




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 122-130.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0873
• 智慧农业 农机装备 • 上一篇
金慧萍1( ), 牟海雯2, 刘腾2, 于佳琳2, 金小俊2,3(
), 牟海雯2, 刘腾2, 于佳琳2, 金小俊2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-28
接受日期:2024-02-06
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-08-12
通讯作者:
金小俊
作者简介:金慧萍 E-mail: jinhuiping713@163.com;
基金资助:
Huiping JIN1( ), Haiwen MOU2, Teng LIU2, Jialin YU2, Xiaojun JIN2,3(
), Haiwen MOU2, Teng LIU2, Jialin YU2, Xiaojun JIN2,3( )
)
Received:2023-11-28
Accepted:2024-02-06
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-12
Contact:
Xiaojun JIN
摘要:
针对青菜田间杂草种类繁多且分布复杂导致识别效率低、精度差和稳健性不足等问题,以苗期青菜及其伴生杂草为研究对象,提出了一种基于深度卷积神经网络的青菜和杂草识别方法。首先使用图像处理方法标记出包含绿色植物的图像,进而利用神经网络模型对青菜和杂草进行区分。为探究不同神经网络模型的识别效果,分别选取DenseNet模型、GoogLeNet模型和ResNet模型对图像中包含青菜或者杂草图像进行识别,并以F1值、总体准确率和识别速度作为评价依据。结果表明,3种神经网络模型均能有效区分青菜和杂草,其中ResNet模型为最优模型,其在测试集的总体准确率和识别速度分别为97.2%和78.34 帧·s-1。提出的青菜和杂草识别方法可有效降低杂草识别的复杂度,并能够提升识别的稳健性和泛化能力,为青菜田间杂草精准防控的研究奠定基础。
中图分类号:
金慧萍, 牟海雯, 刘腾, 于佳琳, 金小俊. 基于深度卷积神经网络的青菜和杂草识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 122-130.
Huiping JIN, Haiwen MOU, Teng LIU, Jialin YU, Xiaojun JIN. Bok Choy and Weed Identification Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 122-130.
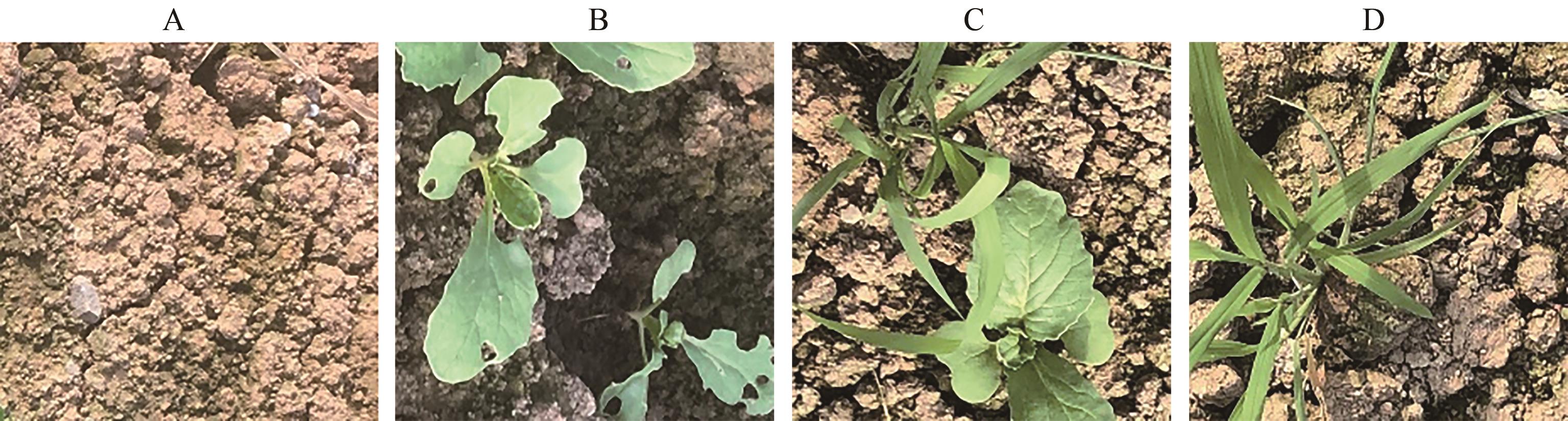
图2 不同场景类型的网格图像A:仅包含土壤;B:仅包含青菜;C:既包含青菜又包含杂草;D:仅包含杂草
Fig. 2 Grid images of different scene typesA: Soil only; B: Bok choy only; C: Contain both bok choy and weed; D: Weed only
神经网络模型 Neural network | 优化器 Optimizer | 初始学习率 Base learning rate | 学习率调整策略 Learning rate policy | 批尺寸 Batch size | 训练周期 Training epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | SGD | 0.001 0 | LambdaLR | 16 | 24 |
| GoogLeNet | Adam | 0.000 3 | StepLR | 16 | 24 |
| ResNet | Adam | 0.000 1 | StepLR | 16 | 24 |
表1 不同模型的超参设置
Table 1 Hyper-parameters used for training the neural networks
神经网络模型 Neural network | 优化器 Optimizer | 初始学习率 Base learning rate | 学习率调整策略 Learning rate policy | 批尺寸 Batch size | 训练周期 Training epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | SGD | 0.001 0 | LambdaLR | 16 | 24 |
| GoogLeNet | Adam | 0.000 3 | StepLR | 16 | 24 |
| ResNet | Adam | 0.000 1 | StepLR | 16 | 24 |
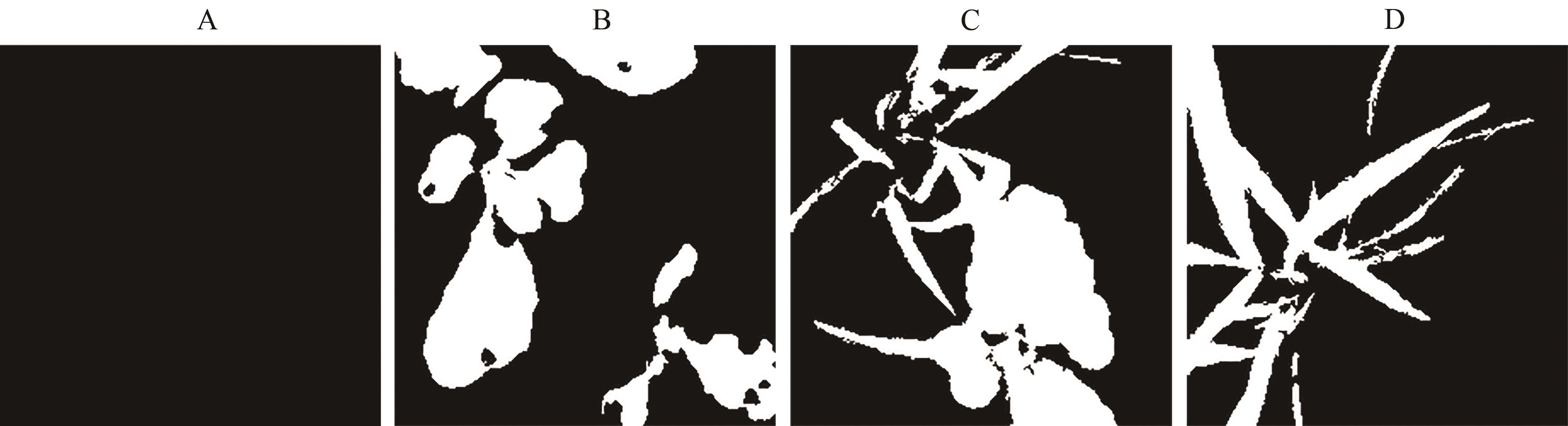
图3 绿色植物分割效果A:土壤背景分割;B:青菜目标分割;C:青菜和杂草目标分割;D:杂草目标分割
Fig. 3 Green plants division effectA: Soil background division; B: Bok choy division; C: Bok choy and weed division; D: Weed division
神经网络模型 Neural network | 目标 Target | 精度 Precision | 召回率 Recall | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy | F1值 F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.976 | 0.968 | 0.972 | 0.972 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.969 | 0.977 | 0.972 | 0.973 | |
| GoogLeNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.948 | 0.967 | 0.957 | 0.957 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.966 | 0.947 | 0.957 | 0.956 | |
| ResNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.977 | 0.973 | 0.975 | 0.975 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.973 | 0.977 | 0.975 | 0.975 |
表2 不同神经网络模型验证集评价数据
Table 2 Evaluation matrix of CNN models in validation datasets
神经网络模型 Neural network | 目标 Target | 精度 Precision | 召回率 Recall | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy | F1值 F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.976 | 0.968 | 0.972 | 0.972 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.969 | 0.977 | 0.972 | 0.973 | |
| GoogLeNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.948 | 0.967 | 0.957 | 0.957 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.966 | 0.947 | 0.957 | 0.956 | |
| ResNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.977 | 0.973 | 0.975 | 0.975 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.973 | 0.977 | 0.975 | 0.975 |
神经网络模型 Neural network | 目标 Target | 精度 Precision | 召回率 Recall | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy | F1值 F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.976 | 0.957 | 0.967 | 0.966 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.958 | 0.977 | 0.967 | 0.967 | |
| GoogLeNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.945 | 0.965 | 0.954 | 0.955 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.964 | 0.943 | 0.954 | 0.953 | |
| ResNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.978 | 0.965 | 0.972 | 0.971 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.965 | 0.978 | 0.972 | 0.971 |
表3 不同神经网络模型测试集评价数据
Table 3 Evaluation matrix of CNN models in testing dataset
神经网络模型 Neural network | 目标 Target | 精度 Precision | 召回率 Recall | 总体准确率 Overall accuracy | F1值 F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.976 | 0.957 | 0.967 | 0.966 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.958 | 0.977 | 0.967 | 0.967 | |
| GoogLeNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.945 | 0.965 | 0.954 | 0.955 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.964 | 0.943 | 0.954 | 0.953 | |
| ResNet | 青菜Bok choy | 0.978 | 0.965 | 0.972 | 0.971 |
| 杂草Weed | 0.965 | 0.978 | 0.972 | 0.971 |
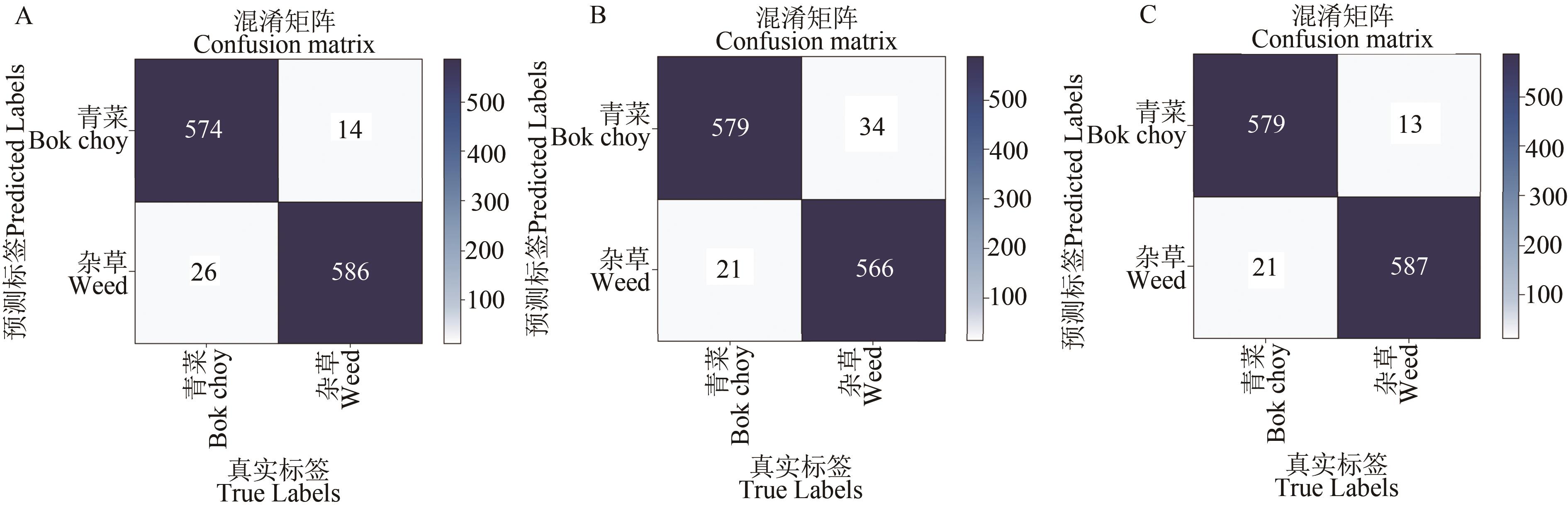
图4 神经网络模型测试集混淆矩阵A: DenseNet模型混淆矩阵;B: GoogLeNet模型混淆矩阵; C:ResNet模型混淆矩阵
Fig. 4 Confusion matrices of the neural networks in testing datasetsA: DenseNet model confusion matrix; B: GoogLeNet model confusion matrix; C: ResNet model confusion matrix
神经网络模型 Neural network | 批尺寸 Batch size | 图像计算数量 Image calculations | 识别速度/(ms·幅-1) Recognition speed/(ms·image-1) | 帧率/(帧·s-1) Frame per second/(frames·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 48 | 1 200 | 19.44 | 51.43 |
| GoogLeNet | 48 | 1 200 | 12.38 | 80.80 |
| ResNet | 48 | 1 200 | 12.76 | 78.34 |
表4 不同模型的识别速度
Table 4 Recognition speed of different models
神经网络模型 Neural network | 批尺寸 Batch size | 图像计算数量 Image calculations | 识别速度/(ms·幅-1) Recognition speed/(ms·image-1) | 帧率/(帧·s-1) Frame per second/(frames·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | 48 | 1 200 | 19.44 | 51.43 |
| GoogLeNet | 48 | 1 200 | 12.38 | 80.80 |
| ResNet | 48 | 1 200 | 12.76 | 78.34 |
| 1 | 陆海涛,吕建强,金伟,等.我国叶类蔬菜机械化收获技术的发展现状[J]. 农机化研究, 2018,40(6):261-268. |
| LU H T, LYU J Q, JIN W, et al.. The current situation of the mechanized harvesting technology development of leaf vegetable in China [J]. J. Agric. Mechan. Res., 2018,40(6):261-268. | |
| 2 | JIANG P H, YI H L, LI P Y, et al.. Acidification and salinization of soils with different initial pH under greenhouse vegetable cultivation [J]. J. Soil Sediments, 2014,14(10):1683-1692. |
| 3 | 廖禺,潘松,黄俊宝,等.蔬菜生产机械化技术的现状与发展研究[J]. 粮食科技与经济, 2018,43(10):99-101. |
| LIAO Y, PAN S, HUANG J B, et al.. Research on the status and development of vegetable production mechanization technology [J]. Grain Sci. Technol. Econ., 2018,43(10):99-101. | |
| 4 | 王璨,武新慧,张燕青,等.基于移位窗口Transformer网络的玉米田间场景下杂草识别[J].农业工程学报, 2022,38(15):133-142. |
| WANG C, WU X H, ZHANG Y Q, et al.. Recognizing weeds in maize fields using shifted window transformer network [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2022,38(15):133-142. | |
| 5 | DEBALINA S H, BERT M C, MANJOT K S. A review of Non-chemical weed control practices in christmas tree production [J]. Forests, 2020,11(5):554. |
| 6 | GAINES T A, BUSI R, KÜPPER A. Can new herbicide discovery allow weed management to outpace resistance evolution? [J]. Pest. Manage. Sci., 2021,77(7):3036-3041. |
| 7 | ANNE M, BENJAMIN F, MIIKA L, et al.. Risk in the circular food economy: Glyphosate-based herbicide residues in manure fertilizers decrease crop yield [J/OL]. Sci.Total Environ., 2021,750:141422 [2024-03-19]. . |
| 8 | 魏春生. 蔬菜田间化学除草技术及注意事项分析[J]. 农民致富之友, 2019(1):134. |
| 9 | GERHARDS R, ANDÚJAR S D, HAMOUZ P, et al.. Advances in site-specific weed management in agriculture-a review [J]. Weed Res., 2022,62(2):123-133. |
| 10 | REKHA R, THUY T N, DAVID C S, et al.. Real-time robotic weed knife control system for tomato and lettuce based on geometric appearance of plant labels [J]. Biosyst. Eng., 2020,194:152-164. |
| 11 | MARTIN V B, CHRISTIAN M, FABIENNE V B, et al.. Thermal weed control technologies for conservation agriculture—a review [J]. Weed Res., 2020,60(4):241-250. |
| 12 | 兰天,李端玲,张忠海,等.智能农业除草机器人研究现状与趋势分析[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2021,29(5):1-7. |
| LAN T, LI D L, ZHANG Z H, et al.. Analysis on research status and trend of intelligent agricultural weeding robot [J]. Comput. Meas. Control, 2021,29(5):1-7. | |
| 13 | 孙艳霞,陈勇,金小俊,等.除草机器人减震悬架越障性能分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013,44(S1):264-268. |
| SUN Y X, CHEN Y, JIN X J, et al.. Structure design and simulation analysis of weeding robot. [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2013,44(S1):264-268. | |
| 14 | 金小俊,陈勇,孙艳霞.农田杂草识别方法研究进展[J]. 农机化研究, 2011,33(7):23-27, 33. |
| JIN X J, CHEN Y, SUN Y X. Research advances of weed identification in agricultural fields [J]. J. Agric. Mechan. Res., 2011, 33(7):23-27, 33. | |
| 15 | 毛文华,张银桥,王辉,等.杂草信息实时获取技术与设备研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013,44(1):190-195. |
| MAO W H, ZHANG Y Q, WANG H, et al.. Advance techniques and equipments for real-time weed detection [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2013, 44(1):190-195. | |
| 16 | PEDRO J H, JOSÉ D, ÁNGELA R. A novel approach for weed type classification based on shape descriptors and a fuzzy decision-making method [J]. Sensors, 2014,14(8): 15304-15324. |
| 17 | TANG L, TIAN L, STEWARD B L. Color image segmentation with genetic algorithm for in-field weed sensing [J]. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2000,43(4):1019-1027. |
| 18 | ADEL B, ABDOLABBAS J, SEYED M N, et al.. Weed segmentation using texture features extracted from wavelet sub-images [J]. Biosyst. Eng., 2017,157:1-12. |
| 19 | 程玉柱,陈勇,车军,等.基于Bayes与SVM的玉米彩色图像分割新算法[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2012,40(7):355-358. |
| 20 | MARCHANT J A, ONYANGO C M. Comparison of a Bayesian classifier with a multilayer feed-forward neural network using the example of plant/weed/soil discrimination [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2003,39(1):3-22. |
| 21 | 毛文华,曹晶晶,姜红花,等.基于多特征的田间杂草识别方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007(11):206-209. |
| MAO W H, CAO J J, JIANG H H, et al.. In-field weed detection method based on multi-features [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2007(11):206-209. | |
| 22 | 何东健,乔永亮,李攀,等.基于SVM-DS多特征融合的杂草识别[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013,44(2):182-187. |
| HE D J, QIAO Y L, LI P, et al.. Weed recognition based on SVM-DS multi-feature fusion [J] Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2013,44(2):182-187. | |
| 23 | KONSTANTINOS G L, PATRIZIA B, DIMITRIOS M, et al.. Machine learning in agriculture: a review [J/OL]. Sensors, 2018,18(8):2674 [2024-03-19]. . |
| 24 | 仇裕淇,黄振楠,阮昭,等.机器视觉技术在农业生产智能化中的应用综述[J].机械研究与应用, 2019,32(2):202-206. |
| QIU Y Q, HUANG Z N, RUAN Z, et al.. Review on application of machine vision in intelligent agricultural production [J]. Mech. Res. Appl., 2019,32(2):202-206. | |
| 25 | 陈自宏,邓干然,崔振德,等.基于深度学习的农作物检测识别研究现状及展望[J].现代农业装备, 2022,43(2):2-7. |
| CHEN Z H, DENG G R, CUI Z D, et al.. Research status and prospect of crop detection and identification based on deep learning [J]. Mod. Agric. Equip., 2022,43(2):2-7. | |
| 26 | WANG A C, ZHANG W, WEI X H. A review on weed detection using ground-based machine vision and image processing techniques [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2019,158:226-240. |
| 27 | ADEL B, ABDOLABBAS J. Evaluation of support vector machine and artificial neural networks in weed detection using shape features [J]. Comput. Electron. Agric., 2018,145:153-160. |
| 28 | 金小俊,陈勇,侯学贵,等.基于机器视觉的除草机器人杂草识别[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,31(2):104-108. |
| JIN X J, CHEN Y, HOU X G, et al.. Weed recognition of the machine vision based weeding robot [J]. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. ( Nat. Sci.), 2012,31(2):104-108. | |
| 29 | OSORIO K, PUERTO A, PEDRAZA C, et al.. A deep learning approach for weed detection in lettuce crops using multispectral images [J]. AgriEngineering, 2020,2(3):471-488. |
| 30 | 孙哲,张春龙,葛鲁镇,等.基于Faster R-CNN的田间西兰花幼苗图像检测方法[J].农业机械学报, 2019,50(7):216-221. |
| SUN Z, ZHANG C L, GE L Z, et al.. Image detection method for broccoli seedlings in field based on faster R-CNN [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2019,50(7):216-221. | |
| 31 | 东辉,陈鑫凯,孙浩,等. 基于改进YOLOv4和图像处理的蔬菜田杂草检测[J]. 图学学报, 2022,43(4):559-569. |
| DONG H, CHEN X K, SUN H, et al.. Weed detection in vegetable field based on improved YOLOv4 and image processing [J]. J. Graph., 2022,43(4):559-569. | |
| 32 | MORID M A, BORJALI A, DEL F G. A scoping review of transfer learning research on medical image analysis using ImageNet [J/OL]. Comput. Biol. Med., 2021,128:104115 [2024-01-13]. . |
| 33 | JIN X J, CHE J, CHEN Y. Weed identification using deep learning and image processing in vegetable plantation [J]. IEEE Access., 2021,9:10940-10950. |
| 34 | SIMON K, DORIT M. DELIMIT PyTorch - an extension for deep learning in diffusion imaging [EB/OL]. (2018-08-04) [2024-03-19]. . |
| 35 | 李梦洁,董峦. 基于PyTorch的机器翻译算法的实现[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2018,28(10):160-163, 167. |
| LI M J, DONG L. Implementation of machine translation algorithm based on PyTorch [J]. Comput. Tech. Dev., 2018,28(10):160-163, 167. | |
| 36 | 贺丹.基于PyTorch的图像修复技术研究[J].电脑知识与技术, 2022,18(9):75-77. |
| 37 | 孙艳霞,陈燕飞,金小俊,等.基于人工智能的青菜幼苗与杂草识别方法[J].福建农业学报, 2021,36(12):1484-1490. |
| SUN Y X, CHEN Y F, JIN X J, et al.. AI differentiation of bok choy seedlings from weeds [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2021,36(12):1484-1490. | |
| 38 | ZHANG B, GENG Z Y, ZHANG H W, et al.. Densely connected convolutional networks with attention long short-term memory for estimating PM2.5 values from images [J/OL]. J. Clean. Prod., 2022,333(20):130101 [2024-03-19]. . |
| 39 | CHRISTIAN S, WEI L, YANG Q J, et al.. Going deeper with convolutions [EB/OL]. (2014-09-17) [2024-03-19]. . |
| 40 | HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S, et al.. Deep residual learning for image recognition [EB/OL]. (2015-12-10) [2024-03-19]. . |
| [1] | 郑果, 姜玉松. 基于多任务学习农作物叶片病害诊断方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 89-98. |
| [2] | 钱政, 杨孙哲, 张国卿, 郭紫微, 张林朋, 万家兴, 杨红云. 基于卷积神经网络的水稻氮素营养诊断[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 113-121. |
| [3] | 林开颜, 梅飞, 吴军辉, 郭文刚, 陈杰, 司慧萍. 基于计算机视觉的作物病害监测服务平台设计与研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 89-96. |
| [4] | 杨超, 韩海斌, 韦波, 张衡, 商宸, 苏冰, 刘思源, 蒋沛雯, 相德龙. 北太平洋远东拟沙丁鱼年龄鉴定方法的构建[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 225-233. |
| [5] | 胡灵炆, 周忠发, 尹林江, 朱孟, 黄登红. 基于无人机RGB影像的苗期油菜识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 116-128. |
| [6] | 赵越, 卫勇, 单慧勇, 穆志民, 张健欣, 吴海云, 赵辉, 胡建龙. 基于深度学习的高分辨率麦穗图像检测方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 96-105. |
| [7] | 刘海涛, 韩鑫, 兰玉彬, 伊丽丽, 王宝聚, 崔立华. 基于YOLOv4网络的棉花顶芽精准识别方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 99-108. |
| [8] | 方逵, 李成, 何潇, 陈益能. 基于三维重建的多角度葡萄叶病害识别方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 86-96. |
| [9] | 吴建伟, 黄杰, 熊晓菲, 高晗, 秦向阳. 基于AI的桃树病害智能识别方法研究与应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 111-118. |
| [10] | 高姻燕, 孙义, 李葆春. 基于无人机RGB影像估测田间小麦穗数[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 103-110. |
| [11] | 黄昊, 谢圣桥, 陈度, 王恒. 深度学习在苹果产业链中的应用与研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 79-89. |
| [12] | 周惠汝, 吴波明. 深度学习在作物病害图像识别方面应用的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 61-68. |
| [13] | 吕纯阳, 刘升平, 郭秀明, 肖顺夫, 刘大众, 杨菲菲, 李路华. 基于SSD模型的巢门蜜蜂检测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 98-107. |
| [14] | 郭阳, 许贝贝, 陈桂鹏, 丁建, 严志雁, 梁华, 吴昌华. 基于卷积神经网络的水稻虫害识别方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 99-109. |
| [15] | 许贝贝1,王文生1,2*,郭雷风1,陈桂鹏3. 基于非接触式的牛只身份识别研究进展与展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 79-89. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号