




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (4): 27-36.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0125
丰扬1( ), 郭凤根1(
), 郭凤根1( ), 王仕玉2, 刘正杰1, 龙雯虹2
), 王仕玉2, 刘正杰1, 龙雯虹2
收稿日期:2023-02-23
接受日期:2023-03-21
出版日期:2024-04-15
发布日期:2024-04-23
通讯作者:
郭凤根
作者简介:丰扬 E-mail:fengyang_ynau@sina.com;
基金资助:
Yang FENG1( ), Fenggen GUO1(
), Fenggen GUO1( ), Shiyu WANG2, Zhengjie LIU1, Wenhong LONG2
), Shiyu WANG2, Zhengjie LIU1, Wenhong LONG2
Received:2023-02-23
Accepted:2023-03-21
Online:2024-04-15
Published:2024-04-23
Contact:
Fenggen GUO
摘要:
为了阐明藜麦CqGAI基因密码子使用特性,克隆获得藜麦CqGAI基因序列,运用CodonW、SPSS软件及EMBOSS在线程序分析藜麦CqGAI基因密码子使用偏好性,并与25种植物的GAI基因进行中性绘图、ENC分析和奇偶偏好偏差性分析。结果表明,藜麦CqGAI基因编码序列(coding sequence,CDS)全长1 782 bp,编码593个氨基酸,包含DELLA基因家族特有结构域DELLA、TVHYNP、NLS、VHIID、LHR、RVER;CqGAI基因能够迅速响应赤霉素(gibberellins,GA),在GA信号通路中起关键作用;密码子偏好性分析显示,CqGAI基因的有效密码子数(effective number of codon,ENC)、密码子适应指数(codon adaptation index, CAI)及GC含量分别为54.14、0.21和46.18%,密码子偏好性较弱,偏好以A/T结尾,有27个高频密码子。聚类分析表明,藜麦CqGAI基因与石竹目植物的亲缘关系较近。碱基组成与相关性分析发现,CqGAI基因密码子偏好性受碱基突变和选择效应影响。密码子使用频率表明,大肠杆菌与酵母菌均适用于藜麦CqGAI基因异源表达,拟南芥、烟草、甜菜均可作为藜麦CqGAI基因功能分析的遗传转化受体。以上研究结果为进一步研究藜麦CqGAI基因功能和异源表达提供了重要参考。
中图分类号:
丰扬, 郭凤根, 王仕玉, 刘正杰, 龙雯虹. 藜麦CqGAI基因密码子偏好性与进化分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 27-36.
Yang FENG, Fenggen GUO, Shiyu WANG, Zhengjie LIU, Wenhong LONG. Codon Bias and Evolution Analysis of CqGAI in Chenopodium quinoa[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 27-36.
| 引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 用途 Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| CqGAI-F | ATGAAGAGGGAACTACCCTTTACG | 目的基因 Target gene |
| CqGAI-R | TCATGTTTCCATTAGACACCCATC | 目的基因 Target gene |
| CqGAI-qF | TGTCGAGGCCGGTTGTTC | qRT-PCR |
| CqGAI-qR | ACGCCGCTAAAAACCCGA | qRT-PCR |
| CqActin-F | GAGCACCCTGTTCTTCTGACTG | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| CqActin -R | GAGAAAGAACAGCCTGAATTGC | 内参基因 Reference gene |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences
| 引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 用途 Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| CqGAI-F | ATGAAGAGGGAACTACCCTTTACG | 目的基因 Target gene |
| CqGAI-R | TCATGTTTCCATTAGACACCCATC | 目的基因 Target gene |
| CqGAI-qF | TGTCGAGGCCGGTTGTTC | qRT-PCR |
| CqGAI-qR | ACGCCGCTAAAAACCCGA | qRT-PCR |
| CqActin-F | GAGCACCCTGTTCTTCTGACTG | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| CqActin -R | GAGAAAGAACAGCCTGAATTGC | 内参基因 Reference gene |
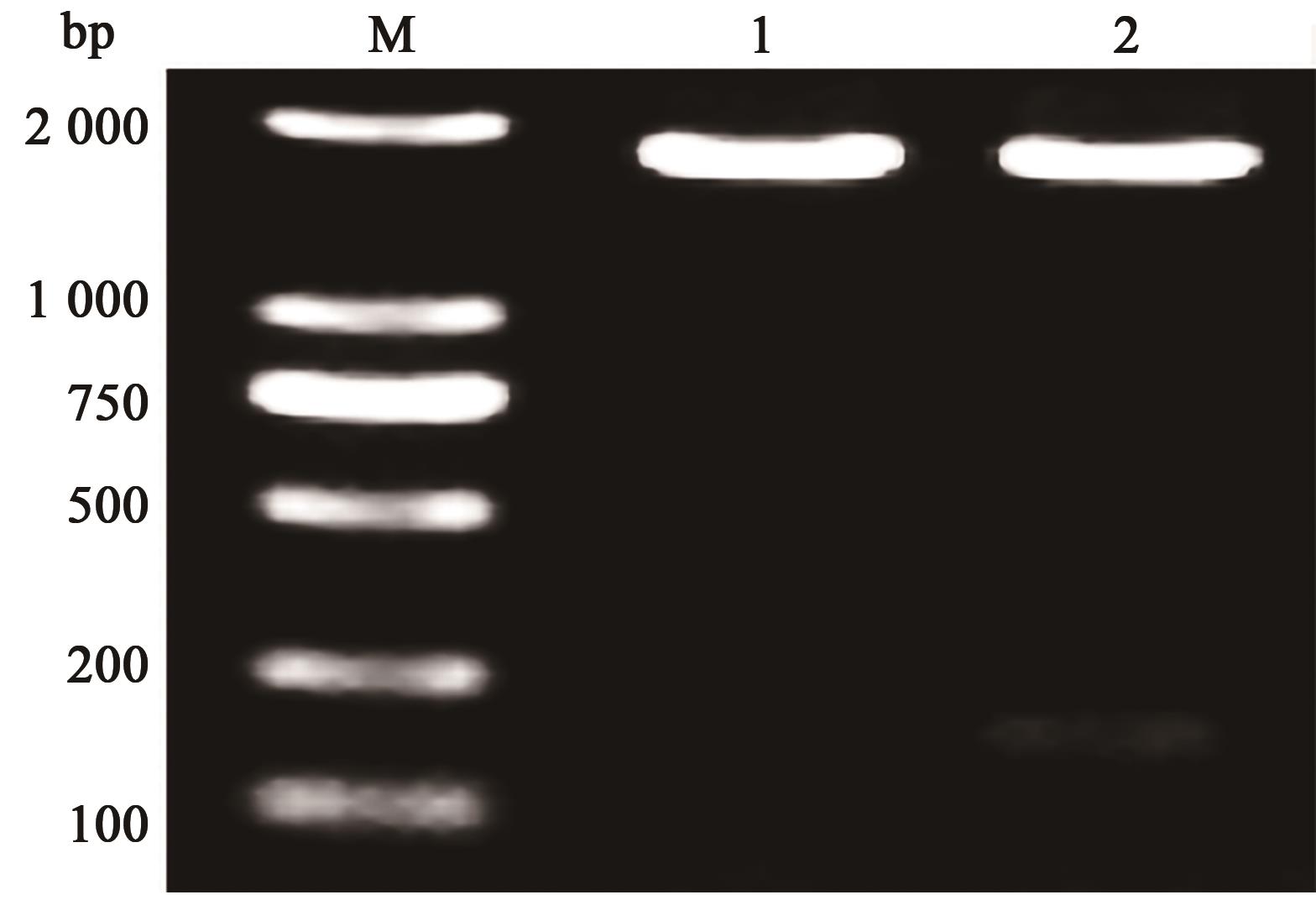
图1 藜麦CqGAI基因的PCR产物注:M—DL 2000 DNA marker;1、2—PCR产物。
Fig. 1 PCR amplification of CqGAI gene in C. quinoa.Note: M—DL 2000 DNA marker; 1, 2—PCR products.

图2 GAI蛋白氨基酸序列比对注:方框与三角表示GAI蛋白保守结构域,依次为DELLA、TVHYNP、NLS、VHIID、LHR、RVER和SAW。CqGAI/CqGAI-like—藜麦;SoGAI—菠菜;BvGAI—甜菜;AtGAI—苋菜。
Fig. 2 Alignment of amino acid sequences of GAI proteinNote: The boxes and triangles refer to the conserved structural domains of GAI proteins, in order of DELLA, VHYNP, NLS and SAW. CqGAI/CqGAI-like—Chenopodium quinoa; SoGAI—Spinacia oleracea; BvGAI—Beta vulgaris; AtGAI—Amaranthus tricolor.
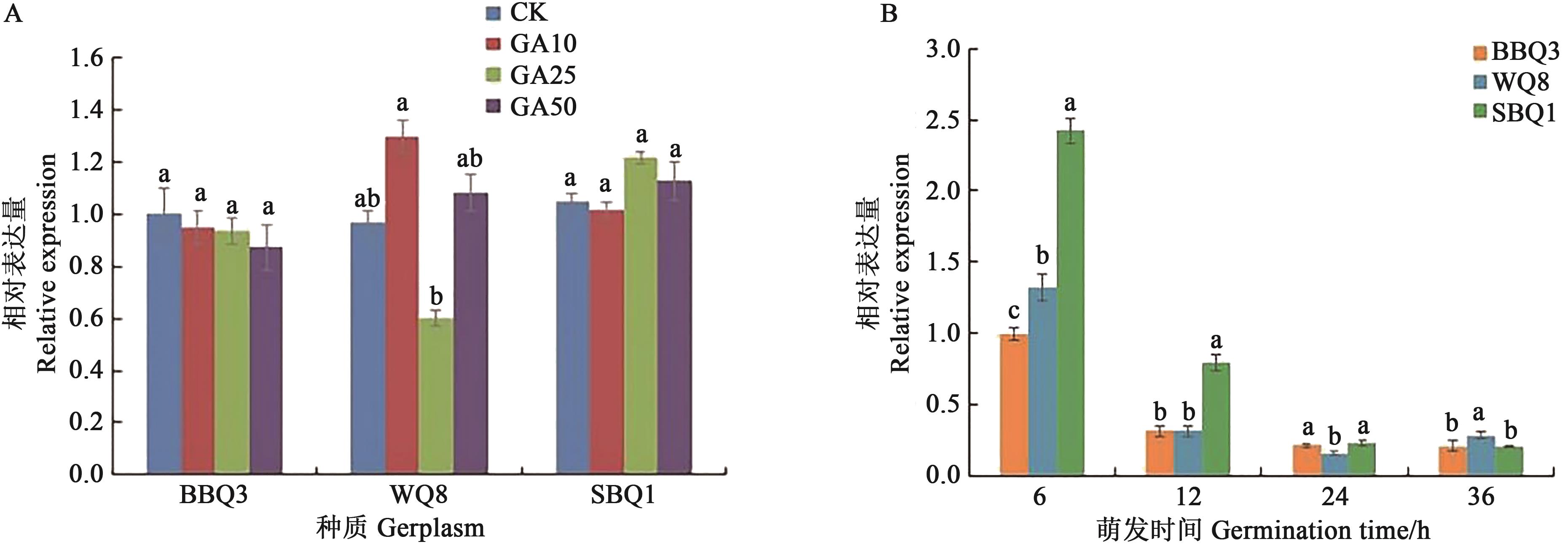
图3 CqGAI基因在不同处理下的相对表达量A:不同水平GA3处理下相对表达量;B:25 mg·L-1 GA3处理下不同萌发时间相对表达量。不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 3 Relative expression of CqGAI gene under different treatmentsNote:Relative expression under different concentrations of GA3 treatment;B:Relative expression at different germination times in seeds under 25 mg·L-1 GA3 treatment. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
物种 Species | 基因登录号 GenBank accession number | G/C含量 G/C content/% | 有效密码 子数 ENC | 密码子适应 指数 CAI | 最优密码子 使用频率 FOC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC | |||||
藜麦 Chenopodium quinoa | OQ067480 | 52.02 | 42.76 | 43.77 | 46.18 | 54.14 | 0.21 | 0.416 |
菠菜 Spinacia oleracea | KX026951.1 | 53.73 | 44.81 | 45.45 | 48.00 | 54.47 | 0.20 | 0.401 |
甜菜 Beta vulgaris | XM_010683580.3 | 50.82 | 42.48 | 35.95 | 43.08 | 50.00 | 0.19 | 0.358 |
苋菜 Amaranthus tricolor | MK049175.1 | 51.65 | 41.91 | 32.18 | 41.91 | 50.61 | 0.20 | 0.395 |
陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum | FJ974045.1 | 54.94 | 41.49 | 49.92 | 48.78 | 54.22 | 0.22 | 0.441 |
李 Prunus salicina | KU845589.1 | 58.99 | 41.64 | 63.25 | 54.63 | 51.24 | 0.25 | 0.480 |
核桃 Juglans regia | JF766606.2 | 57.98 | 42.51 | 63.68 | 54.72 | 52.22 | 0.26 | 0.478 |
牡丹 Paeonia suffruticosa | MH550803.1 | 58.93 | 43.51 | 56.01 | 52.81 | 59.03 | 0.21 | 0.425 |
橡胶树 Hevea brasiliensis | KT696440.1 | 56.85 | 41.73 | 43.31 | 47.30 | 55.41 | 0.23 | 0.424 |
沙梨 Pyrus pyrifolia | KU311003.1 | 60.00 | 42.20 | 72.60 | 58.27 | 47.69 | 0.26 | 0.514 |
杂交玫瑰 Rosa hybrid | KC484652.1 | 58.32 | 41.20 | 72.54 | 57.35 | 47.48 | 0.25 | 0.501 |
拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | NM_101361.3 | 58.80 | 38.76 | 47.94 | 48.50 | 49.73 | 0.25 | 0.472 |
番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | NM_001247436.1 | 51.95 | 42.61 | 29.54 | 41.37 | 44.68 | 0.21 | 0.409 |
毛白杨 Populus tomentosa | JX102471.1 | 55.79 | 41.06 | 45.03 | 47.30 | 56.81 | 0.25 | 0.458 |
葡萄 Vitis vinifera | HQ834311.1 | 60.91 | 42.64 | 64.30 | 55.95 | 51.67 | 0.23 | 0.454 |
樱桃 Prunus avium | XM_021956293.1 | 59.73 | 43.12 | 59.73 | 54.19 | 54.93 | 0.21 | 0.415 |
水蜜桃 Prunus persica | XM_007214894.2 | 59.43 | 43.77 | 60.94 | 54.71 | 54.83 | 0.21 | 0.412 |
梅花 Prunus mume | NM_001326504.1 | 60.37 | 43.98 | 61.20 | 55.18 | 54.12 | 0.21 | 0.415 |
苹果 Malus domestica | FJ535245.1 | 60.13 | 42.70 | 73.00 | 58.61 | 46.64 | 0.25 | 0.507 |
水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | KX905158.1 | 55.61 | 39.47 | 50.00 | 48.36 | 55.41 | 0.20 | 0.388 |
马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum | JF834157.1 | 52.46 | 42.78 | 28.18 | 41.14 | 43.63 | 0.22 | 0.427 |
高粱 Sorghum bicolor | XM_002450738.2 | 64.83 | 50.00 | 84.78 | 66.54 | 38.15 | 0.26 | 0.568 |
小米 Setaria italica | XM_004980464.2 | 63.79 | 51.06 | 86.74 | 67.20 | 37.12 | 0.23 | 0.514 |
玉米 Zea mays | XM_008681950.2 | 64.51 | 50.39 | 90.54 | 68.48 | 34.68 | 0.26 | 0.582 |
水稻 Oryza sativa | AY464568.1 | 68.83 | 52.43 | 86.64 | 69.30 | 37.73 | 0.26 | 0.570 |
表2 不同植物GAI基因密码子选择偏好性相关参数 (续表Continued)
Table 2 Preference related parameters of GAI gene codons among different plants
物种 Species | 基因登录号 GenBank accession number | G/C含量 G/C content/% | 有效密码 子数 ENC | 密码子适应 指数 CAI | 最优密码子 使用频率 FOC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC | |||||
藜麦 Chenopodium quinoa | OQ067480 | 52.02 | 42.76 | 43.77 | 46.18 | 54.14 | 0.21 | 0.416 |
菠菜 Spinacia oleracea | KX026951.1 | 53.73 | 44.81 | 45.45 | 48.00 | 54.47 | 0.20 | 0.401 |
甜菜 Beta vulgaris | XM_010683580.3 | 50.82 | 42.48 | 35.95 | 43.08 | 50.00 | 0.19 | 0.358 |
苋菜 Amaranthus tricolor | MK049175.1 | 51.65 | 41.91 | 32.18 | 41.91 | 50.61 | 0.20 | 0.395 |
陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum | FJ974045.1 | 54.94 | 41.49 | 49.92 | 48.78 | 54.22 | 0.22 | 0.441 |
李 Prunus salicina | KU845589.1 | 58.99 | 41.64 | 63.25 | 54.63 | 51.24 | 0.25 | 0.480 |
核桃 Juglans regia | JF766606.2 | 57.98 | 42.51 | 63.68 | 54.72 | 52.22 | 0.26 | 0.478 |
牡丹 Paeonia suffruticosa | MH550803.1 | 58.93 | 43.51 | 56.01 | 52.81 | 59.03 | 0.21 | 0.425 |
橡胶树 Hevea brasiliensis | KT696440.1 | 56.85 | 41.73 | 43.31 | 47.30 | 55.41 | 0.23 | 0.424 |
沙梨 Pyrus pyrifolia | KU311003.1 | 60.00 | 42.20 | 72.60 | 58.27 | 47.69 | 0.26 | 0.514 |
杂交玫瑰 Rosa hybrid | KC484652.1 | 58.32 | 41.20 | 72.54 | 57.35 | 47.48 | 0.25 | 0.501 |
拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | NM_101361.3 | 58.80 | 38.76 | 47.94 | 48.50 | 49.73 | 0.25 | 0.472 |
番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | NM_001247436.1 | 51.95 | 42.61 | 29.54 | 41.37 | 44.68 | 0.21 | 0.409 |
毛白杨 Populus tomentosa | JX102471.1 | 55.79 | 41.06 | 45.03 | 47.30 | 56.81 | 0.25 | 0.458 |
葡萄 Vitis vinifera | HQ834311.1 | 60.91 | 42.64 | 64.30 | 55.95 | 51.67 | 0.23 | 0.454 |
樱桃 Prunus avium | XM_021956293.1 | 59.73 | 43.12 | 59.73 | 54.19 | 54.93 | 0.21 | 0.415 |
水蜜桃 Prunus persica | XM_007214894.2 | 59.43 | 43.77 | 60.94 | 54.71 | 54.83 | 0.21 | 0.412 |
梅花 Prunus mume | NM_001326504.1 | 60.37 | 43.98 | 61.20 | 55.18 | 54.12 | 0.21 | 0.415 |
苹果 Malus domestica | FJ535245.1 | 60.13 | 42.70 | 73.00 | 58.61 | 46.64 | 0.25 | 0.507 |
水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | KX905158.1 | 55.61 | 39.47 | 50.00 | 48.36 | 55.41 | 0.20 | 0.388 |
马铃薯 Solanum tuberosum | JF834157.1 | 52.46 | 42.78 | 28.18 | 41.14 | 43.63 | 0.22 | 0.427 |
高粱 Sorghum bicolor | XM_002450738.2 | 64.83 | 50.00 | 84.78 | 66.54 | 38.15 | 0.26 | 0.568 |
小米 Setaria italica | XM_004980464.2 | 63.79 | 51.06 | 86.74 | 67.20 | 37.12 | 0.23 | 0.514 |
玉米 Zea mays | XM_008681950.2 | 64.51 | 50.39 | 90.54 | 68.48 | 34.68 | 0.26 | 0.582 |
水稻 Oryza sativa | AY464568.1 | 68.83 | 52.43 | 86.64 | 69.30 | 37.73 | 0.26 | 0.570 |
| 参数 Parameter | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC2 | 0.686** | |||
| GC3 | 0.921** | 0.676** | ||
| GC | 0.949** | 0.757** | 0.990** | |
| ENC | -0.523** | -0.744** | -0.555** | -0.604** |
表3 不同物种GAI基因密码子参数相关性分析
Table 3 Correlative analysis of codon parameters of GAI genes in different species
| 参数 Parameter | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC2 | 0.686** | |||
| GC3 | 0.921** | 0.676** | ||
| GC | 0.949** | 0.757** | 0.990** | |
| ENC | -0.523** | -0.744** | -0.555** | -0.604** |
| 参数 Parameter | CqGAI/At | CqGAI/Nt | CqGAI/Bv | CqGAI/Os | CqGAI/Sc | CqGAI/Ec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
比值≤0.5的密码子个数 Number of condons with ratio≤0.5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
比值≥2.0的密码子个数 Number of condons with ratio≥2.0 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| 总计 Total | 9 | 9 | 10 | 19 | 13 | 13 |
表4 藜麦CqGAI基因与部分模式生物基因组密码子使用偏性比较
Table 4 Comparison of codon usage preference between CqGAI in C.quinoa and representative organisms
| 参数 Parameter | CqGAI/At | CqGAI/Nt | CqGAI/Bv | CqGAI/Os | CqGAI/Sc | CqGAI/Ec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
比值≤0.5的密码子个数 Number of condons with ratio≤0.5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
比值≥2.0的密码子个数 Number of condons with ratio≥2.0 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| 总计 Total | 9 | 9 | 10 | 19 | 13 | 13 |
| 1 | TANG Y, LI X H, CHEN P X, et al.. Characterisation of fatty acid, carotenoid, tocopherol/tocotrienol compositions and antioxidant activities in seeds of three Chenopodium quinoa Willd. genotypes [J]. Food Chem., 2015, 174(5):502-508. |
| 2 | TANG Y, LI X H, ZHANG B, et al.. Characterisation of phenolics, betanins and antioxidant activities in seeds of three Chenopodium quinoa Willd. genotypes [J]. Food Chem., 2015, 166(1):380-388. |
| 3 | MCGINTY E M, MURPHY K M, HAUVERMALE A L. Seed dormancy and preharvest sprouting in quinoa [J/OL]. Plants, 2021, 10(3):458 [2023-01-10]. . |
| 4 | CECCATO D V, BERTERO H D, BATLLA D. Environmental control of dormancy in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) seeds: two potential genetic resources for pre-harvest sprouting tolerance [J]. Seed Sci. Res., 2011, 21(2):133-141. |
| 5 | VETCH J M, STOUGAARD R N, MARTIN J M, et al.. Revealing the genetic mechanisms of pre-harvest sprouting in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. Plant Sci., 2019, 281:180-185. |
| 6 | NONOGAKI H, BARRERO J M, LI C D. Seed dormancy, germination, and pre-harvest sprouting [J/OL]. Front Plant Sci., 2018, 9:1783 [2023-01-10]. . |
| 7 | 徐恒恒,黎妮,刘树君,等.种子萌发及其调控的研究进展[J].作物学报,2014,40(7):1141-1156. |
| XU H H, LI N, LIU S J, et al.. Research progress in seed germination and its control [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2014, 40(7):1141-1156. | |
| 8 | PHOKAS A, COATES J C. Evolution of DELLA function and signaling in land plants [J]. Evol. Dev., 2021, 23(3):137-154. |
| 9 | VELDE K V, RUELENS P, GEUTEN K, et al.. Exploiting DELLA signaling in cereals [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2017, 22(10):880-893. |
| 10 | SERRANO M A, BENCIVENGA S, BUSH M, et al.. DELLA genes restrict inflorescence meristem function independently of plant height [J]. Nat. Plants, 2017, 3(9):749-754. |
| 11 | DAVIERE J, ACHARD P. A pivotal role of DELLAs in regulating multiple hormone signals [J]. Mol. Plant, 2016, 9(1):10-20. |
| 12 | KELLER J, DELCROS P, LIBOUREL C, et al.. DELLA family duplication events lead to different selective constraints in angiosperms [J]. Genetica, 2020, 148(5-6):243-251. |
| 13 | BLANCO T N, SERRANO M A, ALABADI D. Regulation of DELLA proteins by post-translational modifications [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2020, 61(11):1891-1901. |
| 14 | PAN J J, HU Y R, WANG H P, et al.. Molecular mechanism underlying the synergetic effect of jasmonate on abscisic acid signaling during seed germination in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Cell, 2020, 32(12):3846-3865. |
| 15 | LI K L, YU R B, FAN L M, et al.. DELLA-mediated PIF degradation contributes to coordination of light and gibberellin signalling in Arabidopsis [J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7:11868 [2023-01-10]. . |
| 16 | 张以忠,曾文艺,邓琳琼,等.甘蓝S-位点基因SRK、SLG和SP11/SCR密码子偏好性分析[J].作物学报,2022,48(5):1152-1168. |
| ZHANG Y Z, ZENG W Y, DENG L Q, et al.. Codon usage bias analysis of S-locus genes SRK, SLG, and SP11/SCR in Brassica oleracea [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2022, 48(5):1152-1168. | |
| 17 | 任桂萍,董璎莹,党云琨.密码子中的密码:密码子偏好性与基因表达的精细调控[J].中国科学:生命科学,2019,49(7):839-847. |
| REN G P, DONG Y Y, DANG Y K. Codon in codon: preference and fine regulation of gene expression [J]. Sci. Sin. Vitae, 2019, 49(7):839-847. | |
| 18 | WEI L, HE J, JIA X, et al.. Analysis of codon usage bias of mitochondrial genome in Bombyx mori and its relation to evolution [J]. BMC Evol. Biol., 2014, 14(1):1-12. |
| 19 | PEK H B, KLEMENT M, ANG K S, et al.. Exploring codon context bias for synthetic gene design of a thermostable invertase in Escherichia coli [J]. Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2015, 75-76:57-63. |
| 20 | GUN L, YUMIAO R, HAIXIAN P, et al.. Comprehensive analysis and comparison on the codon usage pattern of whole mycobacterium tuberculosis coding genome from different area [J/OL]. Biomed. Res. Int., 2018, 2018:3574976 [2023-01-10]. . |
| 21 | 毛琪,晏兴珠,王仕玉,等.30份藜麦资源的穗发芽抗性评价[J].种子,2021,40(10):62-66. |
| MAO Q, YAN X Z, WANG S Y, et al.. Evaluation of panicle germination resistance of 30 quinoa resources [J]. Seed, 2021, 40(10): 62-66. | |
| 22 | 丰扬,郭凤根,王仕玉,等.藜麦Cq6GT基因的克隆与表达分析[J].植物生理学报,2022,58(10):2017-2024. |
| FENG Y, GUO F G, WANG S Y, et al.. Cloning and expression analysis of Cq6GT gene from Chenopodium quinoa [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2022, (58)10:2017-2024. | |
| 23 | XU H, LANTZOUNI O, BRUGGINK T, et al.. A molecular signal integration network underpinning Arabidopsis seed germination [J]. Curr. Biol., 2020, 30(19):3703-3712. |
| 24 | CHAHTANE H, NOGUEIRA F T, ALLARD P M, et al.. The plant pathogen pseudomonas aeruginosa triggers a DELLA-dependent seed germination arrest in Arabidopsis [J/OL]. Elife, 2018, 7:e37082 [2023-01-10]. . |
| 25 | WANG Y J, DENG D X. Molecular basis and evolutionary pattern of GA-GID1-DELLA regulatory module [J]. Mol. Genet. Genomics, 2014, 289(1):1-9. |
| 26 | PONNU J. Repressing a repressor: E3 ligase COP1/SPA promotes seed germination by targeting the DELLA protein RGL2 [J]. Plant Physiol., 2022, 189(3):1192-1193. |
| 27 | SUN T P. The molecular mechanism and evolution of the GA-GID1-DELLA signaling module in plants [J]. Curr. Biol., 2011, 21(9):338-345. |
| 28 | 宋松泉,刘军,黄荟,等.赤霉素代谢与信号转导及其调控种子萌发与休眠的分子机制[J].中国科学:生命科学,2020,50(6):599-615. |
| SONG S Q, LIU J, HUANG H, et al.. Gibberellin metabolism and signaling and its molecular mechanism in regulating seed germination and dormancy [J]. Sci. Sin. Vitae, 2020, 50(6):599-615. | |
| 29 | BASKIN J M, BASKIN C C. A classification system for seed dormancy [J]. Seed Sci. Res., 2007, 14(1):1-16. |
| 30 | HIRANO K, ASANO K, TSUJI H, et al.. Characterization of the molecular mechanism underlying gibberellin perception complex formation in rice [J]. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(8):2680-2696. |
| 31 | WANG L Y, XING H X, YUAN Y C, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of codon usage bias in four sequenced cotton species [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(3):e0194372 [2023-01-10]. . |
| 32 | MURRAY E E, LOTZER J, EBERLE M. Codon usage in plant genes [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 1989, 17(2):477-498. |
| 33 | 宋芸,贾孟君,陈亮,等.忍冬ICE1基因密码子偏好性分析及受体系统选择[J].植物生理学报,2020,56(11):2459-2468. |
| SONG Y, JIA M J, CHEN L, et al.. Codon bias analysis and receptor system selection of ICE1 gene in Lonicera japonica Thunb [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2020, 56(11):2459-2468. | |
| 34 | 赵春丽,彭丽云,王晓,等.苋菜AtGAI基因密码子偏好性与进化分析[J].中国农业大学学报,2019,24(12):10-22. |
| ZHAO C L, PENG L Y, WANG X, et al.. Codon bias and evolution analysis of AtGAI in Amaranthus tricolor [J]. J. Chin. Agric. Univ., 2019, 24(12):10-22. | |
| 35 | 李翔,范作义,王井源,等.红松查尔酮合成酶基因CHS密码子偏好性分析[J].植物研究,2020,40(3):447-457. |
| LI X, FAN Z Y, WANG J Y, et al.. Codon usage bias of chalcone synthase gene CHS in Pinus koraiensis [J]. Bull. Bot. Res., 2020, 40(3):447-457. |
| [1] | 邓玉荣, 韩联, 王金龙, 韦兴翰, 王旭东, 赵颖, 魏小红, 李朝周. 藜麦SOD家族基因的鉴定及其对混合盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 28-39. |
| [2] | 陈秋静, 杨招娣, 王仕玉, 郭凤根, 赵小雪, 陈凡, 丰扬. 植物生长延缓剂对藜麦抗倒伏能力及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 42-48. |
| [3] | 郭佳星, 黄祥, 杨梅花, 王蕾蕾, 韩彦奇, 李卓怡. 桦木科叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性及系统发育分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 74-83. |
| [4] | 严其伟, 梁湘兰, 陶秋云, 罗秋香, 郭松. 老班瑶药牛耳风叶绿体基因组特征及其密码子使用偏好性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 74-86. |
| [5] | 崔宏亮, 宋晓晓, 姚庆, 安万刚, 邢宝, 秦培友. 伊犁河谷不同藜麦品种对盐胁迫的生理响应及耐盐评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 32-45. |
| [6] | 黄祥, 楚光明, 郑新开, 程锦涛, 陈健豪, 徐迎春, 金奇江, 杨梅花. 睡莲属叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性及系统发育分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 75-84. |
| [7] | 齐天明, 李志坚, 秦培友, 任贵兴, 周帮伟. 藜麦栽培技术研究与应用展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 157-165. |
| [8] | 杨瑞萍1,刘瑞香1,马迎梅1*,郭占斌2,张宏武2,白宇1,赵新宇1. 不同藜麦资源的抗旱性评价及渗透调节剂对其抗旱性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 52-60. |
| [9] | 史梦梦1,温思钰1,赵佳佳2,乔玲2,武棒棒2,郑兴卫1,2*,郑军1,2*. 小麦RCAR基因家族的鉴定、进化与逆境响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 14-24. |
| [10] | 葛川1,杨荣2,李刘军2,张建诚2,郑兴卫2*. 小麦全基因组中YABBY基因家族的筛选与特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(8): 11-18. |
| [11] | 张慧玲1,2,王志伟1,2,周中凯2*. 不同汽爆处理对藜麦秸秆化学组成及纤维结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(7): 105-112. |
| [12] | 张书玲1§,刘莹2§,张惠敏1,刘浩然1,董丽君1,刘紫欣1,刘建凤1*. 棉花WRKY转录因子家族成员的鉴定和生物信息学分析 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(8): 9-15. |
| [13] | 李丽丽1,姜奇彦2*,牛风娟2,胡正2,张辉2*. 藜麦耐盐机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(2): 31-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号