




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 169-176.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0768
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lijuan HE1( ), Zhongju MENG1(
), Zhongju MENG1( ), Xiaohong DANG1, Tao LYU2
), Xiaohong DANG1, Tao LYU2
Received:2020-09-02
Accepted:2020-12-25
Online:2022-02-15
Published:2022-02-22
Contact:
Zhongju MENG
通讯作者:
蒙仲举
作者简介:何丽娟 E-mail: 1324625814@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lijuan HE, Zhongju MENG, Xiaohong DANG, Tao LYU. Effects of Planting Glycyrrhizauralensis on Mechanical Composition and Nutrients of Aeolian Sandy Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 169-176.
何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176.
土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 样地 Experimental plot | 黏粒 Clay/% | 粉沙 Silt/% | 极细沙 Very fine sand/% | 细沙 Fine sand/% | 中沙 Medium sand/% | 粗沙 Coarse sand/% | 极粗沙 Very coarse sand/% | 砾石 Gravel/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—5 | CK | 2.88±0.43 b | 0.87±0.05 c | 0.08±0.01 b | 73.35±1.87 a | 10.52±1.00 b | 9.79±0.26 a | 1.75±0.08 a | 0.13±0.02 a |
| T1 | 2.95±0.25 b | 1.95±0.15 b | 0.20±0.05 b | 74.21±4.20 a | 11.66±0.42 a | 7.70±0.55 b | 1.07±0.05b | 0.09±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 4.55±0.64 b | 2.22±0.13 b | 0.54±0.01 b | 79.85±7.60 a | 8.42±0.39 c | 3.09±0.08 c | 1.05±0.47 b | 0.03±0.00 c | |
| T3 | 6.62±1.75 a | 4.88±1.06 a | 2.05±1.03 a | 77.07±3.17 a | 7.32±0.13 d | 1.67±0.41 d | 0.99±0.28 b | 0.00 c | |
| 5—10 | CK | 2.22±0.67 b | 0.14±0.01 c | 0.10±0.02 b | 78.83±1.26 a | 7.96±0.27 ab | 8.14±1.08 b | 1.82±0.29 a | 0.08±0.01 a |
| T1 | 2.22±1.13 b | 1.53±0.03 b | 0.20±0.07 b | 77.65±0.54 a | 7.59±0.39 b | 9.63±0.36 a | 1.15±0.03 b | 0.05±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 3.64±0.05 b | 1.79±0.41 b | 0.62±0.11 b | 79.85±8.66 a | 8.57±0.11 a | 3.49±0.51 c | 1.14±0.09 b | 0.03±0.01 c | |
| T3 | 5.51±0.58 a | 4.52±1.02 a | 3.93±1.08 a | 74.98±6.38 a | 8.14±0.41 ab | 1.68±0.27 d | 1.04±0.05 b | 0.00 c | |
| 10—15 | CK | 1.69±0.59 b | 0.34±0.03 c | 0.10±0.02 b | 78.23±0.73 a | 9.24±0.33 b | 8.01±1.01 a | 1.66±0.07 a | 0.14±0.02 a |
| T1 | 2.29±0.29 b | 1.99±0.09 b | 0.21±0.04 b | 75.26±2.84 a | 14.39±0.73 a | 7.55±0.01 a | 1.29±0.09 b | 0.03±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 3.02±0.6 ab | 2.03±0.32 b | 0.77±0.15 b | 82.49±5.33 a | 7.02±1.01 c | 2.68±0.07 b | 1.79±0.03 a | 0.03±0.01 b | |
| T3 | 4.63±1.61 a | 4.43±0.10 a | 4.05±0.95 a | 76.12±2.45 a | 7.15±0.04 c | 1.17±0.12 c | 1.75±0.03 a | 0.00 b | |
| 15—20 | CK | 1.99±0.05 c | 0.11±0.01 d | 0.14±0.03 b | 78.49±0.69 a | 9.00±0.33 b | 7.80±1.24 a | 1.96±0.07 a | 0.11±0.01 a |
| T1 | 2.21±0.07 c | 1.62±0.21 c | 0.23±0.02 b | 77.23±1.15 a | 10.21±0.76 a | 7.32±0.36 a | 1.19±0.18 b | 0.05±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 3.29±0.46 b | 2.00±0.11 b | 0.76±0.09 b | 82.00±7.13 a | 7.13±0.78 c | 2.96±0.09 b | 1.83±0.04 a | 0.03±0.00 c | |
| T3 | 4.35±0.31 a | 4.39±0.14 a | 4.14±0.58 a | 76.67±5.61 a | 7.29±0.05 c | 1.67±0.52 b | 1.41±0.15 b | 0.00 c | |
| 20—25 | CK | 0.98±0.98 c | 0.04±0.01 d | 0.17±0.05 b | 76.08±7.3 a | 10.46±0.85 a | 10.10±1.30 a | 1.95±2.42 a | 0.09±0.02 a |
| T1 | 1.84±0.92 b | 1.80±0.13 c | 0.24±0.02 b | 79.85±10.3 a | 8.49±0.99 b | 7.90±0.32 b | 1.66±3.1 b | 0.05±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 1.91±0.98 b | 2.32±0.26 b | 0.76±0.01 b | 83.67±4.05 a | 7.91±0.73 a | 2.41±0.05 bc | 1.03±0.74 c | 0.02±0.01 c | |
| T3 | 4.64±0.14 a | 4.35±0.97 a | 4.18±1.12 a | 75.84±0.46 a | 7.13±0.09 a | 1.69±0.00 c | 1.26±0.08 c | 0.00 c | |
| 25—30 | CK | 0.89±0.08 c | 0.53±0.08 d | 0.48±0.02 b | 75.01±1.29 a | 10.53±0.06 a | 10.43±0.37 a | 1.09±0.01 a | 0.36±0.07 a |
| T1 | 1.81±0.02 b | 1.68±0.14 c | 0.31±0.04 b | 78.09±1.39 a | 10.52±1.72 a | 5.18±0.98 b | 1.67±0.12 b | 0.05±0.02 b | |
| T2 | 1.96±0.27 b | 2.15±0.04 b | 0.78±0.08 b | 84.27±7.91 a | 7.45±0.25 b | 2.05±0.03 c | 1.30±0.04 c | 0.02±0.01 b | |
| T3 | 4.86±0.13 a | 4.34±0.27 a | 4.20±0.43 a | 75.81±4.84 a | 7.03±0.01 b | 2.36±0.20 c | 0.91±0.01 d | 0.00 b |
Table 1 Mechanical composition of licorice soil
土层深度 Soil depth/cm | 样地 Experimental plot | 黏粒 Clay/% | 粉沙 Silt/% | 极细沙 Very fine sand/% | 细沙 Fine sand/% | 中沙 Medium sand/% | 粗沙 Coarse sand/% | 极粗沙 Very coarse sand/% | 砾石 Gravel/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—5 | CK | 2.88±0.43 b | 0.87±0.05 c | 0.08±0.01 b | 73.35±1.87 a | 10.52±1.00 b | 9.79±0.26 a | 1.75±0.08 a | 0.13±0.02 a |
| T1 | 2.95±0.25 b | 1.95±0.15 b | 0.20±0.05 b | 74.21±4.20 a | 11.66±0.42 a | 7.70±0.55 b | 1.07±0.05b | 0.09±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 4.55±0.64 b | 2.22±0.13 b | 0.54±0.01 b | 79.85±7.60 a | 8.42±0.39 c | 3.09±0.08 c | 1.05±0.47 b | 0.03±0.00 c | |
| T3 | 6.62±1.75 a | 4.88±1.06 a | 2.05±1.03 a | 77.07±3.17 a | 7.32±0.13 d | 1.67±0.41 d | 0.99±0.28 b | 0.00 c | |
| 5—10 | CK | 2.22±0.67 b | 0.14±0.01 c | 0.10±0.02 b | 78.83±1.26 a | 7.96±0.27 ab | 8.14±1.08 b | 1.82±0.29 a | 0.08±0.01 a |
| T1 | 2.22±1.13 b | 1.53±0.03 b | 0.20±0.07 b | 77.65±0.54 a | 7.59±0.39 b | 9.63±0.36 a | 1.15±0.03 b | 0.05±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 3.64±0.05 b | 1.79±0.41 b | 0.62±0.11 b | 79.85±8.66 a | 8.57±0.11 a | 3.49±0.51 c | 1.14±0.09 b | 0.03±0.01 c | |
| T3 | 5.51±0.58 a | 4.52±1.02 a | 3.93±1.08 a | 74.98±6.38 a | 8.14±0.41 ab | 1.68±0.27 d | 1.04±0.05 b | 0.00 c | |
| 10—15 | CK | 1.69±0.59 b | 0.34±0.03 c | 0.10±0.02 b | 78.23±0.73 a | 9.24±0.33 b | 8.01±1.01 a | 1.66±0.07 a | 0.14±0.02 a |
| T1 | 2.29±0.29 b | 1.99±0.09 b | 0.21±0.04 b | 75.26±2.84 a | 14.39±0.73 a | 7.55±0.01 a | 1.29±0.09 b | 0.03±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 3.02±0.6 ab | 2.03±0.32 b | 0.77±0.15 b | 82.49±5.33 a | 7.02±1.01 c | 2.68±0.07 b | 1.79±0.03 a | 0.03±0.01 b | |
| T3 | 4.63±1.61 a | 4.43±0.10 a | 4.05±0.95 a | 76.12±2.45 a | 7.15±0.04 c | 1.17±0.12 c | 1.75±0.03 a | 0.00 b | |
| 15—20 | CK | 1.99±0.05 c | 0.11±0.01 d | 0.14±0.03 b | 78.49±0.69 a | 9.00±0.33 b | 7.80±1.24 a | 1.96±0.07 a | 0.11±0.01 a |
| T1 | 2.21±0.07 c | 1.62±0.21 c | 0.23±0.02 b | 77.23±1.15 a | 10.21±0.76 a | 7.32±0.36 a | 1.19±0.18 b | 0.05±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 3.29±0.46 b | 2.00±0.11 b | 0.76±0.09 b | 82.00±7.13 a | 7.13±0.78 c | 2.96±0.09 b | 1.83±0.04 a | 0.03±0.00 c | |
| T3 | 4.35±0.31 a | 4.39±0.14 a | 4.14±0.58 a | 76.67±5.61 a | 7.29±0.05 c | 1.67±0.52 b | 1.41±0.15 b | 0.00 c | |
| 20—25 | CK | 0.98±0.98 c | 0.04±0.01 d | 0.17±0.05 b | 76.08±7.3 a | 10.46±0.85 a | 10.10±1.30 a | 1.95±2.42 a | 0.09±0.02 a |
| T1 | 1.84±0.92 b | 1.80±0.13 c | 0.24±0.02 b | 79.85±10.3 a | 8.49±0.99 b | 7.90±0.32 b | 1.66±3.1 b | 0.05±0.01 b | |
| T2 | 1.91±0.98 b | 2.32±0.26 b | 0.76±0.01 b | 83.67±4.05 a | 7.91±0.73 a | 2.41±0.05 bc | 1.03±0.74 c | 0.02±0.01 c | |
| T3 | 4.64±0.14 a | 4.35±0.97 a | 4.18±1.12 a | 75.84±0.46 a | 7.13±0.09 a | 1.69±0.00 c | 1.26±0.08 c | 0.00 c | |
| 25—30 | CK | 0.89±0.08 c | 0.53±0.08 d | 0.48±0.02 b | 75.01±1.29 a | 10.53±0.06 a | 10.43±0.37 a | 1.09±0.01 a | 0.36±0.07 a |
| T1 | 1.81±0.02 b | 1.68±0.14 c | 0.31±0.04 b | 78.09±1.39 a | 10.52±1.72 a | 5.18±0.98 b | 1.67±0.12 b | 0.05±0.02 b | |
| T2 | 1.96±0.27 b | 2.15±0.04 b | 0.78±0.08 b | 84.27±7.91 a | 7.45±0.25 b | 2.05±0.03 c | 1.30±0.04 c | 0.02±0.01 b | |
| T3 | 4.86±0.13 a | 4.34±0.27 a | 4.20±0.43 a | 75.81±4.84 a | 7.03±0.01 b | 2.36±0.20 c | 0.91±0.01 d | 0.00 b |
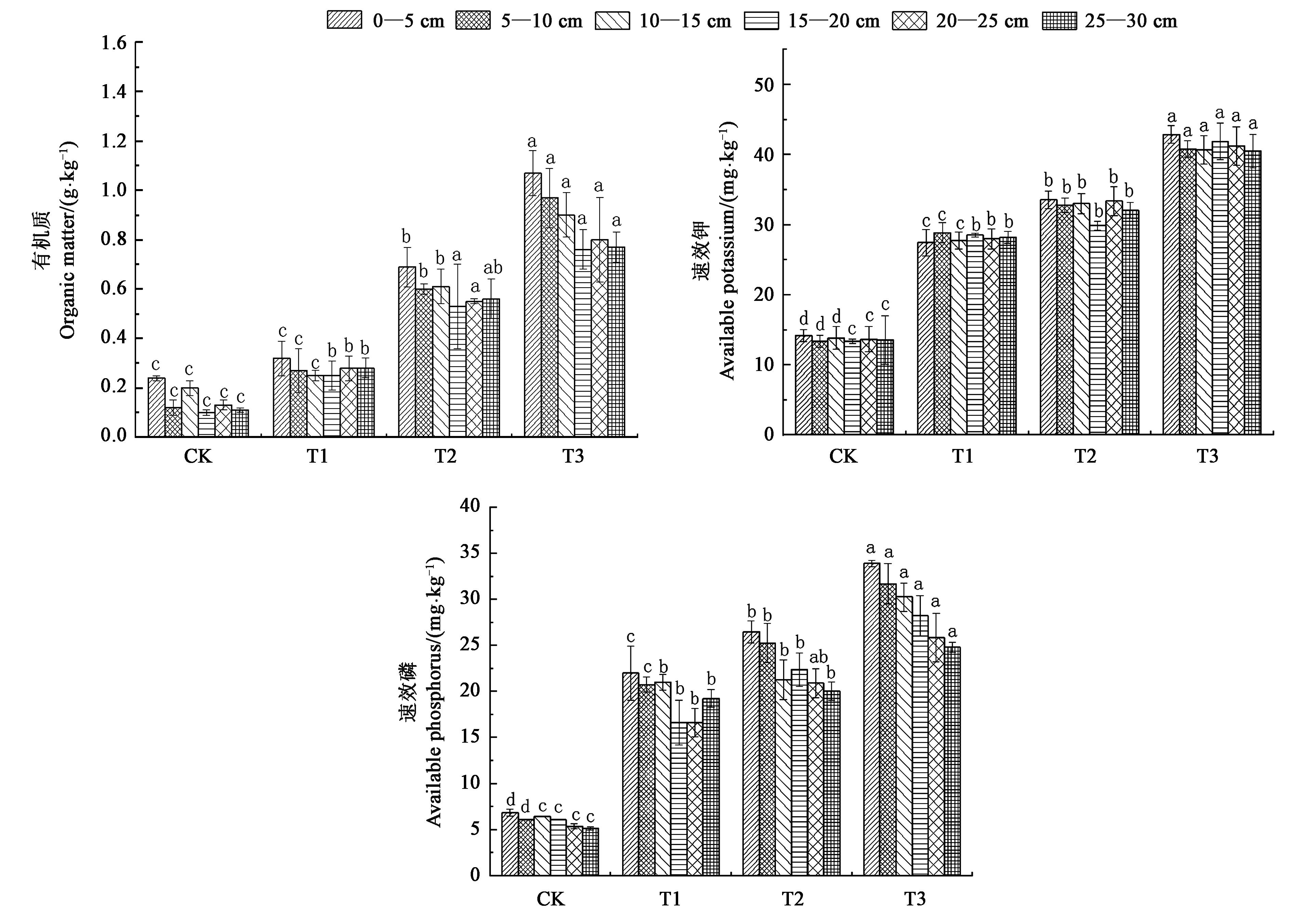
Fig.1 Soil nutrient content in different plotsNote: Different small letters at the same soil layer indicate significant difference between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 指标 Index | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter/% | 0—5 | 133 c | 288 b | 446 a |
| 5—10 | 225 c | 500 b | 808 a | |
| 10—15 | 125 c | 305 b | 450 a | |
| 15—20 | 200 c | 530 a | 760 a | |
| 20—25 | 138 c | 423 a | 615 a | |
| 25—30 | 136 c | 509 ab | 700 a | |
速效钾 Available potassium/% | 0—5 | 194 c | 237 b | 303 a |
| 5—10 | 216 c | 245 b | 305 a | |
| 10—15 | 201 c | 239 b | 295 a | |
| 15—20 | 213 b | 223 b | 313 a | |
| 20—25 | 205 b | 245 b | 302 a | |
| 25—30 | 208 b | 237 b | 299 a | |
速效磷 Available phosphorus/% | 0—5 | 322 c | 388 b | 497 a |
| 5—10 | 342 c | 417 b | 523 a | |
| 10—15 | 328 b | 333 b | 473 a | |
| 15—20 | 274 b | 369 b | 466 a | |
| 20—25 | 310 b | 391 ab | 483 a | |
| 25—30 | 377 b | 393 b | 486 a |
Table 2 Soil enrichment in different licorice plots
| 指标 Index | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter/% | 0—5 | 133 c | 288 b | 446 a |
| 5—10 | 225 c | 500 b | 808 a | |
| 10—15 | 125 c | 305 b | 450 a | |
| 15—20 | 200 c | 530 a | 760 a | |
| 20—25 | 138 c | 423 a | 615 a | |
| 25—30 | 136 c | 509 ab | 700 a | |
速效钾 Available potassium/% | 0—5 | 194 c | 237 b | 303 a |
| 5—10 | 216 c | 245 b | 305 a | |
| 10—15 | 201 c | 239 b | 295 a | |
| 15—20 | 213 b | 223 b | 313 a | |
| 20—25 | 205 b | 245 b | 302 a | |
| 25—30 | 208 b | 237 b | 299 a | |
速效磷 Available phosphorus/% | 0—5 | 322 c | 388 b | 497 a |
| 5—10 | 342 c | 417 b | 523 a | |
| 10—15 | 328 b | 333 b | 473 a | |
| 15—20 | 274 b | 369 b | 466 a | |
| 20—25 | 310 b | 391 ab | 483 a | |
| 25—30 | 377 b | 393 b | 486 a |
| 指标 Index | 黏粒 Clay | 粉沙 Silt | 极细沙 Very fine sand | 细沙 Fine sand | 中沙 Medium sand | 粗沙 Coarse sand | 极粗沙 Very coarse sand | 砾石Gravel | 有机质 Organic matter | 速效钾 Available potassium | 速效磷 Available phosphorus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黏粒Clay | 1 | ||||||||||
| 粉沙Silt | 0.987* | 1 | |||||||||
| 极细沙Very fine sand | 0.966* | 0.959* | 1 | ||||||||
| 细沙Fine sand | 0.485 | 0.502 | 0.252 | 1 | |||||||
| 中沙Medium sand | -0.969* | -0.916 | -0.925 | -0.442 | 1 | ||||||
| 粗沙Coarse sand | -0.902 | -0.866 | -0.761 | -0.768 | 0.913 | 1 | |||||
| 极粗沙Very coarse sand | -0.859 | -0.874 | -0.71 | -0.859 | 0.795 | 0.948 | 1 | ||||
| 砾石Gravel | -0.905 | -0.886 | -0.764 | -0.797 | 0.892 | 0.995** | 0.975* | 1 | |||
| 有机质Organic matter | 0.999** | 0.992** | 0.959* | 0.515 | -0.958* | -0.907 | -0.878 | -0.914 | 1 | ||
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 0.991** | 0.979* | 0.992** | 0.366 | -0.957* | -0.838 | -0.786 | -0.839 | 0.986* | 1 | |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.990** | 0.957* | 0.968* | 0.715 | -0.944* | -0.876 | -0.818 | -0.916 | 0.925 | 0.864 | 1 |
Table 3 Relationship between soil mechanical composition and nutrients under licorice vegetation
| 指标 Index | 黏粒 Clay | 粉沙 Silt | 极细沙 Very fine sand | 细沙 Fine sand | 中沙 Medium sand | 粗沙 Coarse sand | 极粗沙 Very coarse sand | 砾石Gravel | 有机质 Organic matter | 速效钾 Available potassium | 速效磷 Available phosphorus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黏粒Clay | 1 | ||||||||||
| 粉沙Silt | 0.987* | 1 | |||||||||
| 极细沙Very fine sand | 0.966* | 0.959* | 1 | ||||||||
| 细沙Fine sand | 0.485 | 0.502 | 0.252 | 1 | |||||||
| 中沙Medium sand | -0.969* | -0.916 | -0.925 | -0.442 | 1 | ||||||
| 粗沙Coarse sand | -0.902 | -0.866 | -0.761 | -0.768 | 0.913 | 1 | |||||
| 极粗沙Very coarse sand | -0.859 | -0.874 | -0.71 | -0.859 | 0.795 | 0.948 | 1 | ||||
| 砾石Gravel | -0.905 | -0.886 | -0.764 | -0.797 | 0.892 | 0.995** | 0.975* | 1 | |||
| 有机质Organic matter | 0.999** | 0.992** | 0.959* | 0.515 | -0.958* | -0.907 | -0.878 | -0.914 | 1 | ||
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 0.991** | 0.979* | 0.992** | 0.366 | -0.957* | -0.838 | -0.786 | -0.839 | 0.986* | 1 | |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.990** | 0.957* | 0.968* | 0.715 | -0.944* | -0.876 | -0.818 | -0.916 | 0.925 | 0.864 | 1 |
| 颗粒 Particulate | 有机质Organic matter | 速效钾Available potassium | 速效磷Available phosphorus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合方程Fitting equation | R2 | 拟合方程Fitting equation | R2 | 拟合方程Fitting equation | R2 | |
| 黏粒Clay | Y=0.065X+0.026 | 0.996 | Y=24.379X+0.363 | 0.973 | Y=31.301X-0.411 | 0.984 |
| 粉沙Silt | Y=-0.167X+0.294 | 0.974 | Y=21.172X+4.119 | 0.937 | Y=4.789X+6.331 | 0.946 |
| 极细沙 Very fine sand | Y=0.268X+0.194 | 0.878 | Y=27.066X+2.848 | 0.976 | Y=10.317X+0.528 | 0.830 |
Table 4 Quantitative relationship between soil fine particulate matter and nutrients
| 颗粒 Particulate | 有机质Organic matter | 速效钾Available potassium | 速效磷Available phosphorus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合方程Fitting equation | R2 | 拟合方程Fitting equation | R2 | 拟合方程Fitting equation | R2 | |
| 黏粒Clay | Y=0.065X+0.026 | 0.996 | Y=24.379X+0.363 | 0.973 | Y=31.301X-0.411 | 0.984 |
| 粉沙Silt | Y=-0.167X+0.294 | 0.974 | Y=21.172X+4.119 | 0.937 | Y=4.789X+6.331 | 0.946 |
| 极细沙 Very fine sand | Y=0.268X+0.194 | 0.878 | Y=27.066X+2.848 | 0.976 | Y=10.317X+0.528 | 0.830 |
| 1 | MAURER T, HERRMANN L, STAHR K. Wind erosion characteristics of Sahelian surface types [J]. Earth Surf. Proc. Landforms, 2010, 35(12):1386-1401. |
| 2 | 移小勇,赵哈林,李玉强.土壤风蚀控制研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2007,18(4):905-911. |
| YI X Y, ZHAO H L, LI Y Q. Research progress on wind erosion control [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2007, 18(4):905-911. | |
| 3 | 毛东雷,雷加强,曾凡江,等.策勒绿洲-沙漠过渡带风沙活动强度的空间分布特征[J].水土保持学报,2013,27(2):13-19. |
| MAO D L, LEI J Q, ZENG F J, et al.. Spatial distribution characteristics of sand blown activities intensity on cele oasis-desert ecotone [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2013, 27(2):13-19. | |
| 4 | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会编.中国植物志第四十二卷第二分册[M].北京:科学出版社,1998:1-467. |
| 5 | 张志政.土壤深松对乌拉尔甘草(Glycyrrhizauralensis)产量品质和土壤环境的影响[D].新疆石河子:石河子大学,2017. |
| ZHANG Z Z. The effects of subsoiling on production and quality,soil environment of Glycyrrhizauralensis Fisch [D]. Xinjiang Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. | |
| 6 | 王玉庆,贺润喜.固沙植物甘草与土地荒漠化探析[J].中国生态农业学报,2004,12(3):194-195. |
| WANG Y Q, HE R X. Analysis on Glycyrrhizauralensis Fisch and soil desertification [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2004,12(3):194-195. | |
| 7 | 徐小涛,张国荣,赵全仁.甘草产业化开发前景不可估量[J].宁夏科技,2001(4):291. |
| 8 | 李昂,张鸣,陈映全,等.西北风蚀区种植甘草对农田土壤质地及碳、氮含量的影响[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(5):286-290,296. |
| LI A, ZHANG M, CHEN Y Q, et al.. Effects of Glycyrrhizauralensis plantation on soil texture and contents of soil carbon and nitrogen in wind erosion region of northwest China [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2016, 30(5):286-290,296. | |
| 9 | 叶丽娜,吕涛,张立欣,等.不同年龄甘草的生长特征及土壤理化性质分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(11):93-96,99. |
| YE L N, LYU T, ZHANG L X, et al.. Analysis of growth characteristics and physical and chemical properties of soil in different ages licorice [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(11):93-96,99. | |
| 10 | 郭彩贇,韩致文,钟帅,等.库布齐沙漠新材料沙障的风速廓线特征[J].水土保持通报,2017,37(5):260-265. |
| GUO C Y, HAN Z W, ZHONG S, et al.. Wind profile characteristics of new materials sand-barriers in Hobq desert [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2017,37(5):260-265. | |
| 11 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| 12 | 张继,姚健,丁兰,等.甘草的利用研究进展[J].草原与草坪,2000,(2):12-17. |
| ZHANG J, YAO J, DING L, et al.. Advancement of research on the utilization of Glycyrrhiza [J]. Grassland Turf, 2000, (2):12-17. | |
| 13 | YU Y J, LIN Q G, SHI Q H, et al.. Changes of habitat and vegetation in man-made vegetation area of Shapotou section along Baotou-Lanzhou railway [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2002,22(3):433-439. |
| 14 | TAN M L, DUAN Z H, CHEN X H. Study on soil property evolution in recovery process of moving sand land [J]. J. Desert Res., 2008, 28(4):685-689. |
| 15 | 苏永中,赵哈林,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地旱作农田土壤退化的过程和特征[J].水土保持学报,2002,16(1):25-28. |
| SU Y Z, ZHAO H L, ZHANG T H, et al.. Process and character of soil degradation of rainfed farmland in Horqin sandy land [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2002, 16(1):25-28. | |
| 16 | 王学芳,孙万仓,李孝泽,等.我国北方风蚀区冬油菜抗风蚀效果[J].生态学报,2009,29(12):6572-6577. |
| WANG X F, SUN W C, LI X Z, et al.. Wind erosion-resistance of fields planted with winter rapeseed in the wind erosion region of northern China [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2009, 29(12):6572-6577. | |
| 17 | 李昂,高天鹏,张鸣,等.西北风蚀区植被覆盖对土壤风蚀动态的影响[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(6):120-123. |
| LI A, GAO T P, ZHANG M, et al.. Influences of vegetation cover on dynamic changes of soil wind erosion in wind erosion region of northwest China [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2014, 28(6):120-123. | |
| 18 | 王仁德,邹学勇,赵婧研,等.北京市平原区农田土壤蚀积特征分析[J].水土保持学报,2011,25(1):20-24,29. |
| WANG R D, ZOU X Y, ZHAO J Y, et al.. Analysis on farmland soil erosion and deposition features in Beijing plain [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2011, 25(1):20-24,29. | |
| 19 | 闫玉春,王旭,杨桂霞,等.退化草地封育后土壤细颗粒增加机理探讨及研究展望[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(5):1162-1166. |
| YAN Y C, WANG X, YANG G X, et al.. Review on mechanism of fine soil particles increase in enclosed grassland [J]. J. Desert Res., 2011, 31(5):1162-1166. | |
| 20 | 张星杰,刘景辉,李立军,等.保护性耕作方式下土壤养分、微生物及酶活性研究[J].土壤通报,2009,40(3):542-546. |
| ZHANG X J, LIU J H, LI L J, et al.. Effects of different conservation tillage on soil microbes quantities and enzyme activities in dry cultivation [J]. Soil Bull., 2009, 40(3):542-546. | |
| 21 | 秦红灵,高旺盛,马月存,等.免耕对农牧交错带农田休闲期土壤风蚀及其相关土壤理化性状的影响[J].生态学报,2007,27(9):3778-3784. |
| QIN H L, GAO W S, MA Y C, et al.. Effects of no-tillage on soil properties affecting wind erosion during fallow in Ectone of north China [J]. J. Ecol., 2007, 27(9):3778-3784. | |
| 22 | 徐永刚,马强,周桦,等.秸秆还田与深松对土壤理化性状和玉米产量的影响[J].土壤通报,2015,46(2):428-432. |
| XU Y G, MA Q, ZHOU Y, et al.. Effects of straw returning and deep loosening on soil physical and chemical properties and maize yields [J]. Soil Bull., 2015, 46(2):428-432. | |
| 23 | 邓廷飞,刘彦,颜秋晓,等.贵州典型山银花土壤机械组成与养分特性及其关系[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(5):209-214. |
| DENG T F, LIU Y, YAN Q X, et al.. Mechanical composition and soil nutrient characteristics and their relationships in typical Loniceracinfusa soil of Guizhou [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2014, 28(5):209-214. | |
| 24 | 李学斌,张义凡,陈林,等.荒漠草原典型群落土壤粒径和养分的分布特征及其关系研究[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(8):1635-1644. |
| LI X B, ZHANG Y F, CHEN L, et al.. Relationship between soil particle size distribution and soil nutrient distribution characteristics in typical communities of desert grassland [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2017, 37(8):1635-1644. | |
| 25 | YAN Y C, XIN X P, XU X L, et al.. Quantitative effects of wind erosion on the soil texture and soil nutrients under different vegetation coverage in a semiarid steppe of northern China [J]. Plantand Soil, 2013, 369(1):585-598. |
| [1] | PU Quanming1, YANG Peng1*, DENG Yuchuan2, XIANG Chengyong1, LIN Bangmin1, LIU Lisha1, SHI Songmei3, HE Zemin1, YONG Lei1. Effects of Different Fertilization Methods on Soil Enzyme Activity, Soil Nutrients and Quality of Spring Cabbage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 130-139. |
| [2] | WU Xin-jia, WANG Hong, ZHANG Ai-jun, ZHANG Rui-fang, ZHOU Da-mai. Effect of Different Fertilizer Treatments on Nutrient and Enzymatic Activity of Soil in River Ancient Channel [J]. , 2009, 11(6): 118-122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号