




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 177-185.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0054
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Yan KUAI1( ), Xinyue SU2, Jinfeng WANG2(
), Xinyue SU2, Jinfeng WANG2( ), Zhiyong FAN1, Jianhua LI2, Nan SUN3(
), Zhiyong FAN1, Jianhua LI2, Nan SUN3( ), Jiuquan ZHANG4, Minggang XU2,3
), Jiuquan ZHANG4, Minggang XU2,3
Received:2023-01-31
Accepted:2023-04-06
Online:2023-12-15
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Jinfeng WANG,Nan SUN
蒯雁1( ), 苏欣悦2, 王晋峰2(
), 苏欣悦2, 王晋峰2( ), 范志勇1, 李建华2, 孙楠3(
), 范志勇1, 李建华2, 孙楠3( ), 张久权4, 徐明岗2,3
), 张久权4, 徐明岗2,3
通讯作者:
王晋峰,孙楠
作者简介:蒯雁 E-mail:ky2011tricaas@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yan KUAI, Xinyue SU, Jinfeng WANG, Zhiyong FAN, Jianhua LI, Nan SUN, Jiuquan ZHANG, Minggang XU. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Soil Organic Matter and Total Nitrogen in Typical Tobacco-planting Areas of Dali[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 177-185.
蒯雁, 苏欣悦, 王晋峰, 范志勇, 李建华, 孙楠, 张久权, 徐明岗. 大理典型烟区土壤有机质与全氮时空演变特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 177-185.
| 指标 Index | 等级 Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | |
| 有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | <10 | [10,15) | [15,25) | [25,35) | ≥35 |
| 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | <0.5 | [0.5,1.0) | [1.0,1.5) | [1.5,2.0) | ≥2.0 |
Table 1 Classification standards of SOM and TN in tobacco planting soil
| 指标 Index | 等级 Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | |
| 有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | <10 | [10,15) | [15,25) | [25,35) | ≥35 |
| 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | <0.5 | [0.5,1.0) | [1.0,1.5) | [1.5,2.0) | ≥2.0 |
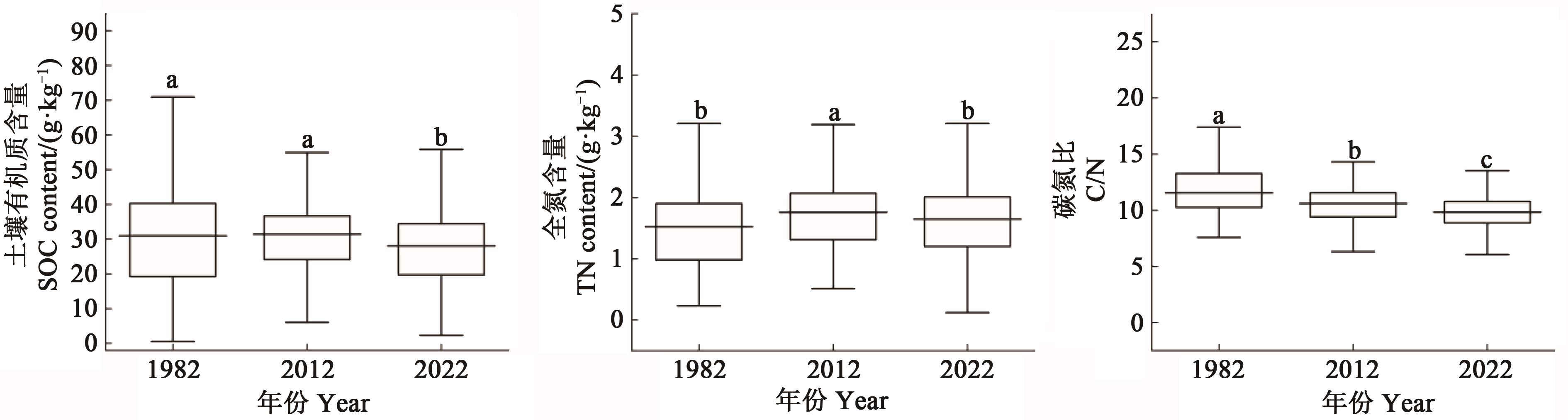
Fig. 1 Distribution characteristics of SOM, TN and C/N ratio in tobacco-planting soilNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
| 指标 Indicator | 年份 Year | 模型 Model | 块金值 Nugget | 基台值 Sill | 块金效应 Nugget effect/% | 变程 Range | 决定系数R2 | 残差 Residuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 球状 Ball | 0.47 | 2.32 | 20.26 | 5 096 | 0.13 | 1.94 |
| 2012 | 指数 Index | 0.62 | 1.52 | 40.41 | 302 400 | 0.88 | 1.50E-02 | |
| 2022 | 指数 Index | 0.32 | 1.12 | 28.38 | 11 789 | 0.51 | 1.20E-01 | |
| 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 高斯 Gaussian | 0.23 | 0.67 | 34.52 | 144 127 | 0.27 | 2.19E-01 |
| 2012 | 高斯 Gaussian | 0.03 | 0.09 | 37.90 | 85 217 | 0.92 | 1.42E-04 | |
| 2022 | 指数 Index | 0.01 | 0.05 | 26.05 | 4 343 | 0.48 | 5.94E-04 | |
碳氮比 C/N | 1982 | 高斯 Gaussian | 7.60 | 35.19 | 21.60 | 113 657 | 0.74 | 4.95E+01 |
| 2012 | 高斯 Gaussian | 1.78 | 6.24 | 28.54 | 54 040 | 0.98 | 4.32E-01 | |
| 2022 | 指数 Index | 0.04 | 0.10 | 42.81 | 39 300 | 0.77 | 5.19E-04 |
Table 2 Semi-variance function models and parameters of SOM, TN and C/N ratio in tobacco-planting soil
| 指标 Indicator | 年份 Year | 模型 Model | 块金值 Nugget | 基台值 Sill | 块金效应 Nugget effect/% | 变程 Range | 决定系数R2 | 残差 Residuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 球状 Ball | 0.47 | 2.32 | 20.26 | 5 096 | 0.13 | 1.94 |
| 2012 | 指数 Index | 0.62 | 1.52 | 40.41 | 302 400 | 0.88 | 1.50E-02 | |
| 2022 | 指数 Index | 0.32 | 1.12 | 28.38 | 11 789 | 0.51 | 1.20E-01 | |
| 全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 高斯 Gaussian | 0.23 | 0.67 | 34.52 | 144 127 | 0.27 | 2.19E-01 |
| 2012 | 高斯 Gaussian | 0.03 | 0.09 | 37.90 | 85 217 | 0.92 | 1.42E-04 | |
| 2022 | 指数 Index | 0.01 | 0.05 | 26.05 | 4 343 | 0.48 | 5.94E-04 | |
碳氮比 C/N | 1982 | 高斯 Gaussian | 7.60 | 35.19 | 21.60 | 113 657 | 0.74 | 4.95E+01 |
| 2012 | 高斯 Gaussian | 1.78 | 6.24 | 28.54 | 54 040 | 0.98 | 4.32E-01 | |
| 2022 | 指数 Index | 0.04 | 0.10 | 42.81 | 39 300 | 0.77 | 5.19E-04 |
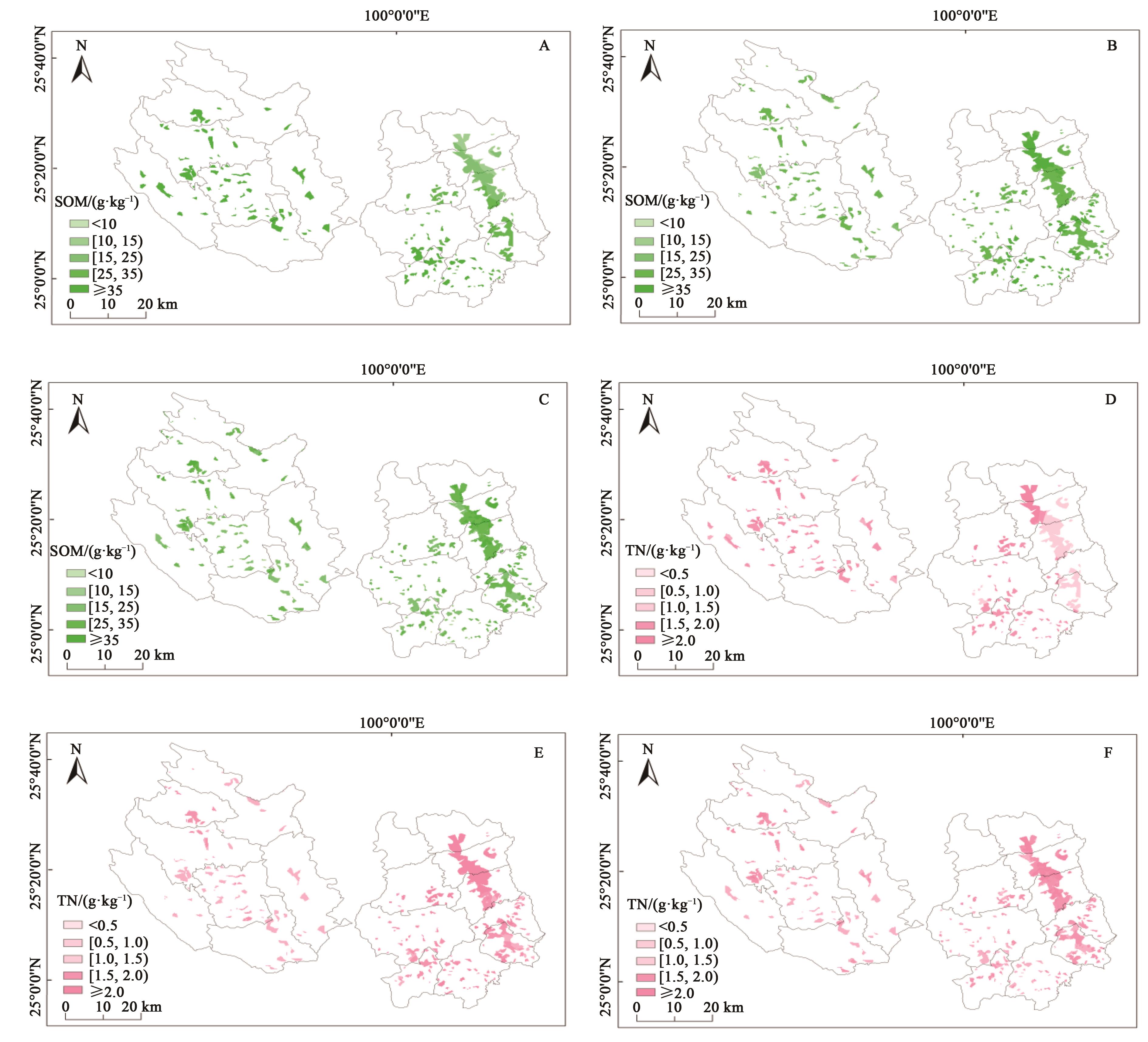
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of organic matter and total nitrogen in tobacco planting soilA~C: Spatial distribution of soil organic matter in tobacco planting soil in 1982, 2012 and 2022, respectively; D~E: Spatial distribution of soil total nitrogen in tobacco planting soil in 1982, 2012 and 2022, respectively
指标 Indicator | 年份 Year | 等级Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | ||
有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 0.14 | 7.02 | 16.43 | 35.36 | 41.05 |
| 2012 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 82.18 | 17.48 | |
| 2022 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 31.16 | 58.52 | 10.04 | |
全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 0.00 | 5.70 | 24.83 | 45.81 | 23.65 |
| 2012 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 44.03 | 31.01 | 24.95 | |
| 2022 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 40.01 | 46.76 | 12.93 | |
Table 3 Grade area proportion of organic matter and total nitrogen content in tobacco planting soil
指标 Indicator | 年份 Year | 等级Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | ||
有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 0.14 | 7.02 | 16.43 | 35.36 | 41.05 |
| 2012 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 82.18 | 17.48 | |
| 2022 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 31.16 | 58.52 | 10.04 | |
全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 1982 | 0.00 | 5.70 | 24.83 | 45.81 | 23.65 |
| 2012 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 44.03 | 31.01 | 24.95 | |
| 2022 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 40.01 | 46.76 | 12.93 | |
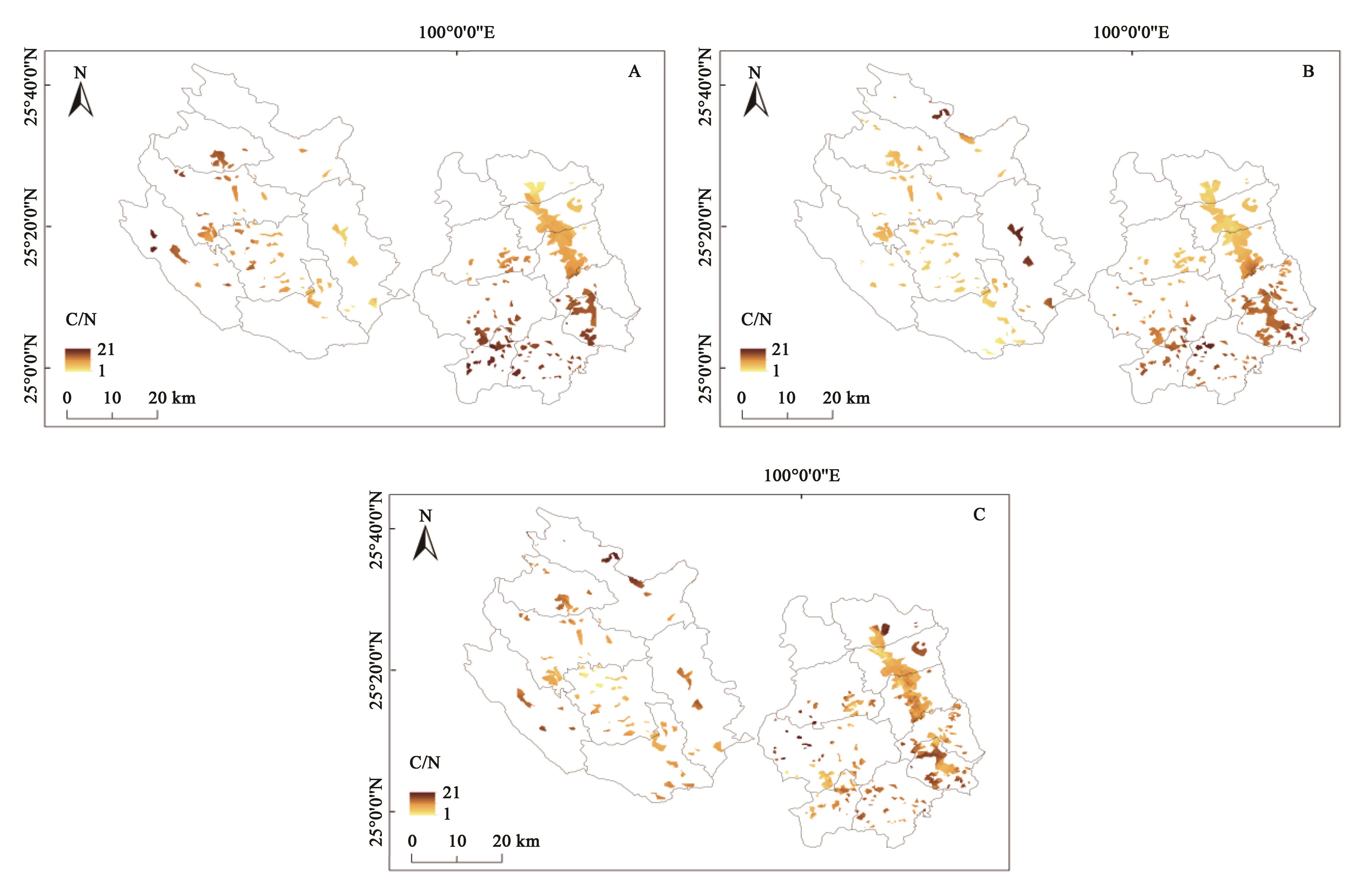
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution of C/N in tobacco planting soilA~C: Spatial distribution of C/N in tobacco planting soil in 1982, 2012 and 2022, respectively
| 1 | 徐辰生, 陈爱国, 徐茜, 等. 南平烟区植烟土壤肥力评价研究[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2016, 37(4): 24-29. |
| XU C S, CHEN A G, XU Q, et al.. Integrated evaluation of soil fertility in Nanping tobacco planting areas [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2016, 37(4): 24-29. | |
| 2 | 李倩, 索炎炎, 景延秋, 等. 南阳植烟土壤养分时空演变特征及肥力评价[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2022, 43(5): 22-30. |
| LI Q, SUO Y Y, JING Y Q, et al.. Spatial-temporal variability of soil nutrients and assessment of soil fertility in Nanyang tobacco planting areas [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2022, 43(5): 22-30. | |
| 3 | 吴杰, 李向鹏, 陈鑫, 等. 重庆市涪陵区植烟土壤养分的适宜性评价及变异分析[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(1): 106-112. |
| WU J, LI X P, CHEN X, et al.. Assessment of feasibility and variation analysis of nutrient contents in tobacco-growing soil in Fuling County, Chongqing [J]. Soils, 2020, 52(1): 106-112. | |
| 4 | 潘晓健, 刘平丽, 李露, 等. 氮肥和秸秆施用对稻麦轮作体系下土壤剖面N2O时空分布的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(2): 364-371. |
| PAN X J, LIU P L, LI L, et al.. Spatial and temporal distribution of soil profile N2O as affected by N fertilization and straw incorporation in the rice-wheat rotation system [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2015, 52(2): 364-371. | |
| 5 | 尚斌, 邹焱, 徐宜民, 等. 贵州中部山区植烟土壤有机质含量与海拔和成土母质之间的关系[J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(3): 446-451. |
| SHANG B, ZOU Y, XU Y M, et al.. Relationship between SOM contents of tobacco fields and elevation and parent materials in Central region of Guizhou province [J]. Soils, 2014, 46(3): 446-451. | |
| 6 | 樊玉星, 张洁洁, 闫凯龙, 等. 不同施氮水平对水稻土氮素供应和烤烟氮素吸收积累的影响[J]. 土壤, 2016, 48(3): 455-462. |
| FAN Y X, ZHANG J J, YAN K L, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen levels on nitrogen supply of paddy soil and nitrogen absorption and accumulation in flue-cured tobacco [J]. Soils, 2016, 48(3): 455-462. | |
| 7 | 穆金丽, 谭钧, 刘国顺, 等. 腐植酸和氮肥用量及其互作对植烟土壤质量的影响[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(1): 27-32. |
| MU J L, TAN J, LIU G S, et al.. Effects of humic acid and nitrogen levels and their interaction on tobacco planting soil quality [J]. Soils, 2017, 49(1): 27-32. | |
| 8 | HUANG B, SUN W, ZHAO Y, et al.. Temporal and spatial variability of soil organic matter and total nitrogen in an agricultural ecosystem as affected by farming practices [J]. Geoderma, 2007, 139(3): 336-345. |
| 9 | 向世鹏, 向德明, 田峰, 等. 湘西植烟土壤有机质和全氮时空变异特征研究[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(2): 372-377. |
| XIANG S P, XIANG D M, TIAN F, et al.. Temporal and spatial variability of soil total nitrogen and organic matter in tobacco-planting area of Xiangxi, Hunan [J]. Soils, 2020, 52(2): 372-377. | |
| 10 | 高旭, 周路阔, 郭婷, 等. 湖南郴州烟区土壤有机质和全氮时空变异及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(3): 686-693. |
| GAO X, ZHOU L K, GUO T, et al.. Spatial and temporal variability of soil organic matter and total nitrogen and influencing factors in Chenzhou tobacco-growing area, Hunan province [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2020, 51(3): 686-693. | |
| 11 | JIANG Y F, RAO L, SUN K, et al.. Spatio-temporal distribution of soil nitrogen in Poyang lake ecological economic zone (South-China) [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 626: 235-243. |
| 12 | 大理州烟草专卖局. 大理州植烟土壤分析评价及应用[M]. 昆明: 云南人民出版社, 2014: 12-13. |
| 13 | MATHERON G. Principles of geostatistics [J]. Econ. Geol., 1963, 58(8): 1246-1266. |
| 14 | 管孝艳, 王少丽, 高占义, 等. 盐渍化灌区土壤盐分的时空变异特征及其与地下水埋深的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(4): 198-206. |
| GUAN X Y, WANG S L, GAO Z Y, et al.. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2012, 32(4): 198-206. | |
| 15 | KRAVCHENKO A N. Influence of spatial structure on accuracy of interpolation methods [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2003, 67(5): 1564-1571. |
| 16 | 刘晓涵, 马静, 韩秋静, 等. 洛阳典型植烟土壤肥力特征及其与土壤盐分关系分析[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2018, 39(6): 21-28. |
| LIU X H, MA J, HAN Q J, et al.. Soil fertility and its relationship with soil salinity in tobacco-planting areas of Luoyang, Henan province [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2018, 39(6): 21-28. | |
| 17 | 段淑辉, 刘天波, 李建勇, 等. 湖南浏阳植烟土壤肥力评价及土壤养分变化[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2017, 38(2): 33-38. |
| DUAN S H, LIU T B, LI J Y, et al.. Evaluation of soil fertility and variability of nutrient contents of tobacco growing areas of Liuyang county of Hunan, China [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2017, 38(2): 33-38. | |
| 18 | 唐春闺, 李帆, 杨红武, 等. 浏阳植烟土壤pH和有机质时空变异及丰缺评价[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2017, 32(1): 134-139. |
| TANG C G, LI F, YANG H W, et al.. Temporal and spatial variability of soil pH and SOM in Liuyang [J]. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. ), 2017, 32(1): 134-139. | |
| 19 | 张恒, 黄莺, 刘明宏, 等. 基于空间插值法的遵义烟区植烟土壤养分时空变化[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2020, 41(3): 36-43. |
| ZHANG H, HUANG Y, LIU M H, et al.. Temporal and spatial variations of soil nutrients in Zunyi tobacco growing area based on spatial interpolation method [J]. Chin. Tob. Sci., 2020, 41(3): 36-43. | |
| 20 | 杨成翠, 徐照丽, 史普酉, 等. 氮肥运筹对烤烟养分积累和产质量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(6): 176-185. |
| YANG C C, XU Z L, SHI P Y, et al.. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on nutrient accumulation, yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020, 22(6): 176-185. | |
| 21 | 张春华, 王宗明, 居为民, 等. 松嫩平原玉米带土壤碳氮比的时空变异特征[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(5): 1407-1414. |
| ZHANG C H, WANG Z M, JU W M, et al.. Spatial and temporal variability of soil C/N ratio in Songnen Plain maize belt [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Sci., 2011, 32(5): 1407-1414. | |
| 22 | 熊杏, 熊清华, 郭熙, 等. 南方典型丘陵区耕地土壤全氮、有机碳和碳氮比空间变异特征及其影响因素[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(9): 1656-1668. |
| XIONG X, XIONG Q H, GUO X, et al.. Spatial variation characteristics of total nitrogen, organic carbon and ratio of carbon to nitrogen of cultivated land in typical hilly areas in south China and its influencing factors [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26(9): 1656-1668. | |
| 23 | 刘勇军, 黎娟, 唐春闺, 等. 宁乡植烟土壤主要养分时空分布研究[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2018(2): 58-62. |
| LIU Y J, LI J, TANG C G, et al.. Study on spatial and temporal distribution of main nutrients in tobacco planting soil in Ningxiang [J]. Hunan Agric. Sci., 2018(2): 58-62. | |
| 24 | 苏煜, 黄劭理. 增施生物有机肥对烤烟光合特性及根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 164-171. |
| SU Y, HUANG S L. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on flue-cured tobacco photosynthetic characteristics and rhizosphere soil microorganism [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(1): 164-171. | |
| 25 | 王丰, 邓小华, 王少先, 等. 黔西南州植烟土壤有机质含量及与其他土壤养分的关系[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2014, 33(5): 63-67. |
| WANG F, DENG X H, WANG S X, et al.. Distribution characteristics of organic matter content in tobacco-growing soil and its relation with other soil nutrients in Qianxinan [J]. J. Mountain Agric. Biol., 2014, 33(5): 63-67. | |
| 26 | 刘金山, 戴健, 刘洋, 等. 过量施氮对旱地土壤碳、氮及供氮能力的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(1): 112-120. |
| LIU J S, DAI J, LIU Y, et al.. Effects of excessive nitrogen fertilization on soil organic carbon and nitrogen and nitrogen supply capacity in dryland [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2015, 21(1): 112-120. | |
| 27 | 郭迎新, 陈永亮, 苗琪, 等. 洱海流域植烟土壤养分时空变异特征及肥力评价[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(10): 1987-1999. |
| GUO Y X, CHEN Y L, MIAO Q, et al.. Spatial-temporal variability of soil nutrients and assessment of soil fertility in Erhai Lake Basin [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2022, 55(10): 1987-1999. | |
| 28 | 李龙, 秦富仓, 姜丽娜, 等. 半干旱区土壤有机碳时空变异特征研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3): 100-107. |
| LI L, QIN F C, JIANG L N, et al.. Spatial-temporal variability of soil organic carbon in semi-arid area [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020, 22(3): 100-107. | |
| 29 | 谢国雄, 楼旭平, 阮弋飞, 等. 浙江省农田土壤碳氮比特征及影响因素分析[J]. 江西农业学报, 2020, 32(2): 51-55. |
| XIE G X, LOU X P, RUAN Y F, et al.. Characteristics and influencing factors of C/N ratio of farmland in Zhejiang province [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2020, 32(2): 51-55. | |
| 30 | 王建林, 钟志明, 王忠红, 等. 青藏高原高寒草原生态系统土壤碳氮比的分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(22): 6678-6691. |
| WANG J L, ZHONG Z M, WANG Z H, et al.. Soil C/N distribution characteristics of alpine steppe ecosystem in Qinhai-Tibetan Plateau [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2014, 34(22): 6678-6691. | |
| 31 | 李雪利, 叶协锋, 顾建国, 等. 土壤C/N比对烤烟碳氮代谢关键酶活性和烟叶品质影响的研究[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2011, 17(3): 32-36. |
| LI X L, YE X F, GU J G, et al.. Effects of soil C/N ratio on activity of key enzymes involved in carbon and nitrogen metabolism and quaIity of flue-cured tobacco leaves [J]. Acta Tab. Sin., 2011, 17(3): 32-36. |
| [1] | Xuting HAO, Yaru HUANG, Yingbin MA, Shuai ZHANG, Chunxia HAN, Jiacheng PANG, Guangfu XU, Huizhong HAO, Yajing LIU. Study on Soil Moisture Dynamics in Growing Season of Sand-fixing Haloxylonammodendron Forest in Ulan Buhe Desert [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 187-196. |
| [2] | Weikang ZHAO, Changqing JING, Chen CHEN. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Xinjiang Natural Grassland and Their Responses to Climate Factors [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 197-206. |
| [3] | Zhixiong HOU, Changqing JING, Gongxin WANG, Wenzhang GUO, Weikang ZHAO. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Natural Grassland Vegetation Coverage and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors in Northern Xinjiang from 1998 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 140-151. |
| [4] | Lu LIU, Xiuping TAO, Jianchao SONG, Bin SHANG, Wenqian XU, Hongmin DONG, Yangyang CAI. Bench-scale Study on Operation Effect and Power Generation Performance Treatment of Dairy Farms Wastewater by Microbial Fuel Cell [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 134-143. |
| [5] |
GUO Han1, ZHANG Xu1*, LU Zhou2, TIAN Ting3, XU Feifei2,LUO Ming2, WU Zhenggui3, SUN Zhenjun5.
Estimation of Organic Matter Content in Southern Paddy Soil Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Images
[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(6): 60-71.
|
| [6] | LIU Cenwei, YE Jing, LI Yanchun, LIN Yi, WANG Yixiang*. Effects of Biochar on Soil Nitrogen Leaching in Acid Red Loam of Tea Garden [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(5): 181-186. |
| [7] | LI Yangzheng, LI Lan, WANG Xiaoer, CAO Xi, PENG Jianyu, XUE Xiaohui, YOU Ping. Effects of Environmetal Factors Such as Surface Cover on Soil Organic Nitrogen Composition in Northwestern District of Guizhou [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(10): 157-166. |
| [8] | CHENG Jiehong1, CHEN Zhengguang1*, ZHANG Qinghua2. Comparison of Different Wavelength Selection Methods in SOM Content Detection [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(1): 162-170. |
| [9] | YANG Chaoyuan, LIU Guotao*, LI Weiyu, LI Lei, XIA Xuan, LI Shibo. Research on Lignin Degradation and Humus Formation During Composting [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(2): 148-154. |
| [10] | ZHU Xi1, LIN Jie2*. Soil Erosion and Soil Nutrients Response to Erosion Based on 137Cs in Southern Hilly Area [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(8): 134-141. |
| [11] | LIN Lihua, ZHI Huyu. Influence of Silkworm Excrement Soil Amendments on Acidic Soil and Growth of Vigna unguiculata [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(4): 108-114. |
| [12] | DAN Junhao1, QI Shaowu1,2*, LI Juan1, ZHU Yi3, JIN Huiyong4, LIANG Zhongzhe1. Effects of Soil Conditioner on Carbon Metabolism Fingerprints of Soil Microbial in Tobacco Fields [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(10): 36-43. |
| [13] | TANG Jie, WANG Changquan*, LI Bing, ZENG Jian, LI Qiquan, XU Qiang, LI Yiding, LI Shan. Spatial Variability and Its influencing Factors of Soil Organic Matter and Alkaline Nitrogen in Central Hilly Area of Sichuan [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(6): 124-130. |
| [14] | NIU Guiyan1, SHAO Huifang1*, ZHU Jinfeng2, HUANG Wuxing1, XU Zicheng1, GUO Li3. Research Progress on Tobacco Planting Soil Restoration in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(3): 115-122. |
| [15] | SUN Shu-bin1, YU Qing-tao2, YAO Xue-mei2, YANG Hong-qi1*, LIU Guang-hui2, ZHANG . Studies on Characteristics of Organic Matter Contents Distribution and Influence Factors in Longhui Soil of Tobacco Growing Areas [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(6): 94-101. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号