




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 169-177.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0541
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Guanqun CHAI1( ), Li WANG1, Guihua LIU1, Xinjian LUOMU1, Ya JIANG1, Hong LIANG2, Chengwu FAN1(
), Li WANG1, Guihua LIU1, Xinjian LUOMU1, Ya JIANG1, Hong LIANG2, Chengwu FAN1( )
)
Received:2022-06-29
Accepted:2022-08-22
Online:2023-03-15
Published:2023-05-22
Contact:
Chengwu FAN
柴冠群1( ), 王丽1, 刘桂华1, 罗沐欣键1, 蒋亚1, 梁红2, 范成五1(
), 王丽1, 刘桂华1, 罗沐欣键1, 蒋亚1, 梁红2, 范成五1( )
)
通讯作者:
范成五
作者简介:柴冠群 E-mail:chaiguanqun@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Guanqun CHAI, Li WANG, Guihua LIU, Xinjian LUOMU, Ya JIANG, Hong LIANG, Chengwu FAN. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals and Differences in Cd Uptake and Accumulation of Three Types of Pod Peppers[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 169-177.
柴冠群, 王丽, 刘桂华, 罗沐欣键, 蒋亚, 梁红, 范成五. 3类朝天椒重金属健康风险评价与镉吸收累积差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 169-177.
| 辣椒类型 Pepper type | 指标Index | 镉 Cd | 砷 As | 铅 Pb | 铜 Cu | 锌 Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
指型朝天椒 Finger pepper | 均值 Mean | 0.29* 0.13~0.55 | 0.044* 0.02~0.08 | 0.07* 0.03~0.17 | 7.44 4.70~11.40 | 19.46 14.70~27.80 |
| 变幅 Range | ||||||
锥型朝天椒 Taper pepper | 均值 Mean | 0.19* 0.09~0.35 | 0.043* 0.03~0.06 | 0.06* 0.03~0.11 | 8.38 4.60~11.00 | 18.85 14.60~23.40 |
| 变幅 Range | ||||||
圆型朝天椒 Circular pepper | 均值 Mean | 0.11 0.06~0.33 | 0.037* 0.03~0.05 | 0.04* 0.02~0.07 | 4.66 3.30~6.70 | 15.18 12.60~17.10 |
| 变幅 Range | ||||||
| 国标限值[ | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |||
Table 1 Heavy metal concent in pepper samples
| 辣椒类型 Pepper type | 指标Index | 镉 Cd | 砷 As | 铅 Pb | 铜 Cu | 锌 Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
指型朝天椒 Finger pepper | 均值 Mean | 0.29* 0.13~0.55 | 0.044* 0.02~0.08 | 0.07* 0.03~0.17 | 7.44 4.70~11.40 | 19.46 14.70~27.80 |
| 变幅 Range | ||||||
锥型朝天椒 Taper pepper | 均值 Mean | 0.19* 0.09~0.35 | 0.043* 0.03~0.06 | 0.06* 0.03~0.11 | 8.38 4.60~11.00 | 18.85 14.60~23.40 |
| 变幅 Range | ||||||
圆型朝天椒 Circular pepper | 均值 Mean | 0.11 0.06~0.33 | 0.037* 0.03~0.05 | 0.04* 0.02~0.07 | 4.66 3.30~6.70 | 15.18 12.60~17.10 |
| 变幅 Range | ||||||
| 国标限值[ | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |||
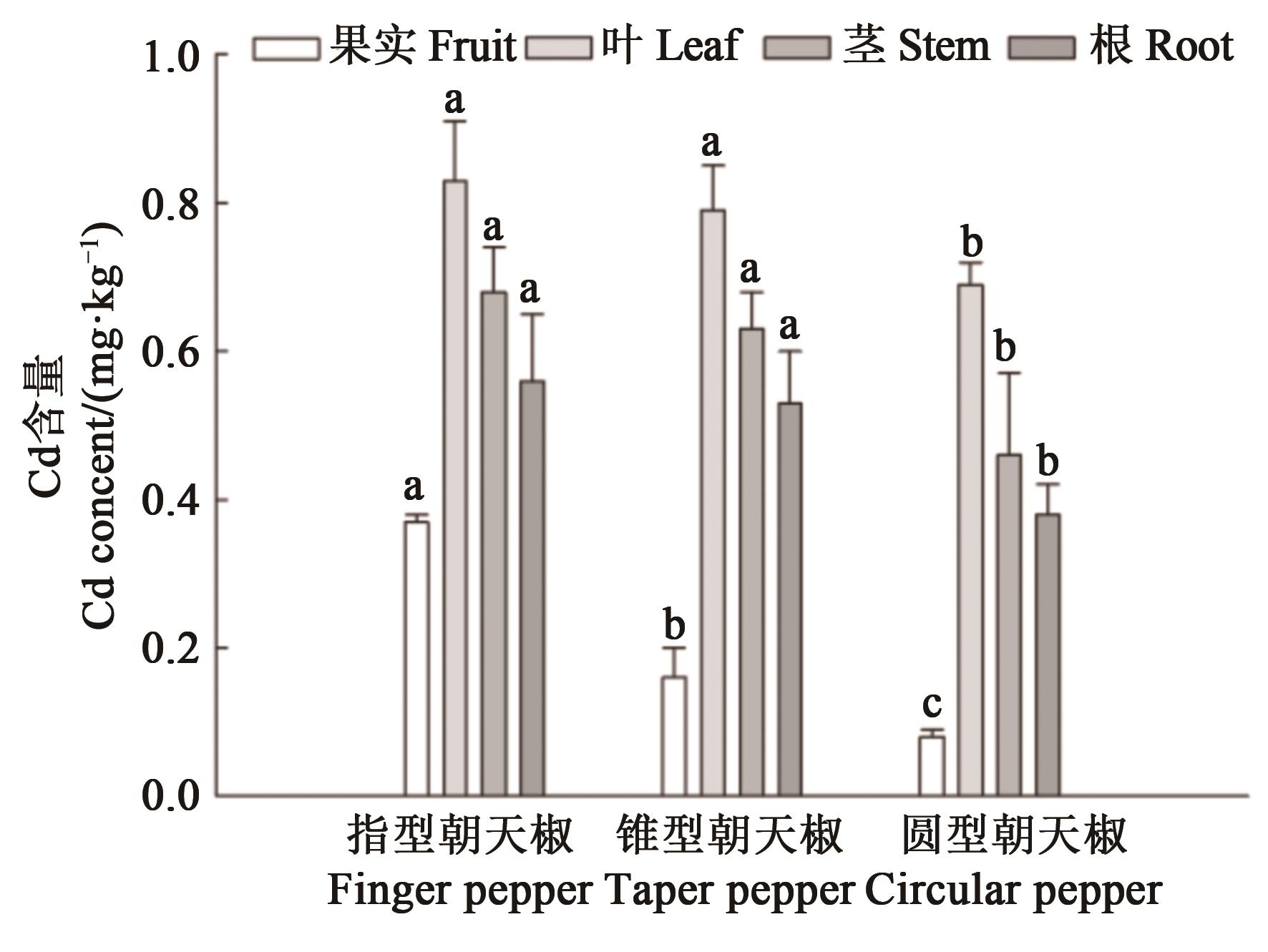
Fig. 3 Cd contents in different part of three types of peppersNote:Different lowercase letters in the same part indicate significant differences of Cd content between different genotype pepper at P<0.05 level.
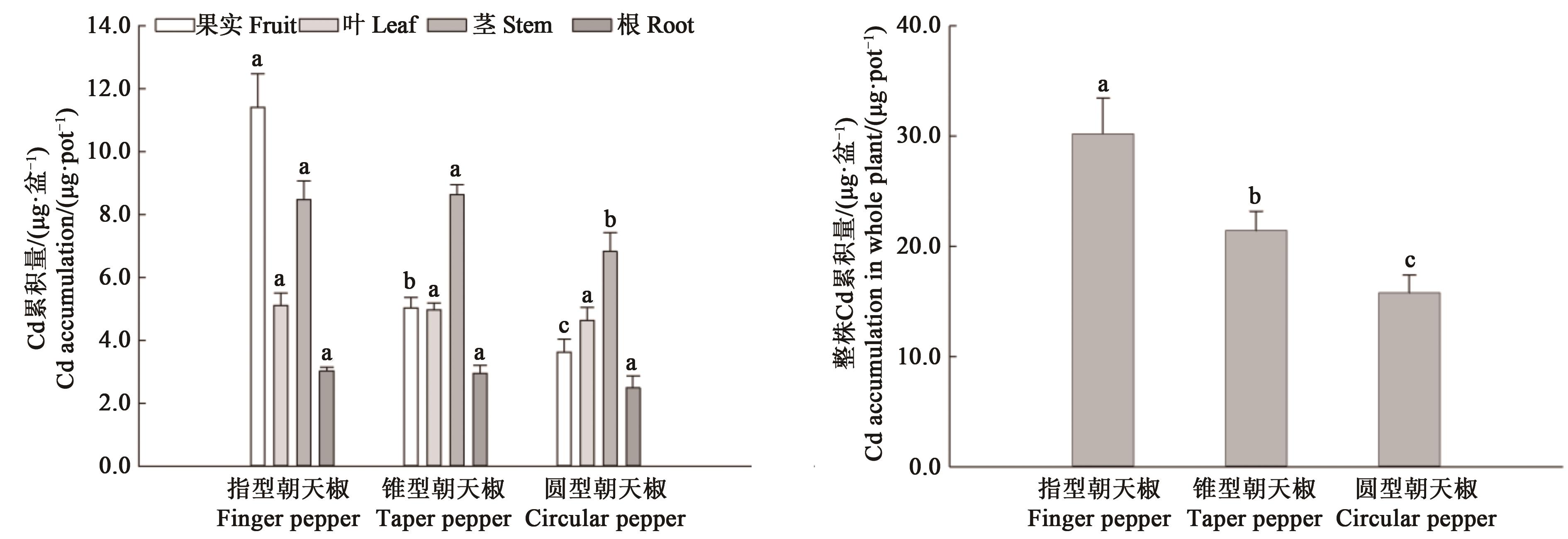
Fig. 4 Cd accumulation in different part and whole plant of three types of peppersNote:Different lowercase letters on the columns indicate significant differences of Cd accumulation in the same part of different genotype pepper at P<0.05 level.
| 辣椒类型 Pepper type | 富集系数 BCF | 转运系数 Transport coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部/根 shoot/root | 果/叶 fruits/leaves | 果/茎 fruits/stems | ||
| 指型朝天椒 Finger pepper | 2.03±0.04 a | 1.11±0.10 a | 0.45±0.08 a | 0.51±0.08 a |
| 锥型朝天椒 Taper pepper | 1.65±0.07 b | 1.00±0.08 a | 0.20±0.04 b | 0.25±0.07 b |
| 圆型朝天椒 Circular pepper | 1.13±0.03 c | 1.04±0.06 a | 0.14±0.04 b | 0.19±0.05 b |
Table 2 Enrichment and transport coefficients of Cd in three types of peppers
| 辣椒类型 Pepper type | 富集系数 BCF | 转运系数 Transport coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部/根 shoot/root | 果/叶 fruits/leaves | 果/茎 fruits/stems | ||
| 指型朝天椒 Finger pepper | 2.03±0.04 a | 1.11±0.10 a | 0.45±0.08 a | 0.51±0.08 a |
| 锥型朝天椒 Taper pepper | 1.65±0.07 b | 1.00±0.08 a | 0.20±0.04 b | 0.25±0.07 b |
| 圆型朝天椒 Circular pepper | 1.13±0.03 c | 1.04±0.06 a | 0.14±0.04 b | 0.19±0.05 b |
| 指标 | 富集系数 BCF | 转运系数 Transport coefficient | 果实质量 Fruit weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部/根 shoot/root | 果/叶 fruits/leaves | 果/茎 fruits/stems | |||
| Cd含量 Cd content | 0.694* | 0.251 | 0.862** | 0.891** | -0.737* |
Table 3 Correlation coefficients between Cd content in pepper fruit and tissues of plant
| 指标 | 富集系数 BCF | 转运系数 Transport coefficient | 果实质量 Fruit weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部/根 shoot/root | 果/叶 fruits/leaves | 果/茎 fruits/stems | |||
| Cd含量 Cd content | 0.694* | 0.251 | 0.862** | 0.891** | -0.737* |
| 1 | 占文婷,胡思卓,黄倞文,等. 辣椒粉中还原型维生素C含量的测定[J]. 中国调味品, 2017, 42(3): 104-109. |
| ZHAN W T, HU S Z, HUANG J W, et al.. Deternination of the reduced vitamin C content in paprika [J]. China Condiment, 2017, 42(3): 104-109. | |
| 2 | 黄道梅,魏江霖,吴世焕,等. 贵州省辣椒加工业发展现状解析[J]. 中国调味品, 2019, 44(10): 187-189, 194. |
| HUANG D M, WEI J L, WU S H, et al.. Analysis on the development status of chili processing industry in Guizhou province [J]. China Condiment, 2019, 44(10): 187-189, 194. | |
| 3 | 张建,杨瑞东,陈蓉,等. 贵州喀斯特地区土壤-辣椒体系重金属元素的生物迁移积累特征[J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(21): 175-181. |
| ZHANG J, YANG R D, CHEN R, et al.. Bioconcentration of heavy metals in soil-Capsicum annuum L. system in karst areas of Guizhou province [J]. Food Sci., 2017, 38(21): 175-181. | |
| 4 | 蔡大为,李龙波,蒋国才,等. 贵州耕地主要元素地球化学背景值统计与分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2020, 37(3): 233-239. |
| CAI D W, LI L B, JIANG G C, et al.. Statistics and analysis of geochemical backgrounds of main elements of cultivated land in Guizhou province [J]. Guizhou Geol., 2020, 37(3): 233-239. | |
| 5 | 邢丹,张爱民,王永平,等. 贵州典型土壤-辣椒系统中镉的迁移富集特征[J]. 西南农业学报, 2016, 29(2): 332-336. |
| XING D, ZHANG A M, WANG Y P, et al.. Transport and enrichment characteristics of Cd in typical Guizhou soil-pepper system [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2016, 29(2): 332-336. | |
| 6 | 陈卫平,杨阳,谢天,等. 中国农田土壤重金属污染防治挑战与对策[J]. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(2): 261-272. |
| CHEN W P, YANG Y, XIE T, et al.. Challenges and countermeasures for heavy metal pollution control in farmlands of China [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2018, 55(2): 261-272. | |
| 7 | YANG Y, WANG M E, CHEN W P, et al.. Cadmium accumulation risk in vegetables and rice in Southern China: insights from solid-solution partitioning and plant uptake factor [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2017, 65(27): 5463-5469. |
| 8 | YANG Y, CHEN W P, WANG M E, et al.. Regional accumulationcharacteristics of cadmium in vegetables influencing factors transfermodel and indication of soil threshold content [J]. Environ. Poll., 2016, 219: 1036-1043. |
| 9 | 张蕾,吴隆坤,李博骞,等. 农作物镉积累的品种差异及其机理研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2017 (2): 184-190. |
| ZHANG L, WU L K, LI B Q, et al.. Research progress on difference of Cd accumulating pattern and its mechanism among crop varieties [J]. Northern Hortic., 2017(2): 184-190. | |
| 10 | 赵首萍,张棋,肖文丹,等. 辣椒不同品种间Cd富集的差异[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2020, 61(10): 2026-2032. |
| ZHAO S P, ZHANG Q, XIAO W D, et al.. Differences of Cd accumulation among different pepper varieties [J]. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2020, 61(10): 2026-2032. | |
| 11 | 刘峰,弭宝彬,魏瑞敏,等. 基于聚类分析法筛选低镉累积辣椒品种[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(5): 979-986. |
| LIU F, MI B B, WEI R M, et al.. Screening out of Cd-pollution-safe pepper cultivars by clustering analysis [J].Acta Hortic. Sin., 2017, 44(5): 979-986. | |
| 12 | LUO K, LIU H Y, LIU Q D, et al.. Cadmium accumulation and migration of 3 peppers varieties in yellow and limestone soils under geochemical anomaly [J]. Environ.Technol., 2022,43 (1/4): 10-20. |
| 13 | WANG Y F, SU Y, LUO S G. Cd accumulation and transfer in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) grown in typical soils of China: pot experiments [J]. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res., 2019, 26(36): 36558-36567. |
| 14 | 赵首萍,叶雪珠,张棋,等. 不同辣椒品种镉吸收积累能力及关键期研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(4): 695-705. |
| ZHAO S P, YE X Z, ZHANG Q, et al.. The capacity and critical stage of Cd absorption and accumulation ofdifferent pepper cultivars [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2021, 27(4): 695-705. | |
| 15 | KASHIWAGI T, SHINDOH K, HIROTSU N, et al.. Evidence for separate translocation pathways in determining cadmium accumulation in grain and aerial plant parts in rice [J]. BMC Plant Biol., 2009, 9(1): 1-8. |
| 16 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品中多元素的测定: [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. |
| 17 | 周艳,陈樯,邓绍坡,等. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. |
| ZHOU Y, CHEN Q, DENG S P, et al.. Principal component analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metalsin farmland soils around a Pb-Zn mine in southwestern China [J]. Environ. Sci., 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. | |
| 18 | 欧灵芝,胡鸣明,安德章,等. 高砷煤矿周围旱作土壤重金属污染特征及农作物健康风险评价[J/OL]. 农业资源与环境学报,2021:0830 [2022-05-11]. . |
| OU L Z, HU M M, AN D Z, et al.. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in dryland soil and crops around a coal mine with high levels of arsenic [J/OL]. J. Agric. Res. Environ.,2021:0830 [2022-05-11]. . | |
| 19 | 郭鹏然,雷永乾,周巧丽,等. 电镀厂周边环境中重金属分布特征及人体健康暴露风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(9): 3447-3456. |
| GUO P R, LEI Y Q, ZHOU Q L, et al.. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in environmental samples around electroplating factories and the health risk assessment [J]. Environ. Sci., 2015, 36(9): 3447-3456. | |
| 20 | 成晓梦,孙彬彬,吴超,等. 浙中典型硫铁矿区农田土壤重金属含量特征及健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 442-453. |
| CHENG X M, SUN B B, WU C, et al.. Heavy metal concentration characteristics and health risks of farmland soils in typical pyrite mining area of the central Zhejiang province, China [J]. Environ. Sci., 2022, 43(1): 442-453. | |
| 21 | 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 绿色食品 辣椒制品: [S].北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020. |
| 22 | 张梓良,林健,冬明月,等. 苏南某区污染耕地农产品镉汞状况调查及健康风险评价[J]. 土壤, 2022, 54(1): 206-210. |
| ZHANG Z L, LIN J, DONG M Y, et al.. Survey of cadmium and mercury pollution and assessment of health risk of crops in polluted farmland in Southern Jiangsu [J]. Soils, 2022, 54(1): 206-210. | |
| 23 | WANG S Y, WU W Y, LIU F, et al.. Accumulation of heavy metals in soil-crop systems: a review for wheat and corn [J/OL]. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. Int., 2017:8909-5 [2022-05-11]. . |
| 24 | 贾艳丽,郝春明,刘敏,等. 锑矿区土壤和蔬菜重金属污染及健康风险评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(7): 2943-2949. |
| JIA Y L, HAO C M, LIU M, et al.. Soil-vegetable pollution of heavy metals and health risk assessment in antimony mining area [J]. Sci. Technol. Eng., 2022, 22(7) : 2943-2949. | |
| 25 | 赵颖,王飞,乔鹏明. 污灌区农田土壤-作物体系重金属复合污染及健康风险评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(23): 270-274. |
| ZHAO Y, WANG F, QIAO P M, et al.. Evaluation of heavy metal complex contamination and health risks in soil-crop systems of agricultural fields in contaminated irigation areas [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(23): 270-274. | |
| 26 | 王宇豪,杨力,康愉晨,等. 镉污染大田条件下不同品种水稻镉积累的特征及影响因素[J], 2021, 42(11): 5545-5553. |
| WANG Y H, YANG L, KANG Y C, et al.. Characteristics and influencing factors of cadmium accumulation in different rice varieties under cadmium contaminated field conditions [J]. Environ. Sci., 2021, 42(11): 5545-5553. |
| [1] | Guanqun CHAI, Guihua LIU, Wei ZHOU, Xiujin ZHANG, Longpin LI, Chengwu FAN. Evaluation of Pollution Risk and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Greenhouse Soils in Wumeng Mountain Area, Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 144-153. |
| [2] | Juntao MA, Wen ZHOU, Jinghao LI, Yizhuo JING, Dan HAN, Huifang SHAO. Research Progress on the Regulation Mechanism of Exogenous Selenium on Heavy Metal Stress in Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 27-35. |
| [3] | Hairong XU, Lin WANG, Congmin WU, Yuanchun YU, Cheng DAI. Effects of Biogas Slurry Application on Green Pepper Growth and Soil Properties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(10): 179-188. |
| [4] | CHENG Yunxia§, WU Hui§, LIU Qianjie, SHI Zhenyu, JIA Kai, CHEN Yilin, YU Anwei, SHEN Jinxiu. Influences of Water-retaining Agent with Different Doses on Growth and Quality of Bag-type Compound Sape Pepper [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 55-62. |
| [5] | BAO Zhijuan, JIN Rong, YANG Jinqing, ZHANG Qi, ZHU Yongli, ZHAO Zhengxiong*. Effects of Pb and Zn Combination on Antioxidant Enzymes and Carbon-nitrogen Metabolism of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 65-72. |
| [6] | LIU Na1, WANG Yan1, ZHAO Chenyang2, GUO Junxian2. Feasibility Study on Mechanized Transplanting of Pepper in Sunlight Greenhouse [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 96-104. |
| [7] | WANG Xinyu1,2, ZHANG Xi2, MENG Haibo2, SHEN Yujun2, XIE Hengyan1*, ZHOU Haibin2, CHENG Hongsheng2, SONG Liqiu2. Impact of Temperature on Adsorption Characteristics of Biochar on Heavy Metals [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 150-158. |
| [8] | ZHANG Lei, LI Yang, ZHANG Yang*. Research Progress on Effects of Common Fertilizers on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Crops and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(2): 123-131. |
| [9] | HUANG Zhi1,2, LIU Xiangnan2*, ZHAO Shuang3, ZHANG Xian4. Deriving the Spectral Characteristic Scale for Heavy Metal Stress Monitoring in Rice Based on Ground Spectral Data#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(12): 58-67. |
| [10] | WANG Wei, LI Yong, WANG Wei, BIAN Xue, LI Xiying*. Anti-disease Effect and Mechanism of Y-S-Y12 Strain Fermentation Mixed with Biomass Pyrolysis Solution on Pepper Anthracnose [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(10): 129-138. |
| [11] | ZHANG Junye1,2, YU Fei3, LIU Xiaodong1, YU Yuanchun1*. Advance of Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Foliar Particulate Matter of Urban Forest Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(10): 140-147. |
| [12] | ZOU Mengmeng1, ZHOU Weihong1,2, ZHANG Jingjing1, LIU Ying1, . Heavy Metal Pollution of Cultivated Soil in Eastern China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(1): 117-124. |
| [13] | DUAN Shuhui1,2, ZHOU Zhicheng2, LIU Yongjun2, XIAO Yansong3, CHEN Pengfeng4, FAN Caiyin5, CHEN Shibao6*. Distribution and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals in Central-South of Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(6): 80-87. |
| [14] | LI Yan, SHI Yi, WANG Yuxiang, HE Xuwen*. Effect and Evaluation of Municipal Sludge Improved Sand Soil on Rape Growth [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(6): 88-95. |
| [15] | HUANG Jiaqi1, WEI Yue1*, CHEN Fang2, WU Liming2*. Studies on Indicative Function of Heavy Metals in Bee Products to Environmental Pollution [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(4): 92-100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号