




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 61-71.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0185
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Songjiang DUAN1( ), Haoran HU1, Chengjie ZHANG1, Wei SUN1, Yifan WU1, Rensong GUO2, Jusong ZHANG1(
), Haoran HU1, Chengjie ZHANG1, Wei SUN1, Yifan WU1, Rensong GUO2, Jusong ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2023-03-13
Accepted:2023-05-29
Online:2025-01-15
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
Jusong ZHANG
段松江1( ), 胡浩然1, 张承洁1, 孙伟1, 吴一帆1, 郭仁松2, 张巨松1(
), 胡浩然1, 张承洁1, 孙伟1, 吴一帆1, 郭仁松2, 张巨松1( )
)
通讯作者:
张巨松
作者简介:段松江 E-mail:1578442341@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Songjiang DUAN, Haoran HU, Chengjie ZHANG, Wei SUN, Yifan WU, Rensong GUO, Jusong ZHANG. Differences in Nitrogen Efficiency of Different Genotypes of Island Cotton and Their Effects on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 61-71.
段松江, 胡浩然, 张承洁, 孙伟, 吴一帆, 郭仁松, 张巨松. 不同基因型海岛棉的氮效率差异及其对光合特性和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 61-71.
土层 Soil layer/cm | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 13.8 | 9.1 | 53.9 | 8.6 |
| 10—20 | 0.6 | 9.8 | 25.3 | 25.4 | 97.7 | 8.8 |
| 20—30 | 0.7 | 11.2 | 47.6 | 40.2 | 130.8 | 8.4 |
| 30—40 | 0.5 | 8.3 | 30.2 | 13.1 | 91.9 | 8.5 |
| 40—50 | 0.4 | 8.6 | 23.7 | 10.2 | 106.1 | 8.6 |
| 50—60 | 0.7 | 9.5 | 35.7 | 30.2 | 116.7 | 8.7 |
| 60—70 | 0.7 | 8.9 | 26.8 | 17.0 | 110.6 | 8.9 |
| 70—80 | 0.3 | 6.3 | 10.9 | 13.0 | 101.5 | 8.5 |
Table 1 Soil base fertility
土层 Soil layer/cm | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 13.8 | 9.1 | 53.9 | 8.6 |
| 10—20 | 0.6 | 9.8 | 25.3 | 25.4 | 97.7 | 8.8 |
| 20—30 | 0.7 | 11.2 | 47.6 | 40.2 | 130.8 | 8.4 |
| 30—40 | 0.5 | 8.3 | 30.2 | 13.1 | 91.9 | 8.5 |
| 40—50 | 0.4 | 8.6 | 23.7 | 10.2 | 106.1 | 8.6 |
| 50—60 | 0.7 | 9.5 | 35.7 | 30.2 | 116.7 | 8.7 |
| 60—70 | 0.7 | 8.9 | 26.8 | 17.0 | 110.6 | 8.9 |
| 70—80 | 0.3 | 6.3 | 10.9 | 13.0 | 101.5 | 8.5 |
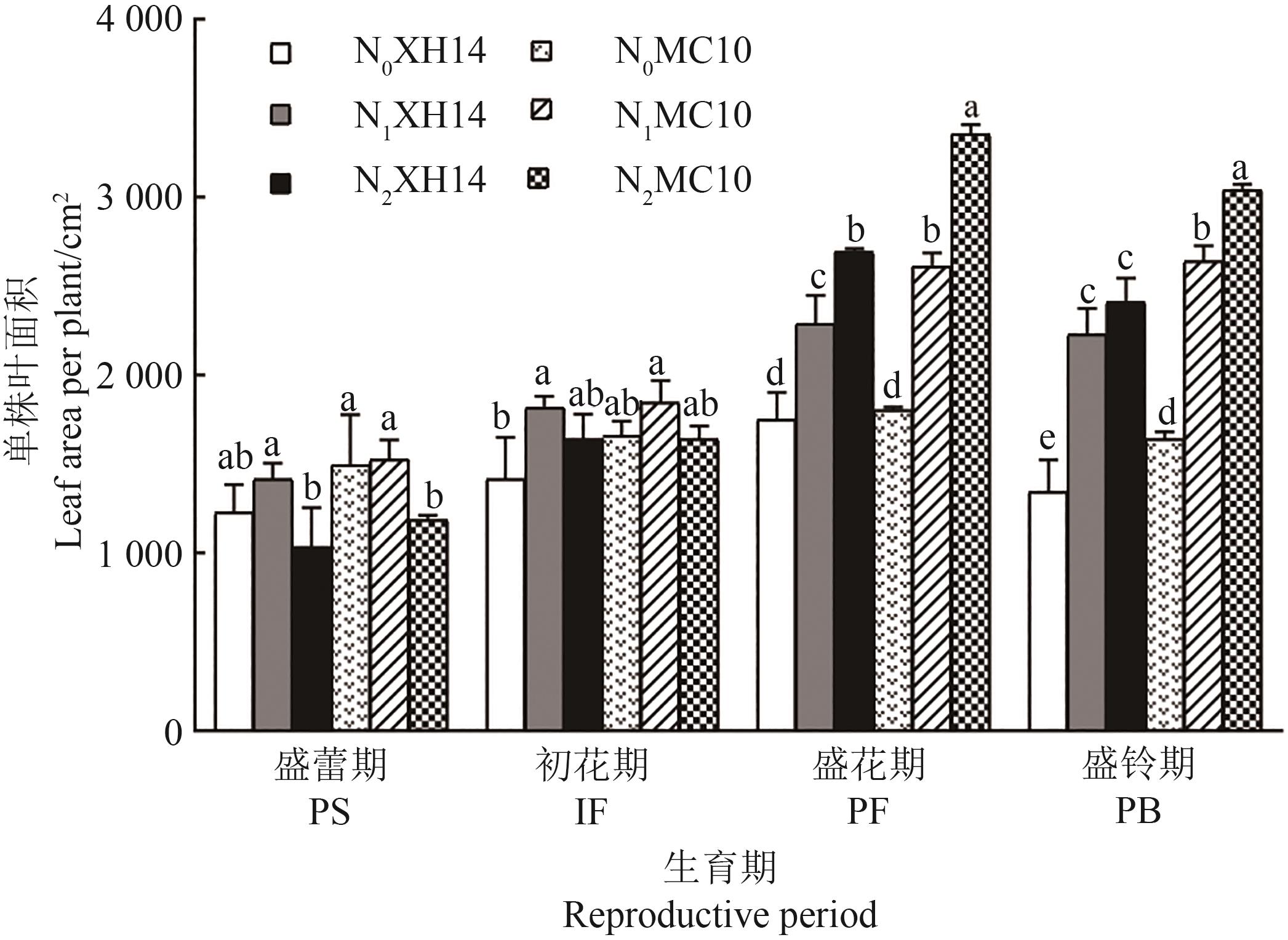
Fig. 2 Leaf area per plant of island cottons with different genotypesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
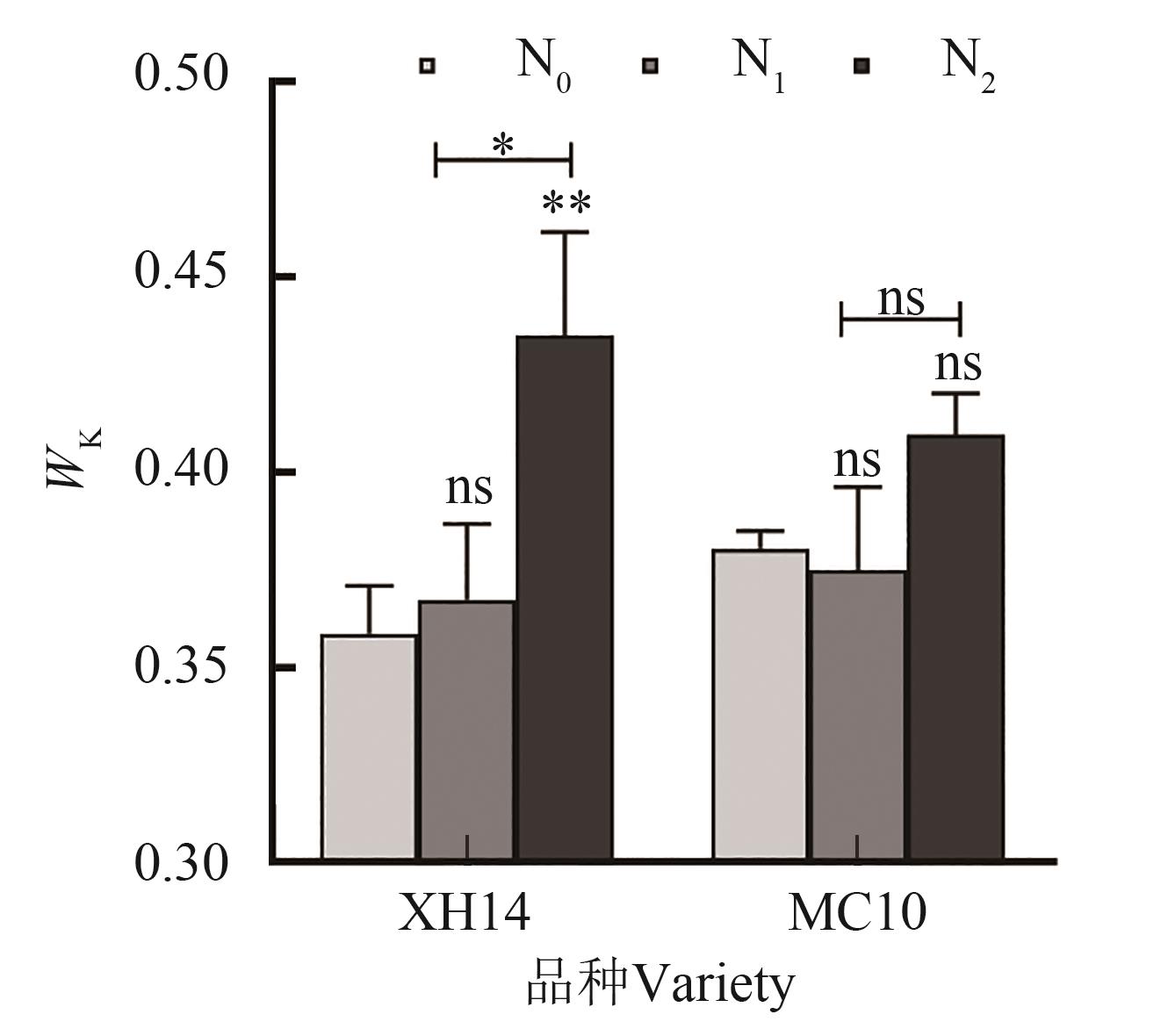
Fig. 5 Genotypic differences in Wk values of island cottons with different genotypesNote: * and ** indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively; ns indicates no significant.
| 品种Variety | 处理Treatment | VJ | Mo | φPo | ψo | φEo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XH14 | N0 | 0.50±0.04 bc | 0.76±0.1 ab | 0.75±0.01 abc | 0.50±0.04 ab | 0.38±0.04 abc |
| N1 | 0.38±0.03 c | 0.54±0.07 b | 0.79±0.04 ab | 0.62±0.03 a | 0.49±0.04 ab | |
| N2 | 0.65±0.11 a | 1.04±0.32 a | 0.68±0.08 c | 0.35±0.11 c | 0.24±0.11 c | |
| MC10 | N0 | 0.53±0.06 ab | 0.79±0.11 ab | 0.75±0.03 abc | 0.47±0.06 bc | 0.35±0.06 bc |
| N1 | 0.37±0.05 c | 0.52±0.05 b | 0.80±0.01 a | 0.63±0.05 a | 0.51±0.04 a | |
| N2 | 0.66±0.09 a | 1.05±0.17 a | 0.71±0.03 bc | 0.34±0.09 c | 0.24±0.08 c | |
| 品种Variety | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| 氮肥Nitrogen fertilizer | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 品种×氮肥Variety×nitrogen fertilizer | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
Table 2 Receptor-side changes in photosynthetic system of leaves of island cottons with different genotypes at the cotton boll period
| 品种Variety | 处理Treatment | VJ | Mo | φPo | ψo | φEo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XH14 | N0 | 0.50±0.04 bc | 0.76±0.1 ab | 0.75±0.01 abc | 0.50±0.04 ab | 0.38±0.04 abc |
| N1 | 0.38±0.03 c | 0.54±0.07 b | 0.79±0.04 ab | 0.62±0.03 a | 0.49±0.04 ab | |
| N2 | 0.65±0.11 a | 1.04±0.32 a | 0.68±0.08 c | 0.35±0.11 c | 0.24±0.11 c | |
| MC10 | N0 | 0.53±0.06 ab | 0.79±0.11 ab | 0.75±0.03 abc | 0.47±0.06 bc | 0.35±0.06 bc |
| N1 | 0.37±0.05 c | 0.52±0.05 b | 0.80±0.01 a | 0.63±0.05 a | 0.51±0.04 a | |
| N2 | 0.66±0.09 a | 1.05±0.17 a | 0.71±0.03 bc | 0.34±0.09 c | 0.24±0.08 c | |
| 品种Variety | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| 氮肥Nitrogen fertilizer | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 品种×氮肥Variety×nitrogen fertilizer | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
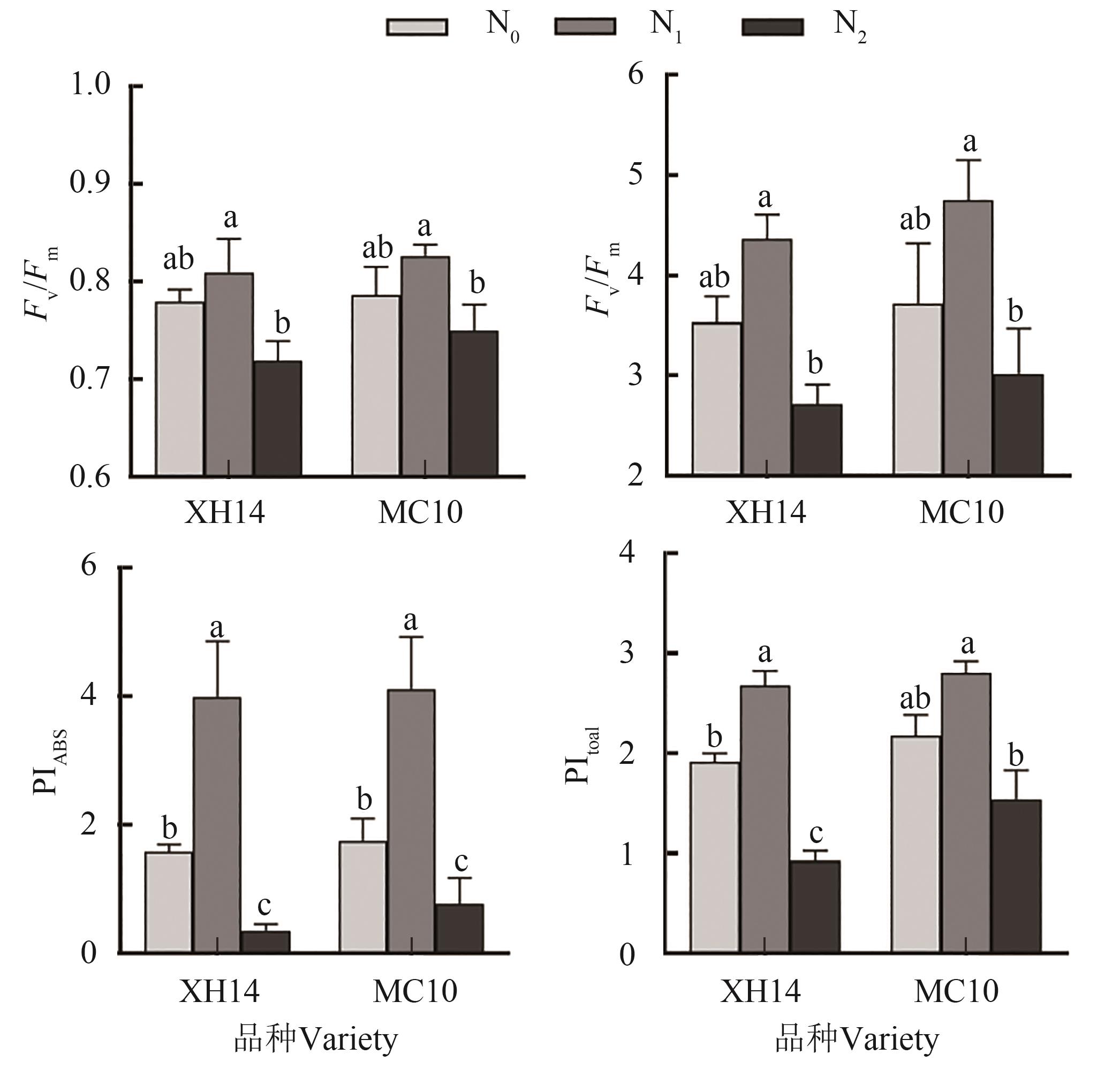
Fig. 6 Leaf fluorescence parameters and photochemical performance indexes of island cottons with different genotypes at boll stageNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same variety at P<0.05 level.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 株数/(×104 株·hm-2) Number of plants (×104 plant·hm-2) | 单株结铃数Boll number per plant | 单铃重 Boll weight/g | 衣分 Lint percentage/% | 籽棉产量 Seed cotton yield/ (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XH14 | N0 | 21.3±1.0 a | 7.1±0.04 bc | 2.6±0.15 c | 33.7±0.005 a | 3 983.4±95.2 d |
| N1 | 21.3±0.8 a | 7.4±0.24 c | 3.0±0.14 ab | 31.7±0.003 a | 4 896.9±141.4 c | |
| N2 | 21.0±0.5 a | 9.0±1.16 ab | 3.1±0.05 ab | 32.7±0.010 a | 4 735.4±783.7 c | |
| MC10 | N0 | 21.2±0.5 a | 7.7 ±0.77 bc | 3.0±0.22 ab | 32.0±0.001 a | 4 883.2±74.7 c |
| N1 | 21.0±0.8 a | 8.4±0.25 bc | 2.8±0.08 bc | 33.3±0.031 a | 5 847.7±345.3 b | |
| N2 | 21.1±0.4 a | 9.9±0.25 a | 3.2±0.07 a | 31.7±0.005 a | 6 711.9±183.2 a | |
| 品种Variety | ns | ** | * | ns | ** | |
| 氮肥Nitrogen fertilizer | ns | ns | ** | ns | ** | |
| 品种×氮肥Variety×nitrogen fertilizer | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | |
Table 3 Yield and yield components of island cottons with different genotypes
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 株数/(×104 株·hm-2) Number of plants (×104 plant·hm-2) | 单株结铃数Boll number per plant | 单铃重 Boll weight/g | 衣分 Lint percentage/% | 籽棉产量 Seed cotton yield/ (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XH14 | N0 | 21.3±1.0 a | 7.1±0.04 bc | 2.6±0.15 c | 33.7±0.005 a | 3 983.4±95.2 d |
| N1 | 21.3±0.8 a | 7.4±0.24 c | 3.0±0.14 ab | 31.7±0.003 a | 4 896.9±141.4 c | |
| N2 | 21.0±0.5 a | 9.0±1.16 ab | 3.1±0.05 ab | 32.7±0.010 a | 4 735.4±783.7 c | |
| MC10 | N0 | 21.2±0.5 a | 7.7 ±0.77 bc | 3.0±0.22 ab | 32.0±0.001 a | 4 883.2±74.7 c |
| N1 | 21.0±0.8 a | 8.4±0.25 bc | 2.8±0.08 bc | 33.3±0.031 a | 5 847.7±345.3 b | |
| N2 | 21.1±0.4 a | 9.9±0.25 a | 3.2±0.07 a | 31.7±0.005 a | 6 711.9±183.2 a | |
| 品种Variety | ns | ** | * | ns | ** | |
| 氮肥Nitrogen fertilizer | ns | ns | ** | ns | ** | |
| 品种×氮肥Variety×nitrogen fertilizer | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | |
| 1 | 郑子漂,徐海江,林涛,等.新疆长绒棉育成品种演变趋势及综合评价[J].中国农业大学学报,2022,27(6):55-70. |
| ZHENG Z P, XU H J, LIN T, et al.. Evolution trend and comprehensive evaluation of Xinjiang long-staple cotton cultivars [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2022, 27(6):55-70. | |
| 2 | 李晨阳,孔祥强,董合忠.植物吸收转运硝态氮及其信号调控研究进展[J].核农学报,2020,34(5):982-993. |
| LI C Y, KONG X Q, DONG H Z, et al.. Nitrate uptake, transport and signaling regulation pathways [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2020, 34(5):982-993. | |
| 3 | 吕钊彦.不同行管比滴灌模式对新疆春小麦产量及品质行间差异形成的影响及其生理机理[D].南京:南京农业大学,2017. |
| LYU Z Y. Effects of different row-tube drip irrigation patterns on yield and quality differences in spring wheat in Xinjiang and their physiological mechanisms [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 4 | SHAH A N, YANG G, TANVEER M, et al.. Leaf gas exchange, source-sink relationship, and growth response of cotton to the interactive effects of nitrogen rate and planting density [J/OL]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2017, 39(5):119 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 5 | 刘瑞显,王友华,陈兵林,等.花铃期干旱胁迫下氮素水平对棉花光合作用与叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].作物学报,2008,34(4): 675-683. |
| LIU R X, WANG Y H, CHEN B L, et al.. Effects of nitrogen levels on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluores-cence characteristics under drought stress in cotton flowering and boll-forming stage [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2008,34(4):675-683. | |
| 6 | PENG J, FENG Y, WANG X, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate on the photosynthetic pigment, leaf fluorescence characteristics, and yield of indica hybrid rice and their interrelations [J]. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1):1-10. |
| 7 | 娄善伟,张巨松,罗新宁,等.施氮水平对棉花农艺性状、倒四叶光合特性及产量的影响[J].新疆农业大学学报,2009,32(1):39-42. |
| LOU S W, ZHANG J S, LUO X N, et al.. Influence of nitrogenous fertilizer level on agronomic characters, fourth leaf from top photosynthetic characteristics and yield of cotton [J]. J. Xinjiang Agric. Univ., 2009, 32(1):39-42. | |
| 8 | 李强,罗延宏,余东海,等.低氮胁迫对耐低氮玉米品种苗期光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(5):1132-1141. |
| LI Q, LUO Y H, YU D H, et al.. Effects of low nitrogen stress on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of maize cultivars tolerant to low nitrogen stress at the seedling stage [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2015, 21(5):1132-1141. | |
| 9 | 石洪亮,严青青,张巨松,等.氮肥对非充分灌溉下棉花花铃期光合特性及产量的补偿作用[J].作物学报,2018,44(8):1196-1204. |
| SHI H L, YAN Q Q, ZHANG J S, et al.. Compensation effect of nitrogen fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics and yield during cotton flowering boll-setting stage under non-sufficient drip irrigation [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2018, 44(8):1196-1204. | |
| 10 | LONG J R, WAN Y Z, SONG C F, et al.. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in flag leaf of super hybrid rice at late growth stage [J]. Rice Sci., 2013, 20(3):220-228. |
| 11 | 牛静.棉花氮高效利用的生理机制及施肥效应[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2021. |
| NIU J. Physiological mechanisms of nitrogen efficient utilization of cotton (G . hirsutum L.) and fertilization effects [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 12 | 丁永刚,汤小庆,梁鹏,等.减氮对不同氮效率小麦品种花后光合物质生产力和产量的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2021,41(4):490-498. |
| DING Y G, TANG X Q, LIANG P, et al.. Effect of reduced nitrogen application on post-anthesis photosynthetic production and grain yield of wheat cultivars with various nitrogen use efficiency [J]. J. Triticeae Crops., 2021, 41(4):490-498. | |
| 13 | 尹晓明,李辰.不同氮效率水稻品种叶片光合作用及氮利用特征的差异分析[J].作物杂志,2019(1):90-96. |
| YIN X M, LI C. Differences in leaf photosynthesis and assimilation of nitrogen between two rice cultivars differing in nitrogen use efficiency [J]. Crops, 2019(1):90-96. | |
| 14 | 张盼盼,张桂堂,黄璐,等.氮肥减施下不同基因型玉米氮效率差异及生理特性研究[J].河南农业科学,2021,50(5):13-23. |
| ZHANG P P, ZHANG G T, HUANG L, et al.. Nitrogen efficiency and physiological characters of different maize genotypes under nitrogen fertilization reduction [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2021, 50(5):13-23. | |
| 15 | 夏小云.不同氮效率小麦品种光合及氮代谢差异[D].南京:南京农业大学,2019. |
| XIA X Y. Differences in photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism of wheat varieties with different nitrogen efficiency [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 16 | IQBAL A, JING N, QIANG D, et al.. Genotypic variation in carbon and nitrogen metabolism in the cotton subtending leaves and seed cotton yield under various nitrogen levels [J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2022, 103(5):2602-2617. |
| 17 | 王芳,李春梅,马云珍,等.连续定位不同施氮水平对棉花光合特性及产量的影响[J].南京农业大学学报,2022,45(1):18-26. |
| WANG F, LI C M, MA Y Z, et al.. Effect of continuous positioning of different nitrogen application levels on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of cotton [J]. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ., 2022, 45(1):18-26. | |
| 18 | 李鹏民,高辉远, STRASSER J R.快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学分析在光合作用研究中的应用[J].植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2005,31(6):559-566. |
| LI P M, GAO H Y, STRASSER J R. Application of rapid chlorophyll fluorescence induced kinetic analysis in photosynthesis research [J]. J. Plant Physiol. Mol. Biol., 2005,31(6): 559-566. | |
| 19 | STRASSER R, SRIVASTAVA A, TSIMILLI-MICHAEl M. The fluorescence transient as a tool to characterize and screen photosynthetic samples [J]. Probing Photosynthesis, 2000, 25(2):445-483. |
| 20 | 窦巧巧,张巨松,何庆雨,等.花铃期减量滴灌对北疆棉花光合特性及产量的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2021,39(3):51-58. |
| DOU Q Q, ZHANG J S, HE Q Y, et al.. Effect of reduced drip irrigation on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of cotton during flowering and bollstagein in Northern Xinjiang [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2021, 39(3):51-58. | |
| 21 | 张旺锋,勾玲,王振林,等.氮肥对新疆高产棉花叶片叶绿素荧光动力学参数的影响[J].中国农业科学,2003,36(8):893-898. |
| ZHANG W F, GOU L, WANG Z L, et al.. Effect of nitrogen on chlorophyll fluorescence of leaves of high-yielding cotton in Xinjiang [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2003,36(8):893-898. | |
| 22 | STIRBET A. On the relation between the Kautsky effect (chlorophyll a fluorescence induction) and photosystem Ⅱ: basics and applications of the OJIP fluorescence transient [J]. J. Photochem. Photobiol., 2011, 104(1-2):236-257. |
| 23 | FURBANK R T, SHARWOOD R, ESTAVILLO G M, et al.. Photons to food: genetic improvement of cereal crop photosynthesis [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2020, 71(7):2226-2238. |
| 24 | 王燕,王树林,韩硕,等.机采棉模式下氮肥用量对棉花株型结构塑造和产量的影响[J].新疆农业科学,2021,58(9):1642-1647. |
| WANG Y, WANG S L, HAN S,et al.. Effect of nitrogen application rates on plant architecture and yield of cotton production with machine picking in Hebei [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2021, 58(9):1642-1647. | |
| 25 | IQBAL A, DONG Q, WANG X, et al.. Variations in nitrogen metabolism are closely linked with nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency in cotton genotypes under various nitrogen supplies [J/OL]. Plants, 2020, 9(2):250 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 26 | DAI J L, LI W J, TANG W, et al.. Manipulation of dry matter accumulation and partitioning with plant density in relation to yield stability of cotton under intensive management [J]. Field Crops Res., 2015, 180(8):207-215. |
| 27 | 孙红春,李存东,周彦珍.不同氮素水平对棉花功能叶生理特性、植株性状及产量构成的影响[J].河北农业大学学报,2005,28(6):9-14. |
| SUN H C, LI C D, ZHOU Y Z. Effects of different levels of nitrogen on physiological characteristics of function leaf and plant traits and yield components of cotton [J]. J. Hebei Agric.Univ., 2005,28(6):9-14. | |
| 28 | 娄善伟,阿斯卡尔·卡地尔,李杰,等.不同氮效棉花品种植株农艺性状、氮素积累及光合特性差异[J].新疆农业科学,2019,56(12):2219-2227. |
| LOU S W, Kadier Asikaer, LI J, et al.. The differences in plant agronomic traits, nitrogen accumulation and photosynthetic characteristics of cotton varieties with different nitrogen efficiency [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2019, 56(12):2219-2227. | |
| 29 | TAYLARAN R D, ADACH S, OOKAWA T, et al.. Hydraulic conductance as well as nitrogen accumulation plays a role in the higher rate of leaf photosynthesis of the most productive variety of rice in Japan [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2011, 62(11):4067-4077. |
| 30 | 张旭.小麦氮素高效利用的基因型差异及形态生理特性[D].南京:南京农业大学,2016. |
| ZHANG X. Differences in the basis type and morphological characteristics of the high efficiency of wheat nitrogen [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 31 | CHEN Y, XIAO C, WU D, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate on grain yield and grain nitrogen concentration in two maize hybrids with contrasting nitrogen remobilization efficiency [J]. Eur. J. Agron., 2015, 62:79-89. |
| 32 | 孙山,王少敏,王家喜,等.黑暗中脱水对‘金太阳’杏离体叶片PSⅠ和PSⅡ功能的影响[J].园艺学报,2008,35(1):1-6. |
| SUN S, WANG S M, WANG J X, et al.. Effects of dehydration in the dark on functions of PSⅠ and PSⅡ in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L. ‘Jin Taiyang’) leaves [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2008,35(1):1-6. | |
| 33 | CUN Z, ZHANG J Y, WU H M, et al.. High nitrogen inhibits photosynthetic performance in a shade-tolerant and N-sensitive species Panax notoginseng [J]. Photosynth. Res., 2021, 147:283-300. |
| 34 | STRASSER B J. Measuring fast fluorescence transients to address environmental questions: the JIP test [J/OL]. Photosynthesis, 1995, 1:1142 [2023-02-20]. . |
| 35 | 王准,张恒恒,董强,等.棉花耐低氮和氮敏感种质筛选及验证[J].棉花学报,2020,32(6):538-551. |
| WANG Z, ZHANG H H, DONG Q, et al.. Screening and verification of low nitrogen tolerant and nitrogen sensitive cotton germplasm [J]. Cott. Sci., 2020, 32(6):538-551. |
| [1] | Yike XU, Shuang LI, Changle LIU, Peiwen KOU, Xiaochun SUN, Wenjing HUANG. Study on Agronomic Characters and Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Pinellia ternata from Different Producing Areas [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 77-89. |
| [2] | Xueyan XIA, Jihan CUI, Meihong HUANG, Shuai GUO, Meng LIU, Yu ZHAO, Yiwei LU, Wenqin ZHAO, Jingxin WANG, Shunguo LI. Analysis of High-efficiency Transcriptome of Nitrogen in Millet Seedlings and Gene Mining [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 41-57. |
| [3] | Shengyan YANG, Man CAO, Baoshi GUO, Chao YANG, Zhixia HOU. Effects of Different Iron Environments on the Growth and Leaf Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics of Blueberry [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 52-62. |
| [4] | Peixin LIANG, Rong TANG, Jianguo LIU. Effects of Mixed Saline-alkali Stress on Photosynthetic Physiology and Yield in Cyperus esculentus L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 195-204. |
| [5] | TANG Xinhua, QU Zicheng, ZHANG Xia, ZHANG Hao, WEI Qiaorong, SHI Ying*. Effect of Irrigating Steady-state Iron Salts on Potato Physiology and Yield During Tuber Formation Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(8): 7-15. |
| [6] | CHEN Biao1, ZHANG Jie1, MA Xiaohan1, WANG Xiaodong2, LI Jiwei2, XU Zicheng1*. Influences of Exogenous Selenium on the Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics and Chemical Composition in Flue-cured Tobacco under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(10): 95-104. |
| [7] | FAN Liping§, ZHU Yafu§, WU Penghao, WANG Liping, WANG Xinyi, . Association Analysis of Island Cotton Fiber Quality Traits [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(8): 16-24. |
| [8] | CHEN Fang-quan1, SHAO Hui-fang1*, JIA Guo-tao1, XU Zi-cheng1, HUANG Wu-xing1, FAN Yi-kuan2, DU Xiu-zhi3, ZHANG Man-man1, ZHAO Rong-rong1. Effect of Water Retaining Agent on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters of Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(5): 157-163. |
| [9] | DUAN Long\|fei1, SHANG Ai\|qin1*, YANG Min\|sheng2, WANG Jin\|mao2, ZUO Li\|hui2. Studies on Diurnal Variations of Photosynthetic Characteristics and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters of Different Clones of Ulmus pumila cv. ‘Zhonghua jinye’ [J]. , 2014, 16(6): 21-27. |
| [10] | CUI Shi-you, MIAO Ya-mei| SHI Chuan-huai| YU Cong-hua. Research and Prospects of Breeding for Nitrogen Efficiency in Rice [J]. , 2006, 8(6): 47-51. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号