




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 42-48.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0594
陈秋静1( ), 杨招娣1, 王仕玉2, 郭凤根1(
), 杨招娣1, 王仕玉2, 郭凤根1( ), 赵小雪1, 陈凡1, 丰扬1
), 赵小雪1, 陈凡1, 丰扬1
收稿日期:2022-07-15
接受日期:2022-09-06
出版日期:2023-11-15
发布日期:2023-11-20
通讯作者:
郭凤根
作者简介:陈秋静 E-mail:3152187537@qq.com;
基金资助:
Qiujing CHEN1( ), Zhaodi YANG1, Shiyu WANG2, Fenggen GUO1(
), Zhaodi YANG1, Shiyu WANG2, Fenggen GUO1( ), Xiaoxue ZHAO1, Fan CHEN1, Yang FENG1
), Xiaoxue ZHAO1, Fan CHEN1, Yang FENG1
Received:2022-07-15
Accepted:2022-09-06
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Fenggen GUO
摘要:
为提高藜麦抗倒伏性,选出降低藜麦倒伏率的最佳植物生长延缓剂水平,采用随机区组试验,以喷施清水为对照,探究多效唑(PP333)、烯效唑(S3307)和缩节胺(MEP)3种植物生长延缓剂在50、100、200和350 mg·L-1时对藜麦生长发育及其产量的影响。结果表明,3种植物生长延缓剂都能有效降低藜麦株高,在一定范围内提高抗折力,降低倒伏指数和倒伏率。其中,烯效唑效果最好,以100 mg·L-1为宜,株高较相同水平的多效唑和缩节胺分别降低6.8%和4.2%,抗折力增加17.4%和25.2%;多效唑在100 mg·L-1时提高抗倒伏能力效果高于其他处理,倒伏率较CK显著降低79.9%;缩节胺在100~200 mg·L-1范围内效果较好。以上结果为藜麦优质种植的化控措施提供了理论参考。
中图分类号:
陈秋静, 杨招娣, 王仕玉, 郭凤根, 赵小雪, 陈凡, 丰扬. 植物生长延缓剂对藜麦抗倒伏能力及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 42-48.
Qiujing CHEN, Zhaodi YANG, Shiyu WANG, Fenggen GUO, Xiaoxue ZHAO, Fan CHEN, Yang FENG. Effects of Plant Growth Retarders on Lodging Resistance and Yield of Quinoa[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 42-48.
| 处理Treatment | 灌浆期Filling stage | 成熟期Maturation stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height/cm | 茎粗 Stem diameter/mm | 穗长 Ear length/cm | 穗粗 Ear diameter/cm | 重心高 Height of gravity center/cm | ||
| CK | 100.13±11.20 a | 6.27±0.63 a | 27.07±3.93 a | 6.13±1.35 a | 67.44±5.76 a | |
| P50 | 65.17±12.36 b | 5.25±0.34 ab | 16.13±3.26 b | 3.37±0.57 bc | 52.79±3.19 b | |
| P100 | 58.77±5.09 bc | 4.79±0.78 abc | 13.97±2.25 b | 3.19±0.48 bc | 39.28±8.85 bc | |
| P200 | 43.47±15.50 bc | 3.14±0.44 cd | 10.45±5.00 bc | 2.85±0.94 bc | 28.54±6.65 e | |
| P350 | 20.08±3.00 d | 2.03±0.46 d | 5.00±0.75 c | 2.13±0.13 c | — | |
| S50 | 57.27±8.84 bc | 4.93±0.74 abc | 16.73±3.23 b | 3.43±0.46 b | 42.11±1.34 cd | |
| S100 | 54.80±5.77 bc | 4.42±0.76 bc | 12.30±3.34 b | 3.52±0.81 b | 36.28±4.18 cde | |
| S200 | 52.10±12.52 bc | 4.38±0.39 bc | 12.00±3.02 b | 3.44±0.23 b | 34.39±1.87 cde | |
| S350 | 42.80±13.59 c | 4.19±1.37 bc | 10.73±1.67 bc | 3.30±0.17 bc | 28.92±6.17 e | |
| M50 | 60.59±9.47 bc | 4.77±1.38 abc | 16.10±3.25 b | 3.69±0.70 b | 44.56±3.86 bc | |
| M100 | 57.10±8.55 bc | 4.59±0.69 abc | 15.90±4.92 b | 3.60±0.84 b | 37.11±7.23 cde | |
| M200 | 55.77±19.38 bc | 4.51±2.08 abc | 14.80±5.07 b | 3.57±0.30 b | 35.17±4.17 cde | |
| M350 | 52.90±10.02 bc | 3.76±0.10 bc | 14.47±2.29 b | 3.06±0.54 bc | 33.28±4.66 cde | |
表1 不同处理下藜麦植株的主要形态特征
Table 1 Main morphological characteristics of quinoa plants under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | 灌浆期Filling stage | 成熟期Maturation stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height/cm | 茎粗 Stem diameter/mm | 穗长 Ear length/cm | 穗粗 Ear diameter/cm | 重心高 Height of gravity center/cm | ||
| CK | 100.13±11.20 a | 6.27±0.63 a | 27.07±3.93 a | 6.13±1.35 a | 67.44±5.76 a | |
| P50 | 65.17±12.36 b | 5.25±0.34 ab | 16.13±3.26 b | 3.37±0.57 bc | 52.79±3.19 b | |
| P100 | 58.77±5.09 bc | 4.79±0.78 abc | 13.97±2.25 b | 3.19±0.48 bc | 39.28±8.85 bc | |
| P200 | 43.47±15.50 bc | 3.14±0.44 cd | 10.45±5.00 bc | 2.85±0.94 bc | 28.54±6.65 e | |
| P350 | 20.08±3.00 d | 2.03±0.46 d | 5.00±0.75 c | 2.13±0.13 c | — | |
| S50 | 57.27±8.84 bc | 4.93±0.74 abc | 16.73±3.23 b | 3.43±0.46 b | 42.11±1.34 cd | |
| S100 | 54.80±5.77 bc | 4.42±0.76 bc | 12.30±3.34 b | 3.52±0.81 b | 36.28±4.18 cde | |
| S200 | 52.10±12.52 bc | 4.38±0.39 bc | 12.00±3.02 b | 3.44±0.23 b | 34.39±1.87 cde | |
| S350 | 42.80±13.59 c | 4.19±1.37 bc | 10.73±1.67 bc | 3.30±0.17 bc | 28.92±6.17 e | |
| M50 | 60.59±9.47 bc | 4.77±1.38 abc | 16.10±3.25 b | 3.69±0.70 b | 44.56±3.86 bc | |
| M100 | 57.10±8.55 bc | 4.59±0.69 abc | 15.90±4.92 b | 3.60±0.84 b | 37.11±7.23 cde | |
| M200 | 55.77±19.38 bc | 4.51±2.08 abc | 14.80±5.07 b | 3.57±0.30 b | 35.17±4.17 cde | |
| M350 | 52.90±10.02 bc | 3.76±0.10 bc | 14.47±2.29 b | 3.06±0.54 bc | 33.28±4.66 cde | |
| 处理Treatment | 根系活力Root activity/(ug·g-1·h-1) | 根长Root length/cm | 根冠比Root-shoot ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 32.16±4.77 d | 12.08±1.09 c | 0.06±0.03 b |
| P50 | 37.41±7.59 d | 12.06±1.45 c | 0.07±0.02 b |
| P100 | 78.06±3.67 b | 13.74±1.80 c | 0.07±0.01 b |
| P200 | 95.12±8.77 a | 17.11±1.25 a | 0.08±0.02 ab |
| S50 | 33.30±1.56 d | 13.39±1.95 c | 0.07±0.01 b |
| S100 | 59.17±7.03 c | 16.61±1.08 ab | 0.08±0.01 ab |
| S200 | 71.57±4.66 b | 14.83±1.64 abc | 0.08±0.03 ab |
| S350 | 102.16±2.52 a | 12.74±1.67 c | 0.09±0.03 ab |
| M50 | 37.56±8.97 d | 12.22±1.50 c | 0.07±0.01 ab |
| M100 | 34.51±6.89 d | 12.84±0.59 c | 0.08±0.02 ab |
| M200 | 38.02±8.61 d | 14.33±2.02 bc | 0.12±0.02 ab |
| M350 | 42.31±6.96 d | 13.83±0.87 c | 0.13±0.03 a |
表2 不同处理下藜麦的根系性状
Table 2 Root characteristics of quinoa under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | 根系活力Root activity/(ug·g-1·h-1) | 根长Root length/cm | 根冠比Root-shoot ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 32.16±4.77 d | 12.08±1.09 c | 0.06±0.03 b |
| P50 | 37.41±7.59 d | 12.06±1.45 c | 0.07±0.02 b |
| P100 | 78.06±3.67 b | 13.74±1.80 c | 0.07±0.01 b |
| P200 | 95.12±8.77 a | 17.11±1.25 a | 0.08±0.02 ab |
| S50 | 33.30±1.56 d | 13.39±1.95 c | 0.07±0.01 b |
| S100 | 59.17±7.03 c | 16.61±1.08 ab | 0.08±0.01 ab |
| S200 | 71.57±4.66 b | 14.83±1.64 abc | 0.08±0.03 ab |
| S350 | 102.16±2.52 a | 12.74±1.67 c | 0.09±0.03 ab |
| M50 | 37.56±8.97 d | 12.22±1.50 c | 0.07±0.01 ab |
| M100 | 34.51±6.89 d | 12.84±0.59 c | 0.08±0.02 ab |
| M200 | 38.02±8.61 d | 14.33±2.02 bc | 0.12±0.02 ab |
| M350 | 42.31±6.96 d | 13.83±0.87 c | 0.13±0.03 a |
| 处理Treatment | 千粒重1 000-grain weight/g | 单株产量Yield per plant/g | 产量Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.66±0.12 a | 16.01±0.27 a | 1 723.47±28.93 a |
| P50 | 2.57±0.29 ab | 6.74±0.94 b | 725.81±10.79 b |
| P100 | 2.40±0.29 abc | 2.51±0.20 d | 269.96±21.03 d |
| P200 | 2.34±0.01 abc | 1.34±0.11 e | 144.52±11.49 e |
| S50 | 2.25±0.02 bcd | 3.46±0.26 c | 372.38±27.78 c |
| S100 | 2.18±0.21 cd | 2.89±0.10 d | 310.26±11.24 d |
| S200 | 2.09±0.23 cd | 2.42±0.21 d | 260.34±23.01 d |
| S350 | 2.07±0.22 cd | 1.11±0.22 e | 119.25±23.27 e |
| M50 | 2.36±0.03 abc | 3.97±0.25 c | 427.53±27.18 c |
| M100 | 2.23±0.13 bcd | 3.82±0.22 c | 410.87±24.19 c |
| M200 | 2.20±0.12 cd | 2.55±0.21 d | 273.96±22.48 d |
| M350 | 1.94±0.09 d | 1.59±0.10 e | 171.49±10.48 e |
表3 不同处理下藜麦的产量
Table 3 Quinoa yield under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | 千粒重1 000-grain weight/g | 单株产量Yield per plant/g | 产量Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.66±0.12 a | 16.01±0.27 a | 1 723.47±28.93 a |
| P50 | 2.57±0.29 ab | 6.74±0.94 b | 725.81±10.79 b |
| P100 | 2.40±0.29 abc | 2.51±0.20 d | 269.96±21.03 d |
| P200 | 2.34±0.01 abc | 1.34±0.11 e | 144.52±11.49 e |
| S50 | 2.25±0.02 bcd | 3.46±0.26 c | 372.38±27.78 c |
| S100 | 2.18±0.21 cd | 2.89±0.10 d | 310.26±11.24 d |
| S200 | 2.09±0.23 cd | 2.42±0.21 d | 260.34±23.01 d |
| S350 | 2.07±0.22 cd | 1.11±0.22 e | 119.25±23.27 e |
| M50 | 2.36±0.03 abc | 3.97±0.25 c | 427.53±27.18 c |
| M100 | 2.23±0.13 bcd | 3.82±0.22 c | 410.87±24.19 c |
| M200 | 2.20±0.12 cd | 2.55±0.21 d | 273.96±22.48 d |
| M350 | 1.94±0.09 d | 1.59±0.10 e | 171.49±10.48 e |
| 处理 Treatment | 倒伏指数 Lodging index | 抗折力 Breaking resistance/g |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 344.48±18.80 a | 19.74±2.19 de |
| P50 | 213.74±66.18 bc | 31.06±3.83 ab |
| P100 | 109.29±11.42 de | 31.28±4.39 ab |
| P200 | 79.99±4.74 e | 14.66±3.64 ef |
| S50 | 251.58±23.83 b | 25.81±3.96 bcd |
| S100 | 166.57±30.03 cd | 36.73±5.08 a |
| S200 | 137.87±16.36 de | 14.82±3.29 ef |
| S350 | 116.47±15.79 de | 9.61±2.86 f |
| M50 | 208.08±83.87 bc | 32.08±4.20 ab |
| M100 | 140.46±14.13 de | 29.33±2.73 bc |
| M200 | 109.96±19.54 de | 24.24±4.42 cd |
| M350 | 111.48±43.13 de | 11.56±2.96 f |
表4 不同处理下藜麦的抗倒伏评价指标
Table 4 Evaluation indexes of lodging resistance of quinoa under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 倒伏指数 Lodging index | 抗折力 Breaking resistance/g |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 344.48±18.80 a | 19.74±2.19 de |
| P50 | 213.74±66.18 bc | 31.06±3.83 ab |
| P100 | 109.29±11.42 de | 31.28±4.39 ab |
| P200 | 79.99±4.74 e | 14.66±3.64 ef |
| S50 | 251.58±23.83 b | 25.81±3.96 bcd |
| S100 | 166.57±30.03 cd | 36.73±5.08 a |
| S200 | 137.87±16.36 de | 14.82±3.29 ef |
| S350 | 116.47±15.79 de | 9.61±2.86 f |
| M50 | 208.08±83.87 bc | 32.08±4.20 ab |
| M100 | 140.46±14.13 de | 29.33±2.73 bc |
| M200 | 109.96±19.54 de | 24.24±4.42 cd |
| M350 | 111.48±43.13 de | 11.56±2.96 f |
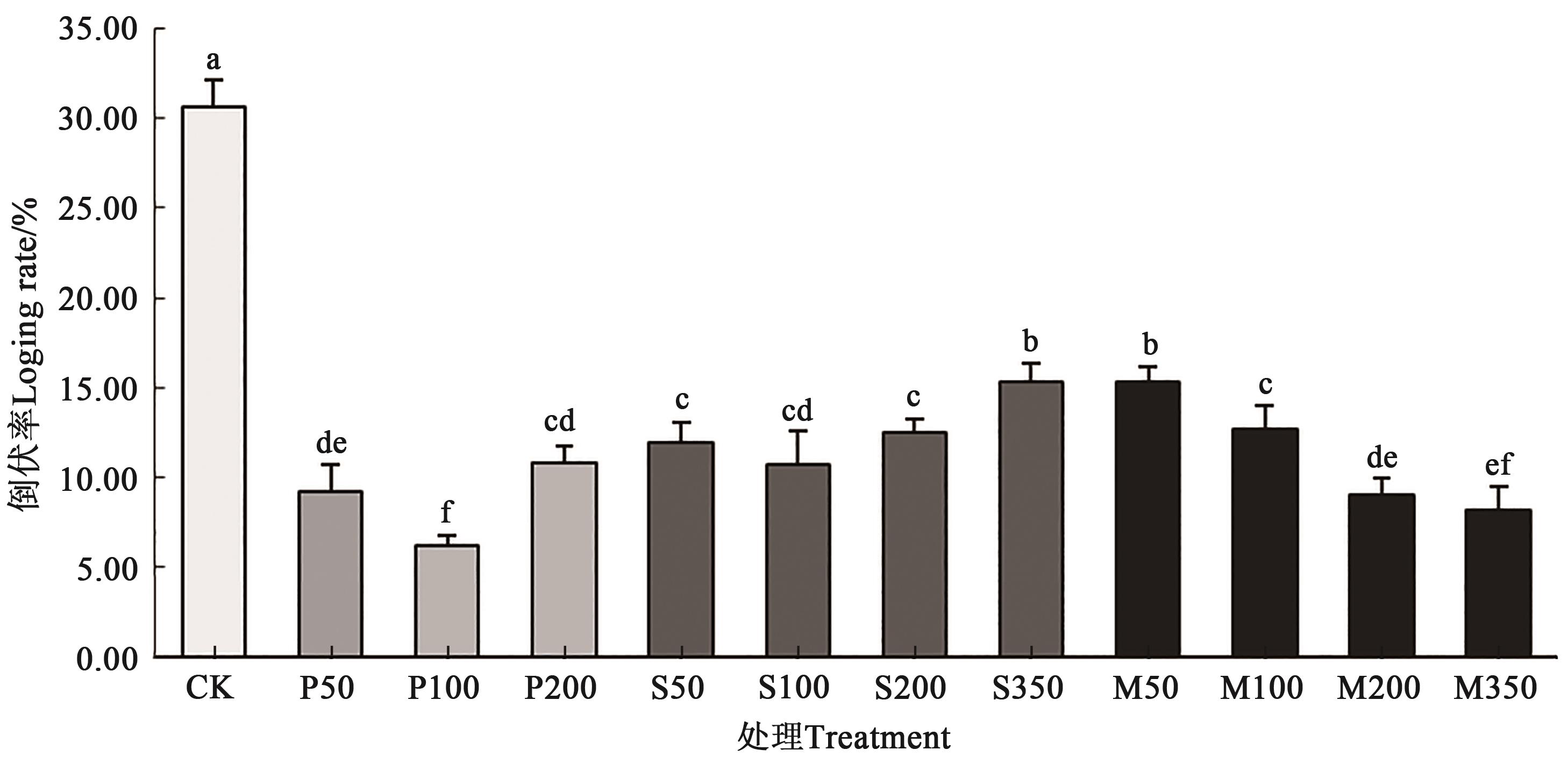
图1 不同处理下的藜麦倒伏率注: 不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Lodging rate of quinoa under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 刘文瑜, 杨发荣, 黄杰, 等. NaCl胁迫对藜麦幼苗生长和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37(9): 1797-1804. |
| LIU W Y, YANG F R, HUANG J, et al.. Response of seedling growth and the activities of antioxidant enzymes of Chenopodium quinoa to salt stress [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2017, 37(9):1797-1804. | |
| 2 | 姚理武, 吴应齐, 叶增新, 等. 不同种植密度与配置方式对藜麦农艺性状和籽粒产量的影响[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2021, 41(5): 99-103. |
| YAO L W, WU Y Q, YE Z X, et al.. Effect of different interplanting densities on agronomic traits and yield of Chenopodium quinoa [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2017, 37(9):1797-1804. | |
| 3 | JACOBSEN S E. The worldwide potential for quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) [J]. Food Rev. Int., 2003, 19(1-2): 167-177. |
| 4 | NAVRUZ-VARLI S, SANLIER N. Nutritional and health benefits of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) [J]. J. Cereal Sci., 2016, 69(5): 371-376. |
| 5 | 贺笑, 庞春花, 张永清, 等. 多效唑和矮壮素浸种对藜麦幼苗生长的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2018, 47(1): 26-31. |
| HE X, PANG C H, ZHANG Y Q, et al.. Effects of soaking seeds with paclobutrazol and chlorocholine chloride on the growth of quinoa seedlings [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2018, 47(1): 26-31. | |
| 6 | WANG N, WANG F X, SHOCK C C, et al.. Evaluating quinoa stem lodging susceptibility by a mathematical model and the finite element method under different agronomic practices [J/OL]. Field Crops Res., 2021, 271:108241 [2022-06-03]. . |
| 7 | 郭建芳, 武小平, 丁健. 静乐县藜麦抗倒伏试验[J]. 现代农业科技, 2019(15): 18-19. |
| 8 | GEREN H. Effects of different nitrogen levels on the grain yield and some yield components of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under Mediterranean climatic conditions [J]. Turkish J. Field Crops, 2015, 20(1): 59-64. |
| 9 | DENG Y, WANG J L, ANWAR S, et al.. Phenology, lodgin and yield traits of Chenopodiutn quinoa under the effect of planting density and row spacings [J]. Fresenius Environ. Bull., 2021, 30(11): 11757-11767. |
| 10 | ALI S, CHATTHA M U, HASSAN M U, et al.. Growth, biomass production, and yield potential of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) as affected by planting techniques under irrigated conditions [J]. Int. J. Plant Prod., 2020, 14(3): 427-441. |
| 11 | 庞春花, 张媛, 李亚妮. 硝酸镧浸种对藜麦种子萌发及盐胁迫下幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(24): 4484-4492. |
| PANG C H, ZHANG Y, LI Y N. Effects of soaking seeds with lanthanum nitrate on seed germination and seedling growth of quinoa under salt stress [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(24): 4484-4492. | |
| 12 | 任永峰, 黄琴, 王志敏, 等. 不同化控剂对藜麦农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(8): 8-16. |
| REN Y F, HUANG Q, WANG Z M, et al.. Effects of chemical control on agronomic traits and yield of quinoa [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2018, 23(8): 8-16. | |
| 13 | 张天俊, 张永亮, 李威, 等. 植物生长延缓剂对羊草非结构性碳水化合物含量及产量的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(2): 407-411. |
| ZHANG T J, ZHANG Y L, LI W, et al.. Effect of growth retardants on content of non-structural carbohydrate and products of ley mus chinensis [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(2): 407-411. | |
| 14 | 马倩, 董连新, 张小燕, 等. 3种植物生长延缓剂对温室甜瓜生长发育的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2020, 33(5): 39-44. |
| MA Q, DONG L X, ZHANG X Y, et al.. Effects of three kind of plant growth retardants on growth and development of muskmelon in greenhouse [J]. China Cucurbits Veg., 2020, 33(5): 39-44. | |
| 15 | 郭建芳, 武小平, 丁健, 等. 矮壮素对藜麦抗倒伏的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2020, 48(7): 1019-1021, 1025. |
| GUO J F, WU X P, DING J, et al.. Effect of chlormequat chloride on lodging resistance of quinoa [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(7): 1019-1021, 1025. | |
| 16 | 刘瑞芳, 贠超, 申为民, 等. 不同浓度矮壮素对藜麦株高的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(23): 156, 160. |
| 17 | WAKJIRA T. A review on: response of crops to paclobutrazol application [J]. Nephron Clinical Practice, 2018, 4(1): 2-9. |
| 18 | 徐富贤, 蒋鹏, 周兴兵, 等. 多效唑对杂交中稻不同密肥群体产量和抗倒伏性的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(5): 1088-1096. |
| XU F X, JIANG P, ZHOU X B, et al.. Effects of paclobutrazol on yield and lodging resistance with different dense-fertilizer population in mid-season hybrid rice [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2020, 34(5): 1088-1096. | |
| 19 | 张盼盼, 杨裕然, 薛佳欣, 等. 烯效唑对盐胁迫下糜子幼苗形态和生理特性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 81-90. |
| ZHANG P P, YANG Y R, XUE J X, et al.. Effects of uniconazole on morphology and physiological characteristics of proso millet seedlings under salt stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2020, 29(10): 81-90. | |
| 20 | 徐一荻, 宋岩, 姜延付, 等. 缩节胺、多效唑对核桃枝叶生长及坚果品质的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2020, 49(10): 108-115. |
| XU Y D, SONG Y, JIANG Y F, et al.. Effects of DPC and PP333 on walnut growth and quality of nuts [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2020, 49(10): 108-115. | |
| 21 | 张兴, 揭雨成, 邢虎成, 等. 洞庭湖区稻田冬播亚麻原茎与种子兼收抗倒伏高产栽培技术研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(15):92-97. |
| ZHANG X, JIE Y C, XING H C, et al.. Cultivation techniques of lodging resistance and high yield of stem and seed of winter flax in paddyfield of Dongting lake [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2014, 30(15): 92-97. | |
| 22 | PELLET D M, PAPERNIK L A, KOCHIAN L V. Multiplealuminum-resist-ance mechanisms in wheat-roles of root apical phosphate and malete exudation [J]. Plant Physiol., 1996, 112(2): 591-597. |
| 23 | 修妤, 梁晓艳, 石瑞常, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫对藜麦苗期植株及根系生长特征的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(4): 89-94. |
| 24 | 朱秀云, 梁梦, 马玉. 根系活力的测定(TTC法)实验综述报告[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(6): 211-212. |
| ZHU X Y, LIANG M, MA Y. A review report on the experiments for the determination of root activity by TTC method [J]. Guangdong Chem. Ind., 2020, 47(6): 211-212. | |
| 25 | 肖应辉, 罗丽华, 闰晓燕, 等. 水稻品种倒伏指数QTL分析[J]. 作物学报, 2005, 31(3): 348-354. |
| XIAO Y H, LUO L H, YAN X Y, et al.. Quantitative trait locus analysis of lodging index in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2005, 31(3): 348-354. | |
| 26 | 杨玉花, 雷阳, 白志元, 等. 开花前不同光周期对大豆主要农艺性状的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(2): 250-257. |
| YANG Y H, LEI Y, BAI Z Y, et al.. Effect of different pre-flowering photoperiod on main agronomic traits of soybean [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2021, 34(2): 250-257. | |
| 27 | 田保明, 杨光圣, 曹刚强, 等. 农作物倒伏及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(4): 163-167. |
| TIAN B M, YANG G S, CAO G Q, et al.. The performent of lodging and root cause snalysis for lodgingresistance in crops [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2006, 22(4): 163-167. | |
| 28 | 陈晓光, 王振林, 彭佃亮, 等. 种植密度与喷施多效唑对冬小麦抗倒伏能力和产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(6): 1465-1470. |
| CHEN X G, WANG Z L, PENG D L, et al.. Effects of planting density and spraying PP333 on winter wheat lodging-resistance and grain [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2011, 22(6): 1465-1470. | |
| 29 | 鱼冰星, 王宏富, 王振华, 等. 多效唑对谷子茎秆特征及抗倒性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 37-44. |
| YU B X, WANG H F, WANG Z H, et al.. Effects of paclobutrazol on stalk characteristics and lodging resistance of foxtail millet [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(8): 37-44. | |
| 30 | WHITE E M. Stem characteristics related to lodging in winter barley [J]. European J. Agron., 1995, 4(3): 327-334. |
| 31 | 娄世杰, 孙鑫博, 梁中银, 等. 多效唑对狼尾草生长及抗倒伏的影响[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2016, 39(4): 78-82. |
| LOU S J, SUN X B, LIANG Z Y, et al.. A study on the effect of paclobutrazol on growth and lodging resistance of Pennisetum alopecuroides [J]. J. Agric. Univ. Hebei, 2016, 39(4): 78-82. | |
| 32 | 朱凤荣, 邱宗波. 种植密度和植物生长调节剂对小麦衰老和产量构成的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2004(8): 18-21. |
| ZHU F R, QIU Z B. Effects of plant density and growth regulator on senescence and yield constitutions of wheat [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2004(8): 18-21. | |
| 33 | 李勇, 吕文河, 吕典秋, 等. 氮、磷、钾施用水平对马铃薯脱毒苗植株性状、产量性状、干物质含量和经济系数的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2014(4): 30-35, 50. |
| LI Y, LYU W H, LYU D Q, et al.. Effect of NPK fertilizer application rate on plant trait, minituber yield, tuber dry matter content and economic coefficient of potato plantlets in vitro transplanted in greenhouse [J]. J. Northeast Agric.Univ., 2014(4): 30-35, 50. | |
| 34 | 胡振阳, 程宏, 卢臣, 等. 施氮量和植物生长调节剂对优质稻抗倒能力及产量的调控效应[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(6): 52-60. |
| 35 | 张伟强, 赵犇, 秦安振, 等. 植物生长调节剂对黄淮井灌区夏玉米水分利用效率的调控[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(6): 43-48, 56. |
| ZHANG W Q, ZHAO B, QIN A Z, et al.. Regulation of water use efficiency of summer maize by plant growth regulator in well-irrigation area of Huang-Huai-Hai River [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2019, 37(6): 43-48, 56. | |
| 36 | 刘文涛, 岳秀峰, 王家民, 等. 多效唑和烯效唑在烟苗和育苗基质中的残留降解动态分析[J]. 现代农业科技, 2016(22): 15, 120. |
| [1] | 段媛媛, 刘晓洪, 唐涛, 王帆帆, 游景茂, 郭晓亮, 郭杰. 种植密度对湖北贝母生长及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [2] | 周影, 李京咏, 戴林秀, 敖弟彩, 李梓逸, 杨帆, 顾军伟, 徐强, 窦志, 高辉. 稻虾共作模式下喷施褪黑素对水稻产量形成和抗倒伏特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 34-42. |
| [3] | 王为, 赵强, 穆妮热·阿卜杜艾尼, 阿里木·阿木力null, 李欣欣, 田阳青. 烯效唑复配不同外源物质对棉花化学封顶及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [4] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [5] | 郑志刚, 向丽, 刘功义, 徐彩, 覃斌, 王慰亲, 郑华斌, 唐启源. 施氮量和密度对有序机抛早稻生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 132-143. |
| [6] | 孟亚轩, 马玮, 姚旭航, 孙颖琦, 钟鑫, 黄山, 瓮巧云, 刘颖慧, 袁进成. 玉米产量对氮肥的响应因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| [7] | 周文, 郭笑恒, 徐锐, 王晓丽, 牛慧伟, 韩丹, 邵惠芳. 烤烟间作半夏对烤烟生长及产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 161-169. |
| [8] | 陈登龙, 张雨翔, 宋佳佳, 陈鹏宇, 温祥珍, 李亚灵. 火山石沉积对鱼菜共生系统运行的探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 207-214. |
| [9] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [10] | 张盼盼, 李川, 张美微, 赵霞, 牛军, 乔江方. 氮肥减施下添加硝化抑制剂对夏玉米氮素累积转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [11] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [12] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [13] | 孙正冉, 张翠萍, 张晋丽, 吴昊, 刘秀艳, 王振凯, 杨玉珍, 贺道华. 喷施化学打顶剂对关中棉区棉花植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 167-177. |
| [14] | 赵文军, 杨继周, 尹梅, 陈检锋, 薛开政, 胡保文, 付利波, 王伟, 王志远, 杨艳鲜, 陈华. 绿肥模式下减量施氮对烤烟产量与品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 189-196. |
| [15] | 王向东, 宋玥, 马艳芝. 不同生姜品种的品质比较与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 56-66. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号