




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (4): 144-152.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.1058
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
季梦婷1( ), 陈长江2, 罗流河1, 林志坚1, 詹梦琳1, 杨丙烨1, 胡方平1, 蔡学清1(
), 陈长江2, 罗流河1, 林志坚1, 詹梦琳1, 杨丙烨1, 胡方平1, 蔡学清1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-05
接受日期:2023-02-24
出版日期:2024-04-15
发布日期:2024-04-23
通讯作者:
蔡学清
作者简介:季梦婷 E-mail:1249169841@qq.com;
基金资助:
Mengting JI1( ), Changjiang CHEN2, Liuhe LUO1, Zhijian LIN1, Menglin ZHAN1, Bingye YANG1, Fangping HU1, Xueqing CAI1(
), Changjiang CHEN2, Liuhe LUO1, Zhijian LIN1, Menglin ZHAN1, Bingye YANG1, Fangping HU1, Xueqing CAI1( )
)
Received:2022-12-05
Accepted:2023-02-24
Online:2024-04-15
Published:2024-04-23
Contact:
Xueqing CAI
摘要:
为明确近年来在福建省宁德市蕉城区石后乡猕猴桃苗圃新发生的一种细菌性病害病的原菌,并进一步探讨其发生流行规律,采用稀释分离法对采集病株进行病原菌的分离和纯化,对获得的细菌菌株进行致病性测定,通过柯赫氏法则验证、常规的细菌生物学特性、生理生化反应、Biolog 鉴定、16S rDNA和内切葡聚糖酶基因(egl)序列分析对病原菌进行分类鉴定。结果表明,从发病猕猴桃病株上获得9株细菌菌株,将其接种在健康的猕猴桃植株后,其发病症状与田间自然发病症状基本一致,且从接种后病株的茎秆和根部又重新分离到与原菌落形态相同的细菌。柯赫氏法则证实这9株细菌菌株为猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病的致病菌。这9株菌株在NA培养基上的菌落形态一致,均呈不规则型、扁平,并逐渐向四周扩散,不产生粘稠状物质,不会使培养基变色;在TTC培养基上,菌落颜色呈暗红色,产生可扩散至培养基中的红褐色色素,其流动性较差;在YDC培养基上,菌落呈乳白色。经综合分析,这9株细菌菌株均被鉴定为假茄科雷尔氏菌(Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum),生化型Ⅲ和演化型Ⅰ(亚洲组),序列变种14。这是首例青枯菌侵染猕猴桃的报道。以上研究结果为制定猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病精准有效的综合防控提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
季梦婷, 陈长江, 罗流河, 林志坚, 詹梦琳, 杨丙烨, 胡方平, 蔡学清. 福建猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病的病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 144-152.
Mengting JI, Changjiang CHEN, Liuhe LUO, Zhijian LIN, Menglin ZHAN, Bingye YANG, Fangping HU, Xueqing CAI. Pathogen Identification of Kiwi Bacterial Wilt in Fujian[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 144-152.
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 扩增片段分类归属 Classify remarks | 大小 Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nmult21:1F | CGTTGATGAGGCGCGCAATTT | 演化型Ⅰ PhylotypeⅠ | 144[ |
| Nmult21:2F | AAGTTATGGACGGTGGAAGTC | 演化型Ⅱ Phylotype Ⅱ | 372 |
| Nmult23:AF | ATTACSAGAGCAATCGAAAGATT | 演化型Ⅲ Phylotype Ⅲ | 91 |
| Nmult22:InF | ATTGCCAAGACGAGAGAAGTA | 演化型Ⅳ Phylotype Ⅳ | 213 |
| Nmult22:RR | TCGCTTGACCCTATAACGAGTA | — | |
| 759F | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC | 青枯菌种特异性 Ralstonia specific-primer | 280[ |
| 760R | GTCGCCGTCAGCAATGCGGAATCG | ||
| 27F | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC | 16S rDNA | 1 500[ |
| 1492R | GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT | ||
| Endo-F | ATGCATGCCGCTGGTCGCCGC | egl基因 egl gene | 750[ |
| Endo-R | GCGTTGCCCGGCACGAACACC |
表1 供试引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers for test
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 扩增片段分类归属 Classify remarks | 大小 Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nmult21:1F | CGTTGATGAGGCGCGCAATTT | 演化型Ⅰ PhylotypeⅠ | 144[ |
| Nmult21:2F | AAGTTATGGACGGTGGAAGTC | 演化型Ⅱ Phylotype Ⅱ | 372 |
| Nmult23:AF | ATTACSAGAGCAATCGAAAGATT | 演化型Ⅲ Phylotype Ⅲ | 91 |
| Nmult22:InF | ATTGCCAAGACGAGAGAAGTA | 演化型Ⅳ Phylotype Ⅳ | 213 |
| Nmult22:RR | TCGCTTGACCCTATAACGAGTA | — | |
| 759F | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC | 青枯菌种特异性 Ralstonia specific-primer | 280[ |
| 760R | GTCGCCGTCAGCAATGCGGAATCG | ||
| 27F | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC | 16S rDNA | 1 500[ |
| 1492R | GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT | ||
| Endo-F | ATGCATGCCGCTGGTCGCCGC | egl基因 egl gene | 750[ |
| Endo-R | GCGTTGCCCGGCACGAACACC |
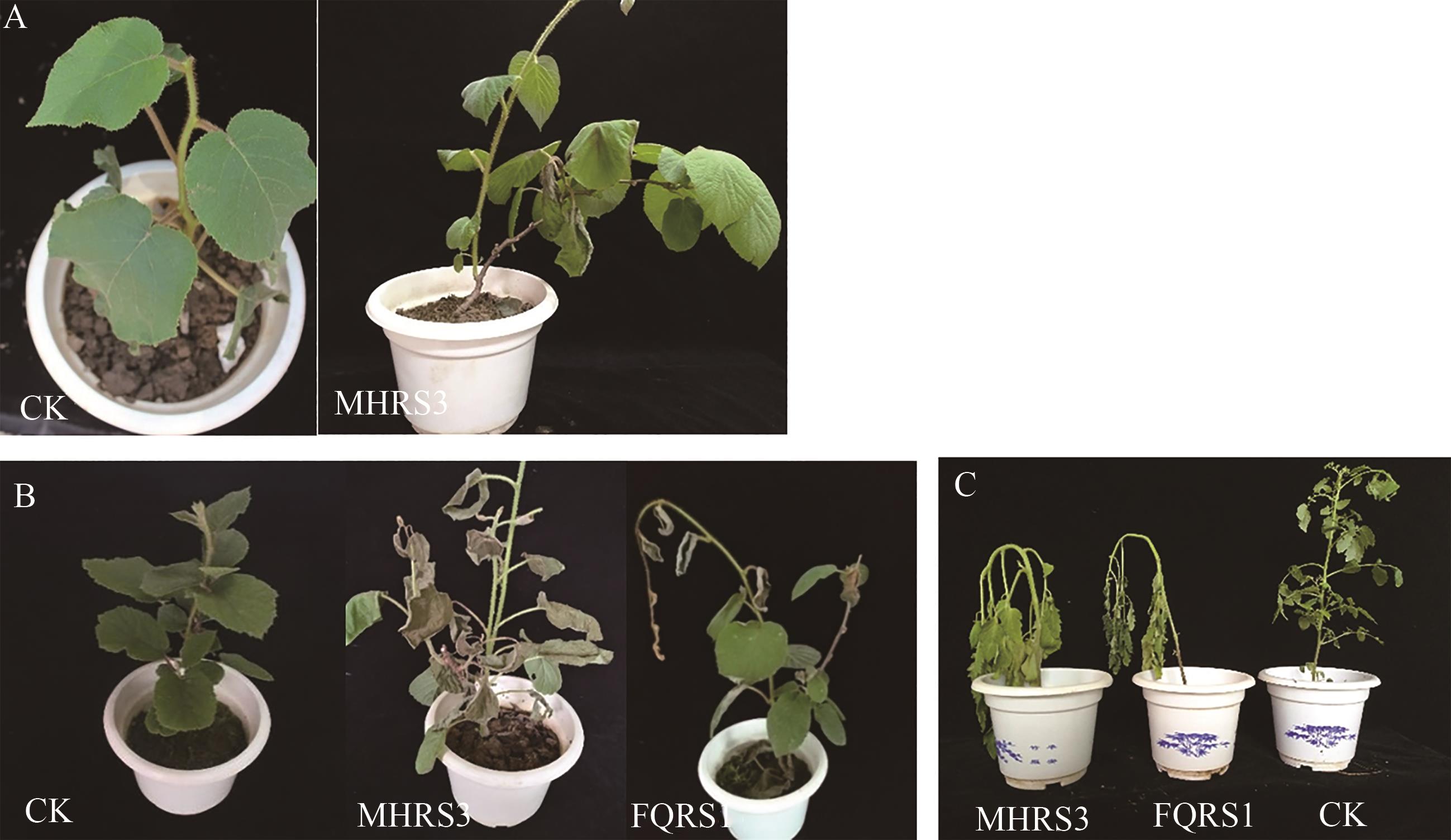

图2 菌株的致病性测定(以MHRS3为例)A:针刺接种猕猴桃苗?7 d;B:伤根接种猕猴桃苗?14 d;C:伤根接种番茄苗?14 d
Fig. 2 Pathogenicity test of strains (MHRS3 as an example)A: 7 d after inoculation kiwi seedlings with stabbing; B: 14 d after inoculation kiwi seedlings through wounded root; C: 14 d after inoculation tomato seedlings through wounded root
测定项目 Measuring item | 供试菌株 Test strain | GSRS1 | FQRS1 | 测定项目 Measuring item | 供试菌株 Test strain | GSRS1 | FQRS1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
淀粉水解 Starch hydrolysis | 弱Weak - | + + | 弱Weak - | 硝酸盐 还原 Nitrate reduction | 封管 Sealing tube | +/产气 +/Gas production | +/产气 +/Gas production | +/产气 +/Gas production |
明胶液化 Gelatin liquefaction | - | + | + | 开管 Open tube | + | + | + | |
果胶酶水解 Hydrolysis of pectinase | + | + | + | 耐盐性 Salt tolerance | 1%NaCl | + | + | + |
果聚糖 Fructan | - | + | + | 1.5%NaCl | + | + | + | |
H2S试验 H2S production | + | - | - | 2%NaCl | - | - | - | |
精氨酸水解 Arginine hydrolysis | - | - | - | 生长温度 Growth temperature | 35 ℃ | + | + | + |
氧化酶试验 Oxidase test | + | - | - | 37 ℃ | + | + | + | |
PHB的积累 PHB accumulate | + | + | + | 40 ℃ | + | + | + | |
水解七叶灵 Esculin hydrolysis | - | - | - | 石蕊牛乳 Litmus milk | + | + | + | |
KB 产荧光 Produce fluorescence on KB medium | - | - | - | 吲哚产物 Indole production | - | - | - | |
YDC培养基 YDC medium | 白色 White | 白色White | 白色 White | 3% KOH | + | + | + | |
表2 供试菌株的生理生化反应结果
Table 2 Results of physiological and biochemical characteristics of the test strains
测定项目 Measuring item | 供试菌株 Test strain | GSRS1 | FQRS1 | 测定项目 Measuring item | 供试菌株 Test strain | GSRS1 | FQRS1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
淀粉水解 Starch hydrolysis | 弱Weak - | + + | 弱Weak - | 硝酸盐 还原 Nitrate reduction | 封管 Sealing tube | +/产气 +/Gas production | +/产气 +/Gas production | +/产气 +/Gas production |
明胶液化 Gelatin liquefaction | - | + | + | 开管 Open tube | + | + | + | |
果胶酶水解 Hydrolysis of pectinase | + | + | + | 耐盐性 Salt tolerance | 1%NaCl | + | + | + |
果聚糖 Fructan | - | + | + | 1.5%NaCl | + | + | + | |
H2S试验 H2S production | + | - | - | 2%NaCl | - | - | - | |
精氨酸水解 Arginine hydrolysis | - | - | - | 生长温度 Growth temperature | 35 ℃ | + | + | + |
氧化酶试验 Oxidase test | + | - | - | 37 ℃ | + | + | + | |
PHB的积累 PHB accumulate | + | + | + | 40 ℃ | + | + | + | |
水解七叶灵 Esculin hydrolysis | - | - | - | 石蕊牛乳 Litmus milk | + | + | + | |
KB 产荧光 Produce fluorescence on KB medium | - | - | - | 吲哚产物 Indole production | - | - | - | |
YDC培养基 YDC medium | 白色 White | 白色White | 白色 White | 3% KOH | + | + | + | |
供试菌株 Test strain | 最佳匹配种类 Best match species | 可能性值 Probable value | 相似性值 Similarity value | 位距值 Bit distance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHRS3 | R. pseudosolanacearum | 0.960 | 0.697 | 3.834 |
| MHRS8 | R. pseudosolanacearum | 0.697 | 0.697 | 4.352 |
表3 供试菌株的 Biolog 测定结果
Table 3 Biolog test results of the strains
供试菌株 Test strain | 最佳匹配种类 Best match species | 可能性值 Probable value | 相似性值 Similarity value | 位距值 Bit distance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHRS3 | R. pseudosolanacearum | 0.960 | 0.697 | 3.834 |
| MHRS8 | R. pseudosolanacearum | 0.697 | 0.697 | 4.352 |
供试菌株 Test strain | 乳糖 Lactose | 麦芽糖Maltose | 纤维二糖Cellobiose | 山梨醇Sorbitol | 甜醇Dulcitol | 甘露醇Mannitol | 生化型Biotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病菌 MHRS~MHRS9 | + | + | + | + | + | + | Ⅲ |
| 番茄青枯菌FQRS1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | Ⅲ |
| 甘薯青枯菌GSRS1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | Ⅲ |
表4 供试菌株的生化型测定
Table 4 Biotypes detection of the tested strains
供试菌株 Test strain | 乳糖 Lactose | 麦芽糖Maltose | 纤维二糖Cellobiose | 山梨醇Sorbitol | 甜醇Dulcitol | 甘露醇Mannitol | 生化型Biotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病菌 MHRS~MHRS9 | + | + | + | + | + | + | Ⅲ |
| 番茄青枯菌FQRS1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | Ⅲ |
| 甘薯青枯菌GSRS1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | Ⅲ |
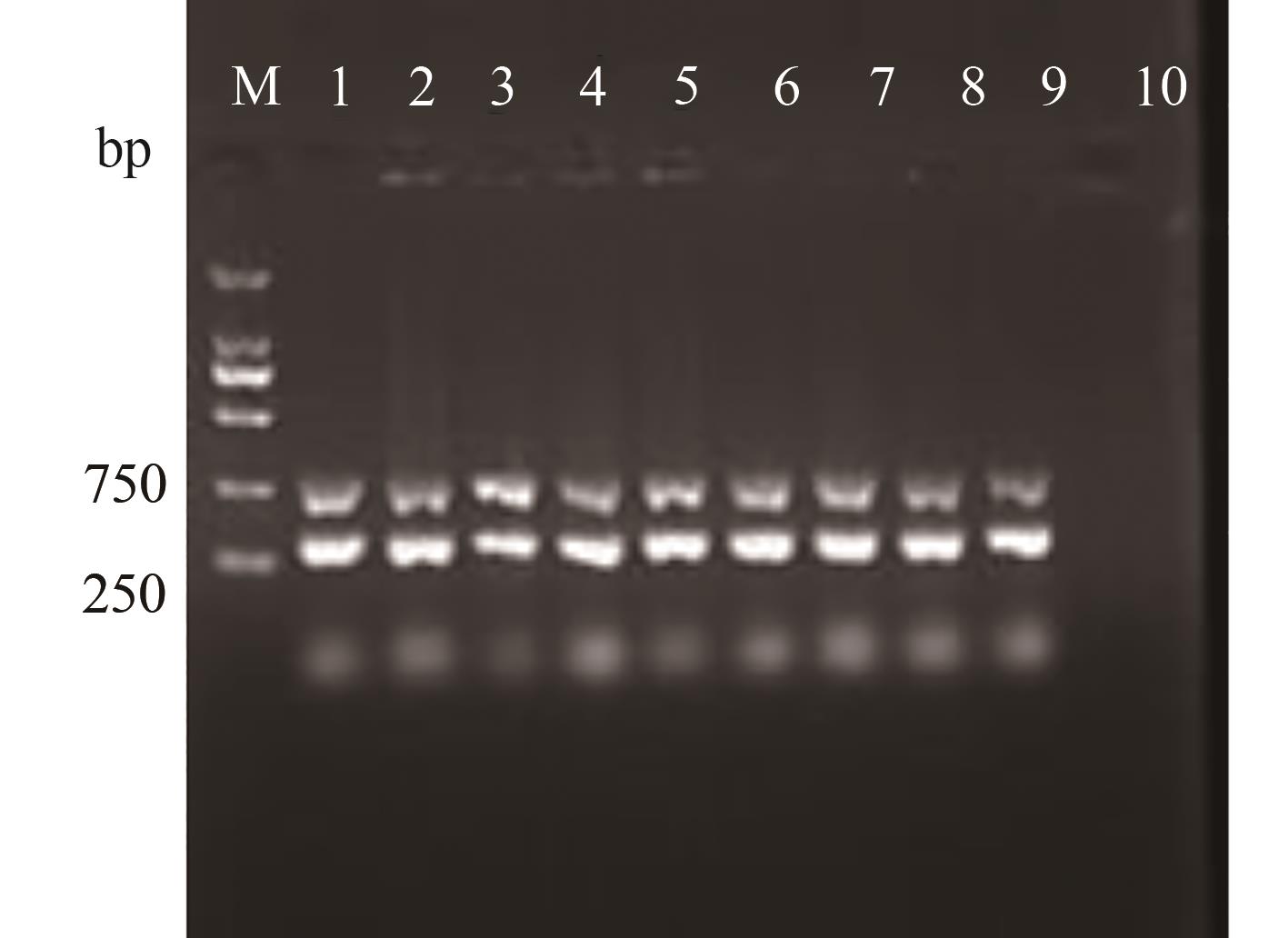
图5 供试菌株的演化型PCR验证注:M—DL 2000 marker;1~8—供试菌株MHRS1~MHRS8;9—FQRS1;10—CK。
Fig. 5 Evolutional type of test strains by PCR verificationNote: M—DL 2000 marker; 1~8—Test strains MHRS1~MHRS8; 9—FQRS1; 10—CK.
| 1 | 肖蓉,石浩,卜范文,等.猕猴桃病害防治研究进展[J].湖南农业科学,2021(8):116-120. |
| XIAO R, SHI H, BU F W, et al.. Research progress of kiwifruit disease control [J]. Hunan Agric. Sci., 2021(8):116-120. | |
| 2 | 王然,周丹,罗静,等.猕猴桃病毒病研究进展[J].果树学报,2017,34(8):1043-1050. |
| WANG R, ZHOU D, LUO J, et al.. Progress report on viruses of kiwifruit [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2017, 34(8):1043-1050. | |
| 3 | 杨莉莉.不同肥料对猕猴桃产量、品质及果园养分的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2016. |
| YANG L L. Effect of different fertilizer application on kiwifruit yield, quality and the orchard nutrient [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2016. | |
| 4 | 庄启国,李明章,王丽华,等.冬施矿物油对红阳猕猴桃桑白蚧防效及药害[J].农药,2011,50(2):146-149. |
| ZHUANG Q G, LI M Z, WANG L H, et al.. Control effect and phytotoxicity investigations of mineral oil to Hongyang kiwifruit in winter for the white peach scale [J]. Agrochemicals, 2011, 50(2):146-149. | |
| 5 | 佘小漫,何自福.作物青枯病研究进展[J].广东农业科学,2020,47(12):82-89. |
| SHE X M, HE Z F. Advances in studies on crop bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2020, 47(12):82-89. | |
| 6 | JIANG G F, WEI Z, XU J, et al.. Bacterial wilt in China: history, current status, and future perspectives [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8:1549 [2022-11-02]. . |
| 7 | 王国芬,李超萍,杨腊英,等.星油藤青枯病病原菌鉴定[J].植物病理学报,2019,49(5):602-611. |
| WANG G F, LI C P, YANG L Y, et al.. Pathogen identification of Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) bacterial wilt [J]. Acta Phytopathol. Sin., 2019, 49(5):602-611. | |
| 8 | LEE I, KIM Y S, KIM J W, et al.. Genetic and pathogenic characterization of bacterial wilt pathogen, Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum (Ralstonia solanacearum Phylotype I), on roses in Korea [J]. Plant Pathol. J., 2020, 36(5):440-449. |
| 9 | HAYWARD A C. Biology and epidemiology of bacterial wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum [J]. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 1991, 29(1):65-87. |
| 10 | 方中达.植病研究方法[M].北京:中国农业出版社,1998:179-181. |
| FANG Z D. Plant Disease Research Methodology [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1998:179-181. | |
| 11 | 东秀珠,蔡妙英.常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:353-398. |
| DONG X Z, CAI M Y. Manual for System Identification of Common Bacteria [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001:353-398. | |
| 12 | 赵延昌. 植物病原细菌鉴定实验指导[M].第三版.中国农业科学技术出版社, 2011:113-121. |
| ZHAO Y C. Laboratory Guide for Identification of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria [M]. 3th ed n. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2011:113-121. | |
| 13 | OPINA N, TAVNER F, HOLLWAY G, et al.. A novel method for development of species and strain-specific DNA probes and PCR primers for identifying Burkholderia solanacearum (formerly Pseudomonas solanacearum) [J]. Asia-Pac. J. Mol. Bio. Biotech., 1997, 5:19-30 |
| 14 | HUANG Q, YAN X R, WANG J F. Improved biovar test for Ralstonia solanacearum [J]. J. Microbiol. Meth., 2012, 88(2):271-274. |
| 15 | FEGAN M, PRIOR P. How complex is the “Ralstonia solanacearum species complex” [M]// Bacterial Wilt Disease and the Ralstonia Solanacearum Species Complex. ASP Press, 2005:449-461. |
| 16 | LANE D J. 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing. In: StackebrandtE, Goodfellow M, editors. Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics [M]. New York: Wiley, 1991:115-175. |
| 17 | FEGAN M, PRIOR P. Diverse members of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex cause bacterial wilts of banana [J]. Australas. Plant Pathol., 2006, 35, 93-101. |
| 18 | HAYWARD A C. Characteristics of Pseudomonas solanacearum [J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 1964, 27 (2):265-277. |
| 19 | SAFNI I, CLEENWERCK I, DE V P, et al.. Polyphasic taxonomic revision of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex: proposal to emend the descriptions of Ralstonia solanacearum and Ralstonia syzygii and reclassify current R. syzygii strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. syzygii subsp.nov., R. solanacearum phylotype Ⅳ strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis subsp. nov., banana blood disease bacterium strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. celebesensis subsp. nov. and R. solanacearum phylotype Ⅰ and Ⅲ strains as Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum sp. nov.[J]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2014, 64(9):3087-3103. |
| 20 | 陈媛媛. 广西植物青枯病菌的演化型和序列变种及葫芦科植物青枯病菌的特性[D].南宁:广西大学, 2018. |
| CHEN Y Y. The phylotype and sequevar of Ralstonia solanacearum and characteristics of bacterial wilt pathogen isolated from Cucurbitaceae plants in Guangxi [D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2018. | |
| 21 | XU J, PAN Z C, PRIOR P, et al.. Genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum strains from China [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2009, 125(4):641-653. |
| 22 | SHE X M, YU L, LAN G B, et al.. Identification and genetic characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex isolates from Cucurbita maxima in China [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8:1794 [2017-10-01]. . |
| 23 | 吴水良,林可竟,张一帆,等.福建仙草细菌性枯萎病的病原菌鉴定[J].亚热带农业研究,2022,18(4):267-273. |
| WU S L, LIN K J, ZHANG Y F, et al.. Identification of an etiological bacterium causing grass jelly wilt in Fujian [J]. Subtrop. Agric. Res., 2022, 18(4):267-273. | |
| 24 | 康彦平,雷永,万丽云,等.我国长江流域和南方地区花生青枯菌遗传多样性分析[J].植物保护学报,2019,46(2): 291-297. |
| KANG Y P, LEI Y, WAN L Y, et al.. Study on genetic diversity of bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum in peanut in Yangtze River Valley and southern China [J]. J. Plant Protect., 2019, 46(2):291-297. | |
| 25 | 娄德钊,武华周,卢芙萍,等.海南桑树青枯病病原菌鉴定及其分子鉴定[J].热带作物学报,2021,42(11):3261-3268. |
| LOU D Z, WU H Z, LU F P, et al.. Pathogen and molecular identification of mubbery (Morus alba L.) bacterial wilt in Hainan [J]. Chin. J. Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(11):3261-3268. | |
| 26 | 潘哲超,徐进,顾钢,等.福建及贵州等地烟草青枯菌系统发育分析[J].植物保护,2012,38(1):18-23, 43. |
| PAN Z C, XU J, GU G, et al.. Phylogeny of tobacco Ralstonia solanacearium strains from Fujian and Guizhou provinces [J]. Pant Protect., 2012, 38(1):18-23, 43. | |
| 27 | LIU Y, WU D S, LIU Q P, et al.. The sequevar distribution of Ralstonia solanacearum in tobacco growing zones of China is structured by elevation [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2017, 147,541-551. |
| 28 | CHEN Y J, LIN Y S, TSENG K J, et al.. Vine cuttings as possible initial inoculum sources of Ralstonia solanacearum race 1 biovar 4 on vegetable sweet potato in fields [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2014, 140: 83-95. |
| [1] | 李鹏声, 黄清泰, 范咏梅, 王萌, 杨叶. 海南省东方市甜瓜细菌性果斑病病原鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 117-123. |
| [2] | 施玉萍, 刘一贤, 李国伟, 唐轶, 戴利铭, 李岚岚, 蔡志英. 橡胶树季风性落叶病病原菌的分离鉴定及其防治药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 114-122. |
| [3] | 张娜娜§, 李双民§, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 王俊凤, 杨文杰, 霍佳欢, 兰淑慧, 孙伟明, 齐慧霞. 板栗红粉病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 145-152. |
| [4] | 温晓蕾1,2,齐慧霞1*,孙伟明1,刘一健1,冯丽娜1,孟童瑶3,韩志玲1,曹佳1,王俊凤1. 北苍术枝枯病病原菌(Fusarium equiseti)的鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 115-121. |
| [5] | 亢菊侠1,蔡鹏2,吴雅茹2. 不同品种猕猴桃园节肢动物群落特征及主要类群生态位分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3): 152-159. |
| [6] | 黄伟伟1,燕怡帆1,杨迪1,张乃群1*,杜戈2,李书林2. 猕猴桃良种‘杨氏金红50号’离体再生技术[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(10): 163-169. |
| [7] | 曾俊棋,岳万福*. 454焦磷酸测序技术对不同猪种肠道菌群差异的分析(英文)[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(6): 44-49. |
| [8] | 宋培勇,郑亚强,李斌,肖仲久. 赤水河流域土壤放线菌及其拮抗活性研究[J]. , 2013, 15(1): 136-143. |
| [9] | 王友娟,李荣峰,李华,李强,徐祥. 辽宁地区养殖淡水鱼感染嗜水气单胞菌的流行病学调查[J]. , 2012, 14(4): 128-134. |
| [10] | 艾日登才次克,于洁,杜晓华,李莉,王炜宏,孙天松,张和平. 6S rDNA-RFLP法快速鉴定蒙古国传统乳制品中的乳酸菌[J]. , 2009, 11(2): 63-68. |
| [11] | 李海红,宛煜嵩,金芜军,王英典,林敏. 草甘膦高抗菌株的分离、鉴定及生理生化特性研究[J]. , 2009, 11(2): 69-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号