




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (10): 186-194.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0060
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles Next Articles
Juan YANG( ), Yong GAO(
), Yong GAO( ), Ruidong WANG, Tianxiao GAO, Wenyuan YANG, Min HAN
), Ruidong WANG, Tianxiao GAO, Wenyuan YANG, Min HAN
Received:2024-01-22
Accepted:2024-06-04
Online:2024-10-15
Published:2024-10-18
Contact:
Yong GAO
通讯作者:
高永
作者简介:杨娟 E-mail:yjhaom@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Juan YANG, Yong GAO, Ruidong WANG, Tianxiao GAO, Wenyuan YANG, Min HAN. Soil Particle Composition and Nutrient Characteristics of Wind Erosion Pits in Sandy Grassland[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 186-194.
杨娟, 高永, 王瑞东, 高天笑, 杨文源, 韩敏. 沙质草原风蚀坑土壤粒度组成及养分特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 186-194.
发育阶段 Developmental stage | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 黏粒 Clay | 粉粒 Powder particle | 砂粒Grit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
极细砂 Very fine sand | 细砂 Fine sand | 中砂 Medium sand | 粗砂 Coarse sand | ||||
未风蚀草地 Unwind-eroded grassland | 0—10 | 13.71±2.02 a | 20.60±9.41 a | 0.16±0.26 a | 33.78±19.30 a | 30.21±7.40 b | 1.54±1.97 b |
| 10—20 | 10.98±2.78 a | 11.11±2.68 a | 0.51±0.88 a | 39.61±18.36 a | 35.56±15.05 a | 2.23±3.05 a | |
| 0—20 | 12.34±2.17 a | 15.85±5.24 a | 0.34±0.57 a | 36.70±18.75 a | 32.88±11.16 b | 1.89±2.50 b | |
裸地沙斑 Bare sand spots | 0—10 | 7.10±1.36 b | 2.93±1.41 b | 0.19±0.29 a | 44.30±12.10 a | 43.43±11.90 ab | 2.05±1.56 b |
| 10—20 | 5.71±0.24 b | 1.53±0.72 c | 0.19±0.16 a | 49.26±12.76 a | 41.59±10.41 a | 1.71±2.00 a | |
| 0—20 | 6.40±0.71 b | 2.23±0.89 b | 0.19±0.20 a | 46.79±11.77 a | 42.51±10.15 ab | 1.88±1.65 b | |
活跃发展 Active development | 0—10 | 3.82±0.64 b | 1.04±0.55 b | 0.01±0.00 a | 25.03±9.29 a | 58.87±4.59 a | 11.24±6.30 a |
| 10—20 | 3.15±1.01 b | 0.70±0.98 c | 0.09±0.09 a | 36.72±21.56 a | 51.13±11.82 a | 8.21±11.39 a | |
| 0—20 | 3.48±0.80 b | 0.87±0.75 b | 0.05±0.04 a | 30.88±14.86 a | 55.00±8.19 a | 9.72±8.01 a | |
固定阶段 Stationary stage | 0—10 | 7.29±2.85 b | 1.53±0.74 b | 0.09±0.09 a | 42.85±12.60 a | 45.62±12.36 ab | 2.62±3.02 b |
| 10—20 | 5.03±1.58 b | 0.60±0.48 c | 0.28±0.48 a | 44.22±18.87 a | 46.54±15.47 a | 3.32±3.21 a | |
| 0—20 | 6.11±1.79 b | 1.07±0.29 b | 0.27±0.32 a | 43.53±13.73 a | 46.06±12.54 ab | 2.96±2.31 b | |
消亡阶段 Extinction stage | 0—10 | 12.24±5.03 a | 4.03±3.00 b | 0.04±0.03 a | 42.36±8.05 a | 40.35±5.81 ab | 0.98±0.58 b |
| 10—20 | 13.61±5.55 a | 7.56±3.84 b | 0.07±0.08 a | 42.49±13.07 a | 35.60±5.31 a | 0.67±0.52 a | |
| 0—20 | 12.92±5.02 a | 5.80±3.16 b | 0.06±0.04 a | 42.42±10.07 a | 37.97±2.01 ab | 0.83±0.37 a | |
活化阶段 Activation stage | 0—10 | 5.10±0.71 b | 1.26±0.60 b | 0.29±0.44 a | 49.94±11.71 a | 41.80±12.00 ab | 1.61±1.20 b |
| 10—20 | 3.99±0.13 b | 0.49±0.13 c | 0.05±0.05 a | 42.66±9.92 a | 49.60±7.28 a | 3.20±2.70 a | |
| 0—20 | 4.54±0.41 b | 0.88±0.36 b | 0.17±0.21 a | 46.30±8.14 a | 45.70±7.02 ab | 2.41±1.66 b | |
Table 1 Soil particle size composition of wind erosion pits at different development stages
发育阶段 Developmental stage | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 黏粒 Clay | 粉粒 Powder particle | 砂粒Grit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
极细砂 Very fine sand | 细砂 Fine sand | 中砂 Medium sand | 粗砂 Coarse sand | ||||
未风蚀草地 Unwind-eroded grassland | 0—10 | 13.71±2.02 a | 20.60±9.41 a | 0.16±0.26 a | 33.78±19.30 a | 30.21±7.40 b | 1.54±1.97 b |
| 10—20 | 10.98±2.78 a | 11.11±2.68 a | 0.51±0.88 a | 39.61±18.36 a | 35.56±15.05 a | 2.23±3.05 a | |
| 0—20 | 12.34±2.17 a | 15.85±5.24 a | 0.34±0.57 a | 36.70±18.75 a | 32.88±11.16 b | 1.89±2.50 b | |
裸地沙斑 Bare sand spots | 0—10 | 7.10±1.36 b | 2.93±1.41 b | 0.19±0.29 a | 44.30±12.10 a | 43.43±11.90 ab | 2.05±1.56 b |
| 10—20 | 5.71±0.24 b | 1.53±0.72 c | 0.19±0.16 a | 49.26±12.76 a | 41.59±10.41 a | 1.71±2.00 a | |
| 0—20 | 6.40±0.71 b | 2.23±0.89 b | 0.19±0.20 a | 46.79±11.77 a | 42.51±10.15 ab | 1.88±1.65 b | |
活跃发展 Active development | 0—10 | 3.82±0.64 b | 1.04±0.55 b | 0.01±0.00 a | 25.03±9.29 a | 58.87±4.59 a | 11.24±6.30 a |
| 10—20 | 3.15±1.01 b | 0.70±0.98 c | 0.09±0.09 a | 36.72±21.56 a | 51.13±11.82 a | 8.21±11.39 a | |
| 0—20 | 3.48±0.80 b | 0.87±0.75 b | 0.05±0.04 a | 30.88±14.86 a | 55.00±8.19 a | 9.72±8.01 a | |
固定阶段 Stationary stage | 0—10 | 7.29±2.85 b | 1.53±0.74 b | 0.09±0.09 a | 42.85±12.60 a | 45.62±12.36 ab | 2.62±3.02 b |
| 10—20 | 5.03±1.58 b | 0.60±0.48 c | 0.28±0.48 a | 44.22±18.87 a | 46.54±15.47 a | 3.32±3.21 a | |
| 0—20 | 6.11±1.79 b | 1.07±0.29 b | 0.27±0.32 a | 43.53±13.73 a | 46.06±12.54 ab | 2.96±2.31 b | |
消亡阶段 Extinction stage | 0—10 | 12.24±5.03 a | 4.03±3.00 b | 0.04±0.03 a | 42.36±8.05 a | 40.35±5.81 ab | 0.98±0.58 b |
| 10—20 | 13.61±5.55 a | 7.56±3.84 b | 0.07±0.08 a | 42.49±13.07 a | 35.60±5.31 a | 0.67±0.52 a | |
| 0—20 | 12.92±5.02 a | 5.80±3.16 b | 0.06±0.04 a | 42.42±10.07 a | 37.97±2.01 ab | 0.83±0.37 a | |
活化阶段 Activation stage | 0—10 | 5.10±0.71 b | 1.26±0.60 b | 0.29±0.44 a | 49.94±11.71 a | 41.80±12.00 ab | 1.61±1.20 b |
| 10—20 | 3.99±0.13 b | 0.49±0.13 c | 0.05±0.05 a | 42.66±9.92 a | 49.60±7.28 a | 3.20±2.70 a | |
| 0—20 | 4.54±0.41 b | 0.88±0.36 b | 0.17±0.21 a | 46.30±8.14 a | 45.70±7.02 ab | 2.41±1.66 b | |
发育阶段 Developmental stage | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 平均粒径 Mean particle size/μm | 分选系数 Sorting factor | 偏度 Skewness | 峰态 Peak state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
未风蚀草地 Unwind-eroded grassland | 0—10 | 3.67±0.06 a | 2.57±0.17 a | 0.74±0.04 a | 1.17±0.91 c |
| 10—20 | 3.41±0.30 a | 2.41±0.19 a | 0.77±0.02 a | 2.23±1.34 ab | |
| 0—20 | 3.55±0.17 a | 2.51±0.17 a | 0.76±0.01 a | 1.34±1.15 b | |
裸地沙斑 Baresand spots | 0—10 | 1.98±0.21 bc | 1.36±0.05 bc | 0.45±0.02 b | 3.65±0.14 a |
| 10—20 | 1.98±0.16 b | 1.29±0.01 b | 0.43±0.01 b | 3.67±0.10 a | |
| 0—20 | 1.98±0.16 bc | 1.33±0.03 bc | 0.44±0.01 bc | 3.67±0.06 a | |
活跃发展 Active development | 0—10 | 1.58±0.17 c | 0.79±0.39 c | 0.22±0.17 c | 1.93±1.47 bc |
| 10—20 | 1.73±0.36 b | 0.74±0.39 b | 0.19±0.19 c | 1.77±1.31 ab | |
| 0—20 | 1.65±0.25 c | 0.78±0.39 c | 0.19±0.19 d | 1.82±1.35 ab | |
固定阶段 Stationary stage | 0—10 | 1.93±0.24 bc | 1.35±0.07 bc | 0.45±0.03 b | 3.81±0.21 a |
| 10—20 | 1.88±0.25 b | 0.84±0.46 b | 0.24±0.18 bc | 2.10±1.67 ab | |
| 0—20 | 1.90±0.21 bc | 1.33±0.05 bc | 0.43±0.01 bc | 3.76±0.24 a | |
消亡阶段 Extinction stage | 0—10 | 2.61±0.97 b | 1.87±0.78 b | 0.59±0.18 ab | 3.35±0.96 ab |
| 10—20 | 3.09±0.85 a | 2.19±0.69 a | 0.70±0.15 a | 2.59±1.73 ab | |
| 0—20 | 2.68±0.94 b | 1.91±0.78 ab | 0.61±0.17 ab | 2.70±1.79 ab | |
活化阶段 Activation stage | 0—10 | 1.98±0.19 bc | 1.24±0.06 bc | 0.41±0.01 b | 3.49±0.21 a |
| 10—20 | 1.84±0.13 b | 0.56±0.02 b | 0.13±0.01 c | 1.12±0.03 b | |
| 0—20 | 1.91±0.12 bc | 1.02±0.39 c | 0.32±0.15 cd | 2.68±1.32 ab |
Table 2 Soil particle size parameters of different soil layers
发育阶段 Developmental stage | 土层 Soil layer/cm | 平均粒径 Mean particle size/μm | 分选系数 Sorting factor | 偏度 Skewness | 峰态 Peak state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
未风蚀草地 Unwind-eroded grassland | 0—10 | 3.67±0.06 a | 2.57±0.17 a | 0.74±0.04 a | 1.17±0.91 c |
| 10—20 | 3.41±0.30 a | 2.41±0.19 a | 0.77±0.02 a | 2.23±1.34 ab | |
| 0—20 | 3.55±0.17 a | 2.51±0.17 a | 0.76±0.01 a | 1.34±1.15 b | |
裸地沙斑 Baresand spots | 0—10 | 1.98±0.21 bc | 1.36±0.05 bc | 0.45±0.02 b | 3.65±0.14 a |
| 10—20 | 1.98±0.16 b | 1.29±0.01 b | 0.43±0.01 b | 3.67±0.10 a | |
| 0—20 | 1.98±0.16 bc | 1.33±0.03 bc | 0.44±0.01 bc | 3.67±0.06 a | |
活跃发展 Active development | 0—10 | 1.58±0.17 c | 0.79±0.39 c | 0.22±0.17 c | 1.93±1.47 bc |
| 10—20 | 1.73±0.36 b | 0.74±0.39 b | 0.19±0.19 c | 1.77±1.31 ab | |
| 0—20 | 1.65±0.25 c | 0.78±0.39 c | 0.19±0.19 d | 1.82±1.35 ab | |
固定阶段 Stationary stage | 0—10 | 1.93±0.24 bc | 1.35±0.07 bc | 0.45±0.03 b | 3.81±0.21 a |
| 10—20 | 1.88±0.25 b | 0.84±0.46 b | 0.24±0.18 bc | 2.10±1.67 ab | |
| 0—20 | 1.90±0.21 bc | 1.33±0.05 bc | 0.43±0.01 bc | 3.76±0.24 a | |
消亡阶段 Extinction stage | 0—10 | 2.61±0.97 b | 1.87±0.78 b | 0.59±0.18 ab | 3.35±0.96 ab |
| 10—20 | 3.09±0.85 a | 2.19±0.69 a | 0.70±0.15 a | 2.59±1.73 ab | |
| 0—20 | 2.68±0.94 b | 1.91±0.78 ab | 0.61±0.17 ab | 2.70±1.79 ab | |
活化阶段 Activation stage | 0—10 | 1.98±0.19 bc | 1.24±0.06 bc | 0.41±0.01 b | 3.49±0.21 a |
| 10—20 | 1.84±0.13 b | 0.56±0.02 b | 0.13±0.01 c | 1.12±0.03 b | |
| 0—20 | 1.91±0.12 bc | 1.02±0.39 c | 0.32±0.15 cd | 2.68±1.32 ab |
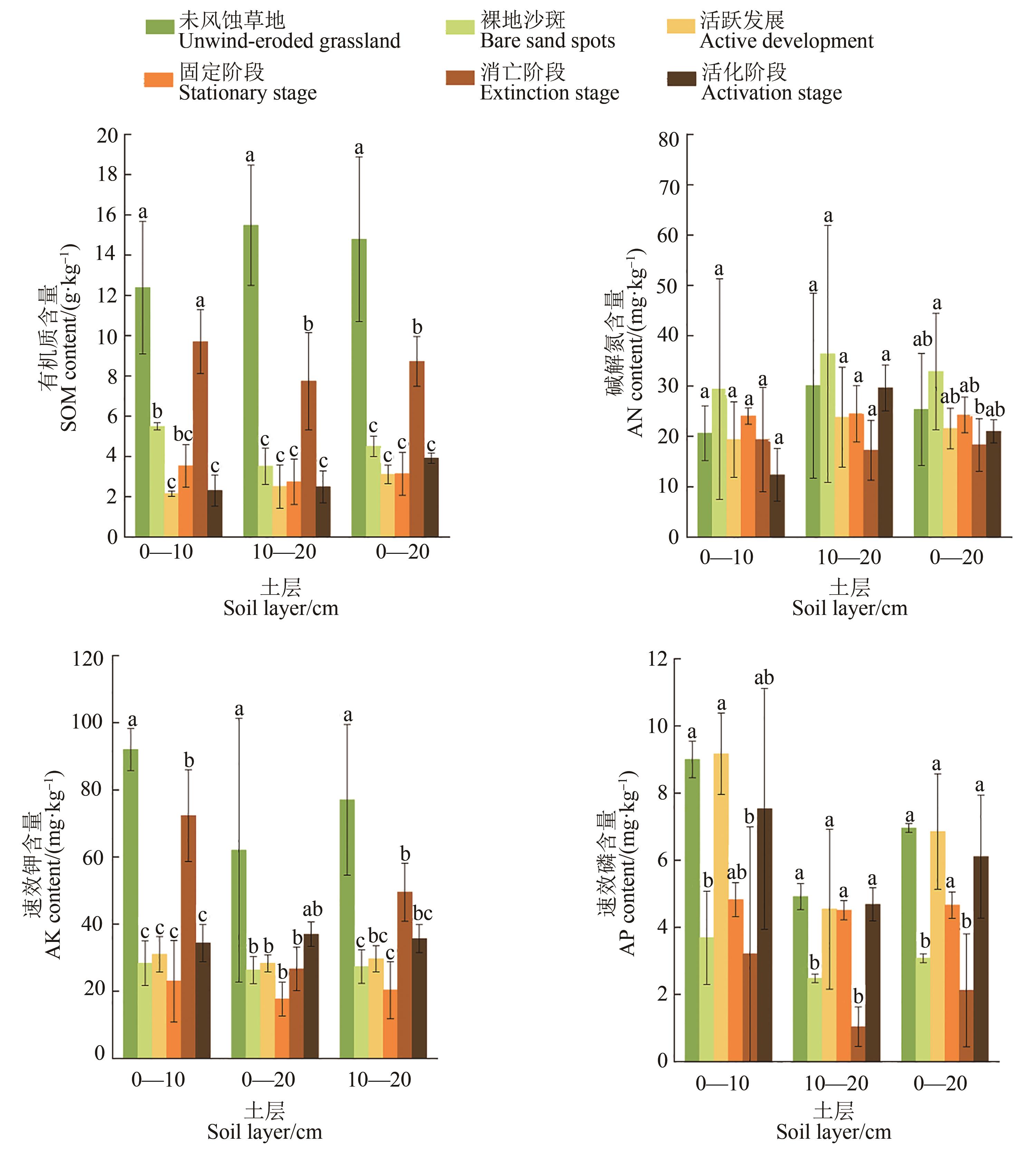
Fig. 3 Soil nutrient content in different development stagesNote: different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different developmental stages of same soil layer at P<0.05 level.
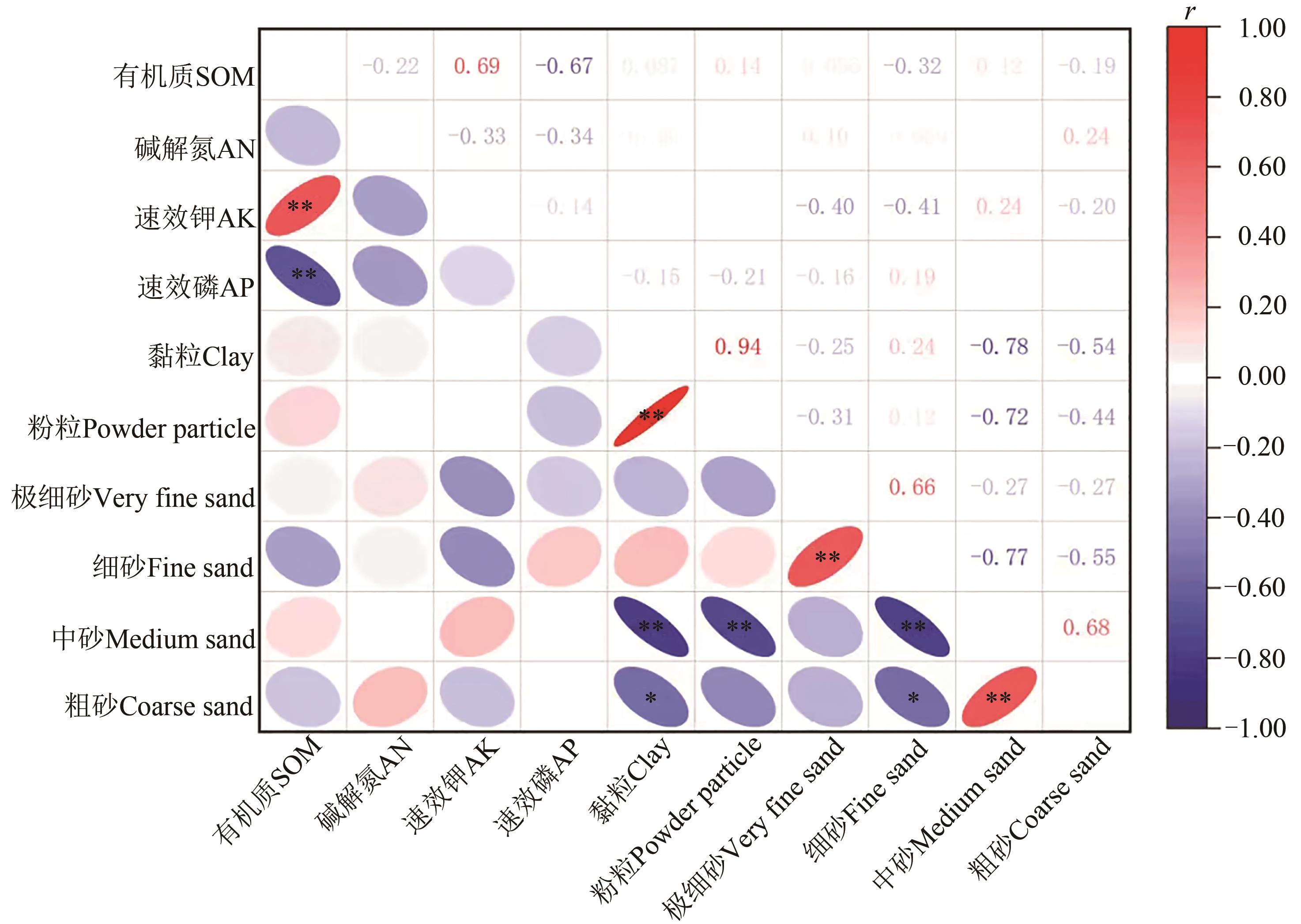
Fig. 4 Correlation analysis of soil nutrients and particle size in different development stagesNote: * , ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05, P<0.01 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 黄麟,李佳慧,张海燕,等.草原生态价值的内涵、核算及评估[J].草业学报,2024,33(6):47-63. |
| HUANG L, LI J H, ZHANG H Y, et al.. Accounting and assessment of grassland ecological values [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2024, 33(6):47-63. | |
| 2 | TEAGUE R, BARNES M. Grazing management that regenerates ecosystem function and grazingland livelihoods [J]. Afr. J. Range Forage., 2017, 34(2):77-86. |
| 3 | 周磊,魏雪,王长庭,等.高寒草地小型土壤节肢动物群落特征及其对草地退化的指示作用[J].草业学报,2022,31(3):34-46. |
| ZHOU L, WEI X, WANG C T,et al..Differences in soil microarthropod community structure in alpine grasslands with differing degrees of degradation [J].Acta Pratac. Sin.,2022,31(3):34-46. | |
| 4 | 唐芳林,宋中山,孙暖,等.关于国有草场建设的思考[J].草地学报,2021,29(5):861-865. |
| TANG F L, SONG Z S, SUN N, et al.. Views on the construction of state-owned rangeland [J].Acta Agrestia Sin.,2021,29(5):861-865. | |
| 5 | 王琪,郑佳华,赵萌莉,等.增温对荒漠草原不同退化程度草地恢复初期影响的研究[J].草地学报,2022,30(5):1077-1085. |
| WANG Q, ZHENG J H, ZHAO M L, et al.. Effects of warming on early restoration of degraded grassland in desert steppe [J].Acta Agrestia Sin., 2022,30(5):1077-1085. | |
| 6 | 张德平,孙宏伟,王效科,等.呼伦贝尔沙质草原风蚀坑研究(Ⅱ):发育过程[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(1):20-24,170-171. |
| ZHANG D P, SUN H W, WANG X K,et al..HulunBuir sandy grassland blowouts(Ⅱ):process of development and landscape evolution [J]. J. Desert Res., 2007,27(1):20-24,170-171. | |
| 7 | 胡日娜,哈斯额尔敦,浩毕斯哈拉图,等.浑善达克沙地东南缘固定沙丘风蚀坑动态变化[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(1):34-43. |
| HU R N, Eerdun Hasi, Halatu Haobisi,et al..Dynamic changes of blowouts on fixed sand dunes in the southeastern fringe of otindag sandy land [J]. J. Desert Res., 2019,39(1):34-43. | |
| 8 | KIMIA C A, LAN J W, PATRICK A H, et al.. Spatial-temporal evolution of aeolian blowout dunes at Cape Cod [J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 236:148-162. |
| 9 | 姬亚芹,单春艳,王宝庆.土壤风蚀原理和研究方法及控制技术[M].北京:科学出版社,2015:1-288. |
| 10 | ZENG Q C, LIU Y, FANG Y, et al.. Impact of vegetation restoration on plants and soil C∶N∶P stoichiometry on the Yunwu Mountain Reserve of China [J]. Ecol. Eng., 2017, 109(12):92-100. |
| 11 | 周炎广,王卓然,青达木尼,等.浑善达克沙地固定沙丘风蚀坑形态变化及其动力学机制[J].科学通报,2023,68(11):1298-1311. |
| ZHOU Y G, WANG Z R,Qingdamuni,et al..Morphological changes and dynamic mechanism of blowouts on fixed dunes in the Otingdag sandy land,China [J]. Chin. Sci. Bull.,2023,68(11):1298-1311. | |
| 12 | 孙禹,杜会石,刘美萍,等.风蚀坑形态-动力学研究进展[J].地理科学,2015,35(7):898-904. |
| SUN Y, DU H S, LIU M P,et al..A review on morphodynamic processes of blowouts [J]. Sci. Geogr. Sin., 2015,35(7):898-904. | |
| 13 | 刘忠闪. 风蚀坑形态动力学响应的数值模拟[D].兰州:兰州大学,2023. |
| LIU Z S. Numerical simulation of dynamic response of wind erosion pit morphology [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2023. | |
| 14 | 车雪华,罗万银,邵梅,等.青海共和盆地不同发育阶段风蚀坑表面气流场与形态反馈研究[J].地球科学进展,2021,36(1):95-109. |
| CHE X H, LUO W Y, SHAO M, et al.. Form-flow feedback within blowouts at different developing stages in the Gonghe Basin,Qinghai province [J]. Adv. Earth Sci., 2021,36(1):95-109. | |
| 15 | 张绍云,董玉祥,哈斯额尔敦,等.福建海坛岛海岸沙地风蚀坑形态动力学与形态演化特征[J].地理研究,2024,43(1):255-271. |
| ZHANG S Y, DONG Y X, Eerdun Hasi, et al.. Morphological dynamics and morphological evolution characteristics of wind erosion pits in coastal sandy land of Haitan Island, Fujian Province [J]. Geography Study, 2024,43(1):255-271. | |
| 16 | 李雨薇,王博,包玉海,等.草原风蚀坑发育对土壤生态化学计量的影响[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(5):166-175. |
| LI Y W, WANG B, BAO Y H, et al.. Effects of the development of grassland blowouts on soil ecological stoichiometry [J]. J. Desert Res., 2023,43(5):166-175. | |
| 17 | 乌吉斯古楞. 内蒙古多伦县乡村空间格局演变及影响因素[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2023. |
| Wujisiguleng. Evolution and influencing factors of rural spatial pattern in Duolun county, Inner Mongolia [D]. Hohhot : Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| 18 | 高海燕,闫德仁,胡小龙,等.纱网沙障对风蚀坑积沙区土壤种子库的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2023,38(5):93-101. |
| GAO H Y, YAN D R, HU X L,et al..Influence of gauze sand barrier on the change of soil seed bank in sand accumulation area of wind erosion pit [J]. J. Northwest For. Univ., 2023,38(5):93-101. | |
| 19 | 张德平,王效科,哈斯,等.呼伦贝尔沙质草原风蚀坑研究(1):形态、分类、研究意义[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(6):894-902,插2-插8. |
| ZHANGD P, WANGX K, HA S, et al.. HulunBuir sandy grassland blowouts:geomorphology,classification,and significances [J]. J. Desert Res., 2006,26(6):894-902, 1052,1058. | |
| 20 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000:1-495. |
| 21 | FOLK R L, WARD W C. Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters [J]. J. Sedimentary Res., 1957, 27(1): 3-26. |
| 22 | 王中原,罗万银,董治宝,等.共和盆地高寒草原风蚀坑表层沉积物粒度特征及动力学意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(1):7-16. |
| WANG Z Y, LUO W Y, DONG Z B,et al..Grain size characteristics of the blowout surface sediments and its aerodynamic significance in the alpine meadow region of the Gonghe Basin [J]. J. Desert Res., 2017,37(1):7-16. | |
| 23 | 王帅,哈斯.沙质草原槽形风蚀坑表面沉积物粒度特征[J].水土保持通报,2008,28(6):122-125. |
| WANG S,HA S.Particle size variation in trough blowout on sandy grassland [J].Bull.Soil Water Conserv.,2008,28(6):122-125. | |
| 24 | 张惜伟,汪季,高永,等.呼伦贝尔沙质草原风蚀坑表层土壤粒度特征[J].干旱区研究,2017,34(2):293-299. |
| ZHANG X W, WANG J, GAO Y, et al.. Grain size characteristics of topsoil in blowouts on sandy grasslands in Hulun Buir [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2017,34(2):293-299. | |
| 25 | DUBROVINA I A, MOSHKINA E V, SIDOROVA V A,et al..The impact of land use on soil properties and structure of ecosystem carbon stocks in the middle taiga subzone of Karelia [J].Eurasian Soil Sci.,2021,54(11):1756-1769. |
| 26 | 张惜伟. 典型沙质草原风蚀坑演化过程与发育机理研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2018. |
| ZHANG X W. Study on the evolution process and development mechanism of wind erosion pit in typical sandy grassland [D]. Hohhot : Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 27 | DEAN W R J, MILTON S J, JELTSCH F. Large trees,fertile islands,and birds in arid savanna [J]. J.Arid Environ.,1999,41(1):61-78. |
| 28 | TAKIMOTO A, NAIR V D, RAMACHANDRAN NAIR P K.Contribution of trees to soil carbon sequestration under agroforestry systems in the West African Sahel [J]. Agrofor. Syst., 2009,76(1):11-25. |
| 29 | FENG Q, ENDO K N, CHENG G D. Soil carbon in desertified land in relation to site characteristics [J]. Geoderma, 2002,106(1/2):21-43. |
| [1] | QI Xiaochen1§, ZHAO Ku1§, YE Zupeng1, WANG Ting2, CHEN Bolang1*. Effects of Sophora alopecuroides Green Manure on Growth and Nutrient Characteristics of Melon [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(6): 104-112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号