




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 68-75.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0078
收稿日期:2021-01-21
接受日期:2021-06-15
出版日期:2022-05-15
发布日期:2022-06-06
通讯作者:
崔鹏
作者简介:崔晨珂E-mail:cck1721@163.com;
基金资助:
Chenke CUI( ), Tao LIN, Yanbo AN, Peng CUI(
), Tao LIN, Yanbo AN, Peng CUI( )
)
Received:2021-01-21
Accepted:2021-06-15
Online:2022-05-15
Published:2022-06-06
Contact:
Peng CUI
摘要:
为了丰富甘薯育成品种的遗传背景,筛选优良亲本,对来自全国各地的37份不同类型(鲜食型,淀粉型和兼用型等)的甘薯品种进行遗传多样性分析,选取的品种在薯皮、薯肉颜色方面有较大差异,采用ISSR分子标记对其多样性及亲缘关系进行分析。结果表明:100条引物中共筛选出19条ISSR多态性引物,共扩增出118条带,其中多态性条带115条,多态性位点频率为97.50%,供试甘薯品种的遗传距离介于0.04~0.36之间。台薯66和红东的遗传距离最近(0.04),观赏型甘薯紫罗兰与花青素加工型徐紫薯8号聚为一类。花青素加工型与菜用型和水果型的遗传距离较远,分别为0.43和0.40,与观赏型遗传关系最近(0.08);水果型与其他8种类型遗传距离较远,均大于0.30,而鲜食型与其他类型的遗传距离均较近。分析了不同类型甘薯品种的遗传关系,相对于形态学标记,ISSR能较好地区分37份甘薯种质资源,其聚类分析结果能更客观地反映不同甘薯类型之间的遗传关系,可为不同用途品种选育的亲本选配提供参考。
中图分类号:
崔晨珂, 林涛, 安艳波, 崔鹏. 不同类型甘薯品种遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 68-75.
Chenke CUI, Tao LIN, Yanbo AN, Peng CUI. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Different Characteristics of Sweetpotato Varieties by ISSR Molecular Marker[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 68-75.
编号 Code | 名称 Name | 特点 Characteristics | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 台薯66 Taishu 66 | 薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 2 | 商薯19 Shangshu19 | 淀粉型Starch | 河南省商丘市农林科学研究所 Shangqiu Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences of Henan |
| 3 | 烟薯25 Yanshu25 | 鲜食型Edible | 山东省烟台市农业科学院 Yantai Academy of Agricultural Sciences of Shandong |
| 4 | 苏薯15 Sushu15 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 江苏省农业科学院 Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 5 | 红香蕉 Hongxiangjiao | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 山东省农业科学院Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 6 | 龙薯9号 Longshu 9 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 福建省龙岩市农业科学研究所 Longyan Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 7 | 秦薯5号 Qinshu 5 | 鲜食淀粉兼用型 Fresh edible and starch | 西北农林科技大学 Northwest A&F University |
| 8 | 紫罗兰 Ziluolan | 观赏型 Ornamental | 不详Unknown |
| 9 | 广薯87 Guangshu 87 | 鲜食淀粉兼用型 Fresh edible and starch | 广东省农业科学院 Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 10 | 烟薯16 Yanshu 16 | 水果型 Fruit | 山东省烟台市农业科学院 Yantai Academy of Agricultural Sciences of Shandong |
| 11 | 徐紫薯2号 Xuzishu 2 | 水果型 Fruit | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 12 | 辽薯15 Liaoshu 15 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 辽宁省农业科学院 Liaoning Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 13 | 赣薯2号 Ganshu 2 | 水果型 Fruit | 江西省红壤研究所 Jiangxi Institute of Red Soil |
| 14 | 166-7 | 水果型 Fruit | 西北农林科技大学 Northwest A&F University |
| 15 | 商薯8号 Shangshu 8 | 淀粉型 Starch | 河南省商丘市农林科学研究所 Shangqiu Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences of Henan |
| 16 | 红东 Hongdong | 薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 日本Japan |
| 17 | 徐紫薯8号 Xuzishu 8 | 花青素加工型 Anthocyanin | 江苏省农业科学院 Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 18 | 普薯32 Pushu 32 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 广东省普宁市农业科学研究所 Puning Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Guangdong |
| 19 | 浙薯13 Zheshu 13 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 浙江省农业科学院 Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 20 | 冀紫薯2号 Jizishu 2 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 河北省农林科学院 Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| 21 | 秦紫薯2号 Qinzishu 2 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 陕西省宝鸡市农业科学院 Baoji Academy of Agricultural Sciences of Shaanxi |
| 22 | 西农431 Xinong 431 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 西北农林科技大学 Northwest A&F University |
表1 37份供试材料的特点和来源
Table 1 Characteristics and geographic origins of 37 sweetpotato varieties
编号 Code | 名称 Name | 特点 Characteristics | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 台薯66 Taishu 66 | 薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 2 | 商薯19 Shangshu19 | 淀粉型Starch | 河南省商丘市农林科学研究所 Shangqiu Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences of Henan |
| 3 | 烟薯25 Yanshu25 | 鲜食型Edible | 山东省烟台市农业科学院 Yantai Academy of Agricultural Sciences of Shandong |
| 4 | 苏薯15 Sushu15 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 江苏省农业科学院 Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 5 | 红香蕉 Hongxiangjiao | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 山东省农业科学院Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 6 | 龙薯9号 Longshu 9 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 福建省龙岩市农业科学研究所 Longyan Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 7 | 秦薯5号 Qinshu 5 | 鲜食淀粉兼用型 Fresh edible and starch | 西北农林科技大学 Northwest A&F University |
| 8 | 紫罗兰 Ziluolan | 观赏型 Ornamental | 不详Unknown |
| 9 | 广薯87 Guangshu 87 | 鲜食淀粉兼用型 Fresh edible and starch | 广东省农业科学院 Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 10 | 烟薯16 Yanshu 16 | 水果型 Fruit | 山东省烟台市农业科学院 Yantai Academy of Agricultural Sciences of Shandong |
| 11 | 徐紫薯2号 Xuzishu 2 | 水果型 Fruit | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 12 | 辽薯15 Liaoshu 15 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 辽宁省农业科学院 Liaoning Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 13 | 赣薯2号 Ganshu 2 | 水果型 Fruit | 江西省红壤研究所 Jiangxi Institute of Red Soil |
| 14 | 166-7 | 水果型 Fruit | 西北农林科技大学 Northwest A&F University |
| 15 | 商薯8号 Shangshu 8 | 淀粉型 Starch | 河南省商丘市农林科学研究所 Shangqiu Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences of Henan |
| 16 | 红东 Hongdong | 薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 日本Japan |
| 17 | 徐紫薯8号 Xuzishu 8 | 花青素加工型 Anthocyanin | 江苏省农业科学院 Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 18 | 普薯32 Pushu 32 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 广东省普宁市农业科学研究所 Puning Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Guangdong |
| 19 | 浙薯13 Zheshu 13 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 浙江省农业科学院 Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| 20 | 冀紫薯2号 Jizishu 2 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 河北省农林科学院 Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| 21 | 秦紫薯2号 Qinzishu 2 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 陕西省宝鸡市农业科学院 Baoji Academy of Agricultural Sciences of Shaanxi |
| 22 | 西农431 Xinong 431 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 西北农林科技大学 Northwest A&F University |
编号 Code | 名称 Name | 特点 Characteristics | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 郑薯20 Zhengshu 20 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 河南省农业科学院 Henan Academy of agricultural sciences |
| 24 | 冀薯4号 Jishu 4 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 河北省农林科学院 Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| 25 | 冀薯982 Jishu 982 | 淀粉型 Starch | 河北省农林科学院 Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| 26 | 徐薯22 Xushu 22 | 淀粉型 Starch | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 27 | 宁紫薯2号 Ningzishu 2 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 28 | 苏薯16 Sushu16 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 29 | 苏薯24 Sushu 24 | 淀粉型 Starch | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 30 | 莆薯20 Pushu 20 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 31 | 遗字138 Yizi 138 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所 Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology,Chinese Academy Sciences |
| 32 | 莆薯90 Pushu 90 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 33 | 南薯99 Nanshu 99 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 四川省南充市农业科学研究所 Nanchong Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Sichuang |
| 34 | 莆薯14 Pushu 14 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 35 | 莆薯53 Pushu 53 | 菜用型 Vegetable | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 36 | 南薯28 Nanshu 28 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 四川省南充市农业科学研究所 Nanchong Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Sichuang |
| 37 | 心香 Xinxiang | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 浙江省农业科学院 Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
表1 37份供试材料的特点和来源 (续表Continued)
Table 1 Characteristics and geographic origins of 37 sweetpotato varieties
编号 Code | 名称 Name | 特点 Characteristics | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 郑薯20 Zhengshu 20 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 河南省农业科学院 Henan Academy of agricultural sciences |
| 24 | 冀薯4号 Jishu 4 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 河北省农林科学院 Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| 25 | 冀薯982 Jishu 982 | 淀粉型 Starch | 河北省农林科学院 Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| 26 | 徐薯22 Xushu 22 | 淀粉型 Starch | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 27 | 宁紫薯2号 Ningzishu 2 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 28 | 苏薯16 Sushu16 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 29 | 苏薯24 Sushu 24 | 淀粉型 Starch | 江苏省徐州甘薯研究所 Xuzhou Sweetpotato Research Institute of Jiangsu |
| 30 | 莆薯20 Pushu 20 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 31 | 遗字138 Yizi 138 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所 Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology,Chinese Academy Sciences |
| 32 | 莆薯90 Pushu 90 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 33 | 南薯99 Nanshu 99 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 四川省南充市农业科学研究所 Nanchong Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Sichuang |
| 34 | 莆薯14 Pushu 14 | 食饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 35 | 莆薯53 Pushu 53 | 菜用型 Vegetable | 福建省莆田市农业科学研究所 Putian Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Fujian |
| 36 | 南薯28 Nanshu 28 | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 四川省南充市农业科学研究所 Nanchong Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Sichuang |
| 37 | 心香 Xinxiang | 鲜食型 Fresh edible | 浙江省农业科学院 Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
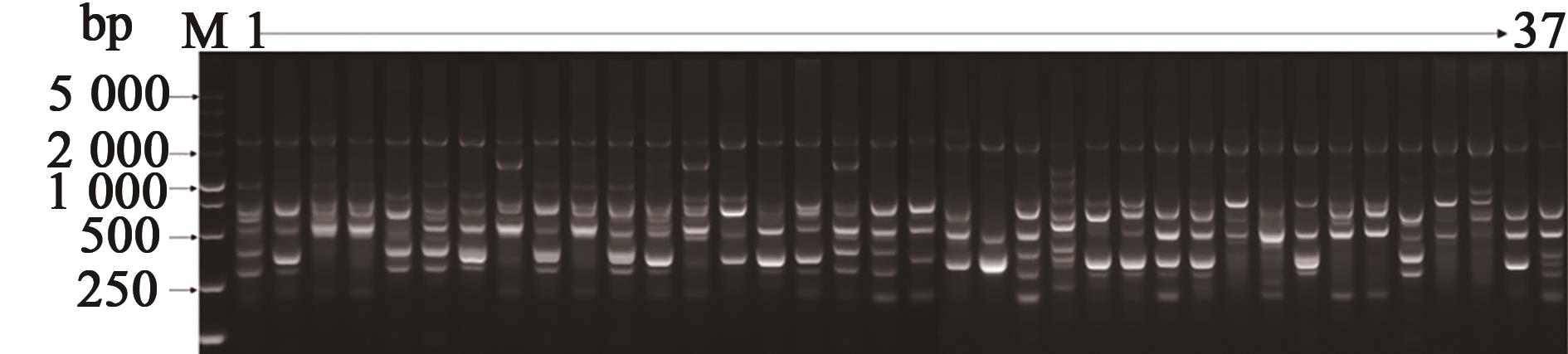
图1 引物UBC850对37个品种的扩增带型注:M为Marker DL5000,1~37对应表1中甘薯品种编号。
Fig. 1 ISSR-PCR profiles of 37 sweetpotato variety with UBC850 primerNote:M is Marker DL2000, and 1~37 indicate sweetpotato varieties listed in Table 1.
引物 Primer | 引物碱基序列 Sequence of primer | 扩增总带数 Total band number | 多态性条带数 Polymorphic band number | 多态性位点频率 Frequency of polymorphic band/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC808 | (AG)8C | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC809 | (AG)8C | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC811 | (GA)8C | 5 | 4 | 80 |
| UBC812 | (GA)8A | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC818 | (CA)8G | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC819 | (GT)8A | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC820 | (GT)8C | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC821 | (GT)8T | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| UBC823 | (TC)8C | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC827 | (AC)8G | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC829 | (TG)8C | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC830 | (TG)8G | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC836 | (AG)8YA | 5 | 5 | 100 |
| UBC841 | (GA)8YC | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC842 | (GA)8YG | 6 | 5 | 83 |
| UBC846 | (CA)8RT | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC847 | (CA)8RC | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC848 | (CA)8RG | 5 | 4 | 80 |
| UBC850 | (GT)8YC | 8 | 8 | 100 |
| 总计Total | 118 | 115 | 97.5 | |
表2 引物序列及扩增结果
Table 2 Amplification efficiency of different primers
引物 Primer | 引物碱基序列 Sequence of primer | 扩增总带数 Total band number | 多态性条带数 Polymorphic band number | 多态性位点频率 Frequency of polymorphic band/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC808 | (AG)8C | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC809 | (AG)8C | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC811 | (GA)8C | 5 | 4 | 80 |
| UBC812 | (GA)8A | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC818 | (CA)8G | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC819 | (GT)8A | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC820 | (GT)8C | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC821 | (GT)8T | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| UBC823 | (TC)8C | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC827 | (AC)8G | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC829 | (TG)8C | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC830 | (TG)8G | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC836 | (AG)8YA | 5 | 5 | 100 |
| UBC841 | (GA)8YC | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC842 | (GA)8YG | 6 | 5 | 83 |
| UBC846 | (CA)8RT | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| UBC847 | (CA)8RC | 7 | 7 | 100 |
| UBC848 | (CA)8RG | 5 | 4 | 80 |
| UBC850 | (GT)8YC | 8 | 8 | 100 |
| 总计Total | 118 | 115 | 97.5 | |
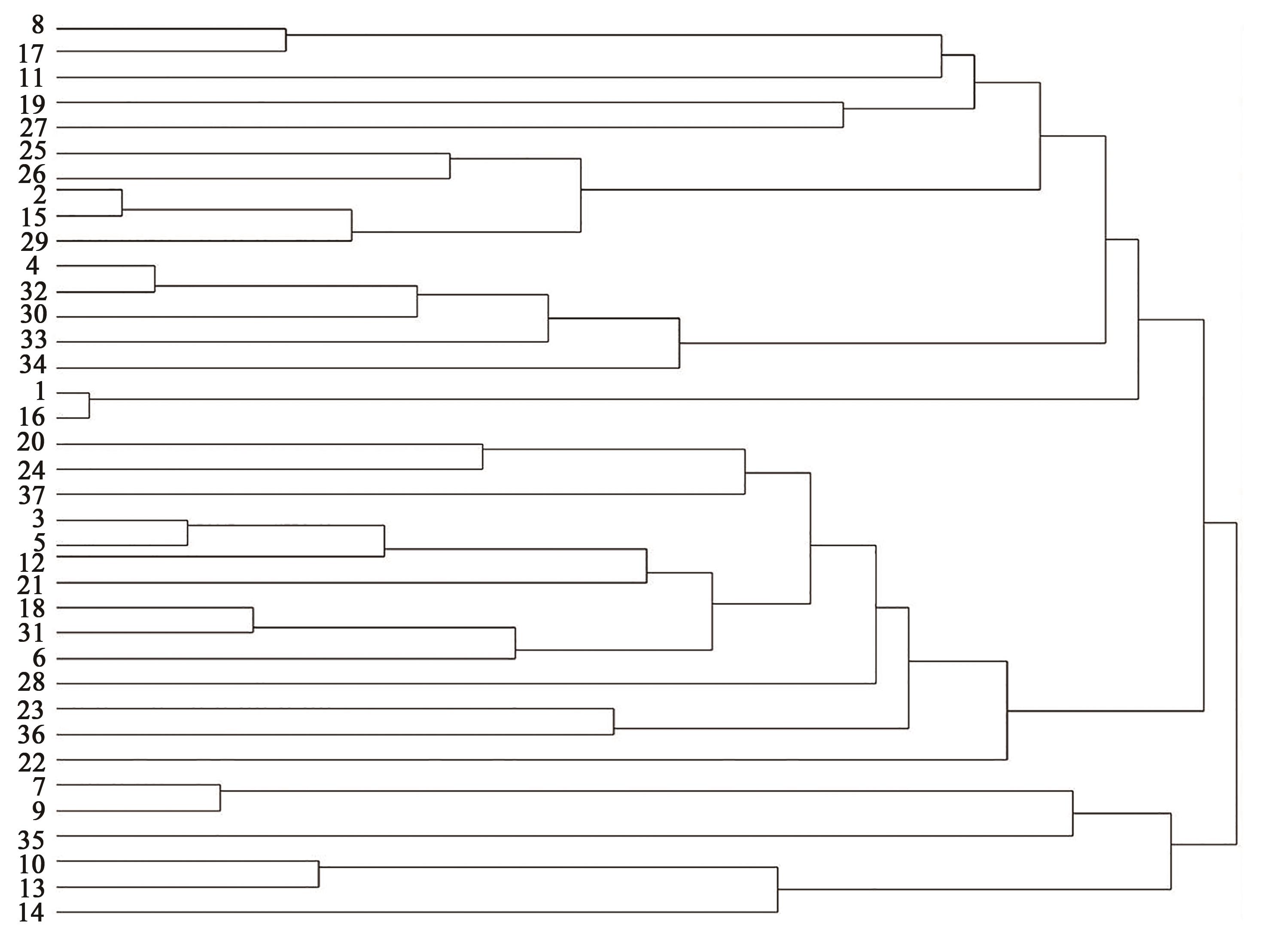
图2 基于ISSR数据的37份甘薯品种聚类分析结果注:1~37对应表1中甘薯品种编号。
Fig. 2 Clustering analysis of 37 sweetpotato varieties based on the results of ISSR dataNote:1~37 indicate sweetpotato varieties listed in Table 1.
品种特点 Characteristics | 薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 淀粉型 Starch | 鲜食型 Edible | 食、饲兼 用型 Edible and feed | 菜用型Vegetable | 水果型 Fruit | 花青素加工型 Anthocyanin | 鲜食、淀粉兼用型 Edible and starch | 观赏型 Ornamental |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 0.041 | ||||||||
| 淀粉型 Starch | 0.358 | 0.104 | |||||||
| 鲜食型 Edible | 0.305 | 0.338 | 0.183 | ||||||
食、饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 0.309 | 0.237 | 0.285 | 0.110 | |||||
| 菜用型 Vegetable | 0.396 | 0.256 | 0.346 | 0.289 | — | ||||
| 水果型 Fruit | 0.351 | 0.358 | 0.368 | 0.346 | 0.312 | 0.199 | |||
花青素加工型 Anthocyanin | 0.296 | 0.243 | 0.311 | 0.281 | 0.434 | 0.401 | — | ||
鲜食、淀粉兼用 Edible and starch | 0.306 | 0.342 | 0.313 | 0.326 | 0.261 | 0.300 | 0.370 | 0.071 | |
| 观赏型 Ornamental | 0.28 | 0.255 | 0.290 | 0.209 | 0.379 | 0.297 | 0.077 | 0.345 | — |
表3 不同类型甘薯品种间的平均遗传距离
Table 3 Mean genetic distances among different types of sweetpotato varieties
品种特点 Characteristics | 薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 淀粉型 Starch | 鲜食型 Edible | 食、饲兼 用型 Edible and feed | 菜用型Vegetable | 水果型 Fruit | 花青素加工型 Anthocyanin | 鲜食、淀粉兼用型 Edible and starch | 观赏型 Ornamental |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
薯脯加工型 Preserved pulp | 0.041 | ||||||||
| 淀粉型 Starch | 0.358 | 0.104 | |||||||
| 鲜食型 Edible | 0.305 | 0.338 | 0.183 | ||||||
食、饲兼用型 Edible and feed | 0.309 | 0.237 | 0.285 | 0.110 | |||||
| 菜用型 Vegetable | 0.396 | 0.256 | 0.346 | 0.289 | — | ||||
| 水果型 Fruit | 0.351 | 0.358 | 0.368 | 0.346 | 0.312 | 0.199 | |||
花青素加工型 Anthocyanin | 0.296 | 0.243 | 0.311 | 0.281 | 0.434 | 0.401 | — | ||
鲜食、淀粉兼用 Edible and starch | 0.306 | 0.342 | 0.313 | 0.326 | 0.261 | 0.300 | 0.370 | 0.071 | |
| 观赏型 Ornamental | 0.28 | 0.255 | 0.290 | 0.209 | 0.379 | 0.297 | 0.077 | 0.345 | — |
| 1 | 刘中华,林志坚,李华伟,等.甘薯种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J].南方农业学报, 2019, 50(11): 2392-2400. |
| LIU Z H, LING Z J, LI H W, et al.. Genetic diversity analysis of sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] by ISSR molecular markers [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2019, 50(11): 2392-2400. | |
| 2 | 刘桂玲,张鹏,郑建利,等.不同类型甘薯品种主要经济性状和营养成分差异[J].中国粮油学报, 2012, 27(2): 10-13. |
| LIU G L, ZHANG P, ZHENG J L, et al.. Variation in major economic traits and nutrition composition among different types of sweet potato cultivars [J]. J. Chin. Cereal Oil Ass., 2012, 27(2): 10-13. | |
| 3 | 苏一钧,董玲霞,王娇,等. 菜用和观赏甘薯种质资源遗传多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(1): 57-64. |
| SU Y J, DONG L X, W J, et al.. Genetic diversity in vegetable and ornamental sweetpotato germplasm [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2018, 19(1): 57-64. | |
| 4 | 李强,刘庆昌,翟红,等.中国甘薯主要亲本遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J].作物学报, 2008, 34(6): 972-977. |
| LI Q, LIU Q C, ZHAI H, et al.. Genetic diversity in main parents of sweet potato in China as revealed by ISSR marker [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2008, 34(6): 972-977. | |
| 5 | WADL P A, OLUKOLU B A, BRANHAM S E, et al.. Genetic diversity and population structure of the USDA sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas) germplasm collections using GBSpoly [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2018, 9: 1-13. |
| 6 | YADA B, BROWN-GUEDIRA G, ALAJO A, et al.. Simple sequence repeat marker analysis of genetic diversity among progeny of a biparental mapping population of sweetpotato [J]. Hortscience, 2015, 50(8): 1143-1147. |
| 7 | WANG Z Y, LI J, LUO Z X, et al.. Characterization and development of EST-derived SSR markers in cultivated sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas) [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2011, 11(1):139 [2021-02-26]. . |
| 8 | 刘中华,林志坚,李华伟,等.基于SRAP标记的甘薯遗传多样性与起源演化分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(3): 468-477. |
| LIU Z H, LIN Z J, LI W H, et al. The genetic diversity, origin and evolution of sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) revealed by SRAP markers [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2018, 19(3): 468-477. | |
| 9 | 季志仙,王美兴,范宏环,等.基于ISSR指纹的甘薯食用品种的遗传多样性分析[J].核农学报, 2014, 28(7): 1197-1202. |
| JI Z X, WANG M X, FAN H H, et al.. Genetic diversity assessment of edible sweetpotato germplasm based on ISSR fingerprint [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2014, 28(7): 1197-1202. | |
| 10 | 张凯,罗小敏,蒋玉春,等.甘薯种质资源的SRAP鉴定及遗传多样性分析[J].核农学报,2013, 27(5): 0568-0575. |
| ZHANG K, LUO X M, JIANG Y C, et al.. Genetic diversity among main sweetpotato germplasm resources using SRAP markers[J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2013, 27(5): 568-575. | |
| 11 | 聂立圆,李爱贤,秦桢,等.基于SSR标记的132份甘薯种质指纹图谱的构建及遗传多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(5): 904-911. |
| NIE L Y, LI A X, QIN Z, et al.. Construction of DNA fingerprints and analysis of genetic diversity based on SSR markers for 132 sweetpotato germplasms [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2018, 19(5): 904-911. | |
| 12 | HUANG J C, SUN M. Genetic diversity and relationships of sweetpotato and its wild relatives in Ipomoea series Batatas (Convolvulaceae) as revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and restriction analysis of chloroplast DNA [J]. Theor. Appl. Genet., 2000, 100(7): 1050-1060 |
| 13 | 崔鹏,李波,吴月燕,等.南方鲜食葡萄品种遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J].核农学报, 2013, 27(9): 1270-1275. |
| CUI P, LI B, WU Y Y, et al. Genetic diversity of table grape varieties in southern China by ISSR markers [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2013, 27(9): 1270-1275. | |
| 14 | 刘桂玲,张鹏,郑建利,等.不同类型甘薯品种主要经济性状和营养成分差异[J].中国粮油学报, 2012, 27(2): 10-13. |
| LIU G L, ZHANG P, ZHENG J L, et al.. Variation in major economic traits and nutrition composition among different types of sweet potato cultivars [J]. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc., 2012, 27(2): 10-13. | |
| 15 | 谢子玉,王可尔,赵雯靓,等.不同肉色甘薯的营养成分与生物活性[J].浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(2): 183-192. |
| XIE Z Y, WANG K E, ZHAO W L, et al.. Nutritional components and bioactivities of sweet potatoes with different flesh colors [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(2): 183-192. | |
| 16 | 贺学勤,刘庆昌,翟红,等.用RAPD、ISSR和AFLP 标记分析系谱关系明确的甘薯品种的亲缘关系[J].作物学报, 2005, 31(10): 1300-1304. |
| HE X Q, LIU Q C, ZHAI H, et al.. The use of RAPD, ISSR and AFLP markers for analyzing genetic relationships among sweetpotato cultivars with known origin [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2005, 31(10): 1300-1304. | |
| 17 | 赵冬兰,唐君,曹清河,等.中国甘薯地方种质资源遗传多样性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(5): 994-1003. |
| ZHAO D L, TANG J, CAO Q H, et al.. Analysis of genetic diversity of sweetpotato landraces in China [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2015, 16(5): 994-1003. | |
| 18 | 罗凯,卢会翔,吴正丹,等.中国西南地区甘薯主要育种亲本的遗传多样性及群体结构分析[J].中国农业科学, 2016, 49(3): 593-608. |
| LUO K, LU H X, WU Z D, et al. Genetic diversity and population Structure Analysis of Main Sweet Potato Breeding Parents in Southwest China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2016, 49(3): 593-608. | |
| 19 | 赵路宽,苏一钧,戴习彬,等.中国甘薯登记品种SSR标记遗传多样性分析[J].西北植物学报, 2019, 39(7): 1212-1220. |
| ZHAO L K, SU Y J, DAI X B, et al.. Genetic diversity of the registered swetpotato varieties in China by SSR markers [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2019, 39(7): 1212-1220. | |
| 20 | 贺学勤,刘庆昌,王玉萍,等.中国甘薯地方品种的遗传多样性分析[J].中国农业科学, 2005, 38(2): 250-257. |
| HE X Q, LIU Q C, WANG Y P, et al.. Analysis of genetic diversity of sweetpotato landraces in China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2005, 38(2): 250-257. | |
| 21 | 张道微,董芳,黄艳岚,等.甘薯种质资源花青素积累的遗传多态性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(2): 347-358. |
| ZHANG D W, DONG F, HUANG Y L, et al.. Genetic diversity analysis of anthocyanin accumulation in sweetpotato germplasm resources [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2019, 20(2): 347-358. |
| [1] | 伊六喜, 萨如拉, 范鑫, 赵灿, 李茹, 斯钦巴特尔. 油用亚麻主要品质和农艺性状的变异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 56-67. |
| [2] | 左茜茜, 宋英杰, 马心妍, 杨云卉, 王轶菲, 郭泽光, 朱雄智, 刘越. 苦荞全基因组SSR位点挖掘及遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 38-51. |
| [3] | 于海天, 吕梅媛, 万述伟, 杨峰, 胡朝芹, 杨新, 张晓艳, 王玉宝, 何春华, 林德明, 王丽萍. 印度鹰嘴豆资源遗传多样性分析及优异资源筛选#br#[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 54-64. |
| [4] | 王平. 我国种业发展的主要问题及对策探析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 7-16. |
| [5] | 李丹阳, 孙玲伟, 吴彩凤, 张树山, 张德福, 戴建军. 长江三角洲白山羊保种群体的SSR遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 74-81. |
| [6] | 相吉山1,张恒儒2,刘涵1,索良喜2,贾姝婧1,张颖1,史景奇1,胡利喆1,蔡一宁1. 不同生态区谷子种质资源表型比较分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 31-41. |
| [7] | 石玉涛1,郑淑琳1,王飞权1,陈荣冰1,李远华1,张渤1,王涵2,林立2. 武夷名丛茶树种质资源矿质元素含量特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 37-50. |
| [8] | 郭亮虎1,王镇1,李楠1,逯腊虎1,高炜1,郭雅娴1,武宗信2*. 温度和湿度对紫甘薯贮藏品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 107-114. |
| [9] | 李纪潮,张金渝,杨天梅,杨美权,杨维泽,许宗亮,左应梅*. 滇重楼种质资源抗旱综合评价及生理机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(10): 49-59. |
| [10] | 王飞权1,冯花1,罗盛财2,陈荣冰1,杨慧珠1,李少华1,张见明3,张渤1,叶江华1. 武夷名丛茶树种质资源农艺性状多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(6): 43-54. |
| [11] | 许美玲1,贺晓辉2,宋玉川2,樊有银2,李永平1. 雪茄烟种质常规化学成分、多酚与感官质量的相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(6): 124-134. |
| [12] | 奉斌,李慧琳,杨胜先,林涛,魏忠芬*. 贵州地方向日葵种质资源表型性状多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(7): 34-41. |
| [13] | 王向东1,王永存1,马艳芝2*,宋玉双2,3,付丽军1,李佳垚2. ISSR标记在生姜品种遗传多样性中的应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(7): 42-47. |
| [14] | 周志林1,2,唐君1,曹清河1,赵冬兰1,张安1. NaCl胁迫对甘薯植株体内K+、Na+和Cl-含量及生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(4): 17-23. |
| [15] | 陈晓,石巍*,陈超,刘之光,王慧华,郭海坤,汤娇. 欧洲蜜蜂遗传改良项目及对中国蜜蜂资源和育种工作的启示[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(10): 14-20. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号