




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 214-225.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0810
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-09-22
接受日期:2023-01-12
出版日期:2024-01-15
发布日期:2024-01-08
通讯作者:
史宏志
作者简介:刘威 E-mail:1185850397@qq.com;
基金资助:
Wei LIU1( ), Yuanyuan ZHAO1, Xiaolong CHEN2, Hongzhi SHI1(
), Yuanyuan ZHAO1, Xiaolong CHEN2, Hongzhi SHI1( )
)
Received:2022-09-22
Accepted:2023-01-12
Online:2024-01-15
Published:2024-01-08
Contact:
Hongzhi SHI
摘要:
为揭示豫中典型浓香型烤烟产区植烟土壤氮素矿化动态变化、土壤微生物多样性以及氮素循环功能基因对水分条件的响应特征,通过室内培养法研究50%(H-50%)、65%(H-65%)和80%(H-80%))持水量条件下,河南许昌植烟土壤细菌和真菌群落功能多样性的差异。结果表明,H-65%处理土壤的无机氮矿化量及矿化速率均高于其他处理。在土壤细菌中,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)、浮霉菌门(Planctomycetes)、芽单胞菌门(Gemmatimonadetes)为优势菌门(相对丰度>3%),其中,H-80%处理中变形菌门的相对丰度显著高于其他处理,而厚壁菌门的相对丰度显著低于其他处理;H-50%处理中放线菌门、绿弯菌门的相对丰度显著高于其他处理。在土壤真菌中,子囊菌门(Ascomycota)占土壤真菌总OTU(operational taxonmic units)数的90%以上,其相对丰度随土壤含水率增加呈倒“V”的变化趋势。LEfSe(LDA effect size)分析结果表明,各处理在细菌属水平共检测出6种活性生物标志物(LDA值>3.5)。细菌群落具有丰富的功能多样性,一级功能层表现为代谢方面较活跃,二级功能层的功能基因丰度在不同含水率条件下发生明显变化;与固氮过程相关的固氮酶基因nifK、nifD、nifH的相对丰度在不同处理中表现为H-50%>H-65%>H-80%,反硝化过程相关基因norB、nirK、nosZ的相对丰度均在H-65%处理最高。综合来看,合理调控土壤含水率可以有效调节豫中烟区土壤氮素矿化动态、土壤微生物群落功能多样性以及氮循环相关功能基因的丰度。
中图分类号:
刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225.
Wei LIU, Yuanyuan ZHAO, Xiaolong CHEN, Hongzhi SHI. Effects of Soil Moisture Content on Microbial Community Diversity and Abundance of Nitrogen Cycling Genes in Central Henan Tobacco-growing Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 214-225.
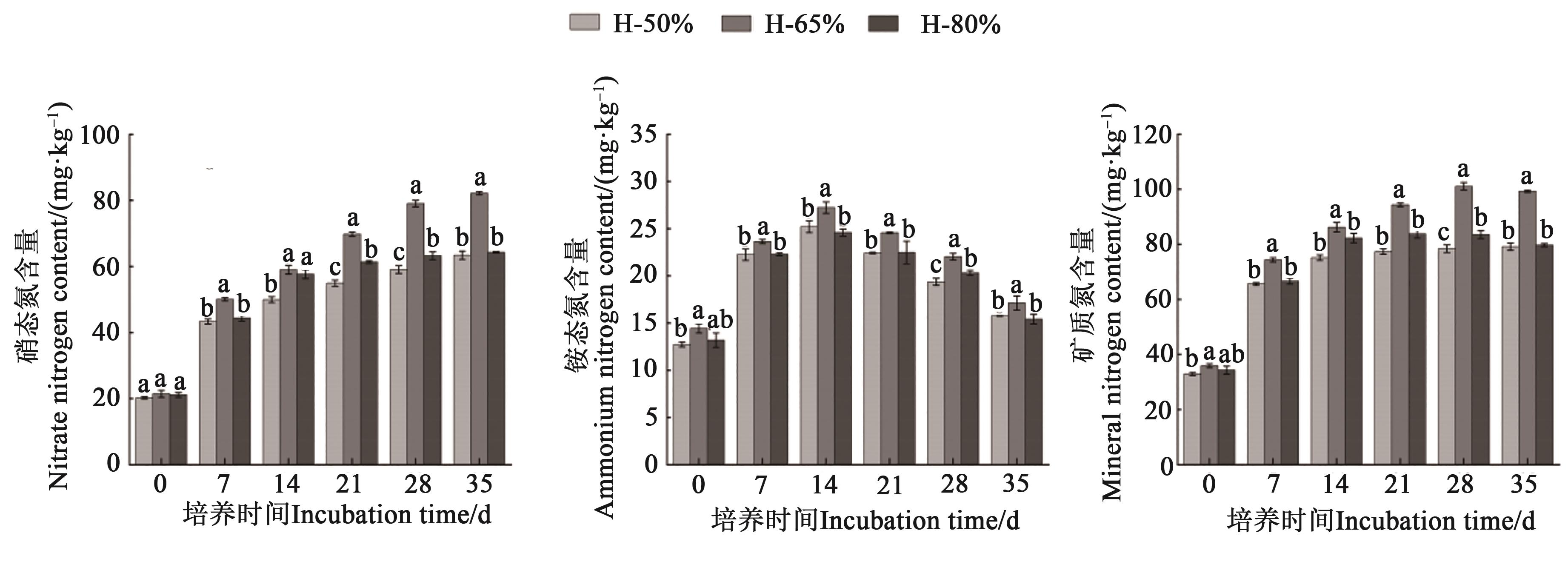
图1 不同含水率下的土壤无机氮矿化量注:同一培养时间不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Mineralization of soil inorganic nitrogen under different soil contentsNote:Different lowercase letters in same incubation time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
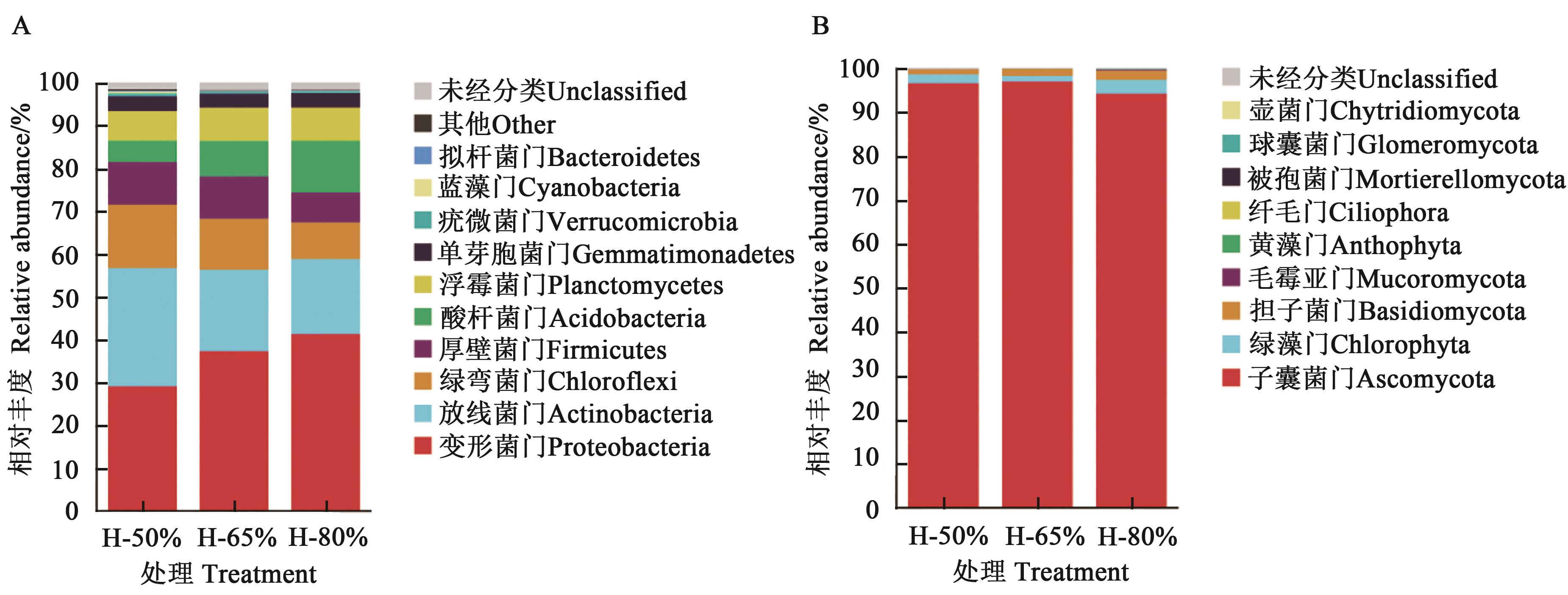
图4 不同含水率下的土壤细菌和真菌在门水平的群落组成A:细菌;B:真菌
Fig. 4 Community composition of soil bacteria and fungi at phylum level under different water contentsA: Bacterium; B: Fungus
微生物类别 Class of microorganism | 门水平 Phylum level | 相对丰度Relative abundame/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-50% | H-65% | H-80% | ||
细菌 Bacterium | 放线菌门Actinobacteria | 27.57±0.58 a | 18.95±0.98 b | 17.49±0.55 b |
| 变形菌门Proteobacteria | 29.10±0.84 c | 37.31±1.57 b | 41.30±0.58 a | |
| 绿弯菌门Chloroflexi | 14.83±0.46 a | 11.91±0.18 b | 8.53±0.29 c | |
| 厚壁菌门Firmicutes | 9.94±1.39 a | 9.89±0.36 a | 7.01±0.49 b | |
| 浮霉菌门Planctomycetes | 6.90±0.29 b | 7.76±0.28 ab | 7.78±0.46 a | |
| 酸杆菌门Acidobacteria | 4.97±0.15 c | 8.28±0.06 b | 12.03±0.12 a | |
| 芽单胞菌门Gemmatimonadetes | 3.47±0.31 a | 3.26±0.05 a | 3.40±0.27 a | |
真菌 Fungus | 子囊菌门Ascomycota | 96.50±1.27 a | 96.88±1.74 a | 94.14±1.22 a |
| 绿藻门Chlorophyta | 2.01±0.81 a | 1.26±0.75 ab | 3.12±0.53 a | |
| 担子菌门Basidiomycota | 1.14±0.40 a | 1.58±0.90 a | 2.10±0.61 a | |
表1 不同含水率下的土壤细菌、真菌在门水平的物种相对丰度
Table 1 Relative abundance of soil bacteria and fungi at phylum level under different water contents
微生物类别 Class of microorganism | 门水平 Phylum level | 相对丰度Relative abundame/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-50% | H-65% | H-80% | ||
细菌 Bacterium | 放线菌门Actinobacteria | 27.57±0.58 a | 18.95±0.98 b | 17.49±0.55 b |
| 变形菌门Proteobacteria | 29.10±0.84 c | 37.31±1.57 b | 41.30±0.58 a | |
| 绿弯菌门Chloroflexi | 14.83±0.46 a | 11.91±0.18 b | 8.53±0.29 c | |
| 厚壁菌门Firmicutes | 9.94±1.39 a | 9.89±0.36 a | 7.01±0.49 b | |
| 浮霉菌门Planctomycetes | 6.90±0.29 b | 7.76±0.28 ab | 7.78±0.46 a | |
| 酸杆菌门Acidobacteria | 4.97±0.15 c | 8.28±0.06 b | 12.03±0.12 a | |
| 芽单胞菌门Gemmatimonadetes | 3.47±0.31 a | 3.26±0.05 a | 3.40±0.27 a | |
真菌 Fungus | 子囊菌门Ascomycota | 96.50±1.27 a | 96.88±1.74 a | 94.14±1.22 a |
| 绿藻门Chlorophyta | 2.01±0.81 a | 1.26±0.75 ab | 3.12±0.53 a | |
| 担子菌门Basidiomycota | 1.14±0.40 a | 1.58±0.90 a | 2.10±0.61 a | |
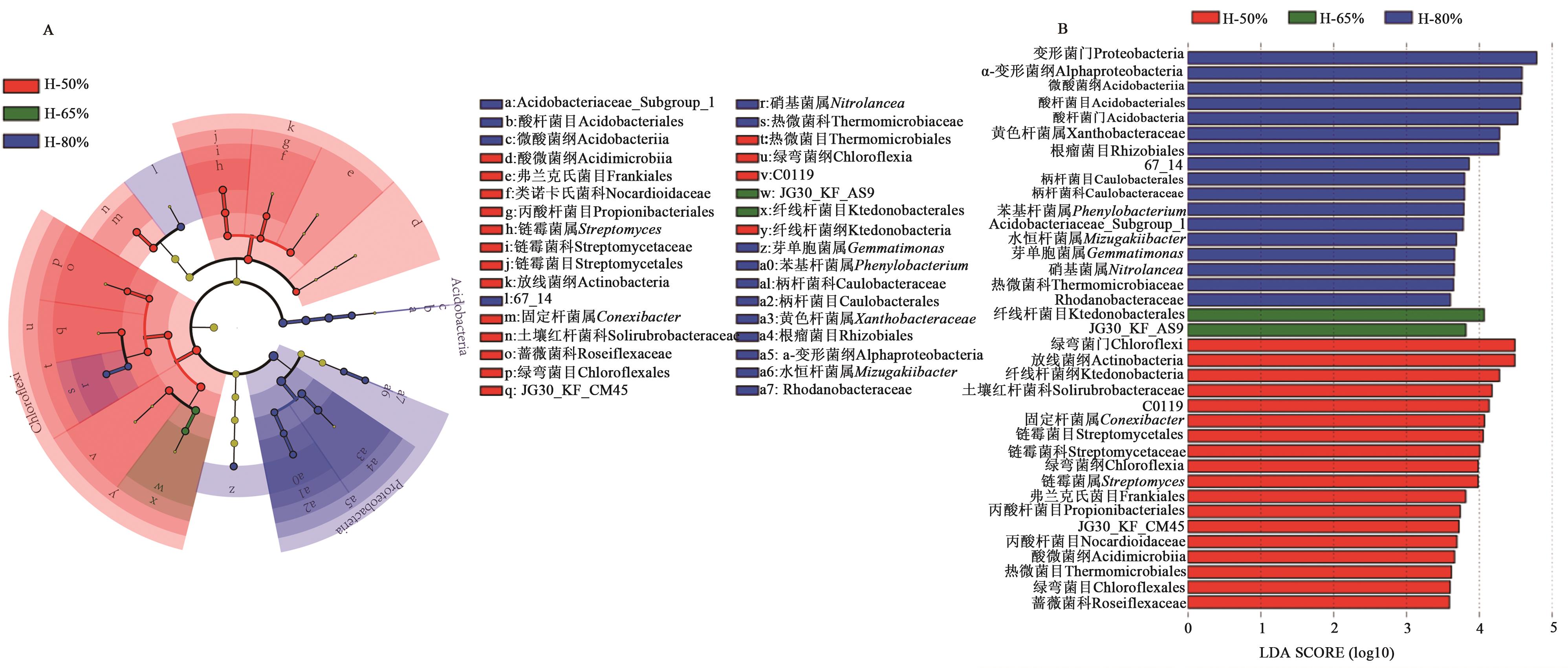
图5 不同含水率下的土壤细菌群落LEfSe分析A:土壤细菌物种层级树图;B:LDA判别柱形图
Fig. 5 LEfSe analysis of soil bacterial community under different water contentsA: Hierarchy dendrogram of soil bacterial species; B: Histogram of LDA discrimination
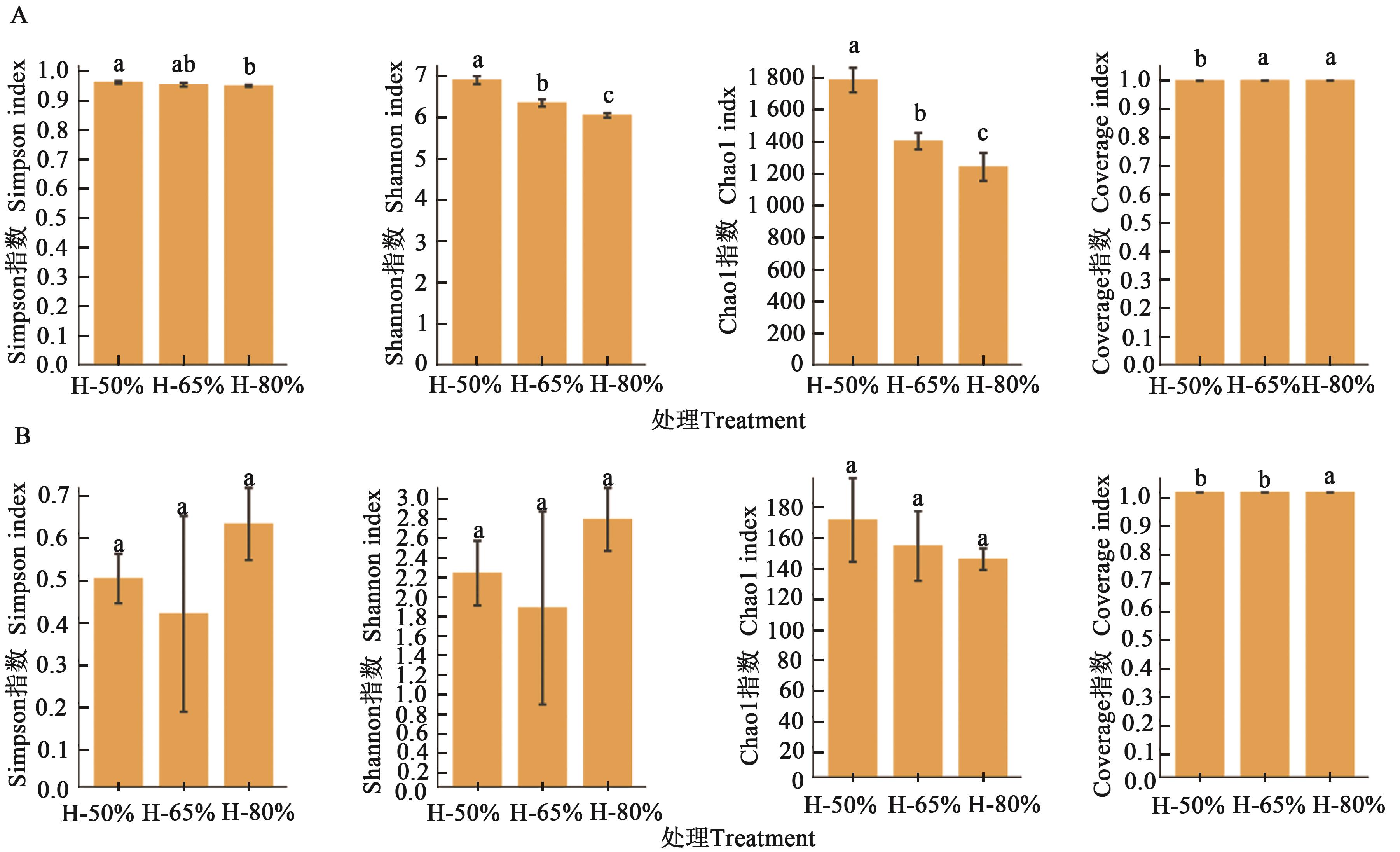
图7 不同含水率下的土壤细菌和真菌的丰富度及多样性A:细菌;B:真菌。图中不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 7 Abundance and diversity of soil bacteria and fungi under different water contentsA: Bacterium; B: Fungus. Different lowercase letters in figure indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
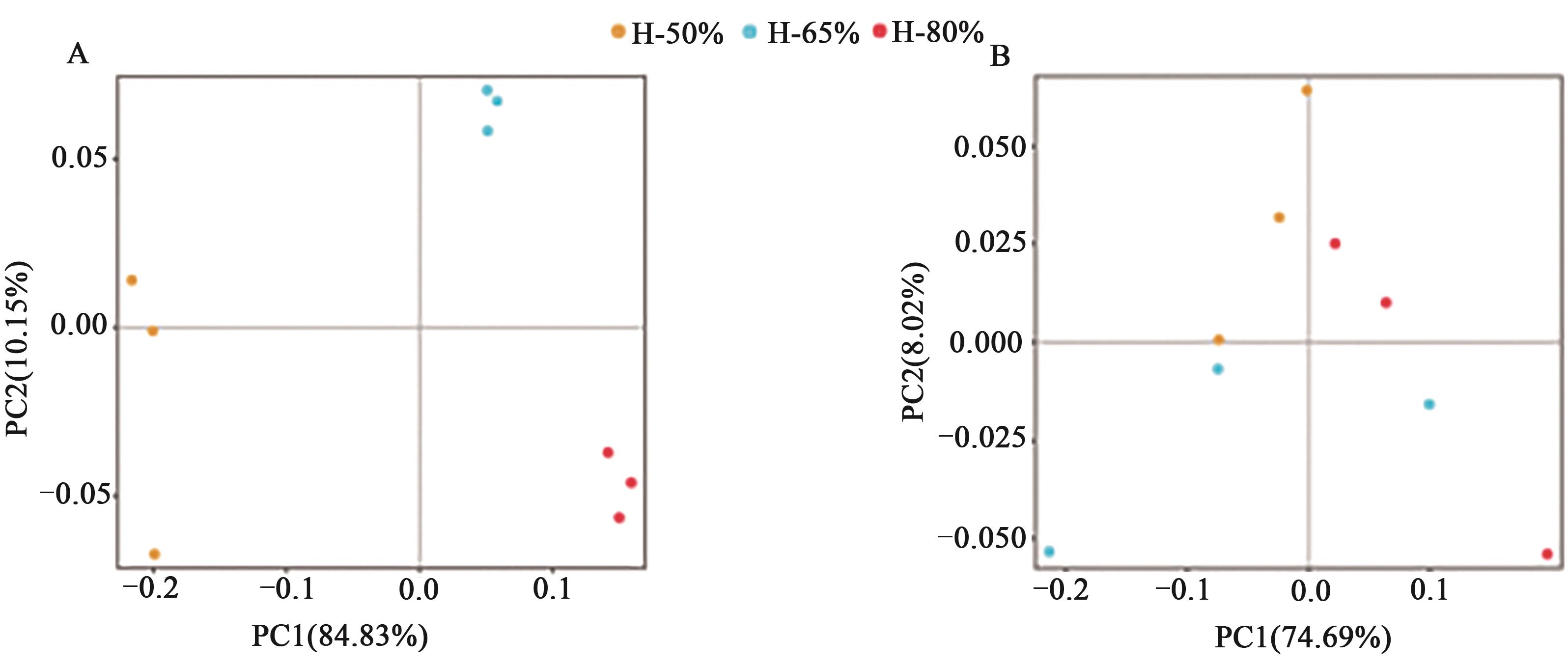
图8 不同含水率下的土壤细菌和真菌的主坐标分析A:细菌;B:真菌
Fig. 8 Principal coordinate analysis diagram of soil bacteria and fungi under different water contentsA: Bacterium; B: Fungus
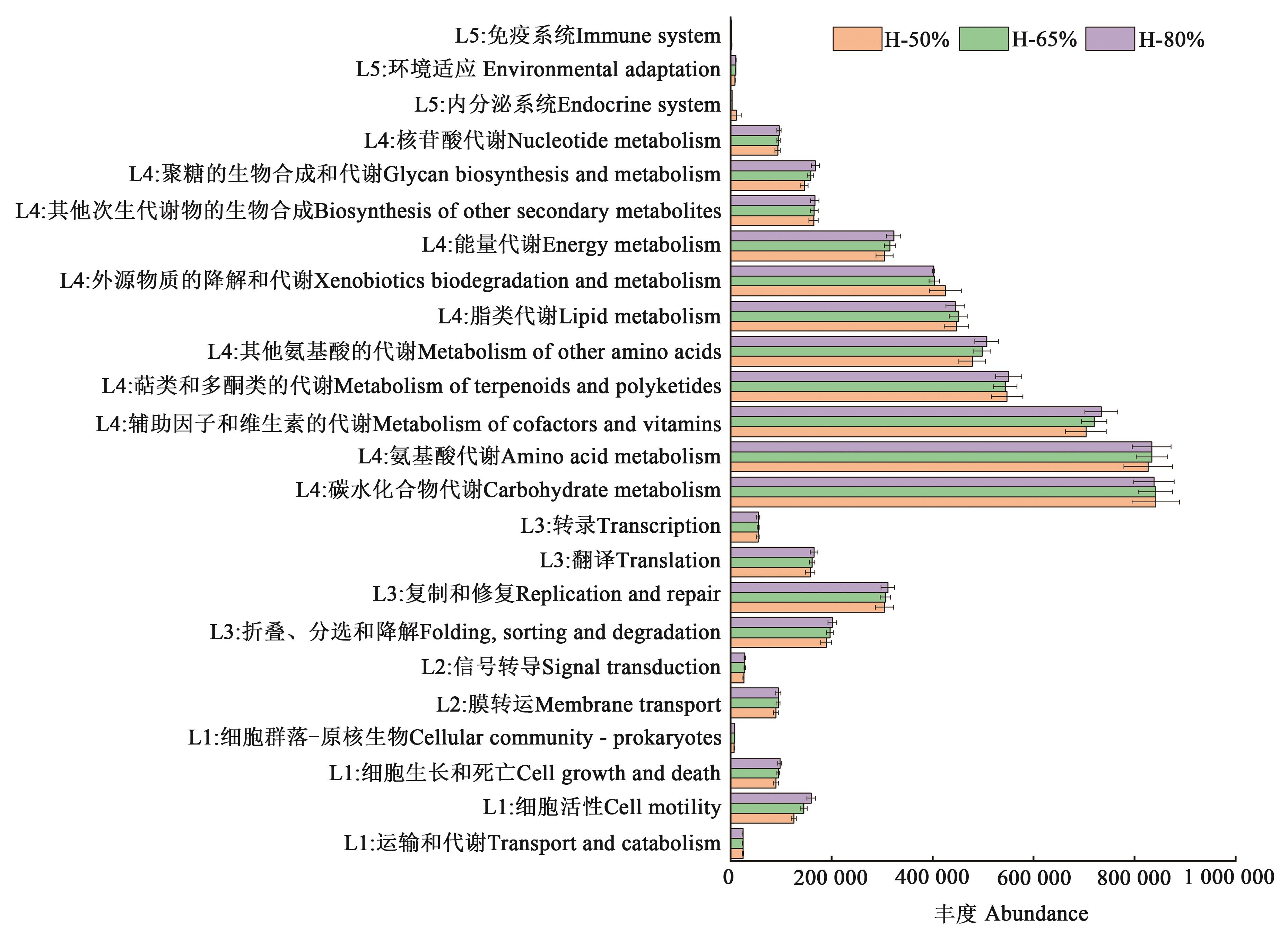
图9 不同含水率下的土壤微生物功能预测图注:L1~L5表示一级功能层;L1 表示细胞过程,L2 表示环境信息处理,L3 表示遗传信息处理,L4 表示代谢,L5 表示生物体系统。
Fig. 9 Prediction map of soil microbial function under different water contentsNote: L1~L5 represent the primary functional layer; L1 represents cell process, L2 represents environmental information processing, L3 represents genetic information processing, L4 represents metabolism, L5 represents biological system.
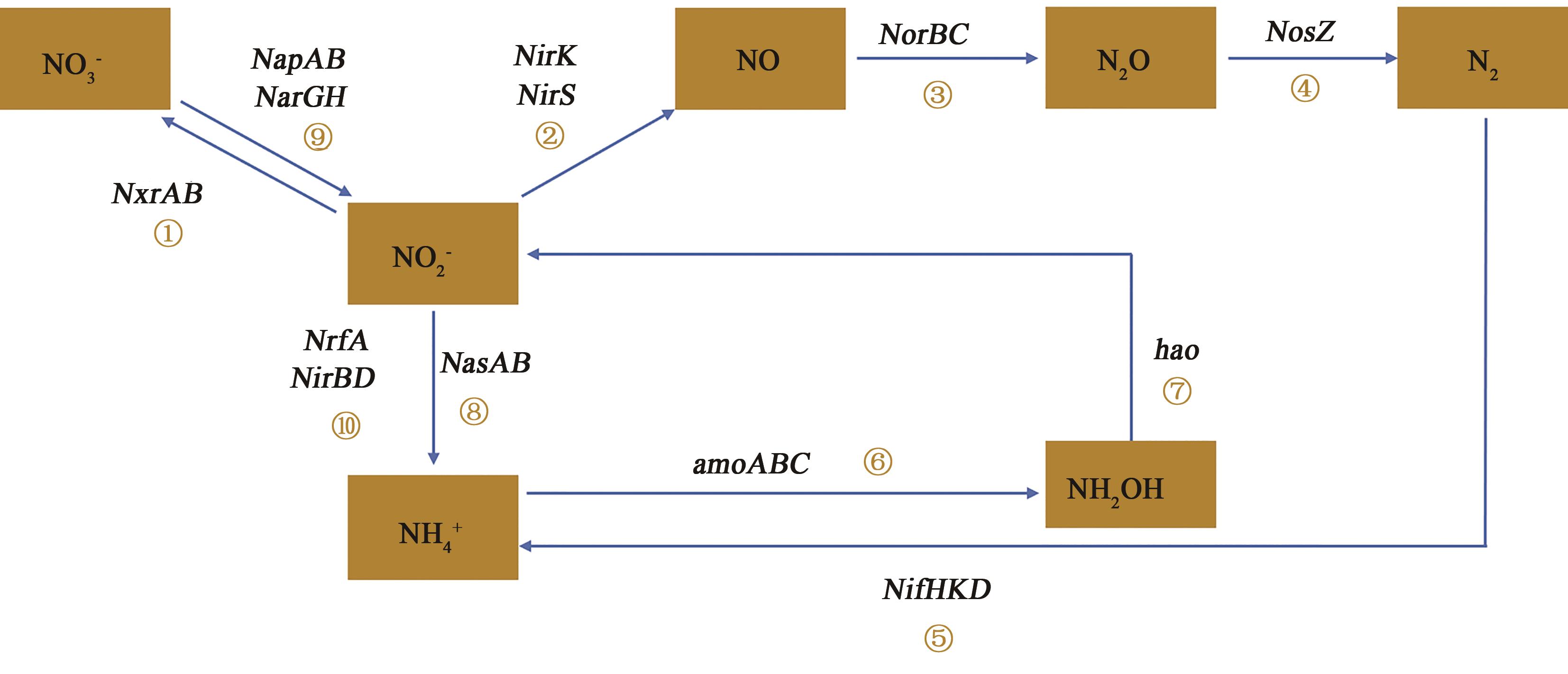
图10 氮代谢途径通路图及相关基因注:图中①⑥⑦ 为硝化反应过程(Ⅰ);⑧为同化硝酸盐还原过程(Ⅱ);⑩为异化硝酸盐还原过程(Ⅲ);⑤为固氮过程(Ⅳ);②③④⑨为反硝化过程(Ⅴ)。
Fig. 10 Pathways of nitrogen metabolism and related genesNote:①⑥⑦ in the figure are the nitrification reaction process(Ⅰ); ⑧ is the assimilation nitrate reduction process (Ⅱ); ⑩ is the dissimilation nitrate reduction process (Ⅲ); ⑤ is the nitrogen fixation process (Ⅳ); ②③④⑨ are the denitrification process(Ⅴ).
| 1 | 范瑞英,杨小燕,王恩姮,等.黑土区不同林龄落叶松人工林土壤微生物群落功能多样性的对比研究[J].北京林业大学学报,2013,35(2):63-68. |
| FAN R Y, YANG X Y, WANG E Y, et al.. Comparative studies on functional diversity of soil microbial community of larch plantations with different ages in black soil region [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2013, 35(2):63-68. | |
| 2 | 仇少君,彭佩钦,荣湘民,等.淹水培养条件下土壤微生物生物量碳、氮和可溶性有机碳、氮的动态[J].应用生态学报,2006,17(11):2052-2058. |
| QIU S J, PENG P Q, RONG X M, et al.. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and soluble organic carbon and nitrogen under submerged cultivation [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2006, 17(11): 2052-2058. | |
| 3 | 马秀艳,蒋磊,宋艳宇,等.温度和水分变化对冻土区泥炭地土壤氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(17):6707-6717. |
| MA X Y, JIANG L, SONG Y Y, et al.. Effects of temperature and water changes on gene abundance of nitrogen cycling function in peatland soil in permafrost region [J]. J. Ecol., 2021, 41(17):6707-6717 | |
| 4 | 吴照祥,刘巧丽,李辉虎,等.有机肥对退化红壤中细菌群落功能组成影响的PICRUSt基因预测分析[J].江苏农业科学,2021,49(16):60-66. |
| WU Z X, LIU Q L, LI H H, et al.. PICRUSt gene prediction analysis of the effect of organic fertilizer on the functional composition of bacterial community in degraded red soil [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2021, 49(16):60-66. | |
| 5 | 谷海红,李岩,刘宏斌,等.土壤氮素矿化及其对烤烟品质的影响研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2008,24(10):327-333. |
| GU H H, LI Y, LIU H B, et al.. Research progress on soil nitrogen mineralization and its effect on flue-cured tobacco quality [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2008, 24(10):327-333. | |
| 6 | ZANG X, WANG Q, LI L, et al.. Seasonal variations in nitrogen mineralization under three land use types in a grassland landscape [J]. Acta Oecol., 2008, 34(3):322-330. |
| 7 | KLAUS B, ELIZABETH M, BAGGS M, et al..Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: how well do we understand the processes and their controls? [J/OL]. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci., 2013, 368(1621):20130122 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 8 | COSKUN D, BRITTO D T, SHI W, et al.. How plant root exudates shape the nitrogen cycle [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2017, 22(8):661-673. |
| 9 | 林伟,李玉中,李昱佳,等.氮循环过程的微生物驱动机制研究进展[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(6):1146-1155. |
| LIN W, LI Y Z, LI Y J, et al.. Research progress on microbial driving mechanism of nitrogen cycle process [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26 (6):1146-1155. | |
| 10 | OUYANG Y, EVANS S E, FRIESEN M L, et al.. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the abundance of nitrogen cycling genes in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis of field studies [J]. Soil Boil. Biochem., 2018, 127(12):71-78. |
| 11 | KIZILOVA A K, TITOVA L V, KRAVCHENKO I K, et al.. Evaluation of the diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soybean rhizosphere by nifH gene analysis [J]. Microbiology, 2012, 81(5):621-629. |
| 12 | 王海涛,郑天凌,杨小茹,等.土壤反硝化的分子生态学研究进展及其影响因素[J].农业环境科学学报,2013,32(10):1915-1924. |
| WANG H T, ZHENG T L, YANG X R, et al.. Advances in molecular ecology of soil senitrification and its influencing factors [J]. J. Agric. Environ. Sci., 2013, 32(10):1915-1924. | |
| 13 | KELLY C N, SCHWANER G W, CUMMING J R, et al.. Metagenomic reconstruction of nitrogen and carbon cycling pathways in forest soil: influence of different hardwood tree species [J/OL]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2021, 156(5):108226 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 14 | 廖李容,王杰,张超,等.禁牧对半干旱草地土壤氮循环功能基因丰度和氮储量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(10):3473-3481. |
| LIAO L R, WANG J, ZHANG C, et al.. Effects of grazing prohibition on gene abundance and nitrogen storage of soil nitrogen cycle function in semi-arid grassland [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(10):3473-3481. | |
| 15 | 刘晓迎,左璇,刘雅星,等. 河南浓香型烟叶产区气候条件分析[J].河南农业科学,2017,46(3):52-58. |
| LIU X Y, ZUO X, LIU Y X, et al.. Analysis on climatic conditions in Henan uzhou flavor tobacco leaf production area [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2017, 46(3):52-58. | |
| 16 | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京:中国农业科技出版社,2000:1-638. |
| 17 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京:中国农业科技出版社: 2000:1-495. |
| 18 | GUO M J, WU F H, HAO G E, et al.. Bacillus subtilis improves immunity and disease resistance in rabbits [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2017, 8:354 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 19 | TOJU H, TANABE A S, YAMAMOTO S, et al.. High-coverage ITS primers for the DNA-based identification of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes in environmental samples [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7):e40863 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 20 | EDGAR R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads [J]. Nat. Methods, 2013, 10(10):996-998. |
| 21 | EDGAR R C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST [J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(19):2460-2461. |
| 22 | CAPORASO J G, KUCZYNSKI J, STOMBAUGH J, et al.. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data [J]. Nat. Methods, 2010, 7(5):335-336. |
| 23 | 徐扬,张冠初,丁红,等.土壤类型对花生根际土壤细菌群落多样性和产量的影响[J].生物技术通报,2022,38(6):221-234. |
| XU Y, ZHANG G C, DING H, et al.. Effects of soil types on bacterial community diversity and yield in peanut rhizosphere soil [J]. Biol. Bull., 2022, 38(6):221-234. | |
| 24 | SEGATA N, IZARD J, WALDRON L, et al.. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation [J]. Genome Biol., 2011, 12(6):1-18. |
| 25 | 周才平,欧阳华.温度和湿度对暖温带落叶阔叶林土壤氮矿化的影响[J].植物生态学报, 2001, 25(2):204-209. |
| ZHOU C P, OUYANG H. Effects of temperature and humidity on soil nitrogen mineralization in warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest [J]. J. Plant Ecol., 2001,25(2):204-209. | |
| 26 | 胡坤. 典型香型烟区植烟土壤氮素矿化及云南大理烤烟减氮增效效果研究[D]. 郑州:河南农业大学,2017. |
| HU K. Study on nitrogen mineralization of tobacco planting soil in typical aromatic tobacco area and effect of nitrogen reduction and efficiency increase of flue-cured tobacco in Dali, Yunnan [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 27 | 韩晓飞,郑文冉,徐畅,等.重庆市植烟区不同肥力植烟土壤氮素矿化特性研究[J].中国农学通报,2010,26(24):188-192. |
| HAN X F, ZHENG W R, XU C, et al.. Study on nitrogen mineralization characteristics of different fertility tobacco planting soils in Chongqing tobacco planting area [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2010, 26(24):188-192. | |
| 28 | REN C J, CHEN J, LU X, et al.. Responses of soil total microbial biomass and community compositions to rainfall reductions [J]. Soil Boil. Biochem., 2018, 11(6):4-10. |
| 29 | WALDROP M P, FIRESTONE M K. Response of microbial community composition and function to soil climate change [J]. Microbiol. Ecol., 2006, 52(4):716-724. |
| 30 | 杨阳,陈克龙,章妮,等.青海湖流域高寒湿地土壤微生物群落对不同降水梯度的响应[J].应用与环境生物学报,2022,28(2):290-299. |
| YANG Y, CHEN K L, ZHANG N, et al.. Response of soil microbial community of alpine wetland in Qinghai Lake basin to different precipitation gradients [J]. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2022, 28(2):290-299. | |
| 31 | LENNON J T, AANDERUD Z T, LEHMKUHL B K, et al.. Mapping the niche space of soil microorganisms using taxonomy and traits [J]. Ecology, 2012, 93(8):1867-1879. |
| 32 | 徐惠风,刘兴土,白军红.长白山沟谷湿地乌拉苔草沼泽湿地土壤微生物动态及环境效应研究[J].水土保持学报,2004,18(3):115-117, 122. |
| XU H F, LIU X T, BAI H J. Study on soil microbial dynamics and environmental effects of carex wula swamp wetland in Changbai mountain valley wetland [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2004,18(3):115-117, 122. | |
| 33 | BARNARD R L, OSBORNE C A, FIRESTONE M K. Responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to extreme desiccation and rewetting [J]. ISME J., 2013, 7(11): 2229-2241. |
| 34 | 刘会会, 喻庆国, 王行, 等. 碧塔海湿地不同水分梯度下土壤真菌群落结构及功能类群研究[J]. 微生物学报,2022,62(8):3007-3023. |
| LIU H H, YU Q G, WANG X, et al.. Study on community structure and functional groups of soil fungi under different water gradients in Bitahai wetland [J]. J. Microbiol., 2022, 62(8):3007-3023. | |
| 35 | TANG Y S, WANG L, JIA J W, et al.. Response of soil microbial community in Jiuduansha wetland to different successional stages and its implications for soil microbial respiration and carbon turnover [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2011, 43(3):638-646. |
| 36 | 张文学,王少先,夏文建,等.脲酶抑制剂与硝化抑制剂对稻田土壤硝化、反硝化功能菌的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2019,25(6):897-909. |
| ZHANG W X, WANG S X, XIA W J, et al.. Effects of urease inhibitor and nitrification inhibitor on functional nitrifier and denitrifier in paddy soil [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2019, 25(6):897-909. | |
| 37 | 国秀丽.温度和水分对土壤碳、氮转化影响的研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学, 2003. |
| GUO X L. The country is beautiful study on the effects of temperature and water on the transformation of soil carbon and nitrogen [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2003. | |
| 38 | LEVY-BOOTH D J, PRESCOTT C E, GRAYSTON S J. Microbial functional genes involved in nitrogen fixation, nitrification and denitrificati on in forest ecosystems [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2014, 75(8):11-25. |
| 39 | 马龙, 高伟, 栾好安, 等. 有机肥/秸秆替代化肥模式对设施菜田土壤氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(10):1767-1778. |
| MA L, GAO W, LUAN H A, et al.. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with manure and/or straw on the abundance of functional genes related to soil N-cycling [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2021, 27(10):1767-1778. |
| [1] | 郝需婷, 黄雅茹, 马迎宾, 张帅, 韩春霞, 庞嘉诚, 徐光甫, 郝惠忠, 刘雅婧. 乌兰布和沙漠固沙梭梭林生长季土壤水分动态研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 187-196. |
| [2] | 朱士江, 李虎, 徐文, 冯雅婷. 三峡库区土壤含水量对柑橘园果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 201-207. |
| [3] | 刘龙1,姚云峰1,郭月峰1*,祁伟1,2,温健1,高玉寒1,尉迟文思1,韩兆敏1. 准格尔旗砒砂岩区三种典型造林树种蒸腾耗水研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(3): 124-131. |
| [4] | 刘龙,姚云峰,郭月峰*,祁伟,高玉寒,韩兆敏,尉迟文思. 农牧交错带柠条锦鸡儿根系与土壤水分空间关系研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(7): 101-107. |
| [5] | 张明艳1,张继光1*,申国明1,张忠锋1,蔡宪杰2,薛林3. 烟田土壤微生物群落结构及功能微生物的研究现状与展望[J]. , 2014, 16(5): 115-122. |
| [6] | 肖景华,吴昌银,张启发. 水稻功能基因组研究进展与发展展望[J]. , 2013, 15(2): 1-7. |
| [7] | 燕永亮1,李力2,李俊2. 根际固氮微生物功能基因组及微生物肥料研究进展[J]. , 2011, 13(5): 93-101. |
| [8] | 刘晓蓓1,吴赓1,张芊2,刘贯山3,路铁刚2,王元英3. 烟草突变体库的创建策略及其应用[J]. , 2010, 12(6): 28-35. |
| [9] | 李志江,刁现民. 谷子分子标记与功能基因组研究进展[J]. , 2009, 11(4): 16-22. |
| [10] | 胡晓梅 祝欣 王健美 杨毅 李旭锋. 油菜花蕾发育及开花过程中ABCD功能基因的表达差异分析[J]. , 2007, 9(5): 80-86. |
| [11] | 白优爱[1] 巨晓棠[2] 等. 商品有机肥及蔬菜残体在菜地土壤中的氮素矿化研究[J]. , 2003, 5(2): 45-49. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号