




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 70-77.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0561
收稿日期:2022-07-05
接受日期:2022-09-06
出版日期:2024-01-15
发布日期:2024-01-08
通讯作者:
张树林
作者简介:贾滢暄 E-mail:1151718529@qq.com;
基金资助:
Yingxuan JIA( ), Shulin ZHANG(
), Shulin ZHANG( ), Dajuan ZHANG, Wei DAI, Xiangdong BI
), Dajuan ZHANG, Wei DAI, Xiangdong BI
Received:2022-07-05
Accepted:2022-09-06
Online:2024-01-15
Published:2024-01-08
Contact:
Shulin ZHANG
摘要:
为探究磷饥饿及磷恢复对铜绿微囊藻光合色素、藻胆蛋白和抗氧化酶等生理指标的影响,将其进行磷饥饿处理7 d后再进行磷恢复,检测磷恢复前后铜绿微囊藻的藻细胞密度、叶绿素a、类胡萝卜素、藻蓝蛋白(phycocyanin,PC)、别藻蓝蛋白(allophycocyanin,APC)、藻红蛋白(phycoerythrin,PE)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)和过氧化氢(H2O2)含量及超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)活性的变化。结果表明,铜绿微囊藻磷饥饿处理7 d后,藻细胞密度为2.54×107 cell·mL-1,显著低于对照组(3.11×107 cell·mL-1)。磷恢复144 h后,处理组藻细胞密度为4.05×107 cell·mL-1,仍显著低于对照组(4.32×107 cell·mL-1);叶绿素a、类胡萝卜素和PC、APC、PE含量均呈现升高趋势,在144 h时分别达到5.96、1.44 μg·mL-1和0.031、0.02、0.065 mg·L-1;MDA、H2O2含量和SOD活性呈先上升后下降趋势,均在48 h达到最大值,较对照组分别增加36.2%、47.7%、51.1%。由此表明,磷恢复后铜绿微囊藻的藻细胞密度、叶绿素a、类胡萝卜素和藻胆蛋白含量虽呈升高趋势,但难以恢复到对照水平;MDA、H2O2含量及SOD活性的变化也说明,从磷饥饿到磷恢复后铜绿微囊藻藻细胞受到氧化损伤,并对细胞膜系统产生破坏。
中图分类号:
贾滢暄, 张树林, 张达娟, 戴伟, 毕相东. 磷恢复对磷饥饿铜绿微囊藻光合色素和部分抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 70-77.
Yingxuan JIA, Shulin ZHANG, Dajuan ZHANG, Wei DAI, Xiangdong BI. Effects of Phosphorus Recovery on Photosynthetic Pigments and Some Antioxidant Enzymes Activities of Phosphorus Starved Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 70-77.
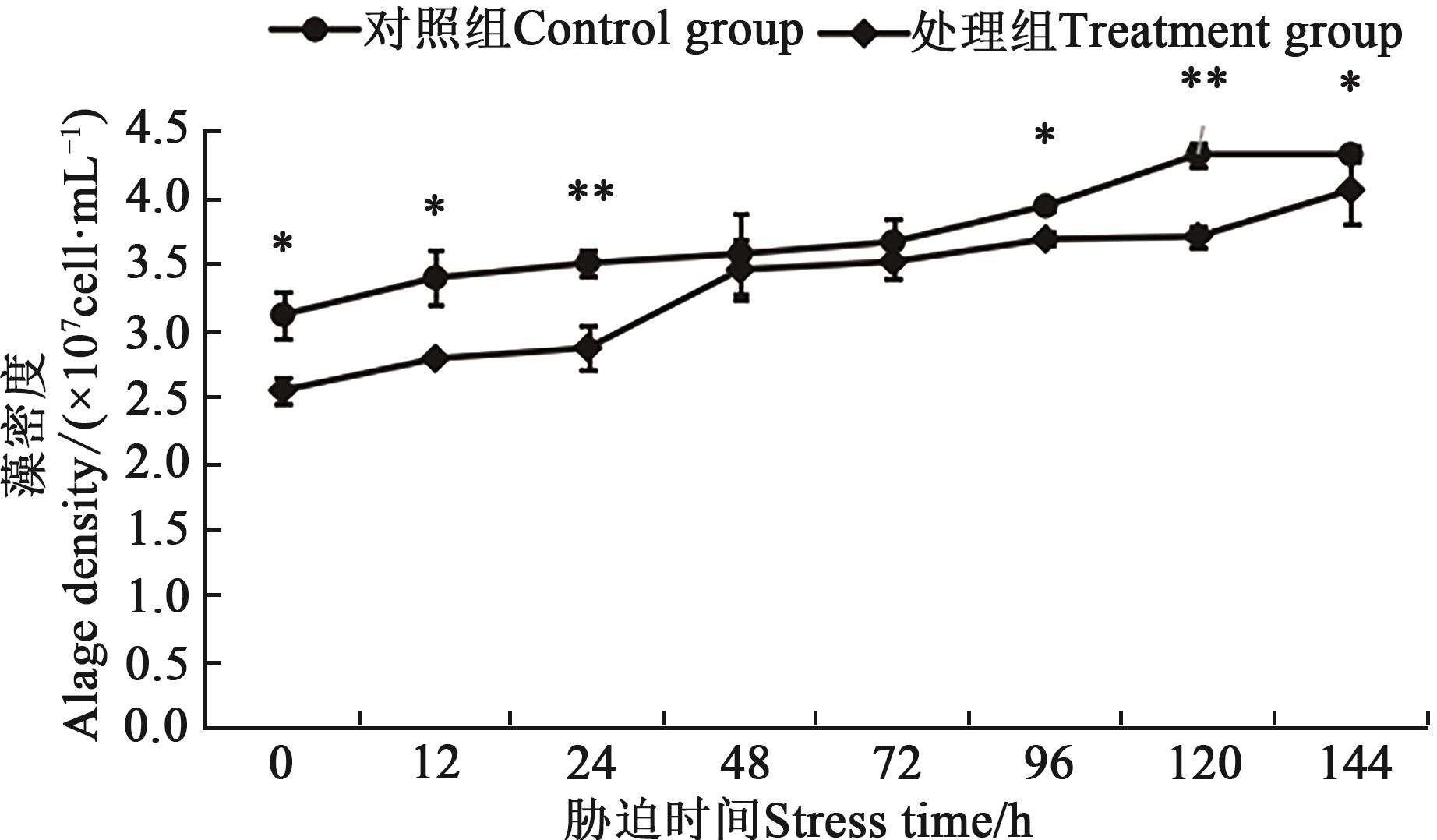
图1 不同处理下铜绿微囊藻的生长曲线注:*和**分别表示处理组与对照组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Growth curve of M. aeruginosa under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between control and treatment at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
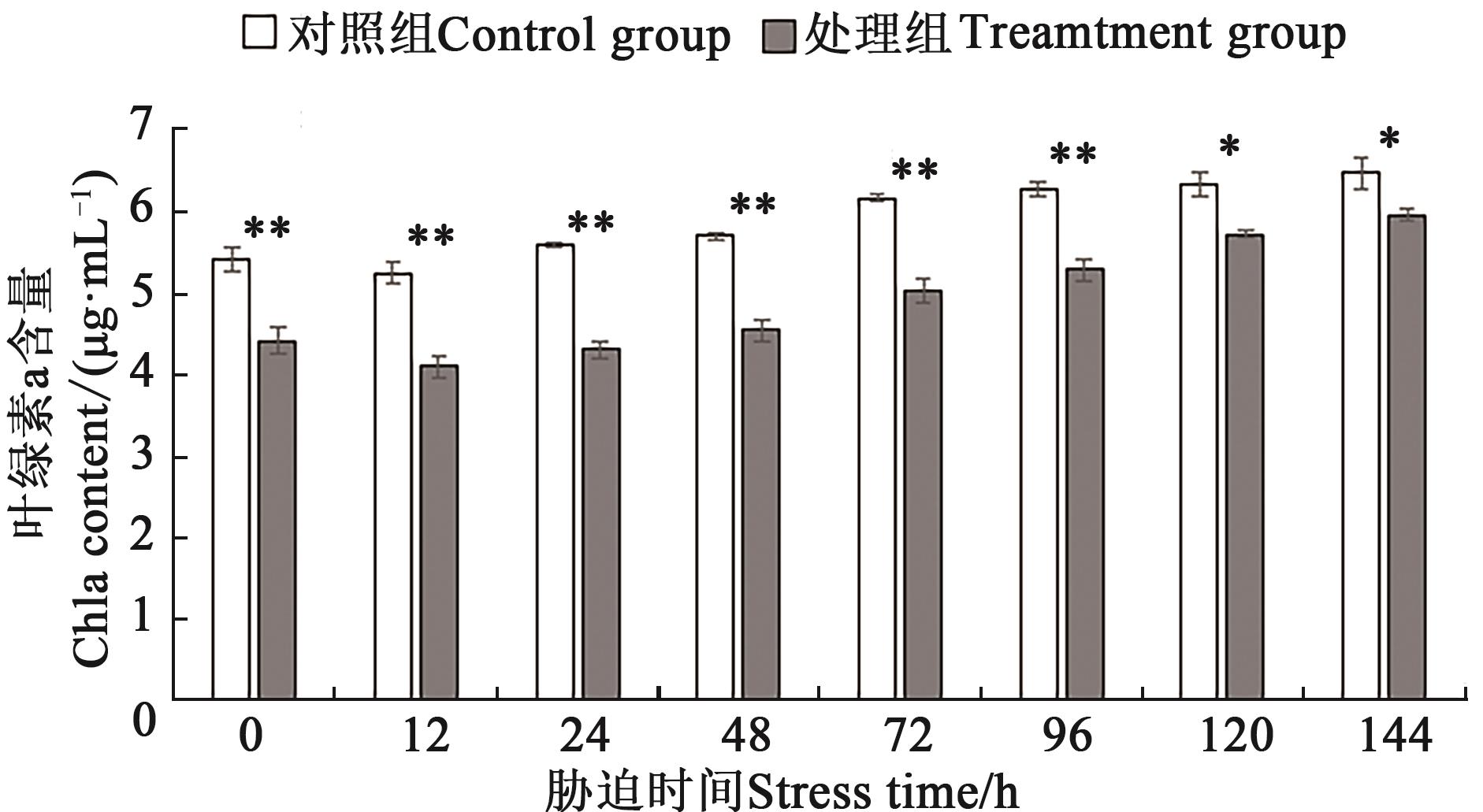
图2 不同处理下铜绿微囊藻叶绿素a含量注:*和**分别表示处理组与对照组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Chlorophyll a content of M. aeruginosa under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between control and treatment at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
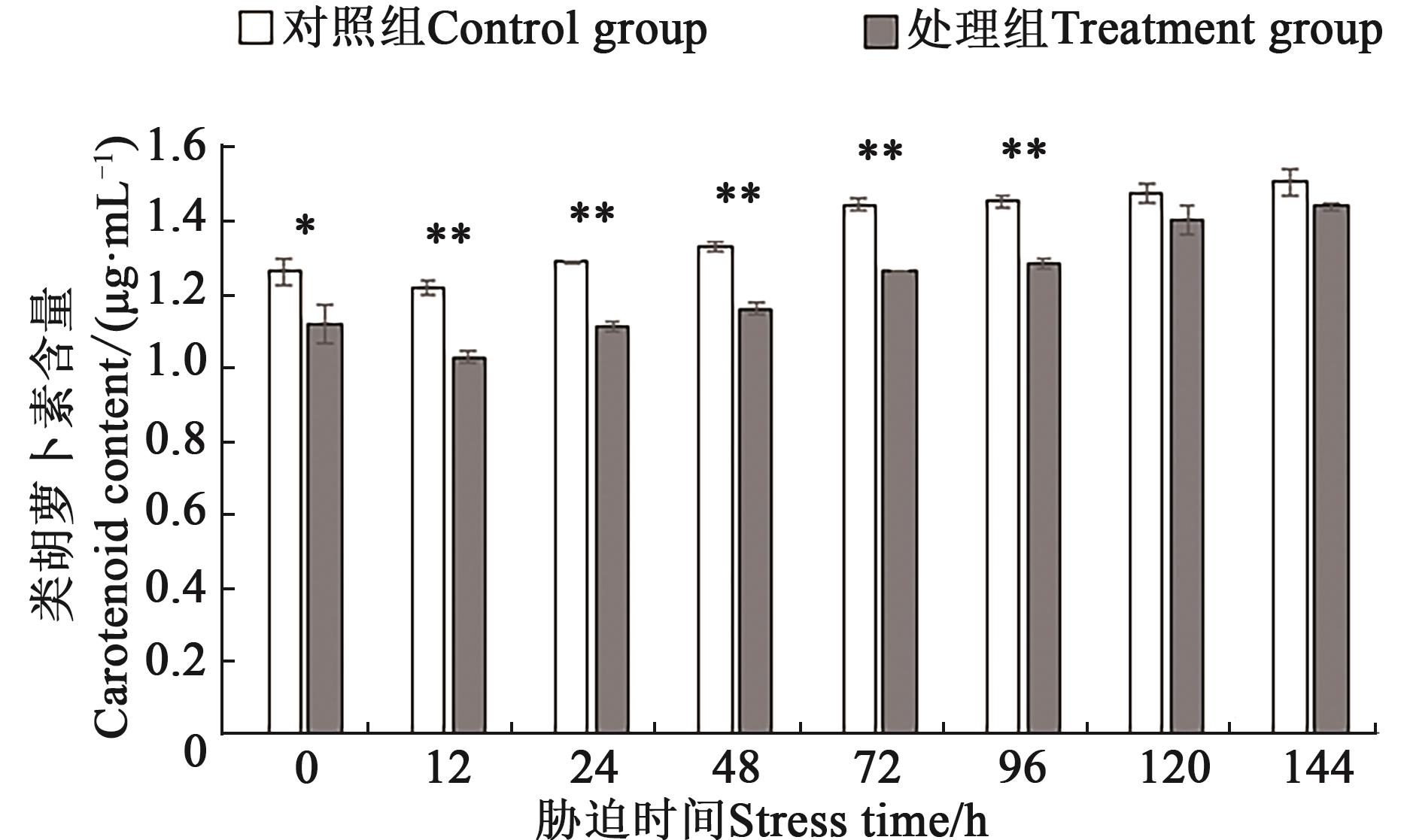
图3 不同处理下铜绿微囊藻类胡萝卜素含量注:*和**分别表示处理组与对照组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Carotenoid content of M. aeruginosa under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between control and treatment at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.

图4 不同处理下铜绿微囊藻的藻胆蛋白含量注:*和**分别表示处理组与对照组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Phycobiliprotein contents of M.aeruginosa under different treatmentsNote: * and ** indicate significant differences between control and treatment at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.

图5 不同处理下铜绿微囊藻MDA及H2O2含量注:*和**分别表示处理组与对照组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 MDA and H2O2 contents of M.aeruginosa under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between control and treatment at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
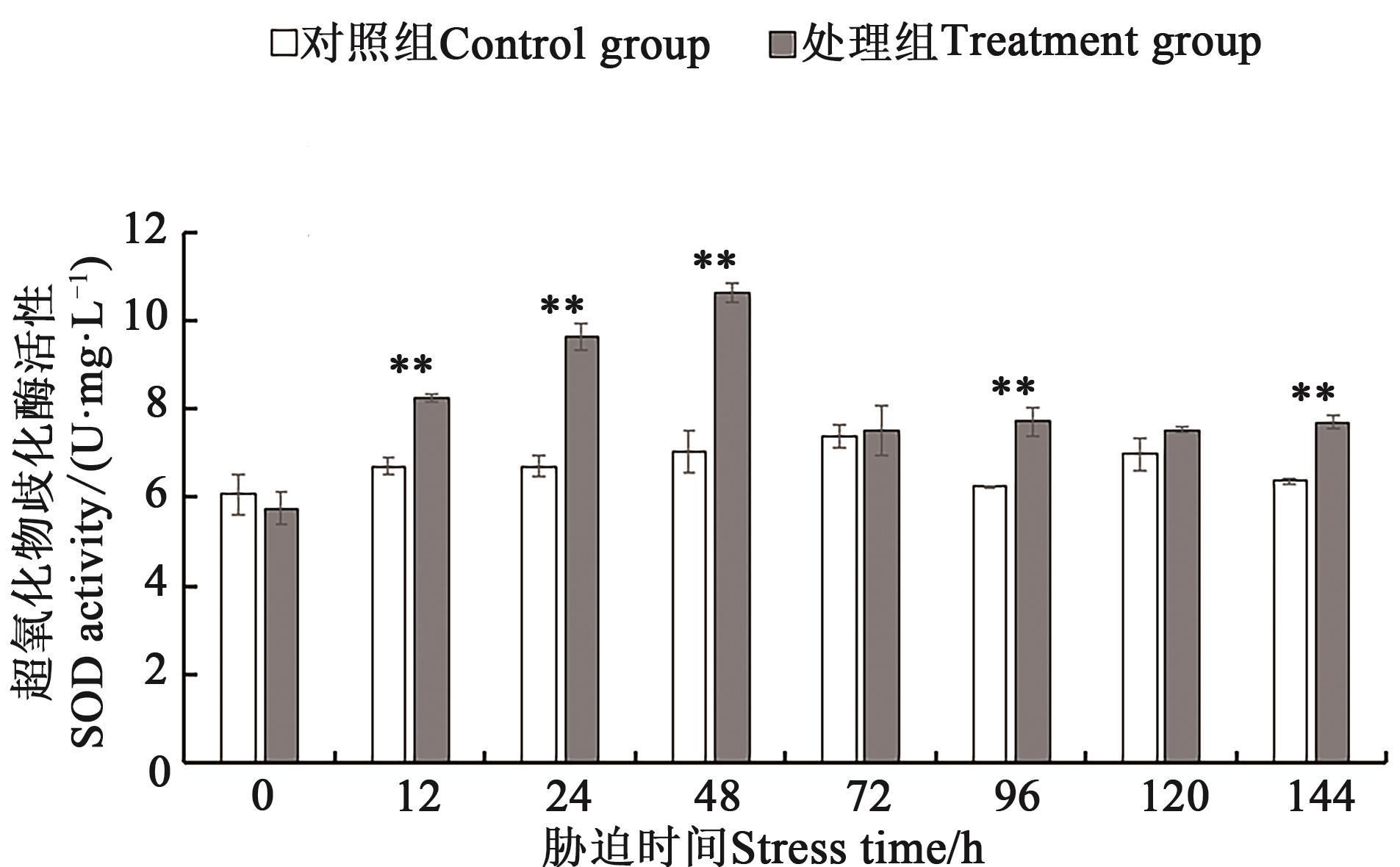
图6 不同处理下铜绿微囊藻SOD活性注:*和**分别表示处理组与对照组间在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 SOD activity of M. aeruginosa under different treatmentsNote:* and ** indicate significant differences between control and treatment at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 张维清,韩丽华,林立清.太湖微囊藻水华暴发现状及其研究进展[J].江西科学,2018,36(5):830-832, 876. |
| ZHANG W Q, HAN L H, LIN L Q. Current situation of Microcystis blooms outbreak in Lake Taihu and its research progress [J]. Jiangxi Sci., 2018, 36(5):830-832, 876. | |
| 2 | 田慧捷,韩帮忠.水库中微囊藻毒素监测技术研究[J].中国资源综合利用,2021,39(2):122-124. |
| TIAN H J, HAN B Z. Study on the monitoring technology of Microcystin in the reservoir [J]. China Resour. Comprehensive Utilization, 2021, 39(2):122-124. | |
| 3 | 邢彤.巢湖蓝藻水华动态变化特征及其控制技术评估研究[D].合肥:合肥学院,2020. |
| XING T. Dynamic characteristics of cyanobacteria bloom in Chaohu Lake and evaluation of its control techniques [D]. Hefei: Hefei College, 2020. | |
| 4 | 鲁男.环境因子对铜绿微囊藻生长及产毒的影响研究[D].沈阳:辽宁大学,2015. |
| LU N. Effect of environmental factors on Microcysis and its toxin production [D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2015. | |
| 5 | 许海,吴雅丽,杨桂军,等.铜绿微囊藻、斜生栅藻对氮磷饥饿的耐受能力研究[J].生态科学,2014,33(5):879-884. |
| XU H, WU Y L, YANG G J, et al.. Tolerance of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scendesmus obliquus to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2014, 33(5):879-884. | |
| 6 | 许慧萍,杨桂军,周健,等.氮、磷浓度对太湖水华微囊藻(Microcystis flos-aquae)群体生长的影响[J].湖泊科学,2014,26(2):213-220. |
| XU H P, YANG G J, ZHOU J, et al.. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration on colony growth of Microcystis flos-aquae in Lake Taihu [J]. Lake Sci., 2014, 26(2):213-220. | |
| 7 | 袁若愚.铜绿微囊藻低磷条件下爆发生长及其化感防治的机理研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2020. |
| YUAN R Y. The mechanism of low dissolved phosphorus and allelopathic inhibition on growth of microcystis aeruginosa [D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020. | |
| 8 | 郑晓宇,金妍,任翔宇,等.不同氮磷浓度对铜绿微囊藻生长特性的影响[J].华东师范大学学报(自然科学版),2012(1):11-18. |
| ZHENG X Y, JIN Y, REN X Y, et al.. Influence of nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. J. East China Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2012(1):11-18. | |
| 9 | 严杨蔚,代瑞华,刘燕,等.氮和磷对有害藻类生长及产毒影响的研究进展[J].环境与健康杂志,2013,30(4):358-362. |
| YAN Y W, DAI R H, LIU Y, et al.. Progress of research on effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth and toxin production of algae: a review of recent studies [J]. Environ. Health, 2013, 30(4):358-362. | |
| 10 | 叶倩.铜绿微囊藻缺氮缺磷下的生理生化响应[D].厦门:厦门大学,2019. |
| YE Q. Physiological and biochemical responses of microcystis aeruginosa to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency [D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2019. | |
| 11 | XIE E, SU Y P, DENG S Q, et al.. Significant influence of phosphorus resources on the growth and alkaline phosphatase activities of Microcystis aeruginosa [J/OL]. Environ. Pollution, 2021, 268: 115807 [2022-06-05]. . |
| 12 | HEE Y Y, SURATMAN S, TAHIR N M, et al.. Seasonal variability and fractionation of P-based nutrients in Sungai Setiu Basin, Terengganu, Malaysia [J]. Sains Malays., 2018, 47:883-891. |
| 13 | 许海,陈丹,陈洁,等.氮磷形态与浓度对铜绿微囊藻和斜生栅藻生长的影响[J].中国环境科学,2019,39(6):2560-2567. |
| XU H, CHEN D, CHEN J, et al.. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus forms and concentrations on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scenedesmus obliquus [J]. China Environ. Sci., 2019, 39(6):2560-2567. | |
| 14 | 岳冬梅,李洁,肖琳.营养盐恢复对氮磷饥饿铜绿微囊藻生长的影响[J].环境科学,2016,37(11):4220-4227. |
| YUE D M, LI J, XIAO L. Nutrients recovery on the growth of nitrogen and phosphorus starved Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. Environ. Sci., 2016, 37(11):4220-4227. | |
| 15 | 戴立洲,成小英,俞珊,等.豆瓣菜有机提取物对铜绿微囊藻的抑制及成分初步分离[J].环境科学学报,2015,35(12):4159-4168. |
| DAI L Z, CHENG X Y, YU S, et al.. Inhibitory effects of organic solvent extract from nasturtium officinale on Microcystis aeruginosa associated with isolation of the allelochemical ingredients [J]. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(12):4159-4168. | |
| 16 | 陈国永,杨振波,马昱,等.氮和磷对铜绿微囊藻细胞生长的影响[J].环境与健康杂志,2007(9):675-679. |
| CHEN G Y, YANG Z B, MA Y, et al.. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa strains [J]. Environ. Health., 2007(9):675-679. | |
| 17 | 谢静,程燕,查燕,等.氮磷营养盐对铜绿微囊藻和斜生栅藻生长及竞争的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2021,43(03):694-702. |
| XIE J, CHENG Y, CHA Y, et al.. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth and competition of Mcirocystis aeruginosa and Scenedesmus obliquus [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2021, 43(3):694-702. | |
| 18 | 许海,吴雅丽,杨桂军,等.铜绿微囊藻、斜生栅藻对氮磷饥饿的耐受能力研究[J].生态科学,2014,33(5):879-884. |
| XU H, WU Y L, YANG G J, et al.. Tolerance of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scendesmus obliquus to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2014, 33(5):879-884. | |
| 19 | 张文珺.无机磷限制对圆海链藻的生长及转录表达的影响[D].舟山:浙江海洋大学,2021. |
| ZHANG W J. Effects of inorganic phosphorus limitation on the growth and transcription expression of Thalassiosira rotula [D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2021. | |
| 20 | 秦梦瑶.铜绿微囊藻有机磷酶解利用及影响因素研究[D].南京:南京师范大学,2021. |
| QIN M Y. Study on enzymatic hydrolysis and utilization of organic phosphorus in Microcystis aeruginosa and its influencing factors [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2021. | |
| 21 | 胡春艳.普通小球藻和波吉卵囊藻的生长特性及其对氮磷利用规律研究[D].荆州:长江大学,2021. |
| HU C Y. Study on the growth characteristics and nitrogen and phosphorus utilization of Chlorella vulgaris and Ootheca bojiensis [D]. Jinzhou: Changjiang University, 2021. | |
| 22 | 侯新星,田如男.有机酸对铜绿微囊藻生长及光合色素的影响[J].生物学杂志,2021,38(4):65-70. |
| HOU X X, TIAN R N. Effects of organic acids on growth and photosynthetic pigment of Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. J. Biol., 2021, 38(4):65-70. | |
| 23 | 田雅琦.环境因素对微囊藻色素及脂肪酸组成的影响规律研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019. |
| TIAN Y Q. Effects of environmental factors on pigment and fatty acid composition of Microcystis aeruginosa [D].Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2019. | |
| 24 | 叶倩.铜绿微囊藻缺氮缺磷下的生理生化响应[D].厦门:厦门大学,2019. |
| YE Q. Physiological and biochemical responses of Microcystis aeruginosa to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency [D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2019. | |
| 25 | 李小梅,夏建荣.氮磷营养限制影响三角褐指藻光合无机碳利用和碳酸酐酶活性[J].水生生物学报,2013,37(3):405-412. |
| LI X M, XIA J R. Effects of nitrogen or phosphorus limitation on photosynthetic inorganic carbon utilization and carbonic anhydrase activity in Phaeodactylum tricornutum [J]. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin., 2013, 37(3):405-412. | |
| 26 | 徐宏洲,杨宸,彭俊,等.氟苯尼考对铜绿微囊藻生长和生理特征的影响[J].上海海洋大学学报,2021,30(1):120-128. |
| XU H Z, YANG C, PENG J, et al.. Effects of florfenicol on the growth and physiology of cyanobacteria (Microcystis aeruginosa) [J]. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ., 2021, 30(1):120-128. | |
| 27 | 郑彩云,卢伟婷,王艳,等.不同氮浓度对紫球藻生长及藻胆蛋白和叶绿素a含量变化的影响[J].中国酿造,2013,32(6):133-135. |
| ZHENG C Y, LU W T, WANG Y, et al.. Effect of different NaNO3 concentration on Porphyridium growth and the content changes of phycobiliproteins and chlorophyll a [J]. China Brew., 2013, 32(6):133-135. | |
| 28 | 刘洁,常学秀,黄丽娟,等.Ni元素对铜绿微囊藻的生长、光谱特性及藻胆蛋白含量的影响[J].云南大学学报(自然科学版),2005(4):365-368. |
| LIU J, CHANG X X, HUANG L J, et al.. Effects of Ni on the growth, absorption spectrum and phycobiliprotein content of Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. J. Yunnan Univ. (Nat. Sci), 2005(4):365-368. | |
| 29 | 付梅,宋秀贤,俞志明,等.伪矮海链藻抗氧化酶活性对磷化氢的响应特征[J].海洋环境科学,2013,32(6):809-813. |
| FU M, SONG X X, YU Z M, et al.. Responses of activity of antioxidant enzyme in Thalassiosira pseudonana to phosphine [J]. Marine Environ. Sci., 2013, 32(6):809-813. | |
| 30 | 郑金秀,彭祺,张甲耀,等.藻类产生及清除过氧化氢的研究[J].微生物学杂志,2006(6):80-84. |
| ZHENG J X, PENG Q, ZHANG J Y, et al.. Advance in H2O2 producing and scavenging induced by algae [J]. J. Microbiol., 2006(6):80-84. | |
| 31 | 马金华,孟希,张淑,等.链状亚历山大藻赤潮衰亡的生理调控[J].生态学报,2013,33(13):3978-3986. |
| MA J H, MENG X, ZHANG S, et al.. Physiological regulation related to the decline of alexandrium catenella [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2013, 33(13):3978-3986. | |
| 32 | LI X, PAN J, LU Z, et al.. Arsenate toxicity to the marine microalga Chlorella vulgaris increases under phosphorus-limited condition [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28(36):50908-50918. |
| 33 | 王小冬,王艳.赤潮异弯藻和海洋卡盾藻抗氧化酶活性对氮磷比失衡的响应[J]. 海洋环境科学,2012,31(3):4. |
| WANG X D, WANG Y. Response of antioxidant enzyme activities in Heterosigma akashiwo and Chattonella marina to lose-balance of N/P ratio [J]. Marine Environ. Sci., 2012, 31(3):4-16. | |
| 34 | 杨蕾.盐胁迫下发状念珠藻抗氧化系统及蛋白质、脂质的研究[D].济南:齐鲁工业大学,2013. |
| YANG L. Effects of salt stress on the antioxidation system, proteins and lipids of cyanobacteria Nostoc flagelliforme [D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2013. |
| [1] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [2] | 刘洋, 张启昌, 张璐, 李玉灵. 水肥耦合对蓝靛果忍冬幼苗细根生长及根抗氧化酶的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 197-207. |
| [3] | 肖雨沁, 雷晓, 张明金, 张远盖, 唐珊, 姬鸿飞, 王川, 马翠玲, 景延秋. 三种芽孢杆菌菌剂对烤烟育苗效果的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 85-92. |
| [4] | 孙晓春, 黄文静, 李铂. 水杨酸对干旱胁迫下桔梗幼苗生理生化指标及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 63-70. |
| [5] | 保志娟,金蓉,杨金清,张琦,朱永立,赵正雄*. Pb、Zn复合作用对烤烟抗氧化酶及碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 65-72. |
| [6] | 郝正刚,赵会君,魏玉清*,曾周琦,王志恒. 甜高粱对镉胁迫的生理生化响应及镉富集研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 30-42. |
| [7] | 陈双双,代领,洪子茜,邓丽,吴国*. 蚕豆幼苗光合特性及抗氧化酶对Cs+胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(7): 37-46. |
| [8] | 林二阁1,李春光2,陈孟起2,李耀光2,王省伟3,张晓娟4,肖先仪5,刘英杰6,喻保华7,景延秋1*. 外源一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下烤烟脂膜过氧化的抑制效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(1): 55-62. |
| [9] | 陈芳泉1,邵惠芳1*,崔登科2,王凯悦1,许自成1,黄五星1,范艺宽3,张慢慢4,赵蓉蓉1. 保水剂对烟草生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(1): 51-57. |
| [10] | 杜世章1,刘婷婷2,代其林2,奉斌2,杨娟2,谢琳2,鲜先毅2,王劲3. 辐照对烟草抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. , 2012, 14(1): 72-75. |
| [11] | 吴琦1,季辉1,张卫建1,2. 土壤铅和镉胁迫对空心菜生长及抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. , 2010, 12(2): 122-127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号