




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 218-228.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0953
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
齐潇雨1( ), 郭艳杰1,2, 柳鹭1, 张子涛1, 张丽娟1,2,3, 吉艳芝1,2,3(
), 郭艳杰1,2, 柳鹭1, 张子涛1, 张丽娟1,2,3, 吉艳芝1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-26
接受日期:2024-06-04
出版日期:2025-06-15
发布日期:2025-06-23
通讯作者:
吉艳芝
作者简介:齐潇雨 E-mail:q15233118871@163.com;
基金资助:
Xiaoyu QI1( ), Yanjie GUO1,2, Lu LIU1, Zitao ZHANG1, Lijuan ZHANG1,2,3, Yanzhi JI1,2,3(
), Yanjie GUO1,2, Lu LIU1, Zitao ZHANG1, Lijuan ZHANG1,2,3, Yanzhi JI1,2,3( )
)
Received:2023-12-26
Accepted:2024-06-04
Online:2025-06-15
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
Yanzhi JI
摘要:
为揭示不同种植年限的设施葡萄园土壤盐渍化特征及其对微生物群落的影响,选取种植0(农田土壤)、1~5、6~10、10~15、>15 a的设施葡萄园进行调研取样,分析土壤含盐量、盐分离子、微生物量碳氮与微生物群落结构。结果表明,设施葡萄园土壤含盐量显著高于农田土壤,有明显的盐渍化趋势;种植年限的增加加剧了土壤盐渍化风险,表层土壤中仅农田土壤为轻度盐渍土,设施葡萄园土壤均为中度或重度盐渍土,含盐量在3.47~5.12 g·kg-1。随种植年限的增加,各土层可溶性阴、阳离子以SO
中图分类号:
齐潇雨, 郭艳杰, 柳鹭, 张子涛, 张丽娟, 吉艳芝. 种植年限对设施葡萄园土壤盐渍化及微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 218-228.
Xiaoyu QI, Yanjie GUO, Lu LIU, Zitao ZHANG, Lijuan ZHANG, Yanzhi JI. Effects of Planting Years on Soil Salinization and Microbial Community in Facility Vineyards[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 218-228.
土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 土壤质地 Soil exture | 有机质 Soil organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorous/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/ (mg·kg-1) | pH | 容重 Bulk density/ (g·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | 壤质砂土 Loamy sand | 13.07~29.20 | 189.46~205.13 | 367.42~422.70 | 6.45~7.70 | 1.02~1.34 |
| 20—40 | 6.55~22.42 | 116.35~124.49 | 396.54~414.60 | 6.92~8.20 | 1.13~1.42 | |
| 40—60 | 4.45~9.54 | 94.72~120.44 | 279.15~301.30 | 7.04~8.46 | 1.00~1.19 | |
| 60—80 | 2.00~3.74 | 33.24~41.38 | 222.00~254.32 | 6.79~8.54 | 1.04~1.15 | |
| 80—100 | 0.83~5.77 | 23.25~47.54 | 197.91~220.60 | 7.38~8.61 | 1.08~1.21 |
表1 研究区土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of soil in the study area
土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 土壤质地 Soil exture | 有机质 Soil organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorous/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/ (mg·kg-1) | pH | 容重 Bulk density/ (g·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | 壤质砂土 Loamy sand | 13.07~29.20 | 189.46~205.13 | 367.42~422.70 | 6.45~7.70 | 1.02~1.34 |
| 20—40 | 6.55~22.42 | 116.35~124.49 | 396.54~414.60 | 6.92~8.20 | 1.13~1.42 | |
| 40—60 | 4.45~9.54 | 94.72~120.44 | 279.15~301.30 | 7.04~8.46 | 1.00~1.19 | |
| 60—80 | 2.00~3.74 | 33.24~41.38 | 222.00~254.32 | 6.79~8.54 | 1.04~1.15 | |
| 80—100 | 0.83~5.77 | 23.25~47.54 | 197.91~220.60 | 7.38~8.61 | 1.08~1.21 |
种植年限 Planting years/a | 养分投入量 Nutrient input/(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 氮 N | 五氧化二磷 P2O5 | 氧化钾 K2O | |
| 0 | 426.26±47.85 | 305.47±24.61 | 72.30±8.83 |
| 0~5 | 663.47±352.40 | 521.53±289.16 | 661.41±305.12 |
| 6~10 | 590.53±335.43 | 453.21±136.45 | 669.00±324.09 |
| 11~15 | 400.48±161.60 | 370.99±113.27 | 483.99±76.67 |
| >15 | 415.63±193.56 | 287.25±96.30 | 414.13±194.82 |
表2 不同种植年限葡萄园化肥纯养分投入量
Table 2 Fertilizer net nutrient input in vineyards with different planting years
种植年限 Planting years/a | 养分投入量 Nutrient input/(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 氮 N | 五氧化二磷 P2O5 | 氧化钾 K2O | |
| 0 | 426.26±47.85 | 305.47±24.61 | 72.30±8.83 |
| 0~5 | 663.47±352.40 | 521.53±289.16 | 661.41±305.12 |
| 6~10 | 590.53±335.43 | 453.21±136.45 | 669.00±324.09 |
| 11~15 | 400.48±161.60 | 370.99±113.27 | 483.99±76.67 |
| >15 | 415.63±193.56 | 287.25±96.30 | 414.13±194.82 |
指标 Index | 盐渍化等级 Salinization grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
非盐渍土 Non-saline soil | 轻度盐渍土 Lightly saline soil | 中度盐渍土 Moderately saline soil | 重度盐渍土 Heavy saline soil | 盐土 Salt soil | |
含盐量 Salt content/(g·kg-1) | ≤1.0 | 1.0~2.0 | 2.0~4.0 | 4.0~6.0 | >6.0 |
电导率 EC/(mS·cm-1) | ≤2.5 | 2.5~5.5 | 5.5~8.5 | 8.5~14.0 | >14.0 |
表3 土壤盐渍化分级标准
Table 3 Grading standard of soil salinization
指标 Index | 盐渍化等级 Salinization grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
非盐渍土 Non-saline soil | 轻度盐渍土 Lightly saline soil | 中度盐渍土 Moderately saline soil | 重度盐渍土 Heavy saline soil | 盐土 Salt soil | |
含盐量 Salt content/(g·kg-1) | ≤1.0 | 1.0~2.0 | 2.0~4.0 | 4.0~6.0 | >6.0 |
电导率 EC/(mS·cm-1) | ≤2.5 | 2.5~5.5 | 5.5~8.5 | 8.5~14.0 | >14.0 |

图1 不同种植年限设施葡萄园0—100 cm土层电导率与含盐量注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同种植年限间含盐量在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Soil EC and salinity content of soil layer from 0 to 100 cm in vineyards with different planting yearsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different planting years of the same soil layer in salt content at P<0.05 level.

图2 不同种植年限阳离子在0—100 cm土层的分布注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同种植年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Distribution of cations in soil layer from 0 to 100 cm with different planting yearsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different planting years of the same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
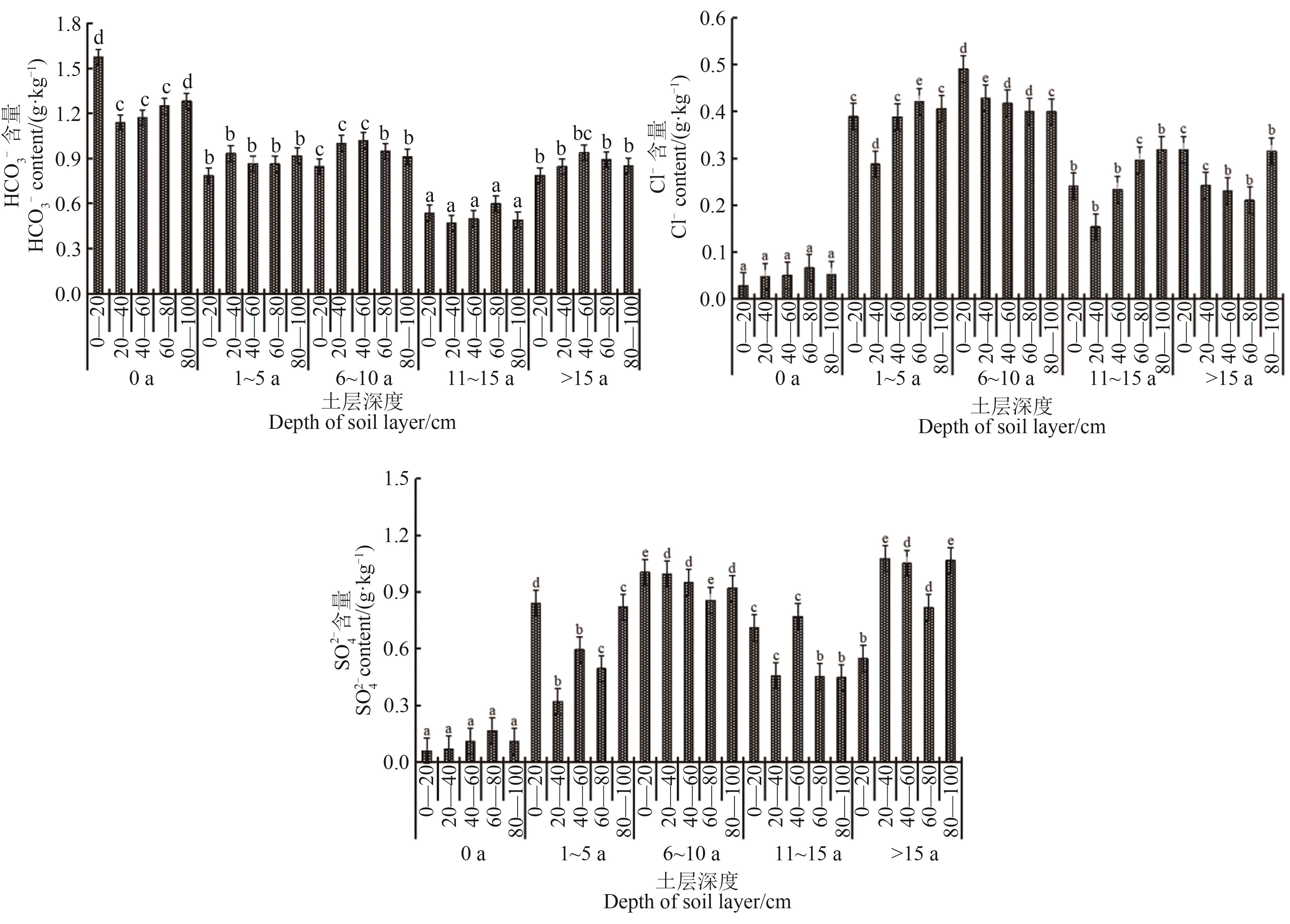
图3 不同种植年限阴离子在0—100 cm土层的分布注:不同小写字母表示同一土层不同种植年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Distribution of anions in soil layer from 0 to 100 cm with different planting yearsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different planting years of the same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
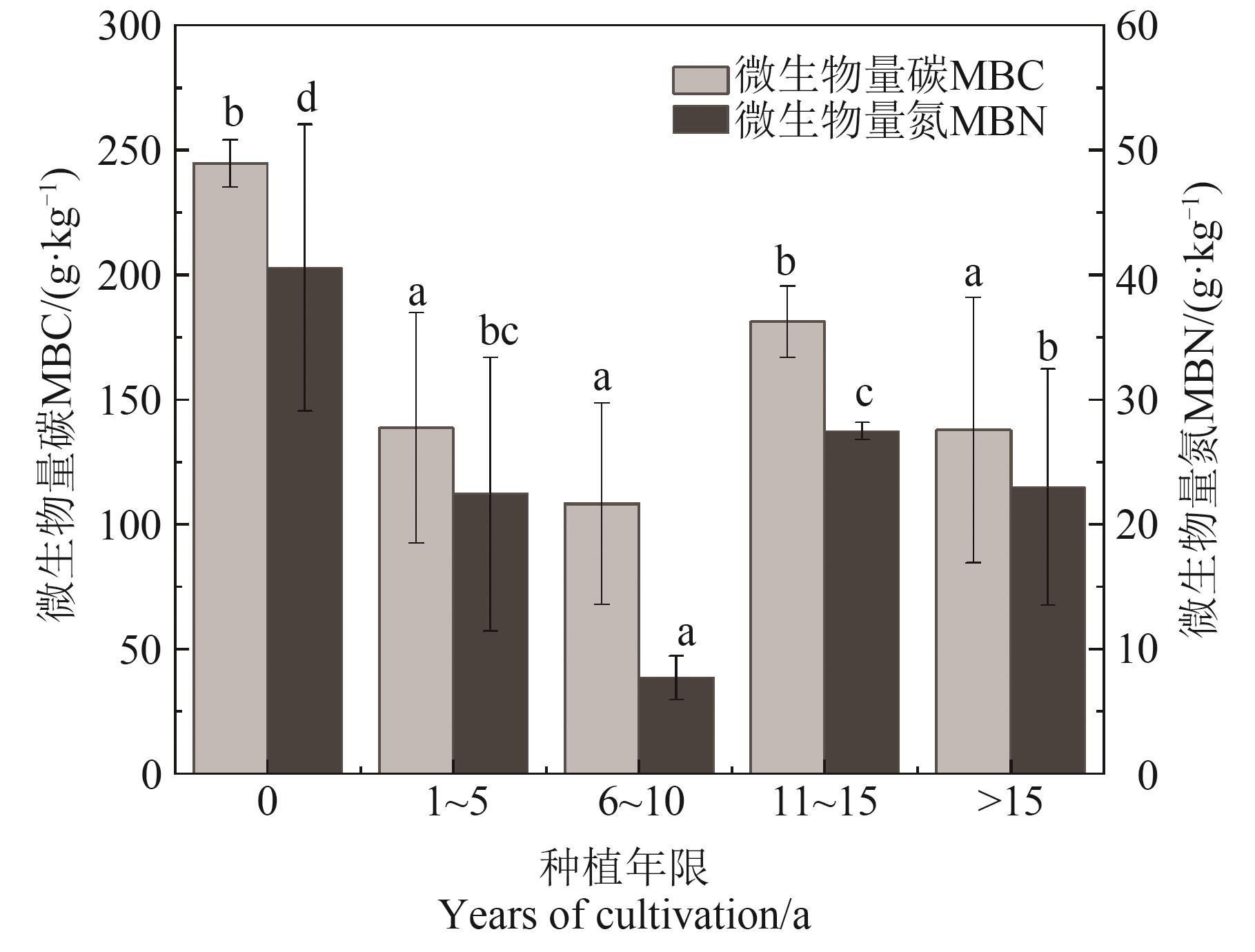
图4 0—20 cm土层微生物量碳、氮含量注:不同小写字母表示不同种植年限间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen from 0 to 100 cm soil layerNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different planting years at P<0.05 level.
菌种 Species | 种植年限 Planting year/a | Observed species指数 Observed species index | Chao 1指数 Chao 1index | Shannon指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | 0 | 4 527.90±65.1 a | 5 214.12±34.2 a | 11.08±0.14 a |
| 1~5 | 4 318.43±125.64 a | 5 002.38±172.53 a | 10.93±0.47 a | |
| 6~10 | 4 111.63±172.43 a | 4 985.93±189.20 a | 10.82±0.36 a | |
| 11~15 | 4 402.13±116.32 a | 5 047.89±174.35 a | 10.93±0.24 a | |
| >15 | 3 902.30±126.12 a | 4 694.06±194.67 a | 10.84±0.24 a | |
真菌 Fungi | 0 | 285.35±24.45 b | 283.07±19.61 b | 5.01±0.01 a |
| 1~5 | 269.6±10.29 b | 272.28±10.27 b | 5.11±0.32 a | |
| 6~10 | 477.08±26.44 a | 485.31±31.35 a | 5.48±0.23 a | |
| 11~15 | 467.03±31.28 a | 469.96±29.67 a | 5.57±0.38 a | |
| >15 | 476.95±0.45 a | 488.46±0.96 a | 5.73±0.46 a |
表4 不同种植年限设施葡萄园土壤细菌、真菌群落多样性指数
Table 4 Community diversity index of bacteria and fungi in vineyard soils with different planting years
菌种 Species | 种植年限 Planting year/a | Observed species指数 Observed species index | Chao 1指数 Chao 1index | Shannon指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | 0 | 4 527.90±65.1 a | 5 214.12±34.2 a | 11.08±0.14 a |
| 1~5 | 4 318.43±125.64 a | 5 002.38±172.53 a | 10.93±0.47 a | |
| 6~10 | 4 111.63±172.43 a | 4 985.93±189.20 a | 10.82±0.36 a | |
| 11~15 | 4 402.13±116.32 a | 5 047.89±174.35 a | 10.93±0.24 a | |
| >15 | 3 902.30±126.12 a | 4 694.06±194.67 a | 10.84±0.24 a | |
真菌 Fungi | 0 | 285.35±24.45 b | 283.07±19.61 b | 5.01±0.01 a |
| 1~5 | 269.6±10.29 b | 272.28±10.27 b | 5.11±0.32 a | |
| 6~10 | 477.08±26.44 a | 485.31±31.35 a | 5.48±0.23 a | |
| 11~15 | 467.03±31.28 a | 469.96±29.67 a | 5.57±0.38 a | |
| >15 | 476.95±0.45 a | 488.46±0.96 a | 5.73±0.46 a |
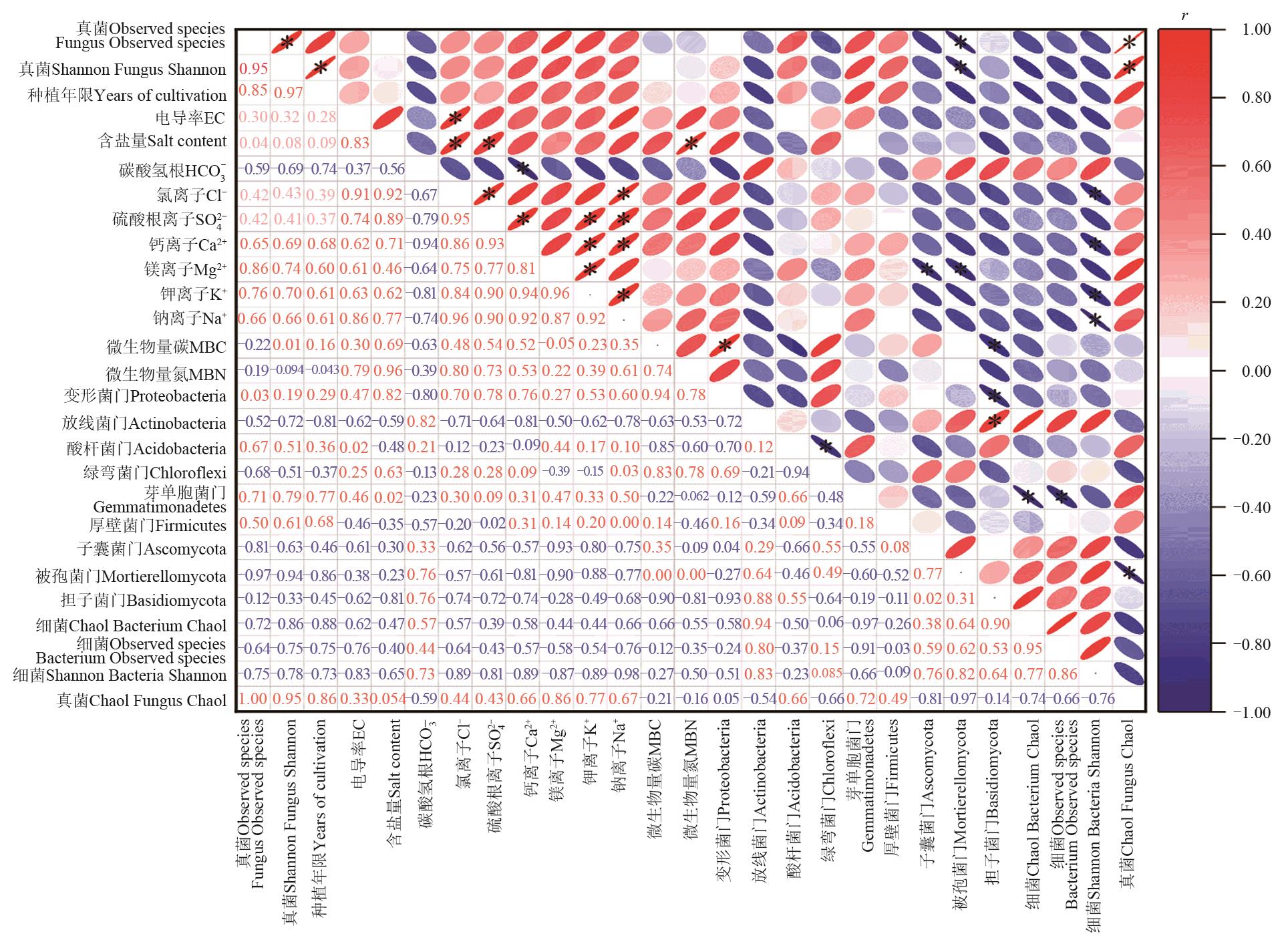
图6 0—20 cm土层种植年限、次生盐渍化与微生物的相关关系注:*表示在P<0.05水平显著相关。
Fig. 6 Relationship between planting years, secondary salinization and the microbes in 0—20 cm soil layerNote:* indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 中国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社,2022: 1-938. |
| 2 | 王世平,李勃.中国设施葡萄发展概况[J].落叶果树,2019,51(1):1-5. |
| 3 | 王朔, 李帅霖, 曾秀丽, 等. 西藏设施葡萄土壤酸化、盐渍化和养分特征[J]. 果树学报, 2018, 35(8): 957-966. |
| WANG S, LI S L, ZENG X L, et al.. Soil acidification, salinization and nutrient characteristics in greenhouse vineyards in Tibet [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2018, 35(8): 957-966. | |
| 4 | 马艳春,姚玉新,杜远鹏,等.葡萄设施栽培不同种植年限土壤理化性质的变化[J].果树学报,2015,32(2):225-231. |
| MA Y C, YAO Y X, DU Y P, et al.. Changes of soil physical and chemical properties in greenhouse of different grapevine planting years [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2015,32(2):225-231. | |
| 5 | 曾希柏,白玲玉,苏世鸣,等.山东寿光不同种植年限设施土壤的酸化与盐渍化[J].生态学报,2010,30(7):1853-1859. |
| ZENG X B, BAI L Y, SU S M, et al.. Acidification and salinization in greenhouse soil of different cultivating years from Shouguang City, Shandong [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010, 30(7):1853-1859. | |
| 6 | 王楠.设施栽培年限对设施土壤生态环境的影响及次生盐渍化土壤的改良[D].重庆:西南大学,2012. |
| WANG N. Effect of Greenhouse age on greenhouse soil eco-environment and amelioration of secondary salinization soil [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2012. | |
| 7 | VARJANI S J, GNANSOUNOU E, PANDEY A. Comprehensive review on toxicity of persistent organic pollutants from petroleum refinery waste and their degradation by microorganisms [J]. Chemosphere, 2017,188:280-291. |
| 8 | VIEIRA S, LUCKNER M, WANNER G, et al.. Luteitalea pratensis gen.nov.,sp.nov.a new member of subdivision 6 Acidobacteria isolated from temperate grassland soil [J]. Int. J.Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2017,67(5):1408-1414. |
| 9 | WU N, LI Z, WU F, et al.. Microenvironment and microbial community in the rhizosphere of dioecious Populus cathayana at Chaka Salt Lake [J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2019,19(6):2740-2751. |
| 10 | 李凤霞, 王学琴, 郭永忠, 等. 宁夏不同类型盐渍化土壤微生物区系及多样性[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(5): 107-111. |
| LI F X, WANG X Q, GUO Y Z, et al.. Microbial flora and diversity in different types of saline-alkali soil in Ningxia [J]. J. Soil. Water Conserv., 2011, 25(5): 107-111. | |
| 11 | 张翔,宋水山,黄亚丽,等.基于高通量测序分析河北省中南部地区耕地土壤细菌多样性[J].华北农学报,2018,33(4):196-203. |
| ZHANG X, SONG S S, HUANG Y L, et al.. Analysis of bacterial diversity in cultivated soils in middle and southern Hebei province based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2018,33(4):196-203. | |
| 12 | 刘银双,牛宏进,赵阳阳,等.河北省不同盐渍化土壤类型的微生物多样性与种群结构[J].环境科学,2023,44(12):7004-7013. |
| LIU Y S, NIU H J, ZHAO Y Y, et al.. Microbial diversity and population structure of different salinized soil types in Hebei province [J]. Environ. Sci., 2023,44(12):7004-7013. | |
| 13 | 王飞, 禇贵新, 杨明凤, 等. 北疆绿洲不同盐分浓度梯度下土壤的生物活性及其功能多样性[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(3): 621-626. |
| WANG F, CHU G X, YANG M F, et al.. Soil biological activity and its functional diversity along with salinity gradient in oasis of northern Xinjiang [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2012, 43(3): 621-626. | |
| 14 | 朱海,杨劲松,姚荣江,等.有机无机肥配施对滨海盐渍农田土壤盐分及作物氮素利用的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2019,27(3):441-450. |
| ZHU H, YANG J S, YAO R J, et al.. Effects of partial substitution of organic nitrogen for inorganic nitrogen in fertilization on salinity and nitrogen utilization in salinized coastal soil [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2019,27(3):441-450. | |
| 15 | 次惠云.饶阳县设施葡萄种植户关键技术采纳行为及影响因素分析[D].保定:河北农业大学,2019. |
| CI H Y. Analysis on key technology adoptions and influencing factors of grape planters in Raoyang county [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 16 | 郭锦瑞. 饶阳县设施葡萄产业发展研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2020. |
| GUO J R. Research on the development of protected grape industry in Raoyang county [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 17 | 张子涛. 河北省典型县域设施葡萄园施肥现状及优化技术[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2022. |
| ZHANG Z T. Current situation and optimization technology of fertilization in vineyard in typical counties of Hebei province [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| 18 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| 19 | 王遵亲.中国盐渍土[M].北京:科学出版社,1993:1-652. |
| 20 | 杨亚红. 不同种植年限果蔬温室大棚土壤理化性质的演变规律[D]. 延安: 延安大学, 2019. |
| YANG Y H. Evolution of physical and chemical properties of soil in greenhouse of fruit and vegetable in different planting years [D]. Yan’an: Yan’an University, 2019. | |
| 21 | 钱晓雍.塑料大棚设施菜地土壤次生盐渍化特征[J].中国土壤与肥料,2017(5):73-79. |
| QIAN X Y. Characteristics of secondary salinization of vegetable soil in plastic film greenhouse [J].Soil Fert. Sci.China, 2017(5):73-79. | |
| 22 | YANG F, AN F H, MA H Y, et al.. Variations on soil salinity and sodicity and its driving factors analysis under microtopography in different hydrological conditions [J]. Water, 2016, 8(6): 2-13. |
| 23 | 姜忠廷. 土壤次生盐渍化及其对设施农业可持续发展的影响[C]//中国环境科学学会. 2010中国环境科学学会学术年会论文集(第四卷). 北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2010: 5. |
| 24 | 蔡祖聪,黄新琦.土壤学不应忽视对作物土传病原微生物的研究[J].土壤学报,2016,53(2):305-310. |
| CAI Z C, HUANG X Q. Soil-borne pathogens should not be ignored by soil science [J]. Acta Pedol.Sin., 2016,53(2):305-310. | |
| 25 | 茅国芳,陆利民,杨晓华,等.沪郊西瓜甜瓜设施栽培土壤次生盐渍化的基本特性与防治技术研究[J].上海农业学报,2005,21(1):58-66. |
| MAO G F, LU L M, YANG X H, et al.. Study on the basic characteristics and control technique of secondary salted soil under protected culture of watermelon and melon in Shanghai suburbs [J]. Acta Agric. Shanghai, 2005,21(1):58-66. | |
| 26 | LIN X G, YIN R, ZHANG H Y, et al.. Changes of soil microbiological properties caused by land use changing from rice-wheat rotation to vegetable cultivation [J]. Environ. Geochem. Health, 2004,26(2):119-128. |
| 27 | MIAO Y X, STEWART B A, ZHANG F S. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient managements in China [J]. Agron. Sustain. Dev., 2011, 31(9): 83-93. |
| 28 | 李涛,于蕾,吴越,等.山东省设施菜地土壤次生盐渍化特征及影响因素[J].土壤学报,2018,55(1):100-110. |
| LI T, YU L, WU Y, et al.. Secondary salinization of greenhouse vegetable soils and its affecting factors in Shandong province,China [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2018,55(1):100-110. | |
| 29 | 肖春萍,杨利民,马锋敏.栽培年限对人参根际土壤微生物活性及微生物量的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2014,39(24):4740-4747. |
| XIAO C P, YANG L M, MA F M. Effects of growing time on Panax ginseng rhizosphere soil microbial activity and biomass [J]. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2014,39(24):4740-4747. | |
| 30 | 国春菲.土壤盐分和pH对滨海盐土土壤微生物多样性的影响[D].杭州:浙江农林大学,2013. |
| GUO C F. Effects of salinity and pH on soil microbial diversity in coastal saline soil [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2013. | |
| 31 | 李桥.基于高通量测序技术下土壤微生物群落结构的研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2014. |
| LI Q. Research of soil microbial community structure based on high-throughput sequencing technology [D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Normal University, 2014. | |
| 32 | 朱家瑞. 盐碱土壤冬枣根际微生物群落及果实品质研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. |
| ZHU J R. Rhizosphere microbial community and fruit quality of winter jujube in saline soil [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. | |
| 33 | 李婧男.园林废弃物堆肥化处理及其产物对滨海盐渍土的改良效应研究[D].北京:北京林业大学,2020. |
| LI J N. Study on composting of green waste and the improvement effect of products on coastal saline soil [D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020. | |
| 34 | JACOBY R, PEUKERT M, SUCCURRO A, et al.. The role of soil microorganisms in plant mineral nutrition-current knowledge and future directions [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci.,2017,8:1617 [2023-11-26]. . |
| 35 | 李玉娇,刘星,吴大付,等.温室黄瓜连作对土壤真菌数量和群落结构的影响[J].华北农学报,2020,35(1):194-204. |
| LI Y J, LIU X, WU D F, et al.. Effects of continuous cropping of greenhouse cucumber on soil fungal abundance and community structure province [J]. Acta Agric.Boreali-Sin., 2020,35(1):194-204. | |
| 36 | 王文团. 耐盐碱细菌筛选与生物菌肥对盐碱地作物的影响 [D].泰安:山东农业大学,2020. |
| WANG W T. Screening of saline-tolerant bacteria and effects of biological fertilizer on saline-alkali crops [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. |
| [1] | 方泰军, 侯璐, 白露超. 柴达木地区患根腐病枸杞根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [2] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [3] | 杨学瑾, 周媛媛, 彭欣怡, 刘建凤, 张爱民, 井爱芹, 赵钢勇, 曹丹丹. 根结线虫危害与健康黄瓜根际土壤微生物群落结构差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 109-118. |
| [4] | 刘辉, 江解增, 张昊, 张永仙, 钱佳宇, 李东昇, 吕艳, 吴桓锐. 浅水土表覆盖秸秆对缓解土壤盐渍化及水生蔬菜生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 202-208. |
| [5] | 何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [6] | 范鹤龄, 朱清, 孙雪冰, 张丽, 李长江, 陈萍, 黄小龙, 张荣萍. 不同农用酵素的微生物多样性和群落结构[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 179-189. |
| [7] | 张磊, 罗泽华, 杨明川, 李世贵, 辛玉华, 蔡斌, 刘好宝, 曾代龙, 顾金刚, 段碧华. 雪茄烟叶原料发酵微生物多样性及酶活变化研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 171-180. |
| [8] | 刘倩1,2,李纪潮1,左应梅1,杨天梅1,杨美权1,张金渝*. 有机覆盖三七对土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 162-175. |
| [9] | 衡通,王振华,张金珠*,李文昊. 新疆农田排水技术治理盐碱地的发展概况[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3): 161-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号