




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 132-140.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0410
刘晓玉( ), 盛锡兴, 廖宗文, 林黎珍, 黎坤婷, 蔡燕飞, 陈火君(
), 盛锡兴, 廖宗文, 林黎珍, 黎坤婷, 蔡燕飞, 陈火君( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-13
接受日期:2021-09-22
出版日期:2022-07-15
发布日期:2022-08-15
通讯作者:
陈火君
作者简介:刘晓玉E-mail:lxy1506191394@163.com;
基金资助:
Xiaoyu LIU( ), Xixing SHENG, Zongwen LIAO, Lizhen LIN, Kunting LI, Yanfei CAI, Huojun CHEN(
), Xixing SHENG, Zongwen LIAO, Lizhen LIN, Kunting LI, Yanfei CAI, Huojun CHEN( )
)
Received:2021-05-13
Accepted:2021-09-22
Online:2022-07-15
Published:2022-08-15
Contact:
Huojun CHEN
摘要:
采用解钾菌和活化剂联用技术,研究不同用量活化剂和处理方式对钾长石的活化效果,通过X射线衍射和玉米盆栽试验探究生物-化学联用的活化机理及其肥效。结果表明,不同解钾菌(YC602、YC605和YC606)与活化剂QN联用对钾长石中水溶性钾和有效钾的释放均有效果,YC602提升效果最佳。选定YC602与QN进行优化试验,其中T1处理(5%QN+100 ℃烘干+YC602)和T3处理(3%QN+水浸泡+200 ℃烘干+YC602)活化效果较好,提高活化剂用量有利于水溶性钾和有效钾的释放。培养时间对于有效钾的释放影响不大,而水溶性钾含量以培养24 h效果最佳。盆栽试验结果表明,减少50%氯化钾施用的条件下,联用技术T2A处理组可有效促进玉米生长。淋溶试验表明,联用技术可有效减少钾素淋溶流失,肥效较持久。联用活化技术在常温常压条件下就可提高钾长石的有效性,明显降低活化成本,并可大幅减少氯化钾用量,具有减量增效和绿色环保的优势。
中图分类号:
刘晓玉, 盛锡兴, 廖宗文, 林黎珍, 黎坤婷, 蔡燕飞, 陈火君. 生物-化学联用对钾长石的活化效果及其肥效[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 132-140.
Xiaoyu LIU, Xixing SHENG, Zongwen LIAO, Lizhen LIN, Kunting LI, Yanfei CAI, Huojun CHEN. Activating Effect and Fertilizer Efficiency of Bio-chemical Combination on Potassium Feldspar[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 132-140.
| 处理Treatment | 处理代号Treatment code | 处理内容Treatment method |
|---|---|---|
| 化学活化Chemical activation | C1 | 5%QN + 钾长石 + 100 ℃烘干 5%QN + K-feldspar + drying at 100 ℃ |
| 生物活化Biological activation | B1 | 钾长石 + YC602 K-feldspar + YC602 |
| B2 | 钾长石 + YC605 K-feldspar + YC605 | |
| B3 | 钾长石 + YC606 K-feldspar + YC606 | |
生物-化学联用 Bio-chemical activation | U1 | C1 + YC602 |
| U2 | C1 + YC605 | |
| U3 | C1 + YC606 |
表1 钾长石不同制备方法的设置
Table 1 Design of different method for making k-feldspar
| 处理Treatment | 处理代号Treatment code | 处理内容Treatment method |
|---|---|---|
| 化学活化Chemical activation | C1 | 5%QN + 钾长石 + 100 ℃烘干 5%QN + K-feldspar + drying at 100 ℃ |
| 生物活化Biological activation | B1 | 钾长石 + YC602 K-feldspar + YC602 |
| B2 | 钾长石 + YC605 K-feldspar + YC605 | |
| B3 | 钾长石 + YC606 K-feldspar + YC606 | |
生物-化学联用 Bio-chemical activation | U1 | C1 + YC602 |
| U2 | C1 + YC605 | |
| U3 | C1 + YC606 |
| 处理Treatment | 处理代号Treatment code | 处理内容Treatment method |
|---|---|---|
| 化学活化Chemical activation | CK1 | 5%QN + 100 ℃烘干 5%QN + drying at 100 ℃ |
| CK2 | 3%QN + 100 ℃烘干 3%QN + drying at 100 ℃ | |
| CK3 | 3%QN + 水浸泡 + 200 ℃烘干 3%QN + water soaking + drying at 200 ℃ | |
生物-化学联用 Bio-chemical activation | T1 | CK1 + YC602 |
| T2 | CK2 + YC602 | |
| T3 | CK3 + YC602 | |
| 生物活化Biological activation | T4 | YC602 + 钾长石 YC602 + K-feldspar |
表2 不同活化优化条件设置
Table 2 Design of difference activation condition
| 处理Treatment | 处理代号Treatment code | 处理内容Treatment method |
|---|---|---|
| 化学活化Chemical activation | CK1 | 5%QN + 100 ℃烘干 5%QN + drying at 100 ℃ |
| CK2 | 3%QN + 100 ℃烘干 3%QN + drying at 100 ℃ | |
| CK3 | 3%QN + 水浸泡 + 200 ℃烘干 3%QN + water soaking + drying at 200 ℃ | |
生物-化学联用 Bio-chemical activation | T1 | CK1 + YC602 |
| T2 | CK2 + YC602 | |
| T3 | CK3 + YC602 | |
| 生物活化Biological activation | T4 | YC602 + 钾长石 YC602 + K-feldspar |
| 处理代号Treatment code | 处理内容Treatment method |
|---|---|
| MCK0 | 无KCl Without KCl |
| MCK1 | 2.28 g钾长石 + YC602 2.28 g K-feldspar + YC602 |
| MCK2 | 0.5 g KCl |
| T1A (5%QN) | 2.28 g活化钾长石 + YC602 2.28 g activated K-feldspar + YC602 |
| T2A (5%QN) | 1.14 g活化钾长石 + 0.25 g KCl + YC602 1.14 g activated K-feldspar + 0.25 g KCl + YC602 |
表3 生物-化学活化钾长石玉米盆栽试验施肥方案
Table 3 Bio?chemical combination of fertilization program in corn pot experiment
| 处理代号Treatment code | 处理内容Treatment method |
|---|---|
| MCK0 | 无KCl Without KCl |
| MCK1 | 2.28 g钾长石 + YC602 2.28 g K-feldspar + YC602 |
| MCK2 | 0.5 g KCl |
| T1A (5%QN) | 2.28 g活化钾长石 + YC602 2.28 g activated K-feldspar + YC602 |
| T2A (5%QN) | 1.14 g活化钾长石 + 0.25 g KCl + YC602 1.14 g activated K-feldspar + 0.25 g KCl + YC602 |
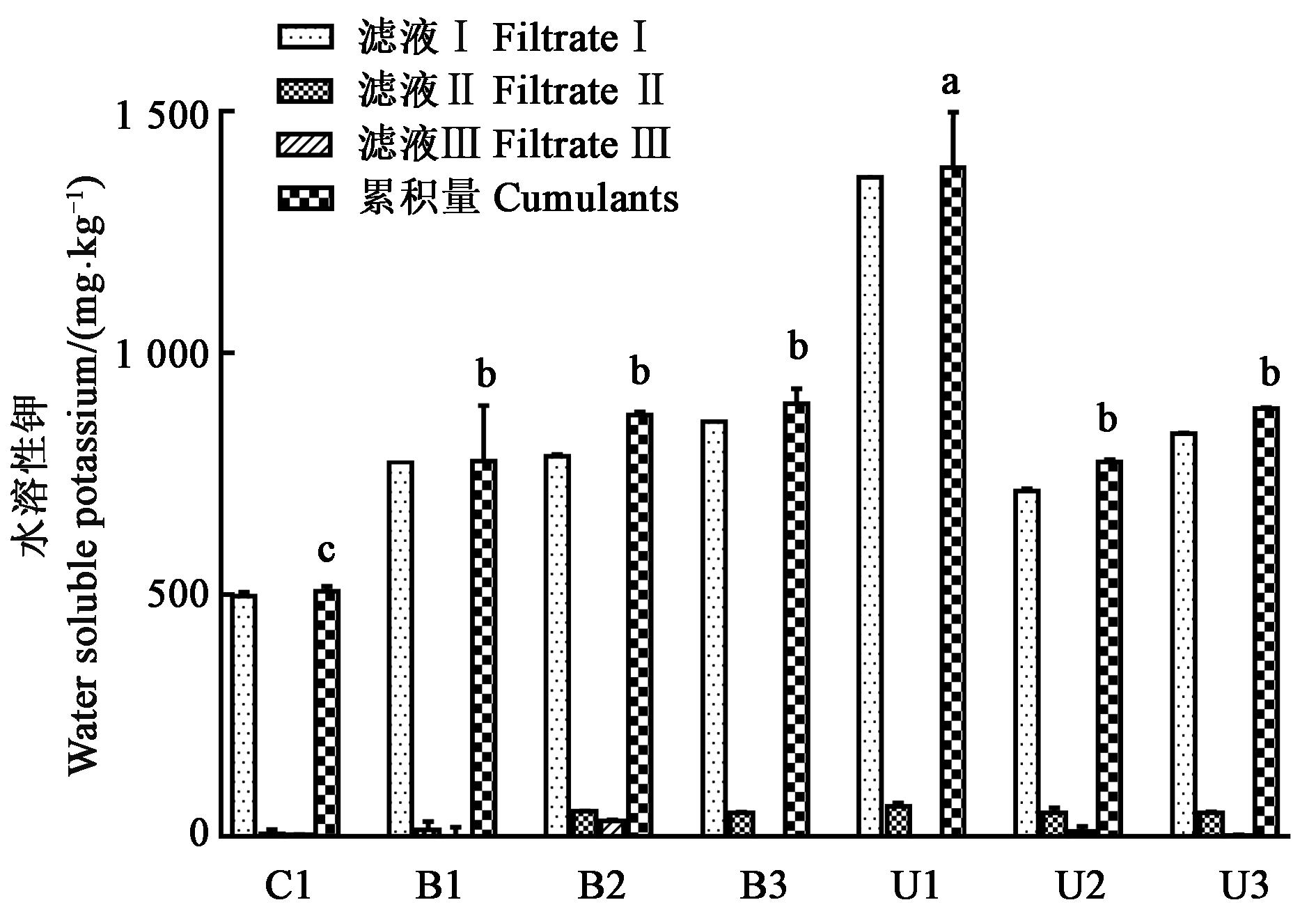
图1 不同解钾菌对钾长石水溶性钾的释放效果注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 1 Release effects of different KSB on the water?soluble K of K?feldsparNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
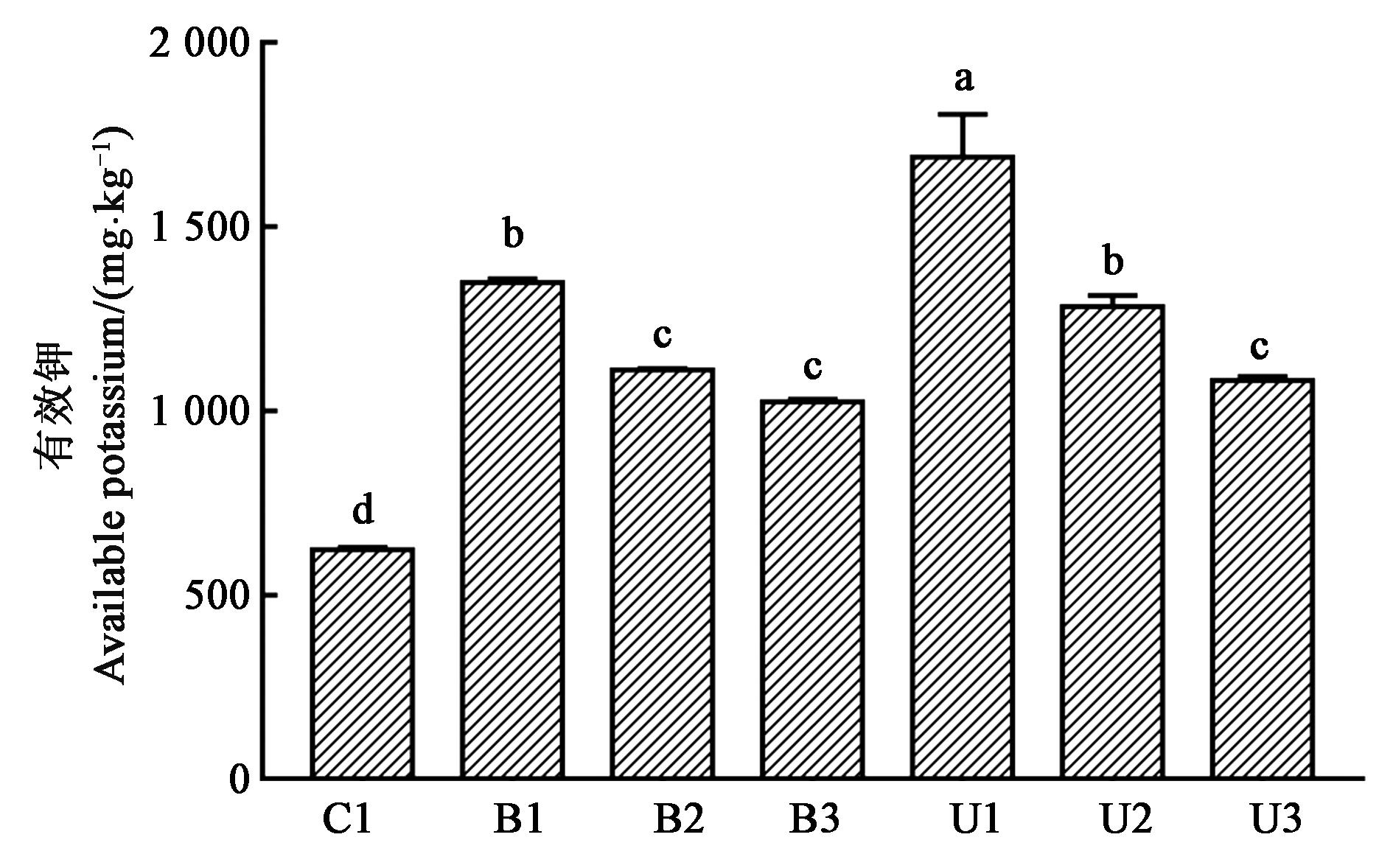
图2 不同活化方法钾长石有效钾的释放效果注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 2 Release effects of under different methods on the available K of K?feldsparNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
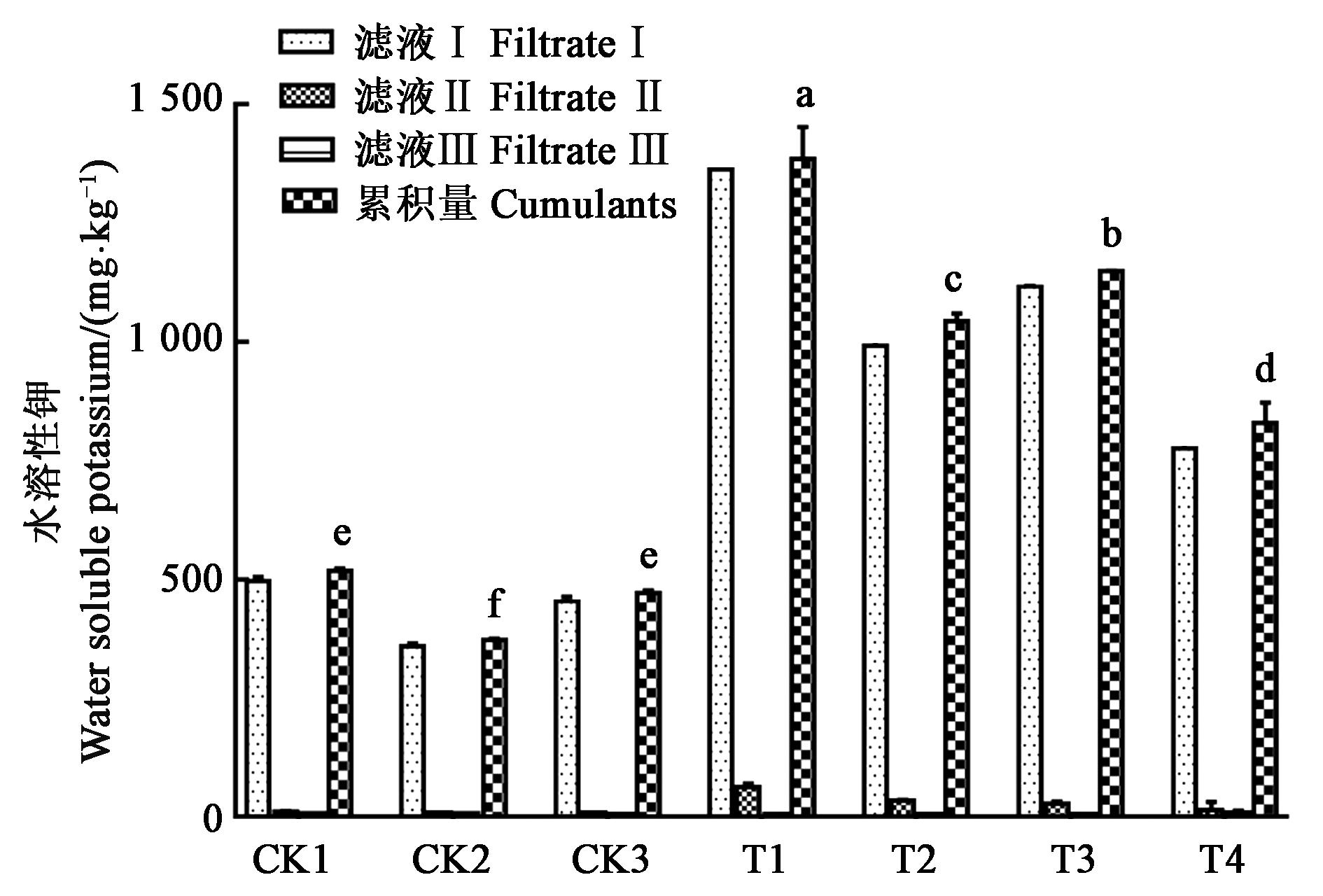
图3 不同处理下钾长石水溶性钾的活化注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 3 Activation of water?soluble K of K?feldspar under different treatmentNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
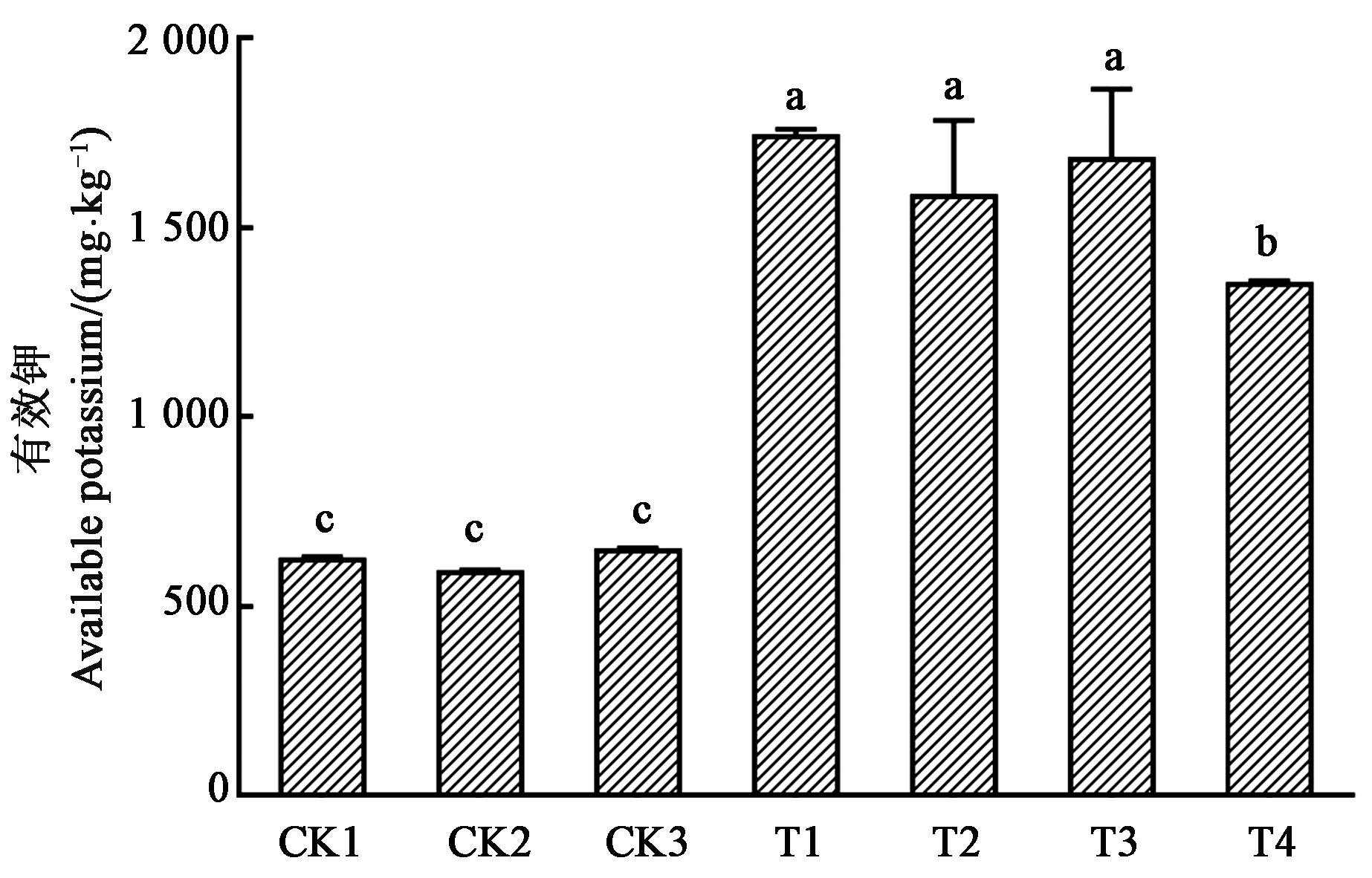
图4 不同处理对钾长石有效钾的活化注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 4 Activation of available K of K?feldspar under different treatmentNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
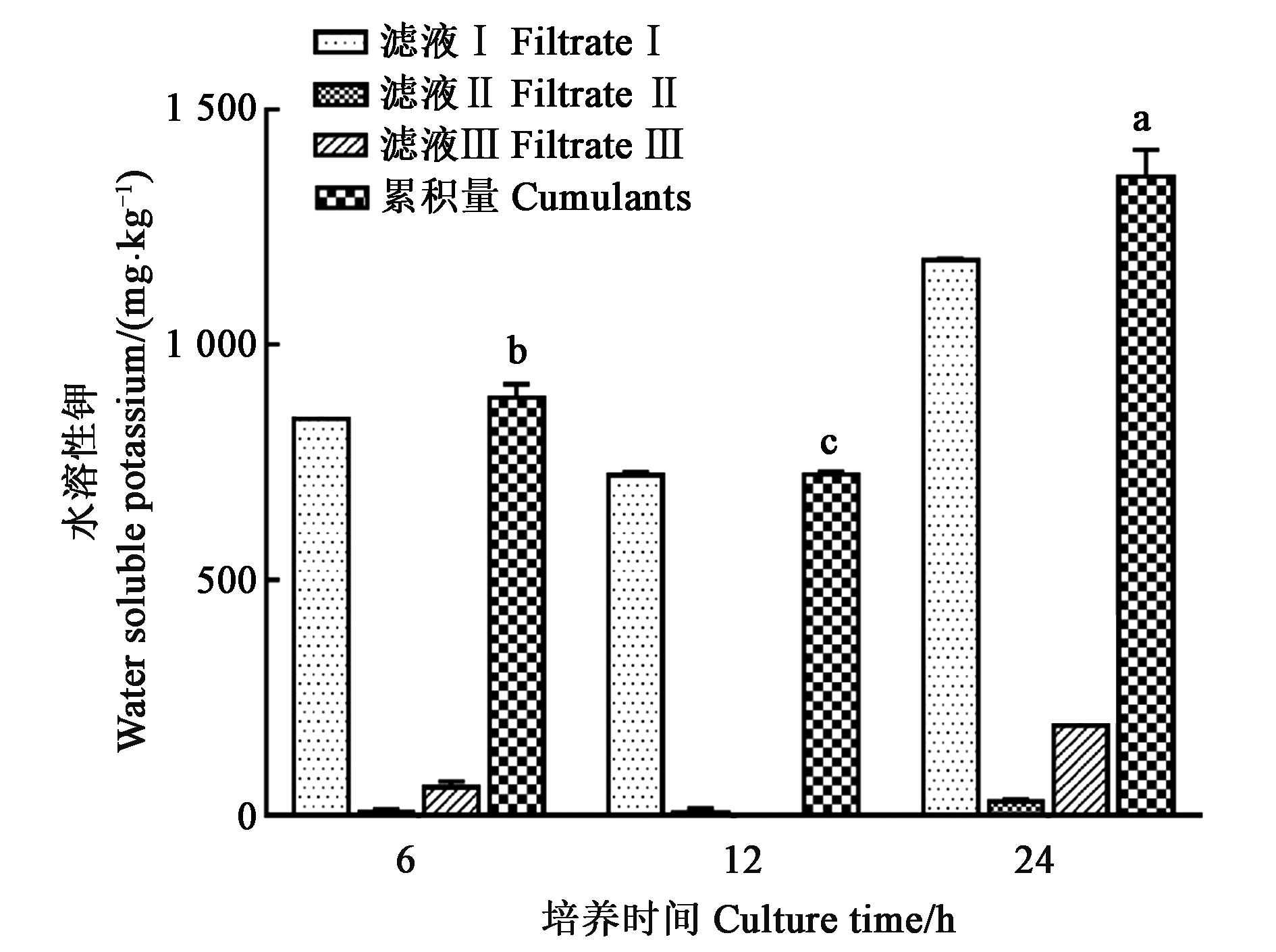
图 5 不同培养时间对水溶性钾释放的影响注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 5 Effect of different incubation time on the release of water?soluble KNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
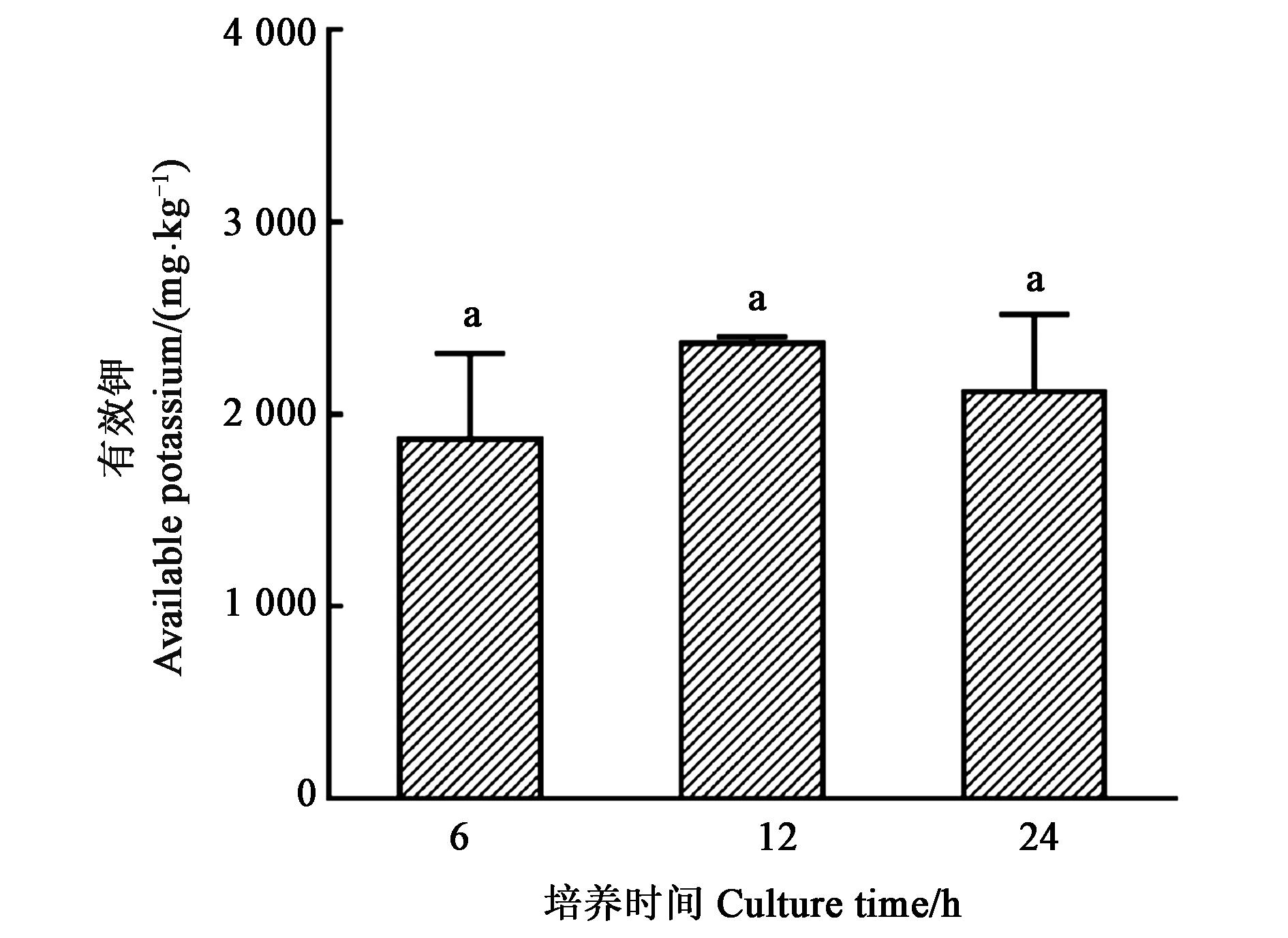
图 6 不同培养时间对有效钾释放的影响注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 6 Effect of different incubation time on the release of available KNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
性状或元素 Characteristics or element | CK0 | CK1 | CK2 | T1A | T2A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height /cm | 86.72±0.74 b | 89.53±1.22 ab | 92.30±1.22 a | 89.68±1.38 ab | 90.15±1.03 ab |
| 茎粗 Stem diameter /mm | 7.36±0.16 c | 7.33±0.11 c | 8.07±0.12 a | 7.46±0.18 bc | 7.84±0.16 ab |
| 鲜重 Fresh weight /g | 19.85±1.09 b | 20.32±1.09 b | 24.16±0.49 a | 21.07±0.80 b | 23.69±0.57 a |
| 干重 Dry weight/g | 2.65±0.14 b | 2.67±0.09 b | 3.01±0.06 a | 2.78±0.09 ab | 3.02±0.10 a |
| 全钾 Total Kpotassium/mg | 40.85±3.31 d | 55.70±2.76 c | 113.18±2.73 a | 54.78±3.30 c | 95.31±7.27 b |
| 全钙 Total calcium /mg | 20.58±0.79 a | 19.77±1.45 a | 20.23±0.33 a | 20.58±0.81 a | 20.06±1.20 a |
| 全镁 Total magnesium /mg | 4.83±0.26 a | 4.81±0.24 a | 4.78±0.61 a | 5.33±0.28 a | 4.83±0.32 a |
表4 玉米农艺性状即茎叶矿物元素含量
Table 4 Agricultural characteristics of corn and content of mineral element in its stem and leaf
性状或元素 Characteristics or element | CK0 | CK1 | CK2 | T1A | T2A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height /cm | 86.72±0.74 b | 89.53±1.22 ab | 92.30±1.22 a | 89.68±1.38 ab | 90.15±1.03 ab |
| 茎粗 Stem diameter /mm | 7.36±0.16 c | 7.33±0.11 c | 8.07±0.12 a | 7.46±0.18 bc | 7.84±0.16 ab |
| 鲜重 Fresh weight /g | 19.85±1.09 b | 20.32±1.09 b | 24.16±0.49 a | 21.07±0.80 b | 23.69±0.57 a |
| 干重 Dry weight/g | 2.65±0.14 b | 2.67±0.09 b | 3.01±0.06 a | 2.78±0.09 ab | 3.02±0.10 a |
| 全钾 Total Kpotassium/mg | 40.85±3.31 d | 55.70±2.76 c | 113.18±2.73 a | 54.78±3.30 c | 95.31±7.27 b |
| 全钙 Total calcium /mg | 20.58±0.79 a | 19.77±1.45 a | 20.23±0.33 a | 20.58±0.81 a | 20.06±1.20 a |
| 全镁 Total magnesium /mg | 4.83±0.26 a | 4.81±0.24 a | 4.78±0.61 a | 5.33±0.28 a | 4.83±0.32 a |
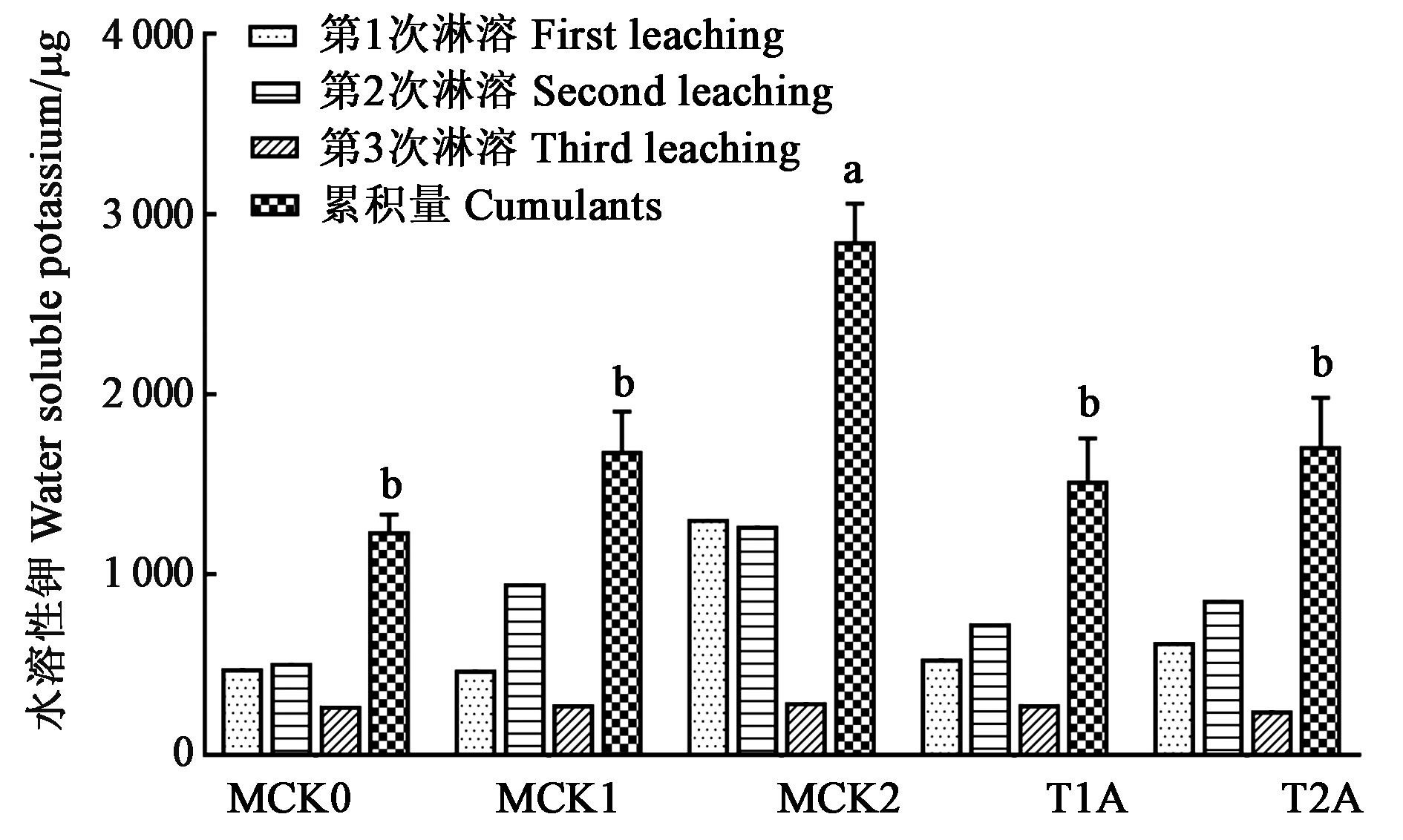
图 9 不同处理下淋溶3次的水溶性钾含量注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 9 Content of water?soluble K leached three times under different treatmentNote: Different small letters indicate significant differences(P<0.05).
| 1 | 商照聪,刘刚,包剑. 我国钾资源开发技术进展与展望[J].化肥工业, 2012, 39(4): 5-8, 49. |
| SHANG Z C, LIU G, BAO J. Progress and prospect of technology for development of potassium resources in China [J]. J. Chem. Fert. Ind., 2012,39(4): 5-8, 49. | |
| 2 | 熊增华,王石军.中国钾资源开发利用技术及产业发展综述[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(6):1-7. |
| XIONG Z H, WANG S J. Overview of potassium resources exploitation & utilization technology and potash industry development [J]. Conservation Utilization Miner. Resour., 2020,40 (6):1-7. | |
| 3 | 陈华丹. NaOH-Na2CO3混合亚熔盐介质中钾长石的分解及其综合利用[D]. 福州:福建师范大学, 2017. |
| CHEN H D. Decomposition of potassium feldspar in NaOH-Na2CO3 mixed sub-molten salt and its comprehensive utilization [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2017. | |
| 4 | 李海龙. 硅酸盐细菌的筛选、鉴定及作用效果的分析[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2011. |
| LI H L. Screening, identification and application of silicate bacteria [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2011. | |
| 5 | 孙科,耿凤英,于秋菊,等. 牛蒡根际土壤中解钾菌筛选、鉴定及解钾条件优化[J]. 中国酿造, 2020, 39(10): 103-108. |
| SUN K, GENG F Y, YU Q J, et al.. Screening and identification of potassium-dissolving bacterium in burdock rhizosphere soil and optomization of potassium-dissolving conditions [J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(10): 103-108 | |
| 6 | HU X, CHEN J, GUO J. Two phosphate- and potassium-solubilizing bacteria isolated from Tianmu mountain, Zhejiang, China [J]. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.,2006, 22(9): 983-990. |
| 7 | ZHANG C, KONG F. Isolation and identification of potassium-solubilizing bacteria from tobacco rhizospheric soil and their effect on tobacco plants [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2014, 82: 18-25. |
| 8 | SHILPA S, BIHARI R M, INDRA B. Solubilization of potassium containing various K-mineral sources by K-solubilizing bacterial isolates on Aleksandrov Medium [J]. Int. J. Current Microbiol. Appl. Sci., 2018, 7(3): 1142-1151. |
| 9 | BAGYALAKSHMI B, PONMURUGAN P, BALAMURUGAN A. Potassium solubilization, plant growth promoting substances by potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) from southern Indian Tea plantation soil [J]. Biocatal.Agric. Biotechnol., 2017, 12: 116-124. |
| 10 | SETIAWATI T C, MUTMAINNAH L. Solubilization of potassium containing mineral by microorganisms from sugarcane rhizosphere [J]. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia, 2016, 9: 108-117. |
| 11 | MEENA V S, MAURYA B R. Influence of K-solubilizing bacteria on release of potassium from waste mica [J]. Agric. Sustainable Dev., 2013, 1(1): 53-56. |
| 12 | 李娜,王其伟,马莹,等. 钾长石制钾肥工艺研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2020, 40(): 54-58. |
| LI N, WANG Q W, MA Y, et al.. Research progress in preparation of potash fertilizers from potash feldspar [J]. Mod. Chem. Ind., 2020, 40(S1): 54-58. | |
| 13 | 李国斌,程东会,王立群. 某难浸金精矿堆浸细菌氧化—氰化浸出试验研究[J]. 黄金,2007(8): 38-41. |
| LI G B, CHENG D H, WANG L Q. Experimental research on heap leaching bio-oxidation cyanidation of refractory gold concentrate [J]. Gold, 2007(8): 38-41. | |
| 14 | BHATTACHARYA S, BACHANI P, JAIN D, et al.. Extraction of potassium from K-feldspar through potassium solubilization in the halophilic Acinetobacter soli (MTCC 5918) isolated from the experimental salt farm [J]. Int. J. Miner. Proc., 2016, 152: 53-57. |
| 15 | 鲍士旦,史瑞和. 土壤钾素供应状况的研究-Ⅱ.土壤供钾状况与水稻吸钾间的关系[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 1984(4): 70-78. |
| BAO S D, SHI R H. Study on the Status of Soil Potassium Supply-Ⅱ. the relationship between the status of soil potassium supply and potassium uptake by rice [J]. J. Nanjing Agric.Univ., 1984(4): 70-78. | |
| 16 | 王忠兵,程常占,王广志,等. 钾长石-NaOH体系水热法提钾工艺研究[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2010, 39(5): 6-7. |
| WANG Z B, CHENG C Z, WANG G Z, et al.. Study on extracting potassium from potassium feldspar-NaOH system by hydrothermal method [J]. Ind. Miner. Proc., 2010, 39(5): 6-7. | |
| 17 | 尹卓忻. 铀(Ⅵ)、钍(Ⅳ)在活性白土和钾长石上的吸附研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2018. |
| YIN Z X. Investigations of U and Th sorption on activated bentonite and K-feldspar [D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2018. | |
| 18 | REN X, LI F, CAI Y, et al.. Paenibacillus sp. strain SB-6 induces weathering of Ca-montmorillonite: illitization and formation of calcite [J]. Geomicrobiol. J., 2016, 34(1): 1-10. |
| 19 | 阮博. 蒙脱石介导鞘氨醇单胞菌GY2B降解菲过程的作用机制研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2020. |
| RUAN B. Mechanism of montmorillonite-mediated biodegradation of phenanthrene by Sphingomonas sp . GY2B [D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 20 | 牛新湘,马兴旺. 农田土壤养分淋溶的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(3): 451-456. |
| NIU X X, MA X W. Research advances on leaching of fertilizer nutrients from agricultural soils [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2011, 27(3): 451-456. | |
| 21 | 梅金飞,刚利萍,余梅霞,等. 烟草秸秆废弃物中纤维素降解菌的筛选、鉴定及产酶条件优化[J]. 烟草科技, 2020, 53(8): 15-23. |
| MEI J F, GANG L P, YU M X, et al.. Screening and identification of cellulose-degrading bacteria in waste tobacco stalks and optimization of enzyme production conditions [J]. Tobacco Sci. Technol., 2020, 53(8): 15-23. | |
| 22 | 王明欢,张小娜,林冰,等. 中药药渣中固氮菌、解磷菌、解钾菌的筛选[J]. 中成药, 2020, 42(2): 531-533. |
| 23 | 狄义宁,刘鲁峰,胡一凡,等. 甘蔗内生菌B9的鉴定及其促生长机制和定殖能力的研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(3): 186-193. |
| DI Y N, LIU L F, HU Y F, et al.. Identification of endophytic B9 from sugarcane and its growth-promoting mechanism and colonization ability [J]. China Soils Fert., 2019(3): 186-193. | |
| 24 | 董艳红,王火焰,周健民,等. 不同土壤钾素淋溶特性的初步研究[J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(2): 225-231. |
| DONG Y H, WANG H Y, ZHOU J M, et al.. Preliminary study on potassium leaching characteristics of different soils [J]. Soils, 2014, 46(2): 225-231. | |
| 25 | 占丽平,李小坤,鲁剑巍,等. 土壤钾素运移的影响因素研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2012, 44(4): 548-553. |
| ZHAN L P, LI X K, LU J W, et al.. Research advances on influence factors of soil potassium movement [J]. Soils, 2012, 44(4): 548-553. |
| [1] | 王帅, 宋伟, 王荣焕, 赵久然. 我国玉米生物学研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 23-31. |
| [2] | 李飞翔, 王鹏, 王云飞, 葛越锋, 唐凯怿, 李得志. 基于堆积试验的玉米包衣种子离散元参数标定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 97-107. |
| [3] | 程名, 朱莹, 王晓楠, 罗平, 陈勇, 郝转芳, 席章营. 玉米ZmSNAC13等位变异对抗旱性的调控研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 24-31. |
| [4] | 成广雷, 邱军, 王晓光, 徐田军, 陈传永, 张春原, 夏千千, 吴元奇, 赵久然, 王荣焕. 我国青贮玉米组合(品种)的农艺性状、生物产量和品质变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. |
| [5] | 孙华, 郭宁, 郑晓娟, 石洁, 张立荣, 闫红飞. 玉米穗腐病病原菌新知镰孢的鉴定及其生物学特性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 145-151. |
| [6] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 罗彦忠, 刘源, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因抗虫、耐除草剂及品质改良复合性状玉米BBHTL8-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 77-85. |
| [7] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因复合抗虫耐除草剂玉米BFL4-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 31-37. |
| [8] | 樊鸿叶, , 李姚姚, 卢宪菊, 顾生浩, 郭新宇, 刘玉华. 基于无人机多光谱遥感的春玉米叶面积指数和地上部生物量估算模型比较研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 112-120. |
| [9] | 李双, 张伟, 王丽, 李孝军, 崔俊涛. 秸秆还田对不同地力黑土培肥与茎腐病害发生的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 80-90. |
| [10] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 陈如冰, 李俐俐. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| [11] | 刘忠祥, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 周文期, 何海军, 周玉乾, 寇思荣. 快中子诱变突变体的表型鉴定及配合力效应分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 184-194. |
| [12] | 杨华1,李江2,张维1,周正富1,燕永亮1,郭嘉3,刘相国3,郝东云3,林敏1,柯秀彬1*. 施氏假单胞菌在玉米根际的固氮效率和促生效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 76-84. |
| [13] | 王秀娟,解占军,韩瑛祚,娄春荣,董环,何志刚. 有机培肥对土壤肥力及玉米氮素利用和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 132-138. |
| [14] | 马文慧, 郑淑波, 李岩, 路明. 吉林省玉米单产发展历程与提升路径分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 13-19. |
| [15] | 高日平, §, 刘小月, §, 杜二小, 韩云飞, 任永峰, 高宇, 赵沛义, 李焕春, 张鹏, . 垄膜沟播与秸秆还田对内蒙古黄土高原玉米农田土壤水分、酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 181-190. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号