




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 179-189.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0525
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
范鹤龄1( ), 朱清1, 孙雪冰1, 张丽1, 李长江1, 陈萍2, 黄小龙3, 张荣萍1(
), 朱清1, 孙雪冰1, 张丽1, 李长江1, 陈萍2, 黄小龙3, 张荣萍1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-06-28
接受日期:2021-08-23
出版日期:2022-11-15
发布日期:2022-11-29
通讯作者:
张荣萍
作者简介:范鹤龄 E-mail:664580513@qq.com;
基金资助:
Heling FAN1( ), Qing ZHU1, Xuebing SUN1, Li ZHANG1, Changjiang LI1, Ping CHEN2, Xiaolong HUANG3, Rongping ZHANG1(
), Qing ZHU1, Xuebing SUN1, Li ZHANG1, Changjiang LI1, Ping CHEN2, Xiaolong HUANG3, Rongping ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2021-06-28
Accepted:2021-08-23
Online:2022-11-15
Published:2022-11-29
Contact:
Rongping ZHANG
摘要:
为分析不同农用酵素的微生物多样性和群落组成,利用高通量测序技术,比较分析了5种菌剂(岛本酵素菌等)、8种液态农用酵素(玉米、蓖麻、黄蒿、木麻黄、青蒿、荆条等秸秆为原材料)、7种固态农用酵素(荆条、黄蒿、青蒿、玉米、鬼针草等秸秆为原材料)的细菌和真菌多样性以及其群落组成。结果表明,岛本酵素菌细菌和真菌的OTU数量分别为292和54;在液态农用酵素中,细菌的OTUs数量为61~467,真菌OTU数量为7~44,由于原材料差异,不同酵素的细菌和真菌群落组成差异较大;固态农用酵素具有较多的OTUs(细菌1 015~1 474,真菌58~93),显著高于菌剂和液态农用酵素;其中变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroides)和放线菌门(Actinobacteria)的相对丰度分别为26.0%~47.5%、9.4%~33.3%、10.7%~28.6%,为细菌群落组成中的优势菌门;真菌群落组成上的优势菌门为子囊菌门(Ascomycetes)。综上所述,微生物群落多样性和组成因剂型和材料的不同存在差异,影响程度为剂型>材料,多样性表现为固态>液态。
中图分类号:
范鹤龄, 朱清, 孙雪冰, 张丽, 李长江, 陈萍, 黄小龙, 张荣萍. 不同农用酵素的微生物多样性和群落结构[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 179-189.
Heling FAN, Qing ZHU, Xuebing SUN, Li ZHANG, Changjiang LI, Ping CHEN, Xiaolong HUANG, Rongping ZHANG. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure of Different Agricultural Jiaosu[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 179-189.
| 菌剂Microbe agent | 液态农用酵素Liquid jiaosu | 固态农用酵素Solid jiaosu | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 名称Name | 编号Code | 名称Name | 编号Code | 名称Name | 编号Code | ||
岛本酵素菌 Shimamoto Jiaosu microbial | B1 | 玉米秸秆 Corn stalk | L1 | 荆条茎叶 Brambles | S1 | ||
哈茨木霉 Hartz trichoderma viride | B2 | 蓖麻秸秆 Castor stalk | L2 | 青蒿+黄蒿 Artemisia carvifolia+Atemisia scoparia | S2 | ||
枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis | B3 | 黄蒿茎叶 Artemisia scoparia | L3 | 玉米秸秆 Corn stalk | S3 | ||
牛粪菌 Microbe of cow dung | B4 | 木麻黄针叶 Casuarina needles | L4 | 玉米秸秆+青蒿+黄蒿 Corn stalk+Artemisia carvifolia+ Artemisia scoparia | S4 | ||
羊粪菌 Microbe of sheep dung | B5 | 青蒿茎叶 Artemisia carvifolia | L5 | 玉米秸秆+荆条 Corn stalk+Brambles | S5 | ||
青蒿+黄蒿 Artemisia carvifolia+Artemisia scoparia | L6 | 玉米秸秆+鬼针草 Corn stalk+ghost needle grass | S6 | ||||
青蒿(自然菌) Artemisia carvifolia (natural fermentation) | L7 | 玉米秸秆+荆条+黄蒿+青蒿 Corn stalk+Brambles+Artemisia carvifolia+Artemisia scoparia | S7 | ||||
荆条+玉米秸秆 Brambles+corn stalk | L8 | ||||||
表1 农用酵素的剂型和原材料
Table 1 Form and raw materials of agricultural Jiaosu
| 菌剂Microbe agent | 液态农用酵素Liquid jiaosu | 固态农用酵素Solid jiaosu | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 名称Name | 编号Code | 名称Name | 编号Code | 名称Name | 编号Code | ||
岛本酵素菌 Shimamoto Jiaosu microbial | B1 | 玉米秸秆 Corn stalk | L1 | 荆条茎叶 Brambles | S1 | ||
哈茨木霉 Hartz trichoderma viride | B2 | 蓖麻秸秆 Castor stalk | L2 | 青蒿+黄蒿 Artemisia carvifolia+Atemisia scoparia | S2 | ||
枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis | B3 | 黄蒿茎叶 Artemisia scoparia | L3 | 玉米秸秆 Corn stalk | S3 | ||
牛粪菌 Microbe of cow dung | B4 | 木麻黄针叶 Casuarina needles | L4 | 玉米秸秆+青蒿+黄蒿 Corn stalk+Artemisia carvifolia+ Artemisia scoparia | S4 | ||
羊粪菌 Microbe of sheep dung | B5 | 青蒿茎叶 Artemisia carvifolia | L5 | 玉米秸秆+荆条 Corn stalk+Brambles | S5 | ||
青蒿+黄蒿 Artemisia carvifolia+Artemisia scoparia | L6 | 玉米秸秆+鬼针草 Corn stalk+ghost needle grass | S6 | ||||
青蒿(自然菌) Artemisia carvifolia (natural fermentation) | L7 | 玉米秸秆+荆条+黄蒿+青蒿 Corn stalk+Brambles+Artemisia carvifolia+Artemisia scoparia | S7 | ||||
荆条+玉米秸秆 Brambles+corn stalk | L8 | ||||||
编号 Code | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
序列数 Sequence number | 平均长度 Mean length/bp | OTU数量 OTUs | 序列数 Sequence number | 平均长度 Mean length/bp | OTU数量 OTUs | |
| B1 | 54 127 | 448.16 | 292 | 50 889 | 401.78 | 54 |
| B2 | 45 339 | 445.92 | 235 | 31 566 | 401.99 | 11 |
| B3 | 59 896 | 450.85 | 64 | 36 785 | 402.10 | 41 |
| B4 | 58 767 | 434.36 | 232 | 65 896 | 402.63 | 69 |
| B5 | 41 921 | 448.20 | 264 | 42 419 | 402.20 | 45 |
| L1 | 44 637 | 435.25 | 379 | 42 501 | 398.09 | 44 |
| L2 | 34 370 | 449.50 | 115 | 41 111 | 398.00 | 7 |
| L3 | 59 808 | 444.56 | 102 | 55 052 | 398.29 | 17 |
| L4 | 49 213 | 435.07 | 467 | 49 736 | 400.26 | 30 |
| L5 | 38 827 | 449.33 | 134 | 34 707 | 398.04 | 13 |
| L6 | 38 648 | 444.43 | 61 | 41 150 | 398.07 | 15 |
| L7 | 40 617 | 442.87 | 121 | 32 573 | 398.03 | 11 |
| L8 | 38 824 | 444.91 | 126 | 35 894 | 398.08 | 9 |
| S1 | 43 249 | 434.90 | 1 015 | 53 247 | 402.61 | 61 |
| S2 | 46 600 | 436.57 | 1 033 | 50 273 | 402.59 | 58 |
| S3 | 51 527 | 435.70 | 1 295 | 57 481 | 400.93 | 93 |
| S4 | 73 188 | 437.07 | 1 400 | 70 842 | 401.98 | 85 |
| S5 | 74 416 | 438.68 | 1 378 | 50 649 | 401.85 | 70 |
| S6 | 54 569 | 436.93 | 1 339 | 46 578 | 401.40 | 81 |
| S7 | 74 735 | 438.42 | 1 474 | 61 107 | 402.13 | 84 |
表2 不同农用酵素的高通量测序数据
Table 2 High-throughput sequencing data of different Jiaosu for agriculture
编号 Code | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
序列数 Sequence number | 平均长度 Mean length/bp | OTU数量 OTUs | 序列数 Sequence number | 平均长度 Mean length/bp | OTU数量 OTUs | |
| B1 | 54 127 | 448.16 | 292 | 50 889 | 401.78 | 54 |
| B2 | 45 339 | 445.92 | 235 | 31 566 | 401.99 | 11 |
| B3 | 59 896 | 450.85 | 64 | 36 785 | 402.10 | 41 |
| B4 | 58 767 | 434.36 | 232 | 65 896 | 402.63 | 69 |
| B5 | 41 921 | 448.20 | 264 | 42 419 | 402.20 | 45 |
| L1 | 44 637 | 435.25 | 379 | 42 501 | 398.09 | 44 |
| L2 | 34 370 | 449.50 | 115 | 41 111 | 398.00 | 7 |
| L3 | 59 808 | 444.56 | 102 | 55 052 | 398.29 | 17 |
| L4 | 49 213 | 435.07 | 467 | 49 736 | 400.26 | 30 |
| L5 | 38 827 | 449.33 | 134 | 34 707 | 398.04 | 13 |
| L6 | 38 648 | 444.43 | 61 | 41 150 | 398.07 | 15 |
| L7 | 40 617 | 442.87 | 121 | 32 573 | 398.03 | 11 |
| L8 | 38 824 | 444.91 | 126 | 35 894 | 398.08 | 9 |
| S1 | 43 249 | 434.90 | 1 015 | 53 247 | 402.61 | 61 |
| S2 | 46 600 | 436.57 | 1 033 | 50 273 | 402.59 | 58 |
| S3 | 51 527 | 435.70 | 1 295 | 57 481 | 400.93 | 93 |
| S4 | 73 188 | 437.07 | 1 400 | 70 842 | 401.98 | 85 |
| S5 | 74 416 | 438.68 | 1 378 | 50 649 | 401.85 | 70 |
| S6 | 54 569 | 436.93 | 1 339 | 46 578 | 401.40 | 81 |
| S7 | 74 735 | 438.42 | 1 474 | 61 107 | 402.13 | 84 |
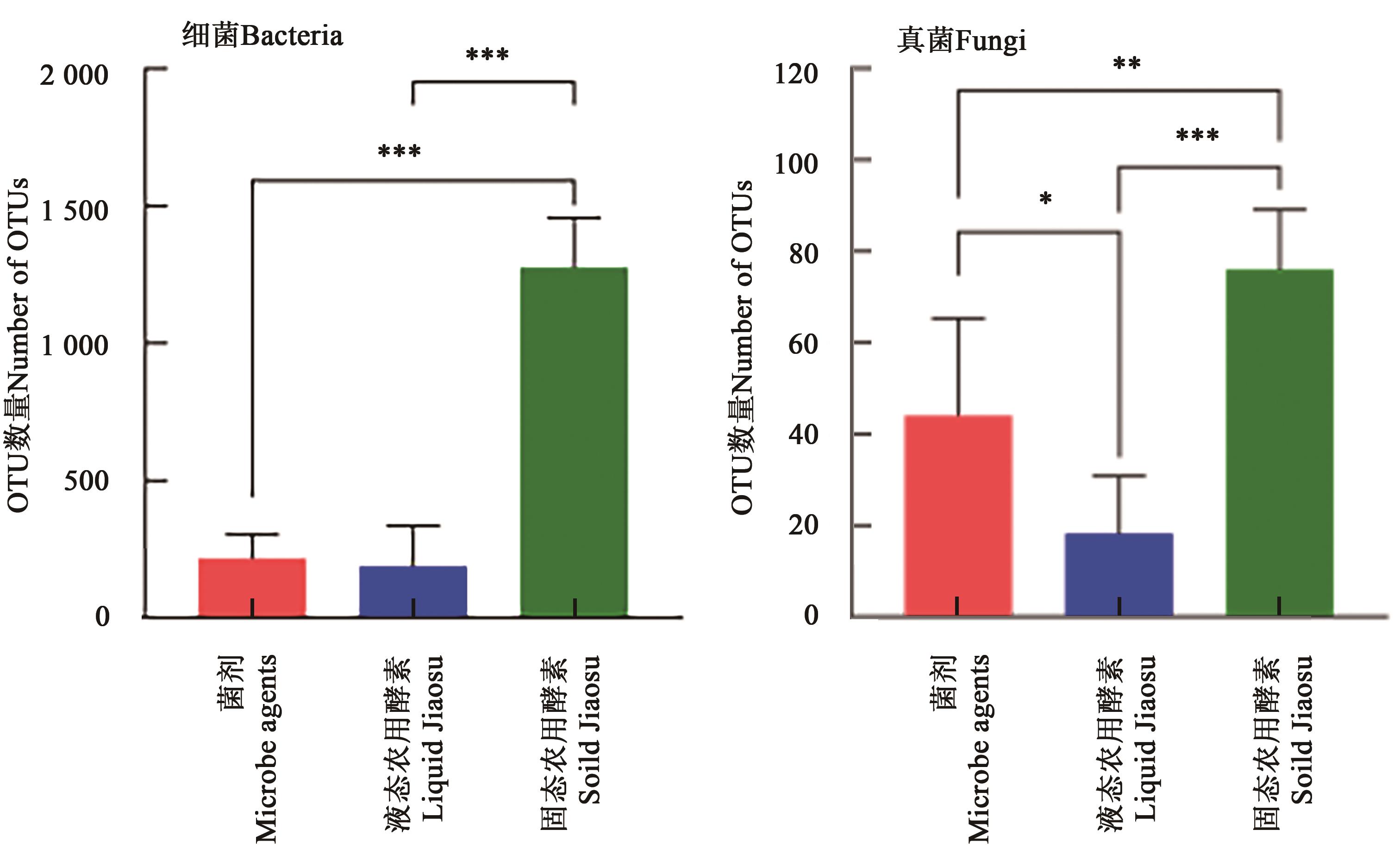
图3 不同剂型的农用酵素的OTU数量注:*、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Number of OTUs of different dosage forms of Jiaosu for agricultureNote: *, ** and *** mean significant differences at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
| 编号 Number | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao 1 | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao 1 | |
| B1 | 2.40 | 0.223 3 | 467 | 404 | 1.68 | 0.275 7 | 59 | 56 |
| B2 | 2.51 | 0.241 6 | 239 | 239 | 0.09 | 0.972 1 | 11 | 11 |
| B3 | 0.23 | 0.927 8 | 140 | 102 | 1.43 | 0.396 0 | 43 | 44 |
| B4 | 3.41 | 0.110 7 | 261 | 279 | 1.53 | 0.451 1 | 75 | 73 |
| B5 | 2.31 | 0.234 8 | 493 | 394 | 1.67 | 0.303 3 | 48 | 47 |
| L1 | 3.42 | 0.059 2 | 716 | 583 | 0.73 | 0.587 5 | 48 | 46 |
| L2 | 0.88 | 0.605 1 | 193 | 156 | 0.04 | 0.989 9 | 7 | 7 |
| L3 | 2.49 | 0.133 1 | 305 | 181 | 0.91 | 0.451 4 | 18 | 19 |
| L4 | 4.37 | 0.055 7 | 504 | 520 | 0.82 | 0.642 6 | 35 | 35 |
| L5 | 1.93 | 0.222 4 | 173 | 166 | 0.59 | 0.671 3 | 15 | 13 |
| L6 | 1.07 | 0.599 2 | 99 | 95 | 0.43 | 0.802 7 | 16 | 16 |
| L7 | 2.22 | 0.279 7 | 156 | 159 | 0.11 | 0.967 3 | 12 | 11 |
| L8 | 1.21 | 0.593 3 | 151 | 159 | 0.23 | 0.919 7 | 11 | 10 |
| S1 | 5.54 | 0.008 6 | 1167 | 1210 | 1.55 | 0.344 0 | 73 | 72 |
| S2 | 5.47 | 0.010 9 | 1199 | 1208 | 1.61 | 0.314 9 | 78 | 75 |
| S3 | 6.08 | 0.005 2 | 1455 | 1488 | 2.67 | 0.115 2 | 98 | 100 |
| S4 | 5.61 | 0.017 3 | 1548 | 1572 | 2.25 | 0.163 1 | 88 | 87 |
| S5 | 5.17 | 0.050 4 | 1556 | 1573 | 2.20 | 0.158 3 | 81 | 90 |
| S6 | 5.55 | 0.012 1 | 1488 | 1522 | 2.37 | 0.146 9 | 92 | 92 |
| S7 | 5.50 | 0.028 5 | 1605 | 1617 | 2.24 | 0.178 9 | 89 | 88 |
表3 不同农用酵素的多样性指数
Table 3 Diversity index of different Jiaosu for agriculture
| 编号 Number | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao 1 | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao 1 | |
| B1 | 2.40 | 0.223 3 | 467 | 404 | 1.68 | 0.275 7 | 59 | 56 |
| B2 | 2.51 | 0.241 6 | 239 | 239 | 0.09 | 0.972 1 | 11 | 11 |
| B3 | 0.23 | 0.927 8 | 140 | 102 | 1.43 | 0.396 0 | 43 | 44 |
| B4 | 3.41 | 0.110 7 | 261 | 279 | 1.53 | 0.451 1 | 75 | 73 |
| B5 | 2.31 | 0.234 8 | 493 | 394 | 1.67 | 0.303 3 | 48 | 47 |
| L1 | 3.42 | 0.059 2 | 716 | 583 | 0.73 | 0.587 5 | 48 | 46 |
| L2 | 0.88 | 0.605 1 | 193 | 156 | 0.04 | 0.989 9 | 7 | 7 |
| L3 | 2.49 | 0.133 1 | 305 | 181 | 0.91 | 0.451 4 | 18 | 19 |
| L4 | 4.37 | 0.055 7 | 504 | 520 | 0.82 | 0.642 6 | 35 | 35 |
| L5 | 1.93 | 0.222 4 | 173 | 166 | 0.59 | 0.671 3 | 15 | 13 |
| L6 | 1.07 | 0.599 2 | 99 | 95 | 0.43 | 0.802 7 | 16 | 16 |
| L7 | 2.22 | 0.279 7 | 156 | 159 | 0.11 | 0.967 3 | 12 | 11 |
| L8 | 1.21 | 0.593 3 | 151 | 159 | 0.23 | 0.919 7 | 11 | 10 |
| S1 | 5.54 | 0.008 6 | 1167 | 1210 | 1.55 | 0.344 0 | 73 | 72 |
| S2 | 5.47 | 0.010 9 | 1199 | 1208 | 1.61 | 0.314 9 | 78 | 75 |
| S3 | 6.08 | 0.005 2 | 1455 | 1488 | 2.67 | 0.115 2 | 98 | 100 |
| S4 | 5.61 | 0.017 3 | 1548 | 1572 | 2.25 | 0.163 1 | 88 | 87 |
| S5 | 5.17 | 0.050 4 | 1556 | 1573 | 2.20 | 0.158 3 | 81 | 90 |
| S6 | 5.55 | 0.012 1 | 1488 | 1522 | 2.37 | 0.146 9 | 92 | 92 |
| S7 | 5.50 | 0.028 5 | 1605 | 1617 | 2.24 | 0.178 9 | 89 | 88 |
| 1 | KANG H Z, YU W J, DUTTA S, et al.. Soil microbial community composition and function are closely associated with soil organic matter chemistry along a latitudinal gradient [J/OL]. Geoderma, 2021, 383:114744 [2021-01-08]. . |
| 2 | COMER J, PERKINS L. Resistance of the soil microbial community to land-surface disturbances of high-intensity winter grazing and wildfire [J/OL]. J. Environ. Manage., 2021, 279:111596 [2021-01-13]. . |
| 3 | LARKIN R P. Relative effects of biological amendments and crop rotations on soil microbial communities and soilborne diseases of potato [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2008, 40(6):1341-1351. |
| 4 | LIU W X, WANG Q L, WANG B Z, et al.. Changes in the abundance and structure of bacterial communities under long-term fertilization treatments in a peanut monocropping system [J]. Plant Soil, 2015, 395(1):415-427. |
| 5 | CARRARA J E, WALTER C A, HAWKINS J S, et al.. Interactions among plants, bacteria, and fungi reduce extracellular enzyme activities under long-term N fertilization [J]. Global Change Biol., 2018, 24(6):2721-2734. |
| 6 | WANG J X, LU X N, ZHANG J E, et al.. Intercropping perennial aquatic plants with rice improved paddy field soil microbial biomass, biomass carbon and biomass nitrogen to facilitate soil sustainability [J/OL]. Soil Till. Res., 2021, 208:104908 [2021-01-06]. . |
| 7 | SAMUEL O D, GRACE A O. Improving soil fertility and performance of tomato plant using the anaerobic digestate of tithonia diversifolia as Bio-fertilizer [J/OL]. IOP Conference Series: Earth Environ. Sci., 2018, 210(1): 012014 [2021-01-08]. . |
| 8 | ZHAO Q Y, DONG C X, YANG X M, et al.. Biocontrol of Fusarium wilt disease for Cucumis melo melon using bio-organic fertilizer [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2011, 47(1):67-75. |
| 9 | AI-SAYED H M, HEGAB S A, YOUSSEF M A, et al.. Evaluation of quality and growth of roselle ( Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) as affected by bio-fertilizers [J]. J. Plant Nutr., 2020, 43(7):1-11. |
| 10 | GENG Y J, WANG J Y, SUN Z R, et al.. Soil N-oxide emissions decrease from intensive greenhouse vegetable fields by substituting synthetic N fertilizer with organic and bio-organic fertilizers [J/OL]. Geoderma, 2021, 383: 114730 [2021-01-08]. . |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 植物酵素: [S].北京:中国轻工业出版社,2018. |
| 12 | 马倩颖.浅析环保酵素在家居和农业上的应用[J].科技风,2018(5):150. |
| 13 | 侯乾.连作马铃薯全生育期根际微生物多样性研究及施肥对其的影响[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2020. |
| HOU Q. The rhizosphere microbial diversity during the growth period of continuous cropping potato and the effect of fertilization [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. | |
| 14 | 范鹤龄,王浩晨,陈伟益,等.酵素对热区土壤理化性状和作物生长的影响[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(22):76-83. |
| FAN H L, WANG H C, CHEN W Y, et al.. Effects of Jiaosu on soil physical and chemical properties and crop growth in tropical region [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021, 37(22):76-83. | |
| 15 | 范鹤龄,陆建明,孙雪冰,等.酵素堆肥对海南冬季辣椒生长的影响[J].中国瓜菜,2022,35(3):70-75. |
| FAN H L, LU J M, SHUN X B, et al.. Effect of microbe compost on pepper growth during winter season in Hainan [J]. China Cucurbits Veget., 2022, 35(3):70-75. | |
| 16 | 岛本邦彦.岛本微生物农业应用法[M].郑重,译.日本磐亚株式会社,1996:23-45. |
| 17 | AMATO K R, YEOMAN C J, KENT A, et al.. Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes [J]. SME J., 2013, 7(7):1344-1353. |
| 18 | 王宁,刘铜,靳亚忠,等.木霉菌对土壤微生物多样性及草莓生长和发病的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2018,46(18):108-112. |
| WANG N, LIU T, JIN Y Z . et al .. Effects of Trichoderma spp. on soil microbial diversity and growth and morbidity of strawberry [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2018, 46(18):108-112. | |
| 19 | CHEN C, LIU B Y. Changes in major components of tea fungus metabolites during prolonged fermentation [J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 2000, 89(5):834-839. |
| 20 | ZHANG Y, GAO Y H, ZHANG Z H, et al.. A microbial ecosystem: agricultural Jiaosu achieves effective and lasting antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea. [J]. AMB Express, 2020, 10(1):216-228. |
| 21 | TAO C Y, LI R, XIONG W, et al.. Bio-organic fertilizers stimulate indigenous soil Pseudomonas populations to enhance plant disease suppression [J]. Microbiome, 2020, 8(1):137-148. |
| 22 | ZHANG H, HUA Z W, LIANG W Z, et al.. The prevention of bio-organic fertilizer fermented from cow manure compost by Bacillus sp. XG-1 on watermelon continuous cropping barrier [J]. Internat. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2020, 17(16):5714-5726. |
| 23 | LU P N, BAINARD L D, MA B, et al.. Bio-fertilizer and rotten straw amendments alter the rhizosphere bacterial community and increase oat productivity in a saline-alkaline environment. [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1):19896 [2021-11-16]. . |
| 24 | AZMAT A, YASMIN H, HASSAN M N, et al.. Co-application of bio-fertilizer and salicylic acid improves growth, photosynthetic pigments and stress tolerance in wheat under drought stress. [J/OL]. Peer J., 2020, 8:e9960 [2021-10-27]. . |
| 25 | 张宇冲,何思蓓,高灵会,等.生物有机肥对芦笋土壤酶活性及细菌群落的影响[J].北方园艺, 2019(12):83-91. |
| ZHANG Y C, HE S B, GAO L H, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on enzyme activity and soil bacterial community in Asparagus cultivated soil [J]. Northern Hortic., 2019(12):83-91. |
| [1] | 闫宁, 战宇, 苗馨月, 王二刚, 陈长宝, 李琼. 强还原土壤灭菌处理对人参连作土壤细菌群落结构及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [2] | 李洁, 林莹, 徐美玉, 王飞, 徐凌川. 泰山白首乌根际土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 70-81. |
| [3] | 赵宏岩, 谭君伟, 张杰, 陈浩楠, 王春旭, 赵地, 李海鹏, 朱李霞, 韩毅强. 小豆和绿豆茎基感病部位真菌群落结构研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 129-136. |
| [4] | 魏艳晨, 陈吉祥, 王永刚, 孟彤彤, 韩亚龙, 李美. 荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [5] | 苏雨萌§,张旭婷§,特日格乐,田敏,尚晓蕊,李国婧,王瑞刚*. 高通量测序鉴定中间锦鸡儿干旱条件下的microRNA[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 51-57. |
| [6] | 刘璐1,名晓东1,张晓艳2,郝俊杰2,付丽平1,王乾坤1,吕鑫1,陈旺1,刘全兰1*. 高通量测序分析蚕豆种子内生细菌的多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 73-80. |
| [7] | 张磊, 罗泽华, 杨明川, 李世贵, 辛玉华, 蔡斌, 刘好宝, 曾代龙, 顾金刚, 段碧华. 雪茄烟叶原料发酵微生物多样性及酶活变化研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 171-180. |
| [8] | 刘倩1,2,李纪潮1,左应梅1,杨天梅1,杨美权1,张金渝*. 有机覆盖三七对土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 162-175. |
| [9] | 杨晶晶,张青青*,吐尔逊娜依·热依木,阿马努拉·依明尼亚孜,雪热提江·麦提努日. 游牧和定居对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤真菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 166-173. |
| [10] | 史芳芳,李向泉*. 葡萄根际土壤真菌群落多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(7): 47-58. |
| [11] | 张艺洁,邵惠芳*,张珂,贾宏昉,黄五星,韩丹. 基于高通量测序研究施肥对连作植烟土壤环境及微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(5): 16-25. |
| [12] | 曲梦楠1,2§,蒋炳军2§,刘薇2,毛婷婷2,马立明2,林抗雪2,韩天富1,2*. 大豆分子育种研究新进展[J]. , 2014, 16(3): 8-13. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号