




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 153-161.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0549
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-07-04
接受日期:2022-10-26
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-02-04
通讯作者:
孟庆峰
作者简介:翟车宇 E-mail:623532298@139.com;
基金资助:
Cheyu ZHAI( ), Jingmei LUO, Changjie LIU, Juan ZHANG, Qingfeng MENG(
), Jingmei LUO, Changjie LIU, Juan ZHANG, Qingfeng MENG( )
)
Received:2022-07-04
Accepted:2022-10-26
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-02-04
Contact:
Qingfeng MENG
摘要:
盐碱土盐碱化程度高、养分有效性低,施加有机肥可以促进土壤盐分淋洗,降低土壤盐碱化程度,增加养分含量和土壤碳、氮、磷的供应能力。根据土壤施加腐熟牛粪的年限,设置施加腐熟牛粪21(Y21)、18(Y18)、15年(Y15)和未施加腐熟牛粪(CK)共4个处理,采集各处理0—20和20—40 cm土层的土壤样品,分析土壤盐碱性质和养分含量。结果表明,0—20和20—40 cm土层Y21、Y18、Y15处理有机碳(soil organic carbon, SOC)、全氮(total-N, TN)和全磷(total-P,TP)含量显著高于CK;土壤水溶性盐离子、pH、电导率(electrical conductance,EC)、钠吸附比(sodium adsorption ratio, SAR)和碱化度(exchangeable sodium percentage,ESP)较CK显著降低。在0—20 和20—40 cm土层,Y21、Y18、Y15处理碳氮比(C/N)较CK显著降低;与CK相比,Y21与Y15处理0—20 cm土层氮磷比(N/P)由0.95显著增加至1.84和2.11,20—40 cm土层N/P由1.15显著增加至2.25和2.44;土壤碳磷比(C/P)在0—20 cm土层规律不明显,在20—40 cm土层Y21、Y18、Y15处理与CK相比差异不显著。多元线性回归模型显示,C/N受SOC、TN和ESP影响,N/P和C/P主要受TP和TN影响。综上所述,松嫩平原西部草甸碱土施加有机肥后土壤盐碱程度降低,SOC、TN、TP含量和N/P增加,C/N降低,且施加有机肥改良15年的土壤供碳、供氮潜力达到最大。
中图分类号:
翟车宇, 骆静梅, 刘昌杰, 张娟, 孟庆峰. 长期施用有机肥对松嫩平原盐碱土壤盐碱性质和化学计量比的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 153-161.
Cheyu ZHAI, Jingmei LUO, Changjie LIU, Juan ZHANG, Qingfeng MENG. Effects of Long-term Manure Fertilizer on Saline-sodic Properties and Stoichiometric Ratio of Saline-sodic Soil in Songnen Plain[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 153-161.
土层深度 Soil depths/cm | 处理 Treatment | 有机碳 SOC/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP/(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | CK | 10.22±1.30 b | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.31±0.03 c |
| Y15 | 22.08±3.29 a | 1.64±0.28 a | 0.78±0.09 b | |
| Y18 | 19.69±2.01 a | 1.17±0.12 a | 1.38±0.26 a | |
| Y21 | 24.62±5.01 a | 1.28±0.33 a | 0.69±0.16 b | |
| 20—40 | CK | 9.52±2.51 c | 0.33±0.06 c | 0.29±0.02 b |
| Y15 | 14.46±3.30 bc | 1.18±0.03 a | 0.43±0.12 ab | |
| Y18 | 18.16±1.49 b | 1.00±0.02 b | 0.50±0.08 a | |
| Y21 | 24.83±4.15 a | 1.13±0.12 ab | 0.51±0.02 a |
表1 施用有机肥措施下各处理的土壤有机碳、全氮和全磷含量
Table 1 Soil organic carbon,total-N and total-P contents in different treatments under cattle manure application
土层深度 Soil depths/cm | 处理 Treatment | 有机碳 SOC/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP/(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | CK | 10.22±1.30 b | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.31±0.03 c |
| Y15 | 22.08±3.29 a | 1.64±0.28 a | 0.78±0.09 b | |
| Y18 | 19.69±2.01 a | 1.17±0.12 a | 1.38±0.26 a | |
| Y21 | 24.62±5.01 a | 1.28±0.33 a | 0.69±0.16 b | |
| 20—40 | CK | 9.52±2.51 c | 0.33±0.06 c | 0.29±0.02 b |
| Y15 | 14.46±3.30 bc | 1.18±0.03 a | 0.43±0.12 ab | |
| Y18 | 18.16±1.49 b | 1.00±0.02 b | 0.50±0.08 a | |
| Y21 | 24.83±4.15 a | 1.13±0.12 ab | 0.51±0.02 a |
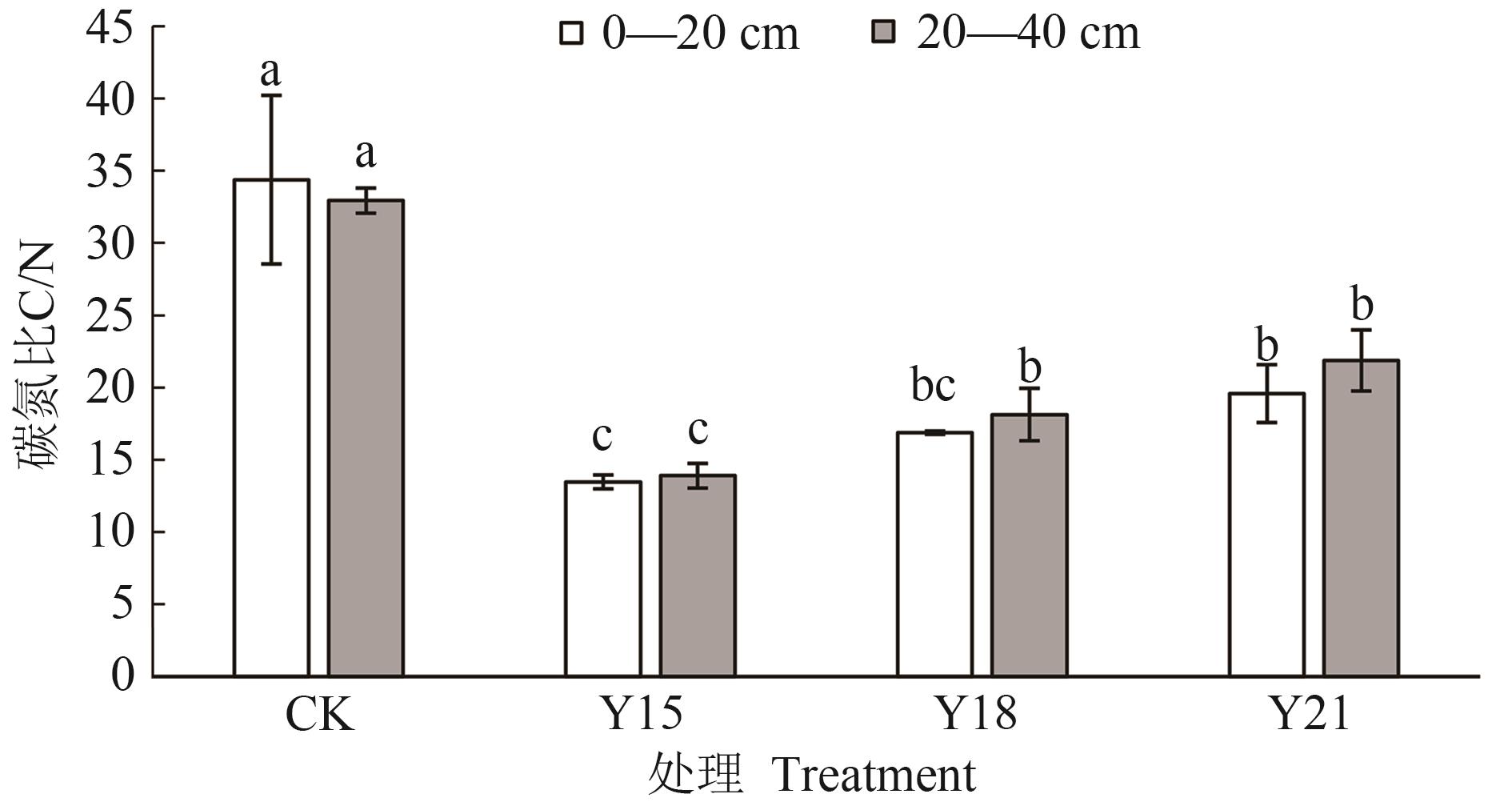
图1 施用有机肥下各处理的土壤碳氮比注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 1 Soil C/N under different treatments for manure fertilizer applicationNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
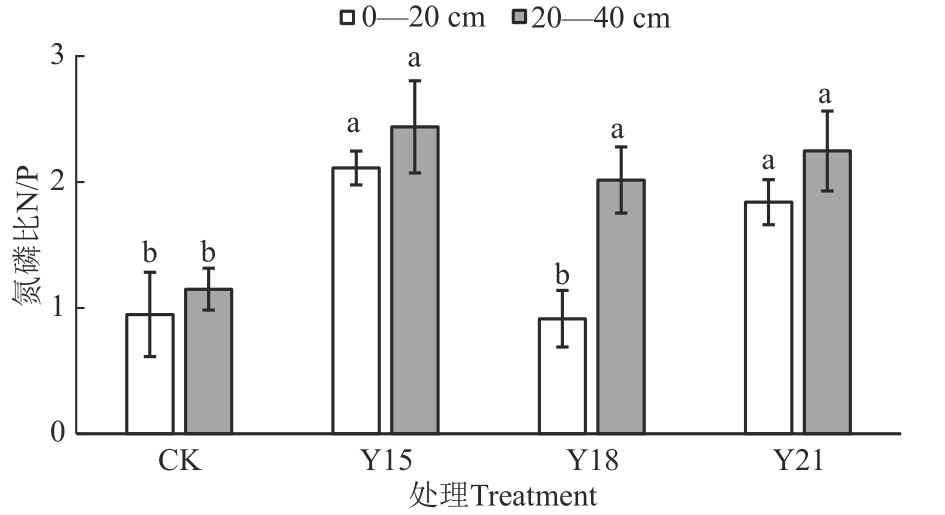
图2 施用有机肥下各处理的土壤氮磷比注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Soil N/P under different treatments for manure fertilizer applicationNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
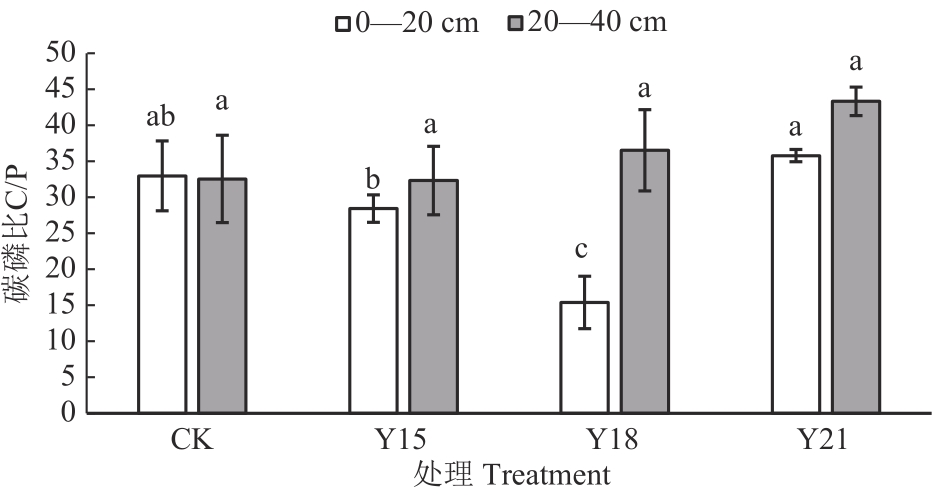
图3 施用有机肥下各处理的土壤碳磷比注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Soil C/P under different treatments for manure fertilizer applicationNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
土层 深度 Soil depth/cm | 处理Treatment | 土壤水溶性盐离子含量 Soil water-soluble salt ion content/(mg·kg-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO | CO | Cl- | SO | ||
| 0—20 | CK | 4 824.34±370.64 a | 63.85±5.73 a | 41.57±2.93 b | 94.40±11.18 a | 69.90±0.53 a | 34.15±10.52 | 96.22±1.79 a | 126.05±12.49 a |
| Y15 | 113.13±30.56 b | 19.87±2.82 bc | 87.61±8.84 a | 51.00±4.14 b | 15.98±3.41 bc | — | 2.66±1.89 b | 13.72±2.66 b | |
| Y18 | 172.05±32.44 b | 27.04±8.43 b | 53.45±6.40 b | 41.43±5.74 bc | 18.49±0.52 b | — | 1.90±1.10 b | 7.50±2.46 b | |
| Y21 | 47.38±16.80 b | 15.96±2.46 c | 102.24±7.26 a | 35.05±3.70 c | 13.97±0.95 c | — | 2.11±1.15 b | 12.42±2.87 b | |
| 20—40 | CK | 3 560.55±285.26 a | 195.79±97.24 a | 24.86±2.93 c | 100.83±10.48 a | 88.34±26.42 a | 19.25±1.19 | 5.22±1.32 a | 72.63±14.91 a |
| Y15 | 139.60±47.44 bc | 14.01±2.26 b | 81.33±4.18 b | 66.86±8.45 b | 16.06±1.09 b | — | 3.42±1.25 b | 15.31±7.79 bc | |
| Y18 | 418.15±147.90 b | 30.95±5.64 b | 33.90±8.69 c | 31.00±1.58 c | 34.72±5.93 b | — | 3.25±1.14 b | 35.72±6.35 b | |
| Y21 | 64.46±25.27 c | 11.73±1.95 b | 129.46±2.98 a | 32.12±5.93 c | 14.97±1.88 b | — | 2.11±0.73 b | 8.07±2.87 c | |
表2 不同处理下土壤水溶性盐离子含量
Table 2 Soil water-soluble salt ion content under different treatments
土层 深度 Soil depth/cm | 处理Treatment | 土壤水溶性盐离子含量 Soil water-soluble salt ion content/(mg·kg-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO | CO | Cl- | SO | ||
| 0—20 | CK | 4 824.34±370.64 a | 63.85±5.73 a | 41.57±2.93 b | 94.40±11.18 a | 69.90±0.53 a | 34.15±10.52 | 96.22±1.79 a | 126.05±12.49 a |
| Y15 | 113.13±30.56 b | 19.87±2.82 bc | 87.61±8.84 a | 51.00±4.14 b | 15.98±3.41 bc | — | 2.66±1.89 b | 13.72±2.66 b | |
| Y18 | 172.05±32.44 b | 27.04±8.43 b | 53.45±6.40 b | 41.43±5.74 bc | 18.49±0.52 b | — | 1.90±1.10 b | 7.50±2.46 b | |
| Y21 | 47.38±16.80 b | 15.96±2.46 c | 102.24±7.26 a | 35.05±3.70 c | 13.97±0.95 c | — | 2.11±1.15 b | 12.42±2.87 b | |
| 20—40 | CK | 3 560.55±285.26 a | 195.79±97.24 a | 24.86±2.93 c | 100.83±10.48 a | 88.34±26.42 a | 19.25±1.19 | 5.22±1.32 a | 72.63±14.91 a |
| Y15 | 139.60±47.44 bc | 14.01±2.26 b | 81.33±4.18 b | 66.86±8.45 b | 16.06±1.09 b | — | 3.42±1.25 b | 15.31±7.79 bc | |
| Y18 | 418.15±147.90 b | 30.95±5.64 b | 33.90±8.69 c | 31.00±1.58 c | 34.72±5.93 b | — | 3.25±1.14 b | 35.72±6.35 b | |
| Y21 | 64.46±25.27 c | 11.73±1.95 b | 129.46±2.98 a | 32.12±5.93 c | 14.97±1.88 b | — | 2.11±0.73 b | 8.07±2.87 c | |
土层深度 Soil depths/cm | 处理 Treatment | pH | 电导率 EC/(dS·m-1) | 碱化度 ESP/% | 钠吸附比 SAR/[(mmol·L-1)1/2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | CK | 10.39±0.07 a | 4.51±0.65 a | 29.08±2.87 a | 69.73±4.05 a |
| Y15 | 8.51±0.08 c | 0.28±0.11 b | 0.76±0.05 b | 1.67±0.44 b | |
| Y18 | 8.79±0.10 b | 0.24±0.02 b | 1.34±0.64 b | 3.28±0.82 b | |
| Y21 | 8.59±0.05 c | 0.14±0.02 b | 0.23±0.08 b | 0.78±0.30 b | |
| 20—40 | CK | 10.34±0.03 a | 2.68±0.20 a | 23.08±2.05 a | 52.57±2.78 a |
| Y15 | 8.69±0.07 c | 0.26±0.05 bc | 1.04±0.52 c | 2.12±0.75 c | |
| Y18 | 9.44±0.08 b | 0.42±0.10 b | 4.08±0.86 b | 7.43±0.49 b | |
| Y21 | 8.89±0.55 c | 0.19±0.04 c | 0.22±0.13 c | 1.11±0.31 c |
表3 不同处理下土壤的盐碱性质
Table 3 Saline-sodic properties of soil under different treatments
土层深度 Soil depths/cm | 处理 Treatment | pH | 电导率 EC/(dS·m-1) | 碱化度 ESP/% | 钠吸附比 SAR/[(mmol·L-1)1/2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | CK | 10.39±0.07 a | 4.51±0.65 a | 29.08±2.87 a | 69.73±4.05 a |
| Y15 | 8.51±0.08 c | 0.28±0.11 b | 0.76±0.05 b | 1.67±0.44 b | |
| Y18 | 8.79±0.10 b | 0.24±0.02 b | 1.34±0.64 b | 3.28±0.82 b | |
| Y21 | 8.59±0.05 c | 0.14±0.02 b | 0.23±0.08 b | 0.78±0.30 b | |
| 20—40 | CK | 10.34±0.03 a | 2.68±0.20 a | 23.08±2.05 a | 52.57±2.78 a |
| Y15 | 8.69±0.07 c | 0.26±0.05 bc | 1.04±0.52 c | 2.12±0.75 c | |
| Y18 | 9.44±0.08 b | 0.42±0.10 b | 4.08±0.86 b | 7.43±0.49 b | |
| Y21 | 8.89±0.55 c | 0.19±0.04 c | 0.22±0.13 c | 1.11±0.31 c |
| 指标Index | SOC | TP | TN | pH | EC | SAR | ESP | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO | Cl- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 0.56** | ||||||||||||
| TN | 0.86** | 0.65** | |||||||||||
| pH | -0.77** | -0.58** | -0.85** | ||||||||||
| EC | -0.72** | -0.51* | -0.74** | 0.88** | |||||||||
| SAR | -0.76** | -0.53** | -0.79** | 0.92** | 0.98** | ||||||||
| ESP | -0.76** | -0.54** | -0.78** | 0.92** | 0.98** | 0.99** | |||||||
| Na+ | -0.75** | -0.53** | -0.78** | 0.91** | 0.99** | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||||||
| K+ | -0.63** | -0.36 | -0.61** | 0.67** | 0.56** | 0.66** | 0.67** | 0.65** | |||||
| Ca2+ | 0.61** | 0.02 | 0.47* | -0.57* | -0.41 | -0.49* | -0.49* | -0.46* | -0.48* | ||||
| Mg2+ | -0.84** | -0.51* | -0.79** | 0.75** | 0.84** | 0.85** | 0.87** | 0.86** | 0.70** | -0.32 | |||
| HCO | -0.75** | -0.51* | -0.77** | 0.89** | 0.87** | 0.92** | 0.93** | 0.91** | 0.91** | -0.58** | 0.81** | ||
| Cl- | -0.68** | -0.48* | -0.68** | 0.84** | 0.99** | 0.97** | 0.96** | 0.98** | 0.54** | -0.36 | 0.82** | 0.82** | |
| SO | -0.72** | -0.55* | -0.72** | 0.87** | 0.97** | 0.96** | 0.95** | 0.96** | 0.56* | -0.51 | 0.73** | 0.83** | 0.95** |
表4 土壤各指标间的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation matrix among the soil index
| 指标Index | SOC | TP | TN | pH | EC | SAR | ESP | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO | Cl- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 0.56** | ||||||||||||
| TN | 0.86** | 0.65** | |||||||||||
| pH | -0.77** | -0.58** | -0.85** | ||||||||||
| EC | -0.72** | -0.51* | -0.74** | 0.88** | |||||||||
| SAR | -0.76** | -0.53** | -0.79** | 0.92** | 0.98** | ||||||||
| ESP | -0.76** | -0.54** | -0.78** | 0.92** | 0.98** | 0.99** | |||||||
| Na+ | -0.75** | -0.53** | -0.78** | 0.91** | 0.99** | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||||||
| K+ | -0.63** | -0.36 | -0.61** | 0.67** | 0.56** | 0.66** | 0.67** | 0.65** | |||||
| Ca2+ | 0.61** | 0.02 | 0.47* | -0.57* | -0.41 | -0.49* | -0.49* | -0.46* | -0.48* | ||||
| Mg2+ | -0.84** | -0.51* | -0.79** | 0.75** | 0.84** | 0.85** | 0.87** | 0.86** | 0.70** | -0.32 | |||
| HCO | -0.75** | -0.51* | -0.77** | 0.89** | 0.87** | 0.92** | 0.93** | 0.91** | 0.91** | -0.58** | 0.81** | ||
| Cl- | -0.68** | -0.48* | -0.68** | 0.84** | 0.99** | 0.97** | 0.96** | 0.98** | 0.54** | -0.36 | 0.82** | 0.82** | |
| SO | -0.72** | -0.55* | -0.72** | 0.87** | 0.97** | 0.96** | 0.95** | 0.96** | 0.56* | -0.51 | 0.73** | 0.83** | 0.95** |
土壤化学计量比 Soil stoichiometric ratio | 回归方程 Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| C/N | YC/N=-19.267-18.068TN+0.954SOC+0.254ESP | 0.768** |
| N/P | YN/P =1.321+1.407TN-1.649TP | 0.793** |
| C/P | YC/P =27.827-28.578TP+1.811SOC-10.114TN | 0.865** |
表5 多元线性逐步回归结果
Table 5 Result of the multiple linear stepwise regression analysis
土壤化学计量比 Soil stoichiometric ratio | 回归方程 Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| C/N | YC/N=-19.267-18.068TN+0.954SOC+0.254ESP | 0.768** |
| N/P | YN/P =1.321+1.407TN-1.649TP | 0.793** |
| C/P | YC/P =27.827-28.578TP+1.811SOC-10.114TN | 0.865** |
| 1 | 胡立煌,史文竹,项剑,等.生物炭、秸秆和粪肥对滨海盐碱土氮矿化和硝化作用的影响[J].生态与农村环境学报,2020,36(8):1089-1096. |
| HU L H, SHI W Z, XIANG J,et al..Effect of biochar,straw and manure fertilizer on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification of coastal saline-alkali soil [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2020,36(8):1089-1096. | |
| 2 | 张晓光,黄标,梁正伟,等.松嫩平原西部土壤盐碱化特征研究[J].土壤,2013,45(2):1332-1338. |
| ZHANG X G, HUANG B, LIANG Z W, et al..Study on slinization characteristics of surface soil in western Songnen plain [J]. Soils, 2013,45(2):1332-1338. | |
| 3 | 袁瑞强,张文新,王仕琴.饱和多孔介质中水流停滞对胶体吸附与解吸的影响[J].环境科学研究,2020,33(2):431-437. |
| YUAN R Q, ZHANG W X, WANG S Q, et al.. Effects of flow stagnation on colloidal retention-release in saturated porous media [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2020,33(2):431-437. | |
| 4 | 周连仁,曾宪楠,孟庆峰,等.不同培肥措施下盐碱旱地土壤肥力特征综合评价[J].东北农业大学学报,2015,46(6):34-39. |
| ZHOU L R, ZEN X N, MENG Q F, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of soil fertility properties under fertilization methods in saline dry land [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Univ., 2015,46(6):34-39. | |
| 5 | 曾德慧,陈广生.生态化学计量学:复杂生命系统奥秘的探索[J].植物生态学报,2005, 29(6):1007-1019. |
| ZENG D H, CHEN G S. Ecological stoichiometry:a science to explore the complexity of living systems [J].Acta Phytoecol. Sin., 2005,29(6):1007-1019. | |
| 6 | 王绍强,于贵瑞.生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征[J].生态学报,2008,28(8):3937-3947. |
| WANG S Q, YU G R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon,nitrigen and phosphorus elements [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2008,28(8):3937-3947. | |
| 7 | 张雅蓉,李渝,刘彦伶,等.长期施肥对西南黄壤碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征的影响[J].土壤通报,2016,47(3):673-680. |
| ZHANG Y R, LI Y, LIU Y L, et al.. Effect of long-term fertilization on ecological stoichiometry characteristics of carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus in southwest yellow soil [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2016,47(3):673-680. | |
| 8 | 成彩霞,马剑,赵维俊,等.甘肃祁连山西水林区典型灌丛土壤C、N、P生态化学计量特征研究[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2022,57(3):121-128. |
| CHENG C X, MA J, ZHAO W J, et al.. Ecological stoichiometry of soils C, N and P of typical shrubs in Xishui forest area of Qilian mountains in China [J]. J. Gansu Agric. Univ., 2022,57(3):121-128. | |
| 9 | 达清珍,崔东,张雨露,等.新疆伊犁不同林龄野苹果林土壤碳、氮、磷生态化学计量特性[J].生态科学,2022,41(5):98-104. |
| DA Q Z, CUI D, ZHANG Y L, et al.. Ecostoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus in wild apple trees of different ages in Yili, Xinjiang [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2022,41(5):98-104. | |
| 10 | 王艮梅,陈捷,范之馨,等.外源有机物料添加对滨海盐碱土细菌群落结构的影响[J].生态与农村环境学报,2022,38(1):85-95. |
| WANG G M, CHEN J, FAN Z X, et al..The shift of bacterial community structure in coastal saline-alkaline soil upon addition of different organic materials [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2022,38(1):85-95. | |
| 11 | JIA R, ZHOU J, CHU J C, et al.. Insights into the associations between soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality driven by fertilization management: a case study from the North China Plain [J/OL]. J. Clean. Prod.,2022,362:132265 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 12 | REN J H, LIU X L, YANG W P, et al.. Rhizosphere soil properties, microbial community, and enzyme activities: short-term responses to partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic manure [J/OL]. J Environ. Manage., 2021,299:113650[2022-06-03]. . |
| 13 | 李取生,李秀军,李晓军,等.松嫩平原苏打盐碱地治理与利用[J].资源科学,2003(1):15-20. |
| LI Q S, LI X J, LI X J, et al.. Sodium bicarbonate soil management and utilization in Songnen plain [J].Resour. Sci., 2003(1):15-20. | |
| 14 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2000:1-495 . |
| 15 | 王世斌,高佩玲,赵亚东,等.生物炭、有机肥连续施用对盐碱土壤改良效果研究[J].干旱地区农业研究,2021,39(3):154-161. |
| WANG S B, GAO P L, ZHAO Y D, et al.. Effect of continuous application of biochar and organic fertilizers on saline-alkali soil improvment [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Aeeas, 2021,39(3):154-161. | |
| 16 | 张文新,张文超,王淑娟,等.脱硫石膏对碱化土壤胶体絮凝的影响[J].土壤, 2021,53(3):555-562. |
| ZHANG W X, ZHANG W C, WANG S J, et al.. Effect of flue gas desulphurization gypsum on colloidal flocculation in sodic soil [J]. Soils, 2021,53(3):555-562. | |
| 17 | 邵孝候,张宇杰,常婷婷,等.生物有机肥对盐渍土壤水盐动态及番茄产量的影响[J].河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,46(2):153-160. |
| SHAO X H, ZHANG Y J, CHANG T T, et al.. Effect of different fertilizer treatments on soil water.salt and crop yield formation in saline soils [J]. J. Hehai Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2018,46(2):153-160. | |
| 18 | FANG H, LIU K L, LI D M, et al.. Long-term effects of inorganic fertilizers and organic manures on the structure of a paddy soil [J/OL]. Soil Till. Res., 2021,213:105137[2022-06-03]. . |
| 19 | 窦森,李凯,关松.土壤团聚体中有机质研究进展[J].土壤学报,2011,48(2):412-418. |
| DOU S, LI K, GUAN S. A review on organic matter in soil aggregates [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2011,48(2):412-418. | |
| 20 | 魏守才,谢文军,夏江宝,等.盐渍化条件下土壤团聚体及其有机碳研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(1):369-376. |
| WEI S C, XIE W J, XIA J B, et al.. Research progress on soil aggregates and associated organic carbon in salinized soils [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2021,32(1):369-376. | |
| 21 | 张娟,徐宁彤,孟庆峰,等.有机肥施用年限对土壤有机碳组分及其来源与玉米产量的影响[J].农业工程学报,2019,35(2):107-113. |
| ZHANG J, XU N T, MENG Q F, et al.. Effect of years of manure fertilizer application on soil organic carbon component, its source and corn yield [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2019,35(2):107-113. | |
| 22 | 朱光艳,刘国锋,徐增洪.冲水洗盐对滨海盐碱地盐分变化的影响[J].灌溉排水学报,2019,38():52-56. |
| ZHU G Y, LIU G F, XU Z H. Effects of washing salt by washing water on salinity variation in coastal saline and alkaline land [J]. J. Irrig. Drain., 2019,38(S2):52-56. | |
| 23 | 杨明,孙毅,高玉山,等.有机肥对苏打盐碱土的改良效果研究[J].吉林农业科学,2013,38(3):43-46, 58. |
| YANG M, SUN Y, GAO Y S, et al.. Effects of organic manure on improving soda saline-alkali soil [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Sci.,2013,38(3):43-46, 58. | |
| 24 | HE Y T, ZHANG W J, XU M G, et al.. Long-term combined chemical and manure fertilizations increase soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in aggregate fractions at three typical cropland soils in China [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2015,532:635-644. |
| 25 | 王秋君,郭德杰,马艳.连续施用有机肥下设施土壤碳氮磷化学计量学特征及其与土壤有效磷的关系[J].江苏农业学报,2021,37(4):893-901. |
| WANG Q J, GUO D J, MA Y. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus and their relationship with soil available phosphorus under continuous application of organic fertilizer for vegetable cultivation in greenhouse [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2021,37(4):893-901. | |
| 26 | RIETZ D N, HAYNES R J. Effects of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on soil microbial activity [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2003,35(6):845-854. |
| 27 | 李凤霞,王学琴,郭永忠,等.银川平原不同类型盐渍化土壤酶活性及其与土壤养分间相关分析研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2012,26(7):121-126. |
| LI F X, WANG X Q, GUO Y Z, et al.. Study of enzymes activity and their correlation with soil nutrients in different types of saline-alkali soil in Yinchuan plain of Ningxia [J].J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2012,26(7):121-126. | |
| 28 | LIU S B, WANG J Y, PU S Y, et al..Impact of manure on soil biochemical properties: a global synthesis [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020,745:141003 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 29 | 青烨,孙飞达,李勇,等.若尔盖高寒退化湿地土壤碳氮磷比及相关性分析[J].草业学报,2015,24(3):38-47. |
| QING Y, SUN F D, LI Y, et al.. Analysis of soil carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus in degraded alpine wetland, Zoige, southwest China [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2015,24(3):38-47. | |
| 30 | ZHANG Y L, SUN C X, CHEN Z H, et al.. Stoichiometric analyses of soil nutrients and enzymes in a cambisol soil treated with inorganic fertilizers or manures for 26 years [J]. Geoderma, 2019,353: 382-390. |
| 31 | 彭佩钦,张文菊,童成立,等.洞庭湖湿地土壤碳、氮、磷及其与土壤物理性状的关系[J].应用生态学报,2005,16(10):1872-1878. |
| PENG P Q, ZHANG W J, TONG C L, et al.. Soil C,N and P contents and their relationships with soil physical properties in wetlands of Dongting lake floodplain [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2005,16(10):1872-1878. | |
| 32 | 卜玉山,梁美英,张广峰,等.不同石灰性土壤磷素形态及其有效性差异[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2011,31(3):193-199. |
| BU Y S, LIANG M Y, ZHANG G F, et al.. Difference of phosphorus fractions and availability of different calcareous soil [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2011, 31(3):193-199. | |
| 33 | 谭海霞,金照光,孙富强,等.滦河口湿地植物-土壤生态化学计量相关性研究[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(2):68-73. |
| TAN H X, JIN Z G, SUN F Q, et al.. Correlation between the stoichiometric characteristics of plants and soil in Luanhe estuary wetland [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2019,26(2):68-73. | |
| 34 | 林诚,王飞,林新坚,等.长期施肥对南方黄泥田土壤磷吸附与解吸的影响[J].福建农业学报,2011,26(6):1034-1038. |
| LIN C, WANG F, LIN X J, et al.. The effection of phosphorus adsorption and desorption of long-term fertilization on south yellow clayey soil [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2011,26(6):1034-1038. |
| [1] | 曾婷, 侯萌, 王耀, 彭博, 汤博宇, 赵晓蕊, 隋跃宇, 焦晓光. 不同土地利用类型对土壤纤维素酶活性及肥力因子的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 193-200. |
| [2] | 刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225. |
| [3] | 杨小虎, 张曼玉, 杨海昌, 张凤华, 江宜霖, 易小兰. 基于组合模型的玛纳斯河流域农田土壤盐分反演[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 134-141. |
| [4] | 何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [5] | 胡朝华, 刘曰明, 庞孜钦, 袁照年. 农田土壤活性氮损失现状和生物炭调控途径研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 120-129. |
| [6] | 王杉杉1,卢秀萍2,许自成1*,李军营2,逄涛2. 云南黄金走廊烟区土壤腐殖质组成特征及其与土壤理化性状的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(1): 154-163. |
| [7] | 孙书斌1,于庆涛2,姚雪梅2,杨虹琦1*,刘光辉2,张保全3. 隆回植烟土壤有机质含量分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(6): 94-101. |
| [8] | 年佳乐,李跃进*,景宇鹏,宋瑶. 盐渍土有效态微量元素含量的空间变异特征研究[J]. , 2013, 15(4): 163-167. |
| [9] | 程宝玉,马京民,程兰,祁春苗,常剑波. 烤烟主产区土壤养分含量现状分析[J]. , 2009, 11(3): 131-136. |
| [10] | 徐秀娟,吴文革. 安徽省农作物秸秆资源及其综合利用[J]. , 2009, 11(2): 39-43. |
| [11] | 彭正萍 王艳群 刘淑桥 王红 王蕾 薛世川. 不同施肥处理对冬小麦干物质积累及土壤养分垂直分布的影响[J]. , 2007, 9(6): 95-99. |
| [12] | 周毅 王传江 曹一平. 喷施硝基黄腐酸盐对春小麦的抗旱效应及其分析[J]. , 2005, 7(4): 46-50. |
| [13] | 程旺大[1,3] 姚海根[1] 吴伟[2] 张国平[3]. 土壤-水稻体系中的重金属污染及其控制[J]. , 2005, 7(4): 51-54. |
| [14] | 白雪梅. 黑河地区耕地土壤存在的主要问题及改良利用措施[J]. , 2005, 7(1): 42-45. |
| [15] | 熊云明 黄国勤 王淑彬 刘隆旺. 稻田轮作对土壤理化性状和作物产量的影响[J]. , 2004, 6(4): 42-45. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号