




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 126-137.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0866
• 智慧农业 农机装备 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-10-12
接受日期:2022-12-29
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-07
通讯作者:
容新民
作者简介:边凤霞 E-mail:bianfengxia123@163.com;
基金资助:
Fengxia BIAN1( ), Kaige LIU2, Xinmin RONG1(
), Kaige LIU2, Xinmin RONG1( )
)
Received:2022-10-12
Accepted:2022-12-29
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-07
Contact:
Xinmin RONG
摘要:
葡萄霜霉病是葡萄上的主要病害之一,该病从葡萄苗期到果实成熟期都可发生,多雨年份常造成毁灭性损失。为了准确预测葡萄霜霉病的发生,最大限度地降低霜霉病对葡萄的危害,基于2020年葡萄生长期间气象数据和病害发生数据,结合4种机器学习算法(二项逻辑斯蒂、支持向量机、决策树、K最近邻)构建了葡萄霜霉病发生预测模型,并用2021年数据进行验证。结果表明,决策树模型在病害发生预测模型构建中的评价指标最优,其准确率达94%,预测发生的精准率、召回率、F1分值分别为91%、90%、91%。经验证,决策树模型对葡萄霜霉病发生的预测精度及性能均优于其他3个模型。因此,可利用此模型进一步开发葡萄霜霉病预警系统,为生产上葡萄霜霉病的防治提供技术支持和决策指导。
中图分类号:
边凤霞, 刘凯歌, 容新民. 基于机器学习构建葡萄霜霉病预测模型及验证[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 126-137.
Fengxia BIAN, Kaige LIU, Xinmin RONG. Development and Verification of Prediction Model for Grape Downy Mildew Based on Machine Learning[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 126-137.
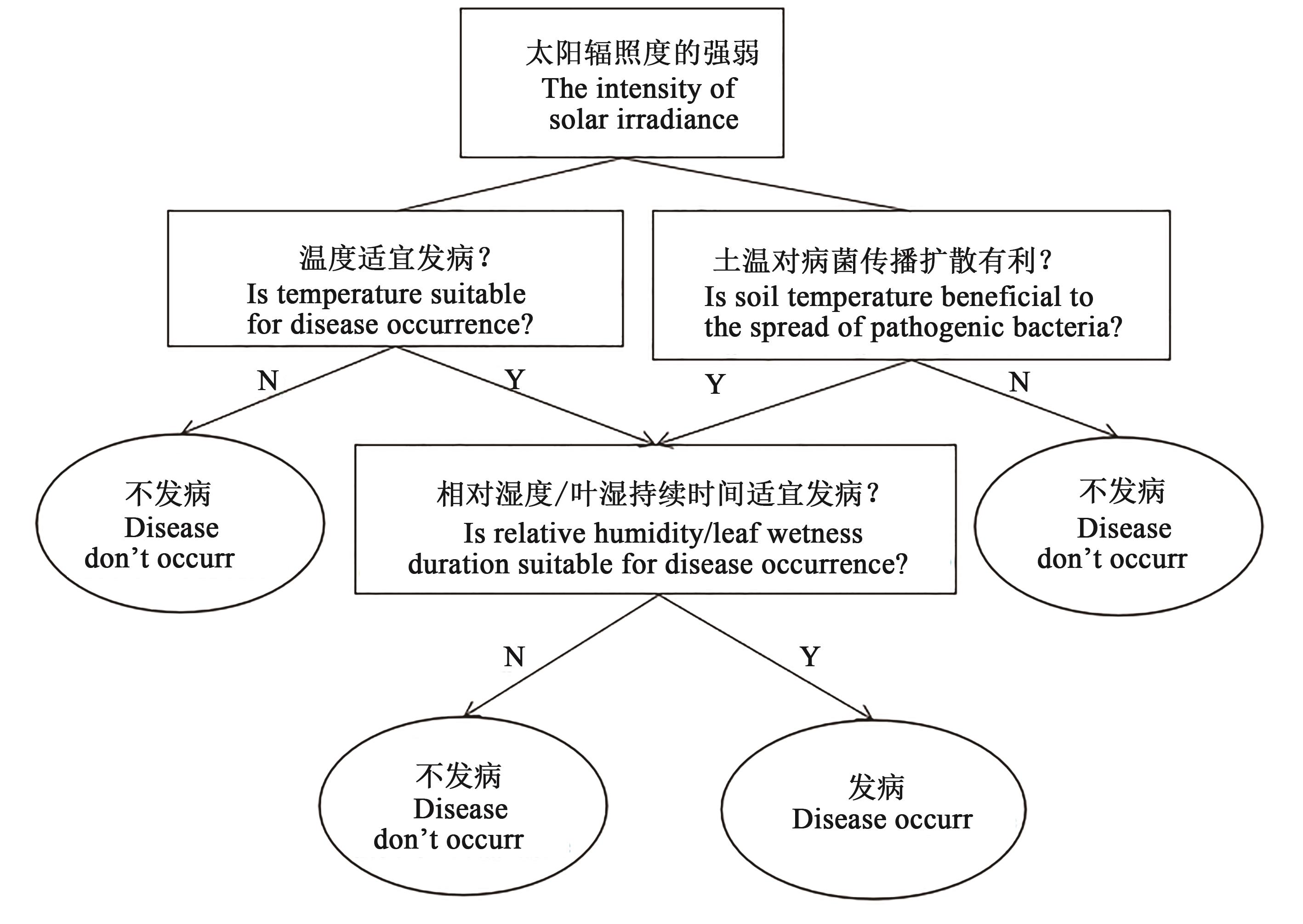
图2 Decision Tree模型原理注:示意图仅表示模型处理问题时的决策过程,不代表以单一特征的决策结果作为预测结果。
Fig. 2 Decision tree model principleNote: The schematic diagram only shows the decision-making process of the model when dealing with the problem, and does not mean that the decision result of a single feature is used as the prediction result.
指标 Index | 样本数Number of samples | |
|---|---|---|
| 预测不发病 Prediction label: 0 | 预测发病Prediction label: 1 | |
实际不发病 True label: 0 | 真阴性 True negative: TN | 假阳性 False positive: FP |
实际发病 True label: 1 | 假阴性 False negative:FN | 真阳性 True positive:TP |
表1 混淆矩阵列联表
Table 1 Confusion matrix contingency table
指标 Index | 样本数Number of samples | |
|---|---|---|
| 预测不发病 Prediction label: 0 | 预测发病Prediction label: 1 | |
实际不发病 True label: 0 | 真阴性 True negative: TN | 假阳性 False positive: FP |
实际发病 True label: 1 | 假阴性 False negative:FN | 真阳性 True positive:TP |
k值 k value | 一致性结果 Consistent result |
|---|---|
| 0≤k<0.2 | 极低Slight |
| 0.2≤k<0.4 | 一般Fair |
| 0.4≤k<0.6 | 中等Moderate |
| 0.6≤k<0.8 | 高度Substantial |
| 0.8≤k<1.0 | 几乎完全Almost perfect |
表2 k值一致性划分标准
Table 2 The k value consistency classification criteria
k值 k value | 一致性结果 Consistent result |
|---|---|
| 0≤k<0.2 | 极低Slight |
| 0.2≤k<0.4 | 一般Fair |
| 0.4≤k<0.6 | 中等Moderate |
| 0.6≤k<0.8 | 高度Substantial |
| 0.8≤k<1.0 | 几乎完全Almost perfect |
模型 Model | 类别标签 Classe label | 分类结果 Classification result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
准确率 Accuracy/% | 精准率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | F1分值 F1-score/% | ||
| BLR | 0 | 86 | 87 | 93 | 90 |
| 1 | 83 | 70 | 76 | ||
| SVM | 0 | 86 | 86 | 94 | 90 |
| 1 | 85 | 69 | 76 | ||
| DT | 0 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 95 |
| 1 | 91 | 90 | 91 | ||
| KNN | 0 | 93 | 96 | 94 | 95 |
| 1 | 88 | 91 | 89 | ||
表3 不同预测模型的分类结果
Table 3 Classification results of different prediction models
模型 Model | 类别标签 Classe label | 分类结果 Classification result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
准确率 Accuracy/% | 精准率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | F1分值 F1-score/% | ||
| BLR | 0 | 86 | 87 | 93 | 90 |
| 1 | 83 | 70 | 76 | ||
| SVM | 0 | 86 | 86 | 94 | 90 |
| 1 | 85 | 69 | 76 | ||
| DT | 0 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 95 |
| 1 | 91 | 90 | 91 | ||
| KNN | 0 | 93 | 96 | 94 | 95 |
| 1 | 88 | 91 | 89 | ||
模型 Model | 类别标签 Classe label | 分类结果 Classification result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
准确率 Accuracy/% | 精准率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | F1分值 F1-score/% | ||
| BLR | 0 | 73 | 73 | 87 | 80 |
| 1 | 74 | 53 | 62 | ||
| SVM | 0 | 75 | 76 | 86 | 81 |
| 1 | 72 | 59 | 65 | ||
| DT | 0 | 90 | 92 | 91 | 92 |
| 1 | 87 | 88 | 88 | ||
| KNN | 0 | 84 | 86 | 87 | 86 |
| 1 | 80 | 79 | 80 | ||
表4 不同预测模型分类验证结果
Table 4 Classification validation results of different prediction models
模型 Model | 类别标签 Classe label | 分类结果 Classification result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
准确率 Accuracy/% | 精准率 Precision/% | 召回率 Recall/% | F1分值 F1-score/% | ||
| BLR | 0 | 73 | 73 | 87 | 80 |
| 1 | 74 | 53 | 62 | ||
| SVM | 0 | 75 | 76 | 86 | 81 |
| 1 | 72 | 59 | 65 | ||
| DT | 0 | 90 | 92 | 91 | 92 |
| 1 | 87 | 88 | 88 | ||
| KNN | 0 | 84 | 86 | 87 | 86 |
| 1 | 80 | 79 | 80 | ||
| 1 | 芦屹,努尔孜亚·亚力麦麦提,付文君,等.新疆伊犁河谷地区葡萄霜霉病流行与气候条件的关系[J].新疆农业科学,2020,57(10):1855-1862. |
| LU Y, Yalimaimaiti Nuerziya, FU W J, et al.. Research the relationship between epidemic of grape downy mildew and climatic conditions in Ili Valley of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2020, 57(10): 1855-1862. | |
| 2 | 吉丽丽.石河子地区葡萄霜霉病菌孢子囊时空扩散动态及品种抗病性研究[D].石河子:石河子大学,2011. |
| JI L L. The dynamics of sporangium of Plasmopara viticola and resistance of different grape varieties in Shihezi region [D]. Shihezi: Shihezi Univ., 2011. | |
| 3 | 张玮,燕继晔,刘梅,等.葡萄霜霉病流行与预测研究进展[J].中国果树,2020,44(3):11-15. |
| ZHANG W, YAN J Y, LIU M, et al.. Research progress on prediction and epidemic of grapevine downy mildew [J]. China Fruits, 2020, 44(3):11-15. | |
| 4 | GILLES T. Forecasting Downy Mildew Diseases in:Advances in Downy Mildew Research—Volume Ⅱ [M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2004:35-67. |
| 5 | ORLANDINI S, CAPPUGI A. Calibration of agrometeorological model for the simulation of grapevine downy mildew in several viticultural areas of Europe [C]// Proceedins of Fifth European Conference on Application of Meteorology. Budapest Hungary, 2001:1-7. |
| 6 | 张雪雪,王斌,田洋洋,等.作物病虫害预测机理与方法研究进展[J].中国农业科技导报,2019,21(5):110-120. |
| ZHANG X X, WANG B, TIAN Y Y, et al.. Research progress on forecasting mechanism and methodology for crop disease and insect pest [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(5):110-120. | |
| 7 | GESSLER C, PERTOT I, PERAZZOLLI M. Plasmopara viticola:a review of knowledge on downy mildew of grapevine and effective disease management [J]. Phytopathol. Mediterr., 2011, 50(1):3-44. |
| 8 | THIND T S, ARORA J K, MOHAN C, et al.. Epidemiology of Powdery Mildew, Downy Mildew and Anthracnose Diseases of Grapevine [M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2004:621-638. |
| 9 | FRANCESCA S, SIMONA G, FRANCESCO NICOLA T, et al.. Downy mildew (Plasmopara viticola) epidemics on grapevine under climate change [J]. Global Change Biol., 2006, 12(7):1299-1307. |
| 10 | ROSSI V, CAFFI T, GIOSUE S, et al.. A mechanistic model simulating primary infections of downy mildew in grapevine [J]. Ecol. Modell., 2008, 212(3-4):480-491. |
| 11 | 白玉娇,马贵龙.葡萄霜霉病流行时间动态模型及防治指标[J].吉林农业大学学报,2020,42(3):286-292. |
| BAI Y J, MA G L. Dynamic model of epidemic period and control index of grape downy mildew [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2020, 42(3):286-292. | |
| 12 | 于舒怡,傅俊范,刘长远,等.沈阳地区葡萄霜霉病流行时间动态及其气象影响因子分析[J].植物病理学报,2016,46(4):529-535. |
| YU S Y, FU J F, LIU C Y, et al.. Epidemic temporal dynamic of grape downy mildew and its meteorological influencing factors in Shenyang, Liaoning [J]. Acta Phytopathol. Sin., 2016, 46(4):529-535. | |
| 13 | BLAISE P, GESSLER C. Development of a forecast model of grape downy mildew on a microcomputer [C]// Proceedings of International Symposium on Computer Modelling in Fruit Research and Orchard Management 276, 1989:63-70. |
| 14 | WILKS D S, SHEN K W. Threshold relative humidity duration forecasts for plant disease prediction [J]. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol., 1991, 30(4):463-477. |
| 15 | 华来庆,熊林平,孟虹,等.AR-EGARCH模型在疾病指数时间序列建模中的应用研究[J].中国卫生统计,2006,23(6):482-485. |
| HUA L Q, XIONG L P, MENG H, et al.. Application of AR-EGARCH model in establishing methods of disease index time series models [J]. Chin. J. Health Stat., 2006, 23(6):482-485. | |
| 16 | POUZESHIMIYAB B, FANI S R. Epidemiology and aerobiology of Pseudoperonospora cubensis in northwest Iran [J]. Ital. J. Agrometeorol., 2020, 13(2):109-116. |
| 17 | NEUFELD K N, KEINATH A P, OJIAMBO P S. Evaluation of a model for predicting the infection risk of squash and cantaloupe by Pseudoperonospora cubensis [J]. Plant Dis., 2018, 102(5):855-862. |
| 18 | LIU Y, LI D, WAN S, et al.. A long short-term memory-based model for greenhouse climate prediction [J]. Int. J. Intell. Syst., 2022, 37(1):135-151. |
| 19 | 张善文,王振,王祖良.结合知识图谱与双向长短时记忆网络的小麦条锈病预测[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(12):172-178. |
| ZHANG S W, WANG Z, WANG Z L. Prediction of wheat stripe rust disease by combining knowledge graph and bidirectional long short term memory network [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2020, 36(12):172-178. | |
| 20 | LIAKOS K G, BUSATO P, MOSHOU D, et al.. Machine learning in agriculture: a review [J]. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res., 2018, 18(8):2674. |
| 21 | MEZEI I, LUKIC M, BERBAKOV L, et al.. Grapevine downy mildew warning system based on NB-IoT and energy harvesting technology [J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(3):356. |
| 22 | VOLPI I, GUIDOTTI D, MAMMINI M, et al.. Predicting symptoms of downy mildew, powdery mildew, and gray mold diseases of grapevine through machine learning [J]. Ital. J. Agrometeorol., 2021, 14(2):57-69. |
| 23 | CHEN M, BRUN F, RAYNAL M, et al.. Forecasting severe grape downy mildew attacks using machine learning [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(3):e0230254 [2022-09-10]. . |
| 24 | 吴宁.基于灰色关联分析和优化SVM的葡萄霜霉病短期预测[D].上海:上海海洋大学,2020. |
| WU N. Short-term prediction of grape downy mildew based on grey correlation analysis and optimized SVM [J]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2020. | |
| 25 | MENESATTI P, ANTONUCCI F, COSTA C, et al.. Multivariate forecasting model to optimize management of grape downy mildew control [J]. Vitis, 2013, 52(3):141-148. |
| 26 | FIRANJ SREMAC A, LALIC B, MARCIC M, et al.. Toward a weather-based forecasting system for fire blight and downy mildew [J/OL]. Atmosphere, 2018, 9(12):484 [2022-09-10]. . |
| 27 | 边凤霞,王富霞,刘静,等.北疆葡萄设施延晚栽培病虫害防治技术[J].农业科技通讯,2019,49(9):344-345, 354. |
| 28 | 王济川,郭志刚. Logistic回归模型——方法与应用[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2001:10-17. |
| 29 | JOSE C, GOYAL P, AGGRWAL P, et al.. Local deep kernel learning for efficient non-linear svm prediction [C]// Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2013:486-494. |
| 30 | SONG Y Y, YING L U. Decision tree methods:applications for classification and prediction [J]. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry, 2015, 27(2):130. |
| 31 | GUO G, WANG H, BELL D, et al.. KNN model-based approach in classification [C]// Proceedings of OTM Confederated International Conferences on the move to Meaningful Internet Systems. Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer, 2003:986-996. |
| 32 | LIU K, ZHANG C, YANG X, et al.. Development of an occurrence prediction model for cucumber downy mildew in solar greenhouses based on Long Short-Term Memory neural network [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(2):442 [2022-09-10]. . |
| 33 | 宋旺.基于SVM的葡萄霜霉病病害发生预测研究[J].中小企业管理与科技,2018,11(5):104-105. |
| 34 | 秦华.基于自适应神经网络的葡萄病害发生预测研究[D].保定:河北农业大学,2009. |
| QIN H. Research on the prediction of grape disease based on adaptive neural networks [J]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| 35 | 于舒怡,李柏宏,王辉,等.基于田间空气中病菌孢子囊浓度的葡萄霜霉病病情估计模型研究[J].果树学报,2021,38(10):1767-1777. |
| YU S Y, LI B H, WANG H, et al.. Study on estimation model for grape downy mildew prediction based on airborne sporangium concentration of Plasmopara viticola in field [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2021, 38(10):1767-1777. | |
| 36 | RODRIGUEZ-RAJO F J, JATO V, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ M, et al.. The use of aerobiological methods for forecasting Botrytis spore concentrations in a vineyard [J]. Grana, 2010, 49(01):56-65. |
| 37 | CAFFI T, ROSSI V, LEGLER S E, et al.. A mechanistic model simulating ascosporic infections by Erysiphe necator, the powdery mildew fungus of grapevine [J]. Plant Pathol., 2011, 60(3):522-531. |
| 38 | GONZALEZ-DOMINGUEZ E, CAFFI T, CILIBERTI N, et al.. A mechanistic model of Botrytis cinerea on grapevines that includes weather, vine growth stage, and the main infection pathways [J/OL]. PloS ONE, 2015, 10(10):e0140444 [2022-09-10]. . |
| 39 | HILL G N, BERESFORD R M, EVANS K J. Automated analysis of aggregated datasets to identify climatic predictors of Botrytis bunch rot in wine grapes [J]. Phytopathology, 2019, 109(1):84-95. |
| [1] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [2] | 王爽, 侯毅兴, 冯琳骄, 卢倩倩, 周龙. 干旱胁迫对鲜食葡萄叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [3] | 周宇, 李佳玉, 王乐, 贾晓爽, 高思琦, 王潇, 焦健. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变体诱导筛选及特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 147-157. |
| [4] | 贾毅男, 张光弟, 张浩宇, 许昌, 张昆明, 王江龙, 侯晓健. 根区施用硅肥对‘玫瑰香’葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 215-223. |
| [5] | 张娜, 闫亚茹, 武运, 张宇宏, 张伟. 信号肽优化提高葡萄糖氧化酶在毕赤酵母中的表达量[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 211-219. |
| [6] | 吴楠, 杨君, 张艳, 孙正文, 张冬梅, 李丽花, 吴金华, 马峙英, 王省芬. 过表达棉花葡萄糖醛酸激酶基因GbGlcAK促进拟南芥细胞伸长[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 36-46. |
| [7] | 刘阳阳, 潘越, 王世伟, 虎海防. 不同山葡萄品种光响应模型拟合及综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 104-114. |
| [8] | 朱燕芳, 白耀栋, 王元元, 李玉斌, 马麒龙, 郝燕, 赵明新. 遮阴处理对酿酒葡萄‘西拉’果实皱缩的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 54-62. |
| [9] | 吴婕, 宫江宁. 大孔树脂纯化甜茶多酚及其对 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性和DPPH·抗氧化性的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 113-119. |
| [10] | 阿依图拉·拜各吐木尔, 李洁, 陈存坤, 刘慧, 李相阳, 林少华. 葡萄柚籽提取物和聚乙烯包装对香椿贮藏品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 116-123. |
| [11] | 孙艳,韩斌,袁军伟,刘长江,李敏敏,尹勇刚,贾楠,郭紫娟,赵胜建*. 不同抗寒性葡萄品种根系形态结构及生理性状差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 47-57. |
| [12] | 孔德谦1,何振嘉2*,刘全祖3,吴永杰1. 施肥对贺兰山东麓滴灌条件下‘赤霞珠’葡萄产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 148-155. |
| [13] | 王东1,曹源倍2,吉遥芳3,傅渝亮3*. 不同滴灌量对红寺堡区酿酒葡萄生长和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 154-161. |
| [14] | 尹勇刚,袁军伟,刘长江,韩斌,李敏敏,孙艳,贾楠,郭紫娟,赵胜建*. NaCl胁迫对葡萄砧木光合特性与叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 49-55. |
| [15] | 张艳丽1,2,任柳3,张宇宏1*,张伟1. 棉铃虫葡萄糖氧化酶HaGOX在毕赤酵母中的重组表达和性质研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 56-63. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号