




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 199-207.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0566
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Lei ZHOU1( ), Zhaolan CHEN1, Yubo YAN1,2(
), Zhaolan CHEN1, Yubo YAN1,2( ), Qiao LI3
), Qiao LI3
Received:2021-07-09
Accepted:2021-09-22
Online:2022-11-15
Published:2022-11-29
Contact:
Yubo YAN
通讯作者:
严玉波
作者简介:周蕾 E-mail:zl19981017@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lei ZHOU, Zhaolan CHEN, Yubo YAN, Qiao LI. Application of Chicken Manure-derived Biochar for Adsorption of Lead[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 199-207.
周蕾, 陈兆兰, 严玉波, 李桥. 鸡粪生物炭吸附固定铅的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 199-207.
| 实测平衡吸附量qe,exp/(mg·g-1) | 准一级动力学模型 Pseudo-first order model | 准二级动力学模型 Pseudo-second order model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 理论平衡吸附量qe,cal/(mg·g-1) | 决定系数R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 理论平衡吸附量qe,cal/(mg·g-1) | 决定系数R2 | |
| 142.6 | 0.30 | 39.00 | 0.983 6 | 0.04 | 142.9 | 0.999 9 |
Table 1 Kinetic parameters for the adsorption of Pb2+
| 实测平衡吸附量qe,exp/(mg·g-1) | 准一级动力学模型 Pseudo-first order model | 准二级动力学模型 Pseudo-second order model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 理论平衡吸附量qe,cal/(mg·g-1) | 决定系数R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | 理论平衡吸附量qe,cal/(mg·g-1) | 决定系数R2 | |
| 142.6 | 0.30 | 39.00 | 0.983 6 | 0.04 | 142.9 | 0.999 9 |
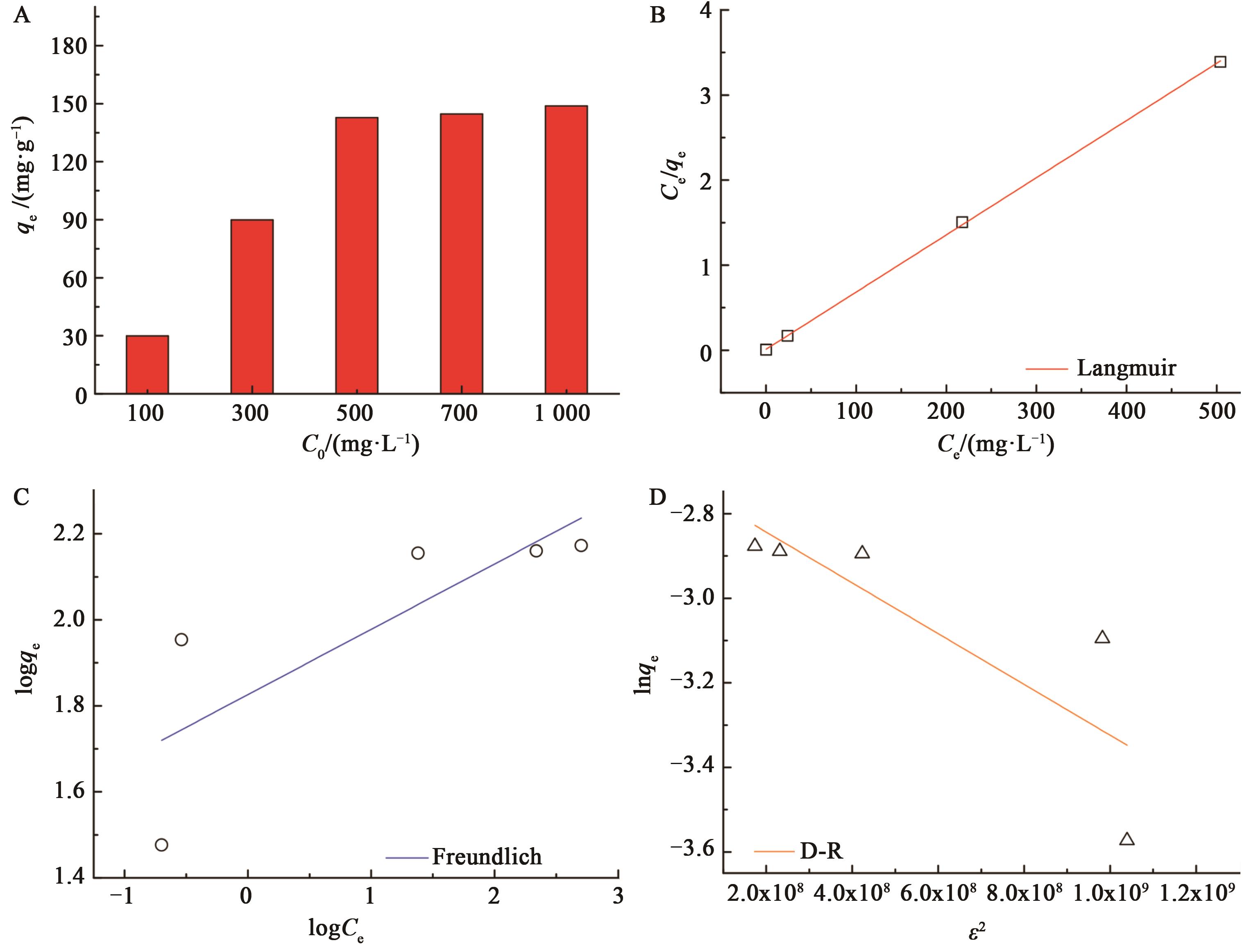
Fig. 2 Adsorption of CMBC-400 on different Pb2+ mass concentrations and linear fitting for adsorption kineticsA: Effect of initial concentration on Pb2+ adsorption; B: Langmuir fitting curves; C: Freundlich fitting curves; D: D-R fitting curves
| Langmuir | Freundlich | D-R | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最大吸附量 qmax/(mg·g-1) | b/(L·mg-1) | 决定系数 R2 | KF/(mg·g-1) | 1/n | 决定系数 R2 | 理论饱和吸附量qm /(mg·g-1) | 吸附自由能 E/(kJ·mol-1) | 决定系数 R2 |
| 149.3 | 0.66 | 0.999 9 | 67.0 | 0.15 | 0.656 0 | 7 352 | 28.86 | 0.694 8 |
Table 2 Isotherm parameters for the adsorption of Pb2+
| Langmuir | Freundlich | D-R | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最大吸附量 qmax/(mg·g-1) | b/(L·mg-1) | 决定系数 R2 | KF/(mg·g-1) | 1/n | 决定系数 R2 | 理论饱和吸附量qm /(mg·g-1) | 吸附自由能 E/(kJ·mol-1) | 决定系数 R2 |
| 149.3 | 0.66 | 0.999 9 | 67.0 | 0.15 | 0.656 0 | 7 352 | 28.86 | 0.694 8 |
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | 最大吸附容量qmax/(mg·g-1) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 鸡粪生物炭 CMBC-400 | 149.30 | 本研究 This study |
| 棉花秸秆生物炭 Cotton straw biochar | 33.78 | [ |
| 木屑生物炭 Sawdust biochar | 77.12 | [ |
| 柚子皮生物炭 Pomelo peel biochar | 93.09 | [ |
| 双孢菇菌糠生物炭 Agaricus bisporus substrate biochar | 266.23 | [ |
| 酒糟生物炭 Wine lees-derived biochar | 79.12 | [ |
| 甘蔗生物炭 Sugar cane bagasse biochar | 86.96 | [ |
| 橙皮生物炭 Orange peel biochar | 27.86 | [ |
| 豚草生物炭 Invasive plant species biochar | 358.70 | [ |
Table 3 Comparison of maximum adsorption capacities for Pb2+ on various adsorbents
| 吸附剂 Adsorbent | 最大吸附容量qmax/(mg·g-1) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 鸡粪生物炭 CMBC-400 | 149.30 | 本研究 This study |
| 棉花秸秆生物炭 Cotton straw biochar | 33.78 | [ |
| 木屑生物炭 Sawdust biochar | 77.12 | [ |
| 柚子皮生物炭 Pomelo peel biochar | 93.09 | [ |
| 双孢菇菌糠生物炭 Agaricus bisporus substrate biochar | 266.23 | [ |
| 酒糟生物炭 Wine lees-derived biochar | 79.12 | [ |
| 甘蔗生物炭 Sugar cane bagasse biochar | 86.96 | [ |
| 橙皮生物炭 Orange peel biochar | 27.86 | [ |
| 豚草生物炭 Invasive plant species biochar | 358.70 | [ |
| 温度 T/K | 自由能变 ΔG | 焓变 ΔH | 熵变 ΔS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | -4.35 | 55.71 | 0.20 |
| 308 | -5.75 | ||
| 323 | -10.55 |
Table 4 Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of Pb2+
| 温度 T/K | 自由能变 ΔG | 焓变 ΔH | 熵变 ΔS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | -4.35 | 55.71 | 0.20 |
| 308 | -5.75 | ||
| 323 | -10.55 |
| 1 | CHEN Z, PANA X H, CHEN H, et al.. Biomineralization of Pb (Ⅱ) into Pb-hydroxyapatite induced by Bacillus cereus 12-2 isolated from Lead-Zinc mine tailings [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2016, 301:531-537. |
| 2 | 张连科,王洋,王维大,等.生物炭负载纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料的制备及对铅离子的吸附特性[J].化工进展,2018,37(9):3492-3501. |
| ZHANG L K, WANG Y, WANG W D, et al.. Preparation of nano hydroxyapatite composite supported by biochar and its adsorption characteristics for lead [J]. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2018, 37(9):3492-3501. | |
| 3 | 杨晶,李丽,季必霄,等.生物炭吸附废水中重金属研究进展[J].能源环境保护,2020,34(6):1-7. |
| YANG J, LI L, JI B X, et al.. Research progress on adsorption of heavy metals in wastewater by biochar [J]. Energy Environ. Prot., 2020, 34(6):1-7. | |
| 4 | 陈温福,张伟明,孟军.生物炭与农业环境研究回顾与展望[J].农业环境科学学报,2014,33(5):821-828. |
| CHEN W F, ZHANG W M, MENG J. Review and prospect of biochar and agricultural environment [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2014, 33(5):821-828. | |
| 5 | ABDALLAH M M, AHMAD M N, WALKER G, et al.. Batch and continuous systems for Zn, Cu, and Pb metal ions adsorption on spent mushroom compost biochar [J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58:7296-7307. |
| 6 | 王泽庆,袁程煜,葛广华,等.棉花秸秆生物炭对重金属Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附性能研究[J].塔里木大学学报,2020,32(1):100-108. |
| WANG Z Q, YUAN C Y, GE G H, et al.. Adsorption of Pb (Ⅱ) by cotton straw biochar [J]. J. Tarim Univ., 2020, 32(1):100-108. | |
| 7 | CHEN Z L, ZHANG J Q, HUANG L, et al.. Removal of Cd and Pb with biochar made from dairy manure at low temperature [J]. J. Integr. Agric., 2019, 18(1):201-210. |
| 8 | 冯巍,程群鹏,李胜兰,等.鸡粪热解制备生物炭及对废水中磷的吸附性能研究[J].武汉轻工大学学报,2021,40(1):75-80. |
| FENG W, CHENG Q P, LI S L, et al.. Preparation of biochar from chicken manure pyrolysis and its adsorption of phosphorus in wastewater [J]. J. Wuhan Polytech. Univ., 2021, 40(1):75-80. | |
| 9 | 张智,乔艳,陈云峰,等.不同菌剂对鸡粪堆肥过程中有害气体排放的影响[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(12):145-150. |
| ZHANG Z, QIAO Y, CHEN Y F, et al.. Effects of three microbial agents on harmful gas emission during chicken manure composing [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(12):145-150. | |
| 10 | 鞠天琛,於斯,李晓军,等.低温鸡粪生物质炭的制备及其对土壤理化性质的影响[J].吉林农业大学学报,2020,42(3):322-328. |
| JU T C, YU S, LI X J, et al.. Preparation of low temperature chicken manure biochar and its effect on soil physical and chemical properties [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2020, 42(3):322-328. | |
| 11 | YAN Y B, SARKAR B, ZHOU L, et al.. Phosphorus-rich biochar produced through bean-worm skin waste pyrolysis enhances the adsorption of aqueous lead [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020, 266:115177 [2021-03-05]. . |
| 12 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,1999:146-195. |
| LU R K. Soil and Agro-chemical Analysis Methods [M]. Beijing: Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1999:146-195. | |
| 13 | YAN Y B, QI F J, SESHADRI B, et al.. Utilization of phosphorus loaded alkaline residue to immobilize lead in a shooting range soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 162(11):315-323. |
| 14 | AHMAD M, RAJAPAKSHA A U, LIM J E, et al.. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 99(3):19-33. |
| 15 | 莫贞林,曾鸿鹄,林华,等.高锰酸钾改性桉木生物炭对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附特性[J].环境科学,2021,42(11):5440-5449. |
| MO Z L, CENG H H, LING H, et al.. Adsorption characteristics of Pb (Ⅱ) on Eucalyptus biochar modified by potassium permanganate [J]. J. Environ. Sci., 2021, 42(11):5440-5449. | |
| 16 | YAN Y B, LI Q, SUN X Y, et al.. Recycling flue gas desulphurization (FGD) gypsum for removal of Pb (Ⅱ) and Cd (Ⅱ) from wastewater [J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 457:86-95. |
| 17 | YAN Y B, ZHANG L, WANG Y H, et al.. Clanis bilineata larvae skin-derived biochars for immobilization of lead: sorption isotherm and molecular mechanism [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 704:135251 [2021-03-05]. . |
| 18 | DING Z, WAN Y, HU X, et al.. Sorption of lead and methylene blue onto hickory biochars from different pyrolysis temperatures: importance of physicochemical properties [J]. J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2016, 37:261-267. |
| 19 | 常帅帅,张学杨,王洪波,等.木屑生物炭的制备及其对Pb2+的吸附特性研究[J].生物质化学工程,2020,54(3):37-44. |
| CHANG S S, ZHANG X Y, WANG H B, et al.. Preparation of sawdust biochar and its adsorption characteristics for Pb2+ [J]. Biomass Chem. Eng., 2020, 54(3):37-44. | |
| 20 | 刘书畅,黄应平,熊彪,等.不同热解温度制备柚子皮生物炭对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附机理[J].武汉大学学报,2020,66(4):361-368. |
| LIU S C, HUANG Y P, XIONG B, et al.. Adsorption mechanism of Pb (Ⅱ) on teak skin biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures [J]. Wuhan Univ. J., 2020, 66(4):361-368. | |
| 21 | 张国胜,程红艳,张海波,等.双孢菇菌糠生物炭吸附Pb2+机制及其环境应用潜力[J].农业环境科学学报,2021,40(3):659-667. |
| ZHANG G S, CHENG H Y, ZHANG H B, et al.. Mechanism of biosorption of Pb2+ by Agaricus bisporus bran biochar and its environmental application potential [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2021, 40(3):659-667. | |
| 22 | ZHU Q, WU J, WANG L, et al.. Adsorption characteristics of Pb (2+) onto wine lees-derived biochar [J]. B. Environ. Contam. Tox., 2016, 97(2):294-299. |
| 23 | ABDELHAFEZ A A, LI J. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by using biochars derived from sugar cane bagasse and orange peel [J]. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2016, 61:367-375. |
| 24 | LIAN W, YANG L, JOSEPH S, et al.. Utilization of biochar produced from invasive plant species to efficiently adsorb Cd (Ⅱ) and Pb (Ⅱ) [J/OL]. Bioresou. Technol., 2020, 317:124011 [2021-03-05]. . |
| 25 | YE X, KANG S, WANG H, et al.. Modified natural diatomite and its enhanced immobilization of lead, copper and cadmium in simulated contaminated soils [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 289:210-218. |
| [1] | Ruixia WANG, Xiaoling ZHAI, Yugang LI, Qiuhuan MU, Yingying SUN, Xianyin SUN, Yong MI, Guangde LYU, Hongmei GE, Zhaoguo QIAN. Genetic Composition of Taishan 22 Using High-density 90K SNP Array [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 21-29. |
| [2] | WANG Xinyu1,2, ZHANG Xi2, MENG Haibo2, SHEN Yujun2, XIE Hengyan1*, ZHOU Haibin2, CHENG Hongsheng2, SONG Liqiu2. Impact of Temperature on Adsorption Characteristics of Biochar on Heavy Metals [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 150-158. |
| [3] | ZHANG Kaiye1,2, LIU Xiaolin2, DONG Xiaoyan2,3, LIU Runjin4, HE Liheng1*, XIE Zhihong2,3*. Isolation of Endophytic Cultures From Sesbania cannabina Seeds and Their Effects on Germination [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(6): 40-48. |
| [4] | ZHAN Shijie1,2, MENG Haibo1*, CHENG Hongsheng1, SHEN Yujun1. Research Progress on the Effect of Physical and Chemical Properties of Biomass Activated Carbon on the Adsorption Properties of VOCs [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(3): 132-138. |
| [5] | MA Yanru1,2, MENG Haibo2, SHEN Yujun2, DING Jingtao2, WANG Liming1*. Research on Adsorption Effect of Ammonia-nitrogen from Biogas Slurry by Modified Biochar [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(11): 135-144. |
| [6] | LI Ran1,2, ZHAO Lixin1, MENG Haibo1, ZHOU Haibin1, WANG Jian1, SHEN Yujun1*. Research Progress of Heavy Metal Immobilization and Its Mechanism During Composting [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(1): 121-129. |
| [7] | YE Jianghua1,2, JIA Xiaoli1,3, CHEN Xiaoting3,4, LIN Shunxian4, . Physiological Response and Subcellular Distribution in Different Tea Plants Under Pb Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(11): 92-99. |
| [8] | CHEN Jie, LUO Haibo*, LIU Fang, CHEN Longjiang, SU Xinjian. Adsorption Effect of Slag Particles on Biogas Slurry [J]. , 2013, 15(1): 152-157. |
| [9] | NIE Zhi-xing, HANG Xiao-ning, LUO Jia, WANG Miao, WANG Yun-long, WU Xiao-yuan, . Research Progress on Farmer-based Participatory Plant Breeding [J]. , 2008, 10(6): 48-55. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号