




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 153-165.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0906
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
李峰1( ), 殷丛培2(
), 殷丛培2( ), 殷冉3, 王凡2, 韩永亮4, 杨志敏1(
), 殷冉3, 王凡2, 韩永亮4, 杨志敏1( ), 刘建成1(
), 刘建成1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-25
接受日期:2022-03-08
出版日期:2023-01-15
发布日期:2023-04-17
通讯作者:
杨志敏,刘建成
作者简介:李峰 E-mail:20234350@qq.com基金资助:
Feng LI1( ), Congpei YIN2(
), Congpei YIN2( ), Ran YIN3, Fan WANG2, Yongliang HAN4, Zhimin YANG1(
), Ran YIN3, Fan WANG2, Yongliang HAN4, Zhimin YANG1( ), Jiancheng LIU1(
), Jiancheng LIU1( )
)
Received:2021-10-25
Accepted:2022-03-08
Online:2023-01-15
Published:2023-04-17
Contact:
Zhimin YANG,Jiancheng LIU
摘要:
为探究燕麦(Avena sativa L.)在不同盐胁迫处理下根际土壤微生物的群落多样性及变化特征,选取领袖(Souris,S)和爱沃(Everleaf,E)2个燕麦品种为试验材料,分别设置0(Y0)、3(Y1)、6(Y2)和9(Y3) g?kg-1 NaCl胁迫处理。采用高通量测序技术对不同盐胁迫处理下燕麦根际土壤微生物进行测序,分析微生物群落多样性及其与土壤盐胁迫的相关性。结果表明,2个燕麦品种根际土壤细菌群落的多样性在4种盐胁迫处理下存在差异,其中S-Y2的群落丰度最高,S-Y3的多样性最丰富。在不同分类水平上,细菌变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、放线菌纲(Actinobacteria)、根瘤菌目(Rhizobiales)、norank_c_Subgroup_6科和norank_c_Subgroup_6属的相对丰度较高。盐胁迫影响燕麦根际微生物的群落组成,随着盐胁迫程度的增加,其菌落组成的相对丰度发生显著变化。通过对操作分类单元(OTU)丰度的16S功能预测和COG、KEGG代谢通路数据库对比发现,燕麦根际微生物的功能富集于新陈代谢、遗传信息处理、环境信息处理、细胞过程和生物体系统等。由此表明,根际微生物在燕麦生长和响应盐胁迫中起重要作用,为进一步挖掘和利用根际功能微生物奠定了理论基础。
中图分类号:
李峰, 殷丛培, 殷冉, 王凡, 韩永亮, 杨志敏, 刘建成. 燕麦根际土壤细菌多样性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 153-165.
Feng LI, Congpei YIN, Ran YIN, Fan WANG, Yongliang HAN, Zhimin YANG, Jiancheng LIU. Response of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community Diversity to Salt Stress in Oat (Avena sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 153-165.
样本编号 Sample ID | 有效序列数 Seq num | 碱基数 Base num | 序列平均长度 Mean length/bp | 最短序列长度 Min length/bp | 最长序列长度 Max length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-Y0 | 162 093 | 67 727 026 | 417.82 | 252.00 | 506.33 |
| S-Y1 | 160 893 | 67 266 875 | 418.08 | 244.33 | 491.67 |
| S-Y2 | 195 869 | 81 822 543 | 417.74 | 214.00 | 475.33 |
| S-Y3 | 172 634 | 72 184 160 | 418.14 | 247.67 | 486.33 |
| E-Y0 | 155 935 | 65 237 362 | 418.36 | 241.33 | 482.00 |
| E-Y1 | 146 417 | 61 178 315 | 417.80 | 250.67 | 499.00 |
| E-Y2 | 176 735 | 73 796 761 | 417.56 | 257.67 | 476.33 |
| E-Y3 | 176 596 | 73 524 218 | 416.35 | 240.67 | 488.67 |
表1 燕麦根际细菌群落测序质量
Table 1 Sequencing quality of rhizosphere bacteria in oat
样本编号 Sample ID | 有效序列数 Seq num | 碱基数 Base num | 序列平均长度 Mean length/bp | 最短序列长度 Min length/bp | 最长序列长度 Max length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-Y0 | 162 093 | 67 727 026 | 417.82 | 252.00 | 506.33 |
| S-Y1 | 160 893 | 67 266 875 | 418.08 | 244.33 | 491.67 |
| S-Y2 | 195 869 | 81 822 543 | 417.74 | 214.00 | 475.33 |
| S-Y3 | 172 634 | 72 184 160 | 418.14 | 247.67 | 486.33 |
| E-Y0 | 155 935 | 65 237 362 | 418.36 | 241.33 | 482.00 |
| E-Y1 | 146 417 | 61 178 315 | 417.80 | 250.67 | 499.00 |
| E-Y2 | 176 735 | 73 796 761 | 417.56 | 257.67 | 476.33 |
| E-Y3 | 176 596 | 73 524 218 | 416.35 | 240.67 | 488.67 |
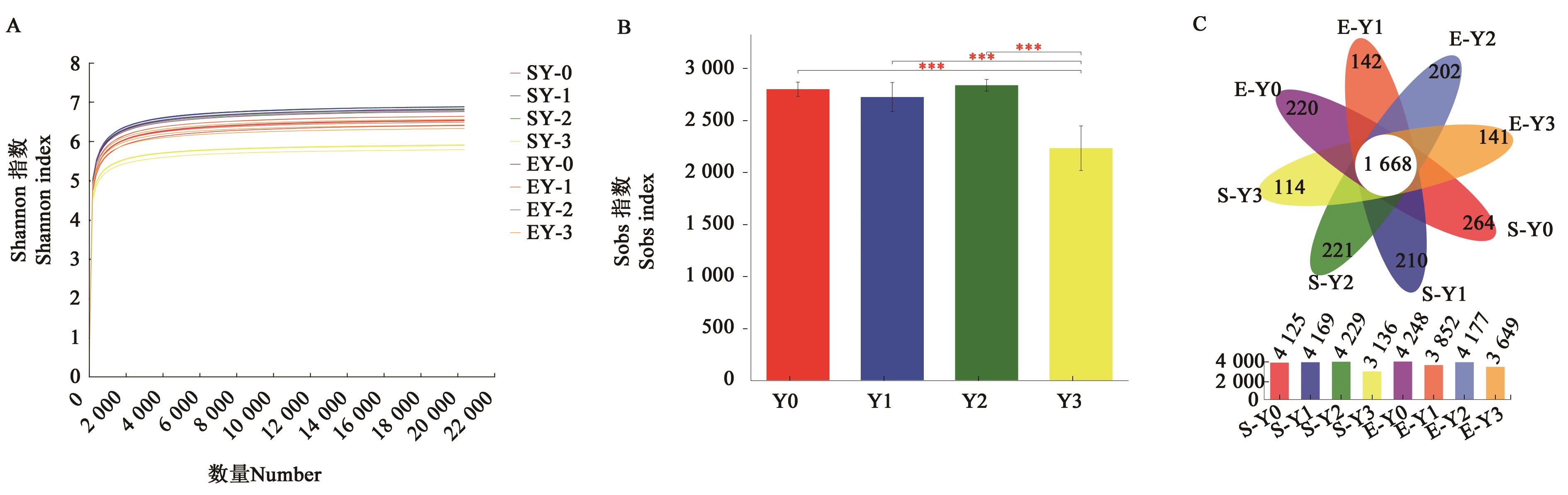
图 1 不同盐胁迫燕麦根际土壤细菌群落组成A:稀释曲线;B:燕麦根际土壤细菌Sobs指数;C:不同样品中 OTUs 数目花瓣图;***表示在P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 1 Bacterial composition of oats rhizosphere soil samples under different salt stressA: Sparse curves; B: Sobs indices of oat rhizosphere soil; C: Flower plot analysis for bacterial species (OTUs) of different samples; *** represents significant differences at P<0.001 level.
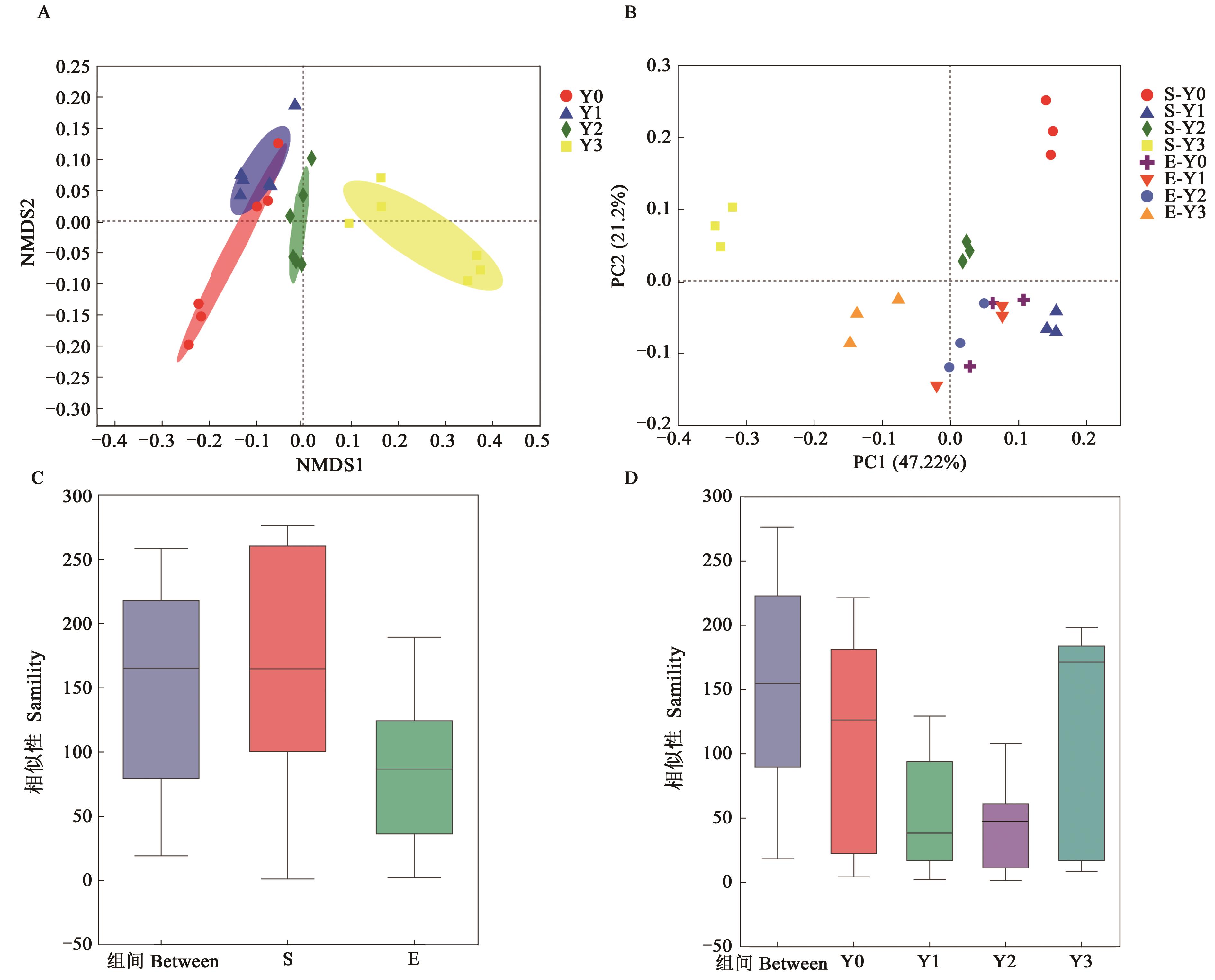
图3 不同盐胁迫下燕麦根际土壤细菌的β多样性A:OTU水平NMDS分析;B:属水平PCoA分析;C:不同品种分组;D:盐胁迫程度分组
Fig. 3 Beta diversity of bacterial in oats rhizosphere soil under different salt stressA: NMDS on OTU level; B: PCoA on genus level; C: Groups of different varieties; D: Groups of different treatment
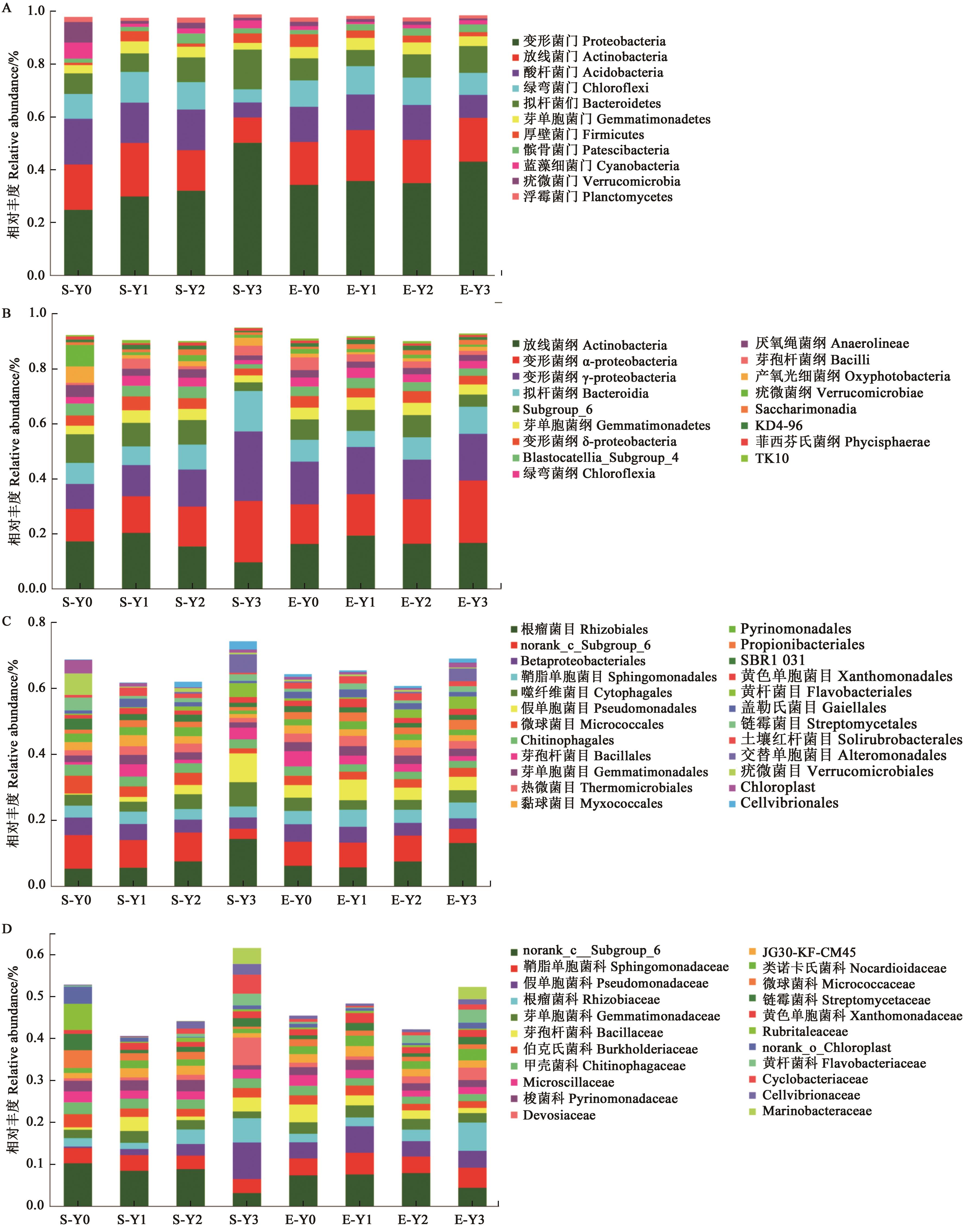
图4 盐胁迫下燕麦根际土壤细菌群落结构A:门水平;B:纲水平;C:目水平;D:科水平
Fig. 4 Bacterial community abundance in oat rhizosphere soil under salt stressA: Phylum level; B: Class level; C: Order level; D: Family level
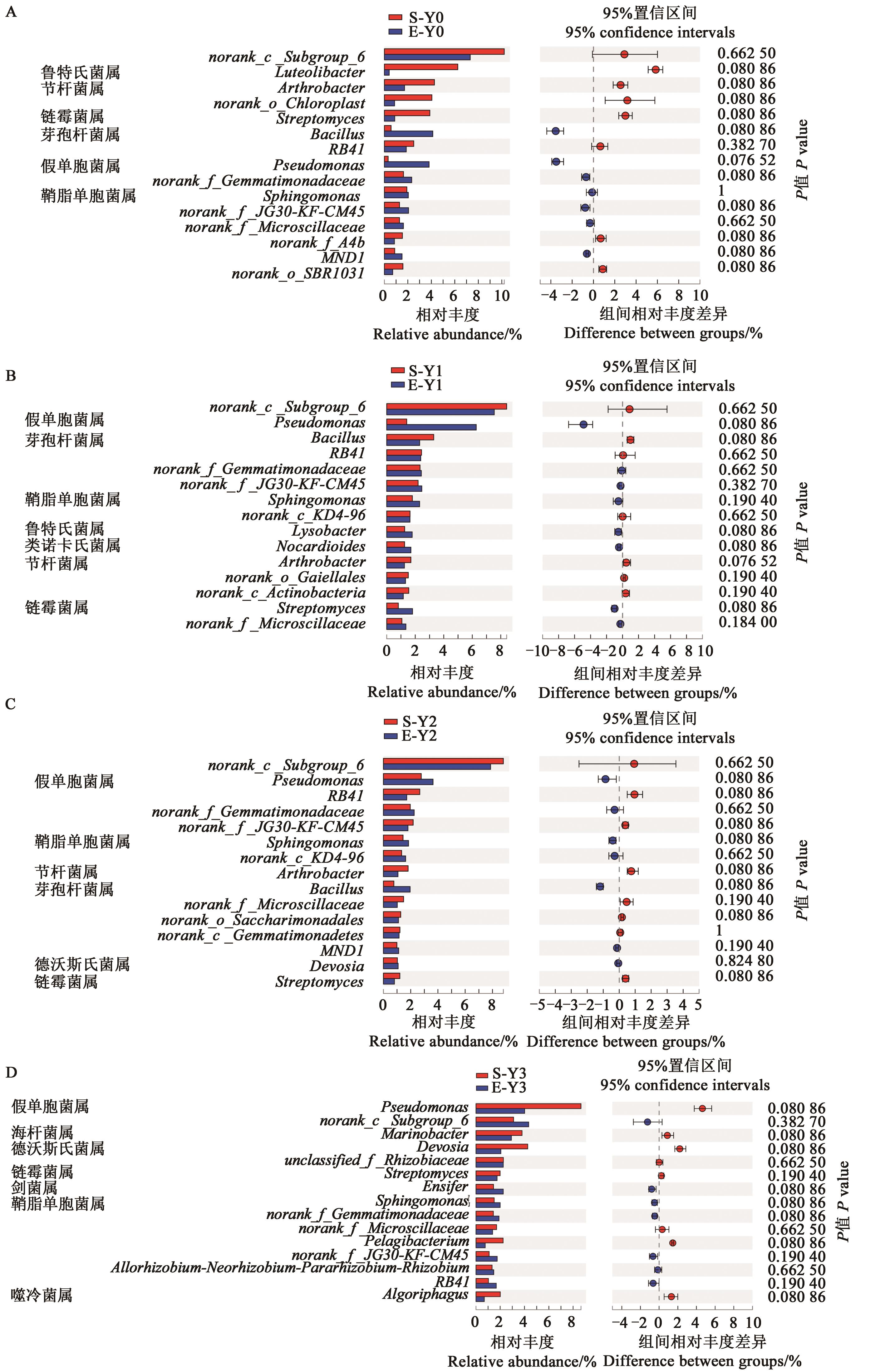
图5 不同盐处理下2个燕麦品种根际细菌属分类水平的相对丰度A:Y0;B:Y1;C:Y2;D:Y3;采用fdr法校正P值(P<0.05)。
Fig. 5 Relative abundance (genera level) of bacteria in rhizosphere soil of two oat varieties under different salt treatmentsA: Y0;B: Y1;C: Y2;D: Y3; corrected P-values are calculated by the fdr false discovery rate approach (P<0.05).
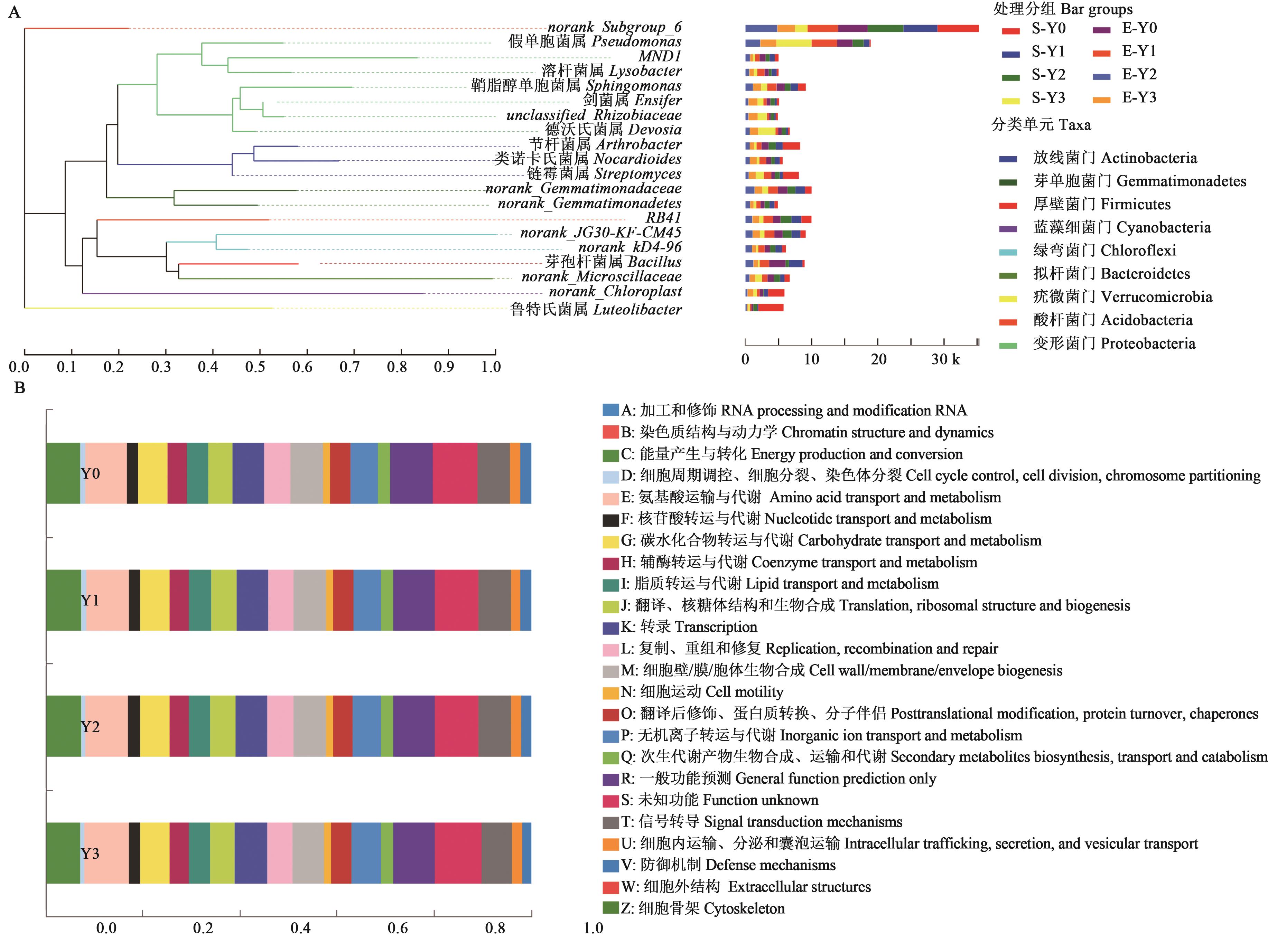
图6 燕麦根际微生物的系统发生进化关系和功能预测A:燕麦根际微生物的系统发生进化关系;B:燕麦根际微生物的一级和二级功能预测
Fig. 6 Evolutionary relationship and function prediction in rhizosphere soil bacterial of oatsA: Evolutionary relationship in rhizosphere soil of oats; B: Function prediction of oat rhizosphere bacterial COG analysis in level 1 and 2

图7 细菌系统发生树及菌群功能预测A:KEGG一级和二级代谢通路;B:KEGG三级代谢通路
Fig. 7 Bacterial phylogenetic tree and prediction of flora functionA: KEGG of level 1,2; B: KEGG of level 3
| 1 | 李建国,濮励杰,朱明,等.土壤盐渍化研究现状及未来研究热点[J].地理学报,2012,67(9):1233-1245. |
| LI J G, PU L J, ZHU M, et al.. The present situation and hot issues in the salt-affected soil research [J]. Acta Geogr. Sin., 2012, 67(9):1233-1245. | |
| 2 | MUNNS R, TESTER M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance [J]. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol., 2008, 59(1):651-681. |
| 3 | MEENA M D, YADAV R K, NARJARY B, et al.. Municipal solid waste (MSW): strategies to improve salt affected soil sustainability: a review [J]. Waste Manag., 2018, 84:38-53. |
| 4 | YANG Y, GUO Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses [J]. New Phytol., 2018, 217:523-39. |
| 5 | 高玉坤,杨溥原,项晓冬,等.不同耐盐高粱品种全生育期对盐胁迫的响应[J].华北农学报,2020,35(6):113-121. |
| GAO Y K, YANG P Y, XIANG X D, et al. Response of different salt tolerant sorghum varieties to salt stress in the whole growth period [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2020, 35(6):113-121. | |
| 6 | YUAN F, LENG B, WANG B. Progress in studying salt secretion from the salt glands in recretohalophytes: how do plants secrete salt? [J/OL]. Front Plant Sci., 2016, 7:977 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 7 | YANG Y, GUO Y. Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2018, 60:796-804. |
| 8 | KAZAN K, LYONS R. The link between flowering time and stress tolerance [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2015, 67:47-60. |
| 9 | LOWRY D B, HALL M C, SALT D E, et al.. Genetic and physiological basis of adaptive salt tolerance divergence between coastal and inland Mimulus guttatus [J]. New Phytol., 2009, 183:776-788. |
| 10 | RODRIGUEZ P A, ROTHBALLER M, CHOWDHURY S P, et al.. Systems biology of plant microbiome interactions [J]. Mol. Plant., 2019, 12:804-821. |
| 11 | PAUL D, LADE H. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria to improve crop growth in saline soils: a review. [J]. Agron. Sustain. Dev., 2014, 34:737-752. |
| 12 | BADRI D V, VIVANCO J M. Regulation and function of root exudates [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2009, 32:666-681. |
| 13 | CASTRILLO G, TEILXEIRA P, PAREDES S, et al.. Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity [J]. Nature, 2017, 543:513-518. |
| 14 | LI H, LA S, ZHANG X, et al.. Salt-induced recruitment of specific root-associated bacterial consortium capable of enhancing plant adaptability to salt stress [J]. ISME J., 2021, 15:2865-2882. |
| 15 | SERRANO R, RODRIGUEZ-NAVARRO A. Ion homeostasis during salt stress in plants [J]. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2001, 13(4):399-404. |
| 16 | 王丹,赵亚光,张凤华.耐盐促生菌筛选、鉴定及对盐胁迫小麦的效应[J].麦类作物学报,2020,40(1):110-117. |
| WANG D, ZHAO Y G, ZHANG F H. Screening and identification of salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria and its promotion effect on wheat seedling under salt stress [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(1):110-117. | |
| 17 | LOUBNA B, FATIMA E K, KHALID O, et al.. Phytobeneficial bacteria improve saline stress tolerance in Vicia faba and modulate microbial interaction network [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 729:139020 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 18 | ZHAO S, LIU J, BANERJEE S, et al.. Biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in saline agricultural soil [J/OL]. Geoderma, 2019, 361(1):114095 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 19 | 陈晓晶,刘景辉,杨彦明,等.盐胁迫对燕麦叶片生理指标和差异蛋白组学的影响[J].作物学报, 2019, 45(9):1431-1439. |
| CHEN X J, LIU J H, YANG Y M, et al.. Effects of salt stress on physiological indexes and differential proteomics of oat leaf [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(9):1431-1439. | |
| 20 | CASTRILLO G, TEILXEIRA P, PAREDES S, et al.. Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity [J]. Nature, 2017, 543:513-518. |
| 21 | MAGOC T, SALZBERG S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies [J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27:2957-2963. |
| 22 | CAPORASO J G, KUCZYNSKI J, STOMBAUGH J, et al.. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data [J]. Nat. Methods, 2010, 7:335-336. |
| 23 | CHAO A, SHEN T J. Nonparametric prediction in species sampling [J]. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Statist., 2004, 9:253-269. |
| 24 | BAI Y, MÜLLER D B, SRINIVAS G, et al.. Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota [J]. Nature, 2015, 528:364-369. |
| 25 | RAAIJMAKERS J M, MAZZOLA M. Soil immune responses [J]. Science, 2016, 352:1392-1393. |
| 26 | FAN K, DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, GUO X, et al.. Biodiversity of key-stone phylotypes determines crop production in a 4-decade fertilization experiment [J]. ISME J., 2020, 15:550-561. |
| 27 | DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, MAESTRE F T, REICH P B, et al.. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems [J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7:10541 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 28 | CHEN Q L, DING J, ZHU Y G, et al.. Soil bacterial taxonomic diversity is critical to maintaining the plant productivity [J/OL]. Environ. Int., 2020, 140:105766 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 29 | GAO Y K, CUI J H, REN G Z, et al.. Changes in the root-associated bacteria of sorghum are driven by the combined effects of salt and sorghum development [J/OL]. Environ. Microbiome, 2021, 16:14 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 30 | YANG Y, SHAO T Y, LONG X H, et al.. Microbiome structure and function in rhizosphere of Jerusalem artichoke grown in saline land [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 724(168):138259 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 31 | 兰汝佳.根际耐盐促生菌的筛选及其对番茄耐盐性的调控研究[D].南京:南京农业大学, 2019. |
| LAN R J. Screening of salt-tolerant rhizosphere-promoting bacteria and its regulation on salt tolerance of tomato [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 32 | 汪焱,张英,苏贝贝,等.高寒区不同地域燕麦根际土壤微生物多样性研究[J].草地学报,2020,28(2):358-366. |
| WANG Y, ZHANG Y, SU B B, et al.. Study on microbial diversity of rhizosphere soil of oat in different areas in alpine region [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2020, 28(2):358-366. | |
| 33 | WAGG C, SCHLAEPPI K, BANERJEE S, et al.. Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning [J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2019, 10:4841 [2021-09-10]. . |
| 34 | VALENZUELA-ENCINAS C, NERIA-GONZÁLEZ I, ALCÁNTARA-HERNÁNDEZ R J, et al.. Changes in the bacterial populations of the highly alkaline saline soil of the former lake Texcoco (Mexico) following flooding [J]. Extremophiles, 2009, 13(4):609-621. |
| 35 | WARD N L, CHALLACOMBE J F, JANSSEN P H, et al.. Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into their lifestyles in soils [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, 75(7):2046-2056. |
| 36 | KRAGELUND C, LEVANTESI C, BORGER A. Identity abundance and ecophysiology of filamentous Chloroflexi species present in activated sludge treatment plants [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2007, 59:671-682. |
| 37 | MALDONADO L A, FENICAL W, JENSEN P R, et al.. Salinispora arenicola gen. nov. sp. nov. and Salinispora tropica sp. nov. obligate marine actinomycetes belonging to the family Micromono sporaceae [J]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol, 2005, 55(5):1759-1766. |
| 38 | VARDHARAJULA, ALI S Z, GROVER M, et al.. Drought-tolerant plant growth promoting Bacillus spp.: effect on growth, osmolytes, and antioxidant status of maize under drought stress [J]. J. Plant Interact., 2011, 6(1):1-14. |
| 39 | RAJKUMAR M, BRUNO L B, BANU J R. Alleviation of environmental stress in plants: the role of beneficial Pseudomonas spp. [J]. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 47(6):372-407. |
| 40 | EGAMBERDIEV D, JABBOROV D, HASHEM A. Pseudomonas induces salinity tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and resistance to Fusarium root rot through the modulation of indole-3-acetic acid [J]. Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2015, 22(6):773-779. |
| 41 | FRĄC M, HANNULA S E, BEŁKA M, et al.. Fungal biodiversity and their role in soil health [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9:707 [2021-09-10]. . |
| [1] | 杨学瑾, 周媛媛, 彭欣怡, 刘建凤, 张爱民, 井爱芹, 赵钢勇, 曹丹丹. 根结线虫危害与健康黄瓜根际土壤微生物群落结构差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 109-118. |
| [2] | 郝艳玲, 闫伟. 混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗形态及生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 69-76. |
| [3] | 杨莉, 于俐, 孙卓, 张桐毓, 张阳, 杨利民. 人参根系分泌物中有机酸及皂苷对人参病原菌与生防菌的化感差异研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 145-155. |
| [4] | 王莉莉, 殷丛培, 李峰, 杨志敏, 刘芳明, 林柏松, 刘晓静, 刘海军, 孙靖, 单东东, 崔江慧, 张振清. 马铃薯根际土壤细菌群落结构及其对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 58-69. |
| [5] | 李洁, 林莹, 徐美玉, 王飞, 徐凌川. 泰山白首乌根际土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 70-81. |
| [6] | 王鑫, 张玉霞, 陈卫东, 林聪颖, 候文慧, 斯日古楞, 丛百明. 追施氮肥对不同饲用燕麦品种产量及光合荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 170-179. |
| [7] | 戴良香, 张冠初, 丁红, 徐扬, 张智猛. 有机肥和钙肥对盐碱土花生根际细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 189-201. |
| [8] | 田翁由, 刘昊, 甘超林, 伍柳芬, 李爱, 杨丽芳, 高英. 盐胁迫下樱桃砧木的光合响应和光谱特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 77-83. |
| [9] | 刘昱茜, 卢发光, 顾立峰, 任桢, 施雨, 卢海潼, 徐振然, 周桂生, 王小山, 张网定, 任志强, 朱广龙, . 沿海滩涂盐碱地燕麦高产栽培技术及相关生理基础研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 160-172. |
| [10] | 张胜珍, 马艳芝. 氯化钙对盐胁迫下荆芥种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 65-71. |
| [11] | 夏洪泽, 黄文植, 张琳琳, 张晓涵, 崔占鸿, 刘书杰. 不同分级指数燕麦干草-苜蓿干草组合对牦牛瘤胃体外发酵的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 199-201. |
| [12] | 李星, 胡杨, 马媛, 贾守义, 李钢铁. 细穗柽柳对3种单盐胁迫的生理响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 52-60. |
| [13] | 杨华1,李江2,张维1,周正富1,燕永亮1,郭嘉3,刘相国3,郝东云3,林敏1,柯秀彬1*. 施氏假单胞菌在玉米根际的固氮效率和促生效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 76-84. |
| [14] | 顾惠敏1,陈波浪1*,孙锦2. 菌根化育苗对盐胁迫下加工番茄生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 166-177. |
| [15] | 张志东1,顾美英1,唐琦勇1,楚敏1,朱静1,孙建1,杨蓉1,徐万里2*. 盐爪爪根际耐盐促生菌的筛选及穴栽验证[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 186-192. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号