Bt棉纤维杀虫蛋白表达量及氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 45-53. |
| [2] | 李琴1,2,陈全家1,孟志刚2,张锐2,梁成真2,孙国清2,孟钊红2,翟红红2,张杰3,郭三堆2*. cry2Ah-M基因杀虫活性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(4): 10-16. |
| [3] | 柳小庆,陈茹梅. 增强外源基因在转基因植物中表达的策略[J]. , 2012, 14(1): 76-84. |
| [4] | 李俊,郑秀丽,邓平建,刘国振. 商品化转基因植物的外源基因及其检测技术[J]. , 2008, 10(3): 31-39. |
| [5] | 张锐 王远 孟志刚 孙国清 郭三堆. 国产转基因抗虫棉研究回顾与展望[J]. , 2007, 9(4): 32-42. |
| [6] | 汪若海 李秀兰. 外源基因及异常种质增强棉花杂种优势[J]. , 2001, 3(4): 46-48. |
| [7] | 郭三堆 崔洪志. 中国抗虫棉GFM Cry1A杀虫基因的合成及表达载体构建[J]. , 2000, 2(2): 21-26. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号