




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 190-200.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0887
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
麻仲花1( ), 陈娟1, 吴娜1, 满本菊1, 王晓港1, 者永清1, 刘吉利2(
), 陈娟1, 吴娜1, 满本菊1, 王晓港1, 者永清1, 刘吉利2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-17
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2023-06-01
发布日期:2023-07-28
通讯作者:
刘吉利
作者简介:麻仲花 E-mail:2504075822@qq.com;
基金资助:
Zhonghua MA1( ), Juan CHEN1, Na WU1, Benju MAN1, Xiaogang WANG1, Yongqing ZHE1, Jili LIU2(
), Juan CHEN1, Na WU1, Benju MAN1, Xiaogang WANG1, Yongqing ZHE1, Jili LIU2( )
)
Received:2021-10-17
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2023-06-01
Published:2023-07-28
Contact:
Jili LIU
摘要:
为探究盐胁迫与供磷水平对不同柳枝稷(Panicum virgatum L.)品种苗期光合特性及总生物量的影响,以八倍体Alamo、Alamo和Pathfinder 3个品种作为水培试验材料,设置2个盐胁迫水平(A1非盐胁迫、A2盐胁迫)和4个供磷水平(B1无磷,B2低磷,B3高磷,B4全磷),分析盐胁迫与供磷水平对3个柳枝稷品种苗期光合指标及总生物量的影响规律,并进一步探究3个柳枝稷品种光合特性与总生物量之间的关系。结果表明,在相同盐处理下,3个柳枝稷品种苗期的净光合速率、气孔导度、蒸腾速率、叶绿素含量及总生物量均随着磷水平的增加而增加,其中,在非盐胁迫和盐胁迫下八倍体Alamo,全磷处理较无磷处理分别提高21.84%、42.86%、21.98%、17.45%、246.52%和14.63%、16.67%、71.10%、115.45%、91.00%;Alamo分别提高15.89%、28.57%、37.62%、95.16%、115.32%和15.28%、100.00%、37.20%、188.33%、113.97%;Pathfinder分别提高18.33%、75.00%、42.60%、86.87%、145.85%和23.35%、100.00%、50.35%、108.20%、405.88%。在相同盐处理下,3个柳枝稷品种苗期的胞间CO2浓度随着磷水平的增加而降低,其中,在盐胁迫下全磷处理较无磷处理分别降低49.68%、40.41%、40.21%;在非盐胁迫下全磷处理较无磷处理分别降低50.12%、68.07%、63.11%。八倍体Alamo总生物量的增加与蒸腾速率、气孔导度、净光合速率呈正相关;Alamo总生物量与叶绿素含量呈正相关;八倍体Alamo和Alamo的总生物量增加均与胞间CO2浓度呈负相关。综合分析表明,八倍体Alamo的适应性较好,更适宜在盐胁迫与低磷胁迫环境下种植。
中图分类号:
麻仲花, 陈娟, 吴娜, 满本菊, 王晓港, 者永清, 刘吉利. 盐胁迫与供磷水平对柳枝稷苗期光合特性与总生物量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 190-200.
Zhonghua MA, Juan CHEN, Na WU, Benju MAN, Xiaogang WANG, Yongqing ZHE, Jili LIU. Effects of Salt Stress and Phosphorus Supply on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Total Biomass of Switchgrass at Seedling Stage[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 190-200.
| 品种Variety | 生态类型Ecotype | 染色体倍数Ploidy | 来源Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alamo | 低地Lowland | 四倍体Tetraploid | 德克萨斯州南部28° N Southern Texas 28° N |
八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | 低地Lowland | 八倍体Octoploid | Alamo (秋水仙素人工加倍) Alamo (Artificial doubling of colchicine) |
| Pathfinder | 高地Upland | 八倍体Octoploid | 堪萨斯州40° N Kansas 40° N |
表1 柳枝稷材料生态类型、染色体倍性及来源
Table 1 Ecological type and chromosome doubling and origin of switchgrass material
| 品种Variety | 生态类型Ecotype | 染色体倍数Ploidy | 来源Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alamo | 低地Lowland | 四倍体Tetraploid | 德克萨斯州南部28° N Southern Texas 28° N |
八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | 低地Lowland | 八倍体Octoploid | Alamo (秋水仙素人工加倍) Alamo (Artificial doubling of colchicine) |
| Pathfinder | 高地Upland | 八倍体Octoploid | 堪萨斯州40° N Kansas 40° N |
| 成分Component | 含量Content/(mol·L-1) | 加入量Volume/mL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母液Mother liquor | 溶液Solution | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | |
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 5.000 0 | 5.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 |
| KNO3 | 2.500 0 | 5.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 2.000 0 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 2.500 0 | 2.500 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 |
| KH2PO4 | 1.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 0.005 0 | 0.200 0 | 2.000 0 | |
| NaH2PO4 | 2.000 0 | |||||
| NaNO3 | 5.000 0 | |||||
| MgCl2 | 2.500 0 | |||||
| NaSO4 | 2.500 0 | |||||
| CaCl2 | 5.000 0 | |||||
| KCL | 2.500 0 | 5.000 0 | 0.800 0 | 0.798 0 | 0.720 0 | |
| EDTA-FeNa | 0.200 0 | 0.020 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 |
| MnSO4·H2O | 0.672 2 | 0.006 7 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.003 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 |
表2 不同磷水平的Hoagland营养液配置
Table 2 Hoagland nutrient solution configuration table with different phosphorus levels
| 成分Component | 含量Content/(mol·L-1) | 加入量Volume/mL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母液Mother liquor | 溶液Solution | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | |
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 5.000 0 | 5.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 |
| KNO3 | 2.500 0 | 5.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 2.000 0 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 2.500 0 | 2.500 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.000 0 |
| KH2PO4 | 1.000 0 | 2.000 0 | 0.005 0 | 0.200 0 | 2.000 0 | |
| NaH2PO4 | 2.000 0 | |||||
| NaNO3 | 5.000 0 | |||||
| MgCl2 | 2.500 0 | |||||
| NaSO4 | 2.500 0 | |||||
| CaCl2 | 5.000 0 | |||||
| KCL | 2.500 0 | 5.000 0 | 0.800 0 | 0.798 0 | 0.720 0 | |
| EDTA-FeNa | 0.200 0 | 0.020 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 |
| MnSO4·H2O | 0.672 2 | 0.006 7 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.003 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.100 0 |

图1 不同盐胁迫与供磷水平下3个柳枝稷品种的叶绿素含量注: 不同小写字母表示同一品种相同盐处理下不同供磷水平间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Chlorophyll content of 3 switchgrass varieties under different salt stress and phosphorus supplyNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different phosphorus levels of same variety under same salt treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.127 3 | 0.026 6* | 0.003 0* |
| FB | 0.175 0 | 0.055 5 | 0.009 0* |
| FA×B | 0.000 4* | 0.003 2* | 0.899 8 |
表3 叶绿素含量方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of chlorophyll content
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.127 3 | 0.026 6* | 0.003 0* |
| FB | 0.175 0 | 0.055 5 | 0.009 0* |
| FA×B | 0.000 4* | 0.003 2* | 0.899 8 |
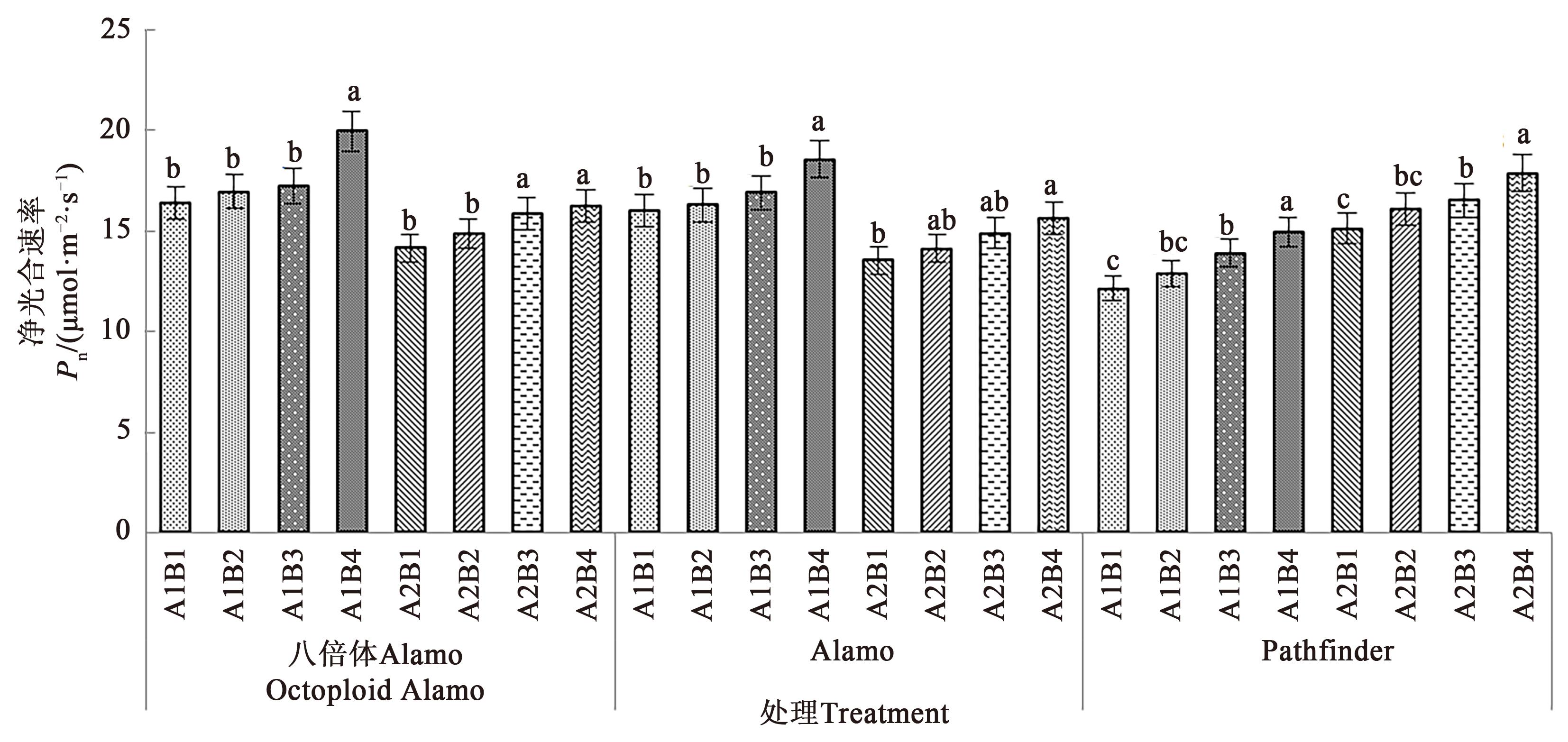
图2 不同盐胁迫与供磷水平下3个柳枝稷品种的净光合速率注: 不同小写字母表示同一品种在相同盐处理下不同供磷处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Pn of 3 switchgrass varieties under different salt stress and phosphorus supply levelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different phosphorus levels of same variety under same salt treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.018 7* | 0.001 2* | 0.000 2* |
| FB | 0.092 6 | 0.012 3* | 0.002 0* |
| FA×B | 0.058 4 | 0.843 4 | 0.963 6 |
表4 净光合速率方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of Pn
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.018 7* | 0.001 2* | 0.000 2* |
| FB | 0.092 6 | 0.012 3* | 0.002 0* |
| FA×B | 0.058 4 | 0.843 4 | 0.963 6 |
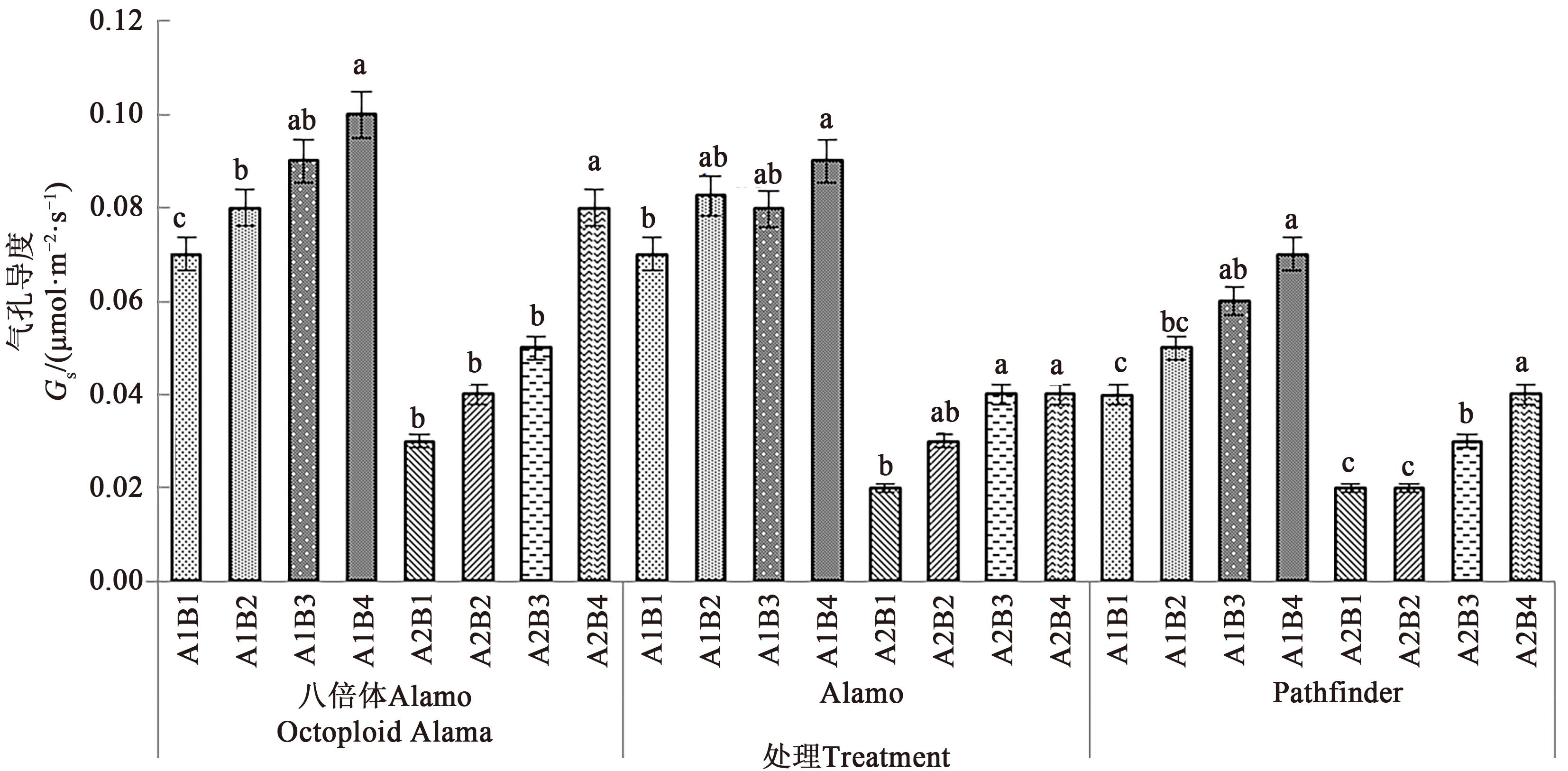
图3 不同盐胁迫与供磷水平下3个柳枝稷品种的气孔导度注: 不同小写字母表示同一品种在相同盐处理下不同供磷处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Gs of 3 switchgrass varieties under different salt stress and phosphorus supply levelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different phosphorus levels of same variety under same salt treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.009 6* | 0.000 4* | 0.000 8* |
| FB | 0.071 3 | 0.053 4 | 0.017 5* |
| FA×B | 0.182 6 | 0.024 5* | 0.440 0 |
表5 气孔导度方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance of Gs
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.009 6* | 0.000 4* | 0.000 8* |
| FB | 0.071 3 | 0.053 4 | 0.017 5* |
| FA×B | 0.182 6 | 0.024 5* | 0.440 0 |
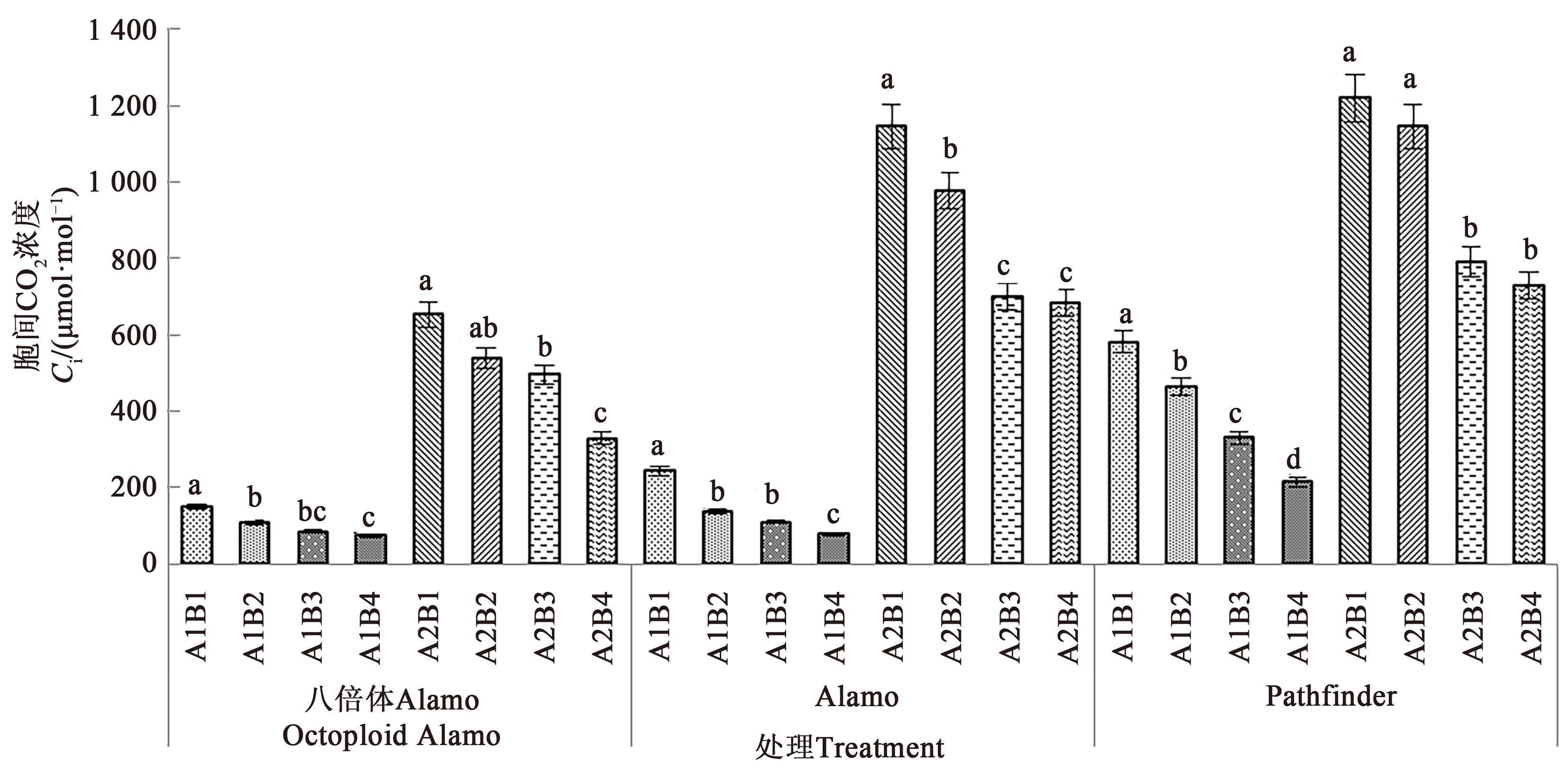
图4 不同盐胁迫与供磷水平下3个柳枝稷品种的胞间CO2浓度注: 不同小写字母表示同一品种在相同盐处理下不同供磷处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Ci of 3 switchgrass varieties under different salt stress and phosphorus supply levelNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different phosphorus levels of same variety under same salt treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.004 7* | 0.002 8* | 0.001 6* |
| FB | 0.237 0 | 0.175 1 | 0.025 9* |
| FA×B | 0.002 6* | 0.000 0* | 0.007 9* |
表6 胞间CO2浓度方差分析
Table 6 Analysis of variance of Ci
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.004 7* | 0.002 8* | 0.001 6* |
| FB | 0.237 0 | 0.175 1 | 0.025 9* |
| FA×B | 0.002 6* | 0.000 0* | 0.007 9* |
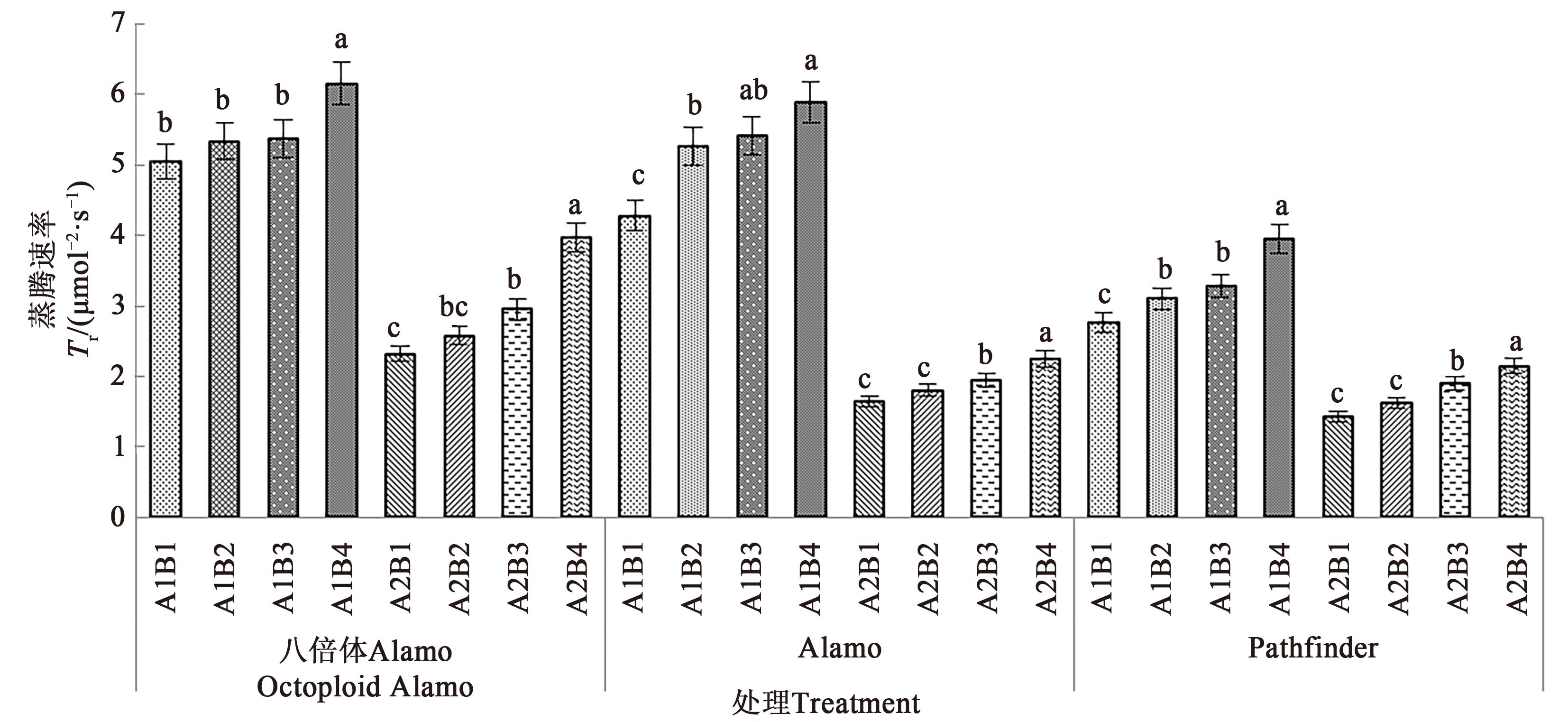
图5 不同盐胁迫与供磷水平下3个柳枝稷品种的蒸腾速率注: 不同小写字母表示同一品种在相同盐处理下不同供磷处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Tr of 3 switchgrass varieties under different salt stress and phosphorus supply levelNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different phosphorus levels of same variety under same salt treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.000 3* | 0.000 7* | 0.000 7* |
| FB | 0.016 9* | 0.135 6 | 0.026 4* |
| FA×B | 0.577 1 | 0.009 9* | 0.039 9* |
表7 蒸腾速率方差分析
Table 7 Analysis of variance of Tr
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.000 3* | 0.000 7* | 0.000 7* |
| FB | 0.016 9* | 0.135 6 | 0.026 4* |
| FA×B | 0.577 1 | 0.009 9* | 0.039 9* |
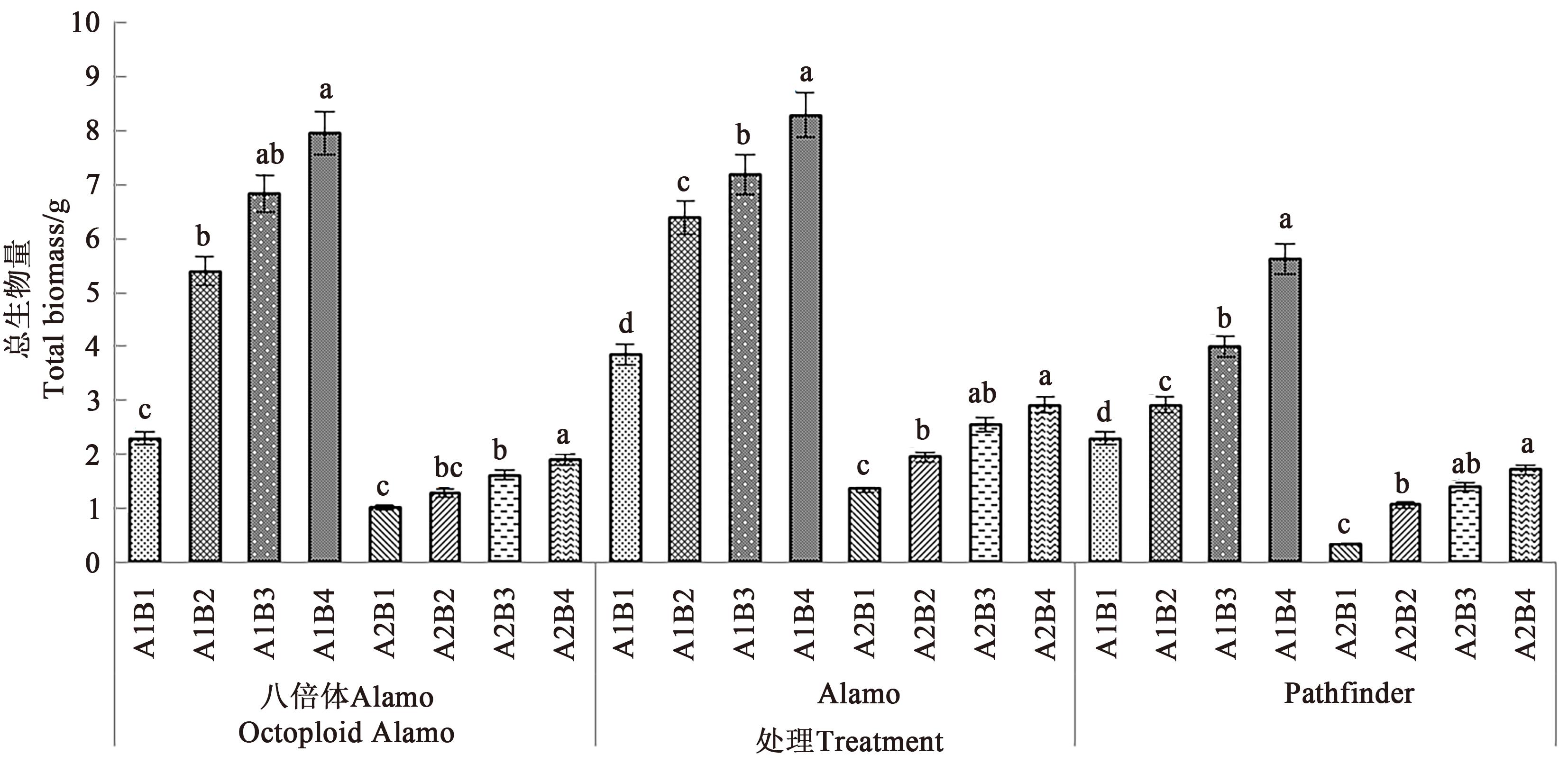
图6 盐胁迫与供磷水平下3个柳枝稷品种的总生物量注: 不同小写字母表示同一品种在相同盐处理下不同供磷处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Biomass of 3 switchgrass varieties under different salt stress and phosphorus supply levelsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different phosphorus levels of same variety under same salt treatment at P<0.05 level.
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.027 8* | 0.006 3* | 0.012 3* |
| FB | 0.311 3 | 0.130 6 | 0.123 9 |
| FA×B | 0.000 1* | 0.000 0* | 0.000 0* |
表8 总生物量方差分析
Table 8 Analysis of variance of total biomass
| 处理Treatment | 八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | Alamo | Pathfinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 0.027 8* | 0.006 3* | 0.012 3* |
| FB | 0.311 3 | 0.130 6 | 0.123 9 |
| FA×B | 0.000 1* | 0.000 0* | 0.000 0* |
| 品种Variety | 指标Index | 总生物量 Total biomass | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 蒸腾速率Tr | 胞间CO2浓度Ci | 气孔导度Gs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content | 0.61 | ||||
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.88** | 0.70 | ||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.83* | -0.75* | -0.98 | |||
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.85** | 0.81* | 0.94 | -0.93 | ||
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.89** | 0.73* | 0.89** | -0.83* | 0.90** | |
| Alamo | 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content | 0.86** | ||||
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.96 | 0.76* | ||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.92** | -0.83* | -0.95** | |||
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.95 | 0.81* | 0.98** | -0.99 | ||
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.94 | 0.90** | 0.90** | -0.91** | 0.93** | |
| Pathfinder | 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content | 0.94 | ||||
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.97 | 0.92** | ||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.93 | -0.92** | -0.97 | |||
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | -0.97 | ||
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.98 | -0.98 | 0.99 |
表9 3个柳枝稷品种苗期总生物量与光合特性的相关性分析
Table 9 Correlation analysis of total biomass and photosynthetic characteristics of 3 switchgrass varieties at different seedling stage
| 品种Variety | 指标Index | 总生物量 Total biomass | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 蒸腾速率Tr | 胞间CO2浓度Ci | 气孔导度Gs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content | 0.61 | ||||
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.88** | 0.70 | ||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.83* | -0.75* | -0.98 | |||
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.85** | 0.81* | 0.94 | -0.93 | ||
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.89** | 0.73* | 0.89** | -0.83* | 0.90** | |
| Alamo | 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content | 0.86** | ||||
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.96 | 0.76* | ||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.92** | -0.83* | -0.95** | |||
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.95 | 0.81* | 0.98** | -0.99 | ||
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.94 | 0.90** | 0.90** | -0.91** | 0.93** | |
| Pathfinder | 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content | 0.94 | ||||
| 蒸腾速率Tr | 0.97 | 0.92** | ||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Ci | -0.93 | -0.92** | -0.97 | |||
| 气孔导度Gs | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | -0.97 | ||
| 净光合速率Pn | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.98 | -0.98 | 0.99 |
| 品种Variety | 总生物量 Total biomass | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 胞间CO2浓 度Ci | 气孔导度Gs | 净光合速率Pn | 均值 Mean | 排序 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | 0.36 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.40 | 0.50 | 1 |
| Alamo | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 2 |
| Pathfinder | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 3 |
表10 3个柳枝稷品种苗期光合特性及总生物量的隶属函数值
Table 10 Membership function values ??of photosynthetic characteristics and total biomass of 3 switchgrass varieties at seedling stage
| 品种Variety | 总生物量 Total biomass | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 胞间CO2浓 度Ci | 气孔导度Gs | 净光合速率Pn | 均值 Mean | 排序 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
八倍体Alamo Octoploid Alamo | 0.36 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.40 | 0.50 | 1 |
| Alamo | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 2 |
| Pathfinder | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 3 |
| 1 | 刘吉利, 常雯雯, 张永乾, 等. 盐碱地不同柳枝稷品种的生理特性[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(11): 2641-2649. |
| LIU J L, CHANG W W, ZHANG Y Q, et al.. Comparison of physiological characteristics of different switchgrass varieties in saline-alkali land [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2018, 35(11): 2641-2649. | |
| 2 | 田志杰, 李景鹏, 杨福, 非生物胁迫下作物磷素利用研究进展 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(8): 2336-2342. |
| TIAN Z J, LI J P, YANG F. Research progress in crop phosphorus utilization under abiotic stress [J]. J. Ecol., 2017, 36(8): 2336-2342. | |
| 3 | 邓力群, 刘兆普, 程爱武, 等. 不同盐分滨海盐土上油葵(G1012B)的氮磷肥效应研究[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2002, 24(4): 35-41. |
| DENG L Q, LIU Z P, CHENG A W, et al.. Study on nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer effects of oil sunflower (G1012B) on coastal saline soil with different salinity [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2002, 24(4): 35-41. | |
| 4 | 黄高鉴, 王斌, 杨治平, 等. 盐胁迫对柳枝稷生物量及品质的影响[J]. 天津科技, 2019, 46(2): 26-28. |
| HUANG G J, WANG B, YANG Z P, et al.. The effect of salt stress on switchgrass biomass and quality [J]. Tianjin Sci. Technol., 2019, 46 (2): 26-28. | |
| 5 | 常雯雯, 刘吉利, 吴娜, 等. 西北盐碱地区不同柳枝稷品种光合特性与产量比较[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(10): 1647-1654. |
| CHANG W W, LIU J L, WU N, et al.. Comparison of photosynthetic characteristics and yield of different switchgrass varieties in saline-alkali areas in Northwestern China [J]. J. Zhejiang. Agric., 2019, 31(10): 1647-1654. | |
| 6 | 刘金彪, 王世琪, 康继月. 水磷供应对柳枝稷和达乌里胡枝子生物量、水分利用效率及种间关系的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1007-0435. |
| LIU J B, WANG S Q, KANG J Y. The effect of water and phosphorus supply on the biomass, water use efficiency and interspecific relationships of switchgrass and Lespedeza daurie [J]. Acta. Agrestia Sin., 2019, 27(6):1007-0435. | |
| 7 | 张蕊, 张富平, 郝艳丽. 水分胁迫条件下磷素营养对小麦抗旱性影响的研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(11): 3313-3314, 3316. |
| ZHANG R, ZHANG F P, HAO Y L. Research progress on the effect of phosphorus nutrition on wheat drought resistance under water stress [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2007, 35(11): 3313-3314, 3316. | |
| 8 | 朱毅, 范希峰, 侯新村, 等. 中性盐胁迫对柳枝稷苗期生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2015, 23(2): 1007-1015. |
| ZHU Y, FAN X F, HOU X C, et al.. Effects of neutral salt stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of switchgrass seedlings [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2015, 23(2): 1007-1015. | |
| 9 | 韩瑞宏, 卢欣石, 高桂娟, 等. 紫花苜蓿抗旱性主成分及隶属函数分析[J]. 草地学报, 2006, 14(2): 142-146. |
| HAN R H, LU X S, GAO G J, et al.. Analysis of the principal components and membership functions of alfalfa drought resistance [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2006, 14(2): 142-146. | |
| 10 | 萧浪涛. 植物生理学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008: 124-156. |
| XIAO L G. Plant Physiology [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2008:124-156. | |
| 11 | 郑殿君, 张治安, 姜丽艳, 等. 不同产量水平大豆叶片净光合速率的比较[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2010, 41(9): 1-5. |
| ZHENG D J, ZHANG Z A, JIANG L Y, et al.. Comparison of net photosynthetic rate of soybean leaves at different yield levels [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Univ., 2010, 41(9): 1-5. | |
| 12 | 王继安, 宁海龙, 罗秋香, 等. 大豆种间叶绿素含量、RUBP活性、希尔反应活力及其与产量间的关系[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2004, 35(2): 129-134. |
| WANG J A, NING H L, LUO Q X, et al.. Soybean interspecific chlorophyll content, RUBP activity, hill reaction activity and their relationship with yield [J]. J. Notheast Agric. Univ., 2004, 35(2): 129-134. | |
| 13 | 张璐颖, 文笑, 林勇明, 等. 盐胁迫对台湾桤木幼苗光合作用和荧光特性的影响[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2013, 33(3):193-199. |
| ZHANG L Y, WEN X, LIN Y M, et al.. The effect of salt stress on photosynthesis and fluorescence characteristics of Alnus taiwanensis seedlings [J]. J. Fujian For. Coll., 2013, 33(3):193-199. | |
| 14 | 张文明, 巢建国, 谷巍, 等. 酸雨胁迫下茅苍术的光合及生理响应[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(7): 1167-1172. |
| ZHANG W M, CHAO J G, GU W, et al.. Photosynthetic and physiological response of Atractylodes lanceolata under acid rain stress [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2017, 48(7):1167-1172. | |
| 15 | 李学孚, 倪智敏, 吴月燕, 等. 盐胁迫对"鄞红"葡萄光合特性及叶片细胞结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(13): 4436-4444. |
| LI X F, NI Z M, WU Y Y, et al.. Effects of salt stress on photosynthetic characteristics and leaf cell structure of “Yinhong” grape [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2015, 35(13):4436-4444. | |
| 16 | 孙云飞, 张文明, 巢建国, 等. 盐胁迫对茅苍术叶绿素含量及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(4): 146-149. |
| SUN Y F, ZHANG W M, CHAO J G, et al.. The effect of salt stress on the chlorophyll content and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Atractylodes lanceolata [J]. Jiangsu. Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(4):146-149. | |
| 17 | YU M M, CHEN Y H, ZHU Z B, et al.. Effect of phosphorus supply on plant productivity, photosynthetic efficiency and bioactive-component production in Prunella vulgaris L. under hydroponic condition [J]. J. Plant. Nutr., 2016, 39(12): 1672-1680. |
| 18 | 王艺, 韦小丽. 不同光照对植物生长、生理生化和形态结构影响的研究进展[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2010, 29(4): 353-359. |
| WANG Y, WEI X L. Advance on the effects of different light envrironments on growth physiological biochemistry and morphostructure of plant [J]. J. Mountain Agric. Biol., 2010, 29(4):353-359. | |
| 19 | 叶子飘, 于强. 植物气孔导度的机理模型[J]. 植物生态学报, 2009, 33(4): 772-778. |
| YE Z P, YU Q. Mechanism model of plant stomatal conductance [J]. J. Plant Ecol., 2009, 33(4): 772-778. | |
| 20 | 李六林, 杨佩芳, 田彩芳, 等. 树莓光合特性的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2003, 30(3): 314-316. |
| LI L L, YANG P F, TIAN C F, et al.. Research on the photosynthetic characteristics of raspberry [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2003, 30(3):314-316. | |
| 21 | 刘群龙, 宁婵娟, 王朵, 等. 翅果油树净光合速率日变化及其主要影响因子[J].中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(3): 474-478. |
| LIU Q L, NING C J, WANG D, et al.. Diurnal changes of the net photosynthetic rate of Elaeagnus serrata and its main influencing factors [J]. J. Ecol. Agric., 2009, 17(3): 474-478. | |
| 22 | 张兆斌. CO2、温度升高对柿幼树光合作用及水分利用效率影响的研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2009. |
| ZHANG Z B. The effect of CO2 and temperature increase on the photosynthesis and water use efficiency of young persimmon trees [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| 23 | 叶菊, 蔺海明, 邱黛玉, 等. 几种甘草(Glycyrrhiza)光合特性、形态特征及生物量比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(2): 456-463. |
| YE J, LIN H M, QIU D Y, et al.. Comparison of photosynthetic characteristics, morphological characteristics and biomass of several licorice (Glycyrrhiza) [J]. J. Desert. Res., 2014, 34(2):456-463. | |
| 24 | 胡煜雯, 巢建国, 陆奇杰, 等. 茅苍术对不同供磷水平的光合及生理响应[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2018(12): 20-24. |
| HU Y W, CHAO J G, LU Q J, et al.. The photosynthetic and physiological response of Atractylodes lanceolata to different levels of phosphorus supply [J]. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci., 2018(12): 20-24. | |
| 25 | 杨洋, 王亚娟, 阴法庭, 等. 盐碱胁迫对油菜苗期生理及光合特性的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2020 (15): 1-8. |
| YANG Y, WANG Y J, YIN F T, et al.. The effect of saline-alkali stress on the physiological and photosynthetic characteristics of rape seedlings [J]. Northern Hortic., 2020 (15): 1-8. | |
| 26 | 姜宗庆, 李成忠, 汤庚国. 薄壳山核桃光合生理特性对磷素响应的研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2018(1): 19-22. |
| JIANG Z Q, LI C Z, TANG G G. Study on the response of photosynthetic physiological characteristics of hickory hickory to phosphorus [J]. Northern Hortic., 2018(1): 19-22. | |
| 27 | 李进, 段婷婷, 郑超, 等. 不同供磷水平下2个甘蔗品种的光合作用及生长特征[J].热带作物学报, 2019, 40(6): 1108-1114. |
| LI J, DUAN T T, ZHENG C, et al.. Photosynthesis and growth characteristics of two sugarcane varieties under different phosphorus supply levels [J]. J. Tropical Crops, 2019, 40(6):1108-1114. | |
| 28 | 陈永亮, 李修岭, 周晓燕, 等. 低磷胁迫对落叶松幼苗生长及根系酸性磷酸酶活性的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2006, 28(6): 46-50. |
| CHEN Y L, LI X L, ZHOU X Y, et al.. Effects of low phosphorus stress on the growth and root acid phosphatase activity of larch seedlings [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2006, 28(6):46-50. |
| [1] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [2] | 白道宽, 郭宝健, 洪益, 张萌娜, 朱娟, 吕超, 王菲菲, 许如根. 一个大麦黄化突变体的突变机理及其遗传机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 34-45. |
| [3] | 侯志雄, 井长青, 王公鑫, 郭文章, 赵苇康. 1998—2018年北疆天然草地植被覆盖度时空变化及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 140-151. |
| [4] | 李峰, 殷丛培, 殷冉, 王凡, 韩永亮, 杨志敏, 刘建成. 燕麦根际土壤细菌多样性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 153-165. |
| [5] | 郝艳玲, 闫伟. 混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗形态及生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 69-76. |
| [6] | 高桐梅, 李丰, 苏小雨, 王东勇, 田媛, 张鹏钰, 李同科, 杨自豪, 卫双玲. 减施氮肥对芝麻农艺性状、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 176-188. |
| [7] | 王鑫, 张玉霞, 陈卫东, 林聪颖, 候文慧, 斯日古楞, 丛百明. 追施氮肥对不同饲用燕麦品种产量及光合荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 170-179. |
| [8] | 王方玲, 张明月, 周亚茹, 管庆林, 李欣燕, 钟秋, 赵铭钦. 干旱胁迫下TS-PAA保水剂对雪茄烟生长发育和光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| [9] | 钟鹏, 苗丽丽, 刘杰, 王建丽, 陆海燕, 于洪久, 张楠. 种植密度和方式对油莎豆群体结构和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 186-196. |
| [10] | 田翁由, 刘昊, 甘超林, 伍柳芬, 李爱, 杨丽芳, 高英. 盐胁迫下樱桃砧木的光合响应和光谱特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 77-83. |
| [11] | 王志丹, 刘吉利, 吴娜. 粉垄耕作对甜高粱光合生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 148-156. |
| [12] | 苏煜, 黄劭理. 增施生物有机肥对烤烟光合特性及根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 164-171. |
| [13] | 蒲全明, 杨鹏, 雍磊, 邓榆川, 何自涵, 林邦民, 施松梅, 向承勇, 方芳. 萝卜紫红叶色突变体的色素含量及光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 45-54. |
| [14] | 张胜珍, 马艳芝. 氯化钙对盐胁迫下荆芥种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 65-71. |
| [15] | 李星, 胡杨, 马媛, 贾守义, 李钢铁. 细穗柽柳对3种单盐胁迫的生理响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 52-60. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号