




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 213-223.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0081
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
徐哲丰1( ), 刘春铄1, 廖旭东2, 隋佳宏2, 陈雨秋1, 陈长宝1, 张涛1,2(
), 刘春铄1, 廖旭东2, 隋佳宏2, 陈雨秋1, 陈长宝1, 张涛1,2( ), 魏丽娜3(
), 魏丽娜3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-09
接受日期:2023-04-20
出版日期:2024-09-15
发布日期:2024-09-13
通讯作者:
张涛,魏丽娜
作者简介:徐哲丰 E-mail:2425747320@qq.com
基金资助:
Zhefeng XU1( ), Chunshuo LIU1, Xudong LIAO2, Jiahong SUI2, Yuqiu CHEN1, Changbao CHEN1, Tao ZHANG1,2(
), Chunshuo LIU1, Xudong LIAO2, Jiahong SUI2, Yuqiu CHEN1, Changbao CHEN1, Tao ZHANG1,2( ), Lina WEI3(
), Lina WEI3( )
)
Received:2023-02-09
Accepted:2023-04-20
Online:2024-09-15
Published:2024-09-13
Contact:
Tao ZHANG,Lina WEI
摘要:
生态环境是导致林地参和农田参质量差异的重要影响因素,以林地参和农田参中人参皂苷含量为指标分析其质量差异,测定根际土壤理化性质,并对测定结果进行相关性、多元逐步回归、变异系数、偏最小二乘法判别和层次分析法综合评价。结果显示,林地参和农田参中人参皂苷含量及其根际土壤理化性质差异显著;变异系数分析显示,农田参中大部分生态因子指标变异系数大于林地参;相关性、多元逐步回归和偏最小二乘法判别分析显示最高气温、最低气温、pH、碱解氮、有效磷等土壤因子与人参皂苷的相关性显著;层次分析结果显示,不同栽培模式的土壤质量差异显著。多项统计结果表明,最高气温、最低气温、pH是影响人参皂苷含量的主要因子,其次为碱解氮、有效磷和土壤含水量。以上结果表明,最高气温、最低气温、pH、碱解氮、有效磷和土壤含水量是影响林地参和农田参质量的重要原因,研究结果为解析人参质量形成和种植生产提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
徐哲丰, 刘春铄, 廖旭东, 隋佳宏, 陈雨秋, 陈长宝, 张涛, 魏丽娜. 生态因子对林地参和农田参质量差异的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 213-223.
Zhefeng XU, Chunshuo LIU, Xudong LIAO, Jiahong SUI, Yuqiu CHEN, Changbao CHEN, Tao ZHANG, Lina WEI. Effects of Ecological Factors on Quality Difference Between Forestland Ginseng and Farmland Ginseng[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 213-223.
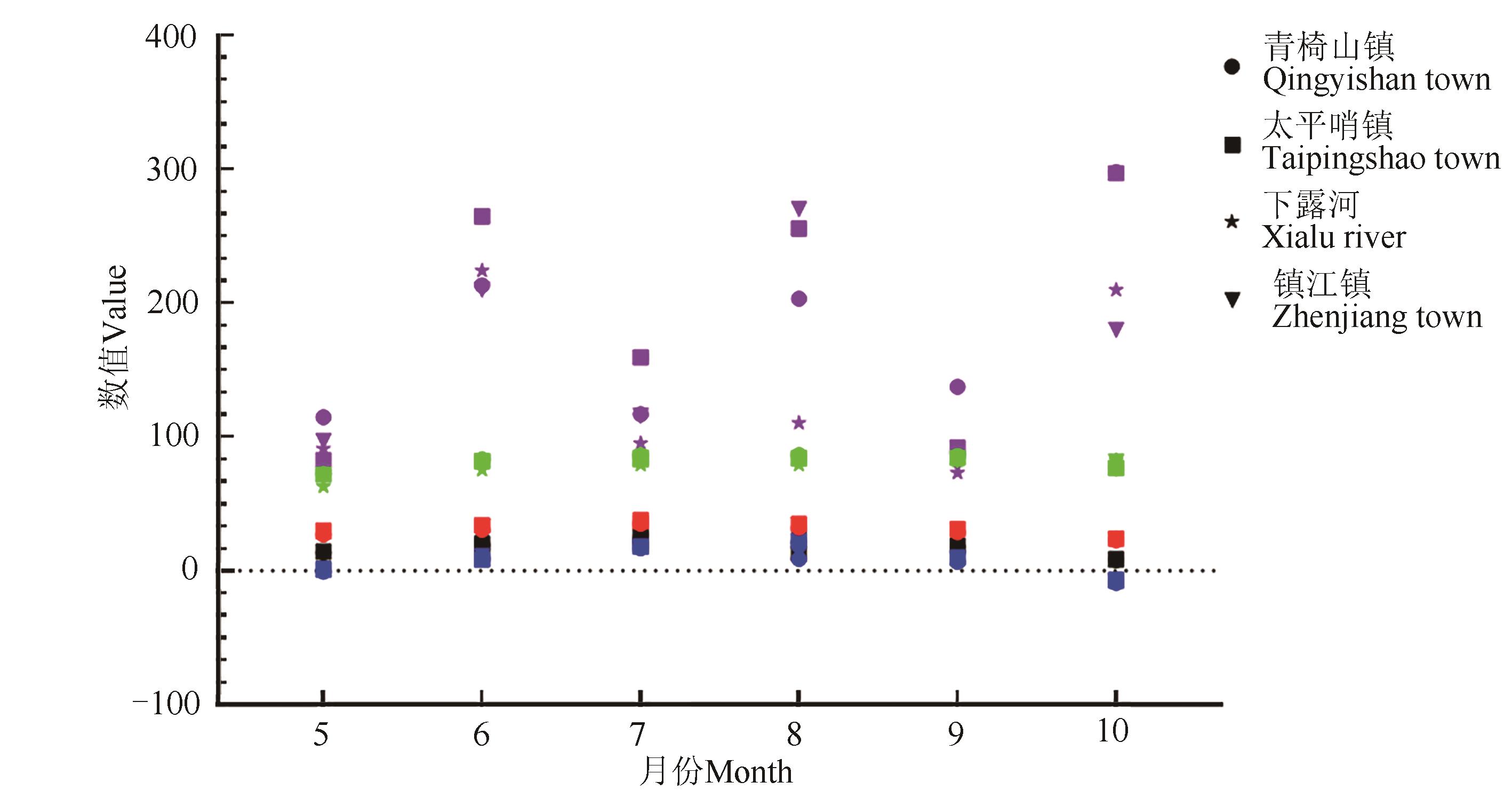
图1 青椅山镇、太平哨镇、下露河和镇江镇2021年5—10月气候因子注:红色代表最高气温(℃),蓝色代表最低气温(℃),黑色代表平均气温(℃),绿色代表平均相对湿度(%),紫色代表平均降水量(mm)。
Fig. 1 Climate factors of Qingyishan town, Taipingshao town, Xialu river and Zhenjiang town from May to October of 2021Note: Red represents the highest temperature (℃), blue represents the lowest temperature (℃), black represents the average temperature (℃), green represents the average relative humidity (%), and purple represents the average precipitation (mm).
类别 Category | 编号 No. | 采收地址 Sampling address | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
林地参 Forestland ginseng | L1 | 镇江镇杨林村 Yanglin village, Zhenjiang town | 40°40′43.58″N | 124°37′17.81″E |
| L2 | 太平哨镇乔家沟 Qiaojiagou, Taipingshao town | 40°44′10.04″N | 125°18′5.86″E | |
| L3 | 下露河二道阳岔 Erdaoyangcha, Xialu river | 40°52′21.32″N | 125°09′54.44″E | |
农田参 Farmland ginseng | N1 | 青椅山镇大沟子村 Dagouzi village, Qingyishan town | 40°53′42.14″N | 125°30′48.56″E |
| N2 | 青椅山镇青椅山村对面 Opposite to Qingyishan village, Qingyishan town | 40°40′43.11″N | 124°37′14.56″E | |
| N3 | 青椅山镇梨树园 Lishu garden, Qingyishan town | 40°39′16.68″N | 124°42′53.44″E |
表 1 林地参与农田参相关信息
Table 1 Related information of tested sample
类别 Category | 编号 No. | 采收地址 Sampling address | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
林地参 Forestland ginseng | L1 | 镇江镇杨林村 Yanglin village, Zhenjiang town | 40°40′43.58″N | 124°37′17.81″E |
| L2 | 太平哨镇乔家沟 Qiaojiagou, Taipingshao town | 40°44′10.04″N | 125°18′5.86″E | |
| L3 | 下露河二道阳岔 Erdaoyangcha, Xialu river | 40°52′21.32″N | 125°09′54.44″E | |
农田参 Farmland ginseng | N1 | 青椅山镇大沟子村 Dagouzi village, Qingyishan town | 40°53′42.14″N | 125°30′48.56″E |
| N2 | 青椅山镇青椅山村对面 Opposite to Qingyishan village, Qingyishan town | 40°40′43.11″N | 124°37′14.56″E | |
| N3 | 青椅山镇梨树园 Lishu garden, Qingyishan town | 40°39′16.68″N | 124°42′53.44″E |
评价指标 Evaluation Index | 林地参 Forestland ginseng | 农田参 Farmland ginseng | 评价指标 Evaluation Index | 林地参 Forestland ginseng | 农田参 Farmland ginseng |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | 6.24 | 6.50 | Ti | 10.23 | 42.55 |
| Re | 4.63 | 3.36 | Fe | 15.58 | 41.09 |
| Rb1 | 2.05 | 5.86 | Mo | 29.55 | 33.25 |
| 总皂苷Total saponins | 3.66 | 7.29 | V | 23.48 | 31.66 |
| Li | 19.32 | 29.84 | Cr | 31.50 | 49.89 |
| Co | 29.85 | 44.92 | Mn | 8.11 | 33.24 |
| Ni | 29.70 | 66.29 | Pb | 24.15 | 28.65 |
| Cu | 21.13 | 39.01 | Cd | 15.12 | 55.45 |
| As | 9.65 | 24.10 | Hg | 9.67 | 26.74 |
| Sn | 13.10 | 26.01 | 水分Moisture content | 18.53 | 28.16 |
| Sb | 16.81 | 26.91 | pH | 3.10 | 6.43 |
| Mg | 11.92 | 5.75 | 电导率Conductivity | 82.04 | 60.47 |
| Si | 47.14 | 96.56 | 容重Bulk density | 40.87 | 16.69 |
| Ca | 13.20 | 58.18 | 有机质Organic matter | 47.18 | 27.08 |
| Zn | 9.56 | 32.40 | 最高气温The highest temperature | 0.73 | 0.00 |
| N | 9.47 | 26.10 | 最低气温The lowest temperature | 11.32 | 0.00 |
| P | 15.36 | 48.96 | 平均气温Average temperature | 4.92 | 0.00 |
| Ba | 2.05 | 22.12 | 平均相对湿度Average relative humidity | 3.77 | 0.00 |
| K | 0.21 | 4.75 | 平均降水量Average precipitation | 24.56 | 0.00 |
| Al | 9.28 | 4.54 |
表 2 人参皂苷含量和生态因子的变异系数 (%)
Table 2 Variation coefficients of ginsenoside content and ecological factors
评价指标 Evaluation Index | 林地参 Forestland ginseng | 农田参 Farmland ginseng | 评价指标 Evaluation Index | 林地参 Forestland ginseng | 农田参 Farmland ginseng |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | 6.24 | 6.50 | Ti | 10.23 | 42.55 |
| Re | 4.63 | 3.36 | Fe | 15.58 | 41.09 |
| Rb1 | 2.05 | 5.86 | Mo | 29.55 | 33.25 |
| 总皂苷Total saponins | 3.66 | 7.29 | V | 23.48 | 31.66 |
| Li | 19.32 | 29.84 | Cr | 31.50 | 49.89 |
| Co | 29.85 | 44.92 | Mn | 8.11 | 33.24 |
| Ni | 29.70 | 66.29 | Pb | 24.15 | 28.65 |
| Cu | 21.13 | 39.01 | Cd | 15.12 | 55.45 |
| As | 9.65 | 24.10 | Hg | 9.67 | 26.74 |
| Sn | 13.10 | 26.01 | 水分Moisture content | 18.53 | 28.16 |
| Sb | 16.81 | 26.91 | pH | 3.10 | 6.43 |
| Mg | 11.92 | 5.75 | 电导率Conductivity | 82.04 | 60.47 |
| Si | 47.14 | 96.56 | 容重Bulk density | 40.87 | 16.69 |
| Ca | 13.20 | 58.18 | 有机质Organic matter | 47.18 | 27.08 |
| Zn | 9.56 | 32.40 | 最高气温The highest temperature | 0.73 | 0.00 |
| N | 9.47 | 26.10 | 最低气温The lowest temperature | 11.32 | 0.00 |
| P | 15.36 | 48.96 | 平均气温Average temperature | 4.92 | 0.00 |
| Ba | 2.05 | 22.12 | 平均相对湿度Average relative humidity | 3.77 | 0.00 |
| K | 0.21 | 4.75 | 平均降水量Average precipitation | 24.56 | 0.00 |
| Al | 9.28 | 4.54 |

图3 林地参和农田参人参皂苷Rg1、Re、Rb1和总皂苷含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig.3 Contents of ginsenosides Rg1, Re, Rb1 and total saponins in forestland ginseng and farmland ginsengNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
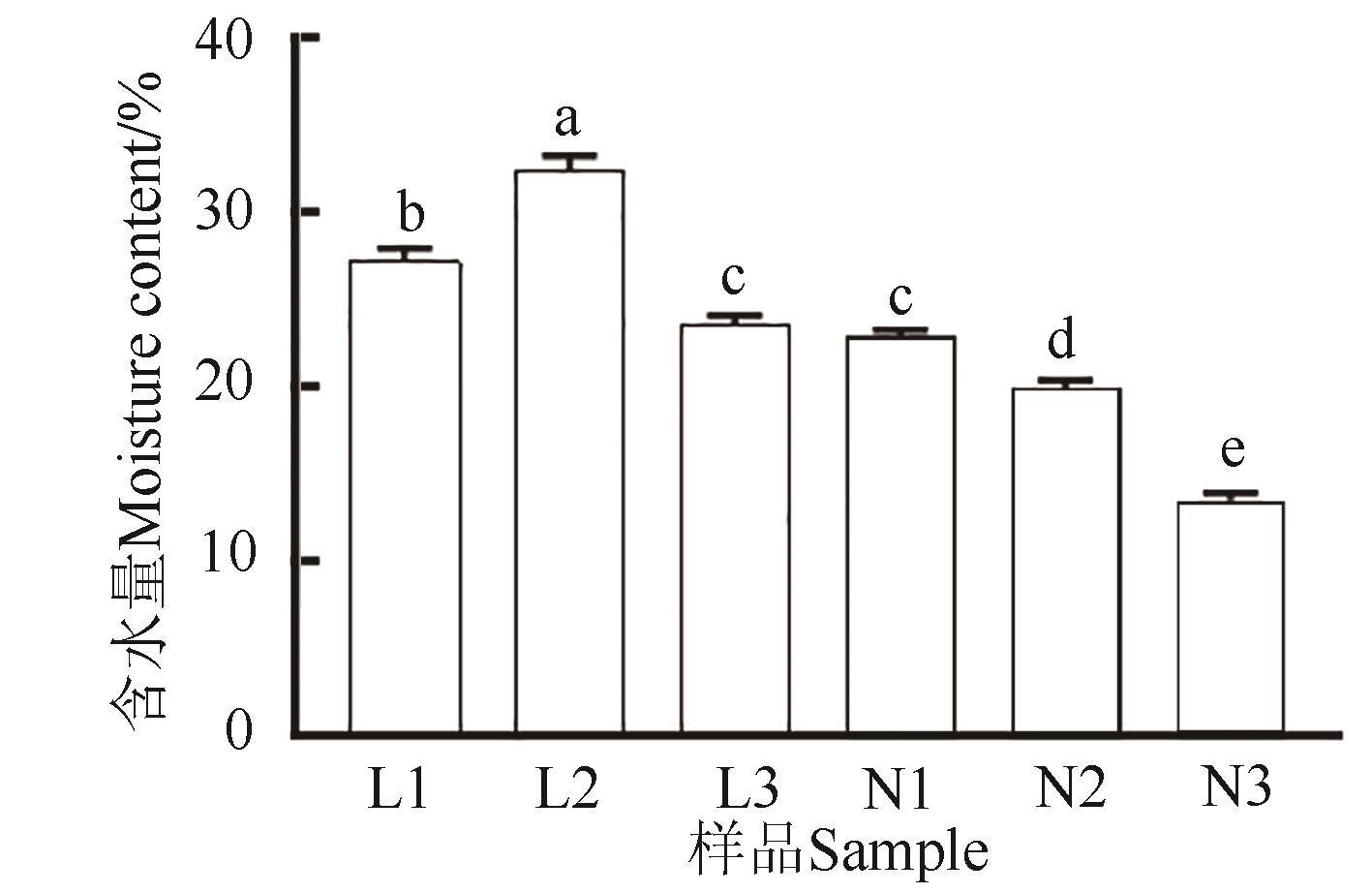
图4 农田参与林地参根际土壤含水量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Moisture content of rhizosphere soil in farmland ginseng and forestland ginsengNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
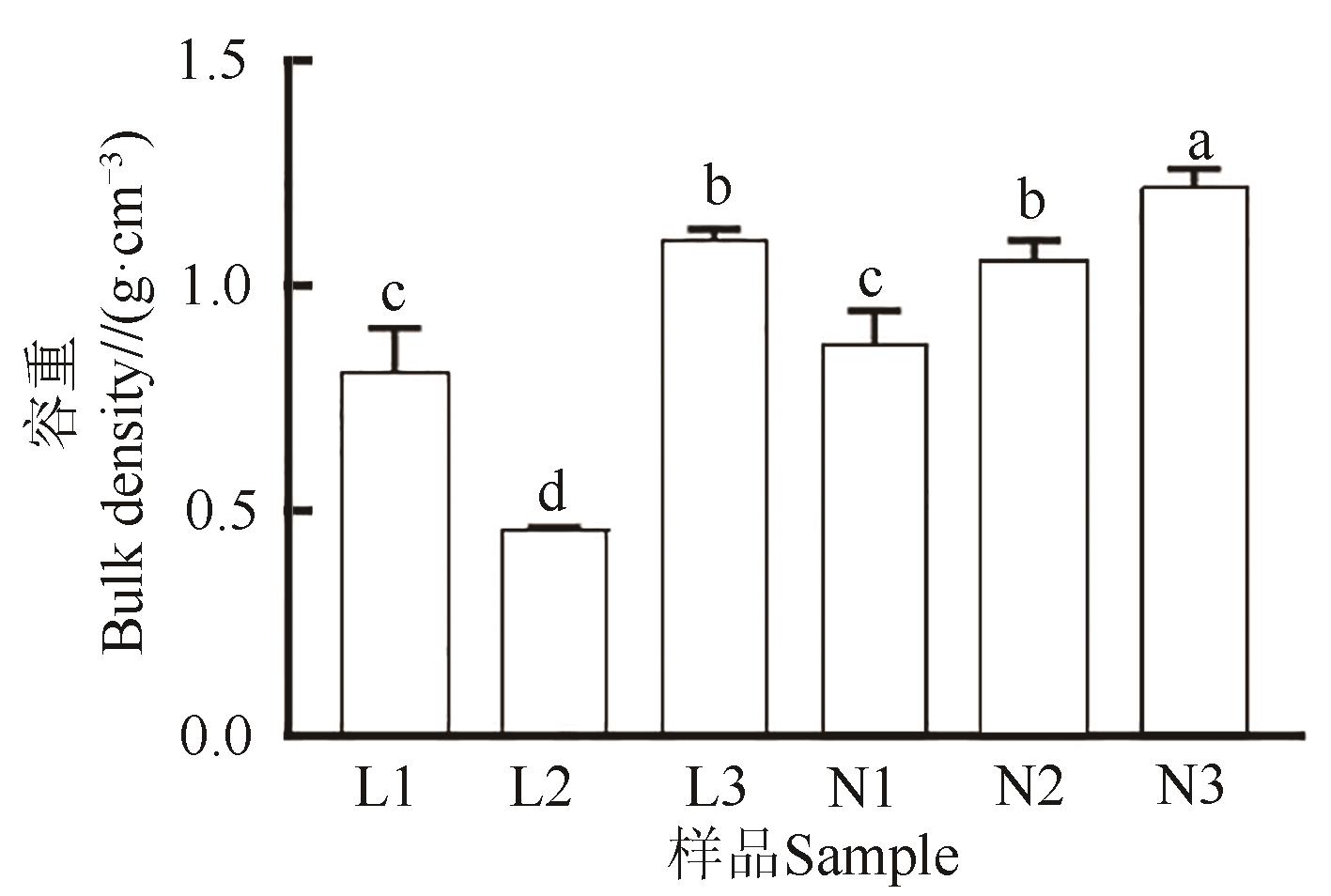
图5 农田参与林地参根际土壤容重注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P <0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Bulk density of rhizosphere soil in farmland ginseng and forestland ginsengNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

图6 农田参与林地参根际土壤pH注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 pH of rhizosphere soil in farmland ginseng and forestland ginsengNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
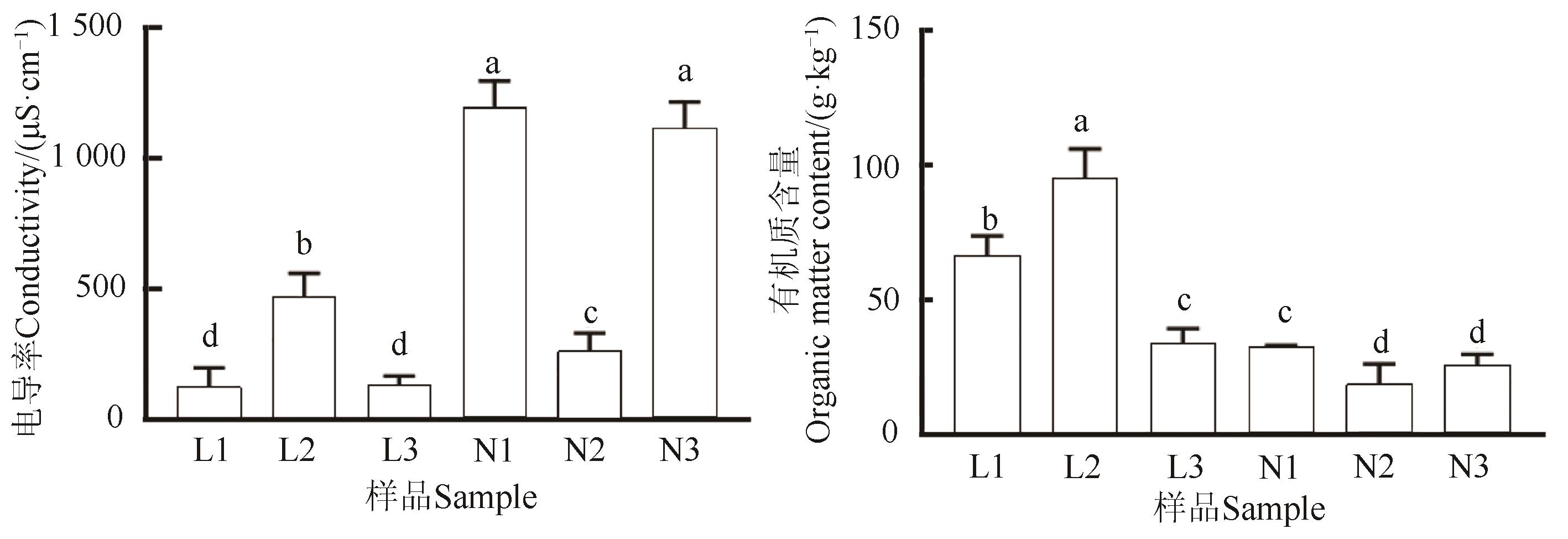
图7 农田参与林地参根际土壤电导率和有机质含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 7 Conductivity and organic matter content of rhizosphere soil in farmland ginseng and forestland ginsengNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

图8 农田参与林地参根际土壤元素含量注:同一指标中不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 8 Contents of elements in farmland ginseng rhizosphere soil and forestland ginseng rhizosphere soilNote: Different lowercase letters in same measurement index indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
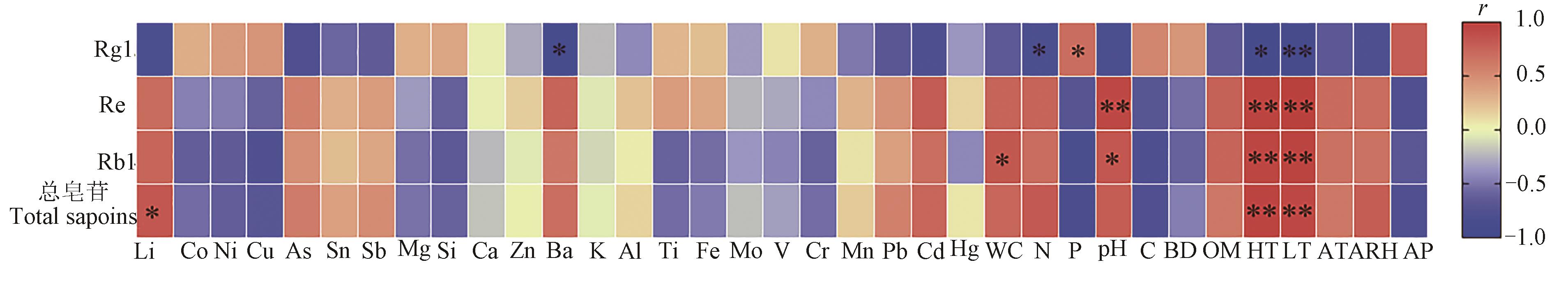
图9 生态因子与人参皂苷含量的相关性分析注:WC—土壤含水量;C—电导率;BD—容重;OM—有机质;HT—最高气温;LT—最低气温;AT—平均气温;ARH—平均相对湿度;AP—平均降水量. *和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 9 Correlation analysis between ecological factors and ginsenoside contentNote:WC—Soil moisture content; C—Conductivity; BD—Bulk density; OM—Organic matter; HT—The highest temperature; LT—The lowest temperature; AT—Average temperature; ARH—Average relative humidity; AP—Average precipitation. * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels,respectively.
指标 Index | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数R2 | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | y=-0.906-0.417X32-0.008X25-0.000 066X13-0.000 044X16 | 1.000 | 395 264.034 | 0.000 |
| Re | y=-6.673+0.498X32+0.542X31 | 0.999 | 889.742 | 0.000 |
| Rb1 | y=5.807+0.432X32 | 0.953 | 39.275 | 0.003 |
总皂苷 Total saponins | y=-91.106+4.405X31 | 0.947 | 34.836 | 0.004 |
表3 人参皂苷与气候和根际土壤因子的逐步回归分析
Table 3 Stepwise regression analysis of ginsenoside, climate factors and rhizosphere soil factors
指标 Index | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数R2 | F值 F value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | y=-0.906-0.417X32-0.008X25-0.000 066X13-0.000 044X16 | 1.000 | 395 264.034 | 0.000 |
| Re | y=-6.673+0.498X32+0.542X31 | 0.999 | 889.742 | 0.000 |
| Rb1 | y=5.807+0.432X32 | 0.953 | 39.275 | 0.003 |
总皂苷 Total saponins | y=-91.106+4.405X31 | 0.947 | 34.836 | 0.004 |
成分 Component | 变量 Variable | 直接系数 Direct coefficient | 通过X13 Through X13 | 通过X16 Through X16 | 通过X25 Through X25 | 通过X32 Through X32 | 通过X35 Through X35 | 通过X36 Through X36 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | X13 | -0.854 | — | -0.178 | -0.006 | 0.024 | ||
| X16 | -0.416 | -0.299 | — | -0.036 | 0.002 | |||
| X25 | -0.089 | -0.038 | -0.175 | — | 0.015 | |||
| X32 | 0.044 | 0.467 | -0.262 | -0.031 | — | |||
| Re | X31 | 0.622 | — | 0.490 | ||||
| X32 | 0.410 | — | 0.323 | |||||
| Rb1 | X32 | 0.953 | ||||||
总皂苷 Total saponins | X31 | 0.947 |
表 4 人参皂苷与气候和根际土壤因子的通径分析
Table 4 Path analysis of ginsenoside, climate factors and rhizosphere soil factors
成分 Component | 变量 Variable | 直接系数 Direct coefficient | 通过X13 Through X13 | 通过X16 Through X16 | 通过X25 Through X25 | 通过X32 Through X32 | 通过X35 Through X35 | 通过X36 Through X36 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | X13 | -0.854 | — | -0.178 | -0.006 | 0.024 | ||
| X16 | -0.416 | -0.299 | — | -0.036 | 0.002 | |||
| X25 | -0.089 | -0.038 | -0.175 | — | 0.015 | |||
| X32 | 0.044 | 0.467 | -0.262 | -0.031 | — | |||
| Re | X31 | 0.622 | — | 0.490 | ||||
| X32 | 0.410 | — | 0.323 | |||||
| Rb1 | X32 | 0.953 | ||||||
总皂苷 Total saponins | X31 | 0.947 |
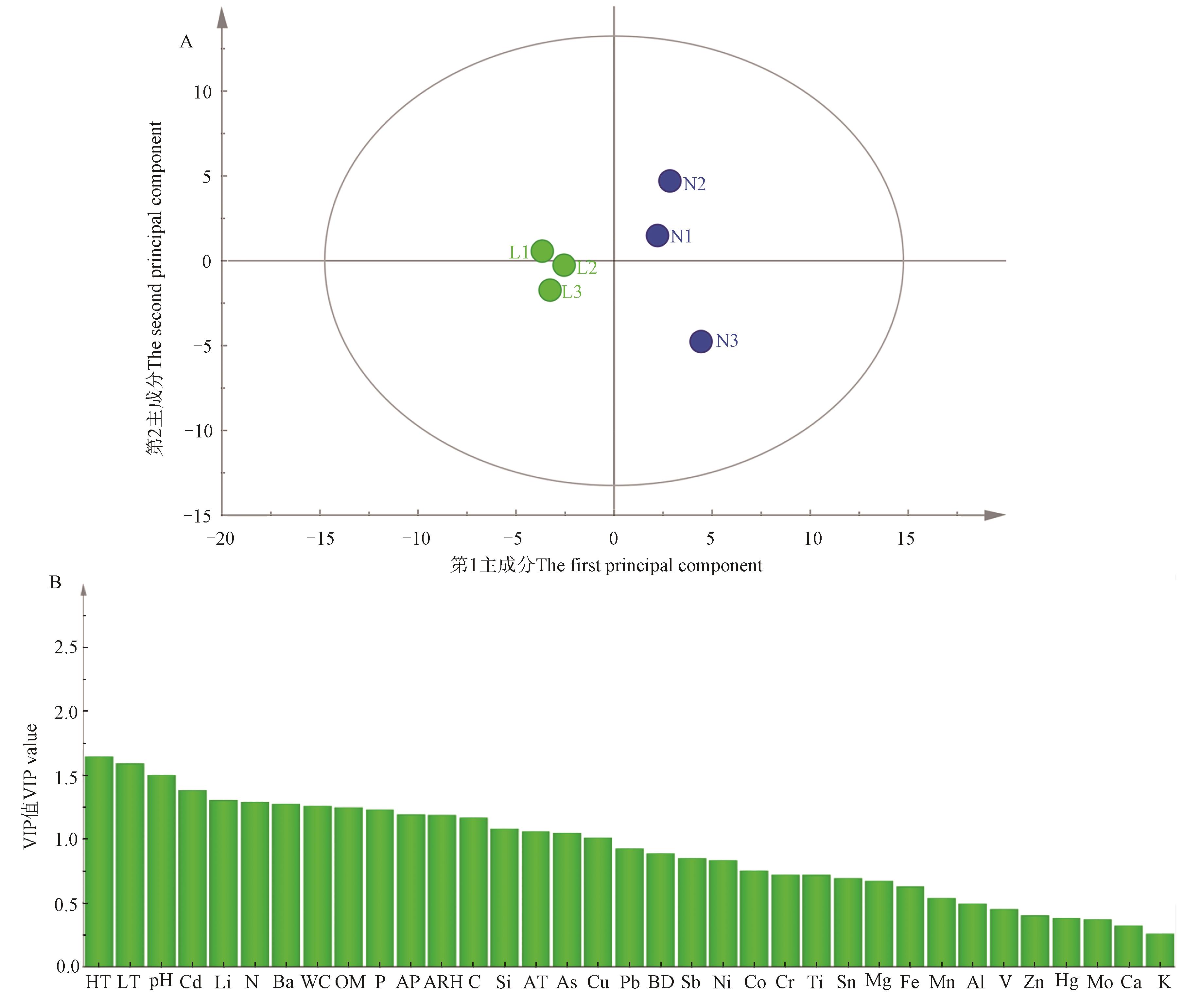
图 10 农田参与林地参根际土壤的PLS-DA得分图及VIP图A: PLS-DA得分图; B: VIP图。HT—最高气温;LT—最低气温;WC—土壤含水量;OM—有机质;AP—平均降水量;ARH—平均相对湿度;C—电导率;AT—平均气温;BD—容重
Fig. 10 PLS-DA score plot and VIP plot for samples obtained by farmland ginseng rhizosphere soil and forestland ginseng rhizosphere soilA: PLS-DA score plot; B: VIP plot. HT—The highest temperature; LT—The lowest temperature; WC—Soil moisture content; OM—Organic matter; AP—Average precipitation; ARH—Average relative humidity; C—Conductivity; AT— Average temperature; BD—Bulk density
类别 Category | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| T2 | 1/3 | 1 | 5/3 | 7/3 | 3 |
| T3 | 1/5 | 3/5 | 1 | 7/5 | 9/5 |
| T4 | 1/7 | 3/7 | 5/7 | 1 | 9/7 |
| T5 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 5/9 | 7/9 | 1 |
表5 土壤中各评价指标成对比较判断优先矩阵
Table 5 Comparative judgement priority matrix of evaluation indexes of soil
类别 Category | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| T2 | 1/3 | 1 | 5/3 | 7/3 | 3 |
| T3 | 1/5 | 3/5 | 1 | 7/5 | 9/5 |
| T4 | 1/7 | 3/7 | 5/7 | 1 | 9/7 |
| T5 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 5/9 | 7/9 | 1 |
样地类型 Plot type | 综合评分 Composite score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.171 6 | 3 |
| L2 | 0.170 9 | 4 |
| L3 | 0.182 3 | 2 |
| N1 | 0.166 4 | 5 |
| N2 | 0.149 8 | 6 |
| N3 | 0.201 3 | 1 |
表 6 层次分析综合评分
Table 6 Analytic hierarchy process comprehensive score
样地类型 Plot type | 综合评分 Composite score | 排名 Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.171 6 | 3 |
| L2 | 0.170 9 | 4 |
| L3 | 0.182 3 | 2 |
| N1 | 0.166 4 | 5 |
| N2 | 0.149 8 | 6 |
| N3 | 0.201 3 | 1 |
| 1 | 国家药典委员会.中国药典[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020: 5. |
| 2 | 宋心东,张国荣,赵岩. 我国人参种植业现状与发展趋势[J].人参研究, 2013,25(3):43-45. |
| 3 | 张晶晶,张宁,华霜,等.人参育种研究进展[J]. 特产研究,2021,43(2):85-90. |
| ZHANG J J, ZAHNG N, HUA S,et al.. Research progress in germplasm resources and breeding of ginseng [J]. Special Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res., 2021,43(2):85-90. | |
| 4 | 常相伟,赵颖,李德坤,等.林下山参化学成分及鉴别评价研究进展[J].中草药,2016,47(11):1982-1991. |
| CHANG X W, ZHAO Y, LI D K,et al.. Research progress in chemical constituents of mountain cultivated ginseng and their identification and evaluation [J]. Chin. Trad. Herbal Drugs,2016,47(11):1982-1991. | |
| 5 | 乔建磊,于海业,宋述荛,等.氮素形态对马铃薯叶片光合色素及其荧光特性的影响[J].中国农业大学学报,2013,18(3):39-44. |
| QIAO J L, YU H Y, SONG S Y,et al.. Effects of nitrogen forms on photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of potato leaves [J]. J. Chin. Agric. Univ.,2013,18(3):39-44. | |
| 6 | 张亚玉,孙海,吴连举,等.多功能微生物制剂对农田栽参土壤容重及人参皂苷的影响研究[J].特产研究,2010,48(1): 35-37. |
| ZHANG Y Y, SUN H, WU L J, et al.. Effects of multi-microbial organic on bulk density of soil and ginsenoside in cultivated ginseng on farmland [J]. Special Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res.,2010,48(1): 35-37. | |
| 7 | 牛玮浩,徐江,董林林,等.农田栽参的研究进展及优势分析[J].世界科学技术,2016,18(11): 1981-1987. |
| 8 | 兰艺鸣,李佳思,韩梅,等.不同林型对林下参产量质量及土壤微生态的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(13):181-188. |
| LAN Y M, LI J S, HAN M,et al.. Yield,quality,and soil microecology of Panax ginseng under different forests [J]. Chin. J. Exp. Trad. Med. Formulae, 2022,28(13):181-188. | |
| 9 | 吴艾轩,王鑫,吕云,等.农田栽参土壤养分研究进展[J].北方园艺,2018(22):177-186. |
| WU A X, WANG X, LYU Y, et al.. Progress of soil nutrients of cultivation of Panax ginseng in farmland [J]. Northern Hortic., 2018(22):177-186. | |
| 10 | 崔潇潇,高原,吕贻忠. 北京市大兴区土壤肥力的空间变异[J].农业工程学报,2010,26(9) :327-333. |
| CUI X X, GAO Y, LYU Y Z. Spatial variability of soil fertility in Daxing district of Beijing [J].Trans. Chin. Soci. Agric. Eng.,2010,26(9) :327-333. | |
| 11 | 吕巧灵,付巧玲,吴克宁,等.郑州市郊区土壤综合肥力评价及空间分布研究[J].中国农学通报,2006,22 (1):166-168. |
| LYU Q L, FU Q L, WU K N,et al.. Studies on the comprehensive evaluation on fertility and spatial distribution of the soil in the suburb of Zhengzhou [J].Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull.,2006,22 (1):166-168. | |
| 12 | 李双异,刘慧屿,张旭东,等. 东北黑土地区主要土壤肥力质量指标的空间变异性[J].土壤通报,2006,37(2):220-225. |
| LI S Y, LIU H Y, ZHANG X D, et al.. Spatial variability of soil fertility quality indices in northeast China [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci.,2006,37(2):220-225. | |
| 13 | 张涛. 人参及其皂苷生物合成对低温的生理生态响应机制研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2019. |
| ZHANG T. Physiological and ecological response mechanism of Panax ginseng and its saponins biosynthesis to low temperature [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University,2019. | |
| 14 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析 [M].北京:中国农业出版社,2013: 56-58,106-108,234-240,229-230,239-240. |
| 15 | 杨玮玮. 磷酸加王水复溶-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定土壤样品中的20种金属元素[J]. 中国无机分析化学,2021,11(5):81-85. |
| YANG W W. Determination of 20 metal elements in soil samples by ICP-MS with phosphoric acid and aqua regia [J]. Chin. J. Inorgan. Anal. Chem.,2021,11(5):81-85. | |
| 16 | 王昌宇,李永利,周文辉,等. 内蒙古包头市固阳县某铁矿区周边土壤多元素测定与健康风险评价[J].岩矿测试,2022,41(3):476-487. |
| WANG C Y, LI Y L, ZHOU W H,et al.. Determination of multiple elements in soils surrounding iron deposits from Guyang county,Baotou city,and health risk assessment [J]. Rock Mineral Anal., 2022,41(3):476-487. | |
| 17 | 何芳.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定土壤和沉积物中12种金属元素[J]. 黑龙江环境通报,2020,33(2):2-3, 6. |
| HE F. Determination of 12 metal elements in soil and sediment by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [J]. Heilongjiang Environ. J., 2020,33(2):2-3, 6. | |
| 18 | 段勤,温光和,杨雪燕,等. 盐酸超声提取-火焰原子吸收光谱法测定加热不燃烧卷烟烟丝中钾、钙、钠、镁的含量[J]. 理化检验-化学分册,2022,58(2):193-196. |
| DUAN Q, WEN G H, YANG X Y, et al.. Detemination of K, Ca, Na, Mg in heat not burning cigarette by flame atomic absorption spectrometry with hydrochloric acid ultrasonic extraction [J]. Phys. Test. Chem. Anal., 2022,58(2):193-196. | |
| 19 | 邹福林. 石墨炉原子吸收法测定土壤样品中的锡[J]. 信息记录材料,2021,22(11):28-30. |
| 20 | 管孝艳,王少丽,高占义,等. 盐渍化灌区土壤盐分的时空变异特征及其与地下水埋深的关系[J]. 生态学报,2012,32(4):1202-1210. |
| GUAN X Y, WANG S L, GAO Z Y,et al.. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2012,32(4):1202-1210. | |
| 21 | YE J, ZHANG X, DAI W X,et al.. Chemical fingerprinting of Liuwei Dihuang Pill and simultaneous determination of its major bioactive constituents by HPLC coupled with multiple detections of DAD,ELSD and ESI-MS [J]. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2009,49(3): 638-645. |
| 22 | 董自亮,李红亮,原欢欢,等. UPLC测定经典名方金水六君煎中11种成分[J]. 中草药,2021,52(3):711-717. |
| DONG Z L, LI H L, YUAN H H,et al.. Determination of 11 components in Jinshui Liujun decoction of classical prescriptions by UPLC [J]. Chin. Trad. herbal Drugs, 2021,52(3):711-717. | |
| 23 | 赵秋龙,张丽,卞晓坤,等.UPLC-QTRAP-MS分析不同产地茯苓药材中8个三萜酸类成分[J].药物分析杂志,2020,40(7):1169-1177. |
| ZHAO Q L, ZHANG L, BIAN X K,et al.. Analysis of 8 triterpene acids in poria from different habitats based on UPLC-QTRAP-MS [J]. Chin. J. Pharma. Anal.,2020,40(7):1169-1177. | |
| 24 | 尹浩,詹亚,张浏, 等.基于层次分析法评价清水廊道陆向缓冲带工程适宜性[J].环境工程,2022,40(5):193-196, 250. |
| YIN H, ZHAN Y, ZHANG L,et al.. Suitability evaluation of riparian zone of clear water gallery based on AHP [J]. Environ. Eng., 2022,40(5):193-196, 250. | |
| 25 | 刘沛,王丹,胡先奇. 镁毒害抑制茉莉酸信号通路增加拟南芥对南方根结线虫敏感性的研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2022,37(2):220-227. |
| LIU P, WANG D, HU X Q. Study on the magnesium toxicity inhibits jasmonic acid signaling pathway and increases Arabidopsis sensitivity to Meloidogyne incognita [J]. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2022,37(2):220-227. | |
| 26 | 杨林林. 不同生长时期人参皂苷合成及其关键酶基因表达对生态因子的响应[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2017. |
| YANG L L. Response of ginsenosides synthesis and its key enzyme genes expression to ecological factors in different growth period [D].Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University,2017. | |
| 27 | ZHANG T, CHEN C B, CHEN Y Q, et al.. Changes in the leaf physiological characteristics and tissue-specific distribution of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng during flowering stage under cold stress [J/OL]. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2021, 9: 637324 [2023-01-08]. . |
| [1] | 胡茜, 王艺凝, 申鹏飞, 李雅倩, 杨阳, 王艳成, 姬文秀, 董微巍. 洋虫内产β-葡萄糖苷酶内生菌发酵液转化人参皂苷产物分析及其抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 119-127. |
| [2] | 李舒欣, 张浩, 郑厚胜, 郑培和, 逄世峰, 许世泉. 转录组分析二马牙和长脖类型林下参表型差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 56-68. |
| [3] | 李紫岩1,朱寿东2,刘澜波3,杨敏1,张磊4,张春红1*,李旻辉1,4*. 内蒙古道地药材蒙古黄芪生态适宜性区划研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 170-176. |
| [4] | 戚文涛1,李剑超1,王晨1,罗容1,2,刘长利1,2*. 不同地理种源北柴胡种子性状及植株生长分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(4): 68-77. |
| [5] | 蔡小雨1,闫培生1*,高秀君1,陈琪琪1,郭长禄1,刘润东2,梁浩2,张明臣2. 人参皂苷生物转化的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(4): 52-60. |
| [6] | 陈征1,任志广1,范艺宽2,赵晖3,陈广晴2,赵攀攀4,许自成1*. 基于灰色关联分析模型的烟叶化学成分评价研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(5): 129-137. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号