




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 169-178.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0721
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
刘岑薇1,2( ), 叶菁1,2, 林怡1,2, 李艳春1,2, 王义祥1,2(
), 叶菁1,2, 林怡1,2, 李艳春1,2, 王义祥1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-27
接受日期:2023-12-05
出版日期:2025-04-15
发布日期:2025-04-15
通讯作者:
王义祥
作者简介:刘岑薇 E-mail:liuc179@163.com;
基金资助:
Cenwei LIU1,2( ), Jing YE1,2, Yi LIN1,2, Yanchun LI1,2, Yixiang WANG1,2(
), Jing YE1,2, Yi LIN1,2, Yanchun LI1,2, Yixiang WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2023-09-27
Accepted:2023-12-05
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Yixiang WANG
摘要:
为减轻长期施用猪粪有机肥导致的土壤重金属污染,长期定位试验设置3个有机肥替代化肥的梯度处理,即替代化肥总养分的25%(L)、50%(M)、100%(H),同时设4个生物炭梯度处理,即添加0%(B0)、3%(B1)、6%(B2)、9%(B3)生物炭,研究有机肥与生物炭配施对叶用甘薯产量、土壤镉(Cd)、铅(Pb)含量及Pb不同形态变化的影响。结果表明,猪粪有机肥和生物炭施用比例对叶用甘薯产量及土壤Pb含量存在显著性交互作用(P<0.05)。L、H用量有机肥处理下,B3处理的叶用甘薯产量最高; B1H和B3L处理分别显著降低叶用甘薯Pb累积含量31.5%和37.6%。M用量有机肥处理中,随着生物炭添加量的增加,叶用甘薯Cd累积含量降低。生物炭配施可促进土壤Pb由生物有效性高的弱酸提取态、可还原态向低生物有效性的可氧化态和残渣态转化。以上结果表明,有机肥与生物炭合理配施可增加叶用甘薯产量,降低长期施用有机肥带来的重金属污染问题,提高土壤质量。
中图分类号:
刘岑薇, 叶菁, 林怡, 李艳春, 王义祥. 炭基猪粪肥对叶用甘薯产量及土壤Pb、Cd钝化效果的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 169-178.
Cenwei LIU, Jing YE, Yi LIN, Yanchun LI, Yixiang WANG. Effects of Combined Application of Organic Pig Manure Fertilizer Combined with Biochar on Pb、Cd Passivation of Leaf Sweet Potato and Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 169-178.
处理 Treatment | 生物炭 Biochar/% | 猪粪有机肥 Organic fertilizer with pig manure/(g·m-2) | 尿素 Urea/(g·m-2) | 过磷酸钙 Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O/ (g·m-2) | 氯化钾 KCl/(g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 |
| CF | 0 | 0 | 78.4 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B0L | 0 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B0M | 0 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B0H | 0 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B1L | 3 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B1M | 3 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B1H | 3 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B2L | 6 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B2M | 6 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B2H | 6 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B3L | 9 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B3M | 9 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B3H | 9 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
表1 施肥处理及施用量
Table 1 Fertilization treatments and application amount
处理 Treatment | 生物炭 Biochar/% | 猪粪有机肥 Organic fertilizer with pig manure/(g·m-2) | 尿素 Urea/(g·m-2) | 过磷酸钙 Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O/ (g·m-2) | 氯化钾 KCl/(g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 |
| CF | 0 | 0 | 78.4 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B0L | 0 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B0M | 0 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B0H | 0 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B1L | 3 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B1M | 3 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B1H | 3 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B2L | 6 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B2M | 6 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B2H | 6 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B3L | 9 | 635 | 58.8 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B3M | 9 | 1 280 | 39.2 | 186.6 | 45 |
| B3H | 9 | 2 560 | 0.0 | 186.6 | 45 |
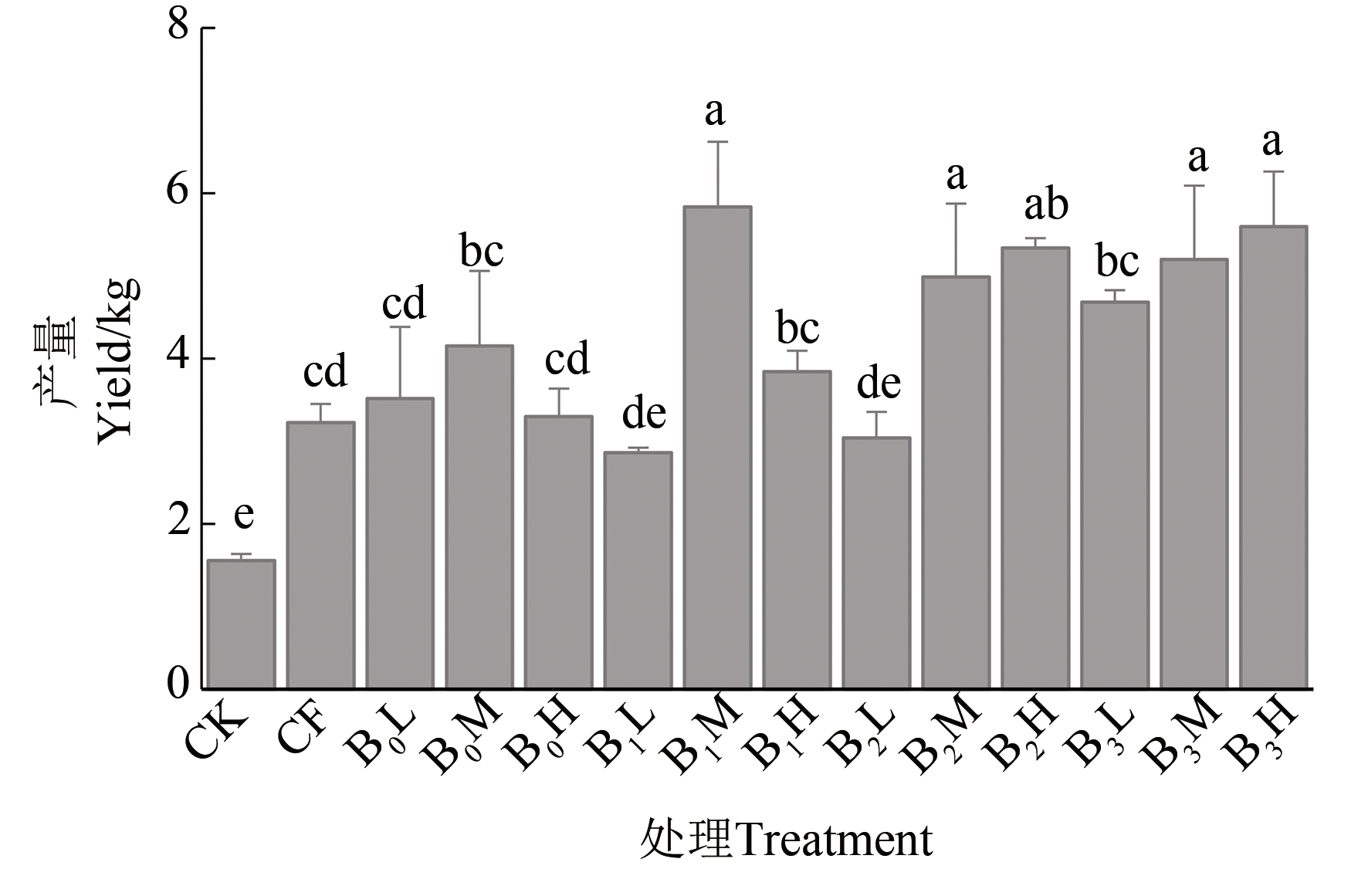
图1 不同施肥处理下叶用甘薯的产量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Yield of leafy sweet potato under different fertilizer treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 生物炭 Biochar | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 生物炭×有机肥 Biochar × organic fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
叶用甘薯产量 Yield of leaf sweet potato | * | ** | ** |
叶用甘薯Pb Pb of leaf sweet potato | * | ns | ns |
叶用甘薯Cd Cd of leaf sweet potato | ns | ns | ns |
土壤Pb Pb of soil | ** | ns | ** |
土壤Cd Pb of soil | ns | ns | ns |
表2 双因素方差分析有机肥替代量和生物炭配施比例对作物产量及重金属的交互作用
Table 2 Two-factor variance analysis of organic fertilizer replacement amount and biochar accessory ratio on crop yield and heavy metals
指标 Index | 生物炭 Biochar | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 生物炭×有机肥 Biochar × organic fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
叶用甘薯产量 Yield of leaf sweet potato | * | ** | ** |
叶用甘薯Pb Pb of leaf sweet potato | * | ns | ns |
叶用甘薯Cd Cd of leaf sweet potato | ns | ns | ns |
土壤Pb Pb of soil | ** | ns | ** |
土壤Cd Pb of soil | ns | ns | ns |

图2 不同施肥处理下叶用甘薯Pb、Cd的含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Pb and Cd content of leafy sweet potato under different fertilizer treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
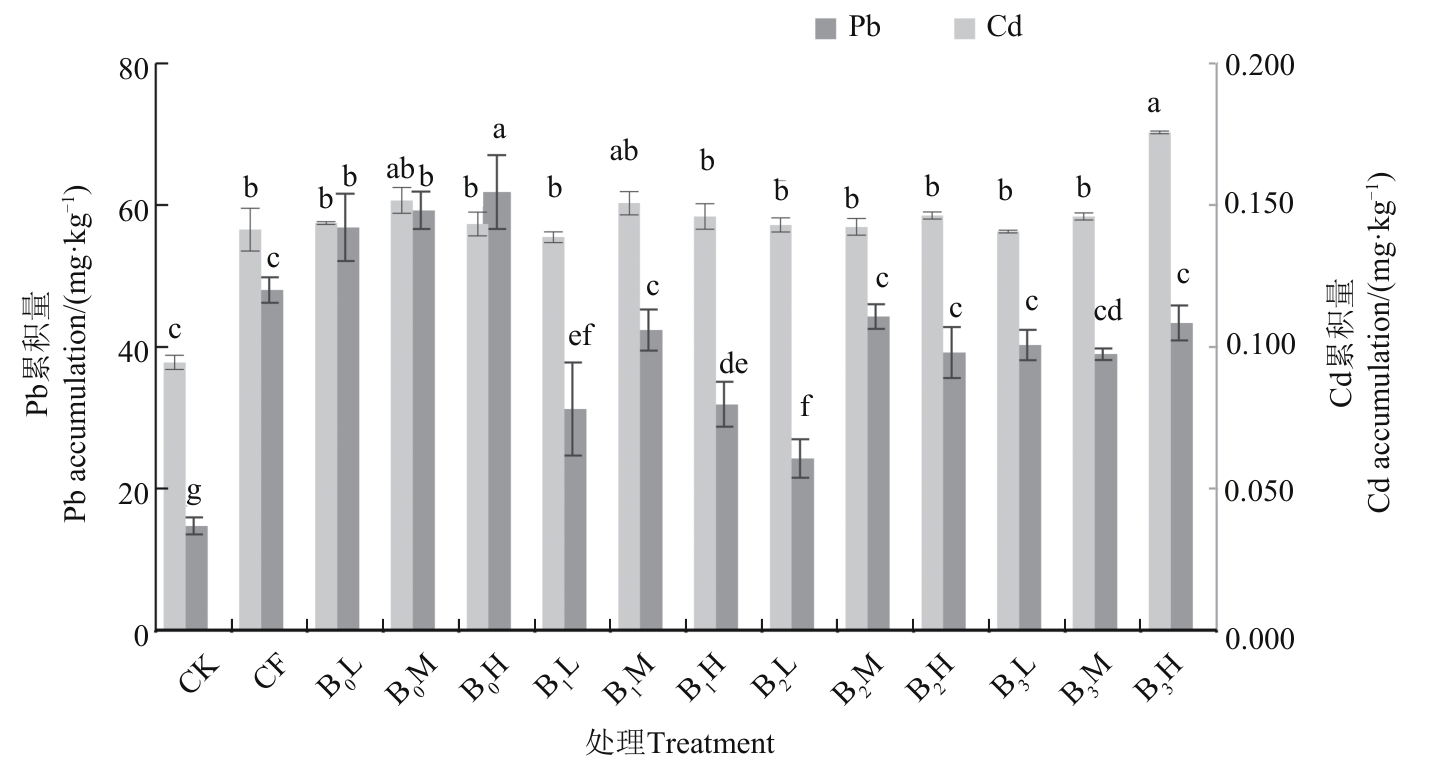
图3 不同施肥处理下土壤Pb、Cd的含量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Pb and Cd content of soil under different fertilizer treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 黄绍文,唐继伟,李春花.我国商品有机肥和有机废弃物中重金属、养分和盐分状况[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2017,23(1):162-173. |
| HUANG S W, TANG J W, LI C H.Status of heavy metals,nutrients,and total salts in commercial organic fertilizers and organic wastes in China [J].J.Plant Nutr.Fert.,2017,23(1):162-173. | |
| 2 | 张连科,刘心宇,王维大,等.两种油料作物秸秆生物炭对土壤中铅的钝化修复[J].生态环境学报,2018,27(1):166-173. |
| ZHANG L K, LIU X Y, WANG W D,et al..Immobilization of lead in contaminated soil by biochar produced from two kinds of oil crops straw [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2018,27(1):166-173. | |
| 3 | 张丽芳,夏文建,张文学,等. 长期施用猪粪和化肥对稻田土壤Cu、Zn和Cd含量及有效性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(9):1944-1954. |
| ZHANG L F, XIA W J, ZHANG W X, et al.. Effects of long-term application of pig manure and chemical fertilizers on soil Cu, Zn, and Cd contents and their availability in paddy soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022, 41(9):1944-1954. | |
| 4 | 秦秦,段海芹,宋科,等.常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J].生态环境学报,2022,31(12):2403-2413. |
| QIN Q, DUAN H Q, SONG K,et al..Effect of conventional fertilization on the adsorption-desorption characteristics and chemical forms of cadmium in soil water-stable aggregates [J].Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2022,31(12):2403-2413. | |
| 5 | 何其辉,谭长银,曹雪莹,等.肥料对土壤重金属有效态及水稻幼苗重金属积累的影响[J].环境科学研究,2018,31(5):942-951. |
| HE Q H, TAN C Y, CAO X Y, et al.. Effects of fertilizer on the availability of heavy metals in soil and its accumulation in rice seedling [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2018,31(5):942-951. | |
| 6 | 葛赞,杨威,王宇航,等.连续施用有机肥的田间土壤和果蔬重金属风险评估[J].华中农业大学学报,2023,42(1):188-196. |
| GE Z, YANG W, WANG Y H,et al..Evaluating risk of heavy metals in fruits,vegetables and soils under continuous application of organic fertilizers in field [J]. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ., 2023,42(1):188-196. | |
| 7 | ALI A, SHAHEEN S M, GUO D, et al.. Apricot shell- and apple tree-derived biochar affect the fractionation and bioavailability of Zn and Cd as well as the microbial activity in smelter contaminated soil [J/OL].Environ.Pollut.,2020,264:114773 [2023-08-26]. . |
| 8 | 邢缤侥,陈永山,叶丽丽,等.有机物料与NPK配施对多重金属污染土壤及甜高粱生长生理的影响[J].西南农业学报,2018,31(4):817-823. |
| XING B Y, CHEN Y S, YE L L,et al..Effects of combined application of organic material and NPK on multiple heavy metals polluted soil and growth physiological characteristics of sweet Sorghum [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2018,31(4):817-823. | |
| 9 | 刘宇,吴云成,赵家印,等.施用猪粪有机肥对土壤特性及有机蔬菜品质的影响[J].江西农业学报,2023,35(3):76-83. |
| LIU Y, WU Y C, ZHAO J Y, et al.. Effects of pig manure organic fertilizer application on soil characteristics and quality of organic vegetables [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2023,35(3):76-83. | |
| 10 | 金洪石,金江华,贺兆伟,等.生物炭和有机肥配施对重金属Pb胁迫下烟叶生长的影响[J].河南农业科学,2020,49(9):43-50. |
| JIN H S, JIN J H, HE Z W, et al.. Effect of biochar and organic fertilizer on growth of tobacco under Pb stress [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2020,49(9):43-50. | |
| 11 | 尤方芳,赵铭钦,陈发元,等.生物炭与不同肥料配施对镉胁迫下烟株生长的影响[J].浙江农业学报,2016,28(3):489-495. |
| YOU F F, ZHAO M Q, CHEN F Y, et al.. Effect of combined application of biochar and fertilizer on growth of tobacco under Cd stress [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2016,28(3):489-495. | |
| 12 | 嵇梦圆,胡逸文,梁程,等.农林废弃物基生物炭对重金属铅和镉的吸附特性[J].生态与农村环境学报,2020,36(1):106-114. |
| JI M Y, HU Y W, LIANG C,et al..Adsorption of lead and cadmium on biochars produced from agroforestry wastes [J]. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ., 2020,36(1):106-114. | |
| 13 | WEI B G, YU J P, CAO Z Q,et al.. The availability and accumulation of heavy metals in greenhouse soils associated with intensive fertilizer application [J/OL]. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health,2020,17(15):5359 [2023-08-26].. |
| 14 | 高文慧,李波,叶菁,等.生物炭添加对猪粪堆肥氮素形态和损失的影响[J].福建农业学报,2019,34(12):1440-1446. |
| GAO W H, LI B, YE J, et al.. Effects of biochar addition on form and loss of nitrogen in composting pig manure [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2019,34(12):1440-1446. | |
| 15 | 王义祥,李波,叶菁,等.生物炭添加对猪粪菌渣堆肥过程中Cu、Zn的钝化作用[J].农业环境科学学报,2019,38(5):1176-1184. |
| WANG Y X, LI B, YE J, et al.. Passivating effect of biochar on heavy metals (Cu and Zn) during composting of pig manure and mushroom residues [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2019, 38(5):1176-1184. | |
| 16 | 王巧红,董金霞,张君,等.Cd污染对3种类型土壤酶活性及Cd形态分布的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报,2017,35(3) :339-344. |
| WANG Q H, DONG J X, ZHANG J,et al..Effects of Cd pollution on soil enzyme activities and cd forms in three soil types [J]. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ., 2017,35(3) :339-344. | |
| 17 | NEMATI K, KABU BAKAR N, RBIN ABAS M,et al..Comparison of unmodified and modified BCR sequential extraction schemes for the fractionation of heavy metals in shrimp aquaculture sludge from Selangor,Malaysia [J]. Environ. Monit. Assess., 2011,176(1):313-320. |
| 18 | 生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行): [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2018. |
| 19 | 梁曼恬,黄科,袁怡鸣,等. 有机肥部分替代化肥对甘蓝生长、品质及土壤状况的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021,42(5):1371-1377. |
| LIANG M T, HUANG K, YUAN Y M, et al.. Effects of partial substitution of organic fertilizer for chemical fertilizer on growth, quality and soil condition of cabbage [J]. Chin. J. Tropic. Crops, 2021,42 (5):1371-1377. | |
| 20 | 孙雪,刘琪琪,郭虎,等.猪粪生物质炭对土壤肥效及小白菜生长的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(9):1756-1763. |
| SUN X, LIU Q Q, GUO H,et al..Effects of swine manure biochar on soil fertility and cabbage (Brassica chinensis) growth [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2016,35(9):1756-1763. | |
| 21 | 刘灿,秦鱼生,赵秀兰.长期不同施肥对钙质紫色水稻土重金属累积及有效性的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2020,39(7):1494-1502. |
| LIU C, QIN Y S, ZHAO X L.Long-term effect of fertilization on accumulation and availability of heavy metal in a calcareous paddy soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2020,39(7):1494-1502. | |
| 22 | 马国泰,杜红艳,刘芝妨,等.猪粪施用量对土壤和辣椒中Cd和Pb积累的影响[J].甘肃农业科技,2021,52(1):28-34. |
| MA G T, DU H Y, LIU Z F,et al..Effect of pig manure application on Cd and Pb accumulation in soil and pepper [J]. Gansu Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021,52(1):28-34. | |
| 23 | 王绍坤,牛小云,邸东柳,等. 施加氮肥、硫肥对杞柳提取土壤中铅、镉的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(10):104-109. |
| WANG S K, NIU X Y, DI D L, et al.. Effects of N and S fertilizers on extracting Pb and Cd by Salix integra Thunb. in contaminated soil [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2021, 49(10):104-109. | |
| 24 | 徐岩,李静,方文.有机肥连续施用对菜田重金属行为的影响——基于地球化学模型研究[J].生态学报,2022,42(4):1512-1526. |
| XU Y, LI J, FANG W.Effect and simulation of continuous application of organic fertilizer on heavy metal behavior in vegetable field soil based on geochemical model [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2022,42(4):1512-1526. | |
| 25 | GONDEK K, MIERZWA-HERSZTEK M. Effect of low-temperature biochar derived from pig manure and poultry litter on mobile and organic matter-bound forms of Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in sandy soil [J]. Soil Use Manage., 2016, 32(3):357-367. |
| 26 | HAMID Y, TANG L, HUSSAIN B,et al..Immobilization and sorption of Cd and Pb in contaminated stagnic anthrosols as amended with biochar and manure combined with inorganic additives [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manage., 2020,257:109999 [2023-08-26].. |
| 27 | 汪洋,艾艳梅,陈泓璐,等.生物炭对铜矿区排土场污染土壤理化性质和重金属形态的影响[J].水土保持研究,2023,30(2):444-450. |
| WANG Y, AI Y M, CHEN H L, et al.. Effects of biochar on the physical and chemical properties and heavy metal forms of polluted soil in the dump of copper mining area [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2023,30(2):444-450. | |
| 28 | 姜晶,邓精灵,盛光遥.生物炭老化及其对重金属吸附影响研究进展[J].生态环境学报,2022,31(10):2089-2100. |
| JIANG J, DENG J L, SHENG G Y. A review of biochar aging and its impact on the adsorption of heavy metals [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2022, 31(10):2089-2100. | |
| 29 | 李顺奇,刘洁,陈杰,等.几种有机肥对紫色土Pb有效性和形态的调控效应[J].农业资源与环境学报,2019,36(1):79-88. |
| LI S Q, LIU J, CHEN J, et al.. Regulation effects of several organic manures on Pb chemical speciation and bioavailability in gray-purple soil [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2019,36(1):79-88. | |
| 30 | 苏焱,全妍红,宦紫嫣,等.磷改性生物炭对云南某铅锌矿周边农田铅锌污染土壤修复效果的影响[J].生态环境学报,2022,31(3):593-602. |
| SU Y, QUAN Y H, HUAN Z Y,et al..Effect of phosphate-modified biochar on remediation of Pb- and Zn-polluted farmlands around a Pb/Zn mine in Yunnan province, China [J].Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2022,31(3):593-602. | |
| 31 | 刘爽,汪东风,徐莹.磷酸活化茶渣生物炭对铅的吸附性能影响和吸附机理研究[J].中国海洋大学学报,2022,52(1):56-64. |
| LIU S, WANG D F, XU Y.Studies on lead adsorption performance of phosphoric acid activated tea residue biochar and associating mechanism [J]. Period. Ocean. Univ. China, 2022,52(1):56-64. | |
| 32 | XU C, ZHAO J, YANG W,et al.. Evaluation of biochar pyrolyzed from kitchen waste,corn straw,and peanut hulls on immobilization of Pb and Cd in contaminated soil [J/OL].Environ. Pollut., 2020,261:114133 [2023-08-26].. |
| 33 | 邵佳,赵远来,冯琰玉,等.生物质炭对长期铅镉复合污染土壤微生物群落丰度及活性的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2022,41(1):66-74. |
| SHAO J, ZHAO Y L, FENG Y Y, et al.. Effects of biochar on microbial community abundance and activity in long-term Pb and Cd contaminated soils [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022,41(1):66-74. | |
| 34 | IGALAVITHANA A D, LEE S E, LEE Y H, et al.. Heavy metal immobilization and microbial community abundance by vegetable waste and pine cone biochar of agricultural soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2017,174:593-603. |
| [1] | 周峻宇, 谷雨, 唐珍琦, 吴海勇, 刘琼峰, 李明德. 复合螯合剂对籽粒苋修复镉污染农田的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 186-194. |
| [2] | 吴敏,韦家少*,孙海东,何鹏,吴炳孙,高乐. 生物质炭对橡胶园土壤酸度及交换性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(3): 98-107. |
| [3] | 牛桂言1,邵惠芳1*,朱金峰2,黄五星1,许自成1,郭利3. 我国植烟土壤修复的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(3): 115-122. |
| [4] | 尹福斌1,季超2, 董红敏1*,陶秀萍1,陈永杏1. 畜禽粪便中残留抗生素对厌氧消化影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(5): 171-177. |
| [5] | 闫志宇1,翟蓓蓓1,张娟2,王树香1,李红亚1,王全1,李术娜1*. 乙草胺降解菌Bacillus subtilis L3的土壤修复效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(2): 65-71. |
| [6] | 刘越1,孟海波1*,沈玉君1,程红胜1,候月卿1,刘宏斌2. 海南省畜禽粪便资源分布及总量控制研究[J]. , 2015, 17(4): 114-121. |
| [7] | 候月卿1,2,沈玉君2,刘树庆1*. 我国畜禽粪便重金属污染现状及其钝化措施研究进展[J]. , 2014, 16(3): 112-118. |
| [8] | 黄叶飞,董红敏,朱志平,陶秀萍,黄宏坤. 畜禽粪便热化学转换技术的研究进展[J]. , 2008, 10(4): 22-27. |
| [9] | 涂德浴, 董红敏,丁为民,尚斌. 畜禽粪便热化学转换特性和可行性分析研究[J]. , 2007, 9(1): 59-63. |
| [10] | 孙振钧 孙永明. 我国农业废弃物资源化与农村生物质能源利用的现状与发展[J]. , 2006, 8(1): 6-13. |
| [11] | 李吉进[1] 郝晋珉[2] 邹国元[1] 张有山[1] 王美菊[1]. 畜禽粪便高温堆肥及工厂化生产研究进展[J]. , 2004, 6(3): 50-53. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号