




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 123-131.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0015
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
栗佳宁1,2( ), 李爱霞3, 霍佳欢1,2, 冯丽娜1,2, 郭思柔1,2, 王建华1,2, 温晓蕾1,2, 孙伟明1,2, 齐慧霞1,2(
), 李爱霞3, 霍佳欢1,2, 冯丽娜1,2, 郭思柔1,2, 王建华1,2, 温晓蕾1,2, 孙伟明1,2, 齐慧霞1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-04
接受日期:2023-03-07
出版日期:2023-04-01
发布日期:2023-06-26
通讯作者:
齐慧霞
作者简介:栗佳宁 E-mail:1305081894@qq.com;
基金资助:
Jianing LI1,2( ), Aixia LI3, Jiahuan HUO1,2, Lina FENG1,2, Sirou GUO1,2, Jianhua WANG1,2, Xiaolei WEN1,2, Weiming SUN1,2, Huixia QI1,2(
), Aixia LI3, Jiahuan HUO1,2, Lina FENG1,2, Sirou GUO1,2, Jianhua WANG1,2, Xiaolei WEN1,2, Weiming SUN1,2, Huixia QI1,2( )
)
Received:2023-01-04
Accepted:2023-03-07
Online:2023-04-01
Published:2023-06-26
Contact:
Huixia QI
摘要:
为明确不同板栗品种对链格孢菌(Alternaria alternata)的抗性并筛选出抑制该病原菌的有效药剂,采用离体菌丝块有伤接种法对14个板栗品种进行抗病性鉴定,通过发病率、病斑平均直径法和系统聚类分析法对不同品种进行抗性分级,并利用菌丝生长速率法测定7种杀菌剂对A. alternata的毒力。结果表明,接种后9 d,板栗品种‘燕山短枝’‘大板红’的发病率和病斑扩展直径分别为44.45%、51.11%和0.13、0.20 cm;‘遵玉’为100%和0.90 cm。供试品种中以‘燕山短枝’‘大板红’对A. alternata的抗性相对较强;‘遵玉’对A. alternata的抗性相对较弱。药剂筛选结果表明,咯菌腈对A. alternata的抑制效果最佳,抑制率达到93.75%,EC50为69.94 mg?L-1。以上结果为板栗在种植中筛选优质抗病品种及开展田间药效试验提供参考。
中图分类号:
栗佳宁, 李爱霞, 霍佳欢, 冯丽娜, 郭思柔, 王建华, 温晓蕾, 孙伟明, 齐慧霞. 几种板栗品种对链格孢菌的室内抗性比较及防治药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 123-131.
Jianing LI, Aixia LI, Jiahuan HUO, Lina FENG, Sirou GUO, Jianhua WANG, Xiaolei WEN, Weiming SUN, Huixia QI. Comparison of Resistance of Several Chestnut Varieties to Alternaria alternata and Fungicide Screening in Laboratory[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 123-131.
品种 Variety | 发病率Disease incidence/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
接种3 d Inoculation 3 d | 接种4 d Inoculation 4 d | 接种5 d Inoculation 5 d | 接种6 d Inoculation 6 d | 接种7 d Inoculation 7 d | 接种8 d Inoculation 8 d | 接种9 d Inoculation 9 d | |
遵玉 Zunyu | 4.45±2.22 dD | 42.22±2.22 aAB | 71.11±2.22 aA | 88.89±2.22 aA | 95.55±2.22 aA | 97.78±2.22 aA | 100.00±0.00 aA |
燕宝 Yanbao | 26.67±0.00 aA | 33.33±0.00 bC | 48.89±2.22 cdeBCD | 48.89±2.22 dBC | 62.22±2.22 cCD | 75.55±2.22 bBC | 82.22±2.22 bB |
老品种 Laopinzhong | 0.00±0.00 dD | 24.45±2.22 cD | 44.45±2.22 eD | 57.78±2.22 bB | 75.55±2.22 bB | 77.78±2.22 bB | 80.00±0.00 bcBC |
紫珀 Zipo | 0.00±0.00 dD | 35.55±2.22 bBC | 55.55±2.22 bB | 57.78±2.22 bB | 66.67±0.00 cC | 68.69±2.22 cdCD | 77.78±2.22 bcdBCD |
燕奎 Yankui | 4.45±2.22 dD | 44.45±2.22 aA | 55.55±2.22 bB | 55.55±2.22 bcB | 66.67±0.00 cC | 75.55±2.22 bBC | 75.55±2.22 cdeBCD |
东陵明珠 Donglingmingzhu | 0.00±0.00 dD | 24.45±2.22 cD | 53.33±0.00 bcBC | 57.78±2.22 bB | 66.67±0.00 cC | 66.67±0.00 cdCD | 75.55±2.22 cdeBCD |
燕紫 Yanzi | 17.78±2.22 bB | 24.45±2.22 cD | 33.33±0.00 fE | 46.67±0.00 dC | 48.89±2.22 eEF | 66.67±0.00 cdCD | 73.33±0.00 deCD |
小薄皮 Xiaobopi | 0.00±0.00 dD | 15.55±2.22 deEF | 46.67±0.00 deCD | 48.89±2.22 dBC | 62.22±2.22 cCD | 68.89±2.22 cCD | 73.33±0.00 deCD |
燕秋 Yanqiu | 13.33±0.00 cBC | 15.55±2.22 deEF | 26.67±0.00 gEF | 33.33±0.00 efDE | 37.78±2.22 fgGH | 57.78±2.22 eE | 71.11±2.22 eD |
燕山早丰 Yanshanzaofeng | 11.11±2.22 cC | 11.11±2.22 efFG | 31.11±2.22 fgE | 31.11±2.22 fDE | 48.89±2.22 eEF | 57.78±2.22 eE | 71.11±2.22 eD |
| 燕丽Yanli | 0.00±0.00 dD | 42.22±2.22 aAB | 51.11±2.22 bcdBCD | 51.11±2.22 cdBC | 55.55±2.22 dDE | 62.22±2.22 deDE | 62.22±2.22 fE |
燕龙 Yanlong | 0.00±0.00 dD | 13.33±0.00 eEFG | 31.11±2.22 fgE | 37.78±2.22 eD | 42.22±2.22 fFG | 48.89±2.22 fF | 53.33±0.00 gF |
大板红 Dabanhong | 11.11±2.22 cC | 20.00±0.00 cdDE | 28.89±2.22 fgE | 31.11±2.22 fDE | 40.00±0.00 fGH | 48.89±2.22 fF | 51.11±2.22 gFG |
燕山短枝 Yanshanduanzhi | 0.00±0.00 dD | 6.67±0.00 fG | 20.00±0.00 hF | 28.89±2.22 fE | 33.33±0.00 gH | 42.22±2.22 gF | 44.45±2.22 hG |
表1 不同板栗品种接种A. alternaria的发病率
Table 1 Incidence of A. alternaria inoculated in different Chinese chestnut varieties
品种 Variety | 发病率Disease incidence/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
接种3 d Inoculation 3 d | 接种4 d Inoculation 4 d | 接种5 d Inoculation 5 d | 接种6 d Inoculation 6 d | 接种7 d Inoculation 7 d | 接种8 d Inoculation 8 d | 接种9 d Inoculation 9 d | |
遵玉 Zunyu | 4.45±2.22 dD | 42.22±2.22 aAB | 71.11±2.22 aA | 88.89±2.22 aA | 95.55±2.22 aA | 97.78±2.22 aA | 100.00±0.00 aA |
燕宝 Yanbao | 26.67±0.00 aA | 33.33±0.00 bC | 48.89±2.22 cdeBCD | 48.89±2.22 dBC | 62.22±2.22 cCD | 75.55±2.22 bBC | 82.22±2.22 bB |
老品种 Laopinzhong | 0.00±0.00 dD | 24.45±2.22 cD | 44.45±2.22 eD | 57.78±2.22 bB | 75.55±2.22 bB | 77.78±2.22 bB | 80.00±0.00 bcBC |
紫珀 Zipo | 0.00±0.00 dD | 35.55±2.22 bBC | 55.55±2.22 bB | 57.78±2.22 bB | 66.67±0.00 cC | 68.69±2.22 cdCD | 77.78±2.22 bcdBCD |
燕奎 Yankui | 4.45±2.22 dD | 44.45±2.22 aA | 55.55±2.22 bB | 55.55±2.22 bcB | 66.67±0.00 cC | 75.55±2.22 bBC | 75.55±2.22 cdeBCD |
东陵明珠 Donglingmingzhu | 0.00±0.00 dD | 24.45±2.22 cD | 53.33±0.00 bcBC | 57.78±2.22 bB | 66.67±0.00 cC | 66.67±0.00 cdCD | 75.55±2.22 cdeBCD |
燕紫 Yanzi | 17.78±2.22 bB | 24.45±2.22 cD | 33.33±0.00 fE | 46.67±0.00 dC | 48.89±2.22 eEF | 66.67±0.00 cdCD | 73.33±0.00 deCD |
小薄皮 Xiaobopi | 0.00±0.00 dD | 15.55±2.22 deEF | 46.67±0.00 deCD | 48.89±2.22 dBC | 62.22±2.22 cCD | 68.89±2.22 cCD | 73.33±0.00 deCD |
燕秋 Yanqiu | 13.33±0.00 cBC | 15.55±2.22 deEF | 26.67±0.00 gEF | 33.33±0.00 efDE | 37.78±2.22 fgGH | 57.78±2.22 eE | 71.11±2.22 eD |
燕山早丰 Yanshanzaofeng | 11.11±2.22 cC | 11.11±2.22 efFG | 31.11±2.22 fgE | 31.11±2.22 fDE | 48.89±2.22 eEF | 57.78±2.22 eE | 71.11±2.22 eD |
| 燕丽Yanli | 0.00±0.00 dD | 42.22±2.22 aAB | 51.11±2.22 bcdBCD | 51.11±2.22 cdBC | 55.55±2.22 dDE | 62.22±2.22 deDE | 62.22±2.22 fE |
燕龙 Yanlong | 0.00±0.00 dD | 13.33±0.00 eEFG | 31.11±2.22 fgE | 37.78±2.22 eD | 42.22±2.22 fFG | 48.89±2.22 fF | 53.33±0.00 gF |
大板红 Dabanhong | 11.11±2.22 cC | 20.00±0.00 cdDE | 28.89±2.22 fgE | 31.11±2.22 fDE | 40.00±0.00 fGH | 48.89±2.22 fF | 51.11±2.22 gFG |
燕山短枝 Yanshanduanzhi | 0.00±0.00 dD | 6.67±0.00 fG | 20.00±0.00 hF | 28.89±2.22 fE | 33.33±0.00 gH | 42.22±2.22 gF | 44.45±2.22 hG |
| 品种Variety | 病斑扩展直径Lesion expansion diameter/cm | AD法抗性等级AD resistance grade |
|---|---|---|
| 遵玉 Zunyu | 0.90±0.02 aA | 4 |
| 东陵明珠 Donglingmingzhu | 0.55±0.03 bB | 3 |
| 燕紫 Yanzi | 0.51±0.01 bBC | 3 |
| 燕宝 Yanbao | 0.50±0.00 bcBC | 3 |
| 紫珀 Zipo | 0.46±0.01 cdCD | 3 |
| 燕秋 Yanqiu | 0.45±0.03 dCD | 3 |
| 小薄皮 Xiaobopi | 0.42±0.00 deDE | 3 |
| 燕山早丰 Yanshanzaofeng | 0.37±0.01 efEF | 2 |
| 燕龙 Yanlong | 0.35±0.03 fgFG | 2 |
| 老品种 Laopinzhong | 0.34±0.01 fgFG | 2 |
| 燕奎 Yankui | 0.30±0.01 gG | 2 |
| 燕丽 Yanli | 0.30±0.01 gG | 2 |
| 大板红 Dabanhong | 0.20±0.01 hH | 1 |
| 燕山短枝 Yanshanduanzhi | 0.13±0.01 iI | 1 |
表2 不同板栗品种对A. alternata的抗性
Table 2 Resistances of different Chinese chestnut varieties to A. alternata
| 品种Variety | 病斑扩展直径Lesion expansion diameter/cm | AD法抗性等级AD resistance grade |
|---|---|---|
| 遵玉 Zunyu | 0.90±0.02 aA | 4 |
| 东陵明珠 Donglingmingzhu | 0.55±0.03 bB | 3 |
| 燕紫 Yanzi | 0.51±0.01 bBC | 3 |
| 燕宝 Yanbao | 0.50±0.00 bcBC | 3 |
| 紫珀 Zipo | 0.46±0.01 cdCD | 3 |
| 燕秋 Yanqiu | 0.45±0.03 dCD | 3 |
| 小薄皮 Xiaobopi | 0.42±0.00 deDE | 3 |
| 燕山早丰 Yanshanzaofeng | 0.37±0.01 efEF | 2 |
| 燕龙 Yanlong | 0.35±0.03 fgFG | 2 |
| 老品种 Laopinzhong | 0.34±0.01 fgFG | 2 |
| 燕奎 Yankui | 0.30±0.01 gG | 2 |
| 燕丽 Yanli | 0.30±0.01 gG | 2 |
| 大板红 Dabanhong | 0.20±0.01 hH | 1 |
| 燕山短枝 Yanshanduanzhi | 0.13±0.01 iI | 1 |
| 杀菌剂 Fungicide | 菌落直径Colony diameter/cm | 抑制率Inhibition ratio/% |
|---|---|---|
| 咯菌腈 Fludioxonil | 0.40±0.00 hH | 93.75±0.00 aA |
| 吡噻菌胺 Pyrithiamide | 1.07±0.03 gG | 83.33±0.52 bB |
| 苯醚甲环唑 Difenoconazole | 1.50±0.00 fF | 76.56±0.00 cC |
| 丙硫菌唑 Prothioconazole | 1.70±0.00 eE | 73.44±0.00 dD |
| 氰烯菌酯 Phenamacril | 2.63±0.02 dD | 58.85±0.26 eE |
| 多抗霉素 Polyoxin | 3.60±0.00 cC | 43.75±0.00 fF |
| 嘧菌酯 Azoxystrobin | 3.92±0.02 bB | 38.80±0.26 gG |
| CK | 6.40±0.00 aA | 0.00±0.00 hH |
表3 不同杀菌剂对A. alternata的抑制效果
Table 3 Inhibitory effects of different fungicides on A. alternata
| 杀菌剂 Fungicide | 菌落直径Colony diameter/cm | 抑制率Inhibition ratio/% |
|---|---|---|
| 咯菌腈 Fludioxonil | 0.40±0.00 hH | 93.75±0.00 aA |
| 吡噻菌胺 Pyrithiamide | 1.07±0.03 gG | 83.33±0.52 bB |
| 苯醚甲环唑 Difenoconazole | 1.50±0.00 fF | 76.56±0.00 cC |
| 丙硫菌唑 Prothioconazole | 1.70±0.00 eE | 73.44±0.00 dD |
| 氰烯菌酯 Phenamacril | 2.63±0.02 dD | 58.85±0.26 eE |
| 多抗霉素 Polyoxin | 3.60±0.00 cC | 43.75±0.00 fF |
| 嘧菌酯 Azoxystrobin | 3.92±0.02 bB | 38.80±0.26 gG |
| CK | 6.40±0.00 aA | 0.00±0.00 hH |
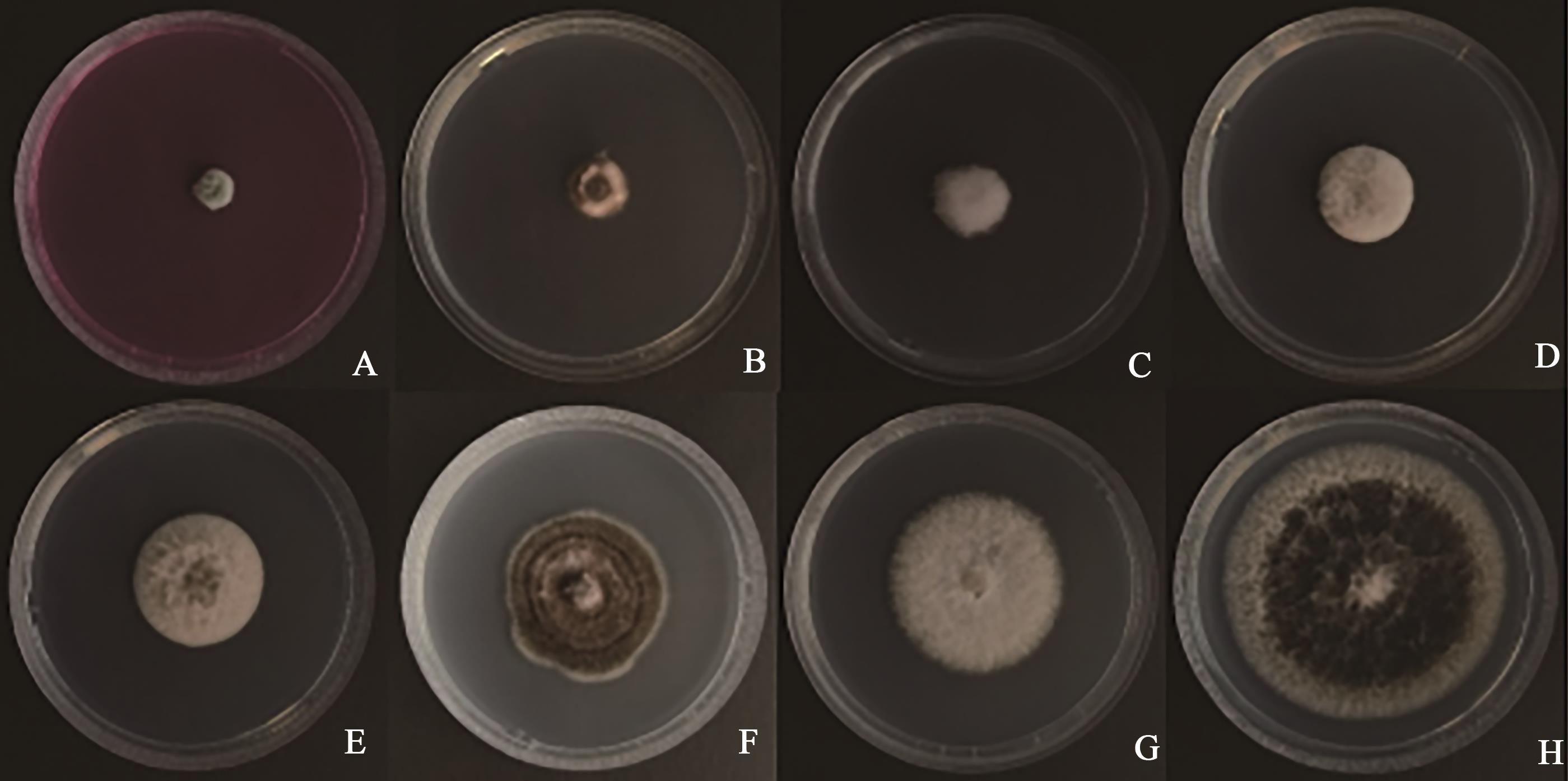
图2 不同杀菌剂下A. alternata的生长A:咯菌腈;B:吡噻菌胺;C:苯醚甲环唑;D:丙硫菌唑;E:氰烯菌酯;F:多抗霉素;G:嘧菌酯;H:CK
Fig. 2 Growth of A. alternata under different fungicidesA: Fludioxonil; B: Pyrithiamide; C: Difenoconazole; D: Prothioconazole; E: Phenamacril; F: Polyoxin; G: Azoxystrobin; H: CK
供试杀菌剂 Fungicide | 含量 Content/(mg·L-1) | 菌落直径 Colony diameter/cm | 抑制率 Inhibition ratio/% | 毒力回归方程 Toxic regression equation | EC50/(mg·L-1) | 相关系数Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 | 6.30±0.03 aA | 0.00±0.00 fF | |||
| 咯菌腈 Fludioxonil | 15.63 | 5.78±0.04 bB | 8.19±1.12 eE | y=-3.487+1.891x | 69.94 | 0.933 |
| 31.25 | 4.15±0.00 cC | 34.13±0.30 dD | ||||
| 62.50 | 3.48±0.02 dD | 44.70±0.50 cC | ||||
| 125.00 | 2.68±0.04 eE | 57.40±0.89 bB | ||||
| 250.00 | 0.55±0.00 fF | 91.27±0.04 aA | ||||
| 吡噻菌胺Pyrithiamide | 62.5 | 3.17±0.02 bB | 49.74±0.13 eE | |||
| 125.0 | 2.75±0.00 cC | 56.35±0.20 dD | ||||
| 250.0 | 2.55±0.00 dD | 59.52±0.18 cC | y=-1.157+0.623x | 71.96 | 0.965 | |
| 500.0 | 1.82±0.04 eE | 71.17±0.57 bB | ||||
| 1 000.0 | 1.45±0.00 fF | 76.98±0.11 aA |
表4 不同含量的杀菌剂下A. alternata菌丝的生长
Table 4 Growth of A. alternata mycelia at different contents of tested fungicides
供试杀菌剂 Fungicide | 含量 Content/(mg·L-1) | 菌落直径 Colony diameter/cm | 抑制率 Inhibition ratio/% | 毒力回归方程 Toxic regression equation | EC50/(mg·L-1) | 相关系数Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 | 6.30±0.03 aA | 0.00±0.00 fF | |||
| 咯菌腈 Fludioxonil | 15.63 | 5.78±0.04 bB | 8.19±1.12 eE | y=-3.487+1.891x | 69.94 | 0.933 |
| 31.25 | 4.15±0.00 cC | 34.13±0.30 dD | ||||
| 62.50 | 3.48±0.02 dD | 44.70±0.50 cC | ||||
| 125.00 | 2.68±0.04 eE | 57.40±0.89 bB | ||||
| 250.00 | 0.55±0.00 fF | 91.27±0.04 aA | ||||
| 吡噻菌胺Pyrithiamide | 62.5 | 3.17±0.02 bB | 49.74±0.13 eE | |||
| 125.0 | 2.75±0.00 cC | 56.35±0.20 dD | ||||
| 250.0 | 2.55±0.00 dD | 59.52±0.18 cC | y=-1.157+0.623x | 71.96 | 0.965 | |
| 500.0 | 1.82±0.04 eE | 71.17±0.57 bB | ||||
| 1 000.0 | 1.45±0.00 fF | 76.98±0.11 aA |

图3 不同水平供试杀菌剂下A. alternata菌丝的生长A:CK;B:咯菌腈15.63 mg·L-1;C:咯菌腈31.25 mg·L-1;D:咯菌腈62.50 mg·L-1;E:咯菌腈125.00 mg·L-1;F:咯菌腈250.00 mg·L-1;G:CK;H:吡噻菌胺62.5 mg·L-1;I:吡噻菌胺125.0 mg·L-1;J:吡噻菌胺250.0 mg·L-1;K:吡噻菌胺500.0 mg·L-1;L:吡噻菌胺1 000.0 mg·L-1
Fig.3 Mycelial growth of A. alternata under different levels of tested fungicidesA: CK; B: Fluoxonil 15.63 mg·L-1;C: Fluoxonil 31.25 mg·L-1; D: Fluoxonil 62.50 mg·L-1; E: Fluoxonil 125.00 mg·L-1;F: Fluoxonil 250.00 mg·L-1; G: CK; H: Pithiamide 62.5 mg·L-1; I: 125.0 mg·L-1;J: Pithiamide 250.0 mg·L-1;K: Pithiamide 500.0 mg·L-1; L: Pithiamide 1 000.0 mg·L-1
| 1 | 鄢丰霞,陈俊红,孙明德,等.产业融合视角下北京市板栗产业发展研究[J].林业经济问题,2012,32(5):422-432. |
| YAN F X, CHEN J H, SUN M D, et al.. The research of development of Beijing chestnut industry from the perspective of industrial convergence [J]. Issues For. Econ., 2012, 32(5): 422-432. | |
| 2 | 曹小艳,李志,张卿,等.不同板栗品种(系)抗性淀粉综合评价[J].中国粮油学报, 2019,34 (7):39-46. |
| CAO X Y, LI Z, ZHANG Q, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of resistant starch in different Chinese chestnut varieties (lines) [J]. J. Chin. Cereal. Oils Assoc., 2019, 34(7):39-46. | |
| 3 | 刘建华,李秀生,吕东林,等.板栗实腐病研究初报[J].森林病虫通讯,1993(3):9-11. |
| 4 | 朱晓清,林彩丽,李志朋,等.北京怀柔区板栗黄化皱缩病害调查[J].中国森林病虫,2011, 30(5):24-26. |
| ZHU X Q, LIN C L, LI Z P, et al.. Survey of Chinese chestnut yellow crinkle disease in Huairou district of Beijing [J]. For. Pest Dis., 2011, 30(5):24-26. | |
| 5 | 杨文杰,温晓蕾,冯丽娜,等.板栗黄化皱缩病的病原菌鉴定及其防治[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(3):148-156. |
| YANG W J, WEN X L, FENG L N, et al.. Identification of the pathogen of Chinese chestnut yellow crinkle and its control [J]. J. Agric Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(3):148-156. | |
| 6 | 姜淑霞,贾雯,邵云华,等.板栗褐缘叶枯病病原菌生物学特性研究[J].山东农业科学,2010 (4):52-55. |
| JIANG S X, JIA W, SHAO Y H, et al.. Biological characteristics of Phomopsis mollissima a pathogen [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2010(4):52-55. | |
| 7 | 姜莉莉,武海斌,宫庆涛,等.板栗贮藏期真菌群落结构分析初报[J].华北农学报,2019,34 ():302-308. |
| JIANG L L, WU H B, GONG Q T, et al.. Preliminary study of chestnut fungus community during storage [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2019, 34(S1):302-308. | |
| 8 | PRATELLA G C. Notes on the bio-pathology and techniques of storage-transport of chestnut [J]. Rivista di Frutticoltura, 1994, 56(4):75-77. |
| 9 | 梅汝鸿,陈宝琨,陈璧,等.板栗干腐病研究:Ⅱ.症状及病原[J].中国微生态学杂志,1991(1): 75-79. |
| MEI R H, CHEN B K, CHEN B, et al.. Studies on the dry rot of chestnut Ⅱ syndrome and pathogens [J]. Chin. J. Microecol., 1991(1):75-79. | |
| 10 | 朱锦茹,廉月琰,华正媛.板栗贮藏期腐烂原因初探[J].浙江林业科技,1992(1):44-46. |
| ZHU J R, LIAN Y Y, HUA Z Y. Preliminary exploration into the cause of Chinese chestnut putrity in storage [J]. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol., 1992(1):44-46. | |
| 11 | 赵忠仁,王冬兰,刘建业,等.板栗贮藏期病害及药剂处理保鲜技术研究[J].落叶果树, 1996 (4):10-14. |
| 12 | 王海霞,刘正坪,朱晓清,等.板栗贮藏期致腐病原真菌种类鉴定及其侵染特性[J].北京农学院学报,2006(4):33-36. |
| WANG H X, LIU Z P, ZHU X Q, et al.. Pathogens caused Chinese chestnut seed rot during storage and their infection process [J]. J. Beijing Agric. Sci., 2006(4):33-36. | |
| 13 | 张斌,梅秀凤,黄峰,等.中国柑橘黑腐病和褐斑病病原菌的系统发育分析[J].植物病理学报,2020,50(1):10-19. |
| ZHANG B, MEI X F, HUANG F, et al.. Phylogenetic analysis of Alternaria spp. causing black rot and brown spot of citrus in China [J]. Acta Phytopathol. Sin., 2020, 50(1):10-19. | |
| 14 | 史晓晶,杨玥,张新茹,等.山西省番茄叶部病害病原菌链格孢种类鉴定[J].植物保护学报, 2022,49(4):1279-1280. |
| SHI X J, YANG Y, ZHANG X R, et al.. Identification of common fungi Alternaria spp. associated with tomato foliar diseases in Shanxi province [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2022, 49(4): 1279-1280. | |
| 15 | 赵艳琴,于华荣,石凯,等.高粱链格孢叶斑病病原鉴定[J].植物病理学报,2017,47(2):282-285. |
| ZHAO Y Q, YU H R, SHI K, et al.. Identification of the pathogen causing leaf spot on sorghum [J]. Acta Phytopathol. Sin., 2017, 47(2):282-285. | |
| 16 | 张馨方,郭燕,李颖,等.板栗内腐病研究进展[J].中国植保导刊,2018,38(11):25-38. |
| ZHANG X F, GUO Y, LI Y, et al.. Research progress on chestnut seed rot [J]. China Plant Prot., 2018, 38(11):25-38. | |
| 17 | PARK J H, CHO S E, LEE S H, et al.. First report of postharvest rot of chestnuts caused by Mucor racemosus f. sphaerosporus in Korea [J]. Plant Dis., 2014, 98(12):1742-1743. |
| 18 | TZIROS G T, DIAMANDIS S. Sclerotinia pseudotuberosa as the cause of black rot of chestnuts in Greece [J]. J. Plant Pathol., 2018, 100(1):131-140. |
| 19 | 梁丽松,王贵禧.不同产区板栗病原菌的种类及其致病力研究[J].林业科学研究, 2003,16 (3):284-288. |
| LIANG L S, WANG G X. Studies on the varieties and pathogenic ability of the pathogenic fungi of Chinese chestnut seed in different production areas of China [J]. For. Res., 2003, 16(3):284-288. | |
| 20 | 张馨方,郭燕,李颖,等.板栗内腐病防治措施[J].北方果树,2018(5):4. |
| ZHANG X F, GUO Y, LI Y, et al.. Prevention and control measures of chestnut internal rot [J]. Northern Fruits, 2018(5):4. | |
| 21 | 李双民,霍佳欢,温晓蕾,等.冀东北板栗果腐病种类、发病原因及防控对策解析[J].河北果树,2022(1):38-39. |
| LI S M, HUO J H, WEN X L, et al.. Analysis on the species, causes and control measures of chestnut fruit rot in Northeast Hebei province [J]. Hebei Fruits, 2022(1):38-39. | |
| 22 | 张娜娜,李双民,温晓蕾,等.板栗红粉病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(7):145-152. |
| ZHANG N N, LI S M, WEN X L, et al.. Identification and biological characteristics of the pathogen causing pink disease of chestnut [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(7):145-152. | |
| 23 | 张娜娜,温晓蕾,王建华,等.不同板栗品种对栗果腐烂病菌抗性的室内评价[J].河北果树, 2022(4):21-23. |
| ZHANG N N, WEN X L, WANG J H, et al.. Laboratory evaluation of resistance of different Chinese chestnut varieties to pathogen rot of chestnut [J]. Hebei Fruits, 2022(4):21-23. | |
| 24 | 霍佳欢. 两种板栗果腐病病原鉴定、室内品种抗性评价与杀菌剂筛选[D].秦皇岛:河北科技师范学院,2022. |
| HUO J H. Identification pathogens of two chestnut fruit rot, indoor resistance variety evaluation and fungicides screening [D]. Qinhuangdao: Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology,2022. | |
| 25 | 林月莉,黄丽丽,索朗拉姆,等.苹果轮纹病室内快速评价体系的建立[J].植物保护学报, 2011,38(1):37-41. |
| LIN Y L, HUANG L L, SUO L L M, et al.. A rapid laboratory evaluation system for apple ring rot [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2011, 38(1):37-41. | |
| 26 | 王冬梅,张雁东,冯小飞,等.11个核桃品种嫁接苗对炭疽病的抗性评价与分析[J].黑龙江农业科学,2022(10):55-61. |
| WANG D M, ZHANG Y D, FENG X F, et al.. Effects of tree chemicals on gemination and emergence of potato [J]. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci., 2022(10):55-61. | |
| 27 | 任艳玲,王涛,沈晖,等.蓝莓灰霉病菌防治药剂室内毒力测定[J].中国南方果树,2019,48 (3):118-120. |
| REN Y L, WANG T, SHEN H, et al.. Laboratory toxicity determination of blueberry botrytis control agents [J]. J. South Chin. Fruits, 2019, 48(3):118-120. | |
| 28 | 王俊凤,温晓蕾,孙伟明,等.板栗腐烂病小刺青霉菌(Penicillium spinulosum)培养条件及药剂筛选[J].中国农业科技导报,2020,22(3):79-84. |
| WANG J F, WEN X L, SUN W M, et al.. Study on cultural conditions of Penicillium spinulosum causing chestnut rot and fungicides screening [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020, 22(3):79-84. | |
| 29 | 欧智涛,陈香玲,陈东奎,等.不同柑橘品种溃疡病抗性及不同时期药剂处理防效评价[J].江苏农业科学,2021,49(17):107-110. |
| OU Z T, CHEN X L, CHEN D K, et al.. Evaluation of canker resistance of different citrus varieties and control effect of different periods of drug treatment [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2021, 49(17):107-110. | |
| 30 | 贾晓辉,王文辉,傅俊范,等.梨和苹果种质对阿太菌果腐病菌的抗性评价及其防治药剂筛选[J].植物保护学报,2020,47(2):394-402. |
| JIA X H, WANG W H, FU J F, et al.. Evaluation of resistance to fruit rot pathogen Athelia bombacina for pear and apple germplasms and screening of fungicides [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2020, 47(2):394-402. | |
| 31 | 冯宝珍,李培谦.月季黑斑病病原菌鉴定及室内药剂初步筛选[J].植物保护学报, 2019,46 (5):1147-1154. |
| FENG B Z, LI P Q. Identification of the pathogen causing black spot of Chinese rose and fungicide screening for the disease control [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2019, 46(5):1147-1154. | |
| 32 | 马凌云,赵亮.3种杀菌剂对甜瓜采后黑斑病菌的抑制效果[J].河南农业科学, 2007(1):77-79. |
| MA L Y, ZHAO L. Controlling effects of 3 fungicides against A. alternata of postharvest melon [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2007(1):77-79. |
| [1] | 张娜娜, 温晓蕾, 李双民, 冯丽娜, 霍佳欢, 兰淑慧, 栗佳宁, 郭思柔, 王建华, 齐慧霞. 三种镰刀菌引起的板栗内腐病病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 117-122. |
| [2] | 杨文杰, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 张娜娜, 孙伟明, 齐慧霞. 板栗黄化皱缩病的病原菌鉴定及其防治[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 148-156. |
| [3] | 张娜娜§, 李双民§, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 王俊凤, 杨文杰, 霍佳欢, 兰淑慧, 孙伟明, 齐慧霞. 板栗红粉病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 145-152. |
| [4] | 王俊凤1§,温晓蕾1§,孙伟明1,刘一健1,时路亭2,张娜娜1,杨文杰1,陈卫东3,齐慧霞1*. 板栗腐烂病小刺青霉菌(Penicillium spinulosum)培养条件及药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3): 79-84. |
| [5] | 伍林涛,钟贵买,王健美,李旭锋,宋旭,杨毅. 转录因子AtWRKY28在拟南芥与甘蓝链格孢菌(Alternaria brassicicola)亲和性互作中的功能分析[J]. , 2012, 14(1): 65-71. |
| [6] | 张新忠,王忆,韩振海. 我国苹果属(Malus Mill.)野生资源研究利用的现状分析[J]. , 2010, 12(3): 8-15. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号